Global Free Speech Survey 2024
- The Future of Free Speech report, conducted in October 2024 by an independent think tank, ranks India 24th among 33 countries, highlighting concerns about the protection of controversial speech.
- While many Indians value free speech, their support for government criticism is notably low. The Future of Free Speech Index ranks countries based on public support for free expression.
- The 2024 survey shows a global decline in free speech support since 2021.
- Notably, democratic nations like the United States and Japan have experienced drops, whereas Scandinavian countries, including Norway and Denmark, lead the rankings with the highest scores.
- India scored 62.6, positioned between South Africa and Lebanon. Despite a strong abstract support for free speech, commitment to protecting controversial speech has weakened.
- A concerning 37% of Indian respondents believe the government should restrict criticism of its policies, the highest percentage among surveyed nations, contrasting with just 5% in the UK. The survey indicates a disconnect in India.
- While many claim to support free speech, actual protections are lacking. This trend mirrors patterns seen in Hungary and Venezuela, where public sentiment does not align with government actions, signaling democratic backsliding.
- When asked about changes in their ability to speak freely, Indians expressed a belief in improvement over the past year.
- However, observers suggest the reality has worsened, pointing to a gap between public perception and the actual state of free speech in India.
- The report notes that free speech extends beyond legal rights and requires a culture of open debate and tolerance for dissent.
- The erosion of willingness to defend controversial speech is evident, threatening the essence of free expression.
- Globally, support for free speech tends to correlate with actual freedom of expression. However, India’s situation is atypical.
- Nations with high public support usually enjoy better protections, yet in India, the opposite is true.
- The survey explored various aspects of free speech, including attitudes toward censorship, criticism of the government, and sensitive topics. Support for free speech often declines when it involves offensive content or criticism of religion, reflecting a complex landscape of public opinion.
With reference to the “Future of Free Speech” report, consider the following statements:
- The 2024 survey indicates that support for free speech has increased globally compared to 2021.
- Scandinavian nations, particularly Norway and Denmark, have ranked the highest in the index.
- India’s ranking in the index suggests that public support for free speech correlates directly with actual protections.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The report highlights a decline in free speech support globally since 2021, especially in democratic nations like the US and Japan.
Statement 2 is correct: Norway and Denmark have consistently scored the highest in the rankings, showing strong public and institutional support for free speech.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The report suggests that while India has public support for free speech, actual protections remain weak. This contradicts the usual correlation seen in other nations.
Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0
- The Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0, introduced by the Union government, aims to overhaul India’s intricate legal system.
- This initiative is part of a broader effort to improve the ease of living by addressing excessive criminalisation and ensuring laws are fair, enforceable, and humane.
- The Vidhi Centre for Legal Policy has highlighted the vast number of criminal provisions in India’s legal framework, many of which impose disproportionate penalties for minor infractions.
India’s Overburdened Legal System
- India currently has 882 central laws, of which 370 contain criminal provisions, covering a staggering 7,305 offences.
- While some laws address serious crimes such as murder and financial fraud, many govern everyday activities like parenting, local community events, and business operations.
- The legal landscape often imposes severe penalties, including life imprisonment and even the death penalty, for offences that may not always warrant such harsh measures.
The Problem of Over-Criminalisation
- A significant issue with India’s current legal system is the criminalisation of minor infractions.
- Citizens can face imprisonment for trivial acts such as failing to report the death of a pet or improper storage of e-cigarettes.
- This overreach blurs the distinction between serious and minor offences, leading to arbitrary enforcement by authorities and increasing the risk of legal exploitation.
Disproportionate Punishments and Legal Inconsistencies
- One of the key concerns is the lack of proportionality in punishments.
- For instance, the Mental Healthcare Act prescribes the same jail term for record-keeping errors as it does for major medical violations.
- Such inconsistencies weaken public trust in the justice system and create a disjointed legal structure that does not align with societal needs.
Social and Economic Impact
- The consequences of harsh legal provisions fall disproportionately on the poor, who often lack access to legal resources.
- With low conviction rates, the judicial process itself becomes a form of punishment, leading to prolonged pretrial detentions.
- Many individuals suffer due to outdated or unjust laws that fail to reflect contemporary realities.
Principles of Legal Reform
The Vidhi Centre for Legal Policy has outlined four key principles for legal reform:
- Preserving Societal Values – Ensuring laws reflect ethical and cultural norms.
- Preventing Justifiable Harm – Criminal laws should address actions that cause significant harm to individuals or society.
- Ensuring Effective Legal Solutions – Laws should provide clear and enforceable
- Proportionality in Punishments – Penalties should correspond to the severity of offences.
Future Legal Reforms
- The Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0 seeks to shift the focus from punitive justice to restorative justice, reducing unnecessary legal burdens and prioritising reforms that benefit citizens.
- A key objective is to decrease the number of undertrial prisoners and streamline judicial procedures to create a more efficient, equitable, and transparent legal system.
- As India moves forward, legal reforms must prioritize justice, fairness, and societal well-being to enhance the quality of life for all citizens.
With reference to the Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0, consider the following statements:
- It aims to reduce excessive criminalisation by eliminating all provisions of imprisonment from central laws.
- The Bill is a step towards prioritising restorative justice over punitive measures.
- It was introduced by the Ministry of Law and Justice to rationalise sentencing in criminal laws.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0 does not eliminate all provisions of imprisonment but seeks to reduce disproportionate criminalisation of minor infractions.
- Statement 2 is correct: The Bill emphasises restorative justice by focusing on proportionality in punishments and rationalising legal penalties.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The Ministry of Law and Justice is not responsible for introducing the Bill; rather, it is a broad government initiative to reform laws across multiple sectors.
India Takes 24th Spot in Free Speech Survey
A global survey by The Future of Free Speech ranked India 24th out of 33 countries on support for free speech.
Constitutional Provisions
- Article 19(1)(a) of the Indian Constitution guarantees every citizen the Right to Freedom of Speech and Expression.
Key Findings:
- Norway and Denmark secured the top positions in the Future of Free Speech Index, with scores of 87.9 and 87.0, respectively.
- Indonesia (56.8), Malaysia (55.4), and Pakistan (57.0) demonstrated the most significant improvements; however, they continued to rank on the lower end of the index.
- Interestingly, some authoritarian-leaning nations, such as Hungary (85.5) and Venezuela (81.8), achieved high scores, indicating a disparity between government-imposed restrictions and public sentiment toward free speech.
The Supreme Court has interpreted this right to include various aspects, such as:
- Right to propagate one’s own views as well as those of others.
- Freedom to remain silent.
- Freedom of the press.
- Right against the imposition of pre-censorship on newspapers.
- Freedom to publish commercial advertisements.
- Right to protection from unlawful telephone tapping.
- Reasonable Restrictions (Article 19(2))
The Right to Freedom of Speech and Expression is not absolute and is subject to reasonable restrictions imposed by the State on the following grounds:
- Security of the State
- Sovereignty and Integrity of India
- Public Order
- Friendly Relations with Foreign States
- Decency and Morality
- Contempt of Court
- Defamation
- Incitement to an Offense
- These restrictions ensure that freedom of speech is exercised responsibly while balancing individual rights with national security and social harmony.
Consider the following statements regarding the Right to Freedom of Speech and Expression under the Indian Constitution:
- The right includes the freedom to propagate both one’s own views as well as those of others.
- Commercial advertisements are not covered under the ambit of Article 19(1)(a).
- The right to remain silent has been recognized as part of the freedom of speech by the Supreme Court of India.
- The state can impose restrictions on free speech on grounds of public interest and economic justice.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 1, 2, and 3 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Supreme Court has ruled that the freedom of speech includes the right to propagate both one’s own views and those of others.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: Commercial advertisements are protected under Article 19(1)(a). However, they can be restricted under reasonable limitations.
- Statement 3 is correct: The right to remain silent was upheld in the Bijoe Emmanuel Case (1986), where students refusing to sing the national anthem were protected under freedom of speech.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: Restrictions under Article 19(2) are limited to sovereignty, integrity, security, friendly relations, public order, decency, morality, contempt of court, defamation, and incitement to an offense. Public interest and economic justice are not valid grounds for restriction.
Finance Commission
Syllabus: Polity
- The Finance Commission (FC) is a constitutional body established under Article 280 of the Indian Constitution.
- It is formed every five years by the President of India to recommend the financial distribution between the Centre and States.
Composition:
- Chairman: An expert in public affairs.
- Four Members: Experts in finance, economics, and administration.
Functions:
- Vertical Devolution: Determines the state’s share in the central divisible pool of taxes (e.g., GST, income tax).
- Horizontal Distribution: Allocates funds among states based on factors like fiscal needs, revenue-generating capacity, and developmental performance.
- Grants-in-Aid: Recommends grants to revenue-deficient states and specific sectors in need of financial assistance.
16th Finance Commission
- Constituted in 2023, it will recommend financial distribution for the period April 1, 2026 – March 31, 2031.
- Expected to address states’ financial concerns, including demands for Special Category Status (SCS).
Special Category Status (SCS): Understanding the Demand
What is SCS?
- Special Category Status (SCS) is a classification granted to states facing severe economic and geographical disadvantages to provide them with additional central assistance.
- It was introduced in 1969 based on the Gadgil Formula, recommended by the 5th Finance Commission (Mahavir Tyagi).
- Initially granted to Assam, Jammu & Kashmir, and Nagaland.
Criteria for Special Category Status (As per Gadgil Formula):
A state must meet the following conditions:
- Hilly and difficult terrain.
- Low population density and/or a significant tribal population.
- Strategic location along international borders.
- Economic and infrastructural backwardness.
- Non-viable state finances.
Evolution and States with SCS
Initially granted to three states (1969), later expanded.
Currently, 11 states hold SCS:
- Northeast states: Assam, Nagaland, Manipur, Meghalaya, Tripura, Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, and Sikkim.
- Hilly states: Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
- Telangana: Granted due to bifurcation from Andhra Pradesh.
States Demanding SCS:
- Andhra Pradesh (Due to bifurcation).
- Bihar (Citing economic backwardness).
- Odisha (Due to natural disaster vulnerability and underdevelopment).
Benefits of Special Category Status (SCS):
Higher Central Assistance:
- 90% of funds as grants and 10% as loans for Centrally Sponsored Schemes (CSS).
- Non-SCS states receive only 30% grants and 70% loans.
Special Plan Assistance:
- Dedicated funding for state-specific projects of strategic importance.
Non-Lapsable Funds:
- Unused funds do not lapse at the end of the financial year, ensuring continuity in funding.
Tax Concessions:
Special tax incentives (many now subsumed under GST).
Conclusion
- The demand for Special Category Status remains a contentious issue, especially for states like Bihar, which seek additional financial support due to economic underdevelopment.
- With the 16th Finance Commission’s recommendations expected in the coming years, the debate on SCS is likely to gain momentum.
With reference to the Finance Commission of India, consider the following statements:
- The Finance Commission is a statutory body established by an Act of Parliament.
- It is responsible for recommending the allocation of financial resources between the Centre and States.
- The recommendations of the Finance Commission are binding on the government.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- The Finance Commission is a constitutional body, not a statutory body, as it is established under Article 280 of the Indian Constitution. Hence, Statement 1 is incorrect.
- Its primary function is to recommend how financial resources should be distributed between the Centre and States. Hence, Statement 2 is correct.
- The recommendations of the Finance Commission are not binding on the government. They are only advisory in nature. Hence, Statement 3 is incorrect.
Vice-President Criticised Freebies Culture
Syllabus :GS 2/Governance
What Are Freebies?
- Freebies refer to goods, services, or financial incentives provided by political parties, often during elections, to attract voters.
- While there is no formal definition, they commonly include free electricity, LPG connections, bicycles, loan waivers, and direct cash transfers.
Challenges and Concerns
Fiscal Burden:
- Excessive spending on freebies strains state finances, leading to fiscal deficits and rising public debt, which can weaken long-term economic stability.
Resource Allocation Issues:
- Prioritizing freebies diverts funds from essential sectors like infrastructure, education, and healthcare, affecting sustainable development.
Economic Inefficiency and Dependency:
- Freebies may encourage inefficient resource utilization and foster dependency, rather than addressing structural issues like poverty and unemployment.
Competitive Populism:
- Political parties engage in a race to outdo each other in offering freebies, often at the cost of sound economic policy and governance reforms.
Impact on Policy Reforms:
- Over-reliance on freebies shifts focus from essential governance measures, such as skill development, employment generation, and education reforms.
Constitutional Perspective:
- While Article 38 of the Indian Constitution mandates the State to promote social welfare and reduce inequalities, unchecked freebies can threaten financial sustainability.
Supreme Court’s Observations
- The Supreme Court has criticized the practice of pre-election freebies, noting that they:
- Distort electoral fairness by influencing voter preferences.
- Undermine work ethic, discouraging economic participation.
Views of Experts
- Former RBI Governor Duvvuri Subbarao warned against freebies’ detrimental impact on state finances.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi has termed the practice of offering freebies as distributing “revris” (sweets) for votes, calling it short-term populism over long-term progress.
