Cities Coalition for Circularity
Context
- India recently launched the Cities Coalition for Circularity C-3 a multi-national alliance fostering collaboration knowledge-sharing and public-private partnerships to advance circular economy principles in urban development.
- This initiative was introduced at the 12th Regional 3R and Circular Economy Forum in Asia and the Pacific held in Jaipur.
Key Highlights of the Event
- Pro-Planet People P3 Approach the Prime Minister reaffirmed India’s commitment to sustainability through Reduce Reuse Recycle 3R principles
- CITIIS 2.0 City Investments to Innovate Integrate and Sustain
- MoU signed for urban sustainability projects worth 1800 crore
- Benefits 18 cities across 14 states serving as model urban projects
Background Regional 3R and Circular Economy Forum
- Established in 2009 to promote sustainable waste management and circular economy in the Asia-Pacific region.
- Hanoi 3R Declaration 2013-2023 Outlined 33 voluntary goals for transitioning to a resource-efficient and circular economy.
- Global Plastic Treaty Negotiations The forum actively works toward international policies on plastic waste management.
- Cities Coalition for Circularity C-3
Objective
C-3 supports urban centers in integrating circular economy principles into urban planning waste management and resource optimization
Key Focus Areas
- Waste Reduction Promoting segregation composting and upcycling
- Resource Efficiency Encouraging reuse and shared material use
- Sustainable Infrastructure Implementing eco-friendly construction and urban design
Significance of C-3 for Urban Sustainability
- Climate Action Reduces waste and emissions combating climate change
- Economic Growth Creates new business opportunities in recycling and waste management, Resilient Cities Reduces reliance on finite resources strengthening urban resilience
- Job Creation Expands employment in green sectors like sustainable construction and
- Renewable energy
- Improved Quality of Life Enhances public health and urban environments
Global and Indian Context
- Internationally Cities like Amsterdam Copenhagen and Tokyo have successfully adopted circular economy strategies under the C-3 framework
- In India Circularity is gaining traction through Swachh Bharat Mission promoting waste segregation and recycling
- Smart Cities Mission integrating sustainability into urban planning
Extended Producer Responsibility EPR holding companies accountable for waste management - GOBAR-Dhan Scheme covering 67.8 percent of districts supporting bio-waste management
Challenges in Implementing Circular Economy in Cities
- Low Awareness and Technical Expertise
- High Initial Investment Costs
- Resistance from Businesses and Consumers
- Weak Policy Support and Implementation
Way Forward
- Policy Enforcement Implement mandatory circular economy regulations
- Investment in R and D Develop sustainable materials and innovative recycling technologies
- Public Awareness Campaigns Educate citizens on circular living practices
Strengthen Public-Private Partnerships Scale up circular economy initiatives through collaboration - C-3 marks a major step in India’s urban sustainability journey driving resource efficiency economic resilience and environmental sustainability in Indian cities and beyond
Consider the following statements regarding the Cities Coalition for Circularity (C-3):
- It was launched at the 12th Regional 3R and Circular Economy Forum in Asia and the Pacific.
- The initiative focuses on urban sustainability through a linear economy approach.
- It promotes the adoption of circular economy principles in urban planning, waste management, and resource optimization.
- The initiative is led by the World Bank in collaboration with the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 1, 2, and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- C-3 was launched at the 12th Regional 3R and Circular Economy Forum in Asia and the Pacific.
- It focuses on a circular economy approach, not a linear one.
- The initiative is driven by the Government of India, not the World Bank or UNEP
Swavalambini
The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), in collaboration with NITI Aayog, has launched Swavalambini, a structured initiative aimed at fostering women entrepreneurship across Higher Education Institutions (HEIs).
About Swavalambini
- The programme is designed to cultivate an entrepreneurial mindset among young women and equip them with the necessary resources, skills, and mentorship to build and scale their ventures.
- It follows a stage-wise approach, ensuring structured guidance from business ideation to venture expansion.
Key Features of Swavalambini
- Faculty Development Programme (FDP)
- Aimed at training faculty members from participating Higher Education Institutions (HEIs).
- Involves intensive five-day training sessions to enable faculty to mentor aspiring women entrepreneurs.
- Mentorship and Networking
- Once participants develop their business plans, they are provided with mentorship from industry experts and successful entrepreneurs.
- The programme also facilitates:
- Access to funding opportunities through government schemes and private investors.
- Networking opportunities with established business leaders and professionals to enhance entrepreneurial success.
- Women Entrepreneurship Development Programme (EDP)
- A comprehensive initiative that provides an in-depth understanding of:
- Business Planning – Strategies for market entry and scalability.
- Leadership and Decision-Making Skills – Enhancing managerial capabilities.
- Financial Literacy and Investment Strategies – Understanding capital allocation and risk management.
- Market Research and Competitive Analysis – Equipping entrepreneurs with insights for a data-driven approach to business.
With reference to the Swavalambini Programme, consider the following statements:
- Swavalambini is a joint initiative of MSDE and NITI Aayog aimed at women entrepreneurship.
- The programme primarily focuses on providing direct financial assistance to women entrepreneurs for their startups.
- It includes a Faculty Development Programme (FDP) that trains educators from Higher Education Institutions (HEIs).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct. Swavalambini is a collaborative effort between MSDE and NITI Aayog, aimed at boosting women entrepreneurship.
- Statement 2 is incorrect. The programme does not provide direct financial aid but facilitates access to funding through various government and private schemes.
- Statement 3 is correct. The Faculty Development Programme (FDP) is a crucial component, training faculty members from HEIs to mentor women entrepreneurs.
Cabinet Nod To Revised Waqf Bill (2024)
Context:
- The Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister of India, has approved the Waqf (Amendment) Bill, 2024 with key recommendations from the Joint Parliamentary Committee (JPC).
- This bill aims to strengthen the regulation, administration, and transparency of Waqf properties while addressing long-standing disputes and inefficiencies in their management.
Background: Waqf & Its Legal Framework
- The Waqf Act, 1995, governs the administration of Waqf properties, which are charitable endowments made by Muslims for religious, educational, or welfare purposes.
- The Waqf (Amendment) Bill, 2024, introduces reforms to enhance efficiency, prevent encroachment, and improve governance of these properties.
Key Amendments in the Waqf (Amendment) Bill, 2024
- Strengthening Regulation of Waqf Properties
- Introduces a stricter legal framework to prevent encroachment and misuse of Waqf lands.
- Empowers state authorities to regulate Waqf assets with more clarity.
- Administrative Overhaul
- Assigns the functions of the Survey Commissioner to the District Collector or an officer not below the rank of Deputy Collector for conducting Waqf property surveys.
- Aims to expedite the identification and legal recognition of Waqf lands.
- Enhanced Government Oversight
- Expands central and state government roles in monitoring Waqf Boards.
- Could introduce provisions for better coordination and auditing mechanisms.
- Transparency & Digital Records
- Mandates compulsory digitization of Waqf properties.
- Aims to curb corruption and mismanagement through real-time digital tracking.
Key Changes Recommended by the Joint Parliamentary Committee (JPC)
- Inclusion of Women & OBC Representation
Mandates two Muslim women members in:
- State Waqf Boards (Section 14)
- Central Waqf Council (Section 9)
- Includes one OBC Muslim representative in State Waqf Boards for broader community representation.
