India’s Claim Over Continental Shelf in Arabian Sea
Syllabus: GS1/Geography; GS2/Global Groupings & Agreements
Strategic Expansion:
- India has expanded its claim in the Central Arabian Sea, adding nearly 10,000 sq. km to its Extended Continental Shelf (ECS), reinforcing its maritime footprint.
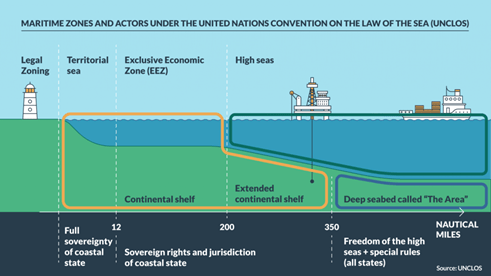
What is the Continental Shelf?
- Defined under the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
- A submerged extension of a nation’s landmass, reaching from the coast to the deep ocean
- Grants nations sovereign rights to explore and exploit seabed resources like oil, gas, and minerals
India’s Latest Move
- Led by NCPOR (Goa), the new claim could bring India’s seabed area close to its land area of 3.274 million sq. km
- Modified Strategy: In response to Pakistan’s objections, India made partial submissions, securing undisputed areas and deferring contentious zones for bilateral resolution
Understanding EEZ and ECS
- EEZ (Exclusive Economic Zone): Extends 200 nautical miles from the coast; exclusive rights to fishing and seabed resource extraction
- ECS: Area beyond the EEZ; requires scientific proof to be claimed under UNCLOS, reviewed by the Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf (CLCS)
Claiming the ECS: The UNCLOS Process
- Scientific Surveys: Geological, bathymetric, and sediment data
- Submission to CLCS: Technical data and boundary maps
- CLCS Review: Recommends changes or approves claims
- Resolving Overlaps: Through negotiations with neighboring countries
- Final Rights: Accepted claims grant rights to seabed resources
Geopolitical Considerations
- Pakistan: Opposed claims near Sir Creek; led to India’s modified strategy
- Oman: Overlapping ECS resolved via 2010 agreement
- Myanmar & Sri Lanka: Challenging India’s ECS in the Bay of Bengal and Indian Ocean (approx. 300,000 sq. km)
To justify an ECS claim under UNCLOS, which combination of the following is required?
- Morphological and geological evidence of continental margin continuity
- Ocean current velocity profiles across the ECS
- Seismic and sediment thickness data supporting natural prolongation
- Baseline calibration based on historical Exclusive Fisheries Zones (EFZs)
Choose the correct combination:
(a) 1, 2, and 4
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2, 3, and 4
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Correct Answer: (b)
Explanation:
To support ECS claims, morphological, geological, and sediment thickness data are required to establish natural prolongation of the continental shelf beyond 200 NM. Ocean current velocity and EFZ history are not scientifically relevant criteria under UNCLOS Annex II.
Bandung Conference
Syllabus: GS2/ International Relations
This year marks 70 years since the historic Bandung Conference, a landmark moment in the rise of the Global South as a political force.
About the Bandung Conference (1955)
- Held in Bandung, Indonesia, the conference brought together 29 newly independent Asian and African nations.
- It aimed to confront the challenges of decolonization, assert sovereignty, and offer an alternative voice in a world dominated by Cold War superpowers.
- The event laid the groundwork for the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) and promoted Afro-Asian solidarity through economic and cultural cooperation.
- It opposed colonialism, imperialism, and neocolonialism in all forms.
Bandung’s Ten Principles (Dasasila Bandung)
- Respect for human rights and the UN Charter
- Sovereignty and territorial integrity of all nations
- Equality of all races and nations
- Non-interference in internal affairs
- Right to self-defense per the UN Charter
- No use of collective defense to serve big power interests
- No aggression or use of force
- Peaceful settlement of disputes
- Promotion of mutual interests and cooperation
- Respect for justice and international obligations
Legacy and Relevance
- The Bandung Conference is remembered as a powerful assertion of self-determination and dignity for post-colonial nations.Its vision continues to inspire efforts toward a just, multipolar world order in an era of global realignments.
What is the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM)?
- Definition: A group of developing countries that remained independent of Cold War power blocs.
