Bihar’s Mukhya Mantri Vidyut Upbhokta Sahayta Yojana
Syllabus GS2/Governance
- The Bihar Cabinet, chaired by the Chief Minister, has approved a subsidy of ₹15,995 crore under the Mukhya Mantri Vidyut Upbhokta Sahayta Yojana for the financial year 2025-26. This allocation is ₹652 crore more than the subsidy granted in the previous year.
- Mukhya Mantri Vidyut Upbhokta Sahayta Yojana: Introduced in Bihar, this scheme aims to provide significant electricity subsidies to ease the financial burden on consumers and promote fair access to power throughout the state.
- The subsidy is designed to reduce the per-unit cost of electricity for consumers, and will be directly provided to the National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC) through the Reserve Bank of India.
- The subsidy will be reflected in consumers’ monthly energy bills, covering the period from April 2025 to March 2026. This move is intended to offset the impact of rising electricity tariff rates.
- Did You Know? The Government of India launched the Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana (SAUBHAGYA) in October 2017, with the goal of achieving universal household electrification.
- This initiative provides electricity connections to all willing un-electrified households in rural areas and to poor households in urban areas across the country.
Consider the following statements regarding the Mukhya Mantri Vidyut Upbhokta Sahayta Yojana:
- The scheme provides subsidies directly to consumers through the Reserve Bank of India to reduce their electricity bills.
- The subsidy aims to alleviate the financial burden on consumers by lowering per-unit electricity costs and is allocated for the period from April 2025 to March 2026.
- The subsidy under the scheme is specifically aimed at reducing the electricity tariffs for commercial consumers in Bihar.
- The Bihar Government has allocated ₹15,995 crore for the scheme in 2025-26, which is an increase of ₹652 crore from the previous year’s budget.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1, 2, and 4 only
(b) 2, 3, and 4 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct – The subsidy is provided through the Reserve Bank of India directly to the National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC), which helps reduce the per-unit cost for consumers.
- Statement 2: Correct – The subsidy will indeed be for the period from April 2025 to March 2026, aimed at reducing the per-unit electricity costs.
- Statement 3: Incorrect – The scheme primarily targets domestic consumers, not commercial consumers.
- Statement 4: Correct – The Bihar government has allocated ₹15,995 crore, which is an increase of ₹652 crore over the previous year’s allocation.
Bandung Conference
Syllabus: GS2/ International Relations
This year marks 70 years since the historic Bandung Conference, a landmark moment in the rise of the Global South as a political force.
About the Bandung Conference (1955)
- Held in Bandung, Indonesia, the conference brought together 29 newly independent Asian and African nations.
- It aimed to confront the challenges of decolonization, assert sovereignty, and offer an alternative voice in a world dominated by Cold War superpowers.
- The event laid the groundwork for the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) and promoted Afro-Asian solidarity through economic and cultural cooperation.
- It opposed colonialism, imperialism, and neocolonialism in all forms.
Bandung’s Ten Principles (Dasasila Bandung)
- Respect for human rights and the UN Charter
- Sovereignty and territorial integrity of all nations
- Equality of all races and nations
- Non-interference in internal affairs
- Right to self-defense per the UN Charter
- No use of collective defense to serve big power interests
- No aggression or use of force
- Peaceful settlement of disputes
- Promotion of mutual interests and cooperation
- Respect for justice and international obligations
Legacy and Relevance
- The Bandung Conference is remembered as a powerful assertion of self-determination and dignity for post-colonial nations.Its vision continues to inspire efforts toward a just, multipolar world order in an era of global realignments.
What is the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM)?
- Definition: A group of developing countries that remained independent of Cold War power blocs.
- Origins: Traces back to Bandung (1955); formally established in 1961 in Belgrade, Yugoslavia.
- Founding Leaders:
- Jawaharlal Nehru (India)
- Gamal Abdel Nasser (Egypt)
- Josip Tito (Yugoslavia)
- Sukarno (Indonesia)
- Kwame Nkrumah (Ghana)
- Structure:
- No permanent secretariat or binding charter
- Second-largest international grouping after the United Nations
- Membership:
- 120 member countries:
- 53 from Africa
- 39 from Asia
- 26 from Latin America & the Caribbean
- 2 from Europe
- Includes Palestine and 17 observer states
With reference to the Bandung Principles, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- They allowed for collective defense only under UN authorization.
- They prohibited any nation from using its military strength to exert influence on smaller nations.
- They emphasized cultural cooperation over economic cooperation among Afro-Asian countries.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Bandung principles align with the UN Charter, allowing defense only in conformity with it.
- Statement 2 is correct: One of the ten principles specifically opposes the use of power to dominate smaller nations.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The conference emphasized both economic and cultural cooperation, not prioritizing one over the other.
World Bank: India’s Extreme Poverty Drops to 2.3%
Syllabus :GS 3/Economy
According to the World Bank’s Poverty and Equity Briefs (PEBs), India has made remarkable strides in reducing extreme poverty, with the proportion of people living in extreme poverty dropping from 16% in 2011–12 to just 2.3% in 2022–23. This substantial reduction represents a major milestone in the country’s ongoing efforts to combat poverty.
About the Poverty and Equity Briefs (PEBs)
The Poverty and Equity Briefs (PEBs) are biannual reports published by the World Bank. These reports provide a snapshot of trends in poverty, inequality, and shared prosperity across over 100 developing countries. The PEBs are released during the Spring and Annual Meetings of the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Their goal is to keep the issue of poverty reduction central to global policy discussions.
Key Indicators and Measurement
- The PEBs track several important indicators to assess poverty and inequality:
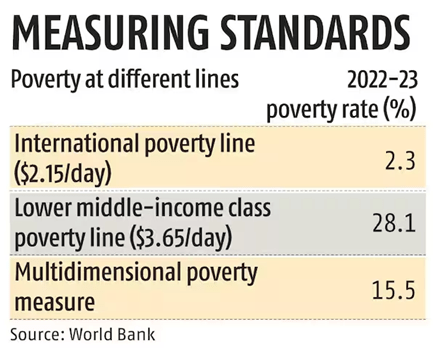
- Poverty rates based on both national and international poverty lines (e.g., $2.15/day in 2017 PPP terms, $3.65 for lower-middle-income countries, and $6.85 for upper-middle-income countries).
- The Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI), which considers deprivations in areas such as education, basic services, and nutrition in addition to income poverty.
- Inequality is measured using the Gini Index, a tool that gauges income or consumption inequality in a population.
India’s Recent Poverty Trends (2022–23)
- India has witnessed a sharp decline in extreme poverty, with significant reductions across both rural and urban areas:
- Extreme poverty, measured at $2.15 per day (PPP), fell from 16% in 2011–12 to 3% in 2022–23, lifting 171 million people above the poverty line.
- Rural areas saw a drop in extreme poverty from 4% to 2.8%, while urban areas experienced a decline from 10.7% to 1.1%, significantly narrowing the rural-urban poverty gap.
- When measured against the $3.65/day threshold for lower-middle-income countries, poverty declined from 8% to 28.1%, with an additional 378 million people moving above this line.
The Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI), which includes factors such as education and basic services, showed a significant decrease in non-monetary poverty, dropping from 53.8% in 2005–06 to 15.5% in 2022–23.
Regional Distribution of Poverty
- India’s most populous states—Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Bihar, West Bengal, and Madhya Pradesh—continue to account for a large portion of the country’s poverty:
- These five states accounted for 54% of India’s extreme poor in 2022–23, and 51% of the multidimensionally poor in 2019–21.
- Despite making significant strides, these states still represent a key focus area for poverty alleviation efforts, although they have also driven much of India’s poverty reduction, contributing to two-thirds of the overall decline.
Inequality and Employment Challenges
- Despite the remarkable reduction in poverty, inequality remains a pressing issue in India:
- Wage inequality is high, with the top 10% of earners making 13 times more than the bottom 10%.
- The Gini Index, which measures consumption inequality, improved from 8 to 25.5, indicating a reduction in consumption inequality, but income inequality rose sharply, with the Gini for income increasing from 52 to 62.
- India also faces challenges in the youth labor market:
- Youth unemployment stands at 3%, and graduate unemployment is significantly higher at 29%. The majority of employment remains in the informal sector, particularly in agriculture.
- Female employment remains low at 31%, with a 234 million gap compared to male employment. However, employment rates have been rising since the 2021–22 fiscal year.
Conclusion
- While India has made significant progress in reducing both monetary and multidimensional poverty, challenges persist.
- The growing inequality, particularly in income, and issues such as youth unemployment and gender disparities in employment require continued focus.
- The progress made in poverty reduction is encouraging, but sustained efforts are necessary to ensure that the benefits of growth reach all sections of society, particularly those in the most vulnerable regions and
Consider the following statements regarding India’s poverty reduction as per the World Bank’s Poverty and Equity Briefs (PEBs):
- India’s extreme poverty rate dropped from 16% in 2011–12 to 2.3% in 2022–23.
- The decline in poverty was equally distributed between rural and urban areas, with both showing identical reductions in extreme poverty.
- The Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI), which includes factors like education and access to basic services, showed a steady decrease in non-monetary poverty from 2005–06 to 2022–23.
- The five most populous states—Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Bihar, West Bengal, and Madhya Pradesh—accounted for 54% of the country’s extreme poor in 2022–23.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1, 3, and 4 only
(b) 1 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct – Extreme poverty has decreased from 16% in 2011–12 to 2.3% in 2022–23, marking significant progress.
- Statement 2: Incorrect – The decline in extreme poverty was not equally distributed. Rural areas saw a drop from 18.4% to 2.8%, while urban areas saw a decrease from 10.7% to 1.1%, showing a significant rural-urban gap.
- Statement 3: Correct – The Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) showed a steady decline in non-monetary poverty from 53.8% in 2005–06 to 15.5% in 2022–23.
- Statement 4: Correct – Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Bihar, West Bengal, and Madhya Pradesh accounted for 54% of India’s extreme poor in 2022–23, and they had contributed to two-thirds of the overall decline in poverty.
Overseas Remittances by Indians under LRS were Down 29%
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
- In February 2025, overseas remittances by Indian residents under the Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) experienced a significant drop of 29%, falling to $1,964.21 million from $2,768.89 million in January.
The Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS)
- The Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS), introduced under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999, governs the outward remittance from India. The scheme allows resident individuals, including minors, to freely remit up to $2,50,000 per financial year for a variety of current and capital account transactions, such as:
- Education expenses abroad
- Medical treatment
- Purchase of property
- Investments in foreign stocks and bonds
- Additionally, the Union Budget of February 2025 increased the threshold for Tax Collected at Source (TCS) on LRS transactions from ₹7 lakh to ₹10 lakh. This change is expected to provide a boost to sectors like travel, foreign exchange, tourism, education, and aviation, as it would benefit individuals undertaking transactions in these areas.
Reasons Behind the Decline in Overseas Remittances
- The 29% drop in remittances in February 2025 can be attributed to several factors:
- Decline in Indian Students Going Abroad: There was a sharp 25% decline in the number of Indian students receiving study permits for top destination countries like Canada, the United States, and the United Kingdom in 2024. This reduction has significantly impacted remittances, as educational expenses abroad constitute a large portion of LRS transactions.
- Postponed or Canceled Travel Plans: The volatile movements in global economies and markets during the period led many individuals to reconsider or postpone their travel plans, affecting outbound remittances.
What Are Remittances?
- Remittances refer to funds transferred by individuals to their family or friends in another country. These transfers are most commonly made by individuals working abroad, often in blue-collar or skilled jobs, to support their families back home.
- Impact of Remittances
- Remittances play a crucial role in the economies of many countries by:
- Providing financial support to families
- Contributing to economic stability
- Supporting local businesses and communities
- Helping finance national trade deficits
Types of Remittances
- There are two main types of remittances based on the purpose of the transaction:
- Inward Remittance: Transfer of funds into a country, either from another country or within the same country.
- Outward Remittance: Transfer of funds out of the country, typically for education, medical treatment, or investments abroad.

India’s Remittances Overview
- India has seen remarkable growth in remittances over the years, with the total amount more than doubling from $55.6 billion in 2010-11 to $118.7 billion in 2023-24.
- Key Contributors to India’s Remittances
- S. and U.K.: Remittances from the U.S. and U.K. have nearly doubled, now contributing 40% of the total inward remittances in FY24, up from 26% in FY17. The U.S. emerged as the largest source of remittances, contributing 28% in FY24, up from 23.4% in FY21.
- UAE: The UAE remains the second-largest contributor to India’s remittances, accounting for 2% in FY24. Indian migrants in the UAE, especially in blue-collar jobs such as construction, healthcare, hospitality, and tourism, play a major role in this inflow.
- Singapore: Singapore’s share of remittances has risen to 6% in FY24, up from 5.5% in FY17, marking the highest share for the country in recent years.
State-wise Distribution of Remittances
- The distribution of remittances across Indian states highlights the concentration of remittance inflows in specific regions:
- Maharashtra, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu together accounted for half of the total remittances received in India.
- States like Haryana, Gujarat, and Punjab had smaller shares, each contributing below 5% of the total remittances.
Size of Remittances
- The distribution of remittances also varies based on the transaction amount:
- 6% of remittances were over ₹5 lakh, reflecting a higher volume of large transfers.
- Meanwhile, 6% of remittances were ₹16,500 or less, indicating the prevalence of smaller transfers from Indian workers abroad.
Conclusion
- The decline in overseas remittances in February 2025 under the Liberalised Remittance Scheme reflects a combination of global economic challenges, reduced student mobility, and postponed travel plans. Despite this temporary setback, India continues to receive substantial remittances, which play a vital role in the nation’s economy, particularly in providing financial support to families and communities. The increase in the TCS threshold and the growing role of countries like the U.S., UAE, and Singapore in remittance inflows indicates ongoing opportunities for growth in this sector.
Consider the following statements regarding the Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI):
- The LRS allows resident individuals, including minors, to remit up to $2,50,000 per financial year for permissible transactions like education, medical treatment, and investments abroad.
- The Union Budget of February 2025 raised the Tax Collected at Source (TCS) threshold for LRS transactions from Rs 7 lakh to Rs 10 lakh, benefiting the travel and tourism sectors.
- Under LRS, only Indian citizens are eligible for outward remittance, excluding non-resident Indians (NRIs).
- The LRS is governed by the Reserve Bank of India under the provisions of the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA).
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1, 2, and 4 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct – The LRS allows individuals, including minors, to remit up to $2,50,000 per year for permitted transactions.
- Statement 2: Correct – The TCS threshold for LRS transactions was raised from Rs 7 lakh to Rs 10 lakh in the 2025 Budget to benefit sectors like tourism, education, and aviation.
- Statement 3: Incorrect – Non-resident Indians (NRIs) are not excluded from the LRS; the scheme is for all resident individuals, including NRIs.
- Statement 4: Correct – The scheme is governed by the RBI under FEMA, 1999.
Medical Tourism in India
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
- India has emerged as one of the most popular destinations for treatment and medical tourism, according to the Minister of State for AYUSH.
- About Medical Tourism:
- Medical tourism refers to the practice of traveling to another country or region for medical treatment, procedures, or health-related services. India has become a prominent hub in the medical tourism industry, valued at approximately $9 billion. The country attracts international patients seeking advanced treatments in fields such as cardiology, orthopedics, oncology, and organ transplants.
- In 2023, medical tourism in India witnessed a growth of around 33%, with approximately 6 lakh international patients. Key cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Bangalore, and Hyderabad are prominent destinations for medical tourism due to their world-class healthcare infrastructure.
- Factors Driving the Growth of Medical Tourism in India:
- Cost-Effective Treatment: India offers medical procedures at a fraction of the cost compared to countries like the US or Europe, making it an attractive option for international patients.
- High-Quality Healthcare: The country boasts internationally accredited hospitals and highly skilled medical professionals.
- Availability of Advanced Medical Technology: Indian hospitals are equipped with state-of-the-art medical technology, particularly in cardiology, oncology, and orthopedics.
- Shorter Wait Times: Compared to some Western healthcare systems, medical tourists in India can access timely treatments without long waiting periods.
- Government Support and Policies: The Indian government has implemented policies to facilitate medical tourism, such as medical visa provisions and promotional activities for the sector.
Significance for India:
- Economic Growth: Medical tourism contributes significantly to India’s economy by generating revenue from international patients and stimulating related industries such as hospitality and transportation.
- Improved Healthcare Infrastructure: To cater to medical tourists, hospitals are investing in modern facilities, which simultaneously improve the quality of healthcare for local patients.
- Promotion of India’s Global Image: India’s rise as a medical tourism destination enhances its international reputation, attracting foreign investment and partnerships in the healthcare sector.
- Technological Advancements: The demand for advanced treatments drives innovation and the adoption of new medical technologies within Indian healthcare.
- Skill Development: Exposure to international patients and standards fosters skill development for healthcare professionals.
- Diplomatic Ties: The influx of medical tourists from various countries promotes cultural exchange and fosters goodwill, strengthening diplomatic relations.
- Challenges:
- Competition: India faces stiff competition from other medical tourism destinations like Malaysia, Thailand, and Singapore.
- Lack of Insurance Coverage: Many medical procedures in India are not covered by insurance, reducing the appeal of medical value travel (MVT).
- Unregulated MVT Sector: The MVT industry lacks comprehensive regulation, leaving the sector disorganized with potential exploitation of medical travelers by unprofessional agents.
- Limited Promotion: While individual hospitals engage in promotional activities, there is no cohesive national campaign to establish India as a top global destination for medical value travel.
- Accreditation Awareness: Though India has a strong accreditation system like the National Accreditation Board for Hospitals and Healthcare Providers (NABH), international patients often prioritize Joint Commission International (JCI) accreditation, which is more recognized globally.
- Way Ahead:
- Rising Demand for Wellness: As modern lifestyles increase the demand for wellness and alternative cures, India has a unique opportunity to attract medical tourists for treatments in AYUSH (Ayurveda, Yoga, Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, and Homoeopathy) and wellness therapies.
- Government Support: Increased government facilitation, regulation, and marketing are essential to establish India as a leading medical value travel destination.
- Promotion of AYUSH: India’s investment in AYUSH places it in a strong position to cater to medical value travelers seeking holistic and alternative cures.
Consider the following statements regarding Medical Tourism in India:
- India’s medical tourism sector is valued at approximately $9 billion, with an annual growth rate of 33%.
- India’s healthcare infrastructure is concentrated primarily in tier-2 cities, such as Patna, Bhopal, and Nagpur.
- Medical tourism in India is primarily driven by the country’s cost-effective treatment options, with procedures available at a fraction of the cost compared to the US and Europe.
- The Indian government has implemented policies such as medical visa provisions and promotional activities to boost the medical tourism sector.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1, 3, and 4 only
(b) 2, 3, and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 4 only
(d) 1, 3 only
Answer: (a) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct: India’s medical tourism sector is indeed valued at approximately $9 billion, and it experienced a growth of about 33% in 2023, attracting around 6.6 lakh international patients. This makes India one of the leading destinations in the global medical tourism market.
- Statement 2: Incorrect: India’s key cities for medical tourism are Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Bangalore, and Hyderabad. These cities are home to advanced healthcare infrastructure and internationally accredited hospitals. Tier-2 cities like Patna, Bhopal, and Nagpur are not primarily noted for their medical tourism appeal.
- Statement 3: Correct: One of the major driving factors behind the growth of medical tourism in India is the cost-effectiveness of medical procedures. Compared to countries like the US and Europe, the costs of treatments in India are significantly lower, which attracts international patients seeking affordable yet high-quality healthcare.
- Statement 4: Correct:The Indian government has implemented various policies, including the facilitation of medical visas and promotional activities, to promote medical tourism. These efforts aim to attract more international patients and boost India’s position as a leading global destination for medical value travel (MVT).
Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT)
Syllabus:Economy
About Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT):
What is CBDT?
- The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) is a statutory authority in India responsible for overseeing the administration of direct tax laws. It operates under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
- Established: 1964
- Formed under: The Central Board of Revenue Act, 1963, after the bifurcation of the Central Board of Revenue (1924).
- Ministry: Ministry of Finance, Government of India
Objectives:
- Formulate and enforce policies for the administration of direct taxes.
- Ensure effective enforcement and compliance of tax laws.
- Broaden and deepen the tax base to support fiscal stability.
- Promote transparency, encourage voluntary tax compliance, and combat tax evasion.
Members:
The CBDT consists of one Chairperson and six members.
Functions:
- Policy Formulation: Responsible for drafting and administering policies related to direct taxes, such as income tax, corporate tax, and wealth tax (which is now abolished).
