National Disaster Management Authority
Establishment of the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
Background:
- The NDMA was created in response to the growing need for disaster management following several national disasters, including the Gujarat earthquake in 2001 and the Indian Ocean tsunami in 2004.
- The Disaster Management Act was enacted in 2005, leading to the formal establishment of the NDMA to provide a cohesive approach to disaster management in India.
- Initially constituted by Executive Order in 2005, the NDMA was officially notified in 2006.
Structure:
- The NDMA is led by the Prime Minister as the ex-officio chairperson, with up to nine members nominated by the chairperson.
- The vice-chairperson of the NDMA holds Cabinet Minister status, while other members hold Minister of State status.
- The authority operates under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
Vision of the NDMA
The NDMA aims to build a safer and disaster-resilient India through:
- A holistic, proactive, and technology-driven strategy that engages all stakeholders.
- Promoting a culture of preparedness and mitigation.
Objectives of the NDMA
The NDMA focuses on:
- Cultivating a culture of resilience and preparedness through knowledge and education.
- Encouraging sustainable mitigation measures and integrating disaster management into development planning.
- Establishing institutional frameworks and promoting compliance.
- Developing risk assessment and monitoring systems.
- Implementing forecasting and early warning systems.
- Supporting vulnerable groups during disasters.
- Leveraging reconstruction efforts to create disaster-resilient infrastructure.
- Partnering with media for effective disaster communication
Functions of the NDMA
The primary functions include:
- Formulating policies for disaster management.
- Approving the National Plan and departmental plans aligned with it.
- Laying down guidelines for State Disaster Management Authorities (SDMAs).
- Coordinating disaster management policies and plans at the national level.
- Recommending funding for mitigation efforts.
- Providing assistance and support to countries affected by major disasters.
- Ensuring effective disaster prevention and response measures.
- Supervising the National Institute of Disaster Management.
Additional Functions
The NDMA also:
- Sets minimum relief standards for disaster-affected individuals.
- Facilitates loan relief and concessions for severe disasters.
- Oversees the National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) for specialized disaster responses.
- Authorizes emergency procurement for relief activities.
- Compiles and submits annual reports to the central government and Parliament.
State Disaster Management Authority (SDMA)
Composition
- Every state must establish an SDMA, headed by the Chief Minister as ex-officio chairperson.
- The SDMA comprises the chairperson (Chief Minister), the chairperson of the State Executive Committee, and up to eight other members nominated by the chairperson.
Functions
The SDMA is responsible for:
- Formulating the state disaster management policy.
- Approving the State Plan based on NDMA guidelines.
- Reviewing and integrating disaster management plans across state departments.
- Coordinating the implementation of the State Plan.
- Recommending funding for preparedness and mitigation.
- Monitoring capacity building and preparedness initiatives at the state level.
This comprehensive framework established by the NDMA ensures a coordinated and effective strategy for disaster management across India, addressing prevention, preparedness, response, and recovery from disasters.
District Disaster Management Authority (DDMA)
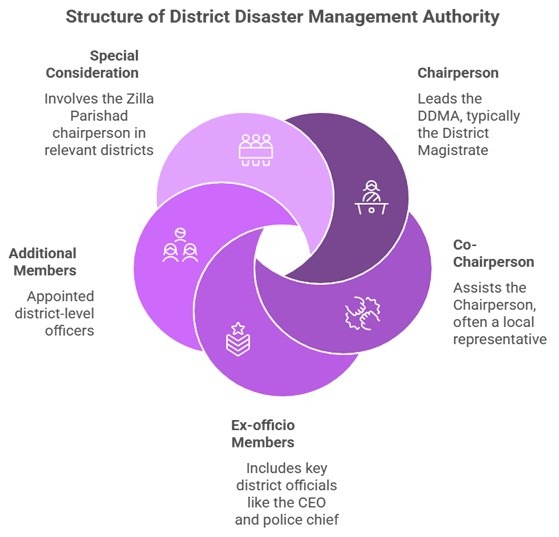
Composition: Each state government must establish a District Disaster Management Authority (DDMA) for every district. The DDMA is composed of the following members:
- Chairperson: The Collector (District Magistrate or Deputy Commissioner) of the district.
-
- Co-Chairperson:
- The elected representative of the local authority, or
- In Tribal Areas (as per the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution), the chief executive member of the district council of the autonomous district.
- Co-Chairperson:
-
- Ex-officio Members:
- Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of the DDMA (appointed by the state government).
- Superintendent of Police.
- Chief Medical Officer of the district.
- Ex-officio Members:
-
- Additional Members: Up to two other district-level officers appointed by the state government.
-
- Special Consideration: In districts with a Zilla Parishad, the chairperson of the Zilla Parishad becomes the co-chairperson of the DDMA.
Functions of the DDMA
The DDMA serves as the planning, coordinating, and implementing body for disaster management within the district, operating under the guidelines set by the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) and the State Disaster Management Authority (SDMA). Its key functions include:
1. Preparation of Disaster Management Plan: Develop a comprehensive disaster management plan, including a district response plan.
2. Coordination and Monitoring: Ensure implementation of the National Policy, State Policy, National Plan, State Plan, and District Plan.
3. Identification of Vulnerable Areas: Identify areas prone to disasters and facilitate preventive measures from government departments and local authorities.
4. Guideline Compliance: Ensure adherence to NDMA and SDMA guidelines on prevention, mitigation, preparedness, and response across all levels of government and local authorities.
5. Training Programs: Organize specialized training for officers, employees, and voluntary rescue workers.
6. Community Awareness: Facilitate community training and awareness initiatives in collaboration with local authorities and NGOs.
7. Early Warning Systems: Establish and maintain mechanisms for early warning and information dissemination to the public.
8. Advisory Role: Advise and coordinate with government departments, statutory bodies, and NGOs involved in disaster management.
9. Identification of Relief Centers: Identify suitable buildings or locations for use as relief centers or camps and arrange for water supply and sanitation.
10. Additional Functions: Undertake any other functions assigned by the state government or SDMA deemed necessary for effective disaster management in the district.
The National and State Disaster Management Authority serves as a crucial institution for coordinating and implementing disaster response and mitigation efforts. With its establishment at national, state, and district levels, it plays a pivotal role in ensuring preparedness, coordination, and effective response to disasters. Through its advisory committees and institutional mechanisms, it facilitates collaboration among various stakeholders to enhance disaster resilience and minimize the impact of calamities on communities.