- Origins: Traces back to Bandung (1955); formally established in 1961 in Belgrade, Yugoslavia.
- Founding Leaders:
- Jawaharlal Nehru (India)
- Gamal Abdel Nasser (Egypt)
- Josip Tito (Yugoslavia)
- Sukarno (Indonesia)
- Kwame Nkrumah (Ghana)
- Structure:
- No permanent secretariat or binding charter
- Second-largest international grouping after the United Nations
- Membership:
- 120 member countries:
- 53 from Africa
- 39 from Asia
- 26 from Latin America & the Caribbean
- 2 from Europe
- Includes Palestine and 17 observer states
With reference to the Bandung Principles, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- They allowed for collective defense only under UN authorization.
- They prohibited any nation from using its military strength to exert influence on smaller nations.
- They emphasized cultural cooperation over economic cooperation among Afro-Asian countries.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Bandung principles align with the UN Charter, allowing defense only in conformity with it.
- Statement 2 is correct: One of the ten principles specifically opposes the use of power to dominate smaller nations.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The conference emphasized both economic and cultural cooperation, not prioritizing one over the other.
NMCG Approves Annual Master Plan to Promote River-Sensitive Urban Planning Under RCA
Syllabus: GS3/Urban Planning
Context:
- The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) has approved an Annual Master Plan under the River Cities Alliance (RCA) to guide the implementation of river-sensitive urban governance across Indian cities.
About the Initiative:
- The initiative is focused on embedding river-sensitive urban planning into India’s expanding urban landscapes. The master plan includes:
- Capacity-building programmes
- Knowledge-sharing platforms
- Development of technical tools
- Expert consultations
- Thematic case studies to inform river-related urban strategies.
Urban River Management Plans (URMPs):
- Launched in 2020 by NMCG and the National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA).
- A first-of-its-kind urban-river planning framework, integrating environmental, social, and economic dimensions of river ecosystems into urban governance.
- Cities with existing URMPs: Kanpur, Ayodhya, Chhatrapati Sambhaji Nagar, Moradabad, and Bareilly.
- Future expansion: 25 additional URMPs to be developed in the first phase; a total of 60 are planned over the next 2–3 years.
- Steering Committees: Constituted in key Ganga basin states (Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal) to guide plan formulation and execution.
River Cities Alliance (RCA):
- Established in 2021 by the NMCG (Ministry of Jal Shakti) in collaboration with NIUA (Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs).
- Objective: To serve as a dedicated platform for urban river cities to collaborate and promote sustainable urban river management.
- Thematic Pillars:
- Networking
- Capacity Building
- Technical Support
- Growth: From an initial 30 member cities, RCA now includes over 145 cities, spanning both Ganga basin and non-Ganga basin urban centers.
- International collaboration: The city of Aarhus, Denmark joined, highlighting RCA’s global outreach.
Global River Cities Alliance (GRCA):
- Launched at COP28 (2024) to scale RCA’s success to the global stage.
- Comprises 275+ river cities across 11 countries, including Denmark, Egypt, Netherlands, Ghana, Australia, Bhutan, Cambodia, and Japan.
- Supported by World Bank, Asian Development Bank (ADB), and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB).
- Aims to enable transnational cooperation on river conservation and sustainable water management.
National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG):
- Established under the Societies Registration Act, 1860, it is the implementation wing of the Namami Gange Programme, India’s flagship river rejuvenation initiative.
- Objective: Pollution abatement, rejuvenation of the Ganga, and ensuring minimum ecological flows while promoting sustainable development.
- Structure: Two-tier governance:
- Governing Council
- Executive Committee (chaired by the Director General, NMCG)
- Financial Powers: The Executive Committee can approve projects up to ₹1000 crore.
Which of the following statements regarding the Urban River Management Plans (URMPs) is/are correct?
- URMPs are implemented solely by the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) without collaboration from any other institution.
- They aim to integrate environmental, social, and economic considerations into urban river governance.
- As of now, only cities in the Ganga Basin have been selected for URMP development.
Options:
(a) 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) All of the above
Answer: (a) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: URMPs are jointly implemented by NMCG and NIUA, not just NMCG alone.
- Statement 2 is correct: URMPs are explicitly designed to integrate environmental, economic, and social dimensions in urban planning around rivers.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: Although initially focused on the Ganga Basin, URMPs are also being developed for non-Ganga basin cities.
