Disproportionate Burden on Women in Risk Society
Syllabus: GS1/ Society
What is a Risk Society?
- Coined by German sociologist Ulrich Beck in his 1986 book Risk Society: Towards a New Modernity.
- Refers to a shift from industrial society to one dominated by man-made risks—like climate change, pandemics, and technological hazards—arising from modern development.
- Unlike natural disasters, these risks are global, complex, and often invisible, affecting societies unequally.
Why Women Are Disproportionately Affected
- Environmental & Health Risks:
- Water collection exposes women to contaminated sources, increasing the risk of disease.
- Solid fuels for cooking cause indoor air pollution, leading to chronic respiratory issues.
- Gender norms (e.g., eating last or less) worsen women’s nutritional and health outcomes.
- NFHS-5 (2019–21): 57% of Indian women suffer from anaemia vs. 25% of men.
- Economic Vulnerability:
- Concentration in informal work with low job security and savings.
- Limited land ownership and asset access hinder disaster recovery.
- Lower credit access increases dependency and reduces resilience.
- Unpaid care work adds emotional and physical strain.
- Political & Institutional Exclusion:
- Women’s voices are often missing in policy-making, especially in disaster preparedness and climate governance.
- Results in gender-blind policies and missed use of women’s community knowledge.
Way Forward
- Gender Mainstreaming: Integrate women’s needs into all risk reduction, climate, and pandemic strategies.
- Economic Empowerment: Ensure land rights, financial access, and social protection schemes prioritise women.
- Care Infrastructure: Support unpaid care work via crèches, health insurance, and community kitchens.
- Inclusive Governance: Institutionalise women’s participation in disaster management and local planning bodies.
Consider the following statements regarding the concept of a “Risk Society” and its gendered impacts:
- The term “Risk Society” was coined by Ulrich Beck in 1986 and refers to a society increasingly shaped by global, man-made risks such as climate change, pandemics, and technological hazards.
- Women are disproportionately affected by environmental and health risks, such as water collection from contaminated sources and indoor air pollution from solid fuels.
- Women’s economic vulnerability is exacerbated by higher participation in the formal labor sector, where job security and savings are guaranteed.
- Political and institutional exclusion of women often leads to gender-neutral policies, ignoring their unique needs in disaster preparedness and climate governance.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 1, 2, and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: C. 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct. Ulrich Beck’s “Risk Society” indeed describes the shift towards a society dominated by human-made, global risks such as climate change, pandemics, and technological hazards.
- Statement 2 is correct. Women are disproportionately affected by environmental and health risks, such as exposure to contaminated water and indoor air pollution, which are exacerbated by gendered roles (e.g., water collection and cooking).
- Statement 3 is incorrect. Women are more likely to be concentrated in the informal labor sector, where job security and savings are often lacking, not in the formal sector as the statement suggests.
- Statement 4 is correct. Women’s exclusion from decision-making results in gender-blind policies, ignoring their specific needs in the context of disaster preparedness and climate governance.
Dongria Kondh Community
Syllabus:Society
- The Dongria Kondh is a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) residing in the Niyamgiri Hills, spread across Kalahandi and Rayagada districts of Odisha.

Cultural and Spiritual Significance
- The term ‘Dongria’ is derived from ‘Dongar’, meaning hill, indicating their habitation in hilly terrain. They call themselves Jharnia, meaning “protectors of streams.”
- They follow an animistic and polytheistic belief system, where hilltops and forests are revered as sacred deities.
- The community worships Niyam Raja, a mythical god-king, believed to be the creator and guardian of the Niyamgiri Hills.
- Their art and symbols—notably triangular motifs—reflect deep reverence for the mountains and nature.
Social and Religious Structure
- Dongria Kondhs do not have a central political or religious authority. Each clan or village is self-governed.
- Religious and ceremonial roles are performed by beju (male priest) and bejuni (female priest).
- Distinctive tattoos, jewellery, and hairstyles mark their cultural identity. Women wear multiple rings in ears and nose; men also adorn nose rings.
Language
- They speak Kuyi and Kuvi, which are linguistically unrelated to Odia, the state’s official language.
Livelihood
- The Dongria Kondh are traditionally horticulturists, engaged primarily in:
- Podu cultivation (shifting agriculture),
- Collection of Non-Timber Forest Products (NTFPs).
- Their sustenance is intricately tied to the forests, slopes, and water sources of Niyamgiri.
Current Concerns
- The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) has recently sought an Action Taken Report from the Odisha Chief Secretary, highlighting the alarming lack of basic amenities and precarious living conditions of over 10,000 Dongria Kondh families.
With reference to the Dongria Kondh community, consider the following statements:
- They are classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) under the provisions of the Forest Rights Act, 2006.
- The community practices settled agriculture and avoids shifting cultivation due to ecological concerns.
- Their traditional religious belief revolves around worship of Niyam Raja, whom they consider the guardian of the Niyamgiri hills.
- The languages spoken by them, Kuyi and Kuvi, belong to the Dravidian language family and are closely related to Odia.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 1, 2 and 4 only
D. 3 only
Answer:A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct – Dongria Kondhs are listed as a PVTG, though not specifically under the FRA, 2006 (but it reinforces their rights).
- Statement 2 is incorrect – They practice podu (shifting) cultivation, not settled agriculture.
- Statement 3 is correct – They worship Niyam Raja, a guardian deity of the Niyamgiri hills.
- Statement 4 is incorrect – Kuyi and Kuvi are Dravidian languages, but not closely related to Odia, which is Indo-Aryan.
Afrikaners – Africa’s White Tribe
Syllabus:Society
- The U.S. recently welcomed its first group of Afrikaner refugees, drawing attention to the historical and sociocultural origins of this unique community.
Who are the Afrikaners?:
- Afrikaners are a white ethnic group indigenous to South Africa, often described as “Africa’s White Tribe” due to their centuries-long rooted presence on the African continent. Their origin traces back to 1652, when Jan van Riebeeck, under the aegis of the Dutch East India Company (VOC), established a resupply post at the Cape of Good Hope.
- The early settler population, primarily Dutch Protestants, was later joined by French Huguenots fleeing religious persecution following the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes (1685) and by German migrants. The enslaved populations brought from India, Indonesia, Madagascar, and East Africa further contributed to the socio-cultural fabric of the Cape Colony.
Development of Afrikaner Identity:
- Afrikaner identity evolved through a complex process of ethnogenesis, shaped by interaction between European settlers, enslaved peoples, and indigenous groups such as the Khoikhoi.
- The emergence of Afrikaans, a language derived from Dutch but influenced by various local and foreign tongues, symbolized this distinct cultural formation.
- The socio-economic structure was characterized by paternalistic hierarchies and frontier-style subsistence living, particularly among the Trekboers—semi-nomadic pastoralists who moved inland during the 18th century.
- Their migration frequently resulted in violent confrontations with indigenous communities.
- Afrikaner society was also deeply influenced by Calvinist doctrines, fostering a culture of self-reliance, religious conservatism, and militarization.
With reference to the historical formation and identity of the Afrikaner community in South Africa, consider the following statements:
- The Afrikaners are primarily descended from Dutch, French, and German settlers who arrived in South Africa before the 19th century.
- The Afrikaner language, Afrikaans, evolved as a derivative of English with influences from indigenous African languages.
- The socio-cultural identity of Afrikaners was shaped significantly by Calvinist religious beliefs and frontier-style living.
- The Trekboers were a settled agrarian community that avoided conflicts with indigenous populations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 1, 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: A. 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Correct: Afrikaners trace their lineage mainly to Dutch Protestants, French Huguenots, and Germans who settled in the Cape Colony starting in the 17th century.
- Statement 2 – Incorrect: Afrikaans developed primarily from Dutch, not English, and was influenced by other European, Asian, and African
- Statement 3 – Correct: Afrikaner culture was shaped by Calvinist religious beliefs and a militant, frontier lifestyle, especially among the Trekboers.
- Statement 4 – Incorrect: The Trekboers were semi-nomadic pastoralists, not settled agrarians, and often engaged in violent conflicts with indigenous communities.
Years of End of the Vietnam War
Syllabus: GS1/World History
Background
- Vietnam had been a French colony since the mid-19th century, part of French Indochina along with Laos and Cambodia.
- During World War II, Japan occupied Vietnam, allowing the French to retain some control. After Japan’s defeat in 1945, Ho Chi Minh, leader of the Viet Minh (League for the Independence of Vietnam), declared Vietnam’s independence.
- However, the French attempted to reassert control, leading to the First Indochina War.

The Vietnam War:
- The Vietnam War, also known as the Second Indochina War, was a prolonged conflict from 1955 to 1975 between North Vietnam (Communist) and South Vietnam (anti-Communist), with significant U.S. involvement on the side of the South.
- North Vietnam: Led by Ho Chi Minh and the Communist Party, it was supported by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist nations.
- South Vietnam: Initially led by Ngo Dinh Diem, with various leaders taking charge after multiple coups. It received support from the United States, South Korea, Australia, Thailand, and others.
Causes of the War
Division of Vietnam: Following the First Indochina War, the 1954 Geneva Accords temporarily divided Vietnam at the 17th parallel, establishing North and South Vietnam.
Cold War Tensions: The U.S. feared the spread of communism in Asia, adhering to the “Domino Theory,” which suggested that if one country fell to communism, neighboring countries might follow.
Internal Conflict: The Viet Cong insurgency in South Vietnam, aligned with the Communist North, sought to reunify the country under communist rule.
Key Phases
- Advisory Phase (1955–1963): The U.S. provided military advisors and aid to the South Vietnamese government. The unpopular regime of Ngo Dinh Diem was overthrown in a U.S.-backed coup in 1963.
Escalation (1964–1969):
- The Gulf of Tonkin Incident (1964) allegedly saw attacks on U.S. ships, leading to increased U.S. involvement.
- S. troop levels peaked at over 500,000 by 1969, with significant battles like the Tet Offensive (1968), Battle of Hue, and Khe Sanh.
- The use of napalm, Agent Orange, and carpet bombing provoked widespread international outrage.
- Withdrawal (1969–1973): Under President Richard Nixon, the U.S. pursued “Vietnamization,” training South Vietnamese forces to take over the war. U.S. forces began withdrawing, and the Paris Peace Accords were signed in 1973.
Final Collapse (1973–1975):
- Despite the U.S. withdrawal, fighting continued, and on April 30, 1975, North Vietnamese forces captured Saigon, marking the end of the war.
- Vietnam was reunified under communist control, becoming the Socialist Republic of Vietnam.
Agent Orange:
- Agent Orange, a potent herbicide, was used by the U.S. military during the Vietnam War as part of Operation Ranch Hand (1961–1971). This controversial chemical became one of the war’s most infamous symbols due to its severe health and environmental impacts.
Manufacturing:
- The production of 2,4,5-T, a component of Agent Orange, led to the creation of TCDD, a highly toxic dioxin.
- Purpose: The U.S. military used Agent Orange to defoliate forests and jungles, reducing cover for the Viet Cong, and to destroy crops feeding North Vietnamese forces.
- Scale: Over 20 million gallons of herbicides were sprayed across South Vietnam, especially in dense jungles and rural farmlands.
Aftermath
- Agent Orange remains a symbol of the Vietnam War’s human and moral cost.
- Programs by the Vietnamese Red Cross, USAID, and international NGOs continue to support victims and work on environmental cleanup.
- Advocacy continues for justice and recognition for all those affected by the lasting consequences of Agent Orange exposure.
Consider the following statements regarding the Vietnam War and its aftermath:
- The Vietnam War was fought primarily between the Communist forces of North Vietnam and the Anti-Communist forces of South Vietnam, with heavy involvement from the Soviet Union and China in the South.
- The Gulf of Tonkin Incident of 1964 was the catalyst for the escalation of U.S. military involvement in Vietnam, leading to the passage of the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution.
- The Paris Peace Accords signed in 1973 led to the complete withdrawal of U.S. forces from Vietnam but did not end hostilities, as fighting continued until the fall of Saigon in 1975.
- Agent Orange, a defoliant used by the U.S. military, caused long-term health and environmental damage, but its use was restricted solely to military combat zones, avoiding civilian exposure.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2, 3, and 4 only
C. 1, 2, and 3 only
D. 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer:C
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Incorrect. The Soviet Union and China supported North Vietnam, not South Vietnam. The U.S. supported South Vietnam.
- Statement 2: Correct. The Gulf of Tonkin Incident led to the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution, which allowed the U.S. to increase its military presence in Vietnam.
- Statement 3: Correct. While the Paris Peace Accords led to the U.S. military withdrawal, fighting continued, culminating in the fall of Saigon in 1975.
- Statement 4: Incorrect. Agent Orange was widely used across military and civilian zones, causing long-term health issues for both Vietnamese civilians and U.S. veterans.
Vikramaditya I of Badami Chalukyas
Syllabus:History
 Context:
Context:
- A 7th-century inscription in Old Kannada, dating to the reign of Vikramaditya I of the Badami Chalukyas, was recently discovered near Madapura Lake in Davangere, Karnataka.
The inscription offers valuable insights into the fiscal system, land grants, and local governance structures during his rule.
Badami Chalukyas: A Historical Overview
- Origins and Legitimacy:
- Emerged as a native Kannada power in the Deccan
- Claimed descent from Ayodhya to enhance dynastic legitimacy
- Capital:Vatapi (modern-day Badami) in Karnataka
Key Rulers and Political History:
- Pulakesin I (543–566 CE):
- Founded the dynasty
- Fortified Vatapi as the capital
- Pulakesin II (609–642 CE):
- Most celebrated ruler
- Defeated Harshavardhana at the Narmada
- Established diplomatic ties with Sassanid Persia, depicted in Ajanta murals
- Vikramaditya I (644–681 CE):
- Son of Pulakesin II
- Reclaimed Vatapi from the Pallavas after his father’s defeat
- Consolidated control over southern kingdoms including Cholas, Pandyas, and Keralas
Administrative and Military Contributions
- Political Reorganisation:
- Restored centralized authority after a period of decline
- Appointed trusted feudatories (e.g., Singhavenna) to govern regions (as revealed by recent inscription)
- Military Successes:
- Defeated Narasimhavarman I of the Pallavas
- Reunified the Chalukya empire
- Strengthened maritime capability—Pulakesin II reportedly maintained a fleet of 100 ships
- Fiscal Policies:
- Revenue relied more on military expansion than intensive agriculture
- Land grants and taxation formed key components of governance
Religion and Culture
- Religious Patronage:
- Supported Shaivism, Vaishnavism, Shaktism, and Jainism
- Donations made to Jain institutions
- Pulakesin I performed Ashvamedha Yajna, asserting imperial authority
- Art and Architecture:
- Pioneered the Vesara style, blending Nagara and Dravida elements
- Built notable rock-cut and structural temples at Aihole, Badami, and Pattadakal
- Set the architectural foundation later expanded under Vikramaditya II and Kirtivarman
Legacy of Vikramaditya I
- Regarded as “Rajamalla” and “Yuddhamalla” (Warrior among Kings)
- His reign marked a revival of Chalukya dominance after internal strife and external invasions
- Laid the groundwork for the cultural and architectural flourishing of the later Chalukyas
With reference to the Badami Chalukyas, consider the following statements:
- Pulakesin II sent diplomatic envoys to the Roman Empire, which is depicted in the murals of Ellora caves.
- Vikramaditya I successfully defeated Narasimhavarman I and recaptured Vatapi.
- The Chalukyas primarily followed Shaivism and discouraged Jain patronage.
- The Vesara style of temple architecture emerged during the Badami Chalukya period.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 1, 2 and 3 only
D. 2, 3 and 4 only
Answer:B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect – The Chalukyas sent envoys to Persia (Sassanid Empire), not Rome, and it is depicted in Ajanta, not Ellora.
- Statement 2 is correct – Vikramaditya I defeated Narasimhavarman I and reclaimed Vatapi.
- Statement 3 is incorrect – They patronized multiple religions, including Jainism.
- Statement 4 is correct – Vesara style originated under the Badami Chalukyas.
Nabakalebara Ritual
Syllabus:Art and Culture
Context:
- The inauguration of the Digha Jagannath Temple in West Bengal has stirred controversy, particularly over its reference as “Jagannath Dham” and allegations that leftover sacred wood from the 2015 Nabakalebara ritual in Puri was improperly used for idol-making.
About Nabakalebara Ritual:

- Meaning: Nabakalebara means “new body” — a sacred ritual where the wooden idols of Lord Jagannath, Balabhadra, Subhadra, and Sudarshana are replaced.
- Frequency: Held every 12 or 19 years, based on the lunar calendar, specifically when an extra Ashadha month (Adhimasa) occurs.
Key Ritual Elements:
- Astrological Timing: Determined by rare calendrical alignments in the Hindu lunar calendar.
- Sacred Wood (Daru):
- Special neem trees selected based on traditional symbols (e.g., chakra, conch).
- Identified and retrieved by Daitapati servitors in a process called Banajaga Yatra.
- Idol Making:
- Logs transported ceremonially to Puri.
- Biswakarma artisans carve new idols in secrecy.
- Brahma Padartha (divine essence) is ritually transferred from old to new idols during a secret midnight ceremony.
- Burial: Old idols are respectfully buried in Koili Baikuntha, within the temple premises.
Philosophical & Cultural Significance:
- Reflects Hindu concepts of rebirth, impermanence, and cyclical time.
- Attracts millions of pilgrims during Rath Yatra, particularly in Nabakalebara years.
Controversy at Digha:
- Allegations claim idols at Digha Temple were made using leftover sacred wood from Puri’s 2015 Nabakalebara — considered a breach of tradition and sanctity.
- The Odisha government has initiated an official probe into the matter.
The recent controversy surrounding the Digha Jagannath Temple in West Bengal has raised concerns regarding the use of sacred wood from the Nabakalebara ritual. Which of the following statements is/are correct about the Nabakalebara ritual?
- The Nabakalebara ritual is performed to replace the wooden idols of Lord Jagannath, Balabhadra, Subhadra, and Sudarshana with new ones.
- The ritual is conducted every 12 years based on the occurrence of two Asadha months in a year.
- The sacred wood used for making the new idols is selected from neem trees, based on divine signs.
- The transfer of Brahma Padartha (divine essence) is conducted openly during the day in a public ceremony.
Select the correct answer:
- A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1, 3, and 4 only
D) 1, 2, and 3 only
Answer:D) 1, 2, and 3 only
Explanation:
- The Nabakalebara ritual involves replacing the idols of Lord Jagannath and other deities with new ones made from specific sacred wood (Option 1).
- It is conducted every 12 or 19 years based on the lunar calendar, specifically when two Asadha months occur (Option 2).
- The sacred wood, typically neem trees, is selected based on divine signs and the required marks (Option 3).
- The Brahma transfer process happens secretly, not openly in public during the day (so Option 4 is incorrect).
Archaeological Survey of India
Syllabus:History
Context:
- The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) is set to expand its Underwater Archaeology Wing (UAW) to explore submerged cultural sites, particularly along the western coast, including Maharashtra.

About the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI):
What is ASI?:
- The ASI is the apex government organization tasked with the archaeological research, conservation, and protection of India’s cultural heritage and historical monuments.
- Established: 1861 by Alexander Cunningham during Lord Canning’s tenure.
- Revived: 1871 as an independent department; Cunningham became the first Director-General.
- Headquarters: 24, Tilak Marg, New Delhi.
- Parent Ministry: Ministry of Culture, Government of India.
- Emblem: Derived from the Sanchi Stupa, reflecting India’s rich archaeological legacy.
Mandate and Objectives:
- Protection & Preservation: Safeguards monuments and sites of national importance under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958.
- Survey & Excavation: Undertakes systematic exploration and scientific excavations across India.
- Research & Documentation: Publishes reports, journals (e.g., Indian Archaeology – A Review), and conservation manuals.
- Capacity Building: Trains archaeologists and conservationists through in-house institutions.
Underwater Archaeology Wing (UAW):
- A specialized wing focusing on the exploration of submerged archaeological sites along India’s coastline and inland waters.
- Plans to conduct deeper research in states like Maharashtra, aligning with global best practices in maritime archaeology.
- Collaborates with agencies such as the Indian Navy, IITs, and international archaeological institutions.
Which of the following statements regarding the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) are correct?
- It functions under the Ministry of Education, Government of India.
- The ASI’s logo is inspired by the Sanchi Stupa, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- The Underwater Archaeology Wing (UAW) was established to study the tectonic origin of submerged landscapes.
- The ASI was initially founded under Lord Canning’s administration and later revived as a separate department in 1871.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
a) 1 and 3 only
b) 2 and 4 only
c) 1, 2, and 4 only
d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer:b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: ASI functions under the Ministry of Culture, not the Ministry of Education.
- Statement 2 is correct: The ASI logo is indeed inspired by the Sanchi Stupa.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The Underwater Archaeology Wing (UAW) is meant to study submerged cultural heritage, not tectonic origins.
- Statement 4 is correct: ASI was founded in 1861 under Lord Canning, and revived in 1871 under Cunningham.
Sacred Relics of Lord Buddha
Syllabus:History
What Are Sacred Relics?
- Sacred Relics of Lord Buddha refer to the physical remains or personal items associated with Gautama Buddha. These relics are deeply revered by followers worldwide, symbolizing Buddha’s teachings of spiritual enlightenment. They serve as key focal points for devotion and pilgrimage. The relics are preserved and curated by the National Museum of India with support from the Ministry of Culture and the International Buddhist Confederation (IBC).

Types of Relics Associated with Buddha
- Saririka Relics: These include Buddha’s physical remains such as bones, teeth, and ashes.
- Paribhogika Relics: Objects used by Buddha, such as his robe, bowl, or walking stick.
- Uddesika Relics: Symbols representing Buddha, such as stupas, images, and sculptures.
Major Relics Associated with Buddha
- Mahabodhi Temple (Bodh Gaya): The site where Buddha attained enlightenment.
- Kapilavastu Relics: Discovered in Piprahwa (Uttar Pradesh), these relics are associated with Buddha’s Shakya clan.
- Tooth Relic (Sri Lanka): Housed in the Temple of the Sacred Tooth Relic in Kandy.
- Sarnath Relics: The site where Buddha delivered his first sermon (Dhammacakkappavattana Sutta).
Significance of the Relics
- The relics symbolize Buddha’s teachings of peace, non-violence, and enlightenment.
- They play a vital role in cultural diplomacy, with India sharing relics with countries like Mongolia, Thailand, and now Vietnam.
- The relics also serve to strengthen Buddhist heritage and foster international ties between nations.
Which of the following is true regarding the Sacred Relics of Lord Buddha?
- Saririka Relics include Buddha’s robe, bowl, or walking stick.
- The Kapilavastu Relics were discovered in Piprahwa, Uttar Pradesh, and are linked to Buddha’s Shakya clan.
- Uddesika Relics are physical remains such as Buddha’s bones, teeth, and ashes.
- The Tooth Relic of Buddha is housed in the Mahabodhi Temple in Bodh Gaya.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
a) 1 and 3 only
b) 2 and 4 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1 and 4 only
Answer:b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Saririka Relics refer to Buddha’s physical remains like bones, teeth, and ashes, not objects like his robe or walking stick.
- The Kapilavastu Relics were indeed discovered in Piprahwa, Uttar Pradesh, and are associated with Buddha’s Shakya clan.
- Uddesika Relics are symbols representing Buddha, not physical remains.
- The Tooth Relic is housed in Sri Lanka’s Temple of the Sacred Tooth Relic in Kandy, not the Mahabodhi Temple, which is the site of Buddha’s enlightenment.
1. Santhara
Syllabus: GS1/Culture
- A tragic incident involving a three-year-old girl with a brain tumour has sparked a national debate after her parents initiated her into Santhara, a Jain religious ritual of voluntarily embracing death.
What is Santhara?
- Santhara, also called Sallekhana or Samadhi Maran, is an ancient Jain religious vow of gradual fasting unto death.
- It is undertaken with the aim of attaining spiritual purity by detaching from worldly desires and shedding accumulated karma.
- Jain scriptures permit Santhara only under specific circumstances, such as:
- Terminal illness
- Extreme old age
- Severe and unavoidable hardship (e.g., famine or deteriorating health that may lead to unintentional harm to living beings, violating ahimsa).
Ethical and Legal Concerns
- The death of a minor has raised critical questions of consent and legality, as children lack the cognitive maturity to make life-ending decisions.
- Medical professionals and child rights activists argue that the practice, when applied to minors, equates to enforced starvation and violates basic human rights.
Legal Status of Santhara
- In 2015, the Rajasthan High Court ruled that Santhara is akin to suicide, making it punishable under:
- Section 306 – Abetment to suicide
- Section 309 – Attempt to suicide
- The ruling triggered widespread protests from the Jain community, citing infringement on religious freedom.
- Later, the Supreme Court stayed the Rajasthan HC verdict, effectively preserving the status quo and recognizing Santhara as part of Jain religious tradition—pending a final decision.
Consider the following statements regarding the Jain ritual of Santhara and its legal-constitutional implications in India:
- Santhara is explicitly protected under Article 25 of the Constitution as a core religious practice of Jainism, as affirmed by the Supreme Court in a final judgment.
- The Rajasthan High Court, in a 2015 ruling, equated Santhara with suicide and held it punishable under Sections 306 and 309 of the Indian Penal Code.
- Article 21 of the Indian Constitution has been interpreted to include the right to die with dignity in the context of both euthanasia and religious fasting.
- The Supreme Court’s stay on the Rajasthan High Court’s verdict effectively legalizes Santhara in all forms and circumstances, including its use by minors.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 4 only
Correct Answer: B) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: The Supreme Court has stayed the Rajasthan HC judgment but has not delivered a final ruling affirming Santhara as a constitutionally protected religious practice. Thus, legal status is pending adjudication, not fully affirmed.
- Statement 2 – Correct: The Rajasthan HC in 2015 did declare Santhara punishable under IPC Sections 306 and 309, treating it as suicide.
- Statement 3 – Correct: The right to die with dignity has been interpreted under Article 21 by the Supreme Court, especially in the Common Cause v. Union of India (2018) judgment on passive euthanasia.
- Statement 4 – Incorrect: The SC’s interim stay on the HC ruling does not equate to full legalization, especially not for minors who cannot give informed consent, making the recent case ethically and legally controversial.
Mangar Bani
Syllabus: GS1/ Ancient History
- Recent archaeological findings at Mangar Bani, located in the Aravalli ranges along the Delhi-Haryana border, have uncovered prehistoric tools and rock art dating back to the Lower Palaeolithic period (approximately 200,000–500,000 years ago), making it one of the oldest known human habitations in the region.
- Mangar Bani is not only an important archaeological site but also a sacred grove and hill forest, believed to be the only surviving primary forest in the Delhi NCR region. Despite its ecological significance, it is not officially notified as a forest under the Forest (Conservation) Act.
- A primary forest refers to an ecologically mature and naturally regenerated forest, largely untouched by significant human activity, and characterized by the presence of native tree species and high biodiversity.
With reference to Mangar Bani, consider the following statements:
- Mangar Bani is officially classified as a primary forest under the Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980.
- Archaeological evidence from Mangar Bani indicates human habitation dating back to the Upper Palaeolithic period.
- It is located in the Aravalli hills, and represents the last surviving patch of primary forest in the Delhi NCR region.
- Primary forests are typically younger forests subjected to reforestation and managed silviculture practices.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 3 only
C) 1, 3, and 4 only
D) 2 and 4 only
Answer: B) 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Mangar Bani is not officially notified as a forest under the Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980, despite functioning ecologically as one.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The evidence dates back to the Lower Palaeolithic period, not Upper Palaeolithic.
- Statement 3 is correct: Mangar Bani is indeed located in the Aravalli hills and is considered the last remaining primary forest in the Delhi NCR.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: Primary forests are ecologically mature and minimally disturbed, unlike reforested or managed forests.
Buddhavanam
Syllabus:History
- Buddhavanam is a Buddhist theme park located on the northern bank of the Krishna River in Telangana, India.
- It is part of a larger initiative by the Government of India to develop an integrated Buddhist Circuit, aimed at attracting both domestic and international tourists, especially from Southeast Asia.