- Supervision: Oversees the operations of the Income Tax Department to ensure efficient tax collection and compliance.
- Investigation: Carries out searches, raids, and tax assessments to detect and prevent tax evasion and black money.
- International Cooperation: Engages in tax treaties, information exchange, and global tax compliance efforts.
- Taxpayer Services: Facilitates ease of compliance through initiatives such as grievance redressal, e-filing platforms, and awareness programs.
- Legislative Initiatives: Reviews and drafts amendments to tax laws and regulations to ensure their relevance and effectiveness.
Which of the following are the main objectives of the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT)?
- Formulation of policies related to direct taxes.
- Ensuring effective tax enforcement and compliance.
- Direct administration of corporate tax laws.
- Prevention of indirect tax evasion.
A. 1, 2, and 3 only
B. 1, 2, and 4 only
C. 1 and 2 only
D. 3 and 4 only
Answer:A
Explanation: The CBDT primarily focuses on direct taxes, formulation of policies, ensuring compliance, and curbing tax evasion, but does not deal directly with corporate tax laws or indirect tax matters.
DRDO’s Breakthrough: India Advances Hypersonic Propulsion
Syllabus: GS3/Science & Technology; Defence
The Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL), a unit of DRDO (Defence Research and Development Organisation), has successfully conducted a ground test of an Active-Cooled Scramjet Subscale Combustor for over 1000 seconds. This milestone is a crucial step in advancing India’s hypersonic weapon technology.
About Hypersonic Propulsion Technology:
Hypersonic propulsion technology is at the forefront of aerospace engineering, enabling vehicles to travel at speeds exceeding Mach 5 (five times the speed of sound). This technology is primarily used in hypersonic cruise missiles and advanced aerospace systems.

Key Features of Hypersonic Propulsion Technology:
- Air-Breathing Engines: Hypersonic vehicles use Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet) engines that rely on atmospheric oxygen for combustion, rather than carrying onboard oxidizers. This makes them more efficient for sustained high-speed flight.
- Scramjet Engine: A Scramjet is an air-breathing engine that efficiently operates at hypersonic speeds by allowing supersonic combustion of incoming air.
- Key Difference from Ramjet: In a Ramjet, the air slows down to subsonic speeds before combustion. In contrast, in a Scramjet, the air remains supersonic throughout the combustion process, enabling higher speeds.
- Working Principle: Scramjets use the vehicle’s forward motion to compress incoming air, eliminating the need for rotating compressors.
- India became the fourth country, after the USA, Russia, and China, to demonstrate flight testing of a Scramjet engine.
Significance of the Scramjet Engine Test:
- Validation of Long-Duration Supersonic Combustion: The successful test validates the design and efficiency of the scramjet combustor, ensuring that it can sustain high-speed flight capabilities for extended periods.
- Incremental Advancements: The test follows a successful 120-second test conducted earlier in January, showcasing incremental progress toward more advanced hypersonic technology.
- Strengthening India’s Hypersonic Missile Program: Scramjet engines facilitate air-breathing propulsion, which reduces reliance on onboard oxidizers and significantly enhances the missile’s range and performance.
- Paving the Way for Full-Scale Flight Testing: The success of this test is a critical step toward the full-scale flight testing of hypersonic cruise missiles, strengthening India’s position in the global hypersonic missile race.
Consider the following statements regarding Hypersonic Propulsion Technology and the recent developments in India’s DRDO research:
- DRDL (Defence Research and Development Laboratory) recently conducted a successful ground test of an Active-Cooled Scramjet Subscale Combustor for over 1000 seconds, marking a key milestone for India’s hypersonic weapon program.
- Hypersonic propulsion technology primarily uses air-breathing engines such as Scramjets, which rely on onboard oxidizers to achieve sustained high-speed flight.
- A Scramjet engine is more efficient than a traditional Ramjet engine because it allows supersonic combustion of air, unlike Ramjets that slow the incoming air to subsonic speeds before combustion.
- With the successful test, India became the fifth country after the USA, Russia, China, and Japan to demonstrate flight testing of a Scramjet engine.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1 and 2 only
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct – DRDL successfully tested an Active-Cooled Scramjet Subscale Combustor, marking an important step for hypersonic weapon technology in India.
- Statement 2 is incorrect – Scramjet engines do not use onboard oxidizers; they rely on atmospheric oxygen for combustion.
- Statement 3 is correct – In Scramjets, air remains supersonic throughout combustion, unlike Ramjets, which slow down the air to subsonic speeds before combustion.
- Statement 4 is incorrect – India became the fourth country to demonstrate a Scramjet engine after the USA, Russia, and China, not the fifth.
Line of Control (LoC)
Syllabus: GS3/ Defence
- The Indian Army recently reported incidents of small arms firing along the Line of Control (LoC) at several locations in Jammu and Kashmir, including Kupwara in the Kashmir Valley.
About the LoC:
- The Line of Control (LoC) serves as the military boundary between Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir (POK) and the Indian-administered regions of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. Established following the 1972 Simla Agreement, the LoC is a military line that was agreed upon bilaterally but is not recognized as an official international border.
- The current LoC has its origins in the first Ceasefire Line (CFL), which was drawn after the India-Pakistan war of 1947-48. A UN-brokered ceasefire was declared in 1949, and the subsequent 1949 Karachi Agreement formalized the points that defined the de facto boundary between the two countries in Jammu and Kashmir.
Consider the following statements regarding the Line of Control (LoC):
- The LoC came into being after the 1972 Simla Agreement between India and Pakistan.
- The LoC is a legally recognized international border between India and Pakistan.
- The 1949 Karachi Agreement demarcated the de facto boundary between India and Pakistan in Jammu and Kashmir.
- The current LoC originates from the first Cease-Fire Line (CFL) established after the 1947 India-Pakistan war.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1, 3, and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 1, 3, and 2 only
Answer: (a) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct – The LoC was formalized following the 1972 Simla Agreement between India and Pakistan.
- Statement 2: Incorrect – The LoC is not a legally recognized international border but a military line agreed bilaterally between India and Pakistan.
- Statement 3: Correct – The 1949 Karachi Agreement between India and Pakistan defined the de facto boundary in Jammu and Kashmir after a UN-brokered ceasefire.
- Statement 4: Correct – The current LoC originates from the Ceasefire Line (CFL) established after the 1947 India-Pakistan war.
National Supercomputing Mission
Syllabus: GS3(Science and Tech)
Overview
- Launched in 2015, the National Supercomputing Mission (NSM) is a flagship initiative of the Government of India aimed at building high-performance computing (HPC) capabilities and fostering indigenous supercomputing infrastructure.
- It is jointly steered by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and the Department of Science and Technology (DST), and implemented by C-DAC, Pune and IISc Bengaluru.
Key Objectives
- Enhance India’s capability in scientific research, innovation, and industrial applications using supercomputing.
- Foster indigenous development in hardware and software for HPC systems.
- Build human resource capacity in HPC and AI across the country.
- Enable R&D across Tier I, II, and III academic and research institutions.
Achievements (As of March 2025)
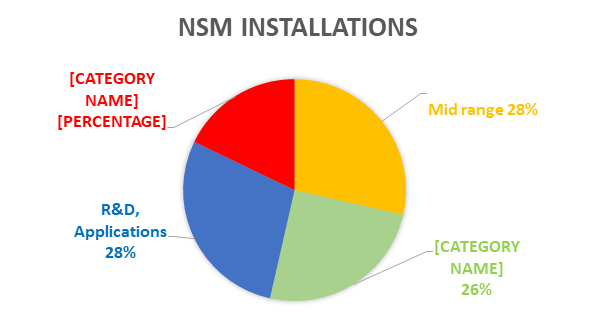
- 34 supercomputers installed with a total computing capacity of 35 Petaflops across premier institutions including IITs, IISc, and C-DAC.
- Over 10,000 researchers including 1,700+ PhD scholars supported across 200+ institutions.
- Over 1 crore compute jobs processed and 1,500+ research papers
- 85%+ utilization rate, with many systems exceeding 95% efficiency.
- More than 22,000 trained in HPC and AI.
- Active participation from startups and MSMEs in leveraging HPC for innovation.
Major Deployments
- Param Shivay (2019) – First indigenously built system, IIT-BHU.
- Param Pravega (2022) – 3.3 PF system at IISc Bengaluru; largest in an Indian academic institution.
- PARAM Rudra Series (2024) – Deployed in Pune, Delhi, and Kolkata; built with indigenous “Rudra” HPC-class servers and software.
Key Innovations
- Trinetra Network – Indigenous high-speed interconnect for supercomputers:
- Trinetra-A (100 Gbps) – Deployed in 1 PF PARAM Rudra, Pune.
- Trinetra-B (200 Gbps) – To power upcoming 20 PF system at Bangalore.
- AIRAWAT AI Supercomputing Platform:
- 200 AI Petaflops, scalable to 790 AI Petaflops.
- Ranked 75th in Top 500 Global Supercomputers (ISC 2023).
- Common AI compute infrastructure for research, start-ups, and industry.
Mission Phases
- Phase I: Basic systems with partial domestic assembly.
- Phase II: Indigenous manufacturing of components; 40% value addition.
- Phase III: Full indigenization of design, development, and deployment.
Human Resource Development (HRD)
- Training centers established in Pune, Kharagpur, Chennai, Palakkad, and Goa.
- Focus on awareness, capacity-building, and skill development in HPC and AI.
Budget and Investment
- 1874 crore allocated for infrastructure, R&D, HRD, and mission operations.
- Target to deploy ~45 additional Petaflops by 2025 using indigenous technologies.
Strengthening through India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- ISM supports domestic manufacturing of critical supercomputing components—processors, memory, accelerators—reducing dependence on imports.
- This synergy boosts speed, affordability, and customization of supercomputers for national needs.
Conclusion
- The NSM is a transformative step toward India’s technological sovereignty in supercomputing. With strategic focus on indigenization, research empowerment, and global competitiveness, the mission positions India as a leading force in the High-Performance Computing (HPC) domain and ensures preparedness for emerging scientific challenges.
Which of the following statements regarding the National Supercomputing Mission (NSM) are correct?
- NSM was launched to enhance India’s technological self-reliance in the field of high-performance computing (HPC).
- The NSM is being implemented solely by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- Trinetra, developed under NSM, is a high-speed communication network that supports supercomputing infrastructure across the country.
