NAKSHA Program
NAKSHA Program Inauguration in Madhya Pradesh
- The Union Minister of Rural Development and Agriculture has launched the NAKSHA program in Raisen, Madhya Pradesh, aiming to modernize land ownership management through digitization.
Digitization of Land Records
- The ongoing digitization of land records is transforming the management of land ownership in rural India, tackling issues such as cumbersome paperwork and ownership conflicts. As of now, nearly 95% of rural land records have been digitized since 2016, significantly enhancing transparency and accessibility.
Benefits of Digitization
- Enhanced Transparency: Reduced instances of illegal encroachments.
- Simplified Dispute Resolution: Alleviates the burden on courts.
- Empowerment of Marginalized Communities: Facilitates access to land rights for underprivileged groups.
- Geospatial Mapping Integration: Supports precise surveys and efficient land management.
Challenges
Land reforms face considerable hurdles, primarily due to outdated and incomplete land records across the country. This challenge is particularly pronounced in northeastern states where community-owned lands have limited documentation. Many cadastral maps are either outdated or missing, leading to inconsistencies in land ownership records.
Initiatives
- Digital India Land Records Modernization Programme (DILRMP): Launched in April 2016, this program aims to establish a transparent and modern land records system with real-time information. Funded entirely by the central government, its goals include reducing land disputes, preventing fraud, and optimizing land use.
- NAKSHA Program: This initiative, with an estimated budget of ₹194 crore and fully funded by the Government of India, targets the development of urban land records. It will cover 152 Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) across 26 states and 3 Union Territories.
- Technical Partnerships: The Survey of India will conduct aerial surveys and provide orthorectified imagery, while the Madhya Pradesh State Electronic Development Corporation (MPSEDC) will develop an end-to-end web-GIS platform. Storage solutions will be managed by the National Informatics Centre Services Inc. (NICSI).
SVAMITVA Scheme: Implemented by the Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR), this Central Sector Scheme aims to provide a ‘Record of Rights’ to households in inhabited village areas.
Conclusion and Future Directions
The government’s initiatives are transforming land governance by enhancing transparency and accessibility, particularly for marginalized communities. This shift towards organized and efficient land record management is not only fostering a more inclusive and equitable society but also supporting economic growth and stability in the long run.
Which of the following statements about the NAKSHA program is/are correct?
- The NAKSHA program was inaugurated in Raisen, Madhya Pradesh.
- It is fully funded by the state government.
- The program aims to cover only rural areas in India.
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: a) 1 only
Explanation: The NAKSHA program was indeed inaugurated in Raisen, Madhya Pradesh, but it is fully funded by the Government of India, not the state government. Additionally, it covers urban local bodies (ULBs) across multiple states and Union Territories, so statement 3 is incorrect.
Extension of PM-AASHA Scheme Until 2025-26
The Union Government has approved the continuation of the Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay Sanrakshan Abhiyan (PM-AASHA) Scheme during the 15th Finance Commission Cycle, extending it up to 2025-26.
Overview of PM-AASHA Scheme
Launched in 2018, the PM-AASHA Scheme serves as an umbrella initiative designed to ensure Minimum Support Price (MSP) for farmers, particularly focusing on pulses, oilseeds, and copra. The scheme aims to provide remunerative prices to farmers and enhance price stability within the agricultural sector.
Key Components of PM-AASHA
Price Support Scheme (PSS):
- The government procures pulses, oilseeds, and copra at the MSP.
- Central Nodal Agencies (CNAs) collaborate with state agencies to carry out the procurement.
- Only produce that meets Fair Average Quality (FAQ) standards is eligible for procurement.
Price Deficiency Payment Scheme (PDPS):
- This scheme provides compensation to pre-registered farmers for the difference between the MSP and the market price.
- Unlike PSS, it does not involve physical procurement of produce.
- It applies to oilseeds through a transparent auction process in notified market yards.
Private Procurement & Stockist Scheme (PPSS) (Pilot Basis):
- This scheme permits states to engage private stockists for oilseed procurement.
- It is currently being implemented in selected Agricultural Produce Market Committees (APMCs) or districts.
Key Changes in the Scheme
- In 2024, the government merged the Price Support Scheme (PSS) and the Price Stabilization Fund (PSF) into the PM-AASHA scheme to improve efficiency for both farmers and consumers.
- This integration aims to protect consumers from extreme price volatility of agri-horticultural commodities by maintaining a strategic buffer stock of pulses and onions. It will also help prevent hoarding and speculative trading, ensuring supplies are available to consumers at affordable prices.
- Additionally, the Market Intervention Scheme (MIS) has been incorporated as a component of the integrated PM-AASHA scheme.