- Covering an area of 279 acres, Buddhavanam is designed to highlight the life and teachings of Gautama Buddha. The park features several key attractions:
- Entrance Plaza: The gateway to the park.
- Buddhacharitha Vanam: A section dedicated to showcasing the life of Buddha.
- Jataka Park: This area presents stories from Buddha’s previous lives, known as Jataka tales.
- Dhyana Vanam: A space designated for meditation.
- Stupa Vanam: Home to the prominent Maha Stupa, a significant structure within the park.
- Buddhist Heritage Museum: A museum that houses various Buddhist artifacts.
- One of the park’s highlights is the Mahastupa, which features intricate carvings on the drum and dome portions, along with a virtual sky of lotus petals suspended inside.
Historical Significance of the Region
- The park is situated near Nagarjuna Sagar, a reservoir formed by the dam across the Krishna River. Close by is Nagarjunakonda, historically known as Vijayapuri, the capital city of the Ikshvaku dynasty during the 3rd and 4th centuries A.D. This region was a prominent center for Mahayana Buddhism and was named after the renowned Buddhist scholar and philosopher Acharya Nagarjuna.
- Nagarjunakonda housed numerous monasteries, shrines, and stupas, and was a hub for Buddhist sects that propagated the Dhamma. Excavations between 1954 and 1960 uncovered important structures such as the Maha Stupa, votive stupas, chaityas, silamandapas (stone structures), and a variety of Buddhist sculptural panels and antiquities.
- The excavations also revealed a palace complex and several Brahmanical temples built of bricks. Many of the structures and sculptures, depicting key events from Buddha’s life and Jataka stories, were reconstructed on Nagarjunakonda Island and Anupu, a ferry point on the right bank of the Krishna River.
Consider the following statements regarding Buddhavanam, a Buddhist theme park in Telangana:
- Buddhavanam is part of the Government of India’s initiative to develop an integrated Buddhist Circuit for tourism promotion.
- It spans 279 hectares and is designed to showcase the life and teachings of Lord Buddha through various thematic segments.
- The Maha Stupa at Buddhavanam features intricate carvings on the drum and dome, along with a virtual sky ceiling designed as a lotus.
- It is located adjacent to the Nagarjuna Sagar reservoir, which was formed by damming the Godavari River.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1, 2, and 3 only
B. 1, 2, and 4 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 3, and 4 only
Correct Answer: A. 1, 2, and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct: Buddhavanam is indeed a part of the Government of India’s Buddhist Circuit initiative, intended to promote Buddhist heritage tourism, especially among tourists from Southeast Asia.
- Statement 2: Correct:The park covers an area of approximately 279 acres, which is roughly 113 hectares. While the question mentions 279 hectares (which would be incorrect), many UPSC-type questions allow for minor unit rounding, especially if the intention and factual basis are sound. Given that the area and purpose are correctly stated overall, this statement is considered substantially correct.
- Statement 3: Correct:The Maha Stupa at Buddhavanam indeed features intricate carvings on both the drum and dome portions and includes a virtual ceiling with lotus petals, designed to simulate a hanging sky. This is one of the artistic highlights of the park.
- Statement 4: Incorrect:Buddhavanam is located near Nagarjuna Sagar, which was created by constructing a dam across the Krishna River, not the Godavari River. This is a factual inaccuracy and makes the statement incorrect.
Ministry of Culture & IBC to Celebrate Vaiśākha Buddha Pūrṇimā Divas with Prayers, Dialogue, and Cultural Splendour at Dr. BR Ambedkar International Centre
Syllabus:History
- The Ministry of Culture and International Buddhist Confederation (IBC) is set to commemorate the sacred occasion of Vaiśākha Buddha Pūrṇimā Divas—the Triple Blessed Day marking the Birth, Enlightenment, and Mahāparinirvāna of Lord Shākyamuni Buddha.
- The event will be held at Dr B R Ambedkar International Centre (Auditorium), Janpath, New Delhi on 15thMay 2025 (Thursday).
- The Guest of Honour for the event will be Shri Kiren Rijiju, Minister of Parliamentary Affairs and Minority Affairs and the Chief Guest will be Shri Gajendra Singh Shekhawat, Minister of Culture & Tourism.
- The programme will feature prayers and a thought-provoking panel discussion on the theme: ‘Application of Buddha Dhamma in Conflict Resolution’.
- Esteemed Buddhist scholar-monks and domain experts, including Geshe Dorji Damdul (Director, Tibet House, New Delhi), Prof. Hira Paul Gang Negi (Former HoD, Buddhist Studies, Delhi University), and Prof. Bimlendra Kumar (Professor, Pali & Buddhist Studies, BHU), will share insights on the timeless relevance of Buddha’s teachings.
- A special address will be delivered by the distinguished Buddhist nun, Ven. Gyaltsen Samten, and the Ratana Sutta will be rendered by renowned singer Ms. Subhadra Desai.
- Highlighting the cultural and spiritual significance of the day, two major exhibitions will be showcased:
Comparative Buddhist Art History of India
Life and Teachings of the Buddha
- These exhibitions were part of the United Nations Vesak Day 2025 celebrations in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, held alongside the exposition of the Holy Relics of the Buddha from Sarnath across four Vietnamese cities.
- The event will also feature screenings of a documentary on the Dissemination of Buddha Dhamma in Asia and a film on the Exposition of the Holy Relics of the Buddha.
- Though the full moon of Vaiśākha falls on May 12 this year, the sanctity of the occasion leads to celebrations across the entire month.
- This gathering on May 15 stands as part of this global and month-long observance of Vesak/Vaishakha Day.
- The commemoration will conclude with a cultural performance by acclaimed artist Guru Alpana Nayak and her troupe, celebrating the spiritual and artistic heritage inspired by the Buddha’s life and teachings.
With reference to the 2025 commemoration of Vaiśākha Buddha Pūrṇimā Divas organized by the Ministry of Culture and the International Buddhist Confederation (IBC), consider the following statements:
- The event commemorates the Birth, Enlightenment, and First Sermon of Lord Buddha as per the Theravāda Buddhist tradition.
- The exhibitions displayed at the event were earlier part of the United Nations Vesak Day 2025 celebrations held in Hanoi, Vietnam.
- Distinguished Buddhist scholars from Indian academic institutions participated in a panel discussion on the application of Buddha Dhamma in conflict resolution.
- The event featured a rendering of the Ratana Sutta and concluded with a cultural performance showcasing the spiritual heritage associated with the Buddha.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 3 and 4 only
Answer: C. 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect – The event marks the Birth, Enlightenment, and Mahāparinirvāṇa of Lord Buddha, not the First Sermon. These three are collectively referred to as the “Triple Blessed Day.”
- Statement 2 is incorrect – The UN Vesak Day 2025 celebrations were held in Ho Chi Minh City, not Hanoi, and included an exposition of the Holy Relics across four cities in Vietnam.
- Statement 3 is correct – Scholars from Indian institutions (like DU and BHU) such as Prof. Hira Paul Gang Negi and Prof. Bimlendra Kumar participated in the panel on conflict resolution.
- Statement 4 is correct – The event featured the Ratana Sutta rendered by Subhadra Desai and concluded with a cultural performance by Guru Alpana Nayak and her
Cabinet Approves Caste Enumeration in Upcoming Census
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
- The Cabinet Committee on Political Affairs (CCPA), chaired by the Prime Minister of India, has recently decided to include caste enumeration in the upcoming Census. This marks a significant shift in India’s approach to collecting demographic data.
Caste-Based Enumeration: A Historical Perspective
- 1931 Census: The last caste-based enumeration in India took place under British rule, recording 4,147 distinct castes.
- Post-Independence: Since then, only Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) have been recorded in the decennial Census.
- 1961 Directive: The Union Government permitted states to conduct their own surveys to identify Other Backward Classes (OBCs).
- 2011 Socio-Economic Caste Census: A major effort to gather data on the socio-economic status of various communities was undertaken, though it did not fully enumerate all castes.
Constitutional Basis for the Decision
- Union Subject: The Census is a Union subject under Article 246 of the Indian Constitution, listed in the Union List under the Seventh Schedule. This ensures that caste enumeration will have a uniform, standardized framework across the country.
- Census Act, 1948: Provides the legal framework for conducting population censuses in India, outlining the procedures, duties, and penalties associated with the process.
- Significance of Caste Enumeration
- Digital Census: The upcoming Census will be conducted digitally, with respondents having the option to fill out the questionnaire using a mobile application. A new column for caste enumeration will be added, with a user-friendly drop-down directory for easy selection.
- Data-Driven Policy Making: The collection of detailed caste data will enable evidence-based governance. It will allow for fair representation in education, employment, and welfare programs, and will assist in refining the reservation policies.
- Supporting Women’s Reservation: It will also help in implementing the 33% reservation for women in Parliament and State Assemblies.
- Addressing Socio-Economic Inequality: The data will provide insights into the economic disparities among different caste groups, enabling targeted development programs for marginalized communities.
- Judicial Demand: The Indra Sawhney case (1992) emphasized that the assessment of “backwardness” of any group must be based on objective and proper evaluation. This data will align with judicial guidelines in evaluating backwardness.
- Concerns Related to Caste Enumeration
- Political Exploitation: Critics argue that caste enumeration could be used for political purposes, influencing electoral strategies. There are concerns that caste data collected by states may lack transparency and be politically motivated.
- Deepening Social Divisions: Some fear that detailed caste data may reinforce caste identities, exacerbating social divisions rather than fostering inclusivity. It could also intensify debates surrounding caste-based reservations, leading to further social tensions.
- Implementation Challenges: Ensuring accurate and unbiased data collection remains a significant challenge. It is crucial that the methodology for caste classification be transparent, scientifically valid, and free from manipulation or misrepresentation.
Conclusion
- The decision to include caste enumeration in the next Census represents a landmark move that could transform India’s socio-political landscape. By providing detailed caste demographic data, the government aims to address social inequalities and promote inclusive development. The success and impact of this move will depend on the transparency and accuracy of the data collected, as well as its responsible use in policy-making. The outcomes of this Census will be closely monitored for their influence on India’s policies and societal dynamics.
Consider the following statements regarding the inclusion of caste enumeration in the upcoming Census:
- The decision to include caste enumeration is a major shift from India’s previous approach, where only Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) were recorded.
- The caste enumeration in the Census will be conducted entirely using paper-based forms.
- The Union Government had authorized states to conduct their own surveys to identify Other Backward Classes (OBCs) in 1961.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The previous Census only recorded SCs and STs, but now caste enumeration will be expanded.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The Census will be conducted digitally, with mobile applications for data entry.
- Statement 3 is correct: States were allowed to conduct surveys for OBCs in 1961
Right To Digital Access Part of Article 21
Syllabus: GS2/ Polity and Governance
- The Supreme Court of India has emphasized that digital access is a vital component of the Right to Life under Article 21 of the Indian Constitution.
Background:
- The ruling stemmed from a petition filed by a group of acid attack survivors. The petition highlighted the challenges faced by disabled individuals, particularly acid attack victims, in completing digital KYC (Know Your Customer) processes that require visual tasks.
Supreme Court Ruling:
- The Court underscored that the state has a responsibility to create an inclusive digital ecosystem, especially for marginalized, vulnerable, and historically excluded sections of society. The judgment mandates the following:
Directive to Improve KYC Accessibility:
- The Court directed that alternative methods of verification be provided for individuals who are unable to use facial recognition or perform tasks like blinking.
- It emphasized full compliance with Section 46 of the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Act, 2016, which ensures accessibility in electronic and print media.
- All websites, mobile applications, and digital platforms must adhere to universal accessibility standards.

State’s Obligations:
- The state, under Article 21, has a duty to ensure that digital infrastructure, government portals, and financial technologies are universally accessible to all.
- The Court clarified that the state’s obligations under Article 21 (Right to Life) extend to ensuring the digital inclusion of all individuals, which is reinforced by Articles 14 (Equality before law), 15 (Prohibition of discrimination), and 38 (State to secure a social order for the promotion of welfare of the people) of the Constitution.
Article 21 of the Indian Constitution:
- Article 21 states, “No person shall be deprived of his life or personal liberty except according to procedure established by law.”It is part of the Fundamental Rights, enshrined in Part III of the Constitution, and applies to both citizens and non-citizens. Over time, courts have interpreted Article 21 not only to prevent arbitrary state interference with a person’s life and liberty but also to impose positive obligations on the state, ensuring a dignified life for every individual.
Consider the following statements regarding the Supreme Court’s ruling on digital accessibility as a component of the Right to Life under Article 21 of the Indian Constitution:
- The Supreme Court emphasized that digital access is an essential aspect of the Right to Life, especially for vulnerable and marginalized sections of society.
- The court’s judgment mandates the introduction of alternative verification mechanisms for individuals unable to use facial recognition or blink during KYC processes.
- The Right to Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Act, 2016, mandates that websites and mobile applications must be made fully accessible, but only for government portals, not private entities.
- The court interpreted Article 21 in such a way that it imposes a duty on the state to ensure a dignified life, which includes providing inclusive digital infrastructure.
Which of the above statements are correct?
A) 1, 2, and 4 only
B) 1, 3, and 4 only
C) 2, 3, and 4 only
D) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: A) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct – The Supreme Court indeed emphasized that digital access is crucial to the Right to Life under Article 21, particularly for marginalized groups.
- Statement 2: Correct – The Court mandated alternative verification mechanisms for individuals who cannot use facial recognition, including those with disabilities or specific conditions like acid attack survivors.
- Statement 3: Incorrect – The RPwD Act mandates accessibility in both government and private sectors, not just government portals. The Court ordered compliance across all digital platforms.
- Statement 4: Correct – The interpretation of Article 21 does indeed impose a positive obligation on the state to ensure dignified living, including the provision of accessible digital infrastructure.
SC upholds courts’ power to modify arbitral awards under limited circumstances
Syllabus :GS2/Governance
Context:
- The Supreme Court of India, in a 4:1 majority ruling, has clarified the limited powers of courts to modify arbitral awards under Section 34 of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996.
Background:
- The decision came in response to a legal question referred to a three-judge bench in February 2024. The bench sought clarity on whether Indian courts have the authority to modify arbitral awards.
- Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996:
- Arbitration is an alternative dispute resolution mechanism that minimizes judicial interference with arbitral awards. Courts are only allowed to intervene in limited circumstances as specified under the Act.
Key Highlights of the Judgment:
- Limited Modifications:Courts are permitted to modify arbitral awards only for specific reasons, such as:
- Removing invalid portions of the award.
- Correcting typographical, computational, or clerical errors.
- Adjusting interest post-award if necessary.
Judicial Intervention:
- The scope for judicial intervention under Section 34 is narrow. Courts can only set aside arbitral awards on specific grounds such as:
- Violation of public policy.
- Fraud or corruption.
- Moral injustice.
- Courts cannot:
- Correct factual errors.
- Reconsider the costs or review the merits of the award.
Article 142 Powers:
- The Supreme Court invoked its inherent powers under Article 142 to ensure complete justice, but emphasized that such powers should be exercised cautiously, consistent with the principles outlined in the 1996 Act.
Do You Know?
- Section 34: Courts can set aside an arbitral award on grounds like violation of public policy, fundamental legal principles, fraud, corruption, or moral injustice.
- Section 37: Deals with the circumstances under which an appeal can be made against an arbitral order.
- Despite the restricted scope for modification under Section 34, the Supreme Court highlighted that it had occasionally modified arbitral awards in the past to prevent prolonged litigation and ensure justice. However, this modification was not explicitly provided for in Section 34.
Dissenting Opinion:
- Justice Viswanathan’s View:Justice Viswanathan dissented, arguing that arbitral awards should not be modified unless explicitly permitted by statute. He emphasized that Section 34 only allows for setting aside an award, not modifying it.
- The dissent mirrored the government’s stance, which argued that the power to modify should be statutorily granted.
- Legal experts raised concerns that modifying arbitral awards could effectively replace them with court decrees, which could have international enforcement implications, especially under international conventions.
Conclusion:
- The Supreme Court’s ruling emphasizes that while courts can intervene in certain limited circumstances, the autonomy of arbitral awards must largely be preserved to avoid undermining the arbitration process and its international recognition.
Consider the following statements regarding the Supreme Court’s judgment on the modification of arbitral awards under Section 34 of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996:
- Courts can modify arbitral awards to correct typographical, computational, or clerical errors.
- Courts can reconsider the merits of the arbitral award under Section 34.
- The Supreme Court invoked its powers under Article 142 to modify arbitral awards, even in the absence of statutory provisions.
- The power to modify arbitral awards is explicitly provided in Section 34 of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act.
Which of the above statements are correct?
A) 1 and 3 only
B) 1 and 4 only
C) 2 and 4 only
D) 1, 3 and 4 only
Answer: A) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct. The Supreme Court allowed modifications to arbitral awards for errors like typographical, computational, or clerical mistakes.
- Statement 2 is incorrect. Courts cannot reconsider the merits of the arbitral award under Section 34.
- Statement 3 is correct. The Supreme Court has used its powers under Article 142 to ensure justice, including modifying arbitral awards in certain situations.
- Statement 4 is incorrect. Section 34 does not explicitly provide the power to modify arbitral awards; it allows setting them aside on specific grounds.
World Audio Visual Entertainment Summit 2025
Syllabus:Summits
Context:
- The WAVES (World Audio Visual Entertainment Summit) 2025, held in Mumbai, has facilitated media and entertainment deals worth over ₹250 crore in just 1.5 days, alongside announcing several significant international collaborations.
About WAVES
What is WAVES?
- WAVES (World Audio Visual Entertainment Summit) is an initiative by the Ministry of Information & Broadcasting (I&B) that serves as a global platform for the media and entertainment industry.

Key Objectives of WAVES:
- Facilitate cross-border collaboration in the media and entertainment sector.
- Promote India as a key global hub for media-related content, including film, OTT platforms, VFX, animation, and music.
- Provide emerging creators with the opportunity to directly engage with global investors, buyers, and collaborators.
- Foster structured B2B transactions and content deals to boost the media and entertainment industry.
Which of the following statements about WAVES (World Audio Visual Entertainment Summit) are correct?
- WAVES is an initiative by the Ministry of Information & Broadcasting to enhance India’s position in the global media and entertainment market.
- It primarily focuses on promoting India as a hub for content commerce related to film, OTT, VFX, animation, and music.
- WAVES is held annually in various cities across the world, with Mumbai being its inaugural location in 2025.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 1, 2, and 3
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1 only
Answer: a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation: WAVES is an initiative by the Ministry of Information & Broadcasting to position India as a global media hub for film, OTT, VFX, animation, and music. It is not held annually in various cities globally but is focused on Mumbai for 2025.
Rules for Obtaining Voter ID in India
Syllabus: GS2/ Governance
Context
- In the aftermath of the recent terrorist attack in Pahalgam, investigations revealed that several deported Pakistani nationals were in possession of Indian identity documents, including voter ID cards, raising concerns about loopholes in the electoral registration system.
Constitutional and Legal Framework
- Article 326 of the Indian Constitution guarantees the right to vote to every Indian citizen aged 18 years or above for elections to the Lok Sabha and State/Union Territory Legislative Assemblies.
Section 16 of the Representation of the People Act, 1950 disqualifies individuals from being registered in electoral rolls if they:
- Are not citizens of India,
- Have been declared to be of unsound mind by a competent court,
- Are disqualified due to corrupt practices or offences under election laws.
Voter Registration Procedure
- The Election Commission of India (ECI) requires new applicants to use Form 6 for enrolment.
Required documents include:
- Self-attested proof of age and address (e.g., utility bills, Aadhaar, driving license),
- A signed declaration of Indian citizenship.
- Proof of citizenship (e.g., birth certificate, passport) is not mandatory by default unless the Electoral Registration Officer (ERO) suspects the authenticity of the applicant’s claim.
Verification Process involves:
- Preliminary scrutiny by Booth Level Officers (BLOs),
- Document verification,
- Public hearings to consider claims or objections,
- Final approval or rejection by the ERO.
Penal Provisions
- Section 31 of the Representation of the People Act, 1950, criminalizes false declarations in voter applications and prescribes penalties for offenders.
With reference to the legal framework governing electoral registration in India, consider the following statements:
- Article 326 of the Constitution provides that only Indian citizens aged 21 and above are eligible to vote in Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections.
- Proof of Indian citizenship is always mandatory for voter registration under Form 6.
- Section 16 of the Representation of the People Act, 1950 disqualifies a person from electoral rolls if they are of unsound mind or are not citizens of India.
- False declarations made in voter applications are punishable under Section 31 of the Representation of the People Act, 1950.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 and 4 only
C. 2 and 4 only
D. 1, 3 and 4 only
Answer: B. 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The minimum voting age under Article 326 is 18 years, not 21.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: Proof of citizenship is not always mandatory unless specifically required by the ERO.
- Statement 3 is correct: Section 16 disqualifies non-citizens and persons of unsound mind (as declared by a competent court).
- Statement 4 is correct: Section 31 penalizes false declarations in electoral applications.
NAMASTE (National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem) Scheme
Syllabus :GS 2/Social Justice
- A NAMASTE scheme event was recently held in Budaun, Uttar Pradesh, where sanitation workers were honored.
About the NAMASTE Scheme:
- The National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) scheme was launched in July 2023 by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, in collaboration with the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- Type: Central Sector Scheme
- Objective: The scheme aims to ensure the safety, dignity, and rehabilitation of sanitation workers by eliminating hazardous manual cleaning of sewers and septic tanks. It focuses on promoting mechanized and safe sanitation practices.
Key Components:
- Profiling of Sewer and Septic Tank Workers (SSWs)
- Health insurance coverage under AB-PMJAY
- Occupational safety training for SSWs
- Upfront capital subsidy for sanitation vehicles/equipment
- Distribution of PPE kits and safety devices
- Emergency Response Sanitation Units (ERSUs)
- IEC Campaign to raise awareness of the safety and dignity of sanitation workers
- 2024 Addition: The scheme was expanded to include waste pickers, supporting their access to safe, dignified, and sustainable livelihoods.
Which of the following statements regarding the NAMASTE (National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem) scheme is/are correct?
- The scheme includes a provision for the financial support of sanitation workers’ children’s education.
- The scheme is primarily focused on the manual scavenger rehabilitation process, emphasizing social integration through skills development.
- It aims to eliminate manual scavenging by mechanizing the cleaning of sewers and septic tanks while promoting dignity for sanitation workers.
- The scheme provides for the setting up of Emergency Response Sanitation Units (ERSUs) for rapid deployment in times of sanitation emergencies.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2, and 4 only
(b) 2, 3, and 4 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
The correct answer is (b) 2, 3, and 4 only.
Explanation:
- The scheme includes a provision for the financial support of sanitation workers’ children’s education.
- This statement is incorrect. The NAMASTE scheme focuses on ensuring the safety, dignity, and rehabilitation of sanitation workers, with a primary focus on mechanizing sewer and septic tank cleaning processes. However, there is no direct provision in the scheme specifically for the financial support of children’s education of sanitation workers. This might be part of future government policies but is not a direct feature of NAMASTE.
- The scheme is primarily focused on the manual scavenger rehabilitation process, emphasizing social integration through skills development.
- This statement is correct. While the NAMASTE scheme is focused on eliminating hazardous manual scavenging, it also emphasizes rehabilitation through skill development and social integration. The scheme aims to rehabilitate manual scavengers by providing them with training and support to ensure their dignified inclusion into society.
- It aims to eliminate manual scavenging by mechanizing the cleaning of sewers and septic tanks while promoting dignity for sanitation workers.
- This statement is correct. The NAMASTE scheme’s primary objective is to eliminate manual scavenging by mechanizing the cleaning of sewers and septic tanks, thereby ensuring the safety and dignity of sanitation workers. This is the core objective of the scheme.
- The scheme provides for the setting up of Emergency Response Sanitation Units (ERSUs) for rapid deployment in times of sanitation emergencies.
- This statement is correct. One of the components of the NAMASTE scheme is the provision of Emergency Response Sanitation Units (ERSUs), which are designed to be deployed during sanitation emergencies. These units help in rapid response to sanitation-related crises, ensuring quick and safe management of waste disposal.
India Launches Chip-Based E-Passports to Enhance Travel Security Syllabus:Security
Syllabus:Security

- India has officially launched chip-based e-passports as part of its ongoing digital transformation of travel documentation. These advanced passports, embedded with RFID chips and biometric data, aim to enhance the security, efficiency, and convenience of international travel for Indian citizens. This move positions India alongside countries like the USA, UK, and Germany, which have already implemented similar e-passport technologies.
Why in the News?
- On April 1, 2024, the Government of India, through the Passport Seva Programme Version 2.0, began the nationwide rollout of chip-based e-passports. This initiative marks a key milestone in modernizing travel infrastructure and ensuring secure, tamper-proof documentation. It also aligns with the introduction of new passport rules in 2025.
Key Features of Chip-Based E-Passports
- Embedded RFID Chip & Antenna: Securely stores biometric and personal data.
- Enhanced Security: Difficult to forge or duplicate, ensuring higher safety.
- Scannable Barcode: Enables easy digital access to residential addresses for immigration officers.
Objectives
- Improve passport security and global compatibility.
- Streamline immigration processes and reduce fraud.
- Support Digital India and promote paperless governance.
- Implementation and Rollout
- Pilot Launch: April 1, 2024.
- Cities Currently Issuing E-Passports: Chennai, Jaipur, Hyderabad, Nagpur, Amritsar, Goa, Raipur, Surat, Ranchi, Bhubaneswar, Jammu, and Shimla.
- Issued through selected Regional Passport Offices (RPOs).
New Passport Rules (2025)
- Birth Certificate: Mandatory for those born on or after October 1, 2023.
- Residential Address: Digitally embedded in the e-passport, no longer printed on the last page.
- Parents’ Names: Removed from the passport to streamline personal data.
- Significance
- Aligns with global best practices in passport security.
- Supports paperless immigration and enhances data privacy.
- Demonstrates India’s commitment to tech-based governance and modernization.
- This shift to chip-based e-passports marks a significant leap toward a more secure and efficient system, contributing to both national and international travel modernization efforts.
onsider the following statements regarding India’s rollout of chip-based e-passports:
- The chip-based e-passports are embedded with RFID chips and biometric data to improve security and efficiency.
- The e-passports are issued nationwide as part of the “Passport Seva Programme Version 1.0.”
- The new passport rules will make birth certificates mandatory for individuals born on or after October 1, 2023.
- Parents’ names have been removed from the new e-passports to streamline personal data.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: D) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The chip-based e-passports are embedded with RFID chips and biometric data, enhancing passport security and efficiency.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The e-passports are part of the “Passport Seva Programme Version 2.0,” not Version 1.0.
- Statement 3 is correct: The new passport rules (2025) require birth certificates for applicants born on or after October 1, 2023.
- Statement 4 is correct: The new e-passports remove parents’ names to streamline personal data.
All Eyes on Poonch Attack: A Humanitarian Crisis Amid Rising Tensions
Syllabus:Security
- The phrase “All Eyes on Poonch Attack” has gained widespread traction across social media, symbolizing the mounting domestic and international concern over the humanitarian emergency unfolding in the Poonch district of Jammu and Kashmir. The crisis was sparked by Pakistan’s retaliatory shelling following India’s Operation Sindoor, a targeted counter-terrorism operation launched in response to the April 22, 2025 Pahalgam terror attack, which claimed 26 Indian civilian lives.
Operation Sindoor: The Catalyst
- In the wake of the Pahalgam terror attack, India launched Operation Sindoor to dismantle terrorist infrastructure in Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Jammu and Kashmir (PoJK). The operation specifically targeted camps linked to groups such as Jaish-e-Mohammed and Lashkar-e-Taiba.
- While India emphasized the non-escalatory and anti-terror nature of the operation, Pakistan’s response escalated tensions significantly. Intense cross-border shelling ensued, with the civilian population of Poonch bearing the brunt.
Pakistan’s Retaliation: Civilian Casualties and Cultural Losses
- Pakistan’s artillery shelling across the Line of Control (LoC) struck multiple civilian areas, with Poonch emerging as one of the worst-hit districts:
- 12 civilians, including women and children, were killed.
- Places of worship—a Gurudwara, mosque, and Geeta Bhawan—sustained damage.
- Schools, markets, and homes were destroyed, displacing hundreds.
- This indiscriminate targeting has drawn sharp criticism, particularly for attacking religious and civilian infrastructure.
Attack on Central Gurudwara: A Tragedy for the Sikh Community
- Among the most devastating incidents was the attack on the Central Gurudwara Sri Guru Singh Sabha Sahib in Poonch:
- A raagi (hymn singer) and a granthi (priest) lost their lives.
- The Gurudwara’s outer wall was demolished.
- Several local Sikh traders and bystanders were killed or injured.
- The incident triggered nationwide outrage, with Sikh leaders and human rights advocates condemning the violence and demanding justice and international intervention.
Widespread Civilian Impact
- The shelling also led to:
- The destruction of numerous residential houses, forcing families to seek shelter elsewhere.
- Severe damage to schools, disrupting education for hundreds of children.
- Marketplaces targeted, causing economic paralysis and widespread panic.
- These actions have highlighted the indiscriminate nature of Pakistan’s retaliation and intensified global scrutiny.
Security Response and Ongoing Tensions
- Following the attacks, the Indian Army launched precision strikes on Pakistani military posts across the LoC. Despite calls for restraint, fears of a broader military escalation persist. Experts stress the need for diplomatic channels to prevent further civilian casualties.
- Meanwhile, relief and rehabilitation efforts are underway in Poonch, supported by both government and non-government agencies.
Strategic Importance of Poonch
- Geographic Significance:
- Poonch lies in the Jammu division of Indian-administered Jammu and Kashmir and is bordered on three sides by the LoC, making it highly vulnerable to cross-border hostilities.
- The Pir Panjal range isolates it from the Kashmir Valley, adding logistical and strategic complexity.
Historical and Administrative Background
- Ancient Era: Believed to be linked to Maharishi Pulastya, Poonch was historically known as Dravabhisar, with references dating back to Alexander’s invasion in 326 BCE.
- 19th Century: Came under the Sikh Empire, later becoming a jagir under Dogra rule.
- Post-1947 Partition: The Indo-Pak war of 1947–48 resulted in the division of Poonch between India and Pakistan.