- Separate Waqf Boards for Specific Communities
- State governments may establish separate Waqf Boards for:
- Aghakhani community
- Bohra community
- Aims to address community-specific governance issues.
- Protection of Women’s Inheritance Rights
- Ensures that in family Waqfs (Waqf Alal Aulad), women receive their rightful inheritance share.
- A waqif (donor) can dedicate property only after ensuring female heirs’ legal entitlement.
- Dispute Resolution Mechanism
- District Collectors will adjudicate disputes on whether a property is Waqf or belongs to the government.
- Designed to reduce prolonged legal battles and streamline resolution.
- Technology Integration
- All Waqf properties must be uploaded onto a central digital portal within six months.
- Enhances accountability, monitoring, and accessibility of Waqf records.
Joint Parliamentary Committee (JPC) – Key Aspects
- Set up by Parliament for detailed scrutiny of specific legislation.
- Composed of members from both Houses, including ruling and opposition parties.
- Dissolved upon completion of its mandate.
Potential Concerns Regarding the Waqf (Amendment) Bill, 2024
- Autonomy of State Waqf Boards
Risk of centralization – may reduce state-level autonomy over Waqf property management.
- Legal & Constitutional Challenges
Possible judicial review if amendments contradict property laws or religious rights.
May raise questions on compensation for landowners affected by Waqf claims.
- Concerns from Minority Communities
Changes may be seen as reducing community control over Waqf assets.
Could trigger opposition from religious groups and political debates.
- Bureaucratic Control vs. Efficiency
While reforms aim to enhance governance, increased bureaucracy could slow down decision-making.
Understanding Waqf & Its Governance Structure
Definition of Waqf
- Under Islamic law, Waqf refers to property dedicated solely for religious or charitable use.
- Cannot be sold, inherited, or repurposed once designated as Waqf.
Central Waqf Council (CWC)
- Established in 1964 under the Ministry of Minority Affairs (formerly under the Waqf Act, 1954).
- Advisory & supervisory body for Waqf management.
- Chairperson: Union Minister for Waqf.
- Members: Not exceeding 20, appointed by the Government of India.
State Waqf Boards – Powers & Functions
- As per Section 40 of the Waqf Act, 1995, State Waqf Boards can:
- Determine whether a property is Waqf or not.
- Identify if a Waqf belongs to Sunni or Shia traditions.
With reference to the Waqf (Amendment) Bill, 2024, consider the following statements:
- It mandates the inclusion of two Muslim women in the State Waqf Boards and Central Waqf Council.
- The bill establishes a separate national Waqf Board for Sunni and Shia Muslims.
- The bill empowers District Collectors to adjudicate disputes regarding whether a property is Waqf or belongs to the government.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct. The JPC recommended the inclusion of two Muslim women in State Waqf Boards and the Central Waqf Council.
- Statement 2 is incorrect. The bill does not establish a separate national Waqf Board for Sunnis and Shias, but allows state-specific Waqf Boards for Aghakhani and Bohra communities.
- Statement 3 is correct. The bill grants District Collectors authority to decide Waqf-related disputes.
Challenges Ahead of Women Panchayat Members in India
Introduction
- The Ministry of Panchayati Raj has recently identified key reasons why male relatives of elected women representatives (EWRs) often act as proxies, undermining their autonomy in governance.
- Despite constitutional provisions for women’s representation, several socio-political and structural challenges persist.
Women’s Participation in Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs)
- The 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992, marked a watershed moment in India’s governance by mandating one-third reservation for women in Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs).
- Over time, several states extended this reservation to 50%, leading to the election of over 1.45 million women representatives at the grassroots level.
Key Challenges Faced by Women Panchayat Members
- Patriarchal Mindset and ‘Sarpanch Pati Syndrome’
- Many male family members (husbands, fathers, brothers) act as de facto decision-makers, reducing elected women to mere figureheads.
- This practice, known as ‘Sarpanch Pati Syndrome’, is particularly prevalent in Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Bihar.
- Lack of Political Training and Awareness
- Many EWRs lack knowledge of governance structures, policy-making, and financial planning.
- This makes them dependent on male counterparts or bureaucrats for decision-making.
- Resistance from Bureaucracy and Male Counterparts
- Bureaucratic bias often results in officials not taking women leaders seriously.
- Delays in fund allocation and policy implementation weaken women-led governance.
- Financial Dependence and Economic Disempowerment
- Economic dependence on male family members restricts women’s ability to act independently in politics.
- Limited access to financial resources and micro-credit schemes further constrains their decision-making power.
- Gender-Based Violence and Intimidation
- Women leaders face harassment, verbal abuse, and physical threats from opposing male politicians or dominant caste groups.
- In extreme cases, women are coerced into resigning due to social pressure or violence.
- Dual Burden of Work and Household Responsibilities
- Women leaders struggle to balance political responsibilities with domestic duties such as childcare and agricultural work.
- Societal norms prioritize household responsibilities, limiting women’s engagement in governance.
- Social and Caste-Based Discrimination
- Women from marginalized communities (Dalits, Adivasis, and OBCs) face intersectional discrimination in political spaces.
- This is particularly severe in states like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Haryana.
Benefits of Strengthening Women’s Leadership in PRIs
- Improved Governance and Policy Implementation
Example: In Kudumbashree (Kerala), empowered women leaders played a critical role in poverty alleviation and welfare schemes.
- Gender-Responsive Policies and Better Representation
Example: In Nagaland, women-led Panchayats focused on reducing gender-based violence and improving maternal health services.
- Economic Empowerment and Financial Independence
Example: In Bihar, EWRs successfully implemented micro-loan schemes, boosting rural women’s entrepreneurship.
- Reduction in ‘Sarpanch Pati Syndrome’
Example: In Rajasthan, capacity-building programs helped reduce male dominance in Panchayat decision-making.
Key Government Initiatives for Women in PRIs
- National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM) – SHG Linkages
- Promotes financial independence and leadership among rural women through Self-Help Groups (SHGs).
- Mahila Sabhas (Women’s Gram Sabha Meetings)
- Held before general Gram Sabha meetings to prioritize women’s issues related to health, education, and safety.
- Panchayat Mahila Evam Yuva Shakti Abhiyan (PMEYSA)
- Focuses on capacity-building for elected women representatives, enhancing decision-making and leadership skills.
- Mission Shakti (2022)
- Comprises Sambal (safety & security) and Samarthya (economic empowerment) schemes to strengthen women’s participation in governance.
- Women’s Leadership Development Programs
- Government and NGOs conduct training and mentorship programs to empower women in governance.
Way Forward: Strengthening Women’s Political Participation
- Capacity-Building and Leadership Training
- Expanding Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan (RGSA) to ensure every EWR receives governance training.
- Strict Implementation of Laws Against Proxy Representation
- Enforcing legal provisions to prevent male relatives from controlling elected women.
- Conducting awareness campaigns to educate women about their rights.
- Financial Empowerment and Direct Access to Resources
- Women leaders should have direct control over Panchayat funds without bureaucratic hurdles.
- Expanding microfinance and economic initiatives to enhance women’s independence.