Towards a new approach for green hydrogen production
GS3(Environment)
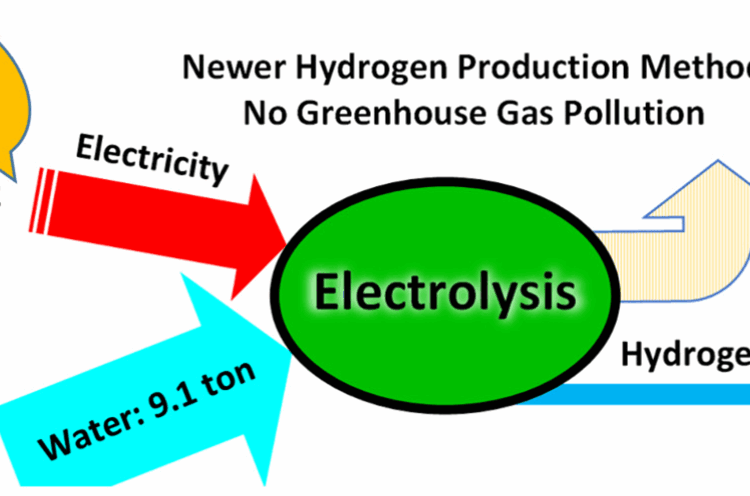
- Researchers have developed advanced insights into proton adsorption behavior on catalyst surfaces, providing a foundational step toward designing efficient electrocatalysts for green hydrogen production.
- While various heterostructures have been studied for hydrogen generation, metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) based p–n heterojunctions stand out due to their robust built-in electric field (BIEF), arising from asymmetric electronic environments.
- Recent research emphasizes the critical role of BIEF at material interfaces, with key parameters such as work function differences, BIEF strength, and Gibbs free energy of adsorption (∆G) being central to understanding the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) The work function differential initiates charge redistribution, creating the BIEF, which significantly influences proton adsorption and desorption dynamics.
- A team from the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, synthesized a CuWO₄–CuO heterostructure by depositing CuWO₄ nanoparticles on a Cu(OH)₂ precursor. This structure was then analyzed for its electrochemical behavior and ∆G profile across various regions. Remarkably, the depletion region and interface zone showed distinct adsorption energies compared to the bulk, forming a gradient that favors enhanced proton adsorption and release.
Their findings revealed that:
- CuO regions exhibit high proton adsorption affinity.
- CuWO₄ regions facilitate proton desorption.
- The system demonstrates negative cooperativity, where increased proton coverage reduces further adsorption affinity, thereby optimizing HER under alkaline conditions.
- Published in Advanced Energy Materials (2025), this study showcases how the interplay between BIEF and thermodynamics can be engineered to significantly boost catalytic performance. The research paves the way for the design of next-generation electrocatalysts, contributing to sustainable energy transitions through green hydrogen technology.
Consider the following statements regarding the CuWO₄–CuO heterostructure developed by the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali:
- The heterostructure was synthesized by depositing CuWO₄ nanoparticles onto a Cu(OH)₂ precursor.
- The built-in electric field (BIEF) at the p–n junction significantly influences proton adsorption and desorption dynamics.
- The system exhibits positive cooperativity, where increased proton coverage enhances further adsorption affinity.
- The study was published in Advanced Energy Materials in 2025.
Which of the above statements are correct?
Options:
(a) 1, 2, and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer: (a) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The CuWO₄–CuO heterostructure was synthesized by depositing CuWO₄ nanoparticles onto a Cu(OH)₂ precursor, as reported by INST, Mohali.
- Statement 2 is correct: The built-in electric field (BIEF) at the p–n junction plays a crucial role in modulating proton adsorption and desorption dynamics, enhancing the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) efficiency.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The system exhibits negative cooperativity, not positive cooperativity. This means that as proton coverage increases, the affinity of the catalyst’s surface for additional proton adsorption decreases, facilitating efficient desorption and promoting HER under alkaline conditions.
- Statement 4 is correct: The findings were published in Advanced Energy Materials in 2025, contributing valuable insights into electrocatalytic hydrogen production.