- Suggestions & Way Forward
National Policy on Freebies:
- Establish clear guidelines on government expenditures to ensure they contribute to sustainable development.
Code of Conduct & National Dialogue:
- A collective effort, led by the Centre, to regulate and rationalize the distribution of freebies.
Targeted Welfare Programs:
- Instead of blanket freebies, focus on data-driven welfare measures that cater to genuinely needy populations, improving long-term outcomes.
With reference to the economic impact of freebies, consider the following statements:
- Freebies contribute to long-term economic growth by increasing aggregate demand in the economy.
- Competitive populism associated with freebies can lead to fiscal imprudence and higher public debt.
- The opportunity cost of freebies often results in underfunding of critical sectors like healthcare and education.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: While freebies may temporarily boost aggregate demand, they do not necessarily contribute to long-term economic growth as they often fail to create productive assets.
Statement 2 is correct: Competitive populism escalates fiscal deficits as states compete to provide more benefits without considering fiscal sustainability.
Statement 3 is correct: The opportunity cost of excessive freebie spending leads to underinvestment in critical infrastructure and social sectors, affecting long-term development.
PM’s Visit to Mauritius
Syllabus:IR
- The Prime Minister of India recently paid a state visit to Mauritius, marking his second visit since 2015. He was the Chief Guest at Mauritius’ National Day Celebrations on March 12.
Key Highlights of the Visit
- Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs): Agreements signed in areas such as civil service training, support for small and medium enterprises (SMEs), blue economy development, combating financial crimes, and local currency settlement for trade.
- INR-Based Credit Line: India extended an INR 487.6 crore line of credit for replacing water pipelines in Mauritius, the first-ever INR-denominated credit line.
- White-Shipping Agreement: A maritime security agreement facilitating information exchange between India and Mauritius.
- Award Conferred: The PM received the Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean, becoming the first Indian recipient of this prestigious award.
- Vision MAHASAGAR: The PM introduced the Mutual And Holistic Advancement for Security And Growth Across Regions (MAHASAGAR) vision, expanding upon the existing Vision SAGAR framework.
About Mauritius
Location: A strategically positioned island nation in the western Indian Ocean near India.
Population: Approximately 1.2 million people, with 70% of Indian origin, strengthening historical and cultural ties.
Colonial History: Initially a French colony, later becoming a British possession before gaining independence.
National Day: Celebrated on March 12, coinciding with Mahatma Gandhi’s Dandi March anniversary.
India-Mauritius Bilateral Relations
- Diplomatic and Economic Ties
- Established Relations: India and Mauritius established diplomatic ties in 1948 and have since become key partners in the Asian and Indian Ocean regions.
Bilateral Trade (2022-2023):
- Indian Exports to Mauritius: USD 462.69 million
- Mauritian Exports to India: USD 91.50 million
- Total Trade Volume: USD 554.19 million
- Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA): Signed in 1982 to prevent double taxation for investors and businesses.
- Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA): India’s first trade agreement with an African nation, signed in 2021, promoting trade and investment.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Mauritius is the second-largest source of FDI into India for FY 2023-24, following Singapore.
Defence and Strategic Cooperation
Preferred Defence Partner: India supports Mauritius in acquiring defence platforms, capacity building, and conducting joint patrols in the Indian Ocean.
Key Defence Agreements:
First Agreement: Transfer of a Dornier aircraft and Advanced Light Helicopter (Dhruv) on lease.
Second Agreement: A USD 100 million Line of Credit (LoC) for defence procurement.
Space Cooperation: An MoU signed in November 2023 for the development of a joint satellite, fostering collaboration in space research.
Historical Indian Migration to Mauritius
French Rule (1700s): Indians from Puducherry arrived as artisans and masons.
British Rule (1834–Early 1900s): Around half a million Indian indentured laborers were brought to Mauritius, many of whom settled permanently, shaping its culture and demographics.
Development Assistance
- Infrastructure Projects: India has supported Mauritius in developing the Metro Express project, hospitals, and Agaléga Island infrastructure.
- Humanitarian Aid: India extended cyclone relief assistance during Cyclone Chido (2023), reinforcing its role as a first responder in the region.
Strategic Significance of Mauritius for India
Maritime and Geopolitical Interests
Strategic Location: Mauritius’ position in the Indian Ocean is vital for India’s maritime security and trade routes.
Agaléga Island: Situated 1,100 km north of Mauritius, the island is strategically important for India’s naval operations.
In 2024, India and Mauritius jointly inaugurated an airstrip and jetty projects to strengthen bilateral cooperation.
Countering China’s Influence: Strengthening ties with Mauritius is crucial for India to counter China’s expanding footprint in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
Geopolitical Competition: The Indian Ocean is witnessing increasing competition from China, Europe, the Gulf nations, Russia, Iran, and Turkey.
Economic and Cultural Importance: Cultural and Diaspora Ties: With 70% of the Mauritian population tracing Indian ancestry, strong cultural and familial bonds exist between both nations.
Blue Economy Partnership: Mauritius plays a critical role in India’s blue economy initiatives, particularly in fisheries, maritime resources, and offshore energy exploration.
Indian Ocean Cooperation: Mauritius is an active member of the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), promoting regional stability and economic integration.
Challenges in India-Mauritius Relations
Economic and Trade Concerns
Tax Treaty Misuse: The DTAA between India and Mauritius has faced criticism for facilitating money laundering and round-tripping of funds.
Trade Imbalance: Despite strong economic ties, Mauritius has significant trade deficits with India, necessitating trade diversification.
Security and Strategic Challenges
Maritime Security: As a key player in the Indo-Pacific strategy, Mauritius’ security concerns align with India’s, yet evolving regional dynamics present new challenges.
Growing Chinese Influence:
- In 2021, China signed a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with Mauritius, helping China expand its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) in Africa.
- This could erode India’s strategic influence in Mauritius.
Way Forward
- Enhanced Defence Cooperation: Strengthening joint training, counterterrorism initiatives, and maritime security collaborations to safeguard regional stability.
- Economic Diversification: Expanding trade relations beyond traditional areas and exploring emerging sectors for bilateral growth.
- People-to-People Ties: Promoting cultural exchanges, educational scholarships, and diaspora engagement to reinforce deep-rooted historical bonds.
- Sustainable Blue Economy Partnership: Leveraging Mauritius’ expertise in ocean resources management to drive mutual economic growth.
- India and Mauritius share a unique, time-tested partnership, and their evolving cooperation will play a crucial role in shaping regional security, economic integration, and strategic alliances in the Indian Ocean region.
Consider the following statements regarding India-Mauritius relations:
- Mauritius is the largest source of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) into India.
- India and Mauritius have signed a Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA), which is India’s first trade agreement with an African nation.
- India has leased the Agaléga Islands from Mauritius for setting up a strategic naval base.
- The White-Shipping Agreement between India and Mauritius facilitates free trade between the two nations without tariff barriers.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (c) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect – While Mauritius has historically been a major source of FDI into India, Singapore overtook Mauritius as the largest FDI contributor in recent years (FY 2023-24). Therefore, this statement is incorrect.
- Statement 2 is correct – India and Mauritius signed CECPA in 2021, which is indeed India’s first-ever trade agreement with an African nation. This statement is correct.
- Statement 3 is incorrect – India has not leased the Agaléga Islands, but developed infrastructure projects there, including an airstrip and a jetty, to enhance maritime security. There is no official declaration of a naval base. This statement is incorrect.
- Statement 4 is incorrect – The White-Shipping Agreement is not about free trade. It is a technical agreement that allows exchange of maritime security data between India and Mauritius to monitor ship movements and counter threats like piracy and smuggling. This statement is incorrect.Thus, only statement 2 is correct, making (c) 2 only the right answer.
PM Modi Receives Mauritius’ Highest Honour
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi has been awarded the Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean by Mauritius.
- This prestigious recognition is the highest civilian honour bestowed by the island nation.
- Modi is the first Indian to receive this honour, reflecting the deep-rooted historical and diplomatic ties between India and Mauritius.
Significance of the Honour
- The Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean is the most distinguished civilian award in Mauritius.
- Since Mauritius became a Republic, this honour has been conferred upon only five foreign dignitaries, including Nelson Mandela.
- The award symbolizes mutual respect, cooperation, and the strong diplomatic relationship between India and Mauritius.
Modi’s Growing List of International Honours
This accolade from Mauritius marks Modi’s 21st international award, adding to a series of global recognitions for his leadership and diplomatic initiatives. Some of the notable awards he has received include:
- Order of Abdulaziz Al Saud (Saudi Arabia, 2016)
- State Order of Ghazi Amir Amanullah Khan (Afghanistan, 2016)
- Grand Collar of the State of Palestine (Palestine, 2018)
- Order of Zayed (UAE, 2019)
- Order of St. Andrew (Russia, 2019)
- Order of the Nile (Egypt, 2023)
- Order of the Druk Gyalpo (Bhutan, 2024)
- Dominica Award of Honour (Dominica, 2024)
India-Mauritius Relations: A Historical Perspective
- The ties between India and Mauritius date back to the 19th century, when Indian indentured labourers were brought to Mauritius. Over time, these historical connections have evolved into a robust economic, cultural, and strategic partnership.
- India is one of Mauritius’ largest trading partners.
- Both countries collaborate extensively in fields such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, and security.
- Mauritius is a key player in India’s diplomatic outreach in the Indian Ocean region, with both nations working closely on maritime security and regional stability.
Conclusion
- The Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean is a testament to India-Mauritius friendship and underscores Modi’s global leadership. This honour further strengthens bilateral ties and reaffirms India’s role as a key partner in Mauritius’ development.
Which of the following statements about the “Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean” is correct?
(a) It is the highest military honour awarded by Mauritius.
(b) It has been awarded to more than 100 foreign dignitaries since Mauritius became a Republic.
(c) Narendra Modi is the first Indian recipient of this honour.
(d) It is an annual award given to prominent global leaders.
Answer: (c)
Explanation:
- The Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean is Mauritius’ highest civilian honour, not a military one. It has been conferred upon only five foreign dignitaries, including Nelson Mandela, since Mauritius became a Republic.
- Modi is the first Indian to receive this honour.
- The award is not an annual event but is given selectively to leaders who have significantly contributed to Mauritius’ growth and bilateral .
Sansad Bhashini Initiative
Syllabus: Government Schemes
- The Lok Sabha Secretariat, in collaboration with the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), has launched ‘Sansad Bhashini’, an AI-driven initiative aimed at enhancing multilingual accessibility in parliamentary proceedings.
- This initiative seeks to streamline access to parliamentary documents for Members of Parliament (MPs) and citizens, thereby improving legislative efficiency and inclusivity.
Key Features of Sansad Bhashini
The initiative integrates several advanced technological solutions to enhance parliamentary operations:
Seamless Multilingual Translation of Parliamentary Documents
- Facilitates real-time translation of key parliamentary materials, including legacy debates, committee reports, and agenda files.
- Ensures greater accessibility for MPs and citizens who prefer regional languages.
AI-Powered Chatbot for Instant Information Retrieval
- Enables MPs and officials to quickly access procedural rules, legislative documents, and parliamentary records.
- Enhances legislative efficiency by reducing time spent on manual document searches.
Real-Time Speech Translation and Transcription
- Converts live parliamentary debates into text format
- Provides real-time translation of discussions into multiple languages, ensuring linguistic inclusivity.
AI-Driven Automatic Summarisation of Debates
- Uses natural language processing (NLP) algorithms to generate concise summaries of lengthy parliamentary discussions.
- Facilitates quick decision-making for MPs, researchers, and legislative staff.
Impact and Benefits
- Enhances Parliamentary Efficiency: Reduces delays in accessing legislative documents and procedural information.
- Promotes Transparency & Inclusivity: Makes parliamentary discussions more accessible to a wider audience by supporting multiple languages.
- Empowers Lawmakers and Citizens: Helps MPs stay informed and engaged, while also enabling citizens to follow parliamentary debates in their preferred language.
- Through Sansad Bhashini, India moves towards a more inclusive, technologically advanced, and transparent parliamentary system, leveraging AI-driven multilingual capabilities for better governance.
With reference to the ‘Sansad Bhashini’ initiative, consider the following statements:
- It is a joint initiative of the Lok Sabha Secretariat and the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- The initiative solely focuses on translating parliamentary documents into Hindi and English.
- It incorporates AI-driven chatbots to assist Members of Parliament in retrieving legislative information.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: The Lok Sabha Secretariat and MeitY have collaborated to implement Sansad Bhashini to enhance multilingual accessibility in parliamentary operations.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The initiative does not restrict translations to only Hindi and English but supports multiple languages to promote inclusivity.
Statement 3 is correct: AI-powered chatbots assist MPs and officials in retrieving procedural rules and legislative documents.
Revised Rashtriya Gokul Mission
Syllabus: Government Policies
- The Revised Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM) is a flagship initiative of the Government of India, aimed at modernizing and enhancing the livestock and dairy sector.