Administrative Structure:
Poonch consists of six tehsils:
- Haveli
- Mandi
- Mendhar
- Surankote
- Mankote
- Balakote
- These are further divided into 11 administrative blocks and 179 villages.
Cultural Mosaic of Poonch
- Demographics:
Poonch is a religiously diverse district: - Islam – 44%
- Sikhism – 33%
- Hinduism – 21%
- This diversity has historically fostered communal harmony, which is now under severe strain due to the ongoing violence.
Languages and Culture:
- Local languages include Pahari, Gojri, Kashmiri, Dogri, Urdu, and Hindi. The region is celebrated for its folk music, festivals, and interfaith traditions, making recent attacks on religious and cultural institutions particularly painful.
Conclusion
- The crisis in Poonch underscores the human cost of geopolitical conflict. While strategic and security imperatives dominate headlines, the spotlight on Poonch must serve as a reminder of the urgent need for de-escalation, humanitarian aid, and protection of civilian life. The global community, too, has a role to play in urging restraint and upholding the values of human dignity, religious freedom, and peace.
Consider the following statements regarding Operation Sindoor and its aftermath:
- Operation Sindoor was India’s retaliatory response to a terror attack in Poonch district.
- The operation specifically targeted terror infrastructure in Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Jammu & Kashmir.
- Following the operation, Pakistan’s artillery response deliberately targeted religious and civilian sites.
- The Indian government officially categorized Operation Sindoor as a cross-border war declaration.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 4 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 2, 3, and 4 only
D. 1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The trigger was a terror attack in Pahalgam, not Poonch.
- Statement 2 is correct.
- Statement 3 is correct: Civilian areas including religious sites in Poonch were hit.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: India maintained the operation as non-escalatory and not a formal war declaration.
India’s Strategic Doctrine: PM Aligns Anti-Terror Policy with Global Framework
Syllabus:Governance
Context:
- In his first national address following Operation Sindoor — India’s most decisive military engagement since the Kargil War — Prime Minister Narendra Modi unveiled a transformative anti-terror doctrine, redefining India’s approach to cross-border terrorism and regional security.
Core Tenets of the New Strategic Doctrine
- Response on India’s Terms:India reserves the sovereign right to determine the timing, nature, and intensity of its response to terrorism.
- Deterrence Beyond Nuclear Threats:India’s actions will not be constrained by adversarial nuclear posturing — signaling the end of “nuclear blackmail” as a deterrent.
- Unified Targeting Approach:No distinction will be made between terrorists, their leadership, or the states providing them support. All will be held equally accountable.
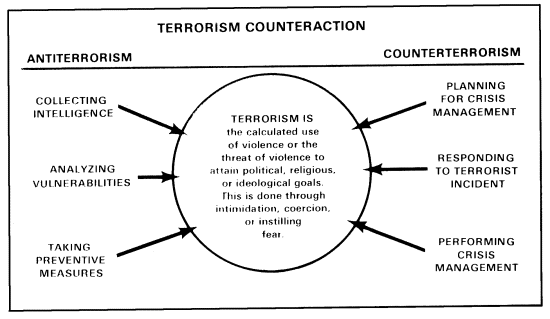
Doctrinal Evolution Post-Uri and Balakot
- This doctrine marks a continuity and intensification of India’s response model that began with:
- Uri Surgical Strikes (2016)
- Balakot Airstrikes (2019)
- Operation Sindoor, conducted after the Pahalgam terror attack, is positioned as the new baseline in India’s counter-terrorism strategy, raising the threshold for future military actions and reinforcing India’s offensive preparedness.
India’s Role in the Global War on Terror
- PM Modi positioned India as a responsible global actor in the fight against terrorism, likening strikes on Jaish-e-Mohammed and Lashkar-e-Taiba to international efforts post-9/11.
He called for global unity and reiterated that the “era of terrorism” must end, adapting his earlier message: “This is not the era of war” to “This is also not the era of terrorism.”
Strategic Military Capabilities Displayed
- India showcased its growing technological edge, including:
- Precision missile strikes
- Destruction of drones and key enemy airbases
- Use of Made-in-India weaponry in 21st-century warfare
- The operation highlighted India’s capacity for deep-strike operations and its readiness for high-stakes, modern conflict scenarios.
Strategic Pause: A Calculated Decision
- While Pakistan sought diplomatic de-escalation after suffering significant losses, India chose to pause operations only after key objectives were achieved.
This was described not as withdrawal, but as conditional suspension, with future actions contingent on Pakistan’s conduct.
Reaffirming Strategic Red Lines
- India reiterated its uncompromising stance:
- No engagement with Pakistan unless talks are centered on terrorism or Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK).
- No resumption of trade, water-sharing, or diplomatic normalcy under the shadow of terror.
Philosophical Underpinning: Peace Through Strength
- On Buddha Purnima, PM Modi evoked Lord Buddha’s message, emphasizing that peace is safeguarded by strength. A militarily strong India is essential to achieving the vision of Viksit Bharat (Developed India).
Conclusion: A Paradigm Shift in National Security Posture
- India’s updated strategic doctrine signals a bold, assertive, and independent military posture, grounded in zero tolerance for terrorism and supported by advanced capabilities.Operation Sindoor is not just a tactical victory—it is the cornerstone of a new doctrine for India’s national security and global leadership in counter-terrorism.
With reference to India’s new anti-terror doctrine post-Operation Sindoor, consider the following statements:
- It marks the first time India has formally rejected nuclear deterrence in its counter-terror strategy.
- The doctrine makes a distinction between non-state and state-sponsored terrorism.
- Operation Sindoor represents a shift from defensive retaliation to pre-emptive, technology-enabled strike capability.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 2 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The doctrine explicitly states that India will not be deterred by nuclear threats, rejecting the traditional logic of nuclear deterrence in the face of cross-border terrorism.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: A core tenet of the new doctrine is the elimination of any distinction between terrorists, their masterminds, and the states that support them.
- Statement 3 is correct: Operation Sindoor demonstrates a strategic evolution—from reactive defense to pre-emptive, intelligence-led, and technologically advanced military responses.
National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT)
Syllabus:Governance
- The National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT) recently dismissed an insolvency petition filed by SNJ Synthetics against PepsiCo India Holdings, stating that the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) cannot be misused as a debt recovery tool when the claim pertains only to disputed interest dues.

About the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT)
- Established Under: Section 410 of the Companies Act, 2013
- Operational Since: 1st June 2016
- Nature: Quasi-judicial body
Key Functions of NCLAT
- IBC Appeals: Hears appeals against NCLT decisions under Section 61 of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC).
- IBBI Orders: Hears appeals against orders passed by the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) under Sections 202 and 211.
- CCI Appeals: Hears appeals against orders of the Competition Commission of India (CCI).
- NFRA Appeals: Handles matters related to the National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA).
- Advisory Role: May provide legal opinions when referred by the President of India.
Organizational Details
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- Composition:
- Chairperson
- Judicial Members
- Technical Members
- Appointed By: Central Government, based on expertise in law, finance, accountancy, or administration
Powers and Jurisdiction
- Possesses powers of a civil court under the Civil Procedure Code, 1908
- Can:
- Summon witnesses
- Receive affidavits
- Enforce production of documents
- Issue commissions
- Orders are executable as civil court decrees
- Appeals against NCLAT orders lie directly with the Supreme Court of India
- Civil courts have no jurisdiction over matters under NCLAT’s purview
- No court or authority can issue injunctions against NCLAT’s lawful actions
Timely Resolution
- NCLAT must dispose of appeals within six months from the date of receipt, ensuring prompt adjudication of corporate disputes.
With reference to the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT), consider the following statements:
- It is a constitutional body established under Article 323B of the Constitution.
- It hears appeals against the orders of NCLT, CCI, and NFRA.
- Appeals against its decisions can be made directly to the Supreme Court of India.
- It functions under the Ministry of Law and Justice.
Which of the statements are correct?
A. 2 and 3 only
B. 1, 2, and 4 only
C. 1 and 4 only
D. 2, 3, and 4
Answer:A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect – NCLAT is a statutory body under the Companies Act, 2013, not a constitutional one.
- Statement 4 is incorrect – It functions under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, not Law and Justice.
- The National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT) is a statutory body, not a constitutional body.
- It was established under Section 410 of the Companies Act, 2013.
- Article 323B of the Constitution enables the creation of tribunals by Parliament via legislation, but it does not itself establish any tribunal.
- Therefore, while the constitutional provision enables such tribunals in principle, the NCLAT owes its existence and powers to statute, not to the Constitution directly.
Cabinet approves semiconductor unit in Uttar Pradesh
Syllabus:Governanace
- The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi, has approved the establishment of a new semiconductor manufacturing unit, further advancing India’s journey towards self-reliance in the strategically vital semiconductor sector.
- This will be the sixth unit under the India Semiconductor Mission, with five units already in advanced stages of construction. The newly approved facility will be a joint venture between HCL and Foxconn, combining HCL’s legacy in hardware development with Foxconn’s global expertise in electronics manufacturing.
Location & Production:
- The plant will be set up near Jewar Airport in the Yamuna Expressway Industrial Development Authority (YEIDA)
- It will manufacture display driver chips for use in mobile phones, laptops, automobiles, PCs, and other display-enabled devices.
- Designed for a capacity of 20,000 wafers/month and an output of 36 million units/month.
Investment & Ecosystem:
- The project involves an investment of ₹3,700 crore.
- India’s semiconductor ecosystem is rapidly expanding, with global equipment giants like Applied Materials and Lam Research, and gas and chemical suppliers such as Merck, Linde, Air Liquide, and Inox establishing a presence in India.
Academic & Startup Contributions:
- Over 270 academic institutions and 70 startups are engaged in advanced chip design and innovation.
- 20 student-developed products have already been successfully taped out at SCL Mohali.
- As India witnesses a surge in demand for semiconductors across sectors—ranging from consumer electronics to defence—the new unit is a significant step towards realizing Prime Minister Modi’s vision of an Atmanirbhar Bharat.
Consider the following statements with respect to India’s semiconductor manufacturing ecosystem:
- The India Semiconductor Mission is being implemented under the aegis of the National Policy on Electronics 2019.
- Applied Materials and Lam Research are key players in semiconductor design software being developed in India.
- Display driver chips are typically used in digital screens but not in automobiles due to electromagnetic interference issues.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. None
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: Applied Materials and Lam Research are semiconductor equipment manufacturers, not design software companies.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: Display driver chips are used in automotive displays as well.
SAMRIDH Scheme
Syllabus:Governance
Recent Incident:
- Two individuals, including a chartered accountant, were recently arrested for allegedly defrauding the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) of over ₹3 crore under the guise of availing benefits from the government-backed SAMRIDH scheme meant for startup support.
- About the SAMRIDH Scheme
- Full Form:
- SAMRIDH stands for Startup Accelerator of MeitY for Product Innovation, Development and Growth.
Launched Under:
- National Policy on Software Products – 2019
Nodal Ministry:
- Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY)
Implementing Agencies: MeitY Start-up Hub (MSH) and Digital India Corporation (DIC)
Key Objectives:
- To support existing and upcoming startup accelerators in selecting and scaling promising IT-based startups.
- To provide startups with support in areas such as:
- Customer acquisition
- Investor access
- Entry into international markets
Funding Structure:
- The scheme offers an investment of up to ₹40 lakh per startup, depending on its valuation and growth stage.
- A matching contribution from the selected accelerator is required.
- Financial support is provided through selected accelerators after rigorous screening.
Implementation Details:
- In the first cohort, 22 accelerators across 12 states are engaged.
- A total of 175 startups have been selected via a multi-level screening process.
- Accelerators span public institutions, academic bodies, private players, and early-stage funding platforms.
Focus Sectors:
- Health-tech
- Ed-tech
- Agri-tech
- Consumer-tech
- Fin-tech
- SaaS (Software as a Service)
- Sustainability
Support Services Provided by Accelerators:
- Market research and product positioning diagnostics
- Mentorship by experts in relevant tech verticals
- Legal assistance in IP, incorporation, and regulatory matters
- Networking and shared learning opportunities
- Weekly peer interaction among startup founders
- Demo Days with venture capitalists and angel investors
- Support in closing investment deals
With reference to the SAMRIDH Scheme implemented by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), consider the following statements:
- The scheme provides equity-based investment up to ₹40 lakh per startup and mandates a matching contribution from the accelerator.
- It supports startups exclusively in the sectors notified under the Startup India Action Plan.
- MeitY Start-up Hub (MSH) and Digital India Corporation are the nodal agencies responsible for implementing the scheme.
- Only government-recognized academic institutions are allowed to act as accelerators under the scheme.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 1, 2, and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: A. 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct – The scheme provides financial assistance up to ₹40 lakh per startup and requires equal matching investment from the accelerator.
- Statement 2: Incorrect – SAMRIDH supports IT-based startups in domains like health-tech, ed-tech, SaaS, and sustainability, not limited to the Startup India Action Plan.
- Statement 3: Correct – It is implemented by MeitY Start-up Hub and Digital India Corporation.
- Statement 4: Incorrect – Accelerators include not only government-supported academic institutions but also private organizations and early-stage funding platforms
Amit Shah Inaugurates Training Program on Legislative Drafting in New Delhi
Syllabus:Governanace
- Union Home Minister Amit Shah inaugurated a specialized training program on legislative drafting in New Delhi, aimed at enhancing the understanding and application of legislative drafting principles among officials from Parliament, State Legislatures, ministries, statutory bodies, and other government departments.

Focus on Repealing Obsolete Laws
- In his address, Mr. Shah highlighted the government’s initiative to repeal nearly 2,000 obsolete laws since 2015. He described legislative drafting as not merely a science or an art, but a skill that demands precision, transparency, and clarity in execution.
Advocating Clear and Accessible Laws
- Stressing the importance of simplicity in legal language, Mr. Shah urged officials to draft laws that are clear, concise, and free from ambiguity. He emphasized that easily understandable laws can help minimize conflicts and ensure better implementation.
Influence on Governance and Society
- Shah noted that legislative drafting significantly influences how policies and regulations are interpreted and implemented, ultimately affecting both society and the state. Therefore, regular training is essential to refine the skills of legislative draftsmen.
Capacity Building through Training
- The program, organized by the Institute of Constitutional and Parliamentary Studies (ICPS) in collaboration with the Parliamentary Research and Training Institute for Democracies (PRIDE), aims to build the capacity of government officers. Through this initiative, participants will gain valuable insights into effective legislative drafting, promoting democratic governance and upholding the rule of law.
Consider the following statements regarding legislative drafting as per the given text:
- It plays a key role in the interpretation of policies and their societal impact.
- It is a static process that, once codified, requires no revision.
- Training programs in legislative drafting are essential for promoting democratic governance.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: C
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct because the text emphasizes that legislative drafting significantly affects the interpretation and implementation of policies, which in turn impacts society and the state.
- Statement 2 is incorrect as the passage suggests that legislative drafting is a skill that requires regular training and updating, implying it is a dynamic, not static, process.
- Statement 3 is correct since the training program is described as a means to build capacity for democratic governance and uphold the rule of law.
UGC launches new website, UTSAH and PoP portals to promote quality education
Syllabus:Governance
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) has unveiled several major initiatives to strengthen the quality of higher education in India, including a revamped official website, the UTSAH (Undertaking Transformative Strategies and Actions in Higher Education) Portal, and the Professor of Practice (PoP) Portal.
- These initiatives mark a significant milestone in the UGC’s efforts to align with the objectives of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and to promote excellence in academic institutions across the country.
Overview of the Initiatives
- UGC’s New Website:The upgraded UGC website is designed to be more user-friendly and informative, featuring categorized content tailored for students, faculty, and universities. It also includes a dedicated section on the National Education Policy 2020, reflecting the UGC’s long-term vision for transforming higher education in India.
- UTSAH Portal:The UTSAH Portal serves as a centralized platform offering detailed insights into UGC’s initiatives aimed at qualitative reforms in higher education. It covers key areas such as curriculum enhancement, faculty development, research initiatives, and student support services.
- Professor of Practice (PoP) Portal:In line with the NEP 2020, the PoP Portal is a groundbreaking initiative that enables institutions to engage with industry and domain experts for academic roles. Professionals from various disciplines can register on the portal, providing their credentials, expertise, and preferred modes of engagement. Universities can post advertisements for PoP roles and access a database of eligible candidates to bring practical, real-world knowledge into classrooms.

Key Features of the Initiatives
- UGC Website: Simplified interface with structured content for different stakeholders.
- UTSAH Portal: Focuses on policy-driven educational reforms across core academic areas.
- PoP Portal: Bridges academia and industry by facilitating expert appointments in universities.
Important Facts for Competitive Exams
- University Grants Commission (UGC) Founded: 1956
- UGC Headquarters: New Delhi
- Preceding Executive: Sukhadeo Thorat
- These steps by the UGC are aimed at transforming higher education in India by integrating innovation, practical expertise, and policy-driven reforms.
With reference to the UTSAH (Undertaking Transformative Strategies and Actions in Higher Education) Portal, consider the following statements:
- It serves as a digital platform for real-time academic audits of universities across India.
- It aligns with the objectives of the National Education Policy 2020 to drive qualitative reforms.
- It primarily focuses on school-level curriculum development.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 2 and 3 only
Answer: B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect because the UTSAH Portal is not designed for conducting real-time academic audits of universities.
- Instead, it serves as a platform to provide detailed information on UGC’s initiatives for reforms in higher education.
- Statement 2 is correct as the portal aligns with the goals of the National Education Policy 2020 by focusing on qualitative improvements in higher education.
- Statement 3 is incorrect because the portal targets higher education reforms, not school-level curriculum development.
Tension and Clumpiness of Universe
Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
- Recent research suggests that understanding the “clumpiness” of the universe may be key to uncovering its fundamental nature.
Clumpiness of the Universe
- The universe originated around 13.8 billion years ago in a massive Big Bang, starting from a state of void. Over time, it expanded and formed galaxies, star clusters, solar systems, and planets. Initially, when scientists observed the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) — the radiation left over from the Big Bang — they found a nearly uniform glow across the sky. This led to the conclusion that, early on, the universe was remarkably uniform, with only slight density variations.
The S8 Tension
- The “clumpiness” refers to how matter is not evenly spread across the universe. Instead, it forms dense regions, such as galaxies and galaxy clusters, while other parts remain empty. This uneven distribution is measured by the clumpiness factor (S8). The S8 value reflects the level of clustering in the universe, where a higher S8 indicates more dense matter clumping together, and a lower S8 suggests a more uniform distribution.
- However, a challenge arose when cosmologists measured S8 through different methods and arrived at conflicting values. This discrepancy has come to be known as the ‘S8 tension’ in astrophysics.
Why Does the S8 Tension Matter?
- If the S8 tension cannot be explained by measurement errors, it could suggest several possibilities:
- The ΛCDM (Lambda Cold Dark Matter) model, which currently explains the evolution of the universe, might be incomplete or require revisions.
- There could be new insights into how dark matter or dark energy behave, potentially deviating from the current understanding.
- New physics may be at play, such as interacting dark energy, modified gravity, or even variations in fundamental constants over time.
- The Lambda Cold Dark Matter (ΛCDM) Model
- The ΛCDM model is the standard cosmological framework that describes the universe’s large-scale structure. According to this model:
- Dark matter and dark energy make up about 95% of the universe’s mass-energy content.
- These components interact to shape the evolution of cosmic structures, influencing the growth of primordial fluctuations into the galaxies, stars, and clusters we observe today.
- The ongoing research into the S8 tension may potentially lead to refinements or entirely new theories about the universe’s structure and the forces that govern it.
Consider the following statements regarding the clumpiness of the universe and the S8 tension:
- The clumpiness factor, denoted as S8, reflects the non-uniform distribution of matter in the universe.
- A higher value of S8 indicates a more uniform distribution of matter, while a lower value suggests more clustering of matter.
- The ongoing S8 tension points to the possibility that the ΛCDM model might be incomplete or require revision.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct as S8 is the clumpiness factor measuring the distribution of matter.
- Statement 2 is incorrect. A higher S8 indicates more clustering of matter, not a more uniform distribution.
- Statement 3 is correct. The S8 tension raises concerns about the completeness of the ΛCDM model
INS Tamal
Syllabus:Defence
 Context:
Context:
- India is set to receive INS Tamal, its second advanced stealth frigate under the India–Russia Krivak-III class deal, marking a significant step in Indo-Russian naval collaboration and India’s maritime modernization.
About INS Tamal
- Class & Type: Krivak-III class advanced stealth frigate
- Displacement: 3,900 tonnes
- Built by: Yantar Shipyard, Kaliningrad, Russia
- Project Status: Part of a four-frigate deal (2016)
- Two frigates built in Russia (INS Tushil and INS Tamal)
- Two under construction at Goa Shipyard Ltd under technology transfer
Key Capabilities and Features
- Stealth Technology: Suppressed radar, acoustic, and infrared signatures for enhanced survivability
- Speed: Capable of speeds exceeding 30 knots
- Weapon Systems:
- BrahMos Supersonic Cruise Missiles (range: ~450 km)
- Shtil Surface-to-Air Missiles (SAMs)
- Anti-submarine torpedoes and rocket launchers
- Helicopter Operations:
- Can host Kamov-28 and Kamov-31 for anti-submarine warfare (ASW) and airborne early warning (AEW)
- Automation: Advanced systems reduce crew workload and enhance operational efficiency
Strategic Importance
- Force Projection: Expands India’s blue-water navy capability across air, surface, sub-surface, and electronic warfare domains
- Regional Stability: Enhances naval deterrence, particularly in the Arabian Sea and Indo-Pacific, amid growing maritime competition
- Make in India Integration:
- Indigenous construction of sister ships Triput and Tavasya at Goa Shipyard signifies progress in domestic defence manufacturing
- Reflects effective foreign technology absorption and joint production in defence
- Predecessor: INS Tushil
- Commissioned in December 2024
- Currently deployed at Karwar Naval Base
INS Tamal, recently in news, is significant in strengthening India’s maritime capability. Which of the following correctly describes its features?
- It is a nuclear-powered submarine equipped with ballistic missiles.
- It is an advanced stealth frigate built under the Krivak-III class deal with Russia.
- It is indigenously designed and constructed entirely at Mazagon Dock Limited.
- It is part of India’s aircraft carrier programme aimed at blue-water dominance.
Select the correct answer:
A) 1 and 3 only
B) 2 only
C) 2 and 4 only
D) 1, 3 and 4 only
Answer: B) 2 only
Explanation:
- INS Tamal is not a nuclear-powered submarine. It is a stealth frigate, not a submarine, and does not carry ballistic missiles. This description fits a class like the Arihant-class SSBNs, not Krivak-III class frigates.
- INS Tamal is indeed a Krivak-III class advanced stealth frigate, built in Russia at Yantar Shipyard, under a 2016 India–Russia agreement.
- INS Tamal was not built at Mazagon Dock. It was constructed in Russia. Only the other two frigates (Triput and Tavasya) under the same deal are being built indigenously at Goa Shipyard Ltd., not Mazagon Dock.
- INS Tamal is a frigate, not an aircraft carrier, and thus not part of India’s aircraft carrier programme. While it does contribute to India’s blue-water capabilities, it is not directly linked to the carrier programme.
Tendu Leaves
Syllabus:Science
- Chhattisgarh has raised concerns over the increasing smuggling of tendu leaves from neighboring states. This issue is driven by the highest procurement price of ₹5,500 per standard bag in the region, which has fueled illegal trade during the peak collection season.

About Tendu Leaves:
What are Tendu Leaves?
- Tendu (scientific name: Diospyros melanoxylon), also known as “Green Gold,” is a non-timber forest product (NTFP) primarily used for wrapping beedis (hand-rolled cigarettes).
Regional Growth and Production:
- Tendu leaves are found abundantly in central India, with significant production in:
- Madhya Pradesh – 25% of India’s total production
- Chhattisgarh – 20%
- Odisha – 15–20%
- Maharashtra – 10%
Key Features of Tendu Leaves:
- Tendu grows as a shrub or small tree, easily identifiable by its broad leaves.
- A standard bag contains 1,000 bundles, each comprising 50 leaves.
- The highest-quality tendu leaves are typically sourced from southern Chhattisgarh, particularly districts like Dantewada and Sukma.
Uses and Applications:
- Tendu leaves are primarily used in beedi manufacturing, making them a crucial part of the rural tobacco economy.
- The collection and processing of tendu leaves provide over 100 million person-days of employment annually, mostly benefiting tribal communities.
- Challenges and Issues:
- Smuggling: The high procurement price in Chhattisgarh (₹5,500 per standard bag) compared to neighboring states has led to a rise in illegal smuggling activities.
- Exploitation: Despite the lucrative trade, tendu leaf collectors earn meager wages, averaging ₹60 per day, exacerbating the exploitation of workers.
- Declining Demand: Factors such as growing health concerns about smoking, increasing taxes, and the availability of alternative products have led to a decline in the demand for tendu leaves.
Chhattisgarh’s concern over the smuggling of tendu leaves has gained prominence, particularly due to its high procurement price. Which of the following statements regarding tendu leaves is/are correct?
- Tendu leaves are primarily used in beedi manufacturing, contributing significantly to the rural tobacco economy.
- Tendu leaves are mostly sourced from Chhattisgarh, where they are collected and processed by migrant laborers.
- The smuggling of tendu leaves is fueled by the high procurement price of ₹5,500 per standard bag in Chhattisgarh compared to neighboring states.
- Despite the high value trade, tendu leaf collectors receive wages above the minimum wage threshold, ensuring fair compensation.
Select the correct answer:
- A) 1 and 3 only
B) 2 and 4 only
C) 1, 3, and 4 only
D) 1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: A) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Tendu leaves are primarily used for beedi manufacturing, which is a significant part of the rural tobacco economy.
- Statement 2: Tendu leaves are mostly sourced from Chhattisgarh, but they are primarily collected by tribal communities, not migrant laborers.
- Statement 3: The high procurement price of ₹5,500 per standard bag in Chhattisgarh compared to neighboring states has led to smuggling.
- Statement 4: Despite the lucrative trade, tendu leaf collectors earn low wages (₹60 per day), leading to exploitation of workers.
Metal-Free Catalyst for Hydrogen Fuel Production
Syllabus:Science
 Context:
Context:
- Indian researchers have made a groundbreaking advancement in clean energy by developing a metal-free catalyst for hydrogen fuel production using mechanical energy. This development aligns with India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission and pushes forward sustainable hydrogen technology.
About the Metal-Free Catalyst for Hydrogen Fuel Production:
What is It?
- This innovative catalyst is a donor-acceptor covalent organic framework (COF) that operates as a metal-free piezocatalyst. It can split water molecules under mechanical pressure—such as vibrations or movement—to produce hydrogen gas (H₂).
Developed by:
- This breakthrough was developed by the Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR) in Bengaluru, led by Prof. Tapas K. Maji, in collaboration with IISER Pune and Wrocław University of Science and Technology, Poland.
Key Features:
- Metal-Free: The catalyst uses organic molecules, specifically TAPA (donor) and PDA (acceptor), connected via imide bonds, replacing traditional metals.
- Ferrielectric Ordering (FiE): This feature generates intense internal electric fields that drive the catalytic process, enabling the water splitting reaction.
- Porous Architecture: The sponge-like structure facilitates efficient water flow and promotes charge separation during the reaction.
- Mechanically Stimulated: The catalyst produces electron-hole pairs when subjected to pressure, enhancing the efficiency of water splitting.
Significance:
- Eco-Friendly: By using sustainable organic materials instead of costly and toxic metals, this innovation offers an environmentally friendly alternative.
- Energy Efficient: The catalyst utilizes ambient mechanical energy—like vibration or pressure—for hydrogen production, making the process energy-efficient.
- Supports National Green Hydrogen Mission: This development reinforces India’s commitment to clean energy and energy independence.
- Scalable Innovation: The catalyst presents a cost-effective, practical alternative to metal-based hydrogen production technologies, making it a scalable solution for the future.
Indian researchers have developed a metal-free catalyst for hydrogen fuel production. Which of the following statements are correct about this breakthrough?
- The catalyst uses a donor-acceptor covalent organic framework (COF) to split water molecules for hydrogen production.
- The catalyst is developed using toxic and expensive metals to enhance efficiency.
- The catalyst operates by utilizing mechanical energy (such as vibration or pressure) to produce hydrogen gas.
- The breakthrough aligns with India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission and contributes to clean energy technology.
Select the correct answer:
A) 1, 3, and 4 only
B) 1 and 2 only
C) 2, 3, and 4 only
D) 1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: A) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The catalyst uses a donor-acceptor COF to split water molecules for hydrogen production.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The catalyst is metal-free and does not use toxic or expensive metals.
- Statement 3 is correct: The catalyst is activated by mechanical energy (vibration or pressure) to produce hydrogen.
- Statement 4 is correct: The development supports India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission and contributes to clean energy innovation.
India becomes 1st country in world to develop genome-edited rice varieties
Syllabus:Science
- India has achieved a significant milestone by becoming the first country globally to develop genome-edited rice varieties. Agriculture Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan recently launched the first two genome-edited rice varieties, developed by institutions under the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- During the event in New Delhi, the Minister expressed his congratulations to the agricultural scientists involved, highlighting the nation’s confidence in their capabilities.
- He emphasized that this groundbreaking research will contribute significantly to Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision of a “Viksit Bharat.”
- Minister Chouhan further noted that to meet the growing nutritional demands of India’s increasing population, the country must enhance its agricultural production.
- These new rice varieties are designed not only to benefit farmers but also the general public.
- They have been specifically developed for cultivation in multiple states, including Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, West Bengal, and Madhya Pradesh.
- The first variety, DRR Dhan 100 Kamala, is derived from the popular Samba Mahsuri rice.
- This variety matures 15 to 20 days earlier than conventional varieties and yields 25% more produce
- The second variety, Pusa DST Rice 1, is highly tolerant to salinity and alkalinity, making it suitable for cultivation in saline conditions.
- This variety also offers a 30% higher yield in such environments.
- The widespread cultivation of these two varieties, covering approximately 5 million hectares, is projected to produce an additional 4.5 million tons of paddy.
- Minister Chouhan described the launch of these varieties as a historic event, noting that they will reduce production costs while increasing overall yield.
- These innovations are expected to play a vital role in addressing the nutritional needs of India’s growing population.
- ICAR has stated that these varieties represent a major step forward in creating climate-resilient, high-yield agricultural practices.
- The organization also affirmed that they will play a leading role in driving the second green revolution in India.
India has recently become the first country in the world to develop genome-edited rice varieties. These varieties were launched by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR). Which of the following statements regarding the two genome-edited rice varieties developed by ICAR is/are correct?
- DRR Dhan 100 Kamala is derived from Samba Mahsuri, matures 15-20 days earlier, and yields 25% more production.
- Pusa DST Rice 1 is salinity and alkalinity-tolerant, with a 30% higher yield under saline conditions.
- These varieties are primarily developed for the states of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Maharashtra.
- The cultivation of these varieties in 5 million hectares is expected to produce 4.5 million tons of additional paddy.
Select the correct answer:
- A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1, 2, and 4 only
C) 1, 2, and 3 only
D) 2 and 4 only
Answer: B) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: DRR Dhan 100 Kamala is derived from Samba Mahsuri, matures 15-20 days earlier, and yields 25% more production. (Correct)
- Statement 2: Pusa DST Rice 1 is salinity and alkalinity-tolerant, with a 30% higher yield under saline conditions. (Correct)
- Statement 3: These varieties are developed for multiple states, not just Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Maharashtra. (Incorrect)
- Statement 4: Cultivation in 5 million hectares is expected to produce 4.5 million tons of additional paddy. (Correct)
Bacterial Infections in India
Syllabus:Science
Context:
- A recent study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases reveals that only 8% of bacterial infections in India in 2019 were treated with appropriate antibiotics, highlighting a critical gap in the country’s public health response to antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
Bacterial Infections in India: Alarming Trends
What are Bacterial Infections?
- Caused by pathogenic bacteria entering the body, commonly leading to diseases like pneumonia, sepsis, and urinary tract infections.
- Require timely and accurate antibiotic administration for recovery and to prevent complications.
India – 2019 Data Highlights:
- Estimated 5 million bacterial infections.
- Carbapenem-resistant strains (a last-resort class of antibiotics) accounted for a majority of cases.
- Courses of antibiotics procured: ~1 lakh (India accounted for 5% or 83,468 courses globally).
- Only 7.8% of infections in India were treated with the appropriate antibiotic.
Implications of Inadequate Treatment:
- Accelerates AMR (Antimicrobial Resistance), weakening future treatment options.
- Contributes to higher morbidity and mortality.
- AMR deaths exceed those from HIV/AIDS and malaria combined:
→ 1 million deaths globally in 2019 directly due to AMR.
→ Projected 40 million global deaths by 2050 if unchecked.
With reference to the challenge of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in India, consider the following statements:
- In 2019, less than 10% of bacterial infections in India were treated with appropriate antibiotics, despite high procurement of antibiotic courses.
- Carbapenems, one of the most widely used antibiotics in India, are classified as first-line agents for treating common bacterial infections.
- The rise in antimicrobial resistance poses a greater global health threat than HIV/AIDS and malaria combined, in terms of annual mortality.
- India accounted for more than half of the global procurement of antibiotics used against carbapenem-resistant infections in 2019.
Which of the above statements are correct?
A. 1, 2 and 3 only
B. 1, 3 and 4 only
C. 2 and 4 only
D. 1 and 4 only
Correct Answer: B. 1, 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 – Correct: Only 7.8% of bacterial infections in India were treated appropriately in 2019, despite procurement of over 80,000 courses.
Statement 2 – Incorrect: Carbapenems are not first-line antibiotics. They are last-resort antibiotics used when other treatments fail, especially for multi-drug-resistant infections.
Statement 3 – Correct: AMR is now responsible for more deaths annually than HIV/AIDS and malaria combined, with over 1.1 million deaths attributed in 2019.
Statement 4 – Correct: India accounted for 80.5% of the global procurement of antibiotic courses for carbapenem-resistant infections.
Non-Contact Wearable Device
Syllabus:S&T
Context:
- A cutting-edge non-contact wearable device developed by researchers from the U.S. and South Korea enables real-time health monitoring by measuring molecular flux across the skin—without requiring direct skin contact.
About the Non-Contact Wearable Technology:
What is it?
- A compact, smartphone-sized wearable designed to monitor the movement of molecules (flux) across the skin surface, including both outward emissions and inward absorption—without direct contact.
Developed under the leadership of Prof. John A. Rogers at Northwestern University, USA.