- This scheme specifically targets perishable agricultural and horticultural products such as onions, potatoes, and tomatoes and is activated when prices decline by at least 10% from the previous normal season.
Significance of the Scheme
- It provides essential price support to farmers, reducing the tendency for distress sales.
- The scheme enhances procurement efficiency through market-based interventions.
- It encourages farmer participation in transparent marketing systems.
- It works to stabilize prices, thus protecting both agricultural producers and consumers.
Concerns
Despite its advantages, the PM-AASHA scheme faces several challenges:
- Limited Implementation: The PDPS and PPSS have experienced low adoption rates among states.
- Procurement Constraints: Coverage of MSP is not consistent across all crops and regions.
- Awareness and Accessibility Issues: Many farmers are unaware of the schemes or encounter bureaucratic barriers during registration.
- Budgetary Concerns: Securing adequate funding for procurement operations continues to be a challenge.
Conclusion
The extension of PM-AASHA until 2025-26 underscores the government’s commitment to securing farmers’ income and implementing reforms in agriculture markets. By strengthening its implementation and addressing existing challenges, the scheme can significantly enhance its effectiveness in ensuring fair prices for farmers.
Which of the following components of the PM-AASHA scheme directly involves the procurement of agricultural produce by the government?
- Price Support Scheme (PSS)
- Price Deficiency Payment Scheme (PDPS)
- Market Intervention Scheme (MIS)
a) 1 only
b) 1 and 3 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 1 and 3 only
Explanation: The Price Support Scheme (PSS) directly involves government procurement of specified crops at the Minimum Support Price (MSP). The Market Intervention Scheme (MIS) also involves procurement for perishable commodities. The Price Deficiency Payment Scheme (PDPS) does not involve physical procurement.
Swami Ramakrishna Paramhansa
The Prime Minister recently paid tribute to Swami Ramakrishna Paramhansa on his Jayanti.

Swami Ramakrishna Paramhansa
- Swami Ramakrishna, originally named Gadadhar Chattopadhyay, was born on February 18, 1836, in Kamarpukur, Bengal, into a modest Brahmin family deeply rooted in religious values.
- His profound spirituality inspired him to explore diverse religious paths, ultimately affirming that all faiths lead to a singular divine truth.
- His life was characterized by a continuous contemplation of God, and his God-consciousness transcends both time and place, resonating universally with seekers from all religions.
Notable Disciple
Among his many disciples, Swami Vivekananda stands out as the most prominent. Vivekananda played a crucial role in bringing the philosophy of Ramakrishna to a global audience. In 1897, he founded the Ramakrishna Mission to actualize the visions of his Guru, dedicating the organization to the service of society.
Teachings and Message
- Sri Ramakrishna’s life significantly influenced modern spiritual thought. He demonstrated that the realization of God is not confined by age, nationality, or social background.
- His teachings emphasized that God transcends materialism and skepticism, thus restoring faith in religion. His spiritual presence and teachings transformed individuals, converting those who were lost into enlightened beings and purifying their souls.
Relevance Today
- One of Ramakrishna’s most significant contributions is his message of religious harmony. In a world increasingly confronted by religious intolerance and global crises, his teachings offer hope.
- They advocate for religious tolerance, mutual respect, and fellowship among varying faiths, fostering a spirit of unity in diversity.
Swami Ramakrishna Paramhansa, born Gadadhar Chattopadhyay, is primarily remembered for which of the following contributions?
- His advocacy for the harmony of all religions.
- Establishing a political movement for India’s independence.
- Founding the Ramakrishna Mission.
a) 1 only
b) 1 and 3 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 1 and 3 only
Explanation: Swami Ramakrishna is especially known for his teachings on the harmony of religions and the influence he had on his disciple Swami Vivekananda, who founded the Ramakrishna Mission. He is not primarily remembered for establishing a political movement for India’s independence.
Anticyclone System
Weather experts have reported that the recent unusual spike in temperatures in Mumbai is attributed to the presence of an anticyclone system along the western coast.
About Anticyclones
An anticyclone is a high-pressure weather phenomenon characterized by a higher air pressure at the surface compared to the surrounding areas.
Key Features of an Anticyclone System:
- High Pressure at the Center: The center of an anticyclone experiences higher air pressure than its surroundings.
- Air Movement: Air flows outward from the center of the anticyclone.
- Sinking Air: Instead of rising, the air within an anticyclone descends, which inhibits cloud formation and typically results in dry and clear weather conditions.
- Impact on Weather: Anticyclones can significantly affect local weather patterns, often leading to extended dry spells or heatwaves.