- Extending Women’s Reservation Beyond PRIs
- While PRIs have 33-50% reservation, similar provisions should be implemented at legislative levels.
- The Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam, 2023, which mandates one-third reservation in Lok Sabha & State Assemblies, must be implemented effectively post-delimitation.
- Strengthening Women’s Support Networks
- Expanding the National Federation of Elected Women Representatives (NFEWR) across all states.
- Ensuring Safety and Protection for Women Leaders
- Strict legal measures against harassment, violence, and political intimidation.
- Establishing fast-track courts for cases related to violence against women in politics.
Conclusion
- Despite remarkable progress in women’s political participation, systemic barriers continue to limit their effectiveness in Panchayati Raj Institutions.
- Addressing these challenges requires a multi-dimensional strategy involving legal enforcement, capacity-building, financial empowerment, and social transformation.
- By empowering elected women representatives and ensuring their full participation in governance, India can move toward gender equality and inclusive development.
With reference to the ‘Sarpanch Pati Syndrome’ in India, consider the following statements:
- It refers to the practice where male relatives exercise de facto control over elected women representatives in PRIs.
- The phenomenon is legally prohibited under the 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992.
- This practice is most commonly observed in urban municipal corporations rather than rural governance structures.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct. ‘Sarpanch Pati Syndrome’ is a well-documented issue where male relatives, especially husbands, exercise real power while women hold the official position.
- Statement 2 is correct. While the 73rd Amendment mandates one-third (now 50% in many states) reservation for women, it does not explicitly mention this issue. However, proxy representation violates constitutional principles of effective representation.
- Statement 3 is incorrect. The issue is primarily seen in rural Panchayat Raj Institutions (PRIs), not urban local bodies.
Article 136 of the Constitution
- Vice-president Jagdeep Dhankhar, speaking at a conference on arbitration, raised concerns about the misuse of Article 136 of the Constitution.
- Article 136 grants the Supreme Court the discretionary power to grant special leave to appeal against any judgment, decree, or order issued by any court or tribunal in India.
- This provision enables the Supreme Court to hear appeals even when no other legal provision guarantees an automatic right of appeal.
- It applies to both civil and criminal cases, but the Supreme Court is not obligated to accept every appeal filed under this article.
Consider the following statements regarding Article 136:
- It allows the Supreme Court to grant special leave to appeal against decisions of any court or tribunal in India.
- It applies exclusively to constitutional and civil cases.
- The Supreme Court is obligated to entertain every petition filed under Article 136.
- It serves as an extraordinary jurisdiction rather than a regular appellate mechanism.
Which of the statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer:(b)
Explanation:
- Article 136 grants the Supreme Court discretionary power to hear appeals from any court or tribunal.
- However, it applies to both civil and criminal matters (not just constitutional and civil cases), and the Supreme Court is not obligated to accept all petitions under this provision.
- It functions as an extraordinary power rather than a routine appellate mechanism.
Punjab’s Success with AIF Scheme
- Punjab has emerged as the leading state in executing the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF) scheme, having fully utilized its allocated ₹4,713 crore and subsequently securing an additional ₹2,337 crore from the central government.
- This proactive financial deployment underscores Punjab’s commitment to strengthening agricultural infrastructure and minimizing post-harvest losses.
Understanding the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)
- Launched in July 2020, the AIF is a medium to long-term financing initiative aimed at facilitating post-harvest agricultural infrastructure development. Its primary objectives include:
- Reduction of post-harvest losses by bolstering storage and processing capabilities.
- Enhancement of rural agrarian infrastructure to improve efficiency and market access.
- Financial empowerment of stakeholders through concessional credit and interest subvention.
Project Eligibility and Expansion
- Initially, the AIF prioritized primary post-harvest management
- However, it has now been expanded to support secondary-level integrated processing.
Key focus areas include:
- Upgrading facilities for grading, waxing, and packaging of agricultural produce.
- Encouraging value-added processing such as juice extraction and jam production.
- Establishing cold chains and warehouses to enhance storage capabilities.
Eligible Beneficiaries Under AIF
The AIF scheme is accessible to a diverse range of stakeholders, ensuring a broad-based impact. Eligible applicants include:
- Individual farmers and agripreneurs
- Primary Agricultural Cooperative Societies (PACS)
- Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs)
- Start-ups and agribusiness enterprises
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) projects
This inclusive approach maximizes the reach and effectiveness of the scheme.
Punjab’s Exemplary Performance Under AIF
- As of February 2025, Punjab has sanctioned 21,740 projects, the highest among all Indian states.
- This milestone was achieved over a year ahead of the March 2026 deadline.
- Other leading states, such as Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra, are also actively participating, but Punjab remains at the forefront in terms of project approvals and fund utilization.
Spectrum of Projects Funded
The AIF has financed a wide array of agricultural infrastructure projects, demonstrating its adaptability and relevance across sectors. Some notable categories include:
- Cashew processing units
- Oil extraction and refining facilities
- Flour mills and food processing plants
- Cold storage and warehouse units
- Solar-powered agricultural infrastructure
Financial Framework and Benefits
The financial structure of the AIF is designed to provide affordable credit access with the following features:
- Interest subvention of 3% on eligible loans.
- Maximum interest rate capped at 9% for loans up to ₹2 crore.
- Flexible repayment period of up to 7 years.
- Integration with other state and central subsidies, enhancing financial feasibility for stakeholders.
Socio-Economic Impact on Farmers and Rural Development
- Approximately 71% of AIF beneficiaries are individual farmers, ensuring that the scheme significantly influences grassroots agricultural communities. Moreover:
- 67% of sanctioned projects have costs below ₹25 lakh, signifying a strong focus on small-scale, farmer-led initiatives.
- The emphasis on localized agricultural infrastructure supports employment generation and economic upliftment of rural areas.
Consider the following statements regarding the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF):
- The AIF was launched in July 2020 to provide long-term financing for agricultural infrastructure projects.
- It focuses on both pre-harvest and post-harvest agricultural infrastructure development.
- The fund offers an interest subvention of 3% on eligible loans.
- The maximum interest rate under the scheme is capped at 7% for loans up to ₹2 crore.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 1, 2, and 3 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The AIF was launched in July 2020 to provide financial support for developing agricultural infrastructure.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The AIF only supports post-harvest infrastructure such as cold storage, warehouses, and processing units. It does not focus on pre-harvest activities like irrigation or seed development.
- Statement 3 is correct: The scheme offers a 3% interest subvention to beneficiaries, reducing the financial burden on them.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: The maximum interest rate under AIF is capped at 9%, not 7%, for loans up to ₹2 crore.
Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maandhan
- The Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maandhan (PM-SYM) is a flagship social security initiative launched by the Government of India in the Interim Budget of 2019.
- The scheme is strategically designed to offer a guaranteed pension to unorganised sector workers, a category that constitutes a significant portion of India’s workforce yet remains largely excluded from formal pension systems.
Significance of PM-SYM in India’s Socio-Economic Context
- The unorganised sector is the backbone of the Indian economy, engaging workers in occupations such as street vending, domestic work, construction labor, and agricultural activities.
- This sector contributes approximately 50% to India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). By the end of 2024, around 51 crore unorganised workers had registered on the e-Shram portal, highlighting the pressing need for robust social security interventions.