National Supercomputing Mission
Syllabus: GS3(Science and Tech)
Overview
- Launched in 2015, the National Supercomputing Mission (NSM) is a flagship initiative of the Government of India aimed at building high-performance computing (HPC) capabilities and fostering indigenous supercomputing infrastructure.
- It is jointly steered by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and the Department of Science and Technology (DST), and implemented by C-DAC, Pune and IISc Bengaluru.
Key Objectives
- Enhance India’s capability in scientific research, innovation, and industrial applications using supercomputing.
- Foster indigenous development in hardware and software for HPC systems.
- Build human resource capacity in HPC and AI across the country.
- Enable R&D across Tier I, II, and III academic and research institutions.
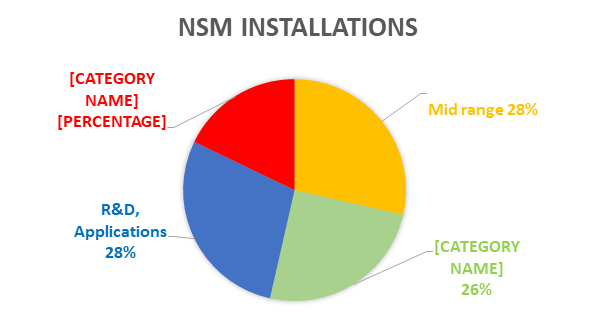
Achievements (As of March 2025)
- 34 supercomputers installed with a total computing capacity of 35 Petaflops across premier institutions including IITs, IISc, and C-DAC.
- Over 10,000 researchers including 1,700+ PhD scholars supported across 200+ institutions.
- Over 1 crore compute jobs processed and 1,500+ research papers
- 85%+ utilization rate, with many systems exceeding 95% efficiency.
- More than 22,000 trained in HPC and AI.
- Active participation from startups and MSMEs in leveraging HPC for innovation.
Major Deployments
- Param Shivay (2019) – First indigenously built system, IIT-BHU.
- Param Pravega (2022) – 3.3 PF system at IISc Bengaluru; largest in an Indian academic institution.
- PARAM Rudra Series (2024) – Deployed in Pune, Delhi, and Kolkata; built with indigenous “Rudra” HPC-class servers and software.
Key Innovations
- Trinetra Network – Indigenous high-speed interconnect for supercomputers:
- Trinetra-A (100 Gbps) – Deployed in 1 PF PARAM Rudra, Pune.
- Trinetra-B (200 Gbps) – To power upcoming 20 PF system at Bangalore.
- AIRAWAT AI Supercomputing Platform:
- 200 AI Petaflops, scalable to 790 AI Petaflops.
- Ranked 75th in Top 500 Global Supercomputers (ISC 2023).
- Common AI compute infrastructure for research, start-ups, and industry.
Mission Phases
- Phase I: Basic systems with partial domestic assembly.
- Phase II: Indigenous manufacturing of components; 40% value addition.
- Phase III: Full indigenization of design, development, and deployment.
Human Resource Development (HRD)
- Training centers established in Pune, Kharagpur, Chennai, Palakkad, and Goa.
- Focus on awareness, capacity-building, and skill development in HPC and AI.
Budget and Investment
- 1874 crore allocated for infrastructure, R&D, HRD, and mission operations.
- Target to deploy ~45 additional Petaflops by 2025 using indigenous technologies.
Strengthening through India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- ISM supports domestic manufacturing of critical supercomputing components—processors, memory, accelerators—reducing dependence on imports.
- This synergy boosts speed, affordability, and customization of supercomputers for national needs.
Conclusion
- The NSM is a transformative step toward India’s technological sovereignty in supercomputing. With strategic focus on indigenization, research empowerment, and global competitiveness, the mission positions India as a leading force in the High-Performance Computing (HPC) domain and ensures preparedness for emerging scientific challenges.
Which of the following statements regarding the National Supercomputing Mission (NSM) are correct?
- NSM was launched to enhance India’s technological self-reliance in the field of high-performance computing (HPC).
- The NSM is being implemented solely by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- Trinetra, developed under NSM, is a high-speed communication network that supports supercomputing infrastructure across the country.
- The NSM Phase III focuses on complete indigenization of HPC systems, including the design, development, and manufacturing of key components in India.