What is a potential impact of an anticyclone on local weather patterns?
a) Increased rainfall and flooding
b) Prolonged dry spells or heatwaves
c) Strong winds and storms
d) Rapid temperature drops
Answer: b) Prolonged dry spells or heatwaves
Explanation: Anticyclones can lead to prolonged dry conditions and heatwaves due to the sinking air and lack of cloud formation, which keeps moisture from accumulating.
Decade of Soil Health Cards:
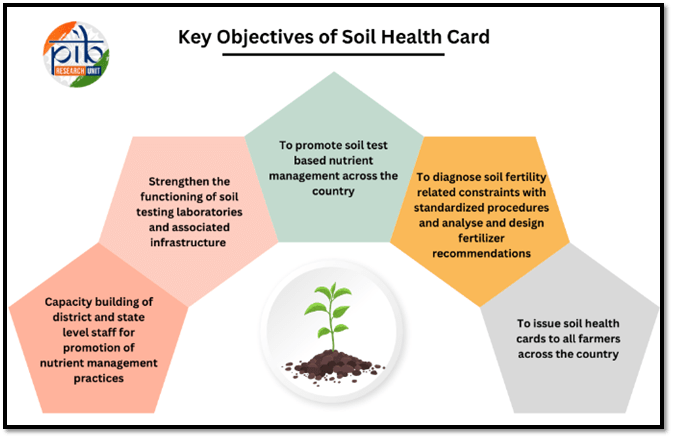
Key Objectives of the Soil Health Card Scheme
- Providing Nutrient Information: The Soil Health Card scheme aims to furnish farmers with detailed information regarding the nutrient status of their soil, enabling them to make informed decisions about soil management.
- Nutrient Recommendations: The scheme offers tailored recommendations on the appropriate dosage of nutrients that farmers should apply to enhance soil health and fertility.
- Supporting State Governments: The initiative assists state governments in issuing Soil Health Cards to farmers across the country, promoting uniformity and facilitating access to essential agricultural information.
- Monitoring Soil Quality: The Soil Health Card assesses soil health based on 12 critical parameters, which include macro-nutrients (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, and Sulfur), micro-nutrients (Zinc, Iron, Copper, Manganese, and Boron), and other vital indicators such as pH level, Electrical Conductivity, and Organic Carbon content.
- Integration with Development Schemes: Since the fiscal year 2022-23, the Soil Health Card scheme has been integrated into the Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) as a component focused on improving soil health and fertility, enhancing its reach and effectiveness in agricultural development.
These objectives collectively aim to improve agricultural productivity and sustainability by promoting scientific and balanced nutrient management practices among farmers.
What is the primary objective of the Soil Health Card Scheme introduced in India?
a) To promote the use of chemical fertilizers among farmers.
b) To provide farmers with information on soil nutrient status and recommendations for nutrient application.
c) To conduct soil erosion assessments across agricultural lands.
d) To encourage the cultivation of genetically modified crops.
Answer: b) To provide farmers with information on soil nutrient status and recommendations for nutrient application.
Explanation: The Soil Health Card Scheme aims to inform farmers about the nutrient status of their soil and to advise them on the appropriate dosage of nutrients to apply for improved soil health and fertility.
Caspian Pipeline Consortium
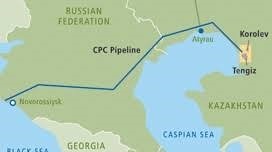
Recently, Russia reported a reduction of 30-40% in oil flows through the Caspian Pipeline Consortium (CPC), a critical route for supplying Kazakhstan and exporting oil to the global market. This decrease followed a Ukrainian drone attack on a pumping station.
Overview of the Caspian Pipeline Consortium (CPC) :The Caspian Pipeline Consortium is a significant $2.6 billion project that features a 935-mile crude oil pipeline extending from the Tengiz oil field in Kazakhstan to the Russian Black Sea port of Novorossiysk.
- Construction of the CPC began in 1999, and the pipeline was commissioned in 2001, with a $5.1 billion expansion project completed in 2018.
- As a key East-West pipeline, the CPC facilitates the transport of oil from the Caspian Sea region to international markets.
- The consortium is jointly owned by the governments of Russia and Kazakhstan, along with major Western energy companies including Chevron, ExxonMobil, and Shell.
- Notably, the CPC accounts for two-thirds of Kazakhstan’s oil exports and has a total capacity of 1.4 million barrels per day, representing 2.3% of global seaborne oil trade.