- With an additional allocation of ₹1,000 crore, the total budget for RGM now stands at ₹3,400 crore for the 15th Finance Commission cycle (2021-22 to 2025-26).
- The revised mission focuses on boosting milk production, improving cattle productivity, and supporting dairy farmers through targeted interventions.
Key Components of the Revised RGM
- Heifer Rearing Centres
- Provides one-time financial assistance covering 35% of capital costs.
- Aims to establish 30 rearing facilities to accommodate 15,000 heifers.
- Ensures the availability of high-quality female calves to improve dairy productivity.
- High Genetic Merit (HGM) IVF Heifers
- Farmers purchasing HGM IVF heifers receive a 3% interest subvention on loans.
- Loans are facilitated through milk unions and financial institutions to promote access to superior breeds.
Ongoing Activities and Enhancements
- The revised mission continues several critical initiatives from the original RGM, including:
- Strengthening semen stations and expanding Artificial Insemination (AI) coverage.
- Accelerating breed improvement through the use of sex-sorted semen and advanced reproductive technologies.
- Skill development and farmer awareness programs to enhance knowledge and best practices in livestock management.
Impact on Milk Production and Productivity
- Since the inception of RGM, India has witnessed a 63.55% increase in milk production over the past decade. Key improvements include:
- Milk availability per capita rose from 307 grams/day (2013-14) to 471 grams/day (2023-24).
- Dairy productivity surged by 26.34% within the same period, benefiting both small and large-scale farmers.
- Nationwide Artificial Insemination Programme (NAIP)
To enhance breed quality and accessibility, the NAIP provides:
- Free Artificial Insemination (AI) services in 605 districts, focusing on areas with AI coverage below 50%.
- Over 8.39 crore animals have been inseminated, benefiting 5.21 crore farmers across India.
- Technological Innovations in Livestock Breeding
The RGM incorporates cutting-edge advancements to improve livestock genetics and productivity, including:
- Establishment of 22 In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) labs for advanced breeding.
Development of genomic chips:
- Gau Chip for indigenous cattle breeds.
- Mahish Chip for buffalo breeds.
- Indigenous development of Gau Sort technology for producing sex-sorted semen, ensuring higher birth rates of female calves for dairy farming.
- Emphasis on Indigenous Breeds and Farmer Livelihoods
The Revised RGM prioritizes the scientific conservation and genetic improvement of indigenous bovine breeds, fostering a sustainable and self-reliant dairy sector.
Key outcomes include:
- Systematic bull production programs to enhance breed purity.
- Expanded use of IVF and genomic technologies to increase productivity.
- Improved economic conditions for over 8.5 crore farmers engaged in dairying, particularly small and marginal farmers.
- By integrating modern scientific techniques with traditional livestock practices, the Revised Rashtriya Gokul Mission is playing a crucial role in strengthening India’s dairy industry, ensuring higher productivity, enhanced farmer incomes, and sustainable livestock management.
With reference to the Revised Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM), consider the following statements:
- It provides capital assistance of 50% for establishing Heifer Rearing Centres.
- It offers an interest subvention on loans for purchasing High Genetic Merit (HGM) IVF heifers.
- The mission aims to increase milk production but does not focus on indigenous bovine breeds.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- The mission provides 35% capital assistance, not 50%, for establishing Heifer Rearing Centres.
- It does offer a 3% interest subvention on loans for purchasing HGM IVF heifers.
- A major focus of RGM is the conservation and development of indigenous bovine breeds, making statement 3 incorrect.
PM Internship Scheme
Syllabus: Government Policies
- PM Internship Scheme: Bridging Youth with Industry Experience.
- Union Minister Nirmala Sitharaman recently launched a dedicated mobile application for the Prime Minister Internship Scheme, encouraging more companies to participate in this transformative initiative.
About the PM Internship Scheme
- The PM Internship Scheme is a flagship initiative by the Government of India, designed to equip young individuals with industry exposure and practical experience.
- It focuses on skill development and employment generation, ensuring that youth from economically weaker sections gain valuable insights into real-world professional environments.
Key Features of the Scheme
- Target Beneficiaries: Young individuals aged 21-24 years from low-income households.
- Internship Duration: 12 months in India’s top 500 companies.
- Pilot Phase: Aims to benefit 25 lakh youth.
- Long-Term Goal: Envisions facilitating internships for one crore young individuals over five years.
Sector Coverage: Spans 24 industries, including:
- Oil & Gas
- Energy
- Travel & Hospitality
- Automotive
- Banking & Financial Services
- Eligibility Criteria
Scheme sets the following Eligibility conditions:
Educational Qualifications:
- Passed 10th, 12th, ITI, Polytechnic, or Diploma courses.
- Fresh graduates from non-premier institutions.
Economic & Family Background:
- Belong to a household with an annual income of ₹8 lakh or less (2023-24).
- No family member should hold a government job.
Exclusions:
- Students from IITs, IIMs, National Law Universities (NLUs).
- Individuals holding professional degrees like CA, MBA, MBBS, etc.
Vision & Impact
- This initiative aligns with the government’s broader strategy to bridge the gap between academic learning and professional expertise.
- By focusing on skill enhancement and employment readiness, it paves the way for greater socio-economic mobility among India’s youth.
With reference to the Prime Minister Internship Scheme (PM Internship Scheme), consider the following statements:
- The scheme is open to all young individuals between the ages of 21-30 years.
- It offers internships in only government enterprises to enhance youth participation in public administration.
- The scheme specifically excludes students from IITs, IIMs, and National Law Universities to ensure inclusivity for underrepresented groups.
- The long-term goal of the scheme is to facilitate internships for 5 crore youth over five years.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: (c) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The scheme targets youth aged 21-24 years, not 21-30 years.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Internships are available in both public and private enterprises, covering 24 industries, including energy, automotive, and financial services.
Statement 3 is correct: To promote inclusivity, students from IITs, IIMs, National Law Universities, and professional courses like CA, MBA, MBBS are excluded.
Statement 4 is incorrect: The scheme’s five-year goal is to facilitate internships for 1 crore youth, not 5 crore.
SwaYaan initiative
Syllabus: Government Policies
- The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), in collaboration with the Drone Federation of India (DFI), has launched the National Innovation Challenge for Drone Application and Research (NIDAR) under the SwaYaan initiative.
- This initiative aims to bolster capacity building in Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) by fostering applied research and entrepreneurship in drone technology.
- The event, held at Electronics Niketan, witnessed participation from key government officials, industry leaders, and students across India through video conferencing.
Launch and Key Highlights
- The challenge was officially inaugurated by Shri S. Krishnan, Secretary, MeitY, who unveiled the NIDAR concept video, launched the website and registration portal, and released the official rulebook and poster.
- Addressing the attendees, Shri Krishnan underscored the transformative role of drones in sectors such as agriculture, disaster management, logistics, healthcare, and infrastructure, emphasizing the need to scale the NIDAR initiative to contribute to India’s goal of becoming a global drone hub by 2030.
- T. G. Sitharam, Chairman, AICTE, highlighted the necessity of integrating the NIDAR challenge into engineering curricula across the country.
- Stressing the importance of collaboration between academia, startups, and industry, he called for innovative engagement in drone technology research and development.
Objectives and Focus Areas of NIDAR
- The NIDAR challenge aims to inspire India’s student and research community to develop collaborative autonomous drones to address real-world challenges in two key domains.
- Disaster Management – Scout and Deliver Drones.
- Autonomous drones for scouting disaster-affected areas.
Assisting survivors through communication and parcel delivery. - Precision Agriculture – Scan and Spray Drones.
- Drones for crop health monitoring.
Precision-based pesticide and nutrient delivery.
Support, Incentives, and Participation
- The challenge offers a prize pool of INR 40 Lakhs, along with startup incubation opportunities, cloud computing credits, software support, and internship placements with India’s leading drone companies.
- Over 100 student teams from higher education institutions are expected to participate, showcasing innovative solutions to challenges in agriculture and disaster response.
- The competition will be conducted in multiple phases, including technology presentation, business case development, and final operational demonstration.
- This comprehensive evaluation will assess the technical skills, problem-solving abilities, teamwork, and entrepreneurial acumen of participants, preparing them for leadership roles in emerging technology domains.
Role of Drone Federation of India (DFI)
- As India’s premier industry body representing over 550 drone companies and 5500 drone pilots, the Drone Federation of India (DFI) will play a crucial role in mentoring student teams by providing industry exposure and guiding them through the innovation process.
Significance of NIDAR in India’s Drone Ecosystem
- The launch of NIDAR represents a strategic milestone in advancing India’s drone research, development, and commercialization.
- It reinforces the Government of India’s efforts to promote entrepreneurship in academia while bridging the gap between technological innovation and real-world applications.
About SwaYaan Initiative
- The SwaYaan initiative, approved by MeitY in July 2022, focuses on capacity building in Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) through formal and non-formal educational programs.
- Its goal is to train 42,560 individuals and develop a skilled workforce in drone technology.
Implementation Model and Key Areas
- The initiative follows a hub-and-spoke model, involving 30 premier institutions, including IISc Bangalore, IITs, IIITs, NITs, CDAC, and NIELIT.
- It is structured around five key research themes, Drone Electronics, GNC Algorithms and Simulation, Aeromechanics, Drone Applications, and Allied UAS Technologies.
- To date, over 14,000 individuals have been trained under SwaYaan.
Notable Achievements
- Launch of M.Tech in UAS Engineering at IIT Kanpur.
- Introduction of minor degree programs in drone technology.
- Successful execution of multiple bootcamps and workshops.
- The program actively engages industry partners through innovation challenges and industry meets, reinforcing the critical link between academic training and industry requirements in drone technology.
Conclusion
- The NIDAR challenge, under the SwaYaan initiative, is set to be a game-changer for India’s drone industry, fostering cutting-edge research, skill development, and entrepreneurship.
- By encouraging technological innovation in drone applications, the initiative is poised to strengthen India’s position as a global leader in unmanned aerial systems.
Which of the following statements regarding the NIDAR challenge is/are correct?
- It is launched by the Ministry of Civil Aviation in collaboration with the Drone Federation of India (DFI).
- The challenge provides incentives such as startup incubation, cloud computing credits, and software support.
- The competition includes multiple evaluation phases such as Technology Presentation, Business Case Development, and Final Operational Demonstration.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 2 and 3 only
(C) 1 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (B) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect because NIDAR is launched by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), not the Ministry of Civil Aviation.
Statements 2 and 3 are correct as the challenge offers startup incubation, cloud computing credits, and software support, along with a rigorous multi-phase evaluation process.
Prime Minister’s Young Authors Mentorship Scheme (YUVA) Scheme
Overview
- The Ministry of Education (MoE) and the National Book Trust (NBT) of India have launched the third edition of the Prime Minister’s Young Authors Mentorship Scheme (PM-YUVA 3.0).
- This initiative aims to identify and nurture young literary talent in India, providing mentorship to aspiring writers under the age of 30.
Previous Editions of the YUVA Scheme YUVA 1.0 (May 2021)
- Launched during the Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav celebrations to commemorate 75 years of India’s independence.
- The central theme focused on the National Movement of India, highlighting unsung heroes, lesser-known facts, and various aspects of the freedom struggle.
- YUVA 2.0 (October 2022)
- Expanded upon the objectives of YUVA 1.0, shifting its theme to Democracy.
- The focus was on nurturing young writers who could explore India’s democratic values, traditions, and governance structures.
PM-YUVA 3.0: Objectives and Themes
- Building on the success of its predecessors, YUVA 3.0 continues the government’s mission to foster literary talent and promote a vibrant reading and writing culture.
- It seeks to provide mentorship and structured guidance to young authors to help them develop their creative writing skills.

- The scheme emphasizes three core themes:
- Contribution of the Indian Diaspora in Nation Building
- Indian Knowledge System
- The Makers of Modern India (1950-2025)
Significance of the YUVA Scheme
- Encourages young authors to explore various dimensions of India’s history, culture, and future aspirations.
- Provides a platform for youth to express their perspectives on India’s contributions in different fields, both ancient and contemporary.
- Aligns with the vision of Ek Bharat, Shreshtha Bharat, promoting the documentation and dissemination of India’s rich cultural heritage and intellectual traditions.
- Through this initiative, the government continues to emphasize nation-building through literary excellence, empowering young minds to contribute meaningfully to India’s intellectual and cultural landscape.
With reference to the Prime Minister’s Young Authors Mentorship Scheme (PM-YUVA 3.0), consider the following statements:
- The scheme is jointly implemented by the Ministry of Education (MoE) and the National Book Trust (NBT) of India.
- It exclusively focuses on themes related to the Indian Freedom Struggle.
- PM-YUVA 3.0 aims to mentor young authors under the age of 30.
- The scheme aligns with the vision of Ek Bharat, Shreshtha Bharat.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 3, and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (b) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct. The scheme is implemented by the Ministry of Education (MoE) and the National Book Trust (NBT) of India.