- The NSM Phase III focuses on complete indigenization of HPC systems, including the design, development, and manufacturing of key components in India.
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The NSM was launched to make India self-reliant in supercomputing, and it enhances the country’s ability to tackle grand challenges in scientific research and technology.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: While the NSM is steered by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and the Department of Science and Technology (DST), it is implemented jointly by C-DAC and IISc Bengaluru, not solely by MeitY.
- Statement 3 is correct: Trinetra is an indigenous high-speed communication network developed under NSM to enhance data transfer between supercomputing nodes.
- Statement 4 is correct: Phase III of the NSM focuses on the complete indigenization of HPC, including the domestic design and manufacturing of critical components.
In 2024, India’s military expenditure was nine times that of Pak.: SIPRI
Syllabus: Defence
- India’s Military Expenditure in 2024: A Comparative Analysis with Pakistan
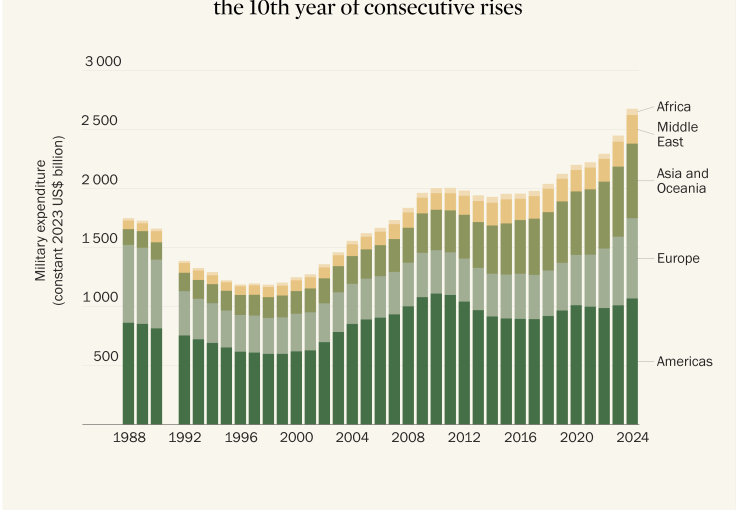
- According to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), India’s military expenditure in 2024 was approximately $86.1 billion, marking a 1.6% increase from the previous year.
- This positions India as the fifth-largest military spender globally. In stark contrast, Pakistan’s defense budget stood at $10.2 billion, making it the 29th largest spender. This disparity indicates that India’s military spending was nearly nine times greater than Pakistan’s in 2024.
- The top five military spenders globally in 2024 were:
- United States – $997 billion
- China – $314 billion
- Russia – $149 billion
- Germany – $88.5 billion
- India – $86.1 billion
- Collectively, these five nations accounted for 60% of the global military expenditure, totaling $1,635 billion.
- In the context of South Asia, India’s defense spending significantly outpaces that of its neighbors. While India has been focusing on modernizing its military capabilities, Pakistan’s defense budget remains limited, reflecting the broader economic and strategic challenges faced by the country.
- This substantial difference in military expenditure underscores the varying defense priorities and capabilities within the region. India’s investment in defense modernization is part of its broader strategy to enhance its geopolitical influence and address security concerns, particularly in the Indo-Pacific region.
With reference to the “Trends in World Military Expenditure 2024” report by the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), consider the following statements:
- India ranked among the top five global military spenders, with its expenditure nearly nine times that of Pakistan.
- In 2024, China accounted for over half of Asia and Oceania’s total military expenditure, marking its 30th consecutive year of increase.
- Ukraine’s military spending in 2024 was higher than that of Russia, given the ongoing conflict and foreign assistance.
- The United States remained the highest military spender globally, accounting for more than half of global military expenditure.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2, and 3 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct – India’s military spending stood at $86.1 billion, nearly nine times that of Pakistan’s $10.2 billion, placing it 5th globally.
- Statement 2: Correct – China’s expenditure reached $314 billion, marking three decades of consistent growth and constituting 50% of Asia and Oceania’s total military outlay.
- Statement 3: Incorrect – Although Ukraine spent $64.7 billion, this was still only 43% of Russia’s spending ($149 billion).
- Statement 4: Incorrect – The U.S. topped global spending but accounted for less than 50% of the total global defense expenditure (~60% shared among top five).
Bio-Input Resource Centres
Syllabus:Science
Context: The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare has introduced guidelines for establishing Bio-Input Resource Centres (BRCs) to promote natural farming under the National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF).
About Bio-Input Resource Centres (BRCs)
- BRCs are cluster-level enterprises that provide farmers with locally prepared natural farming inputs, such as bio-fertilizers, bio-pesticides, and organic formulations.
- They also function as knowledge hubs, offering training and guidance to farmers transitioning to natural farming practices.
- Established Under: Launched under the National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF).
Objectives:
- Ensure easy access to high-quality bio-inputs for farmers.
- Equip farmers with technical knowledge on natural farming methods.
- Promote the expansion of natural farming practices in villages.
Key Features:
- Financial Support: Rs. 1 lakh per centre, provided in two tranches of Rs. 50,000 each.
- Eligibility for Entrepreneurs: Entrepreneurs must either practice or be willing to adopt natural farming.
- Customized Inputs: Bio-inputs will be developed according to local soil conditions, crop patterns, and the specific needs of farmers.
- Training Support: Farmers will be trained in botanical extracts, bio-input preparation, and pest management techniques.
- For-Profit Model: BRCs will operate as sustainable ventures, promoting local economic development.
- Market Facilitation: BRCs will explore partnerships with Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), State Rural Livelihood Missions (SRLMs), and agriculture marketing boards.
About the National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF)
- The National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF) is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme aimed at promoting chemical-free, sustainable agriculture based on local agro-ecology and indigenous knowledge.
Objectives:
- Promote natural farming to ensure the production of safe and nutritious food.
- Reduce the dependency on chemical inputs and lower the costs of cultivation.
- Build healthy soil ecosystems, support biodiversity, and enhance climate resilience.
Which of the following is/are true regarding the Bio-Input Resource Centres (BRCs) under the National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF)?
- BRCs are intended to promote chemical-based farming inputs to improve agricultural productivity.
- Entrepreneurs involved in BRCs must either practice or be willing to adopt natural farming.
- Financial support of Rs. 1 lakh per centre is provided in two tranches of Rs. 50,000 each.
- BRCs will only focus on the production of chemical fertilizers and pesticides for farmers.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
A. 1, 2, and 3 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 3, and 4 only
D. 1 and 4 only
Answer:B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect because BRCs promote natural farming inputs, not chemical-based farming.
- Statement 2 is correct as it emphasizes the importance of natural farming practices for entrepreneurs.
- Statement 3 is correct regarding the financial support provided.
- Statement 4 is incorrect as BRCs focus on bio-fertilizers, bio-pesticides, and organic formulations, not chemical inputs.
National Zero Measles-Rubella Elimination campaign 2025-26
Syllabus: GS2/ Health
- The Union Minister of Health and Family Welfare has launched the National Zero Measles-Rubella Elimination Campaign 2025-26, aiming to eliminate measles and rubella from India.
Measles:
- Measles is a highly contagious viral infection, primarily affecting children. It is transmitted through respiratory droplets from the nose, mouth, or throat of infected individuals. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure and include:
- High fever
- Runny nose
- Bloodshot eyes
- Tiny white spots inside the mouth
Rubella:
- Rubella, also known as German measles, is an acute, typically mild viral infection affecting children and young adults worldwide. Symptoms include:
- Low-grade fever
- Sore throat
- A rash that begins on the face and spreads
Indian Scenario:
- India is focused on maintaining over 95% vaccination coverage with two doses of the Measles-Rubella (MR) vaccine in each district.
- In 2024, there was a significant reduction in cases of measles and rubella. Measles cases dropped by 73%, while rubella cases declined by 17% compared to 2023.
U-WIN Digital Platform:
- The U-WIN Digital Platform has been launched to streamline vaccination services by providing online registration, appointment scheduling, and digital certificates to enhance the vaccination process.
Consider the following statements regarding the National Zero Measles-Rubella Elimination Campaign launched by the Union Minister of Health and Family Welfare:
- The campaign aims to eliminate measles and rubella by 2025-26 with a focus on maintaining over 95% vaccination coverage across all districts.
- Measles is a viral disease that affects primarily adults, with symptoms appearing 10–12 days post-infection, including fever and rashes.
- Rubella is a mild viral disease primarily affecting young adults, and it is also known as German measles. It causes low-grade fever and a rash starting from the face.
- The U-WIN Digital Platform was introduced to streamline vaccination services by offering online registration, appointment booking, and digital certification.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1, 3, and 4 only
(b) 1, 2, and 4 only
(c) 2, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct – The National Zero Measles-Rubella Elimination Campaign focuses on achieving over 95% vaccination coverage with two doses of the Measles-Rubella (MR) vaccine in all districts to eliminate measles and rubella by 2025-26.
- Statement 2: Incorrect – Measles primarily affects children, not adults. Symptoms usually appear 10–12 days after infection, including fever, runny nose, bloodshot eyes, and tiny white spots on the inside of the mouth.
- Statement 3: Correct – Rubella is indeed a mild disease, primarily affecting children and young adults, and is commonly referred to as German measles. The symptoms include a low-grade fever, sore throat, and a rash starting on the face.
- Statement 4: Correct – The U-WIN Digital Platform has been launched to streamline vaccination services by enabling online registration, appointment scheduling, and issuing digital certificates for vaccinations.
Agricultural Land Contaminated by Toxic Heavy Metal Pollution
Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
A recent study has highlighted the significant impact of soil pollution from toxic heavy metals and metalloids on crop yields and food safety globally.
Key Highlights:
- The research reveals that 14% to 17% of the world’s agricultural soils (about 242 million hectares) exceed safe limits for at least one hazardous metal.
- This contamination affects between 900 million and 1.4 billion people living in high-risk areas.
- A heavily polluted region has been identified across low-latitude Eurasia, covering southern Europe, the Middle East, South Asia, and southern China.
- Common contaminants include cadmium, arsenic, cobalt, nickel, and chromium.
Causes of Heavy Metal Accumulation:
Anthropogenic Causes: Mining, smelting, industrial activities, and intensive agriculture (especially the overuse of fertilizers and pesticides).