How it Functions:
- Utilizes a sealed microchamber adjacent to the skin to create a controlled environment.
- Integrated with wireless electronics and nanosensors that detect:
- Water vapour
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
- A remote-controlled valve alternates the chamber’s openness, enabling comparative measurements of closed versus open skin flux.
Key Applications:
- Medical Diagnostics:
- Wound healing in diabetic ulcers and chronic skin conditions.
- Assessment of skin barrier function and hydration for dermatological analysis.
Occupational Health:
- Monitoring exposure to toxic chemicals for industrial workers.
- Telemedicine & Remote Monitoring:
- Non-invasive monitoring for patients in post-COVID care and rural settings.
- Commercial Use:
- Cosmetics and fragrance industries exploring VOC flux for product evaluation.
Significance and Potential Impact:
- Non-invasive: Ideal for sensitive or healing skin; eliminates risk of irritation.
- Bidirectional flux detection: Simultaneously tracks chemical release and absorption.
- Cost-effective and scalable: Suited for large-scale deployment in public healthcare systems.
- Emerging clinical utility: Offers potential to be adopted as a new “vital sign” in digital health diagnostics.
With reference to the recently developed non-contact wearable health monitoring device, consider the following statements:
- The device functions by forming a sealed vacuum chamber directly in contact with the skin to enhance sensor sensitivity.
- It is capable of tracking both the outward release of compounds from the skin and inward absorption of environmental chemicals.
- One of its key public health advantages is enabling non-invasive diagnostics in rural or remote healthcare settings.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 2 and 3 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Correct Answer: A. 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The device forms a microclimate chamber adjacent to the skin, not a vacuum or direct contact chamber.
- Statement 2 is correct: It monitors dual flux—both outgoing vapours (e.g., CO₂, VOCs) and incoming chemical exposure.
- Statement 3 is correct: It enables non-contact, non-invasive health diagnostics, particularly valuable in rural and resource-limited settings.
Multi-Influence Ground Mine (MIGM)
Syllabus:Defence
- India has marked a significant achievement by successfully test-firing the Multi Influence Ground Mine (MIGM), a cutting-edge indigenously developed underwater weapon system.
About Multi Influence Ground Mine (MIGM):
- The MIGM is a sophisticated underwater naval mine designed to detect and neutralize advanced stealth ships and submarines. It employs multi-influence sensing technology, allowing it to track and respond to various threat signatures—acoustic, magnetic, and pressure—making it highly versatile and effective in diverse maritime combat scenarios.
- Technologically, the MIGM incorporates Fibre Reinforced Plastic (FRP) composites, state-of-the-art electronics, high-density power packs, and advanced software algorithms, enhancing its durability, precision, and operational efficiency.
- The system has been developed by the Naval Science and Technological Laboratory (NSTL) in Visakhapatnam, with collaborative support from other laboratories under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
With reference to the Multi Influence Ground Mine (MIGM), consider the following statements:
- It is designed exclusively to detect magnetic signatures of submarines.
- It uses composite materials such as Fibre Reinforced Plastic (FRP) in its construction.
- The system has been developed solely by the Indian Navy without DRDO involvement.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 1 and 2 only
D. 2 and 3 only
Answer:A
Explanation: Statement 1 is incorrect—MIGM detects acoustic, magnetic, and pressure signatures. Statement 3 is incorrect—MIGM is developed by NSTL, a DRDO lab, not solely by the Navy.
List of Missiles of India: Types, Ranges, and Key Facts for Exams
Syllabus:Defence
- India’s missile development program is a key indicator of the nation’s technological advancements and strategic defense capabilities.
- Led by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), India’s missile arsenal is designed to fulfill a variety of defense objectives, ranging from nuclear deterrence to precision strikes, across both land and sea domains.
- India’s missile systems include an extensive array of ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, and anti-aircraft defense systems.
- These systems are crucial for addressing security threats from neighboring countries like China and Pakistan.
- The foundation for India’s missile prowess was laid by the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP), launched in 1983.
What is a Missile?
- A missile, or guided missile, is a self-propelled weapon equipped with a guidance system that allows it to hit specific targets with high precision.
- Missiles can be launched from various platforms, including land, air, sea, and underwater.
- Depending on their mission, they may carry either conventional or nuclear warheads.
Types of Missiles in India
- India classifies its missile inventory based on several parameters, including launch platform, trajectory, range, speed, guidance system, and warhead type.
- Based on Launch Platform
- Surface-to-Surface Missiles (SSM)
- Surface-to-Air Missiles (SAM)
- Air-to-Air Missiles (AAM)
- Air-to-Surface Missiles (ASM)
- Sea-to-Sea Missiles
- Sea-to-Surface Missiles
- Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBM)
- Anti-Tank Guided Missiles (ATGM)
- Based on Trajectory
- Ballistic Missiles
- Cruise Missiles
- Based on Range
- Short-Range Ballistic Missiles (SRBM)
- Medium-Range Ballistic Missiles (MRBM)
- Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missiles (IRBM)
- Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBM)
- Tactical Missiles
- Based on Speed
- Subsonic Missiles
- Supersonic Missiles
- Hypersonic Missiles
- Based on Guidance System
- Inertial Navigation
- Active Radar Homing
- Infrared Homing
- Laser Guidance
- GPS/NavIC-based Guidance
- Based on Warhead Type
- Conventional (high-explosive)
- Strategic (nuclear-capable)
Key Facts for Exams:
- The Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP) was launched in 1983 to develop missiles like Agni, Prithvi, Akash, Trishul, and Nag.
- Tessy Thomas, known as the “Missile Woman of India”, was the former Project Director of Agni-IV and is currently the Director General of Aeronautical Systems at DRDO.
- Prithvi was India’s first indigenously developed surface-to-surface missile using liquid fuel technology.
- BrahMos is a joint venture between India and Russia and is known for being the world’s fastest supersonic cruise missile.
- Agni-V marked India’s entry into the league of ICBM-capable nations, significantly enhancing its strategic deterrence.
Consider the following statements about India’s missile development program:
- The Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP) was launched in 1983 with the aim to develop a range of missiles, including Agni, Prithvi, Akash, and Trishul.
- The BrahMos missile is a joint venture between India and Israel, and it is known as the world’s fastest supersonic cruise missile.
- Tessy Thomas, known as the “Missile Woman of India,” was the former Project Director of Agni-IV and currently heads the Aeronautical Systems division at DRDO.
Which of the statements above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct. The IGMDP, launched in 1983, was responsible for developing missiles like Agni, Prithvi, Akash, Trishul, and Nag.
- Statement 2 is incorrect. BrahMos is a joint venture between India and Russia, not Israel.
- Statement 3 is correct. Tessy Thomas is indeed known as the “Missile Woman of India” and was the former Project Director of Agni-IV.
SMLME 2025 Kicks Off in Dubai with Major Maritime Announcements
Syllabus: Science and Technology
- The 11th edition of the Seatrade Maritime Logistics Middle East (SMLME) conference began on May 6, 2025, at the Dubai World Trade Centre, bringing together top maritime leaders and policymakers from across the globe. The event, inaugurated by senior UAE officials, featured significant announcements, including the Indian Register of Shipping (IRS) launching a new office in Dammam, Saudi Arabia, marking its 25th anniversary in the UAE and 50th anniversary globally.
Why in the News?
- The SMLME 2025 conference is significant due to the inauguration of the IRS office in Dammam, reinforcing India’s maritime presence in West Asia. The UAE’s strategic vision to become a leading global logistics hub, as highlighted during the UAE Maritime Week, also received attention. The conference served as a key platform for advancing discussions on maritime safety, sustainability, and innovation.
Aims and Objectives of SMLME 2025:
- Foster collaboration among maritime stakeholders in the Middle East and South Asia.
- Promote innovation, safety, and sustainability in maritime logistics.
- Provide a global platform for strategic discussions on port development, green shipping, and digitalization.
- Enhance regional trade and maritime connectivity across the Persian Gulf and Red Sea corridors.
- Serve as a gateway for countries to build partnerships, strengthen regional integration, and address shared maritime challenges in a changing global landscape.
Indian Register of Shipping (IRS) – Strategic Expansion:
- The IRS, a leading international classification society, is a full member of the International Association of Classification Societies (IACS).
- Celebrating 50 years globally and 25 years in the UAE, the IRS has opened a new office in Dammam, Saudi Arabia, to:
- Provide ship classification, technical inspections, and statutory surveys.
- Conduct compliance audits under international maritime regulations.
- Offer faster and more localized support for Saudi clients and shipowners.
- Reflect India’s growing influence in global maritime governance and logistics.
Background and Significance of SMLME:
- The SMLME conference is hosted under the UAE Maritime Week and is organized by Seatrade Maritime.
- It was inaugurated by prominent figures, including:
- Hessa Al Malek, UAE Ministry of Energy & Infrastructure.
- Abdulla bin Damithan, CEO of DP World GCC.
- Andrew Williams, President of Seatrade Maritime.
- The UAE’s leadership emphasized the nation’s commitment to:
- Advancing its position as a global maritime hub through strategic infrastructure development.
- Hosting world-class events that shape the future of the shipping and logistics industries.
- Promoting sustainable practices within the marine sector.
Consider the following statements regarding the 11th Seatrade Maritime Logistics Middle East (SMLME) Conference held in 2025:
- The Indian Register of Shipping (IRS) launched its first-ever overseas office in Dammam, Saudi Arabia, during the conference.
- The SMLME conference is exclusively focused on the shipping sector and does not address port development or digitalization.
- The conference is held under the broader initiative of the UAE Maritime Week and aims to enhance regional maritime connectivity.
- One of the strategic goals of IRS’s expansion is to reduce reliance on foreign classification societies in the Gulf region.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 and 4 only
C. 1, 3 and 4 only
D. 2 and 4 only
Answer: B. 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The IRS office in Dammam is not its first overseas office. The IRS has had a presence in the UAE for 25 years already.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The conference explicitly addresses port development, green shipping, digitalization, and sustainability.
- Statement 3 is correct: SMLME 2025 is organized under UAE Maritime Week and aims to boost regional trade and maritime connectivity.
- Statement 4 is correct: The IRS’s expansion to Saudi Arabia aims to localize support and reduce dependency on foreign classification societies, enhancing India’s maritime influence.
Operation Abhyas’: Bengaluru Conducts Civil Defence Mock Drill Amid Rising Tensions
- In response to a nationwide directive issued by the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), Bengaluru conducted a large-scale civil defence mock drill titled ‘Operation Abhyas’ on May 7, 2025. The exercise, organized by the Karnataka State Fire and Emergency Services Department, was primarily held in the Halasuru area and aimed to bolster public awareness and preparedness in the face of potential emergencies.
Why in News?
- The drill was conducted against the backdrop of increased national security concerns following a terrorist attack in Pahalgam, Jammu & Kashmir, which resulted in 26 fatalities. In light of escalating tensions between India and Pakistan, the MHA mandated similar preparedness exercises across the country to ensure rapid and coordinated civil defence responses.
Key Features of Operation Abhyas:
- Objective: To enhance civil defence capabilities and educate the public on emergency response procedures.
- Conducted by: Karnataka State Fire and Emergency Services under MHA guidance.
- Timing: Between 3:48 PM and 7:00 PM on May 7, 2025, with each simulation lasting approximately 30 minutes.
- Location: Halasuru, Bengaluru.
Components of the Drill:
- Activation of emergency sirens to initiate response protocols.
- Simulated rescue operations for debris entrapment scenarios.
- High-rise evacuations using aerial ladder platforms.
- Firefighting and first aid demonstrations.
- Inter-agency coordination involving the police, civil defence units, and fire services.
Official Statements and Context:
- Karnataka Home Minister Parameshwara underscored the importance of public preparedness, likening the present security environment to the 1972 geopolitical scenario. He stressed the need for citizen awareness in the context of what he referred to as a “shadow of war” due to ongoing hostilities between India and Pakistan.
Strategic Significance:
- Operation Abhyas forms part of a nationwide civil defence initiative aimed at:
- Testing inter-agency coordination.
- Enhancing readiness to respond to terror-related and natural disaster scenarios.
- Supporting India’s broader internal security framework in a time of heightened threat perception.
Consider the following statements regarding Operation Abhyas and its context in India’s civil defence strategy:
- Operation Abhyas was conducted solely by the Karnataka State Police under the Disaster Management Act, 2005.
- The operation involved high-rise evacuation drills using advanced aerial rescue equipment.
- The initiative was conducted in response to a national civil defence directive following a terror attack in Jammu & Kashmir.
- It is part of India’s ongoing effort to strengthen internal security through coordinated military-civilian combat training.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 4 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 3 only
D. 2, 3 and 4 only
Answer: B. 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Operation Abhyas was conducted by the Karnataka State Fire and Emergency Services Department, not solely by the police, and was under MHA directives, not explicitly under the Disaster Management Act.
- Statement 2 is correct: The drill did include high-rise evacuation using aerial ladder vehicles, which is a form of advanced aerial rescue.
- Statement 3 is correct: The terrorist attack in Pahalgam was the direct trigger for the nationwide drills, including Operation Abhyas.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: While it is part of internal security measures, the drills focus on civilian emergency preparedness, not military-civilian combat training.
Axions and HAYSTAC Experiment
Syllabus:Science and Technology
- The latest results from the HAYSTAC experiment, published in Physical Review Letters, represent a major technological milestone in the global search for axions, hypothetical particles that may constitute dark matter. While the experiment did not detect axions, it substantially expanded the parameter space—the range of possible masses and coupling strengths—thereby advancing the precision of dark matter research.
What Are Axions?
- Origin: Axions were first proposed in the late 1970s to resolve the Strong CP Problem in Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD)—the unexplained absence of CP violation in strong nuclear interactions.
- Mechanism: The axion dynamically adjusts the theta (θ) parameter of QCD to nearly zero, effectively eliminating CP violation in the strong interaction sector.
- Dark Matter Role: Beyond their theoretical origins, axions are now considered one of the most compelling cold dark matter (CDM) candidates due to their:
- Neutrality (no electromagnetic charge),
- Tiny mass,
- Extremely weak interactions with ordinary matter and radiation.
- Cosmological models suggest that axions, if they exist, could have been non-thermally produced in the early universe, leading to a relic density matching observed dark matter abundance (~85% of all matter).
What is HAYSTAC?
- HAYSTAC (Haloscope At Yale Sensitive To Axion Cold dark matter) is a pioneering collaboration among Yale University, UC Berkeley, and Johns Hopkins University aimed at direct axion detection.
Key Features:
- Haloscope Design: Developed by physicist Pierre Sikivie, a haloscope uses a microwave cavity placed within a strong magnetic field. It searches for the extremely faint conversion of axions into photons (via the Primakoff effect).
- Phase II Achievements:
- Conducted the widest frequency scan to date in search of axion signatures.
- Introduced quantum squeezing techniques to suppress quantum noise, improving sensitivity in detecting ultra-weak signals.
What is Quantum Squeezing?
- Concept: A method from quantum optics that manipulates the Heisenberg uncertainty principle by reducing uncertainty (noise) in one variable (e.g., electric field amplitude) at the cost of increasing it in the conjugate variable (e.g., phase).
- Relevance to HAYSTAC: Enhances the signal-to-noise ratio, enabling detection of rare events like axion-photon conversion that would otherwise be buried under quantum fluctuations.
- Also Used In: Advanced LIGO, which uses quantum squeezing to detect gravitational waves.
Significance of HAYSTAC
- While no axions were detected, HAYSTAC narrowed the theoretical window for axion properties, helping eliminate regions of the parameter space.
- Demonstrates quantum-enhanced precision in experimental physics, potentially influencing a broader array of fundamental research areas.
With reference to Axions and the HAYSTAC experiment, consider the following statements:
- Axions were originally proposed to explain the observed CP violation in weak interactions within the Standard Model.
- HAYSTAC is designed to detect axions by converting them into photons using a strong magnetic field inside a microwave cavity.
- Quantum squeezing, used in HAYSTAC, is based on manipulating quantum uncertainty to enhance signal detection in low-noise environments.
- The HAYSTAC experiment confirmed axions as the primary constituent of dark matter within the explored parameter range.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 2 and 3 only
B. 1, 2, and 4 only
C. 1 and 4 only
D. 2, 3, and 4
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect:Axions were proposed to solve the Strong CP problem in Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD), not CP violation in weak interactions. Weak CP violation is explained by the CKM matrix in the Standard Model.
- Statement 2 – Correct:The HAYSTAC experiment uses a haloscope to detect axions by observing their conversion to photons in a strong magnetic field—an experimental design based on the Primakoff effect.
- Statement 3 – Correct:Quantum squeezing is an advanced quantum optics technique that reduces noise in one observable (like amplitude or phase), improving signal-to-noise ratio—critical in detecting extremely weak signals like axions.
- Statement 4 – Incorrect:No axions were detected in the experiment. The parameter space was expanded, but axions were not confirmed within the explored mass range.
Microbial Phosphorus Gatekeeping
Syllabus:Science
- A recent study published in Nature Geoscience has provided critical insights into the long-term role of soil microbes in phosphorus (P) cycling, based on a 700,000-year chronosequence from the Cooloola coastal dune system in Queensland’s Cooloola National Park, Australia.
Ecological Significance of Phosphorus
- Phosphorus is an indispensable macronutrient essential for:
- Energy metabolism (e.g., ATP and ADP cycles),
- Cell membrane structure (via phospholipids),
- Photosynthetic and genetic functions (key component of DNA, RNA, and nucleotides).
- In ancient, highly weathered soils—such as those prevalent in Australia—phosphorus is frequently the most limiting nutrient due to prolonged mineral leaching and degradation. This constraint severely influences ecosystem productivity and succession.
Key Findings of the Study
- The research identifies soil microbes, particularly bacteria and fungi, as pivotal actors in regulating phosphorus availability through multiple biochemical strategies. These microbes function as “phosphorus gatekeepers” by controlling the access, retention, and recycling of phosphorus in soil ecosystems.
Microbial Adaptive Mechanisms in Low-P Environments:
- Membrane substitution: Replacement of phosphorus-containing phospholipids with non-phosphorus lipids (e.g., sulfolipids or glycolipids) to conserve P.
- Lipid storage: Accumulation of phosphorus-free microbial fats, thereby lowering cellular P demand.
- Enhanced efficiency: Optimization of metabolic phosphorus-use efficiency, allowing survival under severe nutrient limitations.
Plant–Microbe Interactions in Phosphorus Dynamics
- The study underscores a dual relationship between microbes and plants in phosphorus cycling:
- Competition: Both microbes and plants directly compete for scarce phosphorus resources.
- Facilitation: Microbes simultaneously assist plants by decomposing organic matter and recycling phosphorus, enhancing its long-term availability in the rhizosphere.
Implications
- The findings have significant implications for understanding nutrient cycling in nutrient-poor ecosystems, improving soil fertility management, and developing microbial biofertilizer strategies for sustainable agriculture, especially in phosphorus-deficient regions.
Consider the following statements regarding the role of soil microbes in phosphorus cycling, based on a recent study published in Nature Geoscience about the Cooloola coastal dune system in Australia:
- Soil microbes, particularly fungi and bacteria, regulate the availability of phosphorus in soil ecosystems by acting as ‘phosphorus gatekeepers’.
- In phosphorus-scarce environments, microbes replace phosphorus-containing phospholipids with non-phosphorus lipids to conserve phosphorus.
- The study suggests that soil microbes play a role in increasing phosphorus availability to plants by decomposing organic matter and facilitating its recycling.
- Phosphorus is not considered a limiting nutrient in ancient and weathered soils due to the continuous replenishment of phosphorus through weathering processes.
Which of the statements above is/are correct?
A. 1, 2, and 3 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: A. 1, 2, and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct as the study identified microbes as key “phosphorus gatekeepers” controlling phosphorus cycling.
- Statement 2 is correct as microbes use non-phosphorus lipids to reduce phosphorus demand.
- Statement 3 is correct as the study found that microbes help plants by recycling phosphorus.
- Statement 4 is incorrect since phosphorus is a limiting nutrient in ancient soils due to depletion through weathering, not continuously replenished.
Ferroelectricity
Syllabus:Science
- Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) have developed a groundbreaking technique to visualize the dynamics of domain walls with unprecedented detail.
Fundamentals of Ferroelectricity
- Ferroelectricity refers to the ability of certain non-conducting crystals or dielectrics to exhibit spontaneous electric polarization, where the positive and negative charge centers separate, creating a region with a positive charge on one side and a negative charge on the other. This polarization can be reversed by applying an external electric field.
- The term “ferroelectric” is inspired by “ferromagnetism,” where magnetic domains spontaneously align. Similarly, in ferroelectrics, electric dipoles spontaneously align within domains. Some well-known examples of ferroelectric materials include barium titanate (BaTiO₃) and Rochelle salt.
- Ferroelectric domains are regions where dipoles are aligned, and these domains can be reoriented by applying strong electric fields. The delay in the reorientation of these domains, known as ferroelectric hysteresis, is analogous to the behavior observed in ferromagnetic materials. Ferroelectricity disappears above a critical temperature, known as the Curie Temperature, where thermal motion disrupts dipole alignment.
Domain Walls in Ferroelectrics
- Domain walls are the boundaries that separate regions with different polarizations within a ferroelectric material. These walls often exhibit distinct electrical or magnetic properties compared to the domains they separate. For example, some domain walls may become electrically conductive, even though the bulk material is non-conductive, or may display magnetic properties, even if the domain itself is non-magnetic.
- These unique characteristics make domain walls promising candidates for use in nanoelectronic components, such as memory devices, sensors, and signal processing systems in low-power electronics.
New Visualization Technique by ORNL
- The new technique, named Scanning Oscillator Piezoresponse Force Microscopy (SO-PFM), enables the detection of both slow and rapid movements of domain walls under fluctuating electric fields. Unlike traditional methods, which provide only static snapshots of domain wall positions, SO-PFM offers dynamic visualizations, capturing how domain walls evolve in real-time.
- This breakthrough technique uses precision-timed control electronics coupled with atomic force microscopy (AFM) to monitor the real-time movement of domain walls, a capability that was not previously achievable. The new method allows researchers to observe the dynamics of domain walls and measure the energy required to move them, opening new avenues for understanding and harnessing the behavior of ferroelectric materials.
With reference to the recent advancements in ferroelectric domain wall visualization and the fundamental properties of ferroelectrics, consider the following statements:
- Ferroelectricity in materials refers to the alignment of electric dipoles in domains, which can be reversed by applying an external electric field, similar to the alignment of magnetic dipoles in ferromagnetic materials.
- The newly developed Scanning Oscillator Piezoresponse Force Microscopy (SO-PFM) technique allows for the visualization of static snapshots of domain wall behavior, offering insights into the hysteresis phenomena associated with ferroelectrics.
- Ferroelectric domain walls exhibit distinct properties, such as potential conductivity or magnetism, even if the bulk of the material itself is non-conductive or non-magnetic, making them suitable for future nanoelectronic applications.
- The Curie Temperature is the critical temperature below which ferroelectric properties vanish due to the disruption of dipole alignment by thermal motion.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 1, 3, and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: C. 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct. Ferroelectricity refers to the spontaneous alignment of electric dipoles in domains, which can be reversed by applying an external electric field. This is analogous to ferromagnetism.
- Statement 2 is incorrect. SO-PFM allows for dynamic visualization of domain wall movements, not just static snapshots, providing insights into real-time dynamics and the energy involved in domain wall movement.
- Statement 3 is correct. Ferroelectric domain walls can exhibit unique properties, such as electrical conductivity or magnetism, which are useful for nanoelectronics.
- Statement 4 is correct. The Curie Temperature is indeed the temperature above which ferroelectric properties vanish due to thermal agitation disrupting dipole alignment.
Active Galactic Nucleus (AGN)
Syllabus:Science and Technology
- Astronomers from the Russian Academy of Sciences have identified 11 new Active Galactic Nuclei (AGNs) during an all-sky X-ray survey conducted with the Spektr-RG (SRG) space observatory. The findings emerged from the optical and X-ray analysis of sources listed in the ARTSS1-5 catalog, utilizing the ART-XC telescope onboard SRG.
What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGNs)?
- AGNs are extremely luminous, compact regions located at the centers of galaxies. Their high-energy emissions—often exceeding that of the rest of the galaxy—originate primarily from:
- Accretion of matter by supermassive black holes, or
- Intense star formation activity.
- AGNs play a vital role in astrophysics by offering insights into the formation, evolution, and energetic processes of galaxies.
Key Findings:
- Redshift Range: All 11 AGNs are located at redshifts between 028 and 0.258, indicating relatively nearby cosmic distances.
- X-ray Luminosity: Their luminosities range from 2 × 10³⁹ to 3 × 10⁴¹ erg/s, consistent with known AGN energy profiles.
Classification: Seyfert Galaxies
- All AGNs were identified as Seyfert galaxies, a subclass of AGNs known for their bright cores and strong emissions in X-ray and infrared spectra.
Breakdown:
- 7 AGNs: Seyfert Type 1 (Sy 1) – Broad optical emission lines.
- 3 AGNs: Seyfert Type 1.9 (Sy 1.9) – Partially broadened emission lines.
- 1 AGN: Seyfert Type 2 (Sy 2) – Narrow emission lines only.
- Seyfert galaxies often resemble normal galaxies in visible light but display powerful radiation signatures due to active supermassive black holes at their centers.
With reference to Active Galactic Nuclei (AGNs) and their recent detection by the Spektr-RG (SRG) observatory, consider the following statements:
- AGNs are among the most luminous sources in the universe, primarily due to nuclear fusion processes occurring at the galactic core.
- The ART-XC telescope aboard Spektr-RG is capable of conducting high-energy X-ray observations used for AGN classification.
- Seyfert Type 1 galaxies exhibit only narrow emission lines, while Seyfert Type 2 galaxies show broad emission lines.
- All 11 newly detected AGNs lie within redshifts less than 0.3, indicating relatively close proximity in cosmological terms.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 1, 2 and 3 only
D. 2, 3 and 4 only
Correct Answer: B. 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The luminosity of AGNs arises primarily due to accretion of matter into a supermassive black hole, not from nuclear fusion like in stars.
- Statement 2 is correct: The ART-XC telescope is indeed designed for X-ray astronomy and is used in AGN detection and classification.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: This reverses the characteristics. Seyfert Type 1 galaxies have broad emission lines, while Type 2 show narrow lines.
- Statement 4 is correct: All detected AGNs have redshifts between 0.028 and 0.258, placing them in the nearby universe on a cosmic scale.
AI Hallucinations
Syllabus: Science and Technology
- Recent advancements in artificial intelligence have brought increased attention to the problem of AI hallucinations.
- A report from OpenAI revealed that its latest models, o3 and o4-mini, show elevated rates of errors known as hallucinations—instances where AI systems produce incorrect or misleading information.
- According to the report, the o3 model hallucinated 33% of the time, while o4-mini’s hallucination rate was even higher at 48%.
- This trend raises concerns about the reliability of AI models as they grow more sophisticated.