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The NSM was launched to make India self-reliant in supercomputing, and it enhances the country’s ability to tackle grand challenges in scientific research and technology.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: While the NSM is steered by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and the Department of Science and Technology (DST), it is implemented jointly by C-DAC and IISc Bengaluru, not solely by MeitY.
- Statement 3 is correct: Trinetra is an indigenous high-speed communication network developed under NSM to enhance data transfer between supercomputing nodes.
- Statement 4 is correct: Phase III of the NSM focuses on the complete indigenization of HPC, including the domestic design and manufacturing of critical components.
In 2024, India’s military expenditure was nine times that of Pak.: SIPRI
Syllabus: Defence
- India’s Military Expenditure in 2024: A Comparative Analysis with Pakistan
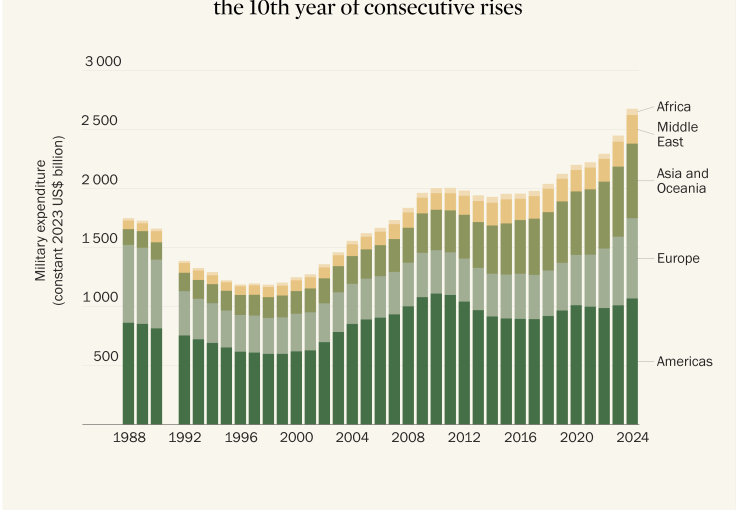
- According to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), India’s military expenditure in 2024 was approximately $86.1 billion, marking a 1.6% increase from the previous year.
- This positions India as the fifth-largest military spender globally. In stark contrast, Pakistan’s defense budget stood at $10.2 billion, making it the 29th largest spender. This disparity indicates that India’s military spending was nearly nine times greater than Pakistan’s in 2024.
- The top five military spenders globally in 2024 were:
- United States – $997 billion
- China – $314 billion
- Russia – $149 billion
- Germany – $88.5 billion
- India – $86.1 billion
- Collectively, these five nations accounted for 60% of the global military expenditure, totaling $1,635 billion.
- In the context of South Asia, India’s defense spending significantly outpaces that of its neighbors. While India has been focusing on modernizing its military capabilities, Pakistan’s defense budget remains limited, reflecting the broader economic and strategic challenges faced by the country.
- This substantial difference in military expenditure underscores the varying defense priorities and capabilities within the region. India’s investment in defense modernization is part of its broader strategy to enhance its geopolitical influence and address security concerns, particularly in the Indo-Pacific region.
With reference to the “Trends in World Military Expenditure 2024” report by the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), consider the following statements:
- India ranked among the top five global military spenders, with its expenditure nearly nine times that of Pakistan.
- In 2024, China accounted for over half of Asia and Oceania’s total military expenditure, marking its 30th consecutive year of increase.
- Ukraine’s military spending in 2024 was higher than that of Russia, given the ongoing conflict and foreign assistance.
- The United States remained the highest military spender globally, accounting for more than half of global military expenditure.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2, and 3 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct – India’s military spending stood at $86.1 billion, nearly nine times that of Pakistan’s $10.2 billion, placing it 5th globally.
- Statement 2: Correct – China’s expenditure reached $314 billion, marking three decades of consistent growth and constituting 50% of Asia and Oceania’s total military outlay.
- Statement 3: Incorrect – Although Ukraine spent $64.7 billion, this was still only 43% of Russia’s spending ($149 billion).
- Statement 4: Incorrect – The U.S. topped global spending but accounted for less than 50% of the total global defense expenditure (~60% shared among top five).