Key Features of the PM-SYM Scheme
- Guaranteed Pension: Provides a minimum assured pension of ₹3,000 per month post-retirement, after the age of 60.
- Government Contribution: The government matches the worker’s contribution on a 1:1 basis, enhancing affordability and financial sustainability.
- Voluntary Participation: Workers self-select their contribution level, making the scheme flexible and inclusive.
- Family Pension Provision: In case of the subscriber’s demise, the spouse receives 50% of the pension amount as a family pension.
- Exit Provisions: Allows premature withdrawal under specified conditions, ensuring adaptability to changing financial circumstances.
- Simplified Enrolment Process: Workers can enroll through Common Service Centres (CSCs) or the Maandhan portal, reducing administrative hurdles.
- Fund Management: The scheme is administered by the Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC), ensuring long-term financial viability and trustworthiness.
Eligibility and Exclusion Criteria
To ensure targeted implementation, PM-SYM applies the following eligibility conditions:
- Eligibility Conditions:
- Age Bracket: Applicants must be between 18 and 40 years old.
- Income Ceiling: Monthly earnings should not exceed ₹15,000.
- Employment Type: Only those engaged in unorganised sector jobs can apply.
Exclusion Criteria:
- Individuals covered under Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF), Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC), or the National Pension System (NPS).
- Income taxpayers are ineligible.
- Workers already benefiting from other government pension schemes cannot enroll.
Administrative and Institutional Framework: The Ministry of Labour and Employment is the nodal agency responsible for administering PM-SYM. It works in collaboration with:
- LIC (for pension disbursal and fund management).
- Common Service Centres (CSCs) (for on-ground enrolment and facilitation).
- State and district-level authorities (for awareness campaigns and grievance redressal).
With reference to the Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maandhan (PM-SYM) scheme, consider the following statements:
- The scheme was introduced in 2019 to provide social security to unorganised sector workers.
- PM-SYM offers a guaranteed pension of ₹3,000 per month post-retirement.
- Government contributions are fixed at 50% of the total pension corpus, regardless of worker participation.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: PM-SYM was launched in 2019 to provide a pension scheme for unorganised sector workers.
- Statement 2 is correct: It guarantees a fixed pension of ₹3,000 per month after attaining the age of 60.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The government does NOT contribute a fixed 50% of the total corpus; rather, it matches the worker’s individual contribution (1:1 ratio).
6 Years of POSHAN Abhiyan
Context: Launched in 2018, POSHAN Abhiyaan has completed seven years of implementation, marking a significant milestone in India’s commitment to eliminating malnutrition and anemia.
Objectives of POSHAN Abhiyaan: The initiative focuses on a multi-pronged approach to address malnutrition and maternal health, with key objectives:
- Reduction of stunting among children (0-6 years).
- Mitigation of under-nutrition (prevalence of underweight children, 0-6 years).
- Lowering anemia prevalence among women and adolescent girls (15-49 years).
- Reduction of low birth weight (LBW) through enhanced maternal and child healthcare services.
- Strategic Pillars of POSHAN Abhiyaan
Access to Quality Services:
- Strengthening maternal and child health services through flagship programs:
- Integrated Child Development Scheme (ICDS)
- National Health Mission (NHM)
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY)
- Special focus on the first 1,000 days of life, critical for early childhood development.
Cross-Sectoral Convergence:
- Integration with various national programs for a holistic approach:
- Swachh Bharat Mission (sanitation and hygiene)
- National Drinking Water Mission (safe drinking water access)
Leveraging Technology:
- Adoption of digital tools, including the Poshan Tracker application, for real-time monitoring and intervention.
Jan Andolan (People’s Movement):
- Community-led initiatives to raise awareness and encourage behavioral shifts in nutrition and maternal health practices.
- Mission Saksham Anganwadi & POSHAN 2.0
Launched in 2021, integrating multiple nutrition-focused programs under a unified framework, including:
- Supplementary Nutrition Programme (SNP)
- POSHAN Abhiyaan
- Strengthened Anganwadi services, emphasizing:
- Infrastructure development
- Nutritional support
- Capacity-building of frontline workers
Funding Pattern:
- For States & UTs with Legislature: 60:40 (Centre: State)
- For Northeastern & Himalayan States: 90:10 (Centre: State)
Conclusion:
- POSHAN Abhiyaan remains a cornerstone initiative in India’s battle against malnutrition, integrating policy, technology, and community engagement to foster a healthier future for children and women.
Consider the following statements regarding POSHAN Abhiyaan:
- It was launched in 2018 with the aim of addressing malnutrition among children and women.
- It exclusively focuses on providing nutritional support to children below five years of age.
- The initiative leverages digital tools like the Poshan Tracker for real-time monitoring.
- It is implemented solely by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
a) 1 and 3 only
b) 2 and 4 only
c) 1, 2, and 3 only
d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- POSHAN Abhiyaan is a multi-sectoral initiative that integrates efforts from different ministries, including the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- It does not focus exclusively on children below five years but also addresses adolescent girls and maternal nutrition.
Surat Food Security Saturation Campaign

Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the Surat Food Security Saturation Campaign Programme in Limbayat, Surat, reinforcing the government’s commitment to ensuring food security for the underprivileged.
The initiative, aimed at benefiting over 2.3 lakh people, underscores Surat’s collective spirit in supporting the marginalized.
Objectives of the Campaign:
- The campaign is designed to expand the reach of the National Food Security Act (NFSA), ensuring that no eligible individual is left out.
- Over 2.5 lakh new beneficiaries have been identified, including elderly individuals and differently-abled persons.
- The initiative moves beyond political appeasement and focuses on fair and inclusive food distribution.
- Beneficiaries will receive free rations and nutritious food, helping combat hunger and malnutrition.
Government Initiatives for Food Security:
- The government has implemented several schemes to enhance food security across India: Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana (PMGKY) – Launched during COVID-19 to provide free food grains to the poor.
- PM Poshan Scheme – Ensures nutritious meals for school children, improving their health and learning outcomes.
- Saksham Anganwadi Program – Focuses on maternal and child nutrition, enhancing early childhood development.
- PM Matru Vandana Yojana – Provides financial aid to pregnant women, promoting maternal and infant health.
Emphasis on Nutrition and Hygiene: Eliminating malnutrition and anaemia is a government priority. Surat has set an example in hygiene and cleanliness, complementing the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan. The Har Ghar Jal campaign ensures clean drinking water, improving public health and sanitation.
Financial Inclusion and Support for the Poor: To empower the underprivileged, the government has introduced key financial initiatives: One Nation, One Ration Card (ONORC) – Allows beneficiaries to access rations from anywhere in India, ensuring food security for migrants. Mudra Yojana – Provides collateral-free loans to small businesses and entrepreneurs. PM SVANidhi Yojana – Offers financial support to street vendors, enabling economic self-reliance.
Strengthening the Middle Class:
The government recognizes the middle class as a pillar of economic growth. Recent tax relief measures allow middle-class families to retain more income. New tax slabs support financial stability and encourage investment and savings.
Surat’s Economic Growth and Infrastructure Development:
Surat is a major hub for textiles, chemicals, and MSMEs. To boost economic activity, the government has invested in MSME-friendly loan schemes, enabling business expansion. Infrastructure projects such as the Surat Metro and the new airport terminal improve connectivity and quality of life.