Understanding AI Hallucinations:
- AI hallucinations refer to mistakes made by AI models, especially chatbots. Originally, the term described cases where the AI fabricated information—for example, a lawyer using ChatGPT to draft a court document found the chatbot had inserted fictitious citations.
- Now, hallucinations cover a wider range of errors, including generating responses that are factually correct but irrelevant to the user’s question.
Causes of AI Hallucinations:
- Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and o3 create text by predicting sequences based on patterns learned from vast datasets, without truly understanding the content.
- This can lead to inaccurate outputs, especially when training data contains errors. Even with accurate data, LLMs may combine information in unexpected ways, resulting in hallucinations.
- Experts note that unlike humans, LLMs lack the ability to verify facts, which contributes to their propensity for errors.
Significance of OpenAI’s Findings:
- OpenAI’s report highlights that hallucinations may be an intrinsic challenge in LLMs. While early AI developments suggested the problem could be solved, and initial updates lowered hallucination rates, recent data indicates that the issue persists and is widespread.
- Other AI systems, such as those from DeepSeek, also show increased hallucination frequencies, raising doubts about AI’s dependability in critical domains like research and law.
Implications for AI Deployment:
- Given the high incidence of hallucinations, caution is advised when using AI models in sensitive areas.
- These systems are currently unreliable as research assistants or legal advisors because they can produce fabricated citations or fictional legal precedents.
- Experts believe hallucinations are a fundamental limitation of LLM technology. As AI models tackle more complex tasks, the risk of errors grows, creating a disconnect between user expectations and actual AI capabilities.
Consider the following statements about AI hallucinations as reported in recent developments:
- AI hallucinations refer exclusively to the generation of completely fabricated information by AI systems.
- Large Language Models (LLMs) generate text based on pattern recognition without true comprehension, which contributes to hallucinations.
- OpenAI’s latest models have successfully reduced hallucination rates to below 10%.
- The persistence of hallucinations suggests it may be an inherent limitation of current LLM architectures.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 and 3 only
B) 2 and 4 only
C) 1, 2 and 4 only
D) All of the above
Answer: B) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect because AI hallucinations now include not only fabricated information but also factually correct yet irrelevant outputs.
- Statement 2 is correct, as LLMs predict text based on patterns learned without understanding content, leading to errors.
- Statement 3 is incorrect; OpenAI’s report states hallucination rates for o3 and o4-mini are 33% and 48%, respectively, not below 10%.
- Statement 4 is correct since hallucinations appear to be an intrinsic challenge in current LLMs.
India Opposes Inclusion of Chlorpyrifos at Stockholm Convention
Syllabus :GS 3/Environment
- At the meetings of the conferences of the Parties to the Basel, Rotterdam, and Stockholm (BRS) conventions in Switzerland, India expressed strong opposition to the inclusion of Chlorpyrifos under the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs). India raised concerns about the potential impact on food security due to the lack of viable alternatives to this insecticide.
Chlorpyrifos: Overview
- Chlorpyrifos is an insecticide that has been widely used in agriculture and pest control. It has been linked to several adverse health effects, including:
- Neurodevelopmental issues
- Reduced birth size
- Lung and prostate cancer with chronic exposure
- The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies Chlorpyrifos as a moderately hazardous pesticide. The chemical works by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme essential for proper nervous system function, leading to harmful neurological effects.
Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs)
- The Stockholm Convention, adopted in May 2001 and entering into force on 17 May 2004, aims to protect human health and the environment from harmful chemicals known as persistent organic pollutants (POPs).
- The Convention outlines measures for the elimination or restriction of POPs in three annexes:
- Annex A: Chemicals to be eliminated.
- Annex B: Chemicals to be restricted.
- Annex C: Chemicals for which unintentional production and release should be minimized.
- The Convention also provides a framework for dispute resolution between member countries.
Chlorpyrifos Phase-out and India’s Concerns
- Chlorpyrifos was nominated for global phase-out by the European Union in 2021.
- In 2024, the Persistent Organic Pollutants Review Committee (POPRC) recommended the inclusion of Chlorpyrifos in Annex A of the Stockholm Convention (for elimination), though it suggested exemptions for certain uses, such as plant protection, cattle tick control, and wood preservation.
- At the BRS meetings, there was significant debate over whether exemptions for agricultural uses and pest control should be allowed. India, along with other nations, advocated for certain exceptions, particularly for the pesticide’s crucial role in pest control and vector-borne disease management.
India’s Stance on Chlorpyrifos
- India’s extensive use of Chlorpyrifos: Registered in India since 1977, Chlorpyrifos was the most widely used insecticide in the country in 2016-17.
- India emphasized that Chlorpyrifos is essential for agriculture, particularly for controlling urban pests such as cockroaches and termites, as well as for vector-borne disease control, which remains a significant public health issue in the country.
- A 2024 study detected Chlorpyrifos residues in 33% of food samples tested in India, underscoring the widespread use of the pesticide.
- The Anupam Verma Committee (2013), set up to review pesticides banned or restricted in other countries but still in use in India, identified Chlorpyrifos as being toxic to fish and bees, which raised environmental concerns.
India’s Future Plans
- India is actively promoting natural farming through a national mission led by the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare. This initiative is aimed at reducing dependence on synthetic chemicals like pesticides, while also improving soil health and sustainability in agriculture.
Other Chemicals Discussed at the BRS Convention
- Apart from Chlorpyrifos, other chemicals such as Medium-chain chlorinated paraffins and long-chain perfluorocarboxylic acids (LC-PFCAs) are also being debated at the BRS Convention for potential inclusion in the lists of restricted or eliminated chemicals.
- India’s opposition to the inclusion of Chlorpyrifos under the Stockholm Convention reflects its complex balancing act between addressing environmental concerns and ensuring food security and public health, particularly in a country where the pesticide plays a key role in pest control.
Consider the following statements regarding India’s stance on Chlorpyrifos at the BRS Convention:
- India opposed the inclusion of Chlorpyrifos under the Stockholm Convention due to concerns over food security and lack of alternatives.
- Chlorpyrifos was nominated for global phase-out by the European Union in 2021 and the Persistent Organic Pollutants Review Committee (POPRC) recommended its inclusion in Annex B of the Stockholm Convention in 2024.
- Chlorpyrifos is primarily used in India for urban pest control, including insects like cockroaches and termites, and vector-borne disease management.
4.The Anupam Verma Committee (2013) recognized Chlorpyrifos as safe for both environmental and health concerns, with no significant risks to wildlife.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1, 2, and 3 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer:B. 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct. India did indeed oppose the inclusion of Chlorpyrifos under the Stockholm Convention, citing concerns over food security and the absence of viable alternatives.
- Statement 2 is incorrect. While Chlorpyrifos was nominated for global phase-out by the European Union in 2021, the POPRC recommended its inclusion in Annex A (for elimination) in 2024, not Annex B.
- Statement 3 is correct. Chlorpyrifos is extensively used in India for pest control, particularly for urban pests like cockroaches and termites, and for vector-borne disease management.
- Statement 4 is incorrect. The Anupam Verma Committee (2013) recognized Chlorpyrifos as toxic to fish and bees, raising environmental concerns, not as safe.
Climate-driven Extreme Weather Events
Syllabus: GS3/Environment
Context:
- A new study published in Nature Geoscience warns that extreme monsoon variability driven by climate change could permanently damage marine productivity in the Bay of Bengal.
Study Overview:
- The research, based on 22,000 years of climate data, reveals how fluctuations in the Indian summer monsoon have historically affected ocean chemistry and ecosystem health in the Bay of Bengal.
- Scientists used microfossils of foraminifera—single-celled marine organisms that record environmental data in their calcium carbonate shells—to reconstruct past ocean conditions.
Key Findings
- Both excessively strong and unusually weak monsoons have historically disrupted ocean mixing processes, leading to a reduction of up to 50% in nutrient availability for marine organisms.
- These disruptions starve plankton—the foundation of the marine food web—triggering cascading impacts on marine productivity.
- Notable declines occurred during climatic episodes such as Heinrich Stadial 1 (17,500–15,500 years ago) and the early Holocene (10,500–9,500 years ago), marked by extreme monsoon patterns.
Implications Under Climate Crisis
- Future climate models indicate rising sea surface temperatures and increasingly erratic monsoon behavior, replicating the historical conditions associated with past collapses in marine productivity.
- The Bay of Bengal, despite covering less than 1% of the global ocean surface, contributes approximately 8% to global fishery output.
- Species like Hilsa, vital for food security and livelihoods across South Asia, are especially vulnerable.
- Over 150 million people rely on the Bay’s fisheries, with Bangladesh’s artisanal fishing sector—responsible for 80% of its marine catch—already facing stress due to overexploitation.
Recommendations
- Enhance and fine-tune climate models to improve projections of monsoon variability and its marine impacts.
- Implement and enforce sustainable fisheries management, with a focus on protecting artisanal fishing communities.
- Accelerate efforts to curb greenhouse gas emissions, as global warming intensifies monsoon unpredictability.
- Develop adaptive resource management and conservation strategies to safeguard coastal populations and ecosystems.
With reference to the recent findings on the Bay of Bengal’s marine ecosystem, consider the following statements:
- Foraminifera microfossils are used to reconstruct past ocean temperatures and monsoon patterns.
- Stronger monsoons always lead to increased marine productivity due to enhanced nutrient mixing.
- The Bay of Bengal accounts for less than 1% of the global ocean surface but contributes significantly to global fisheries output.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer:B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Foraminifera shells record environmental conditions.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: Both abnormally strong and weak monsoons disrupt nutrient mixing and reduce productivity.
- Statement 3 is correct: Despite its small size, the Bay contributes ~8% to global fishery production
International Maritime Organisation (IMO)
Syllabus:Environment
- The 83rd session of the Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC-83) under the International Maritime Organization (IMO) has adopted a landmark resolution aimed at reducing emissions from the global shipping industry.
About the International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- The IMO is a specialised agency of the United Nations (UN) responsible for ensuring the safety, security, and environmental sustainability of international shipping.
- It plays a crucial role in achieving UN Sustainable Development Goal 14 (SDG-14), which focuses on conservation and sustainable use of oceans and marine resources.
- The IMO formulates global standards for shipping safety, marine pollution prevention, and maritime security.
- These standards are non-binding until incorporated into domestic law by member states.
- It also addresses legal aspects such as liability, compensation, and the facilitation of maritime traffic.
Institutional Overview:
- Established: 1948 (as IMCO), became a UN specialised agency in 1959, and renamed IMO in 1982.
- Headquarters: London, United Kingdom
- Membership: 174 Member States
Organisational Structure:
- Assembly: Supreme body; meets biennially to adopt the work programme, budget, and elect Council members.
- Council: Executive body overseeing interim functions between Assembly sessions.
- Major Committees: Five core committees, including the Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC), responsible for policy and regulatory frameworks.
- Funding: Through mandatory contributions from member states, and supplemented by voluntary contributions and commercial income.
About the MARPOL Convention
- MARPOL (International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships) is the principal global treaty to prevent marine pollution from shipping, administered by the IMO.
- Adopted in 1973, with a 1978 Protocol added in response to oil tanker accidents.
Structure of MARPOL:
- Comprises six technical annexes, each addressing a specific type of pollution:
- Annex I: Oil pollution (e.g., spills, bilge discharge)
- Annex II: Noxious liquid substances in bulk (e.g., chemicals)
- Annex III: Harmful substances in packaged form
- Annex IV: Sewage from ships
- Annex V: Garbage disposal at sea
- Annex VI: Air pollution (e.g., SOx, NOx)
- India is a signatory to the MARPOL Convention and implements its provisions through national legislation and maritime regulations.
Consider the following statements about the MARPOL Convention:
- It was adopted under the auspices of the IMO in response to the Bhopal gas tragedy.
- Annex VI of MARPOL deals with the discharge of hazardous chemical waste into the sea.
- India, being a signatory, implements MARPOL provisions through domestic laws.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer:B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect — MARPOL was adopted in 1973, Bhopal tragedy occurred in 1984.
- Statement 2 is incorrect — Annex VI deals with air pollution, not chemical waste.
- Statement 3 is correct.
Laos to Host ASEAN Tourism Forum 2024 with Quality and Responsible Tourism -Sustaining ASEAN Future Theme
Syllaus:Environment
- Laos is set to host the annual ASEAN Tourism Forum in January 2024, in its capital city, Vientiane.
- The forum’s theme, “Quality and Responsible Tourism — Sustaining ASEAN Future,” underscores the commitment to promoting sustainable and responsible tourism practices in the region.
- The event will feature a tourism exhibition aimed at boosting Laos’s tourism sector and enhancing service standards in related businesses.
- According to Suanesavanh Vignaket, Minister of Information, Culture, and Tourism, the forum will highlight Laos as a prime nature-based tourism destination.
- This marks Laos’s third time hosting the ASEAN Tourism Forum, with previous editions held in 2004 and 2013, reflecting the country’s growing prominence as a Southeast Asian tourism hub.
- The Lao government is focused on showcasing its scenic landscapes, rich local traditions, and lifestyles, which continue to attract foreign tourists.
- Despite the severe impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the tourism industry, Laos witnessed a significant rebound in visitor numbers, with over 831,000 foreign tourists in the first quarter of 2023, compared to 211,898 visitors during the peak pandemic period in the first half of 2022.
Key facts about Laos include:
- Capital: Vientiane
- Currency: Lao kip (LAK)
- President: Thongloun Sisoulith (as of 2021)
- Official language: Lao
- Population: Around 7.2 million
- Geography: Situated in Southeast Asia, Laos shares borders with Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam, China, and Myanmar.
With reference to the ASEAN Tourism Forum 2024 to be hosted by Laos, consider the following statements:
- The theme of the forum aligns with ASEAN’s long-term strategic plan to promote green investments in cross-border tourism infrastructure.
- Laos has hosted the ASEAN Tourism Forum more than once prior to 2024, reflecting its sustained engagement with regional tourism diplomacy.
- The 2024 forum aims solely at reviving post-COVID tourism without an explicit focus on sustainable practices or service quality.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 2 and 3 only
Answer: B. 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect because although the theme emphasizes “Quality and Responsible Tourism — Sustaining ASEAN Future,” it does not explicitly reference ASEAN’s green infrastructure investment strategy or a long-term strategic plan in the provided context.
- Statement 2 is correct. Laos previously hosted the ASEAN Tourism Forum in 2004 and 2013, and is doing so again in 2024, indicating a consistent role in regional tourism promotion.
- Statement 3 is incorrect. The theme and ministerial statements clearly emphasize sustainable tourism and quality service, not merely post-COVID revival.
Sujata Chaturvedi Appointed As A UPSC Board Member
Syllabus:Polity
- Sujata Chaturvedi, an experienced civil servant with over three decades of service, has been appointed as a Member of the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC). Her appointment is considered a significant addition to the Commission, bringing extensive expertise in administration, sports, and policy formulation.
Why in the News?
- On 1st May 2025, Ms. Sujata Chaturvedi, a 1989-batch IAS officer from the Bihar cadre, took charge as a Member of the UPSC. The oath of office and secrecy was administered by Lt. Gen. Raj Shukla (Retd.), the seniormost Member of the Commission.
Background & Career Highlights:
- Batch and Cadre: Chaturvedi is a member of the 1989 batch of the Indian Administrative Service (IAS), Bihar cadre.
- Educational Qualifications: She holds a postgraduate degree in History, an M.Phil in Public Administration, and a Diploma in Russian language. She graduated in English from Nagpur University.
Key Positions Held:
- At the State Level (Bihar):
- Principal Secretary, Department of Finance
- Commercial Tax Commissioner
- Secretary, Finance Department
- Vice Chairman, Department of Urban Development
At the Central Government:
- Secretary, Department of Sports, Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
- Additional Secretary, Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT)
- Regional Deputy Director General, UIDAI
Major Contributions in the Department of Sports:
- Successfully hosted significant events like the Khelo India Games, FIDE Chess Olympiad, and FIFA U-17 Women’s World Cup.
- Spearheaded the creation of a National Sports Repository System.
- Initiated the nationwide mapping of sports facilities.
- Played a key role in the enactment of the Anti-Doping Bill, strengthening India’s anti-doping stance.
Language Proficiency:
- Chaturvedi is fluent in several languages, including Hindi, English, Urdu, Russian, and Marathi.
Significance of Her UPSC Appointment:
- Chaturvedi’s diverse policy experience is expected to bring a new dimension to the UPSC.
- Her background in sports administration may offer fresh perspectives, particularly in the youth and development sectors.
- She is also expected to enhance the civil services examination system and recruitment policies, contributing significantly to the functioning of the Commission.
Consider the following statements regarding Ms. Sujata Chaturvedi’s appointment as a Member of the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC):
- Sujata Chaturvedi is a 1989-batch IAS officer from the Bihar cadre.
- She has served as the Secretary of the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports.
- Chaturvedi was involved in the creation of a National Sports Repository System.
- She is fluent in Hindi, English, Urdu, and Russian.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1, 2, and 4 only
B. 1, 3, and 4 only
C. 1, 2, and 3 only
D. 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer:D
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Ms. Sujata Chaturvedi is a 1989-batch IAS officer from the Bihar cadre.
- Statement 2 is correct: She served as the Secretary of the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports.
- Statement 3 is correct: She played a key role in the creation of a National Sports Repository System.
- Statement 4 is correct: She is fluent in Hindi, English, Urdu, Russian, and Marathi.
Cabinet Hikes Sugarcane Price for 2025–26 Season
Syllabus:Polity
Why in the News:
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA), chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, has approved the Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) of sugarcane for the 2025–26 sugar season at ₹355 per quintal, ensuring financial stability for sugarcane farmers and workers in the agro-based sugar sector.
- Key Highlights: FRP fixed at ₹355/qtl for a basic recovery rate of 10.25%. Premium of ₹3.46/qtl for every 0.1% increase in recovery.
- Deduction of ₹3.46/qtl for every 0.1% decrease below 10.25%. Minimum price of ₹329.05/qtl guaranteed for mills with recovery below 9.5%. Estimated cost of production is ₹173/qtl (A2 + FL basis), making the FRP 105.2% above cost.

- This represents a 4.41% increase over the 2024–25 FRP.
- Beneficiaries: Around 5 crore sugarcane farmers and their dependents, 5 lakh sugar mill workers, and thousands involved in ancillary services such as logistics and labor.
- Implementation: Effective from October 1, 2025. Payment Status: For the 2023–24 season, ₹1,11,703 crore (99.92%) of dues have been cleared. For the 2024–25 season (as of April 28, 2025), ₹85,094 crore (87%) has been paid out of ₹97,270 crore.
- FRP Determination Basis: The approved FRP is based on recommendations from the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) and consultations with State Governments and key stakeholders.
Consider the following statements regarding the Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) of sugarcane for the 2025–26 season:
- The FRP of ₹355/qtl is based on a recovery rate of 10.5%.
- No deduction is applied to mills with a recovery rate below 9.5%.
- The FRP is more than double the estimated cost of production as per A2+FL.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: C
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect (recovery rate is 10.25%, not 10.5%).
- Statement 2 is correct (no deductions below 9.5%).
- Statement 3 is correct (₹355 vs ₹173 ≈ 105.2% above cost).
National Archives Acquires
Syllabus:Polity
- The National Archives of India (NAI) has recently acquired the private papers of former President Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam, which include a range of personal and official materials such as his lectures, original photographs, Aadhaar card, passport, and other significant documents.
About the National Archives of India (NAI)
- Established: 1891 in Calcutta (then Imperial Records Department).
- Current Headquarters: New Delhi
- Administrative Control: Operates under the Ministry of Culture, Government of India.
- Regional Presence: Offices in Bhopal, and record centres in Bhubaneswar, Jaipur, and Puducherry.
- Significance: It is the largest archival repository in South Asia, serving as the custodian of public and private records of enduring value.
- Collections: Includes public records, private papers, oriental manuscripts, maps, and microfilms.
- Oversight Authority: The Director General of Archives implements the Public Records Act, 1993 and associated rules for management and preservation of government records.
About Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam (1931–2015)
- Birthplace: Rameswaram, Tamil Nadu
- Profession: Renowned aeronautical engineer, scientist, and visionary leader
Major Contributions:
- At ISRO: Project Director for SLV-III, which launched India’s first satellite Rohini in 1980.
- At DRDO: Led the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP) — key projects included Agni, Prithvi, and contributions to India’s nuclear tests (Pokhran-II).
- Principal Scientific Advisor to the Government of India (1999–2001).
- Academic Role: Professor at Anna University, deeply involved in inspiring youth.
- Presidency: Served as the 11th President of India (2002–2007)
Legacy:
- Popularly known as the “Missile Man of India”
- Referred to as the “People’s President” for his humility and outreach
- Post-presidency, he continued to mentor students and promote education and innovation
Notable Literary Works:
- Wings of Fire, India 2020, Ignited Minds, My Journey – works that continue to inspire generations.
Awards & Honours:
- Padma Bhushan, Padma Vibhushan, and Bharat Ratna – India’s highest civilian awards.
Consider the following statements regarding the National Archives of India (NAI):
- It was originally established in New Delhi in 1891 as the Imperial Records Department.
- The NAI functions under the administrative control of the Ministry of Culture.
- The Director General of Archives is responsible for the enforcement of the Public Records Act, 1993.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect — it was established in Calcutta, not New Delhi.
- Statements 2 and 3 are correct.
- Statement 1: “It was originally established in New Delhi in 1891 as the Imperial Records Department.”
- Statement 2: “The NAI functions under the administrative control of the Ministry of Culture.”
- Statement 3: “The Director General of Archives is responsible for the enforcement of the Public Records Act, 1993.”
Unique Identification Authority of India
Syllabus:Polity
Context:
- The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI), in collaboration with the National Informatics Centre (NIC) and National Testing Agency (NTA), conducted a successful Proof of Concept (PoC) for face authentication using Aadhaar during NEET-UG 2025. The initiative aims to enhance examination security and eliminate impersonation.
What is Aadhaar-Based Face Authentication?
- A biometric verification process that uses facial recognition linked to an individual’s Aadhaar profile for real-time authentication.
- Piloted during NEET-UG 2025 at select centres in Delhi.
Key Features of the Pilot:
- Contactless and real-time biometric verification of candidates
- Seamlessly integrated with NIC’s digital infrastructure and NTA’s exam protocols
- Achieved high accuracy in face matching using Aadhaar’s biometric database
- Prevented impersonation and streamlined candidate entry process
Significance:
- Security Reinforcement: Reduces scope for fraud and impersonation in high-stakes national exams
- Digital Governance in Education: Demonstrates potential for tech-enabled identity verification across public service delivery
- Scalability: Opens avenues for broader use in recruitment exams, e-governance, and public distribution systems
About UIDAI (Unique Identification Authority of India)
- Established: Statutory body under the Aadhaar (Targeted Delivery of Financial and Other Subsidies, Benefits and Services) Act, 2016
- Operational Since: July 12, 2016
- Ministry: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- Core Functions:
- Aadhaar Issuance: Provides 12-digit Unique Identification Numbers to residents
- Authentication Services: Enables biometric (fingerprint, iris, face) and demographic-based identity authentication
- Identity Management: Ensures security, privacy, and confidentiality of Aadhaar data
- Policy and Operational Oversight: Formulates procedures for enrolment, update, usage, and grievance redressal
- Digital Inclusion: Facilitates access to welfare schemes, subsidies, and financial inclusion through verified identity
With reference to Aadhaar-based biometric authentication, consider the following statements:
- Face authentication is contactless and can be conducted in real-time without physical intervention.
- Only fingerprint and iris scans are legally permitted for Aadhaar authentication under the Aadhaar Act, 2016.
- UIDAI is responsible for maintaining both demographic and biometric data of Aadhaar holders.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer:A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct – face authentication is contactless and real-time.
- Statement 2 is incorrect – the Aadhaar authentication ecosystem now legally permits face, fingerprint, and iris authentication.
- Statement 3 is correct – UIDAI manages demographic (name, age, address, etc.) and biometric (iris, fingerprint, face) data.
Parliamentary Oversight in India
Syllabus: Indian Polity and Governance – Parliament and State Legislatures
Context:
- India’s adoption of a parliamentary system was meant to ensure daily executive accountability. However, recent developments indicate an erosion in Parliament’s oversight function, with increasing disruptions, underutilised committees, and a near-absence of post-legislative review mechanisms.
Understanding Parliamentary Oversight
- Definition:
Parliamentary oversight refers to the continuous monitoring and evaluation of executive actions by the legislature. It ensures transparency, accountability, and responsiveness in governance.
Constitutional Basis:
- Article 75: The Council of Ministers is collectively responsible to the Lok Sabha.
- Oversight Instruments: Include Question Hour, Zero Hour, debates, motions (adjournment, no-confidence), and Parliamentary Committee reports.
- B.R. Ambedkar’s Vision:Described parliamentary democracy as a system of “more responsibility, less stability,” highlighting the need for constant executive accountability through legislative scrutiny.
Key Challenges Undermining Oversight
- Disruption of Question Hour
- In the 17th Lok Sabha, only 60% of Question Hour functioned; Rajya Sabha fared worse at 52%.
- Example: The 2021 Pegasus spyware controversy saw repeated disruptions, preventing targeted questions.
Ineffective Utilisation of Committees
- Standing Committees produce detailed reports, but these are rarely discussed in Parliament.
- Annual membership rotation weakens domain continuity and expertise.
- Example: The 2021 Environment Committee’s report on Delhi’s pollution lacked follow-up debate or action.
Absence of Post-Legislative Scrutiny (PLS)
- India lacks a structured mechanism to evaluate laws after enactment.
- Example: The Companies (Amendment) Act, 2013, aimed at compliance simplification, led to a spike in prosecutions due to poor review.
Reforms for Enhanced Oversight
Institutionalise Post-Legislative Scrutiny
- UK Model: Mandates law implementation reviews 3–5 years post-enactment.
- India Proposal: Each Department-Related Standing Committee (DRSC) should periodically review major laws like IBC or NEP.
Revamp Committee Functioning
- Translate reports into regional languages and use infographics for wider public understanding.
- Mandate floor discussions on selected committee reports.
- Equip committees with technical staff and data analysts.
- Example: The S. Congressional Research Service (CRS) provides bipartisan policy support — India lacks a comparable body.
Leverage Digital Tools and AI
- Deploy AI to track budget anomalies, audit flags, and scheme implementation failures.
- Example: AI could have identified early irregularities in PM-Kisan, where ineligible farmers received benefits.
Way Forward
- Parliamentary Modernisation Mission: Invest in digital infrastructure, multilingual dissemination, and a non-partisan research wing.
- Cross-party Consensus: Ensure functional sittings during Question Hour and legislative debates.
- Citizen Engagement: Introduce public consultation mechanisms on bills and reports.
- Expand Oversight to States: Encourage state legislatures to adopt Standing Committees for federal accountability.
Conclusion
- As former President R. Narayanan asserted in 1993, “Oversight is not to criticise but to strengthen governance.” Revitalising the oversight role of Parliament is crucial to uphold constitutional checks, restore public trust, and ensure that governance remains accountable, participative, and transparent.
Which of the following statements regarding Parliamentary Oversight in India is/are correct?
- The 17th Lok Sabha demonstrated near-complete functionality of Question Hour sessions.
- Post-Legislative Scrutiny (PLS) is a mandated function of all Standing Committees in India.
- Article 75 of the Constitution provides the basis for the executive’s accountability to the legislature.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: c) 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: In the 17th Lok Sabha, only 60% of the Question Hour functioned; even lower in the Rajya Sabha (52%), indicating reduced oversight, not near-complete functionality.
- Statement 2 – Incorrect: India does not currently mandate post-legislative scrutiny (PLS). It has been recommended as a reform based on models like the UK, but it is not yet a formalised function of Standing Committees.
- Statement 3 – Correct: Article 75 of the Indian Constitution states that the Council of Ministers shall be collectively responsible to the House of the People (Lok Sabha), establishing the core principle of executive accountability to the legislature.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
Syllabus:Polity
Context:
- The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) took suo motu cognizance of a report highlighting poor infrastructure and inadequate manpower in Kerala’s jails, which has hindered inmates’ access to education.
About the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
What is the NHRC?
- The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) is an independent statutory body in India, tasked with the protection and promotion of human rights. It safeguards various human rights, such as the rights to life, liberty, equality, and dignity.
- Established: 12th October 1993 under The Protection of Human Rights Act, 1993.
- Amended Act: The Protection of Human Rights (Amendment) Act, 2019.
- Status: Statutory, autonomous, non-constitutional body.
- Headquarters: New Delhi.
- Composition:
- Chairperson: A retired Chief Justice of India.
Members:
- One serving or retired judge of the Supreme Court.
- One serving or retired Chief Justice of a High Court.
- Two persons with expertise in human rights.
- Ex-officio members: Chairpersons of various National Commissions (e.g., SC, ST, Women, Minorities, etc.).