Statement 2 is incorrect. While the first edition (YUVA 1.0) focused on the Indian freedom struggle, PM-YUVA 3.0 includes themes such as Indian Knowledge System, the Contribution of the Indian Diaspora in Nation Building, and the Makers of Modern India (1950-2025).
Statement 3 is correct. The scheme is designed for young authors under 30 years of age.
Statement 4 is correct. The scheme aligns with Ek Bharat, Shreshtha Bharat by fostering a deeper understanding of India’s cultural and intellectual traditions.
Swadesh Darshan Scheme
Syllabus: GS2/Governance, Schemes
Context
- The Public Accounts Committee (PAC), chaired by C. Venugopal, has raised concerns over the poor execution of the Swadesh Darshan scheme by the Ministry of Tourism.
- The observations were based on a report by the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG).
- Despite the Ministry’s claims that most sanctioned projects were completed, the PAC identified significant discrepancies in project implementation.
Swadesh Darshan Scheme
- Launched: 2014-15, as a flagship scheme under the Ministry of Tourism.
- Revamped: As Swadesh Darshan 2.0, with a focus on sustainable and responsible tourism, adopting a tourist-centric
Theme-Based Tourist Circuits:
- Spiritual Circuits (e.g., Char Dham Yatra, Buddhist Circuit)
- Cultural Circuits (e.g., North East Circuit, Tribal Circuit)
- Heritage Circuits
- Wildlife Circuits
Coastal Circuits
Funding: The Ministry of Tourism provides financial support to States and Union Territories for circuit development.
Key Issues Identified by PAC
Lapses in Planning: No feasibility studies were conducted before launching projects.
Financial Mismanagement:
- Budget overruns due to inadequate planning.
- Approvals granted without Detailed Project Reports (DPRs).
Weak Monitoring:
- No structured mechanism for project evaluation.
- Delays and incomplete projects despite claims of completion.
Discrepancy in Completion Claims:
- The Ministry claimed 75 out of 76 projects were completed.
- However, PAC found that key projects like the Kanwaria Route in Bihar, Tribal Circuit in Telangana, and Sree Narayana Guru Ashram in Kerala were either incomplete or non-functional.
Recommendations & Way Forward
- The Ministry of Tourism has been directed to physically inspect all projects and submit a detailed report within three weeks.
The Ministry must provide data on:
- The scheme’s impact on employment generation.
- Changes in tourist footfall, as key indicators of the scheme’s success.
About the Public Accounts Committee (PAC)
- Constitutional Status
- Not a constitutional body.
- Formed under Rule 308 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha.
Composition
- 22 Members:
- 15 from Lok Sabha
- 7 from Rajya Sabha
- Elected annually by Parliament.
- Chairperson: Appointed by the Speaker of Lok Sabha, typically from the opposition party.
Functions
- Examines audit reports submitted by the CAG of India.
- Scrutinizes public expenditure to prevent extravagance and irregularities.
- Ensures accountability of the Executive to the Legislature.
- Works alongside CAG to uphold fiscal discipline and transparency.
With reference to the Public Accounts Committee (PAC), consider the following statements:
- It is a constitutional body established under Article 148 of the Indian Constitution.
- The Chairperson of the PAC is always from the ruling party.
- PAC is responsible for examining the reports submitted by the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India.
- The PAC can take suo-motu cognizance of financial irregularities and initiate investigations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: PAC is not a constitutional body; it is formed under Rule 308 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The Chairperson is usually from the opposition party, not the ruling party.
Statement 3 is correct: The PAC examines audit reports of CAG and scrutinizes public expenditure.
Statement 4 is incorrect: PAC cannot take suo-motu cognizance; it works based on reports submitted by the CAG.
Samarth Incubation Programme
Syllabus: Government Policies
- The Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DoT), an autonomous Telecom R&D centre under the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Government of India, has launched the ‘Samarth’ incubation programme to support emerging startups in the telecom sector.
Objectives:
- Foster innovation in telecom software, cybersecurity, 5G and 6G technologies, artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and quantum technologies.
- Promote sustainable and scalable business models by providing access to advanced resources.
- Bridge the gap between ideation and commercialization for startups.
Key Features:
- Implementation Partner: Software Technology Parks of India (STPI) has been selected to execute the programme.
- Mode of Delivery: Hybrid mode with both online and offline engagement.
Cohort Structure:
- Each program will accommodate 18 startups, with a total of 36 startups across two cohorts (each lasting six months).
- Eligibility: Open to DPIIT (Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade) recognized startups.
Support for Startups:
- A grant of up to ₹5 lakh per selected startup.
- Six months of office space at the C-DoT campus.
- Access to C-DoT lab facilities.
- Mentorship from C-DoT technical leaders and industry experts.
Future Prospects: Startups demonstrating significant progress may receive further opportunities under the C-DoT Collaborative Research Program.
Consider the following statements regarding the ‘Samarth’ Incubation Programme launched by the Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DoT):
- It is an initiative to support startups specifically in 5G and 6G technologies, without extending to other domains like cybersecurity or AI.
- The programme is being implemented in collaboration with Software Technology Parks of India (STPI).
- Only startups that have been recognized by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) are eligible for the programme.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Samarth Incubation Programme supports startups not only in 5G and 6G technologies but also in cybersecurity, AI, IoT, and quantum technologies.
Statement 2 is correct: The Software Technology Parks of India (STPI) is the implementation partner for the programme.
Statement 3 is correct: Only DPIIT-recognized startups are eligible for the incubation support.
Implementation of Revised Rashtriya Gokul Mission
Implementation of Revised Rashtriya Gokul Mission
- The Union Cabinet has approved the Revised Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM) with an additional allocation of ₹1,000 crore, increasing the total budget to ₹3,400 crore for the period 2021-2026 under the 15th Finance Commission.
- Launched in December 2014, RGM aims to conserve and develop indigenous bovine breeds.
- It is implemented by the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying, focusing on genetic upgradation, enhancement of milk production and productivity, and improving the profitability of dairy farming for farmers.
The scheme includes several key components.
- The Nationwide Artificial Insemination Program seeks to boost milk productivity, while Progeny Testing and Pedigree Selection focus on producing high-genetic-merit bulls, particularly of indigenous breeds.
- The implementation of In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF) technology plays a crucial role in genetic upgradation within a single generation. Sex-Sorted Semen Production has been established at five government semen stations in Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Uttarakhand, and Uttar Pradesh.
- Additionally, the Multi-purpose Artificial Insemination Technicians in Rural India (MAITRIs) initiative trains and equips technicians to deliver quality artificial insemination services directly to farmers.
- The revised mission will now function as a Central Sector component under the Development Programmes scheme.
- Two new initiatives have been introduced: a 35% capital assistance provision for setting up Heifer Rearing Centres and a 3% interest subvention on loans for purchasing High-Genetic-Merit (HGM) IVF heifers.
- The core activities of strengthening artificial insemination networks, supporting breed improvement programs, and establishing Centres of Excellence will continue.
- The mission has significantly contributed to India’s dairy sector. Over the past decade, milk production has increased by 63.55%, with per capita milk availability rising from 307 grams/day in 2013-14 to 471 grams/day in 2023-24.
- The Nationwide Artificial Insemination Programme has covered over 8.39 crore animals, benefiting 5.21 crore farmers. RGM has also introduced advanced breeding technologies, including 22 IVF labs, resulting in 2,541 high-genetic-merit calves.
- Furthermore, the development of Gau Chip and Mahish Chip for indigenous bovines, along with the introduction of Gau Sort technology, underscores India’s progress toward self-reliance in dairy technology.
Consider the following statements regarding the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY):
- The scheme was launched in the Kharif 2016 season and is mandatory for all States and farmers.
- The government provides a subsidy on the premium amount to ensure affordability for farmers.
- PMFBY covers post-harvest losses for up to 30 days for crops stored in a “cut and spread” condition.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: PMFBY was launched in Kharif 2016, but it is voluntary for both States/UTs and farmers since the 2020 revamp.
Statement 2 is correct: The government subsidizes the remaining premium after the farmers pay their share.
Statement 3 is incorrect: PMFBY provides post-harvest loss coverage for up to 14 days, not 30 days.
Implementation of Revised Rashtriya Gokul Mission
- The Union Cabinet has approved the Revised Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM) with an additional allocation of ₹1,000 crore, increasing the total budget to ₹3,400 crore for the period 2021-2026 under the 15th Finance Commission.
- Launched in December 2014, RGM aims to conserve and develop indigenous bovine breeds.
- It is implemented by the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying, focusing on genetic upgradation, enhancement of milk production and productivity, and improving the profitability of dairy farming for farmers.
The scheme includes several key components.
- The Nationwide Artificial Insemination Program seeks to boost milk productivity, while Progeny Testing and Pedigree Selection focus on producing high-genetic-merit bulls, particularly of indigenous breeds.
- The implementation of In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF) technology plays a crucial role in genetic upgradation within a single generation. Sex-Sorted Semen Production has been established at five government semen stations in Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Uttarakhand, and Uttar Pradesh.
- Additionally, the Multi-purpose Artificial Insemination Technicians in Rural India (MAITRIs) initiative trains and equips technicians to deliver quality artificial insemination services directly to farmers.
- The revised mission will now function as a Central Sector component under the Development Programmes scheme.
- Two new initiatives have been introduced: a 35% capital assistance provision for setting up Heifer Rearing Centres and a 3% interest subvention on loans for purchasing High-Genetic-Merit (HGM) IVF heifers.
- The core activities of strengthening artificial insemination networks, supporting breed improvement programs, and establishing Centres of Excellence will continue.
- The mission has significantly contributed to India’s dairy sector. Over the past decade, milk production has increased by 63.55%, with per capita milk availability rising from 307 grams/day in 2013-14 to 471 grams/day in 2023-24.
- The Nationwide Artificial Insemination Programme has covered over 8.39 crore animals, benefiting 5.21 crore farmers. RGM has also introduced advanced breeding technologies, including 22 IVF labs, resulting in 2,541 high-genetic-merit calves.
- Furthermore, the development of Gau Chip and Mahish Chip for indigenous bovines, along with the introduction of Gau Sort technology, underscores India’s progress toward self-reliance in dairy technology.
Consider the following statements regarding the Revised Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM):
- The scheme is being implemented as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme under the 15th Finance Commission period.
- It aims to enhance the genetic potential of both indigenous and exotic bovine breeds.
- The scheme provides interest subvention on loans for the purchase of IVF-generated High-Genetic-Merit (HGM) heifers.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
Answer: (d) 3 only
Explanation:
- The Revised Rashtriya Gokul Mission is implemented as a Central Sector Scheme, not a Centrally Sponsored Scheme. Hence, Statement 1 is incorrect.
- The mission primarily focuses on the development and conservation of indigenous bovine breeds rather than exotic ones. Hence, Statement 2 is incorrect.
- One of the new initiatives introduced under the revised mission is a 3% interest subvention on loans for purchasing High Genetic Merit (HGM) IVF heifers, making Statement 3 correct.
Oeko-Tex Certification for Eri Silk
Context:
The North Eastern Handicrafts and Handlooms Development Corporation Ltd. (NEHHDC), under the Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region, has received Oeko-Tex certification from Germany for Eri Silk.
Oeko-Tex Certification
- Oeko-Tex is a globally recognized certification system for textiles, ensuring that they are free from harmful substances.
- It applies to raw materials, semi-finished, and finished textile products, covering items like yarns, fabrics, buttons, linens, terry cloth, and threads.
- The certification ensures that the textile is safe for human use and meets environmental and health standards.
Eri Silk: An Overview
- Composition: Silk is a natural protein fiber, primarily made of fibroin, produced by insect larvae to form cocoons.
- Eri Silk is obtained from the Samia Cynthia Ricini
- The name “Eri” is derived from “Erranda”, the Assamese word for castor, as the silkworms feed on castor plant leaves.
- Unlike other silk varieties, Eri Silk is harvested without killing the silkworm, making it known as “Ahimsa Silk” or “Non-Violent Silk.”
- It is considered the “father of all cultured and textured silks.”
- Geographical Spread: Found primarily in Northeast India (Meghalaya, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh), as well as China, Japan, and Thailand.
Silk Production in India
- India is the 2nd largest producer of silk in the world.
It is the only country that produces all four major types of silk:
- Mulberry Silk
- Eri Silk
- Tassar Silk
- Muga Silk
South India is the leading silk-producing region, known for its silk weaving centers like Kancheepuram, Dharmavaram, and Arni.
With reference to the Oeko-Tex certification, consider the following statements:
- It is an internationally recognized certification that ensures textiles are free from harmful substances.
- The certification applies only to finished textile products and not to raw or semi-finished materials.
- Oeko-Tex certification is granted exclusively by the International Silk Association to promote sustainable silk production.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation:
- Oeko-Tex certification applies to all stages of textile production, including raw, semi-finished, and finished products (Statement 2 is incorrect).
- The certification is not issued by the International Silk Association but is granted by the Oeko-Tex Association to ensure safety standards in textile production (Statement 3 is incorrect).
Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE)
- Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE) Poses Health Concerns in Uttar Pradesh
- Despite being a rare disease globally, Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE) remains a significant health concern in Lucknow and Uttar Pradesh, primarily due to low measles vaccination coverage.
What is Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE)?
- SSPE is a progressive and typically fatal brain disorder associated with measles (rubeola) infection.
- It usually develops several years after a person has seemingly recovered from measles.
- Though SSPE has been reported worldwide, it is rare in Western countries.
- Males are more commonly affected than females.
- The disease primarily impacts children and adolescents.
Causes of SSPE
- Normally, the measles virus does not cause brain damage.
- However, in some cases, an abnormal immune response or a variant form of the virus leads to severe brain inflammation.
- This inflammation may persist for years, causing progressive neurological damage.
Symptoms of SSPE
SSPE symptoms appear in stages and progressively worsen over time.
Early Symptoms:
- Declining school performance
- Forgetfulness
- Sudden mood swings (temper outbursts, irritability)
- Distractibility and hallucinations
Progressive Symptoms:
- Sudden muscular jerks in the arms, head, or body
- Seizures
- Uncontrollable muscle movements
- Speech and intellectual deterioration
Severe and Final Stages:
- Increasing muscle rigidity
- Difficulty in swallowing, leading to choking risks and pneumonia
- Blindness
- Abnormal blood pressure and pulse
- Fever in the final phase
Treatment and Prognosis
- High mortality rates are associated with SSPE, and there is no known cure.
- Treatment focuses on symptom management.
- Antiviral drugs and immune-boosting medications may help slow disease progression.
- Given the lack of a cure, the most effective strategy against SSPE remains preventing measles through vaccination.
Consider the following statements regarding Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE):
- SSPE is a progressive brain disorder that occurs due to a previous measles infection.
- The disease primarily affects adults above the age of 40.
- SSPE is more commonly found in developing countries due to lower measles vaccination rates.
- It is caused by a bacterial infection that affects the nervous system.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation: SSPE is a progressive and fatal brain disorder caused by a measles virus infection that usually affects children and adolescents. It is more prevalent in developing countries due to low vaccination rates. The disease is caused by a virus, not bacteria.
Uniyala Keralensis

Overview
- Researchers have recently confirmed the existence of a new plant species, Uniyala keralensis, within the Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve in Kerala.
- This discovery highlights the remarkable biodiversity of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Although the species was originally collected 27 years ago, its classification was only recently finalized, underscoring the importance of continuous botanical research.
Taxonomy and Classification
- Family: Asteraceae
- Initially misidentified as Vernonia multibracteata, Uniyala keralensis was later recognized as a distinct species.
- The genus Uniyala was formally established following in-depth studies and comparisons with herbarium specimens, leading to its separation from Vernonia.
Morphological Characteristics
- Growth Form: Shrub, reaching 1 to 3 meters in height.
- Flowers: Light purple, blooming between August and April.
Leaves:
- Larger compared to closely related species.
- Possess long petioles.
- Feature fewer lateral veins, aiding in species identification.
Habitat and Distribution
- Endemic to southwest India, specifically in the Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve.
- Prefers open landscapes on the western slopes of the region.
- Found at elevations ranging from 700 to 1,400 metres above sea level.
- The estimated population consists of nearly 5,000 individuals, distributed across four subpopulations, covering an area of 250 square kilometres.
Conservation Status
- Classified as Data Deficient (DD) under the IUCN Red List Criteria.
- Due to limited ecological data, its extinction risk remains undetermined.
- Further research is essential to assess its population trends, threats, and conservation requirements.
Significance of the Discovery
- Reinforces the biodiversity richness of the Western Ghats.
- Highlights the need for continued exploration and conservation efforts in this global biodiversity hotspot.
- Enhances scientific knowledge of regional flora, contributing to broader ecological and environmental research.
- This discovery serves as a reminder of the hidden botanical treasures yet to be explored and the urgent need for conservation measures in ecologically sensitive regions like the Western Ghats.
Consider the following statements regarding Uniyala keralensis:
- It belongs to the Fabaceae family and was first classified in 2024.
- It is endemic to the Eastern Ghats and found in tropical lowlands.
- The species was previously misidentified as Vernonia multibracteata.
- It is classified as Critically Endangered under the IUCN Red List.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Uniyala keralensis belongs to the Asteraceae family, not Fabaceae.
Statement 2 is incorrect: It is endemic to the Western Ghats, not the Eastern Ghats. Additionally, it is found at elevations of 700-1,400 metres, not in tropical lowlands.
Statement 3 is correct: The species was originally misidentified as Vernonia multibracteata.
Statement 4 is incorrect: Uniyala keralensis is classified as Data Deficient (DD), not Critically Endangered.
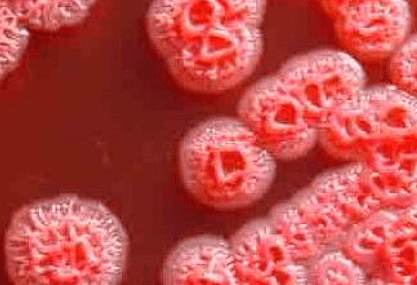
Melioidosis in Odisha
- Recent studies have underscored the increasing concern surrounding melioidosis, particularly in Odisha.
- Research suggests that South Asia accounts for a significant proportion of global melioidosis cases.
- A multidisciplinary collaboration between microbiologists and climate scientists aims to analyze the environmental conditions that drive the transmission of this disease.
Understanding Melioidosis
- Causative Agent: Melioidosis is caused by the bacterium Burkholderia pseudomallei.
- Mode of Transmission: Infection occurs primarily through direct contact with contaminated soil or water, inhalation of aerosols, or ingestion.
- Clinical Manifestations: The disease presents in a spectrum of forms, ranging from localized skin infections to severe pneumonia and septicemia.
- Mortality Risk: In severe cases, the fatality rate can reach up to 50%, making early diagnosis and treatment crucial.
Environmental Factors Influencing Melioidosis
- The incidence of melioidosis is strongly linked to environmental conditions. Key contributing factors include:
- Rainfall Patterns: The disease shows a seasonal peak, particularly during and after the monsoon, due to increased bacterial growth and dispersal in wet soil.
- Temperature Variations: Higher temperatures enhance bacterial survival and transmission dynamics.
Research Collaboration and Findings
- A joint study conducted by AIIMS Bhubaneswar and IIT Bhubaneswar focused on tracking melioidosis cases in Odisha over a nine-year period. The research involved:
- Analyzing meteorological data to identify environmental conditions that correlate with disease outbreaks.
- Establishing a geospatial disease risk map highlighting districts with the highest vulnerability.
High-Risk Regions in Odisha
- The study identified several high-risk districts, particularly those with dense populations and favorable environmental conditions for bacterial growth. These include:
- Cuttack
- Balasore
- Khordha
- Jajpur
- The clustering of cases in these regions suggests increased human exposure to the bacteria, necessitating targeted public health interventions.
Climate Change and Its Role in Disease Dynamics:
- The ongoing shifts in climate patterns pose a significant challenge by altering rainfall distribution and intensifying extreme weather events. These changes may:
- Expand the geographical range of Burkholderia pseudomallei.
- Increase the frequency and severity of melioidosis outbreaks.
- Overburden public health infrastructure, necessitating climate-adaptive disease surveillance.
Broader Implications for Global Disease Modelling
- The insights from Odisha’s research offer a framework for other regions affected by melioidosis. The integration of climate analytics into disease prediction models can:
- Enhance early warning systems for melioidosis and similar infections.
- Improve public health preparedness against emerging climate-driven diseases.
- Provide data-driven policy recommendations for mitigation strategies.
Future Research Directions
- While current studies have provided significant insights, further research is essential to understand additional factors influencing melioidosis, such as:
- Land use changes and their impact on bacterial reservoirs.
- Soil composition and microbial ecology in affected regions.
- Long-term climate projections to anticipate disease expansion patterns.
- By integrating climate science, microbiology, and epidemiology, future research can enhance our ability to combat melioidosis and mitigate its impact on public health.
Consider the following statements regarding Melioidosis:
- It is caused by Burkholderia mallei and primarily affects livestock.
- The bacterium thrives in wet soil and can be transmitted through inhalation, ingestion, or direct skin contact.
- The disease has a high fatality rate and peaks during dry seasons when soil dispersal is at its maximum.
- The recent research in Odisha identified monsoon patterns as a key factor in disease outbreaks.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Burkholderia mallei causes glanders, not melioidosis. Melioidosis is caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei.
- The bacteria can infect humans through inhalation, ingestion, or direct contact with contaminated soil/water.
- The disease peaks during and after the monsoon, not in dry seasons, due to increased bacterial dispersal.
- The Odisha study correlated monsoon patterns with outbreaks, confirming the seasonal link.
Update on elimination of Trachoma and Malaria
- India has been officially declared trauma-free as a public health problem by the World Health Organization (WHO) on October 8, 2024.
- This milestone makes India the third country in the WHO Southeast Asia Region to achieve this status.
- The elimination of Trachoma, a leading cause of preventable blindness, highlights significant advancements in public health, hygiene, and sanitation practices.
Government Initiatives for Trachoma Elimination
- The National Programme for Control of Blindness and Visual Impairment (NPCBVI) played a key role in controlling Trachoma.
India followed the WHO-SAFE Strategy, which includes:
- Surgery for trachomatous trichiasis
- Antibiotics to treat infection
- Facial hygiene promotion
- Environmental cleanliness improvement
- A National Trachomatous Trichiasis (TT-only) survey was conducted in 200 endemic districts between 2021-2024 under WHO guidelines, confirming a decline in prevalence below elimination thresholds.
National Quality Assurance Standards (NQAS)
- The Indian government has implemented the National Quality Assurance Standards (NQAS) to ensure the safety, efficiency, and reliability of public healthcare services.
- Initially developed for District Hospitals, it was later extended to:
- Sub-District Hospitals (SDHs)
- Community Health Centers (CHCs)
- Ayushman Arogya Mandir – Urban & Rural Health Centers (AAM-UPHCs, AAM-PHCs, AAM-SHCs)
- Integrated Public Health Laboratories (IPHLs) (launched on June 28, 2024)
- A Virtual Assessment for NQAS certification was introduced to facilitate compliance. As of December 31, 2024, a total of 22,786 health facilities had received NQAS certification.
Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS)
- The Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS) were introduced in 2007 and revised in 2012 and 2022 to define minimum essential services for:
- District & Sub-District Hospitals
- Community Health Centers (CHCs)
- Primary Health Centers (PHCs)
- Sub-Health Centers (SHCs)
- These standards ensure better healthcare delivery, patient safety, and public trust in the system.
- India’s Exit from the High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) Group for Malaria
- India has exited the High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) group, indicating a major reduction in Malaria prevalence.
- The Government of India adopted a comprehensive, multi-pronged approach under the National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme (NVBDCP).
Key Strategies for Malaria Reduction
- Disease Management
- Early case detection through active, passive, and sentinel surveillance
- Complete and effective treatment for all detected cases
- Strengthening referral services for severe malaria cases
- Rapid response mechanisms for malaria outbreaks
- Integrated Vector Management (IVM)
- Indoor Residual Spraying (IRS) in high-risk regions
- Long-Lasting Insecticidal Nets (LLINs) in endemic zones
- Use of larvivorous fish & bio-larvicides in urban malaria-prone areas
- Environmental engineering & source reduction measures to eliminate breeding sites
- Supportive Interventions
- Behavior Change Communication (BCC) to educate communities
- Inter-Sectoral Convergence for coordinated disease control efforts
- Capacity building of health workers and field staff
- These strategic efforts have significantly reduced malaria transmission, paving the way for India’s goal of Malaria elimination by 2030.
With reference to India’s elimination of Trachoma as a public health problem, consider the following statements:
- India followed the SAFE strategy recommended by WHO, which includes measures like surgery, antibiotics, face washing, and environmental improvement.
- The National Trachomatous Trichiasis (TT-only) survey was conducted under the National Programme for Control of Blindness and Visual Impairment (NPCBVI) to assess prevalence.
- India is the first country in the WHO Southeast Asia Region to eliminate Trachoma as a public health problem.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: WHO’s SAFE strategy (Surgery, Antibiotics, Facial cleanliness, Environmental improvement) was implemented in India.
Statement 2 is correct: The TT-only survey was conducted across 200 endemic districts to determine prevalence.
Statement 3 is incorrect: India is the third country in the WHO Southeast Asia Region (not the first) to eliminate Trachoma as a public health problem.
NBRI Develops GM Cotton Resistant to Pink Bollworm
Development by CSIR-NBRI
- Scientists at the CSIR-National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI) in Lucknow have claimed to develop the world’s first genetically modified (GM) cotton that is completely resistant to the Pink Bollworm (PBW).
Background on GM Cotton in India
- Since the introduction of GM cotton in India in 2002, varieties such as Bollgard 1 and Bollgard 2, developed in collaboration with Monsanto, have been effective against certain bollworm species. However, these varieties have not maintained strong resistance against the Pink Bollworm.