Natural Causes: Metal-rich bedrock and low rainfall in some areas that facilitate the accumulation of pollutants.
Impact of Metal Contamination:
Food Chain Contamination: Crops grown in polluted soils absorb heavy metals such as cadmium, arsenic, lead, and mercury, which then enter the human body through food consumption.
Bioaccumulation: Continuous ingestion of low doses of these metals leads to bioaccumulation, causing chronic health issues, including neurological and developmental disorders.
Biodiversity Loss: Toxic metals harm vital soil organisms like earthworms, insects, and microbes, reducing biodiversity both in the soil and above ground.
Land Degradation: Persistent pollution can make soils barren, contributing to land degradation and desertification.
Concerns:
Data Gaps: Limited data from regions like sub-Saharan Africa, northern Russia, and parts of central India may indicate that the contamination is even more widespread.
Food Trade Risks: Global food trade can inadvertently spread contamination from high-risk regions to low-risk ones, posing a threat to global food security.
Rising Demand for Metals: Increasing industrial demand for metals may worsen the contamination problem without urgent mitigation actions.
Government Initiatives for Soil Conservation:
Soil Health Card Scheme: Provides farmers with reports on soil nutrient status to encourage balanced fertilizer use and improve productivity.
Promotion of Organic Farming: Programs like Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY) promote organic farming practices to maintain soil health.
National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA): Focuses on improving soil health through integrated farming systems and agroforestry.
Global Initiatives:
Global Soil Partnership (GSP): A FAO-led initiative aimed at improving global soil governance and promoting sustainable soil management.
United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD): Works to prevent land degradation and promotes sustainable land management practices globally. The UNCCD has set a goal of land degradation neutrality (LDN) by 2030.
4 per 1000 Initiative: Aims to increase soil carbon stocks by 0.4% annually to fight climate change and enhance soil health.
Way Forward:
Soil Health Observatories: Establish regional soil health observatories and expand soil survey coverage.
Phytoremediation: Use hyperaccumulator plants and microbes to clean up contaminated soils.
Circular Economy: Promote the recycling and management of e-waste and industrial waste to prevent further soil contamination.
Farmer Awareness Programs: Educate farmers about the risks of heavy metal contamination, safe agricultural practices, and alternative cropping systems.
Consider the following statements regarding soil pollution caused by toxic heavy metals and metalloids:
- A significant proportion of the world’s agricultural soils, between 14% and 17%, exceed safe thresholds for at least one hazardous metal, affecting approximately 900 million to 1.4 billion people.
- The primary anthropogenic causes of heavy metal accumulation in soils are mining, smelting, and the use of chemical fertilizers in agriculture.
- Bioaccumulation due to heavy metal ingestion only affects agricultural workers, not the general population.
- The region identified as the most heavily contaminated by toxic metals includes sub-Saharan Africa, northern Russia, and central India.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2, and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 1 only
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct – Studies indicate that 14-17% of global agricultural soils exceed safe limits for hazardous metals, affecting a significant global population.
- Statement 2: Correct – Anthropogenic activities such as mining, industrial processes, and fertilizer overuse are primary causes of soil metal contamination.
- Statement 3: Incorrect – Bioaccumulation from heavy metals affects both agricultural workers and the general population through contaminated food chains.
- Statement 4: Incorrect – The most heavily polluted region identified does not include sub-Saharan Africa or northern Russia; it primarily affects regions like southern Europe, the Middle East, South Asia, and southern China.
Towards a new approach for green hydrogen production
GS3(Environment)
- Researchers have developed advanced insights into proton adsorption behavior on catalyst surfaces, providing a foundational step toward designing efficient electrocatalysts for green hydrogen production.
- While various heterostructures have been studied for hydrogen generation, metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) based p–n heterojunctions stand out due to their robust built-in electric field (BIEF), arising from asymmetric electronic environments.
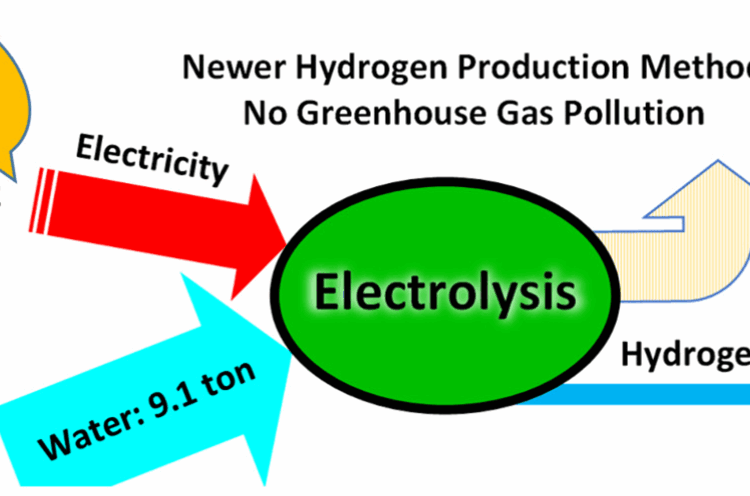
- Recent research emphasizes the critical role of BIEF at material interfaces, with key parameters such as work function differences, BIEF strength, and Gibbs free energy of adsorption (∆G) being central to understanding the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) The work function differential initiates charge redistribution, creating the BIEF, which significantly influences proton adsorption and desorption dynamics.
- A team from the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, synthesized a CuWO₄–CuO heterostructure by depositing CuWO₄ nanoparticles on a Cu(OH)₂ precursor. This structure was then analyzed for its electrochemical behavior and ∆G profile across various regions. Remarkably, the depletion region and interface zone showed distinct adsorption energies compared to the bulk, forming a gradient that favors enhanced proton adsorption and release.
Their findings revealed that:
- CuO regions exhibit high proton adsorption affinity.
- CuWO₄ regions facilitate proton desorption.
- The system demonstrates negative cooperativity, where increased proton coverage reduces further adsorption affinity, thereby optimizing HER under alkaline conditions.
- Published in Advanced Energy Materials (2025), this study showcases how the interplay between BIEF and thermodynamics can be engineered to significantly boost catalytic performance. The research paves the way for the design of next-generation electrocatalysts, contributing to sustainable energy transitions through green hydrogen technology.
Consider the following statements regarding the CuWO₄–CuO heterostructure developed by the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali:
- The heterostructure was synthesized by depositing CuWO₄ nanoparticles onto a Cu(OH)₂ precursor.
- The built-in electric field (BIEF) at the p–n junction significantly influences proton adsorption and desorption dynamics.
- The system exhibits positive cooperativity, where increased proton coverage enhances further adsorption affinity.
- The study was published in Advanced Energy Materials in 2025.
Which of the above statements are correct?
Options:
(a) 1, 2, and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer: (a) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The CuWO₄–CuO heterostructure was synthesized by depositing CuWO₄ nanoparticles onto a Cu(OH)₂ precursor, as reported by INST, Mohali.
- Statement 2 is correct: The built-in electric field (BIEF) at the p–n junction plays a crucial role in modulating proton adsorption and desorption dynamics, enhancing the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) efficiency.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The system exhibits negative cooperativity, not positive cooperativity. This means that as proton coverage increases, the affinity of the catalyst’s surface for additional proton adsorption decreases, facilitating efficient desorption and promoting HER under alkaline conditions.
- Statement 4 is correct: The findings were published in Advanced Energy Materials in 2025, contributing valuable insights into electrocatalytic hydrogen production.
AIM4NatuRe initiative
Syllabus:Environment
Context: The FAO, with support from the UK, launched the AIM4NatuRe initiative to enhance global monitoring of ecosystem restoration efforts, aligning with the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
About AIM4NatuRe Initiative:
- The Accelerating Innovative Monitoring for Nature Restoration (AIM4NatuRe) is a global initiative designed to improve the monitoring and reporting of ecosystem restoration efforts.
- Launched By: The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations.
- Funding Partner:The United Kingdom, which contributed GBP 7 million.
Objective:
- The initiative aims to strengthen countries’ capabilities to monitor and report on restoration progress, supporting the achievement of Target 2 of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, which calls for restoring at least 30% of degraded ecosystems by 2030.

Key Features:
- Technology-Driven: Utilizes advanced satellite and data analysis tools to monitor ecosystem restoration efforts.
- Global Dataset Creation: Aims to create a harmonized global dataset to track restoration activities across the world.
- Capacity Development: Provides training to countries on using data-driven methods to track restoration progress.
- Data Interoperability: Establishes standardized data formats for seamless integration and comparison across nations.
- Inclusivity Focus: Supports Indigenous Peoples’ monitoring efforts, with pilot projects in Brazil and Peru.
- Expansion: Expands beyond the forest sector (building on FAO’s AIM4Forests program) to include all ecosystems, such as wetlands, grasslands, and marine areas.
Significance:
- Transparency & Accountability: Encourages clear reporting and ownership of restoration targets.
- Filling Data Gaps: Addresses significant data and reporting gaps identified by 80% of countries in the CBD capacity survey.
- Nature-Based Solutions: Supports solutions that tackle climate change, biodiversity loss, and land degradation.
Consider the following statements regarding the AIM4NatuRe initiative launched by the FAO:
- AIM4NatuRe aims to restore 50% of degraded ecosystems globally by 2030, in line with the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
- The initiative uses advanced technologies, including satellite and data analysis tools, to improve the monitoring and reporting of ecosystem restoration efforts.
- AIM4NatuRe is funded exclusively by the United Nations, with the UK providing only technical assistance.
- The initiative includes pilot projects in Brazil and Peru to support Indigenous Peoples’ involvement in ecosystem monitoring.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 and 3 only
B) 2 and 4 only
C) 1, 2, and 4 only
D) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: B) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect. The target set by the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework is to restore at least 30% of degraded ecosystems by 2030, not 50%.
- Statement 2 is correct. The AIM4NatuRe initiative employs cutting-edge technologies, including satellite and data analysis tools, to monitor and report ecosystem restoration progress.
- Statement 3 is incorrect. The initiative is funded by the UK with a GBP 7 million contribution, alongside FAO’s efforts, not exclusively by the UN.
- Statement 4 is correct. AIM4NatuRe includes pilot projects in Brazil and Peru, focusing on Indigenous Peoples’ contributions to ecosystem restoration monitoring.