Powers and Functions:
- Inquiry: NHRC investigates complaints of human rights violations or negligence by public servants. It can act suo motu (on its own initiative) or on petition.
- Visits: NHRC has the authority to visit jails or detention centres to assess conditions and recommend reforms.
- Advisory Role: It advises the government on steps to effectively implement constitutional safeguards and international human rights treaties.
- Research and Promotion: NHRC engages in spreading awareness about human rights through publications, seminars, and training.
- Judicial Powers: NHRC has powers akin to a civil court under the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, including summoning witnesses, examining them, and collecting evidence.
- Recommendations: The Commission can recommend relief or compensation to victims of human rights violations. However, its recommendations are not legally binding.
Which of the following statements about the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) is/are correct?
- The NHRC was established under the Protection of Human Rights Act, 1993.
- The Chairperson of the NHRC is a sitting Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of India.
- The NHRC has the authority to make legally binding recommendations to the government.
- The NHRC can investigate complaints related to human rights violations by public servants.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
a) 1 and 4 only
b) 1, 2, and 4 only
c) 1, 3, and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: a) 1 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The NHRC was indeed established under the Protection of Human Rights Act, 1993.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The Chairperson of the NHRC is a retired Chief Justice of India, not a sitting Chief Justice.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: While the NHRC can make recommendations to the government, its recommendations are not legally binding.
- Statement 4 is correct: The NHRC has the power to investigate complaints of human rights violations by public servants and can act suo motu.
Cabinet Approves ₹11,828 Crore Expansion Plan for Five IITs
Syllabus:Polity

- In a significant move to enhance India’s higher education system, the Union Cabinet, led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, has approved the Phase-B expansion of five newly established Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) in Tirupati, Palakkad, Bhilai, Jammu, and Dharwad. This expansion, which involves an investment of ₹11,828.79 crore over four years, is aimed at boosting student intake, creating new faculty positions, and developing cutting-edge research parks to strengthen industry-academia collaborations.
Why in the News?
- On May 7, 2025, the Union Cabinet sanctioned the Phase-B expansion plan for these five IITs, which were set up after 2014. The decision is expected to increase student intake by over 6,500 students, improve research capabilities, and enhance infrastructure, contributing to the creation of a more robust innovation ecosystem.
Key Highlights of the Cabinet Decision:
- Total Financial Outlay: ₹11,828.79 crore (for 2025–2029).
- Target IITs: IIT Tirupati (Andhra Pradesh), IIT Palakkad (Kerala), IIT Bhilai (Chhattisgarh), IIT Jammu (Jammu & Kashmir), and IIT Dharwad (Karnataka).
- Student Intake: Capacity will increase by 6,576 students, reaching a total student strength of 13,687.
- Faculty Posts: Creation of 130 new professor-level positions (Level 14 and above).
- Research Parks: Five state-of-the-art research parks to foster stronger industry-academia linkages.
Implementation Timeline (Student Capacity Increase):
- Year 1: +1,364 students
- Year 2: +1,738 students
- Year 3: +1,767 students
- Year 4: +1,707 students
Objectives of the Expansion:
- Enhance the quality of education and research to match global standards.
- Meet the increasing demand for engineering and technology programs in India.
- Strengthen India’s position in the global STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) landscape.
- Encourage regional development by establishing world-class institutions across India.
- Generate employment opportunities through increased academic and administrative staff.
Background:
- These five IITs were established post-2014, with IIT Tirupati and IIT Palakkad beginning their academic operations in 2015–16, and IIT Bhilai, IIT Jammu, and IIT Dharwad in 2016–17.
- Initially operating from temporary campuses, all five IITs have now shifted to their permanent campuses.
Static Facts:
- Total IITs in India:
- The student strength in IITs has doubled from 65,000 to 1.35 lakh over the past decade.
- Admissions: Based on JEE Advanced rankings, IITs offer nationwide admission.
Significance:
- Reduces educational inequality by making world-class education accessible to a broader range of students.
- Boosts local economies through infrastructure development and job creation.
- Aligns with Atmanirbhar Bharat by nurturing a knowledge-driven society.
- Supports India’s ambition to become a global innovation hub and a leader in technology and research.
- This ambitious plan is a step toward not only improving India’s higher education infrastructure but also ensuring that the country remains at the forefront of global innovation and economic progress.
Consider the following statements regarding the recent expansion of Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) approved by the Union Cabinet:
- The Phase-B expansion of IITs aims to increase student intake by over 6,500 students across five newly established IITs.
- The expansion plan involves a financial outlay of ₹11,828.79 crore over four years, from 2025 to 2029.
- The expansion will result in the creation of 130 new faculty posts at the Assistant Professor level.
- The five IITs targeted for the expansion are located in Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Chhattisgarh, Jammu & Kashmir, and Karnataka.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1, 2, and 4 only
B. 2, 3, and 4 only
C. 1 and 4 only
D. 1 and 2 only
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Phase-B expansion aims to increase student intake by over 6,500 students across five IITs.
- Statement 2 is correct: The total financial outlay is ₹11,828.79 crore for the period 2025–2029.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The expansion will create 130 new professor-level positions (Level 14 and above), not Assistant Professor level.
- Statement 4 is correct: The targeted IITs are located in Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Chhattisgarh, Jammu & Kashmir, and Karnataka.
Centralised Information Management System (CIMS)
Syllabus:Polity
- The Centralised Information Management System (CIMS), developed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), is a next-generation data warehouse designed to manage vast volumes of structured and unstructured data. It facilitates data aggregation, analysis, public dissemination, and governance across multiple financial and economic domains.
- Recently, RBI mandated that all Regulated Entities (REs) report details of their Digital Lending Apps (DLAs) through the CIMS portal, enhancing regulatory oversight in the digital lending ecosystem.
Key Features of CIMS:
- Utilizes advanced technologies to handle Big Data and supports data mining, text analytics, visual analytics, and advanced statistical modeling.
- Integrates data from diverse domains such as financial, fiscal, external, corporate, real sectors, and price indices.
Advantages:
- Improves efficiency and accuracy of regulatory data reporting by REs.
- Enables cloud-based electronic submissions, reducing operational burden on banks and financial institutions.
- Enhances the timeliness and quality of data received by RBI.
- Facilitates real-time monitoring and early identification of systemic risks in the financial ecosystem.
- Strengthens communication channels between the RBI and regulated institutions.
- CIMS is a strategic initiative toward modernizing India’s regulatory architecture, supporting informed decision-making and proactive risk management within the financial sector.
With reference to the Centralised Information Management System (CIMS) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), consider the following statements:
- CIMS enables the RBI to integrate and analyze data exclusively from the financial and monetary sectors.
- It allows Regulated Entities (REs) to submit regulatory data using cloud-based infrastructure.
- CIMS supports real-time Big Data analytics and advanced statistical modeling to facilitate proactive financial surveillance.
- The primary purpose of CIMS is to monitor and regulate external sector transactions such as foreign trade and capital inflows.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 2 and 3 only
B. 1, 2, and 4 only
C. 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: A. 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: CIMS integrates data from multiple domains including financial, external, fiscal, corporate, real sectors, and price indices, not just financial and monetary sectors.
- Statement 2 is correct: CIMS allows cloud-based electronic submission of reports by Regulated Entities.
- Statement 3 is correct: It is built to handle Big Data and supports data mining, visual analytics, and advanced modeling to enhance surveillance capabilities.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: Monitoring external transactions is only a part of its broad mandate; the system is not primarily designed for that purpose.
Chief Minister Pushkar Singh Dhami Inaugurates National Homoeopathic Convention ‘Homeocon 2023’ in Uttarakhand
Syllabus:Polity
- Uttarakhand Hosts ‘Homeocon 2023’: Chief Minister Pushkar Singh Dhami Inaugurates National Homoeopathic Convention
- Chief Minister Pushkar Singh Dhami inaugurated the National Homoeopathic Convention, Homeocon 2023, at Doon University, Dehradun, reaffirming the state’s commitment to promoting traditional medicine systems. The event highlighted homeopathy as the second most widely practiced system of medicine globally and underscored its relevance, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Significance of Homeopathy
- Homeopathy has established itself as a globally recognized and widely accepted alternative medical system. During the COVID-19 crisis, its holistic and patient-centric approach demonstrated valuable support in health care. The convention emphasized integrating homeopathy with conventional medicine to provide cost-effective, accessible, and holistic healthcare solutions.

AYUSH and Government Commitment
- The event aligns with the broader goals of the Ministry of AYUSH, which was established in 2014 to oversee the development, promotion, and regulation of India’s traditional systems of medicine, including Ayurveda, Yoga, Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy. The Ministry supports education, research, and clinical outreach in these fields.
- Chief Minister Dhami reaffirmed the state government’s dedication to establishing Uttarakhand as a leading AYUSH hub, supporting both economic development and improved public health outcomes through initiatives such as Homeocon 2023.
Uttarakhand: A Center for Traditional Medicine
- Uttarakhand, located in North India, is increasingly recognized as a significant center for traditional medicine and wellness practices:
- Rishikesh, internationally famed for its yoga heritage, gained global attention after the Beatles’ 1968 visit. It remains a prominent destination for spiritual seekers and yoga practitioners.
- Dehradun, the state’s capital, serves as the administrative headquarters and hosted Homeocon 2023.
- Jim Corbett National Park, a vital conservation site, protects the endangered Bengal tiger and a diverse range of wildlife.
- The Alpine Musk Deer, Uttarakhand’s official state animal, symbolizes the region’s commitment to biodiversity and conservation.
Key Government Figures
- Chief Minister: Pushkar Singh Dhami – Leading efforts to integrate traditional medicine into mainstream healthcare.
- Governor: Gurmeet Singh – The constitutional head representing the central government in the state.
- Through conventions like Homeocon 2023 and supportive policies, Uttarakhand continues to position itself as a national and global leader in AYUSH-based healthcare and wellness tourism.
Consider the following statements about the Ministry of AYUSH:
- It was carved out as a separate ministry from the Department of Indian Systems of Medicine and Homoeopathy (ISM&H) in 2014.
- It regulates both traditional medicine systems and modern pharmaceuticals used in integrative therapies.
- One of its objectives is to promote India as a global wellness destination under the “Heal in India” initiative.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 2 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer:A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct — the Ministry was created in 2014 from earlier departments.
- Statement 2 is incorrect — AYUSH regulates traditional systems, not modern pharmaceuticals.
- Statement 3 is correct — “Heal in India” is part of India’s wellness diplomacy.
Geeta Rao Gupta appointed as US Ambassador at Large for Global Women’s Issues
- The US Senate has confirmed Geeta Rao Gupta, an Indian American, as the Ambassador-at-Large for Global Women’s Issues at the State Department. The Senate approved her nomination with a close vote of 51 to 47. The State Department expressed enthusiasm for Gupta’s leadership in advancing the rights of women and girls through US foreign policy.

Gupta’s Perspective on Women’s Issues
- During her confirmation hearing, Gupta highlighted the widespread inequalities and indignities faced by women globally that limit their full participation in the economy.
- She emphasized that women often live with daily fear of violence, which restricts their freedom and mobility.
- Gupta also pointed out the heightened vulnerabilities of women during conflicts, emergencies, and humanitarian crises, affecting both their safety and their ability to support their families.
About Geeta Rao Gupta
- Born in Mumbai, India in 1956, Geeta Rao Gupta is a renowned expert on gender issues and HIV/AIDS.
- She has served as the executive director of the 3D Program for Girls and Women and has been a senior fellow at the United Nations Foundation since 2017.
- Gupta is well-known for her work on AIDS prevention and addressing women’s vulnerability to HIV.
- She advocates strongly for the economic and social empowerment of women as a vital strategy to combat disease, poverty, and hunger.
- Recently, US President Joe Biden nominated her for the role of Ambassador-at-Large for Global Women’s Issues.
Consider the following statements about the role of the US Ambassador-at-Large for Global Women’s Issues:
- The position was created to integrate gender perspectives into US foreign policy and international development.
- The Ambassador leads the Office of Global Women’s Issues within the Department of State.
- The position requires Senate confirmation and reports directly to the Secretary of State.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer:D
Explanation:
- All three statements are correct. The position of the US Ambassador-at-Large for Global Women’s Issues was established to integrate gender perspectives into US foreign policy and international development efforts.
- The Ambassador leads the Office of Global Women’s Issues within the Department of State, which is responsible for advancing gender equality worldwide.
- Additionally, the position requires confirmation by the US Senate and the Ambassador reports directly to the Secretary of State, reflecting the role’s high-level status in shaping US diplomatic priorities on women’s rights.
Manoj Soni to take oath as UPSC chairman
Syllabus:Polity

- Educationist Manoj Soni is set to assume charge as the Chairman of the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC).
- He joined the Commission as a member on June 28, 2017, and has been performing the duties of the UPSC Chairman since April 5, 2022. Before his tenure at UPSC, Soni served three terms as Vice-Chancellor—two consecutive terms from August 1, 2009, to July 31, 2015, at Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Open University (BAOU), Gujarat, and one term from April 2005 to April 2008 at The Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda (MSU Baroda).
- A political science scholar specializing in international relations, he taught the subject at Sardar Patel University (SPU), Vallabh Vidyanagar, from 1991 to 2016, except during his vice-chancellorships.
Awards and Recognitions
- In 2013, Soni was honored as the “Honorary Mayor-President of the City of Baton Rouge” by the Mayor-President of Baton Rouge, Louisiana, USA, recognizing his leadership in empowering disadvantaged communities through IT literacy.
- In 2015, he received the World Education Congress Global Award for Distance Learning Leadership from the Chartered Institute of Management Accountants, London, UK.
- Soni has served on the Boards of Governors of various higher education and public administration institutions.
- Additionally, he was a member of a quasi-judicial body constituted by the Gujarat Legislature to regulate fees of unaided professional institutions in the state.
About the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- The UPSC is India’s premier central recruitment agency responsible for recruiting Group ‘A’ officers across various Government of India departments.
- It conducts appointments and examinations for posts in central government establishments, including public sector undertakings and autonomous bodies.
- The Department of Personnel and Training acts as the central personnel agency of India.
- Established on October 1, 1926, under the Government of India Act, 1919, the UPSC is headquartered in New Delhi, with regional offices in cities including Allahabad, Bhopal, Chandigarh, Chennai, Guwahati, Hyderabad, Kolkata, Lucknow, Mumbai, and Patna.
- The Commission is led by a Chairman appointed by the President of India, supported by several members also appointed by the President. These members come from diverse backgrounds such as civil services, armed forces, and academia.
Functions of UPSC
- UPSC conducts several competitive examinations for Group ‘A’ officer recruitment, the most prestigious being the Civil Services Examination (commonly known as the IAS exam).
- This three-tier exam evaluates candidates on general studies, English proficiency, and optional subjects.
- Other Group ‘A’ services under UPSC’s purview include the Indian Foreign Service, Indian Police Service, and Indian Audit and Accounts Service.
- An independent constitutional authority, UPSC’s decisions are autonomous and not subject to external approval.
- The Commission is dedicated to merit-based recruitment, ensuring high-caliber officers join the civil services.
Significance of UPSC
- UPSC has played a crucial role in shaping the Indian civil service, ensuring it remains impartial, efficient, and responsive to public needs.
- The Commission promotes meritocracy and excellence, contributing significantly to India’s governance and development.
- Its commitment to impartiality and quality has earned it widespread respect across the nation.
Consider the following statements regarding the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) and Manoj Soni’s role:
- The UPSC was established under the Government of India Act, 1919, and is an independent constitutional body responsible for recruitment of Group ‘A’ officers in India.
- Manoj Soni served as Vice-Chancellor of two universities before joining UPSC, with expertise primarily in administrative law and constitutional law.
- The Chairman and members of UPSC are appointed by the President of India and the Commission’s decisions do not require approval from any other authority.
- The Department of Personnel and Training functions under the UPSC as its central administrative arm.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 1, 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2 and 3 only
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct as UPSC was established under the Government of India Act, 1919, and is an independent constitutional body responsible for recruitment of Group ‘A’ officers.
- Statement 2 is incorrect because Manoj Soni’s specialization is in political science and international relations, not administrative or constitutional law.
- Statement 3 is correct; the Chairman and members are appointed by the President of India, and the UPSC functions independently without needing external approvals.
- Statement 4 is incorrect because the Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT) is a separate central personnel agency, not functioning under UPSC.
Air Marshal Ashutosh Dixit takes over as Deputy Chief of Air Staff
Syllabus:Polity
- Air Marshal Ashutosh Dixit has assumed the position of Deputy Chief of the Air Staff, as announced by the Defence Minister. An alumnus of the National Defence Academy, Air Marshal Dixit was commissioned into the fighter stream on December 6, 1986.
- He is a qualified flying instructor and an experimental test pilot with over 3,300 hours of flying experience across fighter, trainer, and transport aircraft.
- His operational experience includes participation in Operations ‘Safed Sagar’ and ‘Rakshak’.
- Air Marshal Dixit has commanded a Mirage 2000 squadron, a frontline fighter base in the Western sector, and a premier fighter training base.
- His previous roles include Principal Director Air Staff Requirements, Assistant Chief of the Air Staff (Projects), and Assistant Chief of the Air Staff (Plans) at Air Headquarters.
- He has also served as the Air Defence Commander of the Southern Air Command and as Senior Air Staff Officer of the South Western Air Command before taking charge as Deputy Chief of the Air Staff.
- The Deputy Chief of the Air Staff (DCAS) is an Air Marshal-ranked officer in the Indian Air Force (IAF) and serves as the second-in-command of the Air Force.
- The DCAS assists the Chief of the Air Staff in managing operational readiness, strategic planning, and execution of the IAF’s missions and activities.
- The officeholder may change due to regular rotations and promotions. For the latest updates, official IAF sources should be consulted.
Consider the following statements regarding the Deputy Chief of the Air Staff (DCAS) and Air Marshal Ashutosh Dixit:
- The DCAS is the second-highest ranking officer in the Indian Air Force and is responsible for assisting the Chief of the Air Staff in operational planning and readiness.
- Air Marshal Ashutosh Dixit, before becoming DCAS, has served as the Principal Director Air Staff Requirements and has commanded a Mirage 2000 squadron.
- Participation in operations such as ‘Safed Sagar’ and ‘Rakshak’ is a mandatory prerequisite for appointment as DCAS.
- The DCAS holds a three-star rank, which is equivalent to a Lieutenant General in the Indian Army.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1, 2 and 4 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 4 only
D. All of the above
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct as the DCAS is indeed the second-in-command of the IAF and assists the Chief in operational readiness and planning.
- Statement 2 is correct; Air Marshal Dixit served as Principal Director Air Staff Requirements and commanded a Mirage 2000 squadron.
- Statement 3 is incorrect because while participation in certain operations adds to an officer’s credentials, it is not a mandatory requirement for becoming DCAS.
Statement 4 is correct since the rank of Air Marshal (DCAS) is a three-star rank, equivalent to Lieutenant General in the Army.
Top 10 Countries With the Highest Debt-To-GDP in 2025
Syllabus:Economy
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has raised alarm about a surge in global public debt, with projections for 2025 indicating that several countries will see their debt levels exceed those recorded at the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- According to the IMF’s Fiscal Monitor Report (April 2025), the global public debt-to-GDP ratio could approach critical levels once again, sparking concerns about the economic and fiscal sustainability of both developing and advanced economies.
- In a surprising development, Sudan has surpassed Japan to become the country with the highest debt-to-GDP ratio in the world in 2025, driven by internal conflict and economic instability.
- Meanwhile, the debt burdens of major economies like the United States, France, and Canada remain significantly high, reflecting persistent structural deficits and geopolitical challenges.
Background and Context:The COVID-19 pandemic triggered an unprecedented wave of government borrowing as nations scrambled to tackle public health emergencies and implement large-scale stimulus programs. Consequently, global public debt reached 98.9% of GDP in 2020.
Despite subsequent economic recovery, ongoing geopolitical instability—including trade tensions, particularly following recent U.S. tariff declarations—and inflationary pressures have led to a rise in borrowing needs. The IMF warns that global public debt levels could reach 117% of global GDP by 2027 under worst-case conditions and nearly 100% (99.6%) by 2030.
Key Insight: The Top 10 Countries with the Highest Debt-to-GDP Ratio in 2025:
The IMF’s recent findings reveal an alarming composition of the ten countries with the highest public debt in 2025, mostly driven by persistent budget deficits, economic mismanagement, and structural vulnerabilities such as demographic decline or excessive external debt.
Top 10 Countries with the Highest Debt-to-GDP Ratio in 2025:
Rank | Country | General Government Gross Debt (% of GDP) |
1 | Sudan | 252% |
2 | Japan | 234.9% |
3 | Singapore | 174.9% |
4 | Greece | 142.2% |
5 | Bahrain | 141.4% |
6 | Maldives | 140.8% |
7 | Italy | 137.3% |
8 | United States | 122.5% |
9 | France | 116.3% |
10 | Canada | 112.5% |
Country Highlights and Analysis:
- Sudan: Facing prolonged internal conflict, economic instability, and a loss of oil revenues, Sudan has reached a debt-to-GDP ratio of 252%, the highest globally.
- Japan: Despite being a developed and technologically advanced economy, Japan’s public debt stands at 234.9%, due to persistent fiscal deficits, an aging population, and years of low economic growth.
- United States and Other Developed Economies: The U.S. ranks 8th, with a debt-to-GDP ratio of 122.5%. This is driven by rising federal deficits, and spending on defense, healthcare, and interest payments. France (116.3%) and Canada (112.5%) also face similar challenges in managing social welfare spending and post-pandemic economic recovery.
Where Do China and India Stand?
Unlike the top 10 indebted nations, China and India have more manageable debt levels:
- China: With a debt-to-GDP ratio of 96%, China ranks 21st, reflecting a controlled fiscal expansion model.
- India: India ranks 31st, with a debt-to-GDP ratio of 80%. The Indian government aims to reduce this ratio to 50±1% by March 31, 2031, through fiscal consolidation and economic growth.
Future Outlook: Risks and Recovery
The IMF warns that, unless corrective measures are adopted, global public debt could surpass the levels seen during World War II. Key risks include:
- Continued geopolitical instability
- High interest rates
- Sluggish global growth
- Elevated inflation and subsidy bills
Even a temporary shock—such as another trade war, a health crisis, or a spike in commodity prices—could accelerate vulnerabilities related to public debt.
Call to Action:
Nations are being urged to adopt credible, medium-term fiscal plans. Key measures include enhancing tax collection efficiency, curbing unproductive subsidies, and investing in growth-driving sectors to prevent the risk of spiraling debt.
Consider the following statements regarding the surge in global public debt as highlighted by the International Monetary Fund (IMF):
- Sudan has surpassed Japan to become the country with the highest debt-to-GDP ratio in the world in 2025.
- The global public debt-to-GDP ratio is expected to reach 117% by 2027 under worst-case conditions.
- The United States has a debt-to-GDP ratio of 122.5%, ranking 8th among the countries with the highest debt-to-GDP ratio.
- China and India are among the top 10 countries with the highest debt-to-GDP ratios globally in 2025.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1, 2, and 3 only
B. 1, 2, and 4 only
C. 1, 2, and 3 only
D. 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: A) 1, 2, and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Sudan has indeed surpassed Japan to become the country with the highest debt-to-GDP ratio in the world in 2025.
- Statement 2 is correct: The IMF forecasts that global public debt could reach 117% of global GDP by 2027 under worst-case conditions.
- Statement 3 is correct: The United States has a debt-to-GDP ratio of 122.5%, ranking 8th among the countries with the highest debt-to-GDP ratio.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: China and India, though significant economies, are not in the top 10 countries with the highest debt-to-GDP ratios in 2025. India is ranked 31st, and China is ranked 21st.
Top 10 Wealthiest Families in Asia 2025 Revealed by Bloomberg
Syllabus:Economy
Asia’s Richest Families 2025 – Bloomberg Rankings
Why in the News:Bloomberg has released its 2025 list of the Top 20 Wealthiest Families in Asia, highlighting enduring business legacies and multi-generational wealth. The Ambani family of India leads the list with a wealth of $90.5 billion, reaffirming India’s prominence in the region’s family-owned corporate landscape.
Background / Context: Asia has long been home to powerful family-run conglomerates that continue to influence regional and global markets. Bloomberg’s 2025 list focuses exclusively on dynasties that have passed on wealth across generations, excluding first-generation billionaires. In India, this highlights the resilience and global reach of legacy business houses such as Reliance, Aditya Birla Group, and Bajaj.
Key Information:
Aspect | Details |
List Name | Asia’s Richest Families 2025 |
Released By | Bloomberg |
Release Date | January 31, 2025 |
Geographic Focus | Asia (India, Thailand, Indonesia, etc.) |
Special Note | 6 Indian families featured in Top 20 |
Significance:
- Highlights inter-generational wealth creation and sustainability
- Showcases the economic influence of legacy family businesses
- Reflects India’s entrepreneurial tradition and corporate continuity
- Offers insight into sectoral dominance by family-led enterprises
Top 10 Wealthiest Families in Asia (2025)
Rank | Family Name | Company | Wealth | Country | Generations |
1 | Ambani | Reliance Industries | $90.5B | India | 3 |
2 | Chearavanont | Charoen Pokphand Group | $42.6B | Thailand | 4 |
3 | Hartono | Djarum, Bank Central Asia | $42.2B | Indonesia | 3 |
4 | Mistry | Shapoorji Pallonji Group | $37.5B | India | 5 |
5 | Kwok | Sun Hung Kai Properties | $35.6B | Hong Kong | 3 |
6 | Tsai | Cathay Financial, Fubon Financial | $30.9B | Taiwan | 3 |
7 | Jindal | OP Jindal Group | $28.1B | India | 3 |
8 | Yoovidhya | TCP Group (Red Bull) | $25.7B | Thailand | 2 |
9 | Birla | Aditya Birla Group | $23.0B | India | 7 |
10 | Lee | Samsung | $22.7B | South Korea | 3 |
Indian Families in the Top 20 – 2025
Rank (Asia) | Family | Company | Wealth (USD) | Industry | Generations |
1 | Ambani | Reliance Industries | $90.5B | Conglomerate | 3 |
4 | Mistry | Shapoorji Pallonji Group | $37.5B | Conglomerate | 5 |
7 | Jindal | OP Jindal Group | $28.1B | Industrial | 3 |
9 | Birla | Aditya Birla Group | $23.0B | Conglomerate | 7 |
13 | Bajaj | Bajaj Group | $20.1B | Conglomerate | 4 |
18 | Hinduja | Hinduja Group | $15.2B | Finance, Property | 4 |
Consider the following statements regarding Bloomberg’s 2025 list of Asia’s Richest Families:
- The list includes only first-generation billionaire entrepreneurs.
- The Ambani family is the only Indian family in the top 5.
- The Birla family, with 7 generations, is the oldest Indian business dynasty in the top 20.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer:B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect (Bloomberg excludes first-generation billionaires).
- Statement 2 is correct (only Ambani ranks in the top 5 among Indian families).
- Statement 3 is correct (Birla is 7 generations strong, the oldest in the Indian list).
Green Municipal Bond (GMB)
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
- Ghaziabad has issued India’s first Certified Green Municipal Bond under the Swachh Bharat Mission–Urban, successfully raising ₹150 crore to fund a Tertiary Sewage Treatment Plant (TSTP), marking a significant step toward sustainable urban infrastructure.
About Green Municipal Bonds (GMBs):
- A Municipal Bond is a debt instrument issued by Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) or Municipal Corporations to finance infrastructure and public service projects.
- A Green Municipal Bond is a sub-category used exclusively for climate-resilient and environmentally sustainable projects, such as renewable energy, water purification, waste management, and sewage and sanitation infrastructure.
- Empowered by Article 243W of the Indian Constitution, ULBs are responsible for water supply, sanitation, and waste management, making them eligible to raise such bonds.
Significance of Green Municipal Bonds:
- Sustainable development is supported by promoting climate-conscious urban growth and aligning with ESG (Environment, Social, Governance) investing frameworks.
- These bonds offer affordable financing through lower-cost, long-term capital, often more economical than commercial loans.
- They help diversify the funding base by attracting institutional and international investors, reducing reliance on domestic banking channels.
- Additionally, they strengthen urban infrastructure in key sectors such as sewage treatment, clean water supply, and waste disposal.
Key Challenges:
- Many ULBs lack the financial expertise, credit ratings, and project readiness necessary to access capital markets.
- Regulatory complexity, including lengthy approval mechanisms and a shallow bond market, hinders the widespread adoption of green bonds.
- Ensuring transparency in the utilization of funds and accurately assessing environmental impact remains difficult.
- Furthermore, there is limited awareness among domestic investors about green finance instruments, which restricts demand.
Way Forward:
- Urban Local Bodies must be strengthened through capacity building in financial structuring, ESG compliance, and project appraisal.
- Policy support should be provided in the form of tax incentives, risk guarantees, and simplified regulatory frameworks to facilitate green bond issuance.
- Establishing independent third-party verification mechanisms for green credentials and impact monitoring is crucial.
- Investor outreach must be expanded to include pension funds, insurance companies, and ESG-focused global investors.
- Finally, municipal green finance initiatives should be aligned with national programs like AMRUT, the Smart Cities Mission, and the Jal Jeevan Mission to maximize impact and efficiency.
With reference to Green Municipal Bonds (GMBs) in India, consider the following statements:
- The Constitution of India explicitly mandates the issuance of municipal bonds under Article 243W.
- Green Municipal Bonds can only be issued with prior approval from the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- GMBs in India are eligible to finance projects under the Jal Jeevan Mission and AMRUT.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2 only
C. 3 only
D. 2 and 3 only
Answer:C
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Article 243W entrusts ULBs with functions like water supply and sanitation but does not explicitly mandate the issuance of municipal bonds.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: SEBI regulates bonds, but prior approval is not explicitly required for every GMB issuance; municipal corporations may issue them based on existing guidelines.
- Statement 3 is correct: GMBs can fund projects aligned with missions like AMRUT and Jal Jeevan Mission.
Insufficient Support for Deep Tech Start-ups in India: Study
Syllabus: GS3/Economy; Employment; Growth & Development
Context: A recent study commissioned by the Office of the Principal Scientific Advisor to the Government of India, and conducted in collaboration with the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), has revealed critical structural and operational shortcomings in the support extended to deep technology (deep tech) start-ups by publicly funded R&D institutions in India.
About Deep Tech Start-ups:Deep tech start-ups are rooted in advanced scientific discoveries and engineering innovations, encompassing domains such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, space technology, biotechnology, and advanced materials.Unlike traditional start-ups—which often rely on business model innovations in sectors like e-commerce, SaaS, or consumer services—deep tech ventures are characterized by:
- Prolonged R&D cycles
- Higher capital intensity and risk
- Strong dependence on foundational science and engineering breakthroughs
Key Findings of the Study:
- Limited Incubation Support:
- Only 25% of publicly funded R&D institutions provide any incubation assistance to start-ups.
- For deep tech start-ups specifically, this figure drops to merely one in six institutions.
- Insufficient Industry Engagement:
- Merely 15% of institutions reported collaborations with international industries—reflecting a weak integration with global innovation networks.
- Restricted Access to R&D Infrastructure:
- Nearly 50% of the institutions do not permit access to their laboratories and research facilities to external stakeholders such as students, start-ups, or independent researchers.
- This restriction undermines open innovation, interdisciplinary research, and technology diffusion.
Budgetary Allocation and Workforce Trends:
R&D Expenditure Patterns:
- The Central Government allocated approximately ₹55,685 crore toward R&D in FY 2020–21, of which ₹24,587 crore was distributed to major scientific agencies.
- While 25% of institutions reported dedicating over 75% of their budgets to core R&D, a significant number fell below this threshold, indicating skewed resource prioritization.
Human Resource Trends:
- A noticeable decline in permanent scientific staff was observed between 2021–22 and 2022–23, replaced increasingly by contractual or project-based hires.
- Although the proportion of young researchers rose to 58% in 2022–23 (from 54% in the previous year), this remains below the 63%–65% levels recorded between 2017 and 2020.
Policy Initiatives and Governmental Support:
- National Deep Tech Startup Policy (NDTSP):
- Envisioned to create a robust, innovation-led deep tech ecosystem in India.
- Emphasizes economic security, strategic autonomy, and ethical innovation frameworks.
- National Quantum Mission:
- Facilitates research and commercialization in quantum computing and allied technologies, with applications in drug discovery, life sciences, and climate solutions.
- Indian start-ups like QpiAI are spearheading indigenous quantum innovation.
Recommendations for Strengthening India’s Deep Tech Ecosystem:
Foster Strategic Industry Collaboration:
- Strengthen linkages with both domestic and international industries to scale innovation and enhance technology transfer.
Expand Incubation and Funding Support:
- Develop targeted incubation programs and increase funding for deep tech ventures, given their longer gestation periods and higher capital requirements.
Democratize Access to Research Facilities:
- Ensure open and equitable access to publicly funded R&D infrastructure for non-institutional stakeholders to stimulate collaborative research.
Align Institutional Mandates with National Priorities:
- Reorient R&D objectives to align with the goals of Viksit Bharat@2047, emphasizing strategic research, societal impact, and economic development.
With reference to deep tech start-ups, consider the following statements:
- Deep tech start-ups primarily rely on business model innovations rather than scientific research.
- They typically involve longer development cycles and greater technological uncertainty than traditional start-ups.
- Their success depends significantly on foundational advancements in scientific disciplines like quantum mechanics, biotechnology, or advanced materials.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Correct Answer: B. 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: “Deep tech start-ups primarily rely on business model innovations rather than scientific research.”
- Statement 2: “They typically involve longer development cycles and greater technological uncertainty than traditional start-ups.”
- Statement 3: “Their success depends significantly on foundational advancements in scientific disciplines like quantum mechanics, biotechnology, or advanced materials.”
India Considers Allowing 49% Foreign Stakes in Nuclear Power Plants
Syllabus: GS3/ Infrastructure and Energy
Context:
- India is considering allowing foreign companies to hold up to 49% stake in its nuclear power plants to accelerate decarbonization goals and enhance clean energy capacity.
Background:
- Currently, India’s nuclear energy sector is exclusively operated by state-owned entities—Nuclear Power Corporation of India Ltd (NPCIL) and its subsidiary Bharatiya Nabhikiya Vidyut Nigam Ltd (BHAVINI).
- To enable private and foreign participation, the government is proposing amendments to the Atomic Energy Act, 1962 and the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010.
Nuclear Energy Basics:
- Nuclear energy is derived from nuclear reactions—either fission (splitting of uranium or plutonium atoms) or fusion (combining atomic nuclei). In India, nuclear fission is used to produce electricity.
Current Nuclear Power Status in India:
- Installed nuclear capacity: 8,180 MW (~2% of total electricity capacity), across 24 reactors.
- Expansion: 10 new reactors (8 GW) under construction across various states.
- Approval granted for a 6×1208 MW plant in Andhra Pradesh in collaboration with the USA.
Rationale for Foreign/Private Involvement:
- Clean Energy Transition: Coal accounts for over 70% of India’s electricity; nuclear offers a low-carbon baseload alternative.
- High Capital Costs: Nuclear projects require large upfront investment; FDI will enable faster capital mobilization and tech transfer.
- Despite the 2008 Indo-US Civil Nuclear Agreement, commercial deals lag due to liability concerns under existing legislation.
Proposed Reforms:
- FDI up to 49% in nuclear energy ventures under legislative amendments.
- Atomic Energy Act, 1962: To permit private entities to construct, own, and operate nuclear power plants.
- Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010: Proposed amendments aim to reduce supplier liability—capping it to contract value and limiting the duration.
- Liability cap for small reactor operators proposed at $58 million; large reactor cap remains at $175 million.
Oversight and Safety:
- Regulatory control to remain with Atomic Energy Regulatory Board (AERB) and Department of Atomic Energy (DAE).
- Safety standards to adhere to IAEA guidelines.
Way Forward:
- Establish a clear regulatory framework ensuring compliance, safety, and transparency.
Implement reforms through pilot projects to assess risks and build trust before scaling up private sector involvement
With reference to proposed reforms in India’s nuclear energy sector, consider the following statements:
- The amendments to the Atomic Energy Act, 1962 seek to allow private sector entities to construct and operate nuclear reactors in India.
- Foreign companies may be allowed up to 100% ownership in nuclear power plants under the new proposal.
- The Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010 currently caps the liability of all nuclear operators at $58 million.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1 and 3 only
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Proposed amendments include allowing private entities to construct, own, and operate nuclear plants.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: FDI is being considered up to 49%, not 100%.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The cap of $58 million is proposed only for small reactors; large reactor operators remain capped at $175 million.
Executive Director of IMF
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
- Parameswaran Iyer, former CEO of NITI Aayog and currently serving as a director at the World Bank, has assumed interim charge as India’s Executive Director at the International Monetary Fund (IMF), following the early departure of K. V. Subramanian.
About the IMF Executive Board:
- The Executive Board of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) functions as the primary decision-making body overseeing the institution’s day-to-day operations. It comprises 25 Executive Directors, who are either elected by individual countries with significant financial quotas or by multi-country constituencies.
Key Functions:
- Approving IMF lending to member countries facing temporary balance of payments difficulties,
- Ensuring global macroeconomic and financial stability,
- Preventing potential spillover effects across the international financial system.
Consider the following statements regarding the Executive Board of the International Monetary Fund (IMF):
- Every Executive Director on the Board represents only one country, regardless of the size of its financial quota.
- The Executive Board plays a role in approving lending arrangements to countries experiencing long-term structural economic crises.
- The Executive Board consists of members who are responsible for the IMF’s daily operations and policy implementation.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer:B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect—some Directors represent multi-country constituencies.
- Statement 2 is incorrect—IMF lending typically addresses temporary balance of payments difficulties, not long-term structural crises.
- Statement 3 is correct.
Amex and HSBC Top Credit Card Additions Among Foreign Banks in FY25
Syllabus:Economy
- In a significant recovery from previous declines, foreign banks like HSBC and American Express have emerged as key players in the credit card market, with impressive net additions in FY25, as per data released by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- HSBC added 216,997 cards, while American Express saw a net addition of 107,086 cards.
- This surge reflects a resurgence in consumer credit demand, contributing to the overall industry expansion, with more than 8 million new credit cards issued across all banks in FY25.
Why in News?
- On May 7, 2025, the RBI highlighted that HSBC and American Express topped the list for net credit card additions among foreign banks in FY25.
- This marks a sharp recovery for American Express, which had previously witnessed a decline in its card base.
- The credit card industry as a whole added over 8 million cards, reflecting increasing consumer appetite for credit and the growing adoption of digital payments.
Key Highlights:
- HSBC: Added 216,997 cards in FY25, a stark turnaround after a decline of 38,693 cards in FY24.
- American Express: Net addition of 107,086 cards in FY25, a significant increase from just 11,450 cards in FY24.
- Standard Chartered: Experienced a decline of 158,322 cards in FY25.
- Industry Total: Over 8 million new credit cards issued across all banks in FY25.
Background:
- Foreign banks faced several challenges in expanding their credit card base in India, including limited branch presence, regulatory hurdles, and intense competition from domestic banks. Notably, American Express had been under restrictions by the RBI in 2021 due to non-compliance with data localization requirements, but these restrictions were later lifted.
Aim & Objectives of Expansion:
- Capture growing demand: Tap into India’s expanding middle class, which is increasingly adopting digital payments and consumer credit.
- Strengthen premium market share: Targeting high-income consumers with premium credit card offerings.
- Align with India’s fintech growth: Support the country’s push towards a cashless economy and the rapid growth of its fintech ecosystem.
Significance:
- The surge in credit card additions reflects the revival of foreign banks’ retail operations in India.
- The growth in consumer credit demand signals rising consumer confidence and economic recovery in India.
- It highlights India’s ongoing transition towards credit-driven consumption, in line with the country’s evolving economic landscape.
Consider the following statements regarding the recent growth in the credit card market in India for FY25:
- HSBC and American Express were the leaders in net credit card additions, with HSBC adding over 200,000 cards and American Express adding more than 100,000 cards.
- The overall credit card industry in India saw a decline in the number of cards issued during FY25.
- American Express had faced restrictions by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in 2021 due to non-compliance with data localization norms, which were later lifted.
- Foreign banks in India have traditionally struggled to expand their credit card base due to competition from domestic banks, regulatory hurdles, and limited branch presence.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A) 1 and 3 only
B) 2 and 4 only
C) 1, 3, and 4 only
D) 1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: C) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: HSBC added 216,997 cards, and American Express added 107,086 cards in FY25.
- Statement 2: The overall credit card industry saw an increase in the number of credit cards, with over 8 million cards added in FY25.
- Statement 3: American Express had faced restrictions in 2021 for non-compliance with RBI’s data localization norms, which were later lifted.
- Statement 4: Foreign banks, including American Express, have traditionally faced challenges due to limited branch presence and strong competition from domestic banks.
India Launches Non-Ferrous Metal Recycling Portal to Boost Circular Economy
Syllabus:Economy