POCSO cases can be quashed based on settlement in certain circumstances: HC
- The Kerala High Court recently observed that the mere fact that offences under the POCSO Act are alleged does not automatically prevent the possibility of quashing the proceedings based on a settlement between the parties, particularly when such a settlement has led to the marriage between the accused and the victim.
- Justice C. Jayachandran made this observation while quashing two separate cases filed under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, where the accused had married the survivors. The court emphasized that if offences under Section 307 of the Indian Penal Code (attempt to murder) can be quashed through a genuine settlement between the parties, then there is no reason why a less severe offence under the POCSO Act cannot be terminated in a similar manner.
- However, the judge clarified that serious crimes such as rape under the IPC or penetrative sexual assault under the POCSO Act cannot be quashed based on a settlement. The court also noted that in cases where extreme mitigating circumstances exist, strict adherence to the rule against quashing would lead to injustice. Therefore, the decision to quash proceedings should be based on the specific facts of the case, rather than solely on the classification of the offence under the law.
Which of the following statements are correct regarding the Kerala High Court’s recent observation on quashing proceedings under the POCSO Act?
- The Kerala High Court observed that offences under the POCSO Act cannot be quashed if there is a settlement between the parties.
- The court allowed quashing of cases under the POCSO Act when the accused and the victim have married, considering the marriage as a settlement.
- Serious offences like rape and penetrative sexual assault under the IPC and POCSO Act cannot be quashed based on settlement between the parties.
- The court emphasized that the decision to quash proceedings should be based on the nomenclature of the statute rather than the specific facts of the case.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
(a) 1, 3, and 4
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The court allowed quashing of cases under the POCSO Act when there was a settlement between the parties and the accused married the victim.
- Statement 2 is correct: The court quashed the cases considering the marriage as a settlement between the parties.
- Statement 3 is correct: Serious offences such as rape or penetrative sexual assault cannot be quashed based on a settlement.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: The court emphasized that the decision to quash should be based on the specific facts of the case, not the statute’s nomenclature.
President Honored 71 Individulas With Padma Awards
Syllabus:Awards
- In a grand Civil Investiture Ceremony held at the Durbar Hall of Rashtrapati Bhawan, President Droupadi Murmu presented the Padma Awards—India’s highest civilian honors—to 71 distinguished individuals on April 29, 2025.
- These awards recognize outstanding contributions in diverse fields such as art, public service, science, medicine, literature, education, and sports.
- The Padma Awards are categorized into three levels: Padma Vibhushan, Padma Bhushan, and Padma Shri.
Key Highlights of the 2025 Padma Awards:
- Padma Bhushan in the Field of Art:
- Shekhar Kapur: Acclaimed filmmaker, honored for his contributions to Indian and international cinema.
- Pankaj Udhas (Posthumous): Renowned ghazal singer, posthumously awarded. His wife, Farida Udhas, accepted the honor.
- Nandamuri Balakrishna: Veteran actor and politician from Andhra Pradesh, recognized for his dual contribution to cinema and public life.
- Ajith Kumar: Prominent actor known for his impactful work in Indian cinema.
- R. Sreejesh: Former Indian hockey goalkeeper, awarded for his significant achievements in sports and service to Indian hockey.
- Padma Vibhushan:
- Subramaniam: World-renowned violinist, honored for his extraordinary impact on Indian classical music.
- Notable Padma Shri Awardees:
- Jaspinder Narula: Playback singer celebrated for her contribution to Indian music.
- Ravichandran Ashwin: Indian cricketer, recognized for his excellence and consistent performance in international cricket.
- Ganeshwar Shastri Dravid: Esteemed Vedic scholar honored for determining auspicious timings for major religious events such as the Ram Lalla consecration and Kashi Vishwanath Corridor.
- Stephen Knapp: American author and researcher awarded for his work in promoting Vedic culture and spirituality through literature and education.
- These awards reflect the nation’s deep appreciation for individuals who have made significant and lasting contributions to their respective fields, both in India and globally.
Which of the following statements about the Padma Awards 2025 is/are correct?
- The Padma Vibhushan was conferred upon seven individuals, including M.T. Vasudevan Nair and Osamu Suzuki.
- The Padma Bhushan category recognized 19 recipients, with notable awardees such as Nandamuri Balakrishna and Pankaj Udhas (posthumous).