Draft Greenhouse Gases Emissions Intensity (GEI) Target Rules, 2025
Syllabus:Environment
Context:
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has released the Draft Greenhouse Gases Emissions Intensity (GEI) Target Rules, 2025, to implement India’s Carbon Credit Trading Scheme and support the achievement of its climate commitments.
About Draft Greenhouse Gases Emissions Intensity (GEI) Target Rules, 2025:
The GEI Target Rules, 2025 set mandatory targets for reducing emissions intensity in energy-intensive industries, forming a crucial part of India’s strategy to foster low-carbon industrial growth.
Released By: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India.
Objectives:
- Emission Reduction: Aim to reduce the greenhouse gas emissions intensity in key industrial sectors.
- Carbon Credit Trading: Operationalize the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS), 2023.
- Climate Commitment: Help India meet its Paris Agreement target to reduce emissions intensity of GDP by 45% by 2030, relative to 2005 levels.
- Promote Sustainable Practices: Encourage climate-resilient and innovative industrial practices.
Key Features:
- Baseline Year: The baseline for emissions intensity is set at 2023–24 levels.
- Reduction Timeline: Targets apply for the periods 2025–26 and 2026–27.
- Sector Focus: The rules target energy-intensive industries, including aluminium, cement, chlor-alkali, and pulp & paper sectors.
- Coverage: The rules cover 282 industrial units, including:
- 13 aluminium plants
- 186 cement plants
- 53 pulp & paper plants
- 30 chlor-alkali plants
- Compliance Mechanism: Carbon credits are awarded for emission reductions, with penalties imposed for non-compliance.
- Trading Platform: Carbon credits will be traded within the Indian Carbon Market, supervised by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency.
- Enforcement Authority: The Central Pollution Control Board will monitor compliance and enforce penalties for non-compliance.
- These rules are central to India’s efforts in reducing industrial emissions and creating a robust market for carbon credits, helping the country meet its climate commitments under the Paris Agreement.
Consider the following statements regarding the Draft Greenhouse Gases Emissions Intensity (GEI) Target Rules, 2025:
- The GEI Target Rules primarily focus on reducing emissions intensity across the energy-intensive sectors, including aluminium, cement, chlor-alkali, and pulp & paper industries.
- The rules are designed to help India achieve its Paris Agreement target of reducing emissions intensity of GDP by 40% by 2030, relative to 2005 levels.
- The compliance mechanism includes awarding carbon credits for emissions reductions and imposing penalties for industries failing to meet their targets.
- The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) is tasked with overseeing the trading of carbon credits under the Indian Carbon Market.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 1, 3, and 4 only
C. 1, 2, and 3 only
D. 2 and 4 only
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The rules focus on reducing emissions intensity in energy-intensive industries such as aluminium, cement, chlor-alkali, and pulp & paper.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The target in the Paris Agreement is to reduce emissions intensity of GDP by 45%, not 40%.
- Statement 3 is correct: The rules include carbon credits for emission reductions and penalties for non-compliance.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) monitors the carbon credits under the Indian Carbon Market, not the CPCB.
Over 160 Killed by Lightning in March-April 2025
Syllabus: GS1/ Geography
- Between March and mid-April 2025, 162 people tragically lost their lives due to lightning strikes across 12 Indian states. The worst-hit region was Bihar, which recorded 99 deaths, accounting for 61% of the national total, followed by Uttar Pradesh.
What is Lightning?
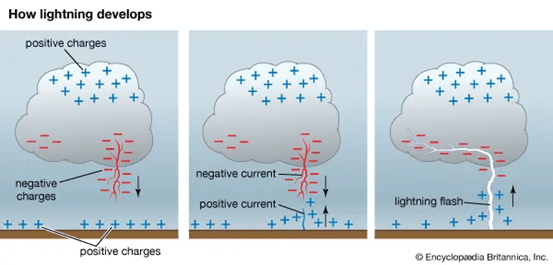
- Lightning is an electrical discharge that occurs between charged particles in a cloud and the ground. When the voltage in the atmosphere reaches approximately 3 million volts per meter, the air’s insulating properties break down, allowing a powerful electric current to flow. This results in a sudden burst of energy, creating a bright flash of light and a thunderous sound.
How Does Lightning Develop?
- Several factors contribute to the development of lightning, including:
- High humidity in regions like eastern states and coastal areas, which promotes thunderstorms.
- Topographical features like the Himalayas and Western Ghats, influencing lightning frequency.
- Monsoon dynamics, where moist air rises, driving thunderstorms and lightning.
- Rapid urbanization and industrialization, which increase the occurrence of artificial heat sources and aerosols that enhance thunderstorms.
- Climate change, which alters weather patterns and potentially increases the frequency and intensity of lightning events.
- Agricultural practices, such as burning agricultural residues, which add particulates to the atmosphere and heighten the risk of thunderstorms.
Government Initiatives
- To mitigate the risks posed by lightning, several government efforts have been made:
- The CROPC (Climate Resilient Observing Systems Promotion Council) developed India’s first Lightning Early Warning System to predict lightning strikes and issue alerts.
- The SACHET mobile app was launched to provide timely lightning hazard alerts to the public.
- In 2020, the Damini Lightning App was developed by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) to track lightning strikes and raise awareness.
Moving Forward
- To reduce lightning fatalities, it is crucial to:
- Strengthen communication systems so that warnings reach vulnerable populations efficiently.
- Train local authorities to act swiftly based on early warnings.
- Increase public awareness about lightning safety, especially during the pre-monsoon and monsoon seasons.
- Improve ground-level implementation of NDMA (National Disaster Management Authority) protocols to minimize the impact and save lives.
- With these measures in place, we hope to reduce the devastating impact of lightning and protect more lives in the future.
Consider the following factors contributing to the increased frequency of lightning strikes in India:
- High humidity in coastal areas and eastern states.
- The orographic effect caused by the Himalayas and Western Ghats.
- Increased aerosol concentration due to urbanization and industrialization.
- The effect of global warming on atmospheric convection and storm dynamics.
Which of the factors listed above is/are most directly responsible for the increased frequency and intensity of lightning strikes in India?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2, 3, and 4 only
c) 1, 2, and 3 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
- Explanation:
All the factors listed contribute significantly to the increased frequency of lightning strikes. - High humidity in coastal and eastern regions promotes thunderstorms, which often result in lightning.
- Orographic lifting in regions like the Himalayas and Western Ghats leads to intense storm formations and lightning.
- Urbanization and industrialization increase the concentration of aerosols in the atmosphere, enhancing cloud formation and intensifying lightning events.
- Climate change alters temperature and moisture dynamics, further driving more intense lightning occurrences.
India’s Claim Over Continental Shelf in Arabian Sea
Syllabus: GS1/Geography; GS2/Global Groupings & Agreements
Strategic Expansion:
- India has expanded its claim in the Central Arabian Sea, adding nearly 10,000 sq. km to its Extended Continental Shelf (ECS), reinforcing its maritime footprint.
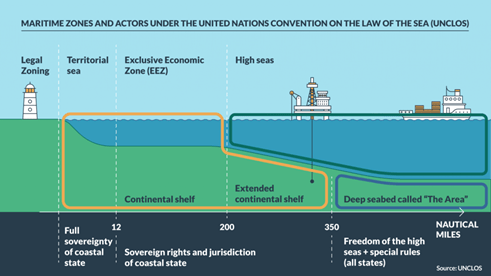
What is the Continental Shelf?
- Defined under the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
- A submerged extension of a nation’s landmass, reaching from the coast to the deep ocean
- Grants nations sovereign rights to explore and exploit seabed resources like oil, gas, and minerals
India’s Latest Move
- Led by NCPOR (Goa), the new claim could bring India’s seabed area close to its land area of 3.274 million sq. km
- Modified Strategy: In response to Pakistan’s objections, India made partial submissions, securing undisputed areas and deferring contentious zones for bilateral resolution
Understanding EEZ and ECS
- EEZ (Exclusive Economic Zone): Extends 200 nautical miles from the coast; exclusive rights to fishing and seabed resource extraction
- ECS: Area beyond the EEZ; requires scientific proof to be claimed under UNCLOS, reviewed by the Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf (CLCS)
Claiming the ECS: The UNCLOS Process
- Scientific Surveys: Geological, bathymetric, and sediment data
- Submission to CLCS: Technical data and boundary maps
- CLCS Review: Recommends changes or approves claims
- Resolving Overlaps: Through negotiations with neighboring countries
- Final Rights: Accepted claims grant rights to seabed resources
Geopolitical Considerations
- Pakistan: Opposed claims near Sir Creek; led to India’s modified strategy
- Oman: Overlapping ECS resolved via 2010 agreement
- Myanmar & Sri Lanka: Challenging India’s ECS in the Bay of Bengal and Indian Ocean (approx. 300,000 sq. km)
To justify an ECS claim under UNCLOS, which combination of the following is required?
- Morphological and geological evidence of continental margin continuity
- Ocean current velocity profiles across the ECS
- Seismic and sediment thickness data supporting natural prolongation
- Baseline calibration based on historical Exclusive Fisheries Zones (EFZs)
Choose the correct combination:
(a) 1, 2, and 4
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2, 3, and 4
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Correct Answer: (b)
Explanation:
To support ECS claims, morphological, geological, and sediment thickness data are required to establish natural prolongation of the continental shelf beyond 200 NM. Ocean current velocity and EFZ history are not scientifically relevant criteria under UNCLOS Annex II.
Sandy Cay Reef Dispute
Syllabus:Geography
Context: China and the Philippines have exchanged accusations over the Sandy Cay reef dispute in the South China Sea, escalating maritime tensions as both nations assert sovereignty over the area.
About Sandy Cay Reef:
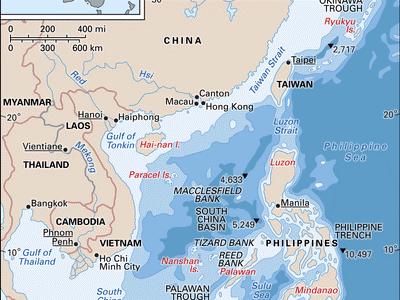
Location:
Sandy Cay Reef is part of the northern Thitu Reefs, located within the Spratly Islands in the South China Sea. It is situated approximately northwest of Thitu Island (Pag-asa) and northeast of Subi Reef.
Disputed Claims:
The reef is claimed by China, Philippines, Taiwan, and Vietnam. In 2025, China announced that it had implemented “maritime control” over Sandy Cay, a claim that was strongly rejected by the Philippines.