- The CSIR-National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI) is a leading research institution in India that focuses on botanical research and conservation.
Pink Bollworm (PBW): The Pink Bollworm, also known as gulabi sundhi, is a pest that damages the cotton crop by burrowing its larvae into the cotton bolls. This infestation cuts and stains the lint, making it unsuitable for use.
- The Pink Bollworm primarily spreads through the air. Residual infected crops left by farmers in the fields as fuel sources can also harbour PBW larvae, which may later infect future crops.
- To prevent further infestation, farmers are advised not to plant cotton in fields where PBW has been detected for at least one season. Burning crop residues at the earliest and ensuring no mixing between healthy and infected seeds are recommended preventive measures.
Genetically Modified (GM) Crops
- Genetically modified crops are plants that have undergone genetic engineering to alter their DNA. This process is carried out to introduce desirable traits such as pest resistance, herbicide tolerance, improved nutritional content, or increased yield.
- The creation of GM crops involves several steps, including the identification of desired traits, isolation of genes, insertion into the crop genome, and the expression of the trait.
- Techniques used in genetic modification include gene guns, electroporation, microinjection, and agrobacterium-mediated transformation.
- There are different types of genetic modifications, including transgenic (genes introduced from unrelated species), cis-genic (genes transferred within the same species), subgenic (genome editing without foreign gene insertion), and multiple trait integration (combining multiple modifications).
- The main genetically engineered traits in crops include herbicide tolerance (HT), insect resistance (IR), and stacked traits that combine multiple beneficial features.
Genetically Modified Crops in India
- Bt cotton was the first and, to date, the only GM crop to receive commercial approval in India. The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) approved its commercial release in 2002.
- Bt cotton contains two alien genes from the soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), which help the crop develop a protein toxic to the Pink Bollworm.
- Several other GM crops are currently in different stages of development in India, including Bt brinjal and DMH-11 mustard.
Regulatory Framework for GM Crops in India
- The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC), which functions under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC), is responsible for assessing proposals related to the commercial release of GM crops in India.
There are multiple acts and rules that regulate GM crops in India. These include:
- The Environment Protection Act, 1986
- The Biological Diversity Act, 2002
- The Plant Quarantine Order, 2003
- GM policy under the Foreign Trade Policy
- The Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006
- The Drugs and Cosmetics Rule (8th Amendment), 1988
- The development of PBW-resistant GM cotton by CSIR-NBRI marks an important step in India’s agricultural biotechnology sector. It represents a potential solution to a major pest problem while highlighting the ongoing debate over the role of GM crops in India’s agriculture.
Consider the following statements regarding the Pink Bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella):
- It primarily spreads through seed contamination rather than air transmission.
- The infestation damages the cotton lint, making it unfit for use.
- Burning crop residues is a recommended preventive measure against its infestation.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation: The Pink Bollworm primarily spreads through air transmission and through infected crop residues left on fields, not just through seed contamination. The damage to cotton lint and the recommendation to burn infected crop residues are correct
Vikram and Kalpana: ISRO Develops High-speed Microprocessors
Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Overview
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Semiconductor Laboratory (SCL), Chandigarh, have collaboratively developed two state-of-the-art 32-bit microprocessors—Vikram 3201 and Kalpana 3201.
Key Features and Specifications
Vikram 3201
- India’s first fully indigenous 32-bit microprocessor designed for space applications.
- Optimized to function under harsh conditions encountered in launch vehicles.
- Capable of processing 32 bits of data at a time.
- Supports floating-point computations, enhancing its efficiency in numerical and scientific calculations.
- Offers high-level language compatibility, ensuring ease of programming and integration into complex space systems.
Kalpana 3201
- A 32-bit SPARC V8 RISC microprocessor, adhering to the IEEE 1754 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA).
- Designed to be compatible with open-source software toolsets, increasing its adaptability for various applications.
- Successfully tested with flight software, demonstrating its reliability in mission-critical operations.
- These indigenous microprocessors mark a significant step towards self-reliance in semiconductor technology, particularly for aerospace and defense
With reference to ISRO’s newly developed Vikram 3201 microprocessor, consider the following statements:
- It is India’s first fully indigenous 64-bit microprocessor designed for space applications.
- It is specifically designed to function in the harsh conditions of launch vehicles.
- It supports floating-point computations, which enhances its numerical processing capabilities.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect because Vikram 3201 is a 32-bit microprocessor, not 64-bit.
Statement 2 is correct as Vikram 3201 is optimized for harsh launch vehicle conditions.
Statement 3 is correct since the microprocessor supports floating-point computations, which improve its efficiency in numerical processing.
ASTRA MK-III Renamed Gandiva
Syllabus: GS3/ Defence
- In News: India’s latest and most advanced beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air missile, Astra MK-III, has been officially renamed Gandiva.
Key Features of Gandiva Missile
- Extended Operational Range
- Capable of striking aerial targets at 340 km when launched from an altitude of 20 km.
- Effective up to 190 km when engaging enemy aircraft at 8 km altitude.
- Cutting-Edge Propulsion System
- Powered by a dual-fuel ducted ramjet engine, an advanced propulsion system that utilizes atmospheric oxygen for sustained high-speed flight.
- Operates within a launch speed range of 0.8 to 2.2 Mach and can engage enemy aircraft moving at speeds between 0 and 3.6 Mach.
Advanced Target Neutralization
- Designed to effectively engage and destroy a variety of aerial threats, including fighter jets, bombers, and military transport aircraft.
- The Gandiva missile significantly enhances India’s aerial combat capabilities, offering a superior beyond-visual-range interception system to counter modern aerial threats.
Consider the following statements regarding the Gandiva missile (Astra MK-III):
- It is India’s latest beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air missile.
- It is powered by a solid-fuel rocket engine for sustained high-speed flight.
- It has a maximum operational range of 340 km when launched from an altitude of 8 km.
- It is capable of engaging enemy aircraft moving at speeds between 2.0 and 3.6 Mach.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Correct Answer: (a) 1 and 4 only
Explanation:
Correct – The Gandiva missile is India’s latest beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air missile, enhancing aerial combat capabilities.
Incorrect – It is not powered by a solid-fuel rocket engine but by a dual-fuel ducted ramjet engine, which utilizes atmospheric oxygen for sustained high-speed flight.
Incorrect – The missile has a maximum operational range of 340 km when launched from an altitude of 20 km, not 8 km. At 8 km altitude, it has an effective range of 190 km.
Correct – It is capable of engaging enemy aircraft moving at speeds between 2.0 and 3.6 Mach.
TROPEX-2025
Syllabus: GS3/ Defence
Context
The Theatre-Level Operational Readiness Exercise (TROPEX) 25 is being conducted over a span of three months, from January to March 2025.
About TROPEX 25
- Largest Biennial Maritime Exercise organized by the Indian Navy, with significant participation from the Indian Army, Indian Air Force, and Coast Guard.
- Executed in multiple phases, both in Harbour and at Sea, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of operational preparedness.
Encompasses various dimensions of modern naval warfare, including:
- Cyber and Electronic Warfare Operations
- Live Weapon Firings during the Joint Work-Up Phase
- Amphibious Exercise (AMPHEX) focusing on integrated land-sea operations
- TROPEX 25 serves as a crucial platform for enhancing combat readiness, interoperability, and joint operational synergy among India’s armed forces.
.Consider the following statements regarding TROPEX 25:
- It is an annual maritime exercise conducted by the Indian Navy.
- It involves participation from the Indian Army, Indian Air Force, and the Coast Guard.
- The exercise includes cyber and electronic warfare, live weapon firings, and an amphibious exercise.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
TROPEX is a biennial (not annual) maritime exercise organized by the Indian Navy. It features participation from multiple branches of the armed forces and includes cyber warfare, live weapon firings, and amphibious operations.
Exercise Khanjar-XII
Syllabus: Defence
Context:
- The 12th edition of the India-Kyrgyzstan Joint Special Forces Exercise, Khanjar-XII, is scheduled to take place from March 10 to March 23, 2025, in Kyrgyzstan.
- This annual exercise, which began in 2011, alternates between the two countries.
- The Indian contingent consists of troops from the Parachute Regiment (Special Forces), while the Kyrgyzstan contingent includes the Kyrgyz Scorpion Brigade.
- The primary focus of the exercise is to enhance cooperation in counter-terrorism and special operations, particularly in urban and mountainous terrains.
Objectives of Khanjar-XII
The main aim of the exercise is to exchange expertise and best practices in counter-terrorism operations. Key focus areas include:
Sniping techniques
- Complex building interventions
- Mountain warfare training
- These skills are vital for both nations in tackling modern security threats, terrorism, and insurgency.
Cultural Exchange and Diplomatic Relations
- Beyond military training, Khanjar-XII also serves as a platform for cultural exchange. Participants will engage in cultural activities, including the celebration of Nowruz, a significant Kyrgyz festival.
- This fosters stronger diplomatic ties, mutual respect, and understanding between the two nations.
Strategic Importance
- The exercise underscores the deepening strategic ties between India and Kyrgyzstan.
- It reflects their shared commitment to regional security, counter-terrorism cooperation, and military preparedness.
- By jointly addressing transnational threats, both countries aim to contribute to peace and stability in the region.
Previous Editions of Khanjar Exercise
- Since its inception, the Khanjar series has continuously evolved, enhancing interoperability and operational readiness.
- The 11th edition was held in India in January 2024, building upon past experiences to strengthen counter-terrorism strategies.
India’s Broader Defence Cooperation
- In addition to Khanjar-XII, India is actively expanding its defence partnerships. Recently, India and Japan conducted the 7th Army-to-Army Staff Talks in New Delhi, focusing on:
- Military education
- Technological collaborations
- Operational training
- These initiatives highlight India’s growing defence cooperation with global partners, reinforcing its role in regional security and stability.
With reference to the India-Kyrgyzstan Joint Special Forces Exercise ‘Khanjar-XII,’ consider the following statements:
- The exercise has been conducted annually since 2011 and is held exclusively in Kyrgyzstan.
- The Indian contingent primarily consists of personnel from the Ghatak Platoon of the Indian Army.
- The Kyrgyzstan contingent in Khanjar-XII includes the Kyrgyz Scorpion Brigade.
- The exercise mainly focuses on naval warfare and maritime security cooperation.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 3 only
c) 1, 3, and 4 only
d) 2 and 4 only
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 – Incorrect: While the exercise began in 2011, it is not exclusively held in Kyrgyzstan. It alternates between India and Kyrgyzstan.
Statement 2 – Incorrect: The Indian contingent consists of troops from the Parachute Regiment (Special Forces), not the Ghatak Platoon.
Statement 3 – Correct: The Kyrgyz Scorpion Brigade is the designated unit from Kyrgyzstan participating in the exercise.
Statement 4 – Incorrect: The exercise focuses on counter-terrorism, special operations, and mountain warfare, not naval warfare or maritime security.
WMO’s State of Climate 2024 Report
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has released the State of Climate 2024 report, revealing alarming trends in greenhouse gas concentrations, global temperatures, and environmental changes.
Greenhouse Gas Concentration
- In 2023, carbon dioxide (CO₂) levels reached 420 parts per million (ppm)—the highest recorded in 800,000 years.
- Alongside CO₂, concentrations of methane (CH₄) and nitrous oxide (N₂O) also surged to record levels, intensifying the greenhouse effect and contributing to unprecedented temperature rises.
Global Temperature Milestone
- The year 2024 marked a critical threshold in global warming.
- The global mean near-surface temperature was 1.55°C above pre-industrial levels, exceeding the 1.5°C limit set by the Paris Agreement for the first time in a single year.
- While this does not necessarily mean a permanent breach of the target, it signals increased risks to ecosystems and human societies.
Long-Term Warming Trends
- The WMO estimates long-term warming to be between 1.34°C and 1.41°C above pre-industrial levels (1850–1900).
- Climate projections indicate that, if current trends persist, the 1.5°C threshold could be permanently exceeded by 2029, pushing the planet closer to critical climate tipping points.
Ocean Heat and Sea Level Rise
- The past eight years have recorded the highest ocean heat content, with 90% of excess heat from greenhouse gases absorbed by the oceans.
- Sea levels continue to rise at an accelerated pace, doubling since satellite measurements began. The primary contributors to this rise are the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers.
Intensified Extreme Weather Events
- The increase in greenhouse gas levels has fueled more frequent and severe extreme weather events, including tropical cyclones, heavy rainfall, floods, and droughts.
- In 2024, climate-related displacements reached their highest levels since 2008, highlighting the worsening humanitarian impact of climate change.
Cryosphere Changes and Ice Loss
- The cryosphere is undergoing dramatic transformations, with glaciers retreating at an alarming rate.
- Antarctic sea ice has recorded its second-lowest extent ever, while seven of the last ten years have witnessed the highest negative mass balance of glaciers, indicating substantial ice loss.
- These trends threaten global sea levels, freshwater availability, and ecosystems dependent on frozen water reserves.