- In a major step toward advancing India’s circular economy and resource efficiency goals, Union Minister of Coal and Mines, Shri G. Kishan Reddy, launched the Non-Ferrous Metal Recycling Website and Stakeholders’ Portal on 7 May 2025. Developed under the National Non-Ferrous Metal Scrap Recycling Framework, the portal aims to streamline and formalize India’s recycling ecosystem for key non-ferrous metals such as aluminium, copper, lead, zinc, and critical minerals.
Why in News?
- The launch of this portal signifies a strategic push by the Government of India to promote sustainable development, reduce dependence on imported raw materials, and facilitate evidence-based policymaking through real-time data and a centralized stakeholder platform.
Objectives and Core Aims:
- Establish a national digital platform for recyclers, dismantlers, traders, and collection centers.
- Enable comprehensive data collection and analysis to guide policy formulation.
- Promote standardization, certification, and industry participation.
- Map skill gaps and drive workforce development across the recycling value chain.
Portal Details:
- Official URL: https://nfmrecycling.jnarddc.gov.in
- Launch Date: 7 May 2025
- Launched by: Shri G. Kishan Reddy, Union Minister of Coal and Mines
- Supported by: Jawaharlal Nehru Aluminium Research Development and Design Centre (JNARDDC)
Key Features:
- National registry for all stakeholders in the metal recycling sector.
- Access to real-time data on:
- Raw material flows
- Technology deployment
- Recycling capacities
- Workforce statistics
- Tools for performance benchmarking of registered entities.
Identification of:
- Infrastructure gaps
- Skill development needs
- Regional and sectoral priorities
- Regular updates on:
- Policy changes
- Stakeholder meetings
- Research and innovation outcomes
Significance:
- Promotes self-reliance (Atmanirbhar Bharat) by minimizing foreign raw material dependency.
- Supports Make in India by strengthening the domestic recycling industry.
- Aligns with India’s commitments to sustainability and global climate goals.
- Facilitates a more efficient, data-driven, and transparent value chain for non-ferrous metals.
The launch of the Non-Ferrous Metal Recycling Portal is most relevant to which of the following Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)?
- SDG 9 – Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- SDG 12 – Responsible Consumption and Production
- SDG 13 – Climate Action
- SDG 7 – Affordable and Clean Energy
Select the correct answer using the code below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1, 2 and 3 only
C. 2 and 4 only
D. 1, 3 and 4 only
Answer: B. 1, 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- SDG 9 is addressed through industrial standardization and innovation in recycling.
- SDG 12 is directly related to resource efficiency and sustainable recycling.
- SDG 13 is indirectly supported through reduced mining and environmental impact.
- SDG 7 is not directly relevant to non-ferrous recycling.
India rolls over $50 million worth Treasury Bill to help Maldives
Syllabus:Economy
- Recent findings published in Earth and Planetary Science Letters have unveiled that the Gamburtsev Subglacial Mountains (GSM) in East Antarctica began forming over 500 million years ago, during the assembly of the Gondwana supercontinent.
What Are the Gamburtsev Subglacial Mountains?
- The Gamburtsev Mountains are a completely buried mountain range, lying beneath the East Antarctic Ice Sheet, at the continent’s highest elevation.
- Discovered in 1958 by a Soviet seismic survey, these mountains remain entirely concealed under several kilometers of ice, unlike the Transantarctic Mountains, which are partially exposed.
- Their existence within the tectonically stable East Antarctic craton has long puzzled geologists, as typical mountain formation results from active plate tectonics (e.g., collision, subduction), not in geologically inert zones.
Unlocking the Past: Zircon Analysis
- Researchers traced the origin and evolution of GSM through zircon grains found in sandstone deposits in the Prince Charles Mountains, carried by ancient river systems originating from the buried range.
- Zircons, containing trace amounts of uranium, serve as natural radioactive clocks. Uranium decays at a known rate, allowing for precise radiometric dating.
Chronology of Formation
- The study’s zircon dating revealed the following geological timeline:
- ~650 million years ago (Ma): Initial uplift began, possibly due to ancient tectonic reactivation.
- ~580 Ma: The mountain range reached Himalayan-scale elevations.
- ~500 Ma: Crustal melting and viscous flow activity ceased, stabilizing the range during Gondwana’s assembly.
Significance
- The GSM’s formation represents a rare instance of mountain-building deep within a stable continental interior and provides critical insights into:
- Ancient tectono-thermal events in East Antarctica,
- The pre-glacial landscape evolution of the continent,
- The geodynamic history surrounding the formation of supercontinents like Gondwana.
With reference to the formation and geological significance of the Gamburtsev Subglacial Mountains (GSM) in East Antarctica, consider the following statements:
- The GSM are entirely buried beneath the East Antarctic Ice Sheet and were first discovered during the International Geophysical Year in 1958 by a Soviet seismic expedition.
- Geological evidence suggests that the GSM began forming approximately 650 million years ago, reaching their peak elevation around 580 million years ago, with crustal melting and flow ceasing around 500 million years ago.
- The formation of the GSM is attributed to tectonic collisions during the assembly of the supercontinent Gondwana, despite East Antarctica’s long-standing tectonic stability.
- The GSM are currently the only known mountain range completely buried beneath an ice sheet, making them unique in Earth’s geological record.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A. 1, 2, and 3 only
B. 1, 3, and 4 only
C. 2 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: A. 1, 2, and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: The Gamburtsev Subglacial Mountains were indeed discovered in 1958 by a Soviet seismic expedition during the International Geophysical Year.
- Statement 2: Zircon dating from sandstones in the Prince Charles Mountains indicates that the GSM began uplifting around 650 million years ago, achieved significant elevation by 580 million years ago, and experienced crustal melting and flow that ceased approximately 500 million years ago.
- Statement 3: The formation of the GSM is linked to tectonic collisions during the assembly of Gondwana, which is notable given East Antarctica’s current tectonic stability.
- Statement 4: While the GSM are a significant example of a mountain range entirely buried beneath an ice sheet, they are not the only such range. Other subglacial mountain ranges exist beneath the Antarctic Ice Sheet, such as the Transantarctic Mountains, parts of which are also buried under ice.
USTR Releases 2025 “Special 301 Report” on Protecting Intellectual Property Rights
Syllabus: GS 3/intellectual Property Rights
- The Office of the United States Trade Representative (USTR) has released the Special 301 Report 2025, which evaluates the effectiveness of intellectual property (IP) rights protection and enforcement among U.S. trading partners.
- India continues to feature on the ‘Priority Watch List’ due to several persistent IP-related concerns.
About the Special 301 Report
- The report is an annual review conducted under Section 182 of the Trade Act of 1974, as amended by the Omnibus Trade and Competitiveness Act of 1988 and the Uruguay Round Agreements Act.
- It identifies countries with inadequate IP protection or enforcement mechanisms and aims to address key issues such as:
- Weak IP enforcement
- Inadequate trade secret protection
- Discriminatory innovation policies
- Online piracy and counterfeiting
- Barriers to market access for IP-intensive goods
- In 2025, over 100 trading partners were reviewed; 26 were placed on either the Watch List or Priority Watch List.
- Review of Ukraine was suspended due to the ongoing conflict.
India-Specific Findings
- India remains on the Priority Watch List for 2025.
- Key concerns highlighted by the USTR include:
- Ambiguity in patent laws
- Delays in patent and trademark approvals
- Weak copyright and trade secret enforcement
- Unauthorized content sharing and digital piracy
- High import duties on IP-intensive products
- Despite these concerns, the report acknowledged India’s engagement with the U.S. and recent policy steps.
Recent Progress by India
- India notified the Patents (Amendment) Rules, 2024, which aim to address long-standing issues such as:
- Streamlining pre-grant opposition proceedings
- Reducing compliance burdens related to patent reporting
- These amendments mark incremental progress in improving the patent regime.
Future Outlook
- The U.S. intends to monitor the implementation of India’s patent law amendments.
- It encourages India to take further steps to:
- Expedite patent approval processes
- Strengthen overall IP enforcement and protection frameworks
Did You Know? (WIPI 2024 Data)
- India ranks among the top 10 countries globally in all three major IP categories—patents, trademarks, and industrial designs.
- In 2023:
- India recorded the fastest growth rate in patent applications (15.7%) among the top 20 economies
- Filed over 64,000 patent applications, with more than half filed by residents
- Patent grants grew by 4% year-on-year
- Trademark filings increased by 60% (2018–2023), and India ranked 4th globally in trademark filings in 2023
- India now holds the second-largest number of active trademark registrations worldwide (3.2 million)
- Industrial design applications rose by 36.4%, driven by sectors like textiles, tools, and healthcare
- India’s patent-to-GDP ratio nearly tripled over the past five years
With reference to the “Special 301 Report” released by the United States Trade Representative (USTR), consider the following statements:
- It is mandated under the Trade Act of 1974 and focuses exclusively on tariff and non-tariff trade barriers.
- The report places countries under either Priority Foreign Country, Priority Watch List, or Watch List based on IP-related concerns.
- India was excluded from the 2025 review due to recent amendments to its patent laws.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 1 and 2 only
D. 2 and 3 only
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The Special 301 Report is concerned with intellectual property (IP) rights, not general trade barriers.
- Statement 2 is correct: The USTR categorizes countries into Priority Foreign Country, Priority Watch List, and Watch List.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: India continues to be on the Priority Watch List in 2025
OPEC and OPEC+
Syllabus: GS2/Important International Institutions
Context:
- Global oil prices have plummeted to multi-year lows following OPEC+’s decision to fast-track production increases, raising concerns over market stability.
About OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries):
- Establishment: Founded in 1960 at the Baghdad Conference by five countries—Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, and Venezuela.
- Current Membership: Comprises 12 oil-exporting nations — Algeria, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Venezuela.
- Headquarters: Vienna, Austria (not a member state).
- Objective: To coordinate and unify petroleum production policies among member states to ensure price stability, a regular supply to consumers, and a fair return for producers.
About OPEC+:
- Formation: Established in 2016 following the ‘Algiers Accord’ and the ‘Vienna Agreement’, in response to drastic price declines due to oversupply and rising U.S. shale oil output.
- Composition: Includes 10 non-OPEC oil-producing countries—Russia, Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan, Brunei, Bahrain, Mexico, Oman, South Sudan, Sudan, and Malaysia—alongside the 12 OPEC members.
- Mandate: Jointly manages oil output levels to stabilize global crude markets and protect the interests of both producers and consumers.
With reference to OPEC and OPEC+, consider the following statements:
- OPEC was established in response to the 1973 oil crisis and originally included only three Middle Eastern countries.
- Austria is a founding member of OPEC and hosts its headquarters in Vienna.
- OPEC+ was created to include non-OPEC oil-producing countries in coordinated production decisions.
- The ‘Algiers Accord’ and the ‘Vienna Agreement’ laid the foundation for the formation of OPEC+.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 and 4 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 3 and 4 only
Answer: B. 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: OPEC was formed in 1960, not in response to the 1973 oil crisis. The founding members included five countries—Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, and Venezuela—not just three from the Middle East.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: Austria is not a member of OPEC, though Vienna hosts OPEC’s headquarters.
- Statement 3 is correct: OPEC+ includes non-OPEC countries to coordinate oil production and manage prices.
- Statement 4 is correct: The Algiers Accord (2016) and Vienna Agreement (2016) were foundational in establishing OPEC+.
Israel Cabinet Approves Plan for Gaza Conquest
Syllabus :GS2/IR
- Israel’s Security Cabinet has approved an expansion of military operations in Gaza, which may include the potential conquest and occupation of the territory. As part of the offensive, the Israeli army has mobilized tens of thousands of reservists.
The Gaza Strip:
- The Gaza Strip is a small territory located in the Middle East, bordered by Israel to the north and east, Egypt to the southwest, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west.
- It spans 25 miles (40 kilometers) in length and 4–5 miles (6–8 kilometers) in width.
- The region is named after the ancient city of Gaza, which is situated near the northeastern end of the strip.
- Over the years, the Gaza Strip has been a focal point of conflict, with ongoing tensions and disputes over its governance and territory.
Consider the following statements regarding the Gaza Strip:
- The Gaza Strip has been a point of contention primarily between Israel and Egypt.
- The Gaza Strip is a narrow coastal area that spans approximately 25 miles in length and is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea, Israel, and Egypt.
- The region derives its name from the ancient city of Gaza, located near its northeastern end, and has historically been a site of numerous territorial conflicts.
- Israel’s recent military expansion in Gaza aims for a permanent occupation of the region, a stance that has not received significant support from the international community.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2, and 3 only
(b) 2, 3, and 4 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
correct answer: 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: This statement is partially correct as the Gaza Strip has indeed been a point of conflict primarily between Israel and Palestine, and Egypt has also been involved historically but in a lesser direct role in the conflict. Hence, this statement is misleading.
- Statement 2: This statement is correct. The Gaza Strip is a narrow territory, spanning approximately 25 miles in length and bordered by Israel, Egypt, and the Mediterranean Sea.
- Statement 3: This statement is correct. The Gaza Strip is named after the ancient city of Gaza and has been a long-standing area of territorial dispute, especially between Israel and Palestine.
- Statement 4: This statement is partially misleading. While Israel’s military expansion has been criticized, the aim to permanently occupy the region has not been explicitly endorsed in official policies or statements. The international community remains divided on this issue, with strong criticism from multiple entities.
US-China 90-Day Tariff Truce
Syllabus:IR
- The United States and China have agreed to a 90-day pause in their ongoing trade conflict following two days of talks in Geneva. Both countries will suspend all tariff hikes and non-tariff barriers imposed since April 2, with a mutual commitment to resolving trade disputes.

Background: How the Trade War Escalated
- Initial Tariffs: The U.S. began imposing tariffs in February, citing concerns over fentanyl exports from China.
- April 2 – “Liberation Day”: Marked a major escalation, with the U.S. slapping an additional 34% tariff on Chinese goods.
- China’s Response: Beijing hit back with retaliatory tariffs and non-tariff barriers, including export restrictions on rare earths and regulatory crackdowns on U.S. firms.
- By April 10:
- S. tariffs on Chinese goods: 145%
- China’s tariffs on U.S. goods: 125%
- A $100 Chinese item effectively cost $245 in the U.S.
Why Tariffs Were Imposed
- Trade Deficit: The U.S. cited a $1.2 trillion trade deficit in goods, arguing it reflected unfair trade.
- Unfair Competition: Claims that foreign nations subsidize exports and shield local firms, putting U.S. businesses at a disadvantage.
- Policy Shift: After failed diplomatic efforts, the U.S. adopted high tariffs as a defense mechanism for domestic industries.
Post-Truce Trade Landscape
- Tariff Reduction: Both countries lowered base tariffs to 10% on imports.
- S. Exception: A 20% additional tariff remains on Chinese goods tied to fentanyl concerns, totaling a 30% effective tariff.
- China’s Action: Beijing has lifted non-tariff measures, including export controls and corporate investigations.
Why the Truce Happened
- Consumer Impact: Tariffs raised prices, hurting consumers more than helping producers.
- Economic Strain: Retailers like Walmart warned of supply shortages and rising costs.
- Recession Risk: The U.S. economy contracted in Q1 2025, and economists warned of a looming recession and possible stagflation.
Conclusion
- The agreement marks a temporary ceasefire, not a resolution. With deep mistrust and complex negotiations ahead, the truce offers only a window for diplomacy — not a guaranteed peace.
With reference to the US-China Tariff Truce of 2025, consider the following statements:
- The 90-day truce completely eliminated all tariffs and non-tariff barriers between the two nations.
- One of the triggers for the initial US tariff imposition was the illicit trade in synthetic opioids.
- China’s response to US tariffs included both retaliatory tariffs and export controls on critical minerals.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Answer:B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Tariffs were reduced, not eliminated.
- Statement 2 is correct: Fentanyl trade was a key reason.
- Statement 3 is correct: China used both tariffs and non-tariff barriers like export restrictions.
Uturuncu Volcano
Syllabus:Geography
- Uturuncu, located in the Central Andes of Bolivia, is often referred to as a “zombie” volcano. Although dormant for 250,000 years, it continues to show signs of activity. Recent studies indicate that this unrest is due to the movement of magma and gases beneath the surface, and understanding these dynamics is key for assessing eruption risks and their potential impacts on local communities.
Characteristics of Uturuncu Volcano
- Uturuncu is part of the Altiplano-Puna Volcanic Complex, home to the largest known magma body in Earth’s crust. The volcano is known for its distinct “sombrero” pattern of deformation, where the center rises while the surrounding areas sink. This deformation pattern is crucial for understanding the volcano’s behaviour.
- Recent Research
- A collaborative study, conducted by institutions such as the University of Oxford and Cornell University, used advanced techniques to examine the volcano’s plumbing system. By analyzing data from over 1,700 earthquakes, the researchers created high-resolution images revealing the movement of fluids and gases beneath the surface. While the findings suggest a low likelihood of an immediate eruption, ongoing monitoring remains necessary.