Women Empowerment Initiatives: Women’s empowerment remains a key focus of the government. Women are encouraged to share their success stories, inspiring greater participation in economic and social development. Special events and programs celebrate women’s contributions across various sectors.
The Surat Food Security Saturation Campaign is a significant milestone in ensuring that every citizen has access to essential nutrition and financial support, fostering growth, inclusivity, and empowerment.
Consider the following statements regarding the Surat Food Security Saturation Campaign:
- The campaign aims to strengthen the implementation of the National Food Security Act (NFSA) by including newly identified beneficiaries.
- It focuses primarily on providing subsidized food grains to beneficiaries in Surat.
- The initiative has identified over 5 lakh new beneficiaries, including the elderly and differently-abled individuals.
- The campaign extends beyond food security, incorporating elements of nutrition, hygiene, and financial inclusion.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 3 only
b) 1, 3, and 4 only
c) 2 and 4 only
d) 1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: (b) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Correct: The campaign aims to expand the coverage of NFSA, ensuring that no eligible person is left out.
- Statement 2 – Incorrect: Beneficiaries receive free rations and nutritious food, not just subsidized grains.
- Statement 3 – Correct: Over 5 lakh new beneficiaries have been identified under the campaign.
- Statement 4 – Correct: The initiative integrates nutrition, hygiene (Swachh Bharat Abhiyan), and financial inclusion.
Revised Rashtriya Gokul Mission
- The Revised Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM) is a flagship initiative of the Government of India, aimed at modernizing and enhancing the livestock and dairy sector.
- With an additional allocation of ₹1,000 crore, the total budget for RGM now stands at ₹3,400 crore for the 15th Finance Commission cycle (2021-22 to 2025-26).
- The revised mission focuses on boosting milk production, improving cattle productivity, and supporting dairy farmers through targeted interventions.
Key Components of the Revised RGM
- Heifer Rearing Centres
- Provides one-time financial assistance covering 35% of capital costs.
- Aims to establish 30 rearing facilities to accommodate 15,000 heifers.
- Ensures the availability of high-quality female calves to improve dairy productivity.
- High Genetic Merit (HGM) IVF Heifers
- Farmers purchasing HGM IVF heifers receive a 3% interest subvention on loans.
- Loans are facilitated through milk unions and financial institutions to promote access to superior breeds.
Ongoing Activities and Enhancements
- The revised mission continues several critical initiatives from the original RGM, including:
- Strengthening semen stations and expanding Artificial Insemination (AI) coverage.
- Accelerating breed improvement through the use of sex-sorted semen and advanced reproductive technologies.
- Skill development and farmer awareness programs to enhance knowledge and best practices in livestock management.
Impact on Milk Production and Productivity
- Since the inception of RGM, India has witnessed a 63.55% increase in milk production over the past decade. Key improvements include:
- Milk availability per capita rose from 307 grams/day (2013-14) to 471 grams/day (2023-24).
- Dairy productivity surged by 26.34% within the same period, benefiting both small and large-scale farmers.
- Nationwide Artificial Insemination Programme (NAIP)
To enhance breed quality and accessibility, the NAIP provides:
- Free Artificial Insemination (AI) services in 605 districts, focusing on areas with AI coverage below 50%.
- Over 8.39 crore animals have been inseminated, benefiting 5.21 crore farmers across India.
- Technological Innovations in Livestock Breeding
The RGM incorporates cutting-edge advancements to improve livestock genetics and productivity, including:
- Establishment of 22 In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) labs for advanced breeding.
Development of genomic chips:
- Gau Chip for indigenous cattle breeds.
- Mahish Chip for buffalo breeds.
- Indigenous development of Gau Sort technology for producing sex-sorted semen, ensuring higher birth rates of female calves for dairy farming.
- Emphasis on Indigenous Breeds and Farmer Livelihoods
The Revised RGM prioritizes the scientific conservation and genetic improvement of indigenous bovine breeds, fostering a sustainable and self-reliant dairy sector.
Key outcomes include:
- Systematic bull production programs to enhance breed purity.
- Expanded use of IVF and genomic technologies to increase productivity.
- Improved economic conditions for over 8.5 crore farmers engaged in dairying, particularly small and marginal farmers.
- By integrating modern scientific techniques with traditional livestock practices, the Revised Rashtriya Gokul Mission is playing a crucial role in strengthening India’s dairy industry, ensuring higher productivity, enhanced farmer incomes, and sustainable livestock management.
With reference to the Revised Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM), consider the following statements:
- It provides capital assistance of 50% for establishing Heifer Rearing Centres.
- It offers an interest subvention on loans for purchasing High Genetic Merit (HGM) IVF heifers.
- The mission aims to increase milk production but does not focus on indigenous bovine breeds.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- The mission provides 35% capital assistance, not 50%, for establishing Heifer Rearing Centres.
- It does offer a 3% interest subvention on loans for purchasing HGM IVF heifers.
- A major focus of RGM is the conservation and development of indigenous bovine breeds, making statement 3 incorrect.
SwaYaan initiative
- The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), in collaboration with the Drone Federation of India (DFI), has launched the National Innovation Challenge for Drone Application and Research (NIDAR) under the SwaYaan initiative.
- This initiative aims to bolster capacity building in Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) by fostering applied research and entrepreneurship in drone technology.
- The event, held at Electronics Niketan, witnessed participation from key government officials, industry leaders, and students across India through video conferencing.
Launch and Key Highlights
- The challenge was officially inaugurated by Shri S. Krishnan, Secretary, MeitY, who unveiled the NIDAR concept video, launched the website and registration portal, and released the official rulebook and poster.
- Addressing the attendees, Shri Krishnan underscored the transformative role of drones in sectors such as agriculture, disaster management, logistics, healthcare, and infrastructure, emphasizing the need to scale the NIDAR initiative to contribute to India’s goal of becoming a global drone hub by 2030.
- T. G. Sitharam, Chairman, AICTE, highlighted the necessity of integrating the NIDAR challenge into engineering curricula across the country.
- Stressing the importance of collaboration between academia, startups, and industry, he called for innovative engagement in drone technology research and development.
Objectives and Focus Areas of NIDAR
- The NIDAR challenge aims to inspire India’s student and research community to develop collaborative autonomous drones to address real-world challenges in two key domains.
- Disaster Management – Scout and Deliver Drones.
- Autonomous drones for scouting disaster-affected areas.
Assisting survivors through communication and parcel delivery. - Precision Agriculture – Scan and Spray Drones.
- Drones for crop health monitoring.
Precision-based pesticide and nutrient delivery.
Support, Incentives, and Participation
- The challenge offers a prize pool of INR 40 Lakhs, along with startup incubation opportunities, cloud computing credits, software support, and internship placements with India’s leading drone companies.
- Over 100 student teams from higher education institutions are expected to participate, showcasing innovative solutions to challenges in agriculture and disaster response.
- The competition will be conducted in multiple phases, including technology presentation, business case development, and final operational demonstration.
- This comprehensive evaluation will assess the technical skills, problem-solving abilities, teamwork, and entrepreneurial acumen of participants, preparing them for leadership roles in emerging technology domains.