With reference to the WMO’s State of Climate 2024 report, consider the following statements:
- The global mean near-surface temperature in 2024 was recorded at 1.55°C above pre-industrial levels, marking the first instance of exceeding the Paris Agreement threshold of 1.5°C for an entire decade.
- The rise in greenhouse gases, including CO₂, CH₄, and N₂O, has led to ocean heat content reaching its highest levels in recorded history.
- The report indicates that the melting of glaciers and polar ice caps is solely responsible for rising sea levels worldwide.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is partially correct; the 1.55°C rise was recorded in a single year, not over a decade. However, it does indicate growing climate instability.
Statement 2 is correct; 90% of excess heat is absorbed by oceans, increasing ocean heat content.
Statement 3 is incorrect; while glacier and ice cap melting contributes significantly to rising sea levels, thermal expansion of seawater due to global warming is another major factor.
Phansad Wildlife Sanctuary
Phansad Wildlife Sanctuary: Conservation & Ecological Significance
- First honey harvest near Phansad Wildlife Sanctuary marks a major success for conservationists, naturalists, and tribal communities in Maharashtra.
- This initiative aligns with sustainable conservation practices while promoting local livelihoods and biodiversity preservation.
Phansad Wildlife Sanctuary: Geographical & Ecological Overview
Location & History:
- Situated in the Murud region of Raigad district, Maharashtra.
- Created to protect the unique coastal woodland ecosystem of the Western Ghats.
Historical Significance:
- The area was once a hunting reserve of the princely state of Murud-Janjira.
Geographical Features:
- Total area: 17,250 acres.
- Comprises forests, grasslands, and wetlands.
Mals:
- Pockets of open grassland within the sanctuary.
Flora:
Notable tree species:
- Ain (Terminalia tomentosa)
- Kinjal (Terminalia paniculata)
- Teak (Tectona grandis)
- Hirda (Terminalia chebula)
- Jamba
- Mango (Mangifera indica)
- Ficus species
Fauna:
- Mammals:
- Leopard (Panthera pardus fusca)
- Hyena (Hyaena hyaena)
- Sambar Deer (Rusa unicolor)
- Mouse Deer (Tragulus kanchil)
Avian Species:
- Malabar Pied Hornbill (Anthracoceros coronatus)
- Black Eagle (Ictinaetus malaiensis)
- Yellow-Footed Green Pigeon (Treron phoenicopterus)
- Pompadour Green Pigeon (Treron pompadora)
- Forest Wagtail (Dendronanthus indicus)
- White-rumped Vulture (Gyps bengalensis) – Critically Endangered
Consider the following statements regarding Phansad Wildlife Sanctuary:
- It is located in the Sindhudurg district of Maharashtra.
- The sanctuary was historically a hunting reserve of the princely state of Murud-Janjira.
- It is part of the Western Ghats and protects a unique coastal woodland ecosystem.
- The White-rumped Vulture, a critically endangered species, is found in the sanctuary.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3, and 4 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect – The sanctuary is in Raigad district, not Sindhudurg.
Statement 2 is correct – The princely state of Murud-Janjira used this area as a hunting reserve.
Statement 3 is correct – The sanctuary is part of the Western Ghats’ coastal woodland ecosystem.
Statement 4 is correct – The White-rumped Vulture (Gyps bengalensis), a critically endangered species, is found in the sanctuary.
Kanger Valley National Park
- Kanger Valley National Park (KVNP), situated in the formerly Maoist-affected region of Bastar district in Chhattisgarh, has recently been added to UNESCO’s tentative list of World Heritage Sites under the ‘Natural’ category.
- This recognition highlights the park’s ecological significance and rich biodiversity.
Overview of Kanger Valley National Park
Location & Geography
- KVNP is located in Jagdalpur, Bastar district, Chhattisgarh.
- The park is named after the Kanger River, which flows from Northwest to Southeast through the valley.
- The Kanger River is a tributary of the Kolab River, which eventually merges with the Godavari River.
- The terrain consists of flatlands, gentle slopes, steep inclines, plateaus, deep gorges, valleys, and winding streams.
- The Tirathgarh Waterfall, formed by the Kanger River, cascades from a height of 150 feet, offering a spectacular sight.
- The park houses over 15 limestone caves, including the Kotumsar, Kailash, and Dandak caves, known for their geological formations and underground ecosystems.
Flora
- KVNP exhibits a mixed moist deciduous forest, with dominant species such as Sal, Teak, and Bamboo.
Fauna
- Mammals: The park is home to tigers, leopards, mouse deer, wildcats, sambar, chital, barking deer, langurs, jackals, rhesus macaques, and flying squirrels.
- Avian Species: The aerial biodiversity includes common hill mynas, red jungle fowls, spotted owlets, racket-tailed drongos, and various species of parrots.
- The inclusion of Kanger Valley National Park in UNESCO’s tentative list underscores its ecological importance, unique geological formations, and diverse wildlife, making it a crucial conservation site in central India.
Consider the following statements regarding Kanger Valley National Park (KVNP):
- It is located in the Durg district of Chhattisgarh.
- The Kanger River, after flowing through the park, directly merges with the Godavari River.
- KVNP is characterized by the presence of limestone caves, plateaus, deep gorges, and waterfalls.
- It has been included in the tentative list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites under the ‘Cultural’ category.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: (c) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: KVNP is located in Bastar district, not Durg district.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The Kanger River is a tributary of the Kolab River, which eventually joins the Godavari River, but it does not merge directly with the Godavari.
Statement 3 is correct: The park is known for limestone caves, deep gorges, plateaus, waterfalls (Tirathgarh Falls), and diverse topography.
Statement 4 is incorrect: KVNP has been added to UNESCO’s tentative list under the ‘Natural’ category, not the ‘Cultural’ category.
Caracal
- A rare caracal has been recently sighted in Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve, Rajasthan, generating excitement among wildlife enthusiasts.
About Caracal
- The caracal is a medium-sized, nocturnal wildcat known for its agility and striking black-tipped ears.
- Indian Name: Siya Gosh (Persian: “Black Ear”).
- Scientific Name: Caracal caracal
Distribution & Habitat
- Found in Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia.
- In India, their population is critically low, with an estimated 50 individuals, primarily in Rajasthan and Gujarat.
- They inhabit rocky hills, grasslands, savannas, scrublands, and forests, showcasing high adaptability to various environments.
Physical Features
- Slender body, long legs, and largest among small African cats.
- Size: 8–18 kg in weight, up to 1 meter in length.
- Fur: Short, dense, and varies from tawny-brown to reddish-tan, with whitish underparts.
- Facial markings: Dark lines and white spots around the eyes.
- Distinctive black-tipped ears with tufts, aiding in communication.
Unique Abilities
- Renowned for leaping over 2 meters to catch birds mid-air.
- Can sprint at speeds of up to 80 km/h (50 mph).
- Solitary by nature, but may occasionally form small groups.
- Shy and elusive, making sightings in the wild extremely rare.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern (globally), but faces severe population decline in India.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I (providing the highest level of legal protection in India).
- The recent sighting in Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve highlights the need for focused conservation efforts to protect this elusive species in India.
: With reference to the Caracal (Caracal caracal) in India, consider the following statements:
- The caracal is listed as Critically Endangered under the IUCN Red List in India.
- It is known for its ability to leap several meters into the air to catch birds in flight.
- In India, its population is mainly found in Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Madhya Pradesh.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The caracal is listed as “Least Concern” globally on the IUCN Red List, though its population in India is highly threatened.
Statement 2 is correct: Caracals are exceptional jumpers and can leap over 2 meters to catch birds in mid-air.
Statement 3 is incorrect: In India, the caracal is primarily found in Rajasthan and Gujarat, but not significantly in Madhya Pradesh.
Sustainable Development vs. Environmental Protection
- The Supreme Court recently overturned the National Green Tribunal (NGT) order that had halted the Auroville Foundation’s township project in Puducherry due to the absence of environmental clearance.
Key Aspects of the Judgment
- The Supreme Court reaffirmed the precautionary principle and the polluter pays principle as integral components of India’s environmental law.
- It recognized the right to a clean environment as a fundamental right under Articles 14 (equality) and 21 (right to life) of the Constitution.
- Simultaneously, the Court acknowledged that the right to development through industrialization is also a fundamental right, deriving its legitimacy from Articles 14, 19 (right to practice any profession, trade, or business), and 21 of the Constitution.
- The judgment emphasized the necessity of maintaining a “golden balance” between environmental protection and economic development.
Which of the following principles were recognized by the Supreme Court as part of India’s environmental law in the Auroville case?
1.Polluter Pays Principle
2. Precautionary Principle
3. Sustainable Development Principle
4. Intergenerational Equity Principle
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2, and 3 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation: The Supreme Court explicitly cited the Polluter Pays Principle and Precautionary Principle as fundamental to India’s environmental jurisprudence. While the Sustainable Development Principle and Intergenerational Equity Principle are also important in environmental law, they were not explicitly highlighted in this judgment
Corbett Tiger Reserve
Recent Developments
The Supreme Court recently criticized the Uttarakhand government for its slow action against senior officials accused of illegal constructions within the Corbett Tiger Reserve.
About Corbett Tiger Reserve
Location: Situated in the foothills of the Himalayas in Uttarakhand.
Establishment:
- Established in 1936 as Hailey National Park, making it India’s first national park.
- Renamed Corbett National Park in 1957 to honor Jim Corbett, a renowned conservationist and naturalist.
Area:
- Initially designated as a national park, later expanded to cover 1,288.31 sq. km as a Tiger Reserve.
Topography:
- Characterized by an undulating terrain with multiple valleys.
- Major rivers: Ramganga, Pallaen, and Sonanadi.
- Predominantly located in the Bhabar and lower Shivalik regions, featuring porous soil, boulder deposits, and a deep water table.
Flora
Dominated by Sal forests, along with Sheesham and Kanju trees, particularly along ridges.
Grasslands (locally called ‘Chaur’) are remnants of abandoned settlements and clearings.
- Riparian vegetation thrives along riverbanks.
- Invasive species: Lantana, an aggressive weed, poses a significant ecological challenge.
Fauna
- Flagship species: Tigers and elephants.
- Other carnivores: Leopards, small carnivores.
- Herbivores: Sambar, hog deer, spotted deer.
- Avifauna: A diverse range of bird species.
- Reptiles: Gharials, crocodiles.
- Aquatic life: Rich fish diversity in reserve rivers.
Consider the following statements regarding the Corbett Tiger Reserve:
- It was originally established as Corbett National Park in 1936 and later renamed Hailey National Park in 1957.
- The reserve is predominantly located in the Terai region of Uttarakhand.
- The Ramganga, Pallaen, and Sonanadi rivers flow through the reserve.
- Lantana, an invasive species, poses a serious ecological threat to the reserve’s biodiversity.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The park was originally established as Hailey National Park in 1936, later renamed Corbett National Park in 1957.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The reserve is predominantly located in the Bhabar and lower Shivalik regions, not the Terai region.
Statement 3 is correct: Ramganga, Pallaen, and Sonanadi are the major rivers that flow through the reserve.
Statement 4 is correct: Lantana, an invasive weed, has spread extensively in the forest and poses a significant ecological challenge.
Global Forest Vision 2030
About the Forest Declaration Assessment (FDA)
- Initially launched in 2015 as the New York Declaration on Forests (NYDF) Progress Assessment.
- The NYDF, adopted in 2014 at the UN Climate Summit, is a voluntary, non-binding
It establishes 10 goals, including:
- Halting deforestation by 2030.
- Restoring 350 million hectares of degraded landscapes.
- India is not a signatory to the NYDF.

Key Findings of the 2023 FDA Report
- Alarming Forest Loss
- 37 million hectares of forest lost in 2023 alone (equivalent to 9 million soccer fields).
- Major drivers of deforestation:
- Palm oil
- Soy production
- Beef cattle ranching
- Timber harvesting
- Affected regions: Amazon, Southeast Asia, Africa.
- Impact on Biodiversity
- Amazon: Cattle ranching causes 80% of deforestation across all Amazonian countries.
- Southeast Asia: Palm oil plantations threaten species like orangutans and Sumatran tigers.
- Palm oil alone contributes 5% to global tropical deforestation.
- Key Recommendations of the Report
- Align national policies with global forest conservation goals under UNFCCC COP30 (to be held in Brazil, 2025).
- Strengthen deforestation-free trade agreements and ban imports of products linked to forest destruction.
Increase financial incentives, such as:
- Results-based payments for forest conservation.
- Forest carbon finance mechanisms.
- Protect Indigenous Peoples and Local Communities (IPs & LCs) by securing land and resource rights.
- Ensure financial institutions integrate forest-related risks into investment decisions.
- Redirect harmful subsidies toward sustainable land-use practices.
- Improve forest governance by strengthening environmental commitments.
- Integrate forest natural capital into national debt management frameworks.
India’s Role: Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges:
- High dependency on imported palm oil and timber.
- Lack of trade restrictions on products linked to deforestation.
- Small farmers may struggle to prove deforestation-free production due to limited access to technology.