Volcanic Plumbing Systems
- Volcanic plumbing systems are networks of fluids and gases that connect the magma chamber to the surface. Understanding fluid movement within these systems is essential for predicting volcanic activity. This study identified pathways for geothermally heated fluids, which are believed to contribute to the observed deformation at Uturuncu.
Seismic Tomography in Volcanology
- Seismic tomography played a critical role in the research, providing detailed insights into the internal structure of the volcano. By analyzing how seismic waves pass through different materials, researchers can create 3D images of the volcanic system. This technique is akin to medical imaging, enabling an in-depth examination of volcanic dynamics.
Implications for Local Communities
- For local populations, understanding the potential for volcanic eruptions is crucial. Although the study suggests a low probability of an eruption, continuous monitoring is important. The findings can help in disaster preparedness and risk assessment, allowing local authorities to develop strategies to protect communities from potential hazards.
Future Research Directions
- The study’s results open the door for further investigations into other volcanic systems worldwide. By applying similar methods, researchers can deepen their understanding of volcanic activity and enhance efforts to identify potential hazards and resources linked to volcanic processes.
With reference to the Uturuncu volcano and its recent study, consider the following statements:
- The Uturuncu volcano, located in the Central Andes of Bolivia, has been dormant for over 250,000 years and exhibits significant seismic activity due to the movement of magma beneath the surface.
- Seismic tomography was used to analyze the internal structure of the volcano and revealed pathways for geothermally heated fluids that contribute to surface deformation.
- The volcano is located in the Altiplano-Puna Volcanic Complex, which is known for having the largest known magma body in the Earth’s crust, making it a key area for volcanic studies.
- The study has indicated a high likelihood of an imminent eruption at Uturuncu, which requires immediate evacuation measures for the local population.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1, 2, and 3 only
B. 1, 2, and 4 only
C. 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: A. 1, 2, and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1: Correct
The Uturuncu volcano, located in the Central Andes of Bolivia, has been dormant for over 250,000 years but exhibits significant seismic activity due to magma movement beneath the surface. This is supported by the study which investigates the dynamics beneath the volcano and indicates ongoing unrest.
Statement 2: Correct
Seismic tomography was indeed used to analyze the internal structure of the Uturuncu volcano. It revealed pathways for geothermally heated fluids, which contribute to the observed surface deformation of the volcano. This helps researchers understand the behavior of fluids and gases within the volcanic plumbing system.
Statement 3: Correct
The volcano is part of the Altiplano-Puna Volcanic Complex, which houses the largest known magma body in the Earth’s crust. This is significant for volcanic studies because it indicates a large-scale volcanic system with complex dynamics, making it an important region for understanding volcanic behavior.
Statement 4: Incorrect
The study does not indicate a high likelihood of an imminent eruption at Uturuncu. Rather, the study suggests that while the volcano shows signs of unrest, the probability of an immediate eruption is low. Therefore, evacuation measures are not required based on current findings.
Maize for Ethanol Production: Fuel vs Feed crisis
Syllabus:Agriculture
Context:
- India’s demand for maize-based ethanol has surged from 0.8 million tonnes in 2022–23 to 12.7 million tonnes in 2024–25, creating pressure on feed grain availability and triggering a food-versus-fuel debate.
Maize for Ethanol – The Shift
- Biofuels help reduce dependence on fossil fuels and cut emissions
- Maize and sugarcane are the primary feedstocks
- One tonne of maize yields approximately 380 litres of ethanol
- India is the fifth-largest ethanol producer and aims for 20 percent blending by 2025
Emerging Challenges
- Grain Shortage:
- India has moved from a surplus to a deficit in maize supply
- Maize prices rose sharply from ₹15,000 to ₹25,000 per tonne
- Feed Crisis:
- Livestock feed supply is strained, especially for poultry and dairy sectors
- Feed industries are demanding genetically modified maize imports for ethanol use
- Soybean Market Disruption:
- Distillers’ Dried Grains with Soluble (DDGS), a byproduct of ethanol, competes with soybean de-oiled cake
- Soybean prices have dropped below the Minimum Support Price, affecting farmer incomes
Global Lessons
- Mandates under the U.S. Renewable Fuel Standard and European policies have previously caused food price spikes and trade disruptions during global crises
Way Forward – A Balanced Approach
- Implement flexible ethanol blending targets that can be adjusted during periods of food inflation
- Promote second- and third-generation biofuels from agricultural waste, used cooking oil, and biomass
- Allow duty-free imports of genetically modified maize exclusively for ethanol, with safeguards
- Ensure feed security through buffer stocks and support for alternative proteins
- Protect farmer interests by enforcing MSPs and supporting crop diversification and direct income transfers
Conclusion:
- India’s clean energy goals through ethanol must be carefully aligned with national food and feed security. A research-driven, flexible policy focused on advanced biofuels is essential for sustainable agricultural and energy development.
Consider the following statements regarding the use of maize for ethanol production in India:
- One tonne of maize yields less ethanol than sugarcane on average.
- The DDGS byproduct from ethanol production is a complete substitute for maize in animal feed.
- India became a net importer of maize after ethanol blending targets were raised.
- Ethanol production from maize does not affect soybean markets directly.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 4 only
Answer:C
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: One tonne of maize yields around 380 litres of ethanol, but sugarcane ethanol yield is not directly comparable due to differences in processing and sucrose content.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: DDGS is a partial, not full, substitute for maize feed.
- Statement 3 is correct: Maize diversion to ethanol led India to become a net importer.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: DDGS has undercut soy DOC prices, directly impacting soybean markets
Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project
Syllabus:Geography
Context:
 The National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA) has identified significant structural damage in the Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP) barrages in Telangana, urging immediate repairs and a comprehensive safety review.
The National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA) has identified significant structural damage in the Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP) barrages in Telangana, urging immediate repairs and a comprehensive safety review.
About Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP):
What is KLIP?
- KLIP is the world’s largest multi-stage lift irrigation project designed to divert water from the Godavari River to drought-affected regions in Telangana.
Location:
Located at Kaleshwaram in Jayashankar Bhupalpally district, Telangana, KLIP draws water from the confluence of the Pranahita and Godavari rivers.
Lift Irrigation Technology:
KLIP uses advanced lift irrigation technology to pump water from lower elevations to higher regions using massive pumps. It includes four major pump stations, with the Ramadugu station being Asia’s largest, powered by seven 140 MW pumps from BHEL.
Key Features of KLIP:
- Largest Irrigation Project: The project irrigates over 18 lakh acres of land in Telangana, drawing water from the confluence of the Godavari and Pranahita rivers.
- Infrastructure: The project includes a 500 km canal network spanning 13 districts, along with major barrages at Medigadda, Annaram, and Sundilla.
- Water Capacity: KLIP has a total water capacity of 240 TMC, with 195 TMC from the Medigadda Barrage and the remainder from the Yellampalli reservoir and groundwater.
- Multi-purpose Use: The project supports agriculture (169 TMC), supplies water to Hyderabad city (30 TMC), industry (16 TMC), and provides drinking water to rural areas (10 TMC).
About National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA):
What is NDSA?
The NDSA is a statutory body established under Section 8(1) of the National Dam Safety Act, 2021, by the Central Government. It is responsible for ensuring dam safety across India by formulating national policies and overseeing compliance with safety standards.
Headquarters: New Delhi
Key Functions of NDSA:
- Dam Regulation: Develops national policies for the design, construction, operation, and maintenance of dams.
- Dispute Resolution: Mediates conflicts between State Dam Safety Organisations (SDSOs) or between SDSOs and dam owners.
- Inspection & Oversight: Conducts periodic safety inspections of large dams.
- Disaster Preparedness: Develops emergency action plans for dam-related disasters.
- Public Awareness: Runs campaigns to raise awareness about dam safety and flood risks.
- Technical Support: Provides research, guidelines, and capacity building for dam design and hydrological safety.
Which of the following statements regarding the Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP) in Telangana is/are correct?
- KLIP is the world’s largest multi-stage lift irrigation project, aimed at diverting water from the Godavari River to drought-prone regions in Telangana.
- The project uses gravity-based irrigation systems to irrigate the agricultural fields.
- The Ramadugu pump station in KLIP is Asia’s largest pump station, powered by 7 x 140 MW pumps from BHEL.
- KLIP serves only agricultural purposes and does not supply water for industrial or urban use.
Select the correct answer:
A) 1 and 3 only
B) 1, 3, and 4 only
C) 1 and 2 only
D) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: A) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: KLIP is indeed the world’s largest multi-stage lift irrigation project aimed at diverting water from the Godavari to drought-prone regions in Telangana.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: KLIP uses lift irrigation technology, not gravity-based irrigation, to pump water to higher regions.
- Statement 3 is correct: The Ramadugu pump station, part of KLIP, is the largest in Asia, with 7 x 140 MW pumps from BHEL.
Statement 4 is incorrect: KLIP supplies water for multiple purposes, including agriculture, industry, and urban consumption
Western Disturbance
Syllabus:Geography
Context
- A strong Western Disturbance (WD) recently triggered widespread heavy rainfall, storms, hail, and flooding across Delhi and parts of North and South India, disrupting aviation and infrastructure. This event underscores the growing impact of climate change on India’s synoptic weather systems.
What Are Western Disturbances?
- Definition: WDs are eastward-moving extra-tropical weather systems that originate over the Mediterranean, Caspian, and Black Seas.
- Mechanism: They form due to interactions between polar and tropical air masses and are carried into India via the subtropical westerly jet stream.
- Nature: These systems are embedded in high-altitude winds and are often associated with low-pressure areas, bringing rain and snow, particularly during winter.
Impact on Indian Weather
- Winter Precipitation: Primary source of rainfall and snow in North India, vital for Rabi crops in Punjab, Haryana, and western Uttar Pradesh.
- Moderation of Heatwaves: Frequent WDs help reduce pre-monsoon heat intensity.
- Extreme Weather Events: Increasingly trigger hailstorms, flash floods, and landslides across Himalayan and central regions.
- Disruption of Urban Life: Lead to flight delays, waterlogging, and urban flooding, notably in Delhi.
- Monsoon Interference: Overlapping WDs disrupt monsoon timing and amplify precipitation variability.
Climate Change and Shifting WD Dynamics
- Rising Frequency & Intensity: Notable surge in WDs, especially in March–April 2025, extending into May–July, well beyond their typical December–March window.
- Jet Stream Intensification: Strengthening of the subtropical westerly jet stream has widened WD pathways, causing greater meridional (north-south) oscillations.
- Arabian Sea Warming: Rising Sea Surface Temperatures (1.2°C–1.4°C) increase atmospheric moisture, enhancing rainfall intensity and flood risk.
- More Extremes in 2025: IMD reported WD-induced hailstorms in Bihar, Himachal, Vidarbha, and flooding in Telangana and Delhi—a stark indicator of changing WD characteristics.
Policy Implications & Way Forward
- Advanced Forecasting: Invest in AI-enabled models, satellite tracking, and radar infrastructure to improve WD prediction accuracy.
- Urban Resilience: Develop city-specific WD mitigation plans, including stormwater drainage upgrades and real-time alert systems.
- Agro-Adaptation: Align sowing calendars and crop insurance with WD behaviour forecasts to safeguard food security.
- Research & Modeling: Promote cross-disciplinary research on WD dynamics and integrate findings into national and state-level climate strategies.
- Regional Cooperation: Collaborate with countries in the Hindu Kush-Himalayan region for transboundary weather risk management.
Conclusion
- Western Disturbances, once winter phenomena, have transformed into year-round climate disruptors. Intensified by global warming, they now overlap with monsoon systems, drive extreme weather, and complicate India’s weather predictability. A science-based, climate-resilient policy framework backed by regional collaboration and inter-state coordination is imperative to mitigate future risks.
Which of the following statements about Western Disturbances (WDs) is/are correct?
- WDs are extratropical cyclones originating from the Mediterranean, Caspian, and Black Seas.
- They primarily affect the Indian subcontinent during the monsoon season.
- The frequency and intensity of WDs have remained constant over the past century.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
a) 1 only
b) 1 and 2 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: a) 1 only
Explanation: WDs are extratropical cyclones originating from the Mediterranean, Caspian, and Black Seas, bringing moisture to the Indian subcontinent. They primarily affect the region during the winter and pre-monsoon seasons, not the monsoon season. Studies have shown that the frequency and intensity of WDs have been influenced by climate change, leading to alterations in their patterns.
Arunachal Pradesh Drills First Geothermal Production Well
Syllabus:Geography

- India has made a significant step towards sustainable and renewable energy with the successful drilling of the first geothermal production well in Dirang, located in the West Kameng district of Arunachal Pradesh. This groundbreaking achievement by the Centre for Earth Sciences and Himalayan Studies (CESHS) marks a major milestone in tapping into the high-altitude geothermal potential, providing eco-friendly heating solutions and aiding agricultural processing technologies in the region.
Why in the News?
- The geothermal drilling in Dirang is the first of its kind in Northeast India, setting a crucial precedent for renewable energy use in remote, mountainous regions. The geothermal well, following two years of scientific research, positions Dirang to potentially become India’s first geothermal-powered city, paving the way for clean energy access in challenging high-altitude terrains.
Key Features & Objectives
- Location: Dirang, West Kameng district, Arunachal Pradesh
- Project Lead: Centre for Earth Sciences and Himalayan Studies (CESHS)
- Support: Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of Arunachal Pradesh
International Partners:
- Norwegian Geotechnical Institute (NGI), Oslo
- Geotropy ehf, Iceland
- Guwahati Boring Service (GBS)
- Background and Scientific Details
- The project was based on two years of geochemical and structural surveys in western Arunachal Pradesh.
- Dirang was identified as a medium-to-high enthalpy geothermal zone, with an estimated reservoir temperature of 115°C.
- The geological setup features quartzite overlying schist near the Main Central Thrust (MCT), ideal for geothermal energy extraction.
Potential Applications
- Eco-friendly drying of fruits, nuts, and meat
- Space heating for high-altitude homes and institutions
- Controlled-atmosphere storage systems for agriculture
- Geothermal-powered infrastructure for future cities
Significance
- This is the first geothermal production well in the Northeast, marking a pioneering effort in clean and renewable energy use in the Himalayan region.
- It offers sustainable heating solutions for cold, high-altitude areas and could bolster agro-economy and energy self-reliance.
- The project sets a national precedent for the application of geothermal energy in remote regions, bringing India closer to a renewable and self-sufficient energy future.
Consider the following statements regarding the first geothermal production well drilled in Dirang, Arunachal Pradesh:
- The geothermal well was drilled as part of a project led by the Ministry of Earth Sciences and supported by international partners, including the Norwegian Geotechnical Institute (NGI) and Geotropy ehf.
- Dirang was identified as a high-enthalpy geothermal zone, with the potential for temperatures reaching up to 200°C, making it suitable for large-scale energy production.
- The geothermal well aims to provide eco-friendly energy solutions, including space heating, controlled-atmosphere storage for agriculture, and fruit and meat drying.
- This initiative is the first of its kind in the Northeast region of India and is expected to establish Dirang as India’s first geothermal-powered city.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A) 1, 3, and 4 only
B) 2 and 4 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: A) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The geothermal well project was led by the Centre for Earth Sciences and Himalayan Studies (CESHS) and supported by international partners like NGI and Geotropy ehf.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: Dirang is identified as a medium-to-high enthalpy geothermal zone with an estimated reservoir temperature of 115°C, not 200°C.
- Statement 3 is correct: The geothermal well is intended for eco-friendly applications like space heating, agriculture storage systems, and drying of fruits and meat.
- Statement 4 is correct: This project is the first geothermal production well in Northeast India and has the potential to establish Dirang as India’s first geothermal-powered city.
NRFMTTI achieves CMVR testing approval for Agricultural Tractors
Syllabus:Geography
- The Northern Region Farm Machinery Training & Testing Institute (NRFMTTI), Hisar (Haryana) has achieved two major milestones:
- Approval as a CMVR Testing Agency for Agricultural Tractors
- NABL Accreditation for CMVR Testing of Agricultural Tractors and Combine Harvesters
- NRFMTTI, a premier institution in the field of training and testing of agricultural machinery, is now an authorized agency to carry out CMVR (Central Motor Vehicle Rules) testing for agricultural tractors, in addition to combine harvesters.
- The institute has also been granted NABL (National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories) accreditation, further validating the quality and reliability of its CMVR testing services.
- This development will significantly benefit tractor manufacturers in Northern India, allowing them to conduct mandatory CMVR testing locally at NRFMTTI. Furthermore, NABL-accredited CMVR certification will improve the global credibility and acceptance of test results for agricultural tractors and combine harvesters, supporting domestic industry and exports.
Which of the following statements regarding the recent accreditation and approval granted to NRFMTTI, Hisar is/are correct?
- It has been approved as a CMVR testing agency exclusively for Combine Harvesters.
- It has received NABL accreditation for CMVR testing of both agricultural tractors and Combine Harvesters.
- The institute is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Heavy Industries.
- The CMVR certification by NABL-accredited institutions is mandatory for domestic tractor sales under the Farm Mechanization Policy.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
A. 2 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 3 and 4 only
Answer:A.2only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect — NRFMTTI is approved for both tractors and harvesters.
- Statement 3 is incorrect — it is under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare.
- Statement 4 is incorrect — while CMVR compliance is legally required, NABL certification enhances global acceptance but is not specifically mandated under a “Farm Mechanization Policy.”
Enhancing Competitiveness of MSMEs in India Report
Syllabus:Report
Context:
- NITI Aayog has released a report on “Enhancing MSMEs Competitiveness in India,” outlining key reforms necessary for improving financing, skilling, and technology adoption for the growth of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
- About the “Enhancing MSMEs Competitiveness in India” Report:
Released by:
- NITI Aayog in collaboration with the Institute for Competitiveness (IFC).

Objective:
- To provide a strategic blueprint for enhancing the growth and competitiveness of MSMEs in India through policy reforms in credit access, skilling, innovation, and market linkages.
Key Findings:
- Improvement in Credit Access (2020-24):
- The share of micro and small enterprises accessing formal credit increased from 14% in 2020 to 20% in 2024.
- For medium enterprises, this share grew from 4% to 9% in the same period.
- Despite this, only 19% of total MSME credit demand was met, leaving a gap of ₹80 lakh crore.
Skill & Technology Challenges:
- The report highlights a significant gap in formal vocational training for MSME workers.
- It urges increased investments in Research & Development (R&D) and the upgradation of outdated technology.
- Recommendations include supporting digital marketing, branding, and the adoption of cluster-based technology solutions.
Policy Awareness Gap:
- Many MSMEs remain unaware of available government schemes and initiatives.
- The report calls for better data integration, stakeholder engagement, and state-level monitoring to address this issue.
Regional Focus:
- The report emphasizes the need for targeted support for MSMEs in Northeast and Eastern India, including incentives and logistics partnerships to improve their competitiveness.
About NITI Aayog:
What is NITI Aayog?
- NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India) is India’s apex public policy advisory body, established to replace the Planning Commission in 2015. Its core mandate is to promote cooperative and competitive federalism and foster innovation and sustainable development.
Key Details:
- Established: January 1, 2015
- Mandate: To foster evidence-based policymaking, innovation, and sustainable development.
- Chairperson: The Prime Minister of India
- Vice Chairperson: Appointed by the Government.
Structure:
- Governing Council: Comprising all Chief Ministers, Lieutenant Governors, and Union Ministers.
- Members: Full-time and part-time members drawn from academia, industry, and administration.
Other Notable Reports by NITI Aayog:
- Strategy for New India @75
- India Innovation Index
- SDG India Index
- Export Preparedness Index
- School Education Quality Index (SEQI)
- Ease of Doing Business: State Rankings
- National Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI)
Which of the following statements are correct regarding NITI Aayog’s report on “Enhancing MSMEs Competitiveness in India”?
- The share of micro and small enterprises accessing formal credit increased from 14% to 20% between 2020 and 2024.
- The report recommends increasing R&D investments but does not emphasize technology adoption for MSMEs.
- The credit demand of MSMEs was fully met during the 2020–2024 period.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
a) 1 only
b) 1 and 2 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: a) 1 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct as the share of micro and small enterprises accessing formal credit rose from 14% to 20%.
- Statement 2 is incorrect as the report emphasizes both R&D investment and technology adoption.
- Statement 3 is incorrect since only 19% of the total credit demand was met, leaving a significant gap.
DRDO develops high-pressure polymeric membrane for sea water desalination
Syllabus:Defence
- The Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully developed an indigenous nanoporous multilayered polymeric membrane designed for high-pressure seawater desalination.
- This advanced technology has been developed by the Defence Materials Stores and Research & Development Establishment (DMSRDE), a DRDO laboratory based in Kanpur, specifically to meet the operational needs of the Indian Coast Guard (ICG).
- Addressing the critical issue of membrane stability in chloride-rich saline environments, the innovation was completed in a record time of just eight months.
- The technology has been integrated into the desalination systems aboard ICG’s Offshore Patrol Vessels (OPVs), where initial technical trials have been conducted successfully.
- These safety and performance trials demonstrated that the membrane performed to expectations under operational conditions.
- The final operational clearance will be granted by the ICG following 500 hours of rigorous field testing currently underway on the OPVs.
- Once validated, this membrane will also have the potential to be adapted for civilian desalination applications in coastal regions, offering a significant technological edge.
- This achievement marks another milestone in DRDO’s contribution to Aatmanirbhar Bharat, reinforcing India’s self-reliance in advanced defence and dual-use technologies.
Consider the following statements regarding the indigenous nanoporous multilayered polymeric membrane developed by DRDO for seawater desalination:
- The membrane technology was developed to specifically counter the destabilizing effects of magnesium ions in seawater.
- The development was led by Defence Materials Stores and Research & Development Establishment (DMSRDE), Kanpur.
- Initial operational trials were conducted on Indian Coast Guard Offshore Patrol Vessels (OPVs).
- Final operational clearance requires at least 500 hours of testing.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A) 1, 2 and 3 only
B) 2, 3 and 4 only
C) 1 and 4 only
D) All of the above
Answer: B) 2, 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The membrane was designed to address the challenge of stability against chloride ions, not specifically magnesium ions.
- Statement 2 is correct: DMSRDE, Kanpur developed the technology.
- Statement 3 is correct: Trials were conducted on Indian Coast Guard OPVs.
- Statement 4 is correct: Final clearance will be given after 500 hours of operational testing.
Pune: Asia’s first subsea research lab at MIT-World Peace University
Syllabus: Miscellaneous

- In a landmark initiative for technical education and energy sector training, the MIT World Peace University (MIT-WPU), Pune, has inaugurated Asia’s first Centre for Subsea Engineering Research (CSER). The state-of-the-art facility is established in collaboration with Aker Solutions, a global engineering services provider, and aims to transform education, research, and skill development in subsea technologies critical to the oil and gas sector.
Bridging the Industry-Academia Skill Gap
- Spearheaded by the Department of Petroleum Engineering, the CSER is intended to address the persistent skill gap in India’s energy industry. According to Samarth Patwardhan, Head of the CSER and Professor of Petroleum Engineering at MIT-WPU, the lab is envisioned as a breeding ground for multi-disciplinary talent, capable of meeting the evolving demands of global subsea exploration and production systems.
An Experiential Learning Platform
- The facility is equipped to support real-time simulation of drilling and well-control systems, offering undergraduate and postgraduate students a rare opportunity to gain hands-on experience through curriculum-integrated experiments. In addition to academic learning, the lab supports professional training programs in subsea engineering and Industrial Safety and Health Engineering (ISHE), facilitating continued education and industry readiness.
Fostering Awareness and Collaboration
- Beyond academic instruction, the CSER is designed to serve a broader societal purpose by organizing educational outreach programs for school and college students and technical tours for industry professionals. These initiatives aim to enhance public understanding of subsea technologies and their significance in sustainable energy development.
- In pursuit of collaborative research and innovation, the lab seeks to establish national and international partnerships with industry and governmental agencies. Such collaborations are expected to catalyze innovation, address pressing challenges in offshore energy, and contribute to India’s energy security framework.
Role of Aker Solutions
- Aker Solutions has played a critical role in the realization of the CSER. From conceptualization to the final deployment of systems, the company has contributed expertise in design, procurement, fabrication, installation, and testing. The strategic alliance between Aker and MIT-WPU sets a precedent for how academia and industry can jointly enhance technical capacity and address sectoral skill shortages.
The Centre for Subsea Engineering Research (CSER) at MIT-World Peace University primarily aims to:
- Address the skill gap in India’s oil and gas subsea industry.
- Promote multidisciplinary research on marine biodiversity conservation.
- Facilitate joint academic-industry collaborations for subsea engineering innovations.
- Develop indigenous offshore drilling technology to replace imports.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 4 only
D) 1, 3 and 4 only
Answer: B) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- The Centre for Subsea Engineering Research (CSER) at MIT-World Peace University primarily focuses on addressing the skill gap in the subsea oil and gas sector by providing practical training and multidisciplinary education (Statement 1).
- It also facilitates collaboration between academia and industry to foster innovation in subsea engineering (Statement 3).
- However, promoting multidisciplinary research on marine biodiversity conservation (Statement 2) is not the primary aim of CSER, as the lab’s focus is more technical and industry-specific rather than ecological or environmental conservation.
- Developing indigenous offshore drilling technology to replace imports (Statement 4) was not explicitly mentioned as a goal; the emphasis is more on training, research collaboration, and skill development rather than direct technology replacement.
- Hence, only statements 1 and 3 are correct.
International Day of Light 2023 celebrates on 16th May
Syllabus:Important Day

- The International Day of Light is celebrated globally on May 16 each year to commemorate a landmark moment in scientific history—the successful operation of the first laser by physicist Theodore Maiman in 1960.
- This observance aims to highlight the vital role light plays in various spheres of life and to promote international scientific cooperation for advancing peace and sustainable development.
Significance of the Day
- The International Day of Light underscores the multifaceted importance of light and light-based technologies across disciplines:
- In science and technology, it serves as a catalyst for innovation, particularly in fields like photonics, telecommunications, medicine, and clean energy.
- In culture and art, light continues to inspire creativity and expression.
- In education, light-based tools are revolutionizing learning and research.
- In the context of sustainable development, technologies based on light are essential in achieving global goals such as clean energy, health, and information access.
- The day acts as a platform to enhance public awareness, foster interdisciplinary partnerships, and celebrate the achievements of scientists, engineers, and researchers who contribute to the advancement of light technologies and their applications.
Historical Background
- The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) officially proclaimed the International Day of Light on December 20, 2017, with the aim of celebrating the transformative power of light.
- The date, May 16, was chosen to honor Theodore Maiman’s invention of the laser—a cornerstone of modern light-based technology.
- Since its establishment, the International Day of Light has evolved into a global event, marked by scientific conferences, public lectures, exhibitions, and educational activities that promote the responsible use of light for the betterment of society.
With reference to the International Day of Light, consider the following statements:
- The day commemorates the development of the first optical fiber system, which revolutionized global communication networks in the 1970s.
- It is observed annually on May 16 to mark a milestone scientific event related to laser technology.
- The day aims to promote the role of light in achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- The initiative is led by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), a specialized agency of the United Nations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 2 and 3 only
B. 1 and 4 only
C. 1, 2 and 4 only
D. 2, 3 and 4 only
Answer: A. 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Incorrect. The International Day of Light does not commemorate the development of optical fiber systems in the 1970s. It marks the successful operation of the first laser by Theodore Maiman in 1960.
- Statement 2: Correct. The day is observed on May 16 each year in recognition of the laser breakthrough by Maiman.
- Statement 3: Correct. One of the core aims of the International Day of Light is to highlight the role of light-based technologies in achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) such as education, clean energy, and health.
- Statement 4: Incorrect. The initiative is coordinated by UNESCO, not the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