Role of Drone Federation of India (DFI)
- As India’s premier industry body representing over 550 drone companies and 5500 drone pilots, the Drone Federation of India (DFI) will play a crucial role in mentoring student teams by providing industry exposure and guiding them through the innovation process.
Significance of NIDAR in India’s Drone Ecosystem
- The launch of NIDAR represents a strategic milestone in advancing India’s drone research, development, and commercialization.
- It reinforces the Government of India’s efforts to promote entrepreneurship in academia while bridging the gap between technological innovation and real-world applications.
About SwaYaan Initiative
- The SwaYaan initiative, approved by MeitY in July 2022, focuses on capacity building in Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) through formal and non-formal educational programs.
- Its goal is to train 42,560 individuals and develop a skilled workforce in drone technology.
Implementation Model and Key Areas
- The initiative follows a hub-and-spoke model, involving 30 premier institutions, including IISc Bangalore, IITs, IIITs, NITs, CDAC, and NIELIT.
- It is structured around five key research themes, Drone Electronics, GNC Algorithms and Simulation, Aeromechanics, Drone Applications, and Allied UAS Technologies.
- To date, over 14,000 individuals have been trained under SwaYaan.
Notable Achievements
- Launch of M.Tech in UAS Engineering at IIT Kanpur.
- Introduction of minor degree programs in drone technology.
- Successful execution of multiple bootcamps and workshops.
- The program actively engages industry partners through innovation challenges and industry meets, reinforcing the critical link between academic training and industry requirements in drone technology.
Conclusion
- The NIDAR challenge, under the SwaYaan initiative, is set to be a game-changer for India’s drone industry, fostering cutting-edge research, skill development, and entrepreneurship.
- By encouraging technological innovation in drone applications, the initiative is poised to strengthen India’s position as a global leader in unmanned aerial systems.
Which of the following statements regarding the NIDAR challenge is/are correct?
- It is launched by the Ministry of Civil Aviation in collaboration with the Drone Federation of India (DFI).
- The challenge provides incentives such as startup incubation, cloud computing credits, and software support.
- The competition includes multiple evaluation phases such as Technology Presentation, Business Case Development, and Final Operational Demonstration.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 2 and 3 only
(C) 1 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (B) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect because NIDAR is launched by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), not the Ministry of Civil Aviation.
- Statements 2 and 3 are correct as the challenge offers startup incubation, cloud computing credits, and software support, along with a rigorous multi-phase evaluation process.
Swadesh Darshan Scheme
Context
- The Public Accounts Committee (PAC), chaired by C. Venugopal, has raised concerns over the poor execution of the Swadesh Darshan scheme by the Ministry of Tourism.
- The observations were based on a report by the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG).
- Despite the Ministry’s claims that most sanctioned projects were completed, the PAC identified significant discrepancies in project implementation.
Swadesh Darshan Scheme
- Launched: 2014-15, as a flagship scheme under the Ministry of Tourism.
- Revamped: As Swadesh Darshan 2.0, with a focus on sustainable and responsible tourism, adopting a tourist-centric
Theme-Based Tourist Circuits:
- Spiritual Circuits (e.g., Char Dham Yatra, Buddhist Circuit)
- Cultural Circuits (e.g., North East Circuit, Tribal Circuit)
- Heritage Circuits
- Wildlife Circuits
Coastal Circuits
Funding: The Ministry of Tourism provides financial support to States and Union Territories for circuit development.
Key Issues Identified by PAC
Lapses in Planning: No feasibility studies were conducted before launching projects.
Financial Mismanagement:
- Budget overruns due to inadequate planning.
- Approvals granted without Detailed Project Reports (DPRs).
Weak Monitoring:
- No structured mechanism for project evaluation.
- Delays and incomplete projects despite claims of completion.
Discrepancy in Completion Claims:
- The Ministry claimed 75 out of 76 projects were completed.
- However, PAC found that key projects like the Kanwaria Route in Bihar, Tribal Circuit in Telangana, and Sree Narayana Guru Ashram in Kerala were either incomplete or non-functional.
Recommendations & Way Forward
- The Ministry of Tourism has been directed to physically inspect all projects and submit a detailed report within three weeks.
The Ministry must provide data on:
- The scheme’s impact on employment generation.
- Changes in tourist footfall, as key indicators of the scheme’s success.
About the Public Accounts Committee (PAC)
- Constitutional Status
- Not a constitutional body.
- Formed under Rule 308 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha.
Composition
- 22 Members:
- 15 from Lok Sabha
- 7 from Rajya Sabha
- Elected annually by Parliament.
- Chairperson: Appointed by the Speaker of Lok Sabha, typically from the opposition party.
Functions
- Examines audit reports submitted by the CAG of India.
- Scrutinizes public expenditure to prevent extravagance and irregularities.
- Ensures accountability of the Executive to the Legislature.
- Works alongside CAG to uphold fiscal discipline and transparency.
With reference to the Public Accounts Committee (PAC), consider the following statements:
- It is a constitutional body established under Article 148 of the Indian Constitution.
- The Chairperson of the PAC is always from the ruling party.
- PAC is responsible for examining the reports submitted by the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India.
- The PAC can take suo-motu cognizance of financial irregularities and initiate investigations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: PAC is not a constitutional body; it is formed under Rule 308 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The Chairperson is usually from the opposition party, not the ruling party.
- Statement 3 is correct: The PAC examines audit reports of CAG and scrutinizes public expenditure.
Statement 4 is incorrect: PAC cannot take suo-motu cognizance; it works based on reports submitted by the CAG.
Concerns Raised over the Amendment into the RTI Act, 2005
Context
Over 30 civil society organizations have urged the Union government to safeguard the Right to Information (RTI) Act, 2005, amid concerns about potential restrictions imposed by the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023.
Concerns Raised
- Activists caution against fully implementing amendments that may weaken the RTI Act under the DPDP Act.
- Section 8(1)(j) of the RTI Act now broadly prohibits disclosing personal information, even when it serves the public interest.
- The government justifies the change by citing the Supreme Court’s ruling in the Justice K.S. Puttaswamy v. Union of India (2017) case, which recognized privacy as a fundamental right.
Challenges Posed by the Amendment
- Restricting access to information may hinder social audits and make it difficult to uncover corruption or misuse of public funds.
- RTI requests have been instrumental in verifying government programs, such as food ration distribution and welfare schemes.
- Activists argue that the original RTI framework already balanced privacy with transparency, rejecting claims that the changes align with the Supreme Court’s privacy ruling.
- Right to Information Act, 2005
Objectives and Scope
- Aims to enhance transparency and accountability in governance by granting citizens the right to access information from public authorities.
- Applicable to government departments, ministries, and organizations substantially funded by the government.
Key Provisions
- Information Access: Citizens can request government records, documents, and other relevant data.
- Exemptions: Information related to national security, confidentiality, and ongoing investigations is excluded.
- Response Time: Public authorities must respond within 30 days, extendable to 45 days in specific cases.
- Penalties: Officials withholding information without valid reasons or providing false details may face penalties.
Significance of the RTI Act
- Empowering Citizens: Enables individuals to seek information, ensuring government transparency and accountability.