Opportunities:
- Introduce deforestation-free import laws to regulate trade practices.
- Support small farmers through capacity building, financial aid, and technological advancements.
- Lead South-South cooperation on sustainable agriculture and responsible trade practices.
- Integrate deforestation-free strategies with existing initiatives such as:
- Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA)
- National Agroforestry Policy
- National Bio-Energy Mission
With reference to the Forest Declaration Assessment (FDA) Report 2023, consider the following statements:
- The FDA was originally launched as the New York Declaration on Forests (NYDF) Progress Assessment in 2015.
- India is a signatory to the NYDF, committing to halt deforestation by 2030.
- The FDA report highlights that palm oil is responsible for nearly 50% of global tropical deforestation.
- The Amazon rainforest is primarily affected by illegal mining and urban expansion, rather than cattle ranching.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4
Answer: (c) 1 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The FDA was launched in 2015 as a continuation of the New York Declaration on Forests (NYDF) Progress Assessment.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: India is not a signatory to the NYDF.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: Palm oil contributes 5%, not 50%, to global tropical deforestation.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: Cattle ranching, not illegal mining or urban expansion, is the largest cause (80%) of deforestation in the Amazon.
Iguana

- Iguanas are large, robust lizards predominantly found in the tropical regions of the Americas.
- Characterized by scaly skin adorned with warts and spines along their backs, they also possess a distinctive dewlap (flap of flesh) under their necks.
- These herbivorous reptiles exhibit a variety of color morphs, including green, blue, and grey, adapting to diverse environments ranging from arid deserts to dense rainforests.
Geographic Distribution
- Native Habitat: Found across Central and South America, spanning from Mexico to Paraguay and Brazil.
- Introduced Regions: Established populations in Florida, Hawaii, and Caribbean islands.
- Largest Lizard in the USA: The green iguana holds the title of the largest lizard species within U.S. borders.
- Arboreal Nature: Primarily tree-dwelling, descending only for nesting.
- Preferred Habitats
- Terrestrial Biomes: Forests & rainforests
- Aquatic Biomes: Rivers, lakes, and coastal waters
- Wetlands: Swamps
- Urban & Agricultural Areas: Display adaptability to suburban environments
Conservation Status & Threats
- IUCN Red List: Currently not threatened.
- CITES Listing: Appendix II, meaning trade is regulated to prevent overexploitation.
Major Threats:
- Overexploitation due to demand in the pet trade and leather industry.
- Habitat destruction resulting from deforestation and urban expansion.
How Did Iguanas Reach Fiji?
- A recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences suggests that the ancestors of Fijian iguanas undertook an extraordinary 8,000 km journey across the Pacific Ocean from the Americas, using rafts of floating vegetation.
The Rafting Hypothesis
- Rafting: A process where animals travel across oceans by drifting on natural floating debris.
- Common among: Small invertebrates such as insects, but rare for large vertebrates due to survival challenges.
Previous Evidence of Iguana Rafting
- 1995 Caribbean Observation: Scientists observed 15 green iguanas rafting 300 km across the ocean on hurricane debris.
- Galápagos Iguanas: Likely rafted 1,000 km from South America to the Galápagos Islands.
- Fijian Iguana Migration: The 8,000 km voyage remains one of the longest known instances of vertebrate rafting, making it an exceptional biological phenomenon.
Consider the following statements regarding iguanas:
- Iguanas are exclusively carnivorous and thrive in desert ecosystems.
- They possess a dewlap, a flap of flesh under their neck, which helps in thermoregulation and communication.
- The largest lizard found within U.S. borders is the Komodo dragon.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: b) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Iguanas are primarily herbivorous, feeding on leaves, flowers, and fruits. While they are adaptable to different environments, they are not exclusive desert dwellers and are more commonly found in tropical forests and wetlands.
Statement 2 is correct: The dewlap helps in communication, thermoregulation, and dominance displays among iguanas.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The largest lizard within U.S. borders is the green iguana (Iguana iguana), not the Komodo dragon, which is native to Indonesia.
World Happiness Report 2025
- The World Happiness Report 2025, recently released by the Wellbeing Research Centre at the University of Oxford, evaluates global happiness levels based on citizens’ self-assessed life satisfaction.
Methodology of the Report
- The rankings are derived from global surveys measuring individuals’ perceptions of their lives.
- The study is a collaboration between the Wellbeing Research Centre, Gallup, and the United Nations Sustainable Development Solutions Network.
- Key factors influencing happiness include GDP per capita, healthy life expectancy, social support, freedom, generosity, and perceptions of corruption.
Key Insights on Happiness Determinants
- The report highlights that happiness is influenced by more than just economic wealth. Strong social bonds, trust, and acts of kindness play a critical role in determining life satisfaction.
- Individuals who regularly share meals and have reliable social support networks report higher happiness levels. Interestingly, people underestimate the kindness of others—studies show that actual rates of returning lost items are significantly higher than expected.
Global Rankings and Trends
- In 2025, Finland continues to hold the top position, followed by Denmark, Iceland, and Sweden.
- Israel secures the eighth spot despite ongoing conflicts. Costa Rica and Mexico enter the top ten for the first time, ranking sixth and tenth, respectively.
- Meanwhile, the United States drops to its lowest position at 24, and the United Kingdom ranks 23rd.
- Afghanistan remains the least happy nation, followed by Sierra Leone and Lebanon.
Rising Loneliness Among Young Adults
- A troubling trend observed in the report is the increasing loneliness among young adults.
- Since 2006, there has been a rise in social isolation, with 19% of young people reporting they lack social support.
- This lack of human connection significantly reduces happiness levels, emphasizing the need to foster stronger community ties for overall well-being.
India’s Position in the Happiness Index
- India is ranked 118 out of 147 countries in the 2025 report.
- Despite strong social support structures, the country faces challenges with perceptions of freedom.
- Among its neighbors, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Nepal, and China rank lower than anticipated, with China at 68.
The Role of Kindness and Community in Happiness
- The report underscores the reciprocal benefits of caring and sharing, where both the giver and receiver experience an uplift in well-being.
- Encouraging community participation, trust, and generosity could significantly improve happiness levels across societies.
Consider the following factors used in the World Happiness Report to rank countries:
- GDP per capita
- Social support
- Military expenditure as a percentage of GDP
- Perceptions of corruption
- Healthy life expectancy
Which of the above factors are considered in the report’s methodology?
a.1, 2, 3, and 5
b.1, 2, 4, and 5
c.2, 3, 4, and 5
d.1, 3, 4, and 5
Answer: (b) 1, 2, 4, and 5
Explanation:
- The World Happiness Report considers GDP per capita, social support, perceptions of corruption, and healthy life expectancy as key determinants.
- However, military expenditure is not included as a ranking factor. The report primarily focuses on factors influencing individual well-being rather than national security metrics.
World Puppetry Day
About World Puppetry Day
- World Puppetry Day is observed annually on March 21st to celebrate puppetry as a global art form and to honor puppeteers worldwide.
- This day highlights the significance of puppetry in cultural storytelling, entertainment, and artistic expression across various mediums, including stage, television, and film.
Understanding Puppetry
- Puppetry is an ancient performing art that involves crafting and manipulating puppets—figures representing humans, animals, or abstract forms—without mechanical aid.
- Puppets are controlled manually to create theatrical performances that engage audiences through storytelling and social commentary.
Puppetry in India
- India has a rich tradition of puppetry, deeply rooted in folklore, mythology, and artistic expression.
- The art has been used for centuries to narrate historical epics, moral tales, and social issues.

Major Types of Puppetry in India
- String Puppets (Kathputli): Predominantly found in Rajasthan and Gujarat, these puppets are manipulated using strings and often depict folk tales and traditional narratives.
- Shadow Puppets: Crafted from leather, these puppets are used to cast shadows on a screen. This form is especially popular in Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala.
- Rod Puppets: Controlled with rods, these puppets are commonly used in West Bengal and Assam, often portraying mythological stories.
- Glove Puppets: Worn on the puppeteer’s hands, these puppets are particularly known in Kerala (Pavakathakali), blending elements of classical dance with puppetry.
The celebration of World Puppetry Day emphasizes the cultural importance of puppetry and encourages the preservation and promotion of this unique art form.
With reference to puppetry in India, consider the following statements:
- The Kathputli form of puppetry, primarily found in Rajasthan, is a type of rod puppetry.
- Shadow puppetry is practiced in states such as Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Pavakathakali, a type of glove puppetry, is influenced by Kathakali dance traditions.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Kathputli is not rod puppetry but a string puppetry form, primarily found in Rajasthan and Gujarat. (Statement 1 is incorrect.)
- Shadow puppetry is a traditional art form seen in Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh, where leather puppets cast shadows on a screen. (Statement 2 is correct.)
- Pavakathakali, a glove puppet tradition from Kerala, is inspired by Kathakali dance, incorporating similar costume styles and expressions. (Statement 3 is correct.)
Rang Panchami
Rang Panchami is celebrated five days after Holi, serving as the grand conclusion to the festive revelries.
Significance and Meaning
- The term “Rang Panchami” is derived from two words—”Rang” (color) and “Panchami” (fifth day)—indicating its occurrence on the fifth day after Holi.
Regional Observance
- This vibrant festival is predominantly celebrated in Maharashtra, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and parts of Rajasthan with great enthusiasm.
Traditions and Festivities
- Rang Panchami signifies the arrival of spring, bringing communities together to rejoice in the spirit of color.
- People mark the occasion by throwing and applying colored powders (gulal) on each other, creating an atmosphere of joy and togetherness.
Consider the following statements regarding Rangpanchami:
- It is celebrated on the full moon day of the Hindu month of Phalguna.
- The festival marks the end of Holi celebrations and is observed primarily in western and central India.
- Unlike Holi, Rangpanchami is associated with invoking spiritual and cosmic energies through colors.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Rangpanchami is celebrated five days after Holi, not on the full moon day (Purnima) of Phalguna.
Statement 2 is correct: It is mainly observed in Maharashtra, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
Statement 3 is correct: Unlike Holi, which is more social and playful, Rangpanchami has a spiritual aspect, where colors are believed to activate cosmic energies.
Project Pari
Public Art of India (PARI) Project
- The PARI project is an initiative launched by the Ministry of Culture to promote and enrich India’s public art landscape. It is implemented by the Lalit Kala Akademi and the National Gallery of Modern Art (NGMA).
- The project showcases the country’s diverse regional art forms, including Phad, Thangka, Gond, and Warli, featuring the work of over 200 artists.
- Currently, the PARI project is operational only in Delhi, where it aims to foster public engagement through artistic expression. It encourages dialogue and reflection by integrating India’s rich cultural heritage with contemporary themes.
- As part of the government’s broader efforts, the initiative provides incentives to talented artists, ensuring the preservation and promotion of India’s artistic traditions in modern public spaces.

With reference to the “Public Art of India (PARI) Project”, consider the following statements:
- The project is implemented by the Ministry of Culture in collaboration with private institutions.
- It primarily focuses on integrating India’s ancient art traditions with modern artistic expressions.
- As of now, the project has been implemented in multiple cities across India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The project is implemented by the Ministry of Culture but executed through Lalit Kala Akademi and the National Gallery of Modern Art (NGMA), not private institutions.
Statement 2 is correct: PARI aims to blend India’s rich cultural heritage with contemporary themes, making it a fusion of traditional and modern art.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Currently, the project is limited to Delhi and has not yet been expanded to other cities.
Indo-U.S. Cultural Property Agreement
Context:
- India has signed the Cultural Property Agreement (CPA) with the United States of America (USA) to prevent the smuggling of Indian antiquities.
Key Highlights of the Indo-U.S. Cultural Property Agreement:
Objective: Aims to prevent the illicit trafficking of Indian cultural artifacts and antiquities.
Legal Framework:
- Aligns with Article 9 of the 1970 UNESCO Convention, which allows countries facing threats to their cultural heritage to seek international assistance.
- Focuses on preventive measures rather than specific timelines or numerical targets.
Impact:
- A total of 588 antiquities have been repatriated from the USA, with 297 returned in 2024 alone.
- Strengthens cooperation in areas of technical assistance, combating illicit trade, and addressing the looting of cultural property.
International Collaboration:
- India engages with UNESCO, INTERPOL, and other global bodies to protect and repatriate cultural heritage.
Consider the following statements regarding the Indo-U.S. Cultural Property Agreement (CPA):
- The agreement is time-bound and aims to repatriate a minimum number of artifacts per year.
- It is focused only on the repatriation of stolen artifacts and does not involve broader cooperation in cultural heritage protection.
- India collaborates with international agencies like UNESCO and INTERPOL to combat illicit trafficking of cultural property.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A.1 only
B. 2 only
C. 3 only
D. 2 and 3 only
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The CPA is preventive in nature and does not have specific timelines or a target number for repatriations.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The agreement includes technical cooperation and measures to prevent illicit trade, not just repatriation.
Statement 3 is correct: India collaborates with UNESCO, INTERPOL, and other global organizations to combat the trafficking
