Attorney General of India
Attorney General of India
The Attorney General of India (AG) is the highest legal officer in the country, serving as the chief law advisor to the Government of India. The role and responsibilities of the Attorney General are outlined in Article 76 of the Constitution.
Appointment and Term
1. Appointment:
- The Attorney General is appointed by the President of India.
- To qualify for the position, the individual must meet one of the following criteria:
- Must be a citizen of India.
- Must have served as a judge of a High Court for at least five years.
- Must have practiced as an advocate in a High Court for at least ten years.
- Must be considered an eminent jurist in the opinion of the President.
2. Term of Office:
- The term of office for the Attorney General is not specified in the Constitution; he holds office during the pleasure of the President.
- The President can remove the Attorney General at any time, and the AG may resign by submitting his resignation to the President.
3. Remuneration:
- The AG’s salary is not fixed by the Constitution. The President determines the remuneration of the Attorney General.
Duties and Functions
The Attorney General has several key responsibilities as the principal legal advisor to the Government of India:
1. Legal Advice:
- The AG provides legal advice to the Government of India on matters referred by the President.
2. Assigned Duties:
- The President may assign additional legal duties to the AG, which he is required to perform.
3. Constitutional and Legal Functions:
- The AG discharges functions conferred upon him by the Constitution or any other law.
Representation in Legal Matters
The Attorney General has specific duties related to representing the Government of India in legal matters:
1. Supreme Court Representation:
- The AG appears on behalf of the Government of India in all cases before the Supreme Court involving the government.
2. Advisory Role:
- The Attorney General represents the government in any reference made by the President to the Supreme Court under Article 143of the Constitution, which pertains to advisory opinions.
3. Representation in High Courts:
- The AG may also be called upon to appear in any High Court on behalf of the Government of India when required.
The Attorney General of India plays a vital role in the country’s legal framework by providing legal advice to the government and representing it in judicial matters. The appointment process and the significant responsibilities outlined in the Constitution reflect the importance of the AG in upholding the rule of law and facilitating effective governance in India. The AG’s independence ensures that legal opinions and representations are made without bias, serving the interests of justice and the Constitution.
Rights and Limitations of the Attorney General of India
The Attorney General of India (AG) plays a critical role as the chief legal advisor to the Government of India. While the AG possesses significant rights and privileges, there are also important limitations placed on his duties to prevent conflicts of interest and maintain the integrity of the office.
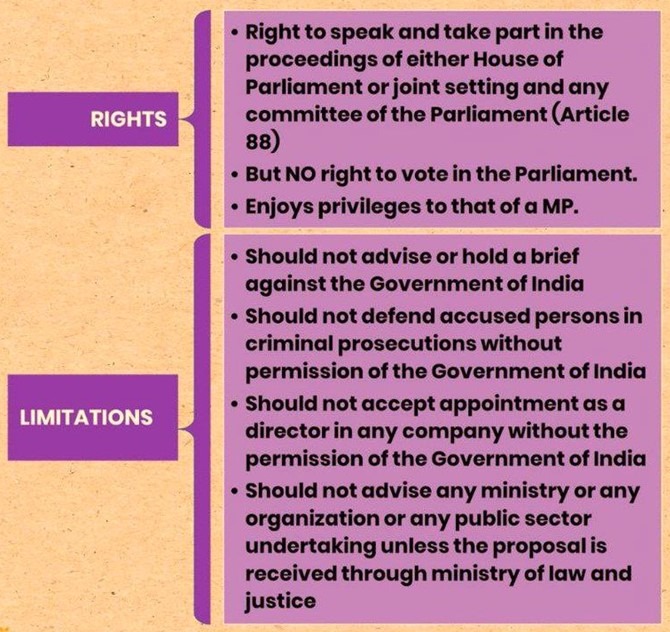
Rights of the Attorney General
1. Right of Audience:
- The Attorney General has the right to appear and be heard in all courts across India.
2. Parliamentary Participation:
- The AG has the right to speak and participate in the proceedings of both Houses of Parliament, including joint sittings.
- While the AG can participate in debates and discussions, he does not have a right to vote.
3. Privileges and Immunities:
- The Attorney General enjoys the same privileges and immunities as available to members of Parliament, ensuring protection during the performance of official duties.
Limitations on the Attorney General
To avoid complications and conflicts of interest, the following limitations are placed on the Attorney General:
1. No Adverse Representation:
- The AG should not advise or represent cases against the Government of India.
2. Incompatibility of Responsibilities:
- The AG cannot advise or represent parties in cases where he is called upon to support the Government of India.
3. Criminal Prosecutions:
- The AG cannot defend accused persons in criminal cases without prior permission from the Government of India.
4. Director Positions:
- The AG must obtain permission from the Government of India before accepting any appointment as a director in any company or corporation.
5. Official Advising Procedure:
- The AG should not advise any ministry, department, or statutory body unless approached through the Ministry of Law and Justice, Department of Legal Affairs.
Nature of Employment
- The Attorney General is not a full-time counsel for the Government of India and does not fall under the category of government servants.
- The AG is not prohibited from engaging in private legal practice, allowing him to work outside his duties to the government.
Solicitor General of India
In addition to the Attorney General, there are other law officers, such as the Solicitor General of India and Additional Solicitor General of India, who assist the AG in fulfilling his responsibilities:
- Appointment: The offices of the Solicitor General and the Additional Solicitor General are not established by the Constitution (unlike the AG) and are appointed as required.
- Role: They provide legal support and represent the government in various legal proceedings but do not hold the same constitutional status as the AG.
Relationship with the Government
- The Attorney General is not a member of the Central Cabinet, and there is a separate Law Minister responsible for overseeing legal matters at the governmental level.
Articles Related to the Attorney General of India
Below are key articles pertaining to the Attorney General of India:
Article No. | Subject-matter |
76 | Attorney-General of India |
88 | Rights of Attorney-General as respects the Houses of Parliament and its Committees |
105 | Powers, privileges, and immunities of the Attorney-General |
The Attorney General of India serves an essential function in maintaining the rule of law and providing legal guidance to the executive branch of government. While the AG enjoys substantial rights and responsibilities, the limitations imposed on his office help ensure impartiality and integrity in legal representation and governmental decision-making. The role of the Solicitor General and Additional Solicitor General complements that of the Attorney General, contributing to the legal framework within which the government operates.