- The Padma Shri category honored 113 individuals, including Arijit Singh and Harvinder Singh.
Options:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
Explanation:
- The Padma Awards 2025 recognized a total of 139 distinguished individuals across three categories:
- 7 Padma Vibhushan awardees, including M.T. Vasudevan Nair and Osamu Suzuki.
- 19 Padma Bhushan recipients, notably Nandamuri Balakrishna and Pankaj Udhas (posthumously).
- 113 Padma Shri honorees, including figures like Arijit Singh and Harvinder Singh for their contributions in music and sports respectively.
Digha gears up for inauguration of Jagannath temple
Syllabus:Art and Culture
- The coastal town of Digha in West Bengal’s Purba Medinipur district was abuzz with activity on Monday as it prepared for the inauguration of the ₹250-crore Lord Jagannath temple. Spanning 20 acres, the temple is modeled after the 12th-century shrine in Puri.
- Chief Minister Mamata Banerjee visited the temple twice on the day of the inauguration to oversee the final preparations. She highlighted the temple’s potential to boost Digha’s tourism, noting that it would help the town achieve international recognition. “This temple will add a new feather to Digha’s tourism and bring more visitors here. The town’s development has already begun to attract more tourists,” Banerjee stated.
- She further emphasized the theme of “Shorbo Dhormo Somonnoy” (religious harmony), asserting that the temple would stand as a symbol of both spirituality and unity. Digha, known for its coastal charm, is set to benefit from this new spiritual destination, which she believes will bring in more pilgrims and tourists alike. “The sculptors have done an excellent job,” she added.
- The inauguration of the temple is slated to take place after the ‘Maha Yajna’ and ‘Prana Pratistha’ (consecration ceremony) on Tuesday and Wednesday (Akshay Tritiya). The temple’s construction began in May 2022 following an idea proposed by the Chief Minister in December 2018. The temple, adorned in blue and white, is surrounded by illuminated roads and has been promoted as the Jagannath Dham Sanskriti Kendra by the West Bengal government. The Housing Infrastructure Development Corporation (HIDCO) was responsible for its development.
- However, political controversy arose when senior BJP leader and Leader of the Opposition Suvendu Adhikari questioned the nature of the newly inaugurated structure. Adhikari sought clarification on whether the facility was a temple or a cultural center. “The tender documents reveal that the Jagannath Dham Sanskriti Kendra has been built at Digha. The invitation card should reflect this clearly,” he remarked.
- Amidst these developments, Adhikari also announced that the BJP would begin efforts to rebuild and restore vandalized Hindu temples in Murshidabad district starting April 30. He emphasized that no funds would be sought or accepted from the state government for this initiative. The communal clashes in Murshidabad earlier this month had led to the deaths of three individuals.
- Following the inauguration of the temple, Chief Minister Mamata Banerjee is expected to visit Murshidabad to address the ongoing tensions.
Which of the following statements regarding the inauguration of the Lord Jagannath temple in Digha are correct?
- The Lord Jagannath temple in Digha is modeled after the 12th-century temple in Puri.
- The temple’s inauguration is accompanied by a ‘Maha Yajna’ and ‘Prana Pratistha’ (consecration ceremony).
- The Chief Minister of West Bengal, Mamata Banerjee, proposed the idea for the temple in December 2022.
- The Housing Infrastructure Development Corporation (HIDCO) is responsible for the temple’s construction.
- BJP leader Suvendu Adhikari raised concerns over the nature of the temple and questioned if it is a cultural center or a religious temple.
Options:
(a) 1, 2, and 4 only
(b) 1, 2, 4, and 5 only
(c) 1, 3, 4, and 5 only
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(b) 1, 2, 4, and 5 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Lord Jagannath temple in Digha is modeled after the 12th-century shrine in Puri.
- Statement 2 is correct: The inauguration of the temple includes a ‘Maha Yajna’ and ‘Prana Pratistha’ (consecration ceremony).
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The idea for the temple was proposed by Mamata Banerjee in December 2018, not 2022.
- Statement 4 is correct: The Housing Infrastructure Development Corporation (HIDCO) was responsible for the temple’s construction.
- Statement 5 is correct: Suvendu Adhikari questioned whether the structure is a cultural center or a temple, raising concerns about its nature.