Other Notable Locations:
- Thitu Island (Pag-asa): Administered by the Philippines, it has a military base and a Coast Guard station.
- Subi Reef: Heavily militarized by China, located near Sandy Cay.
About the South China Sea:
- Location:
The South China Sea is an arm of the western Pacific Ocean, bordered by Southeast Asia and East Asia. - Nations Bordering the South China Sea:China, Taiwan, Philippines, Malaysia, Brunei, Vietnam, and Indonesia.
Disputed Islands and Claimants:
- Spratly Islands: Disputed among China, Philippines, Vietnam, Malaysia, Taiwan, and Brunei.
- Paracel Islands: Claimed by China, Taiwan, and Vietnam.
- Scarborough Shoal: Contested primarily between China and the Philippines.
Rivers Flowing into the South China Sea:
- Mekong River (Vietnam)
- Red River (Vietnam)
- Pearl (Zhu) River (China)
- Other Features:
- China Sea Basin: The deepest part of the South China Sea, with depths reaching up to 5,016 meters.
- Sunda Shelf: A broad, shallow shelf that connects the South China Sea to the Gulf of Thailand and Java Sea.
- Key Straits: Taiwan Strait, Luzon Strait, and Strait of Malacca.
Consider the following statements regarding the South China Sea:
- The Mekong River and Pearl River flow into the South China Sea.
- The Sunda Shelf connects the South China Sea to the Gulf of Thailand and Java Sea.
- The deepest point in the South China Sea is located in the Paracel Islands.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A. 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Mekong River flows through Southeast Asia (China, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam) and empties into the South China Sea via Vietnam.
- Pearl River (Zhujiang) flows through southern China and drains into the South China Sea near Hong Kong and Macau.
NMCG Approves Annual Master Plan to Promote River-Sensitive Urban Planning Under RCA
Syllabus: GS3/Urban Planning
Context:
- The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) has approved an Annual Master Plan under the River Cities Alliance (RCA) to guide the implementation of river-sensitive urban governance across Indian cities.
About the Initiative:
- The initiative is focused on embedding river-sensitive urban planning into India’s expanding urban landscapes. The master plan includes:
- Capacity-building programmes
- Knowledge-sharing platforms
- Development of technical tools
- Expert consultations
- Thematic case studies to inform river-related urban strategies.

Urban River Management Plans (URMPs):
- Launched in 2020 by NMCG and the National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA).
- A first-of-its-kind urban-river planning framework, integrating environmental, social, and economic dimensions of river ecosystems into urban governance.
- Cities with existing URMPs: Kanpur, Ayodhya, Chhatrapati Sambhaji Nagar, Moradabad, and Bareilly.
- Future expansion: 25 additional URMPs to be developed in the first phase; a total of 60 are planned over the next 2–3 years.
- Steering Committees: Constituted in key Ganga basin states (Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal) to guide plan formulation and execution.
River Cities Alliance (RCA):
- Established in 2021 by the NMCG (Ministry of Jal Shakti) in collaboration with NIUA (Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs).
- Objective: To serve as a dedicated platform for urban river cities to collaborate and promote sustainable urban river management.
- Thematic Pillars:
- Networking
- Capacity Building
- Technical Support
- Growth: From an initial 30 member cities, RCA now includes over 145 cities, spanning both Ganga basin and non-Ganga basin urban centers.
- International collaboration: The city of Aarhus, Denmark joined, highlighting RCA’s global outreach.
Global River Cities Alliance (GRCA):
- Launched at COP28 (2024) to scale RCA’s success to the global stage.
- Comprises 275+ river cities across 11 countries, including Denmark, Egypt, Netherlands, Ghana, Australia, Bhutan, Cambodia, and Japan.
- Supported by World Bank, Asian Development Bank (ADB), and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB).
- Aims to enable transnational cooperation on river conservation and sustainable water management.
National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG):
- Established under the Societies Registration Act, 1860, it is the implementation wing of the Namami Gange Programme, India’s flagship river rejuvenation initiative.
- Objective: Pollution abatement, rejuvenation of the Ganga, and ensuring minimum ecological flows while promoting sustainable development.
- Structure: Two-tier governance:
- Governing Council
- Executive Committee (chaired by the Director General, NMCG)
- Financial Powers: The Executive Committee can approve projects up to ₹1000 crore.
Which of the following statements regarding the Urban River Management Plans (URMPs) is/are correct?
- URMPs are implemented solely by the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) without collaboration from any other institution.
- They aim to integrate environmental, social, and economic considerations into urban river governance.
- As of now, only cities in the Ganga Basin have been selected for URMP development.
Options:
(a) 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) All of the above
Answer: (a) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: URMPs are jointly implemented by NMCG and NIUA, not just NMCG alone.
- Statement 2 is correct: URMPs are explicitly designed to integrate environmental, economic, and social dimensions in urban planning around rivers.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: Although initially focused on the Ganga Basin, URMPs are also being developed for non-Ganga basin cities.
President Honored 71 Individulas With Padma Awards
Syllabus:Awards
- In a grand Civil Investiture Ceremony held at the Durbar Hall of Rashtrapati Bhawan, President Droupadi Murmu presented the Padma Awards—India’s highest civilian honors—to 71 distinguished individuals on April 29, 2025.
- These awards recognize outstanding contributions in diverse fields such as art, public service, science, medicine, literature, education, and sports.
- The Padma Awards are categorized into three levels: Padma Vibhushan, Padma Bhushan, and Padma Shri.
Key Highlights of the 2025 Padma Awards:
- Padma Bhushan in the Field of Art:
- Shekhar Kapur: Acclaimed filmmaker, honored for his contributions to Indian and international cinema.
- Pankaj Udhas (Posthumous): Renowned ghazal singer, posthumously awarded. His wife, Farida Udhas, accepted the honor.
- Nandamuri Balakrishna: Veteran actor and politician from Andhra Pradesh, recognized for his dual contribution to cinema and public life.
- Ajith Kumar: Prominent actor known for his impactful work in Indian cinema.
- R. Sreejesh: Former Indian hockey goalkeeper, awarded for his significant achievements in sports and service to Indian hockey.
- Padma Vibhushan:
- Subramaniam: World-renowned violinist, honored for his extraordinary impact on Indian classical music.
- Notable Padma Shri Awardees:
- Jaspinder Narula: Playback singer celebrated for her contribution to Indian music.
- Ravichandran Ashwin: Indian cricketer, recognized for his excellence and consistent performance in international cricket.
- Ganeshwar Shastri Dravid: Esteemed Vedic scholar honored for determining auspicious timings for major religious events such as the Ram Lalla consecration and Kashi Vishwanath Corridor.
- Stephen Knapp: American author and researcher awarded for his work in promoting Vedic culture and spirituality through literature and education.
- These awards reflect the nation’s deep appreciation for individuals who have made significant and lasting contributions to their respective fields, both in India and globally.
Which of the following statements about the Padma Awards 2025 is/are correct?
- The Padma Vibhushan was conferred upon seven individuals, including M.T. Vasudevan Nair and Osamu Suzuki.
- The Padma Bhushan category recognized 19 recipients, with notable awardees such as Nandamuri Balakrishna and Pankaj Udhas (posthumous).
- The Padma Shri category honored 113 individuals, including Arijit Singh and Harvinder Singh.
Options:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
Explanation:
- The Padma Awards 2025 recognized a total of 139 distinguished individuals across three categories:
- 7 Padma Vibhushan awardees, including M.T. Vasudevan Nair and Osamu Suzuki.
- 19 Padma Bhushan recipients, notably Nandamuri Balakrishna and Pankaj Udhas (posthumously).
- 113 Padma Shri honorees, including figures like Arijit Singh and Harvinder Singh for their contributions in music and sports respectively.
Padma Awards
Syllabus:Awards
About Padma Awards:
- The Padma Awards are among India’s highest civilian honors, recognizing exceptional service across diverse fields that contribute to public welfare.
Origin and Classification:
Instituted in 1954 and reclassified in 1955 into three categories:
- Padma Vibhushan (highest honor)
- Padma Bhushan
- Padma Shri

Presentation:
- The President of India presents these awards at a formal ceremony at Rashtrapati Bhavan.
- Selection Process:
- Constituted by: The Prime Minister annually.
- Headed by: The Cabinet Secretary.
- Members: The Home Secretary, Secretary to the President, and 4-6 eminent personalities.
- Selection Criteria:
- Focuses on life-long achievements and public service.
Awards span a range of fields, including:
- Arts, Social Work, Science, Public Affairs, Trade, Medicine, Sports, Literature, Education, Civil Service.
- Inclusivity: Open to all citizens regardless of race, occupation, or gender.
- Ineligibility: Active government servants (except doctors/scientists) cannot be nominated.
Posthumous Awards:
- Rare but allowed in exceptional cases.
Nomination Process:
- Nominations can be made by the public, with self-nominations also accepted.
- The Padma Awards Committee screens the nominees.
- The Prime Minister reviews the recommendations, which are then sent to the President for approval.
Award Limits and Restrictions:
- Maximum of 120 awards can be conferred annually, excluding posthumous, foreign, NRI, or OCI awards.
- No title conferred: Awardees cannot use the award as a title in their name.
Historical Context:
- Suspension: The awards were discontinued in 1978–79 by the Janata Party under PM Morarji Desai.
- Resumption: In 1993–97, the awards were suspended due to PILs questioning their validity, but the Supreme Court upheld the award system in 1995 (Balaji Raghavan case), leading to full conferment resumption from 1997.
Recent Ceremony: In Padma Awards 2024, 71 personalities were honored for their distinguished service in various sectors, with the President of India presiding over the ceremony at Rashtrapati Bhavan.
Consider the following statements regarding the Padma Awards:
- The Padma Awards are conferred on Republic Day each year by the President of India.
- The awards are limited to Indian citizens only and cannot be conferred on foreigners.
- The Padma Vibhushan is the highest of the three categories of Padma Awards.
- Active government servants are eligible for Padma Awards in all categories.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 1, 3, and 4 only
C. 1 and 2 only
D. 1 and 3 only
Answer: A Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Padma Awards are conferred annually by the President of India on Republic Day.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The Padma Awards are also conferred on foreign nationals and NRIs in certain categories.
- Statement 3 is correct: The Padma Vibhushan is the highest honor, followed by Padma Bhushan and Padma Shri.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: Active government servants (except doctors/scientists) are not eligible for these awards.
Role in a Risk Society: Women and the Unequal Burden
Syllabus: Women and Society
- Ulrich Beck’s concept of the “risk society” underscores how modern crises—driven by technological advancement and environmental change—generate global risks that disproportionately affect women, particularly in developing countries.
- A risk society represents a stage of modernity in which manufactured risks, created through human activity, surpass natural threats in shaping daily life.
- Unlike earlier societies that managed localized, natural dangers such as famines or plagues, today’s world faces unpredictable and far-reaching hazards, many of which are unintended consequences of industrial and technological progress.
- Key features of a risk society include reflexive modernization, where societies must constantly adapt to the challenges generated by earlier innovations.
- These modern risks are global in nature—such as pandemics, nuclear accidents, and climate change—that transcend national boundaries. Furthermore, these risks are marked by unpredictability, making them difficult to foresee and even harder to control.

- The evolution of risk can be understood through three distinct historical phases. In the pre-industrial society, risks were local and natural, typically managed through traditional practices and community-based responses.
- The industrial society introduced urbanization and technological growth, which led to new risks such as pollution and the overexploitation of natural resources.
- In today’s risk society, human activities are the main source of hazards, ranging from nuclear disasters to large-scale climate events, demanding collective global action and systemic change.
- Risks can be categorized into two types: natural and manufactured. Natural risks arise from environmental phenomena, such as the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami, which affected millions.
- Manufactured risks are a product of human decisions and technology, exemplified by the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear disaster, which had long-term health and environmental consequences.
- Within this risk society, women bear a disproportionate burden. Their traditional roles, particularly in domestic and caregiving settings, expose them to health risks such as indoor air pollution from biomass cooking fuels and contaminated water sources.
- The UNDP reports that women are 14 times more likely to die in climate-related disasters due to factors such as restricted mobility, caregiving responsibilities, and lack of access to early warning systems.
- In terms of livelihoods, women—who make up 43% of India’s rural agricultural workforce according to FAO 2023—are often the first to suffer when environmental challenges like droughts or floods damage crops and reduce income.
- Post-disaster recovery relies heavily on women for caregiving, food preparation, and health care—tasks that are unpaid and unrecognized.
- Moreover, as climate change worsens water and food scarcity, women are often forced to travel longer distances for basic resources and may receive less food during shortages.
- To address these challenges, several policy measures are recommended. Gender-disaggregated disaster data systems should be mandated to enable targeted, gender-sensitive risk management.
- Community-led resource management must be encouraged, empowering women to lead initiatives in water conservation, seed preservation, and sustainable agriculture.
- Climate-resilient social protection programs—like MGNREGA—should be expanded to provide immediate support to women-headed households after disasters.
- Financial reforms are also essential, with increased access to microfinance and insurance enabling rural women to rebuild their livelihoods.
- Finally, inclusive governance is crucial, with mandatory quotas for women’s representation in local climate adaptation bodies and Panchayati Raj institutions that oversee natural resource management.
- In conclusion, the concept of a risk society reveals not only the growing complexity of modern hazards but also the systemic gender inequalities that deepen their impact. Ensuring gender equity in risk response and governance is critical to building a resilient and just future for all.
Consider the following statements regarding the impact of a risk society on gender dynamics in developing countries:
- Women are less affected by modern risks due to their limited participation in industrial work.
- Women face higher mortality during disasters due to restricted mobility and caregiving roles.
- Environmental degradation disproportionately affects women involved in agriculture and household care.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect. Although women may not dominate industrial labor, they are disproportionately vulnerable to the consequences of modern risks due to structural inequalities, care responsibilities, and exposure to environmental hazards. Statements 2 and 3 are correct and supported by UNDP and FAO data, highlighting women’s greater vulnerability during disasters and higher livelihood dependence on natural resources.
SIPRI Report on Military Expenditure
Syllabus:Reports
- According to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) report titled ‘Trends in World Military Expenditure 2024’, India’s military expenditure reached $86.1 billion, marking a 1.6% increase from the previous year and positioning India as the fifth-largest military spender globally.
- This amount is nearly nine times greater than Pakistan’s defense budget of $10.2 billion, highlighting a significant regional disparity and reinforcing India’s strategic posture in South Asia.
- Globally, India follows the United States, China, Russia, and Germany in terms of defense spending.
- Together, these top five nations accounted for 60% of the world’s total military expenditure, illustrating a concentration of military capabilities among a few powers.
- In the regional context, both India and China emerged as key drivers of military expenditure growth in Asia and Oceania, reflecting their expanding strategic interests and evolving security concerns.
- India’s defense strategy continues to emphasize domestic capability enhancement, with 75% of its capital outlay earmarked for indigenous defense production.
- This represents 22% of the overall military budget and aligns with the government’s broader Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative aimed at achieving self-reliance in critical defense manufacturing.
- However, despite this push for indigenization, India remains reliant on foreign imports for advanced platforms and technologies, particularly in areas like combat aircraft, precision weaponry, and defense electronics.
- Strategically, India’s increased military spending underscores its ambition to serve as a key security provider in the Indo-Pacific region, particularly in light of ongoing tensions with neighboring China and Pakistan. The rise in expenditure is not only a response to conventional security threats but also an effort to assert influence in a rapidly shifting geopolitical environment, reinforcing India’s role in regional and global security architecture.
Consider the following statements regarding India’s military expenditure as per the SIPRI report ‘Trends in World Military Expenditure 2024’:
- India’s defense expenditure in 2024 reached $86.1 billion, making it the 5th largest military spender globally.
- India’s defense budget is nearly nine times higher than that of Pakistan, which stood at $10.2 billion.
- India and China were not significant contributors to the growth of military expenditure in Asia and Oceania.
- 75% of India’s capital outlay is dedicated to domestic defense production, supporting the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- Despite efforts at indigenization, India remains largely independent of foreign defense imports.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1, 2, and 4 only
B. 1, 2, and 5 only
C. 1, 2, and 3 only
D. 1, 2, 4, and 5
Answer: A (1, 2, and 4 only)
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: India’s military expenditure in 2024 is indeed $86.1 billion, placing it as the 5th largest military spender globally.
- Statement 2 is correct: India’s spending is nearly nine times higher than Pakistan’s defense budget of $10.2 billion, emphasizing the regional disparity.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: India and China were key drivers of military expenditure growth in Asia and Oceania, reflecting their expanding strategic interests. This statement contradicts the context of both countries’ roles.
- Statement 4 is correct: A substantial portion (75%) of India’s capital outlay is dedicated to indigenous defense production, aligning with the Atmanirbhar Bharat
- Statement 5 is incorrect: Despite efforts to indigenize, India remains dependent on imports for advanced systems like combat aircraft and defense electronics, indicating a reliance on foreign technology.
Digha gears up for inauguration of Jagannath temple
Syllabus:Art and Culture
- The coastal town of Digha in West Bengal’s Purba Medinipur district was abuzz with activity on Monday as it prepared for the inauguration of the ₹250-crore Lord Jagannath temple. Spanning 20 acres, the temple is modeled after the 12th-century shrine in Puri.
- Chief Minister Mamata Banerjee visited the temple twice on the day of the inauguration to oversee the final preparations. She highlighted the temple’s potential to boost Digha’s tourism, noting that it would help the town achieve international recognition. “This temple will add a new feather to Digha’s tourism and bring more visitors here. The town’s development has already begun to attract more tourists,” Banerjee stated.

- She further emphasized the theme of “Shorbo Dhormo Somonnoy” (religious harmony), asserting that the temple would stand as a symbol of both spirituality and unity. Digha, known for its coastal charm, is set to benefit from this new spiritual destination, which she believes will bring in more pilgrims and tourists alike. “The sculptors have done an excellent job,” she added.
- The inauguration of the temple is slated to take place after the ‘Maha Yajna’ and ‘Prana Pratistha’ (consecration ceremony) on Tuesday and Wednesday (Akshay Tritiya). The temple’s construction began in May 2022 following an idea proposed by the Chief Minister in December 2018. The temple, adorned in blue and white, is surrounded by illuminated roads and has been promoted as the Jagannath Dham Sanskriti Kendra by the West Bengal government. The Housing Infrastructure Development Corporation (HIDCO) was responsible for its development.
- However, political controversy arose when senior BJP leader and Leader of the Opposition Suvendu Adhikari questioned the nature of the newly inaugurated structure. Adhikari sought clarification on whether the facility was a temple or a cultural center. “The tender documents reveal that the Jagannath Dham Sanskriti Kendra has been built at Digha. The invitation card should reflect this clearly,” he remarked.
- Amidst these developments, Adhikari also announced that the BJP would begin efforts to rebuild and restore vandalized Hindu temples in Murshidabad district starting April 30. He emphasized that no funds would be sought or accepted from the state government for this initiative. The communal clashes in Murshidabad earlier this month had led to the deaths of three individuals.
- Following the inauguration of the temple, Chief Minister Mamata Banerjee is expected to visit Murshidabad to address the ongoing tensions.
Which of the following statements regarding the inauguration of the Lord Jagannath temple in Digha are correct?
- The Lord Jagannath temple in Digha is modeled after the 12th-century temple in Puri.
- The temple’s inauguration is accompanied by a ‘Maha Yajna’ and ‘Prana Pratistha’ (consecration ceremony).
- The Chief Minister of West Bengal, Mamata Banerjee, proposed the idea for the temple in December 2022.
- The Housing Infrastructure Development Corporation (HIDCO) is responsible for the temple’s construction.
- BJP leader Suvendu Adhikari raised concerns over the nature of the temple and questioned if it is a cultural center or a religious temple.
Options:
(a) 1, 2, and 4 only
(b) 1, 2, 4, and 5 only
(c) 1, 3, 4, and 5 only
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(b) 1, 2, 4, and 5 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Lord Jagannath temple in Digha is modeled after the 12th-century shrine in Puri.
- Statement 2 is correct: The inauguration of the temple includes a ‘Maha Yajna’ and ‘Prana Pratistha’ (consecration ceremony).
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The idea for the temple was proposed by Mamata Banerjee in December 2018, not 2022.
- Statement 4 is correct: The Housing Infrastructure Development Corporation (HIDCO) was responsible for the temple’s construction.
- Statement 5 is correct: Suvendu Adhikari questioned whether the structure is a cultural center or a temple, raising concerns about its nature.