Which major international oil companies are stakeholders in the Caspian Pipeline Consortium?
a) Gazprom, BP, and Total
b) Chevron, ExxonMobil, and Shell
c) Aramco, Eni, and Equinor
d) ConocoPhillips, Repsol, and ENI
Answer: b) Chevron, ExxonMobil, and Shell
Explanation: The Caspian Pipeline Consortium includes Western energy majors such as Chevron, ExxonMobil, and Shell, along with the Russian and Kazakh governments.
Navika Sagar Parikrama II

On February 18, 2025, the Indian Naval Sailing Vessel (INSV) Tarini successfully entered Port Stanley, marking the completion of the third and most challenging phase of the Navika Sagar Parikrama II initiative.
About Navika Sagar Parikrama II
- The Navika Sagar Parikrama initiative highlights the Indian Navy’s commitment to promoting gender empowerment and maritime excellence.
- This expedition is crewed by two remarkable women officers, Lieutenant Commander Dilna K and Lieutenant Commander Roopa A, who aim to advance ocean sailing, self-reliance, and celebrate India’s rich maritime heritage.
The historic voyage was inaugurated from Goa on October 2, 2024, by the Chief of the Naval Staff. Navika Sagar Parikrama II will cover over 21,600 nautical miles (approximately 40,000 kilometers) and consists of five legs, with scheduled stopovers at four ports for necessary replenishment and maintenance. The broad outline of the voyage is as follows:
- Goa to Fremantle, Australia
- Fremantle to Lyttleton, New Zealand
- Lyttleton to Port Stanley, Falkland Islands
- Port Stanley to Cape Town, South Africa
- Cape Town back to Goa
About INSV Tarini
- The INSV Tarini is a 56-foot sailing vessel built by Aquarius Shipyard Ltd, officially inducted into the Indian Navy on February 18, 2017.
- Since its induction, the vessel has traversed over 66,000 nautical miles (122,223 kilometers) and participated in the first edition of Navika Sagar Parikrama in 2017.
- The boat is equipped with advanced navigation, safety, and communication systems, ensuring a safe and effective journey across the oceans.
With the successful arrival at Port Stanley, the mission continues to exemplify the spirit of adventure and determination inherent in the Indian Navy’s efforts to uplift women’s roles in maritime activities
What is the primary objective of the Navika Sagar Parikrama II expedition?
a) To conduct scientific research in the Indian Ocean
b) To promote gender empowerment and showcase India’s maritime heritage
c) To establish India’s dominance in maritime trade routes
d) To set a world record for the longest sailing voyage
Answer: b) To promote gender empowerment and showcase India’s maritime heritage
Explanation: The Navika Sagar Parikrama initiative underscores the Indian Navy’s commitment to gender empowerment and maritime excellence while promoting ocean sailing and India’s rich maritime heritage.
Biennial Transparency Report (BTR)

India is in the final stages of preparing its first Biennial Transparency Report (BTR), a key commitment as a signatory to the 2015 Paris Agreement on climate change.
Overview of the Biennial Transparency Report (BTR)
The BTR is a report compiled and submitted by Parties to the Paris Agreement within the framework of the Enhanced Transparency Framework (ETF). It provides a comprehensive overview of each country’s progress in achieving various aspects of the Agreement.
Components of the BTR
The BTR consists of five separate chapters, some of which are mandatory while others are optional:
- National Inventory Report of Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions: Required for all Parties – Mandatory
- Progress in Implementing and Achieving Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs): Required for all Parties – Mandatory
- Climate Change Impacts and Adaptation: Applicable to all Parties – Optional
- Financial, Technology Transfer, and Capacity-Building Support Provided: Required for developed country Parties – Mandatory; optional for other Parties providing support.
- Financial, Technology Transfer, and Capacity-Building Support Needed and Received: Optional for developing country Parties.
All Parties to the Paris Agreement, except for small island developing states (SIDS) and least developed countries (LDCs), are mandated to submit country-specific information regarding the implementation of the Agreement in the form of BTRs every two years.
Recognizing the unique challenges faced by SIDS and LDCs, these nations have the option to submit BTRs at their convenience, providing necessary flexibility based on their individual circumstances.
As the reporting mechanism under the Paris Agreement, BTRs foster mutual trust and confidence between nations. They enable both Parties and non-party stakeholders to assess the overall state of climate action in individual countries.
What role do Biennial Transparency Reports (BTRs) play in the context of the Paris Agreement?
a) They serve as a legal document for climate litigation.
b) They facilitate mutual trust and confidence among countries regarding climate action.
c) They provide funding for climate adaptation projects.
d) They outline the penalties for non-compliance with the agreement.
Answer: b) They facilitate mutual trust and confidence among countries regarding climate action.
Explanation: BTRs help foster mutual trust and allow parties and non-party stakeholders to understand the state of climate action in each country.