- Preventing Corruption: RTI has exposed fund mismanagement in schemes like the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS).
- Promoting Good Governance: Enhances trust in government by fostering openness in decision-making.
- Facilitating Social Audits: NGOs and activists use RTI to verify government service delivery, such as the Public Distribution System (PDS).
- Ensuring Public Access to Records: RTI requests help uncover inefficiencies and corruption in government contracts.
- Strengthening Democracy: Encourages citizen participation in governance and policymaking.
Criticism and Challenges
- Administrative Burden: High volumes of RTI requests strain public authorities, diverting resources from primary duties.
- Misuse of RTI: Some requests are used for harassment or personal/political agendas.
- Delays in Processing: Authorities struggle to meet response deadlines, leading to frustration among applicants.
- Lack of Training and Infrastructure: Many government offices lack the expertise and resources for effective RTI implementation.
- Ambiguity in Exemptions: Vaguely defined exemptions create loopholes for withholding crucial public information.
Way Forward
- Parliament should define “personal information” and “public interest” more precisely.
- Personal data disclosure should be permitted when it serves a greater public good, such as exposing corruption or verifying the misuse of funds.
- Any amendments to the RTI Act should involve consultations with multiple stakeholders, including RTI activists, legal experts, and data protection specialists.
- The government must balance privacy rights with the need for transparency to ensure democratic accountability.
- The RTI Act remains a cornerstone of democracy, empowering citizens and ensuring government accountability. Its preservation is crucial for upholding transparency, reducing corruption, and promoting good governance.
With reference to the Right to Information (RTI) Act, 2005, consider the following statements:
- The RTI Act applies only to government departments and ministries but not to organizations that receive substantial government funding.
- The Act allows disclosure of personal information if it serves a larger public interest.
- The government can reject an RTI request if the information sought affects national security or ongoing criminal investigations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The RTI Act not only applies to government departments and ministries but also covers organizations that receive substantial funding from the government (such as NGOs and public-private partnerships).
- Statement 2 is correct: The RTI Act permits disclosure of personal information if it serves a larger public interest, but the recent amendment under the Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDP), 2023 has created hurdles in this regard.
- Statement 3 is correct: The Act exempts disclosure of information that affects national security, foreign relations, or ongoing investigations under Section 8(1).
Sub-categorisation of SCs in Andhra Pradesh
The Andhra Pradesh Cabinet approved the one-member commission’s recommendations on the sub-categorisation of SCs to ensure equitable distribution of reservation benefits.
- The demand for sub-categorisation has existed for over 30 years, with previous efforts including the Justice Ramachandra Rao Commission (1996).
- Understanding Sub-Categorisation of SCs
- Sub-categorisation divides the SC category into smaller sub-groups to ensure a fair distribution of reservation benefits in education, employment, and affirmative action.
Historical Context & Supreme Court Rulings
- In 1975, Punjab issued a notification giving first preference in SC reservations to Balmiki and Mazhabi Sikh communities, which was challenged in 2004 after a similar Andhra Pradesh law was struck down in E.V. Chinnaiah v. State of Andhra Pradesh (2004).
- The Supreme Court in E.V. Chinnaiah ruled that SCs and STs form a single, indivisible class under Article 341/342 and that states cannot sub-classify or create internal quotas within SC/ST reservations.
- In 2020, the Supreme Court reconsidered E.V. Chinnaiah, acknowledging “unequals within the list of SCs” and citing Jarnail Singh v. Lachhmi Narain Gupta (2018), which extended the “creamy layer” concept to SCs.
- In 2024, the Supreme Court ruled that sub-classification within SCs and STs is allowed, clarifying that Article 341 does not prevent sub-classification but only limits the President’s power to add or exclude SC groups.
Arguments in Favour of Sub-Categorisation
- Some SC communities remain underrepresented despite reservation, justifying separate quotas within SC/ST categories.
- The SC category includes groups with vastly different socio-economic conditions, requiring sub-classification to address disparities.
- Article 14 (Right to Equality) allows sub-classification to ensure substantive equality among SC/ST groups.
- A caste census could provide accurate data to assess representation and correct inequities in reservation distribution.
Arguments Against Sub-Categorisation
- Sub-categorisation may be politically misused to alter quotas based on vote-bank politics rather than social justice.
- It may violate constitutional intent, as the President’s list of SCs can only be changed by Parliament.
Conclusion & Way Forward
- States now have legal backing to sub-categorise SCs but must ensure transparency, data-driven policy-making, and judicial oversight to prevent misuse.
- Sub-categorisation must be based on quantifiable and demonstrable data rather than political motives to ensure equitable distribution of benefits.
- Excluding the “creamy layer” within SC/STs from reservation benefits could help ensure that affirmative action reaches the most disadvantaged groups.
Consider the following statements regarding the sub-categorisation of Scheduled Castes (SCs) in India:
- The Supreme Court in E.V. Chinnaiah (2004) ruled that States have the power to sub-categorise SCs for ensuring equitable reservation benefits.
- The 2024 Supreme Court ruling clarified that Article 341 does not prevent sub-classification within SCs and STs.
- Sub-categorisation aims to provide a separate quota within SC reservations for communities that remain underrepresented.
- The power to include or exclude a community from the SC list rests solely with the State Government.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect because in V. Chinnaiah (2004), the Supreme Court held that SCs form a single, indivisible class and States cannot create sub-classifications.
- Statement 2 is correct as the 2024 Supreme Court ruling stated that Article 341 does not prevent sub-classification but only limits the President’s power to add or remove SC groups.
- Statement 3 is correct because the purpose of sub-categorisation is to ensure that the most disadvantaged communities within SCs receive a fair share of reservation benefits.
- Statement 4 is incorrect as only the President, in consultation with Parliament, has the authority to include or exclude a group from the SC list under Article 341.
Madras High Court on the NIRF Ranking
Context
- The Madurai Bench of the Madras High Court has temporarily restrained the Ministry of Education and the National Board of Accreditation (NBA) from publishing the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) 2025.
About NIRF:
- Launched in 2015 by the National Board of Accreditation (NBA) under the Ministry of Education.
- It annually ranks higher education institutions in India across various categories.
- Institutions submit data on parameters such as student and staff strength, salaries, graduation index, placements, and research funding via the NIRF portal.
- Significance of NIRF
- Informed Decision-Making – Assists students in selecting institutions based on performance and ranking across disciplines.
- Quality Assessment – Establishes a standardized benchmark for evaluating higher education institutions.
- Multi-Dimensional Evaluation – Uses a broad set of criteria to assess institutional performance.
- Encourages Competition – Motivates institutions to enhance academic and research standards.
- Policy Planning – Provides data-driven insights for policymakers to improve the education sector.
Criticism and Challenges
- Ranking Disparities – The methodology may not adequately capture qualitative aspects of education.
- Over-Reliance on Quantitative Data – Heavy emphasis on numerical indicators like placements and salaries can overshadow holistic academic excellence.
- Institutional Bias – Well-established institutions may have an advantage over emerging ones due to historical reputation and resources.
- Self-Reported Data – Institutions upload their own data, raising concerns about accuracy and potential manipulation.
- Limited International Benchmarking – The framework does not fully align with global ranking systems like QS World Rankings and Times Higher Education Rankings.
- The ongoing legal developments highlight concerns regarding transparency, accuracy, and methodology in institutional rankings. The outcome of the court’s decision could influence future ranking policies in India.
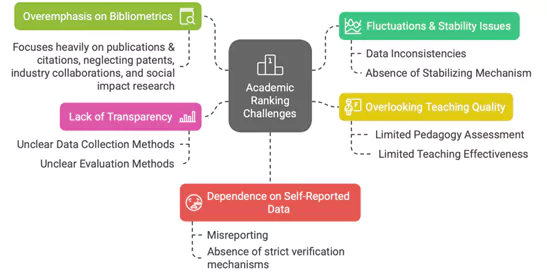
With reference to the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF), consider the following statements:
- It is administered by the National Board of Accreditation (NBA) under the University Grants Commission (UGC).
- The ranking methodology primarily relies on self-reported data submitted by institutions.
- NIRF rankings are internationally recognized and directly influence global rankings such as QS and Times Higher Education Rankings.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: NIRF is administered by the National Board of Accreditation (NBA) but it functions under the Ministry of Education, not the UGC.
- Statement 2 is correct: Institutions self-report data on various parameters such as student strength, placements, and research output, raising concerns over transparency and data manipulation.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: NIRF rankings are not internationally recognized and do not influence global rankings like QS and Times Higher Education Rankings, which use different methodologies.
Eklavya Schools
Recent Developments
- A parliamentary panel on social justice has urged the Union government to expedite the centralization process of Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS).
About EMRS
- Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS) are a network of government-run institutions established to provide quality education to Scheduled Tribe (ST) students residing in remote and rural areas.
Key Features
- Targeted Coverage: Every block with more than 50% ST population and at least 20,000 tribal persons will have an EMRS.
- Expansion Plan: The Ministry of Tribal Affairs aims to set up 728 EMRSs across India by 2026.
- Establishment: Introduced in 1997-98 by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
- Curriculum: Follows the National Curriculum Framework (NCF), covering education from the elementary level to Class 12.
Facilities Provided
- Fully Residential Schooling: Boarding and lodging facilities.
- Free Education: Includes uniforms, textbooks, and essential learning materials.
- Holistic Development: Sports, cultural activities, and vocational skill training to enhance employability.
Funding Mechanism
- The Ministry of Tribal Affairs funds EMRSs through grants allocated under Article 275(1) of the Indian Constitution, ensuring financial support for their establishment and operation.
Consider the following statements regarding Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS):
- EMRSs were introduced under the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 to enhance tribal education.
- These schools are fully funded by the Ministry of Education under the Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan.
- Every block with more than 50% Scheduled Tribe (ST) population and at least 20,000 tribal persons is eligible for an EMRS.
- The curriculum of EMRS follows the National Curriculum Framework (NCF).
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: EMRS was introduced in 1997-98 under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, not under NEP 2020.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The schools are funded by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, not the Ministry of Education, and the funds come under Article 275(1) of the Constitution.
- Statement 3 is correct: The criteria for establishing an EMRS include 50% ST population and at least 20,000 tribal persons in a block.
- Statement 4 is correct: EMRS follows the National Curriculum Framework (NCF) for education.
Kerala Became First State To Establish Senior Citizens Commission
Kerala has made history by becoming the first state in India to establish a Senior Citizens Commission with the passage of the Kerala State Senior Citizens Commission Bill, 2025.
- This groundbreaking initiative reflects the state’s commitment to safeguarding the rights, welfare, and dignity of elderly citizens.
- The commission will serve as a statutory body dedicated to addressing the needs of senior citizens while also acting as an advisory panel for policy formulation and implementation.
What is the Senior Citizens Commission?
- A statutory body established under the Kerala State Senior Citizens Commission Act, 2025.
- The first commission of its kind in India, focusing exclusively on elderly welfare.
- Functions as an advisory authority for state policies concerning senior citizens.
Objectives of the Commission
- Ensure the protection, welfare, and rehabilitation of elderly individuals.
- Safeguard the rights and dignity of senior citizens.
- Encourage the active participation of elderly individuals in societal development.
- Promote inclusive policies to integrate senior citizens into various sectors.
Key Features and Functions
- Policy Advisory: Develops and recommends policies for the welfare and empowerment of senior citizens.
- Grievance Redressal: Addresses complaints related to neglect, abuse, financial exploitation, and social exclusion.
- Skill Utilization: Encourages senior citizens to contribute their knowledge, skills, and experience to society.
- Legal Support: Provides legal assistance, particularly in cases of elder abuse, property disputes, and financial exploitation.
- Awareness Campaigns: Conducts public awareness programs to educate people about the rights of senior citizens and the responsibilities of families and institutions.
- Regular Reports: Submits periodic recommendations to the state government for necessary policy updates and improvements.
With the establishment of this commission, Kerala has set a precedent for other states to prioritize elderly welfare and create a more inclusive, supportive, and dignified environment for senior citizens.
With reference to the Kerala State Senior Citizens Commission, consider the following statements:
- It is the first statutory body in India dedicated to senior citizens’ welfare.
- The commission has the power to issue legally binding directives on cases of elder abuse.
- It functions as both an advisory and grievance redressal body for elderly-related policies.
- The establishment of this commission was mandated under the Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act, 2007.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Kerala is the first Indian state to establish a statutory Senior Citizens Commission.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The commission does not have judicial powers to issue legally binding directives but can recommend legal action.
- Statement 3 is correct: The commission serves as an advisory and grievance redressal
- Statement 4 is incorrect: It was established under state legislation (Kerala State Senior Citizens Commission Act, 2025), not under the 2007 national act.
Pay Hike for MPs
Context:
- The Central Government has notified a 24% increase in the salaries of Members of Parliament (MPs), effective from April 1, 2023. This marks the first revision since April 2018.
Details of the Pay Hike:
- The revision has been implemented under the Salary, Allowances, and Pension of Members of Parliament Act, in accordance with the Cost Inflation Index specified in the Income Tax Act of 1961.
- The monthly salary of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha members has been raised from ₹1,00,000 to ₹1,24,000.
- The daily allowance has been increased from ₹2,000 to ₹2,500.
- Pension for former MPs has been raised from ₹25,000 to ₹31,000 per month.
- MPs also receive rent-free housing in New Delhi during their tenure.
Structure of the Parliament:
- Rajya Sabha (Council of States):
- Comprises a maximum of 250 members:
- 238 members represent States and Union Territories.
- 12 members are nominated by the President for their expertise in fields such as literature, science, art, and social service.
- Permanent House: It is not subject to dissolution; however, one-third of its members retire every two years, with newly elected members replacing them.
- Each Rajya Sabha member serves a six-year term.
- Lok Sabha (House of the People):
- Members are directly elected through Universal Adult Suffrage.
- The maximum strength of Lok Sabha is 550 members:
- 530 members represent States.
- 20 members represent Union Territories.
Consider the following statements regarding the recent salary hike for Members of Parliament (MPs) in India:
- The increase in salaries has been implemented under the Parliamentary Pay Commission, which revises MPs’ salaries every five years.
- The hike is determined based on the Cost Inflation Index under the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- The pension for former MPs has been increased to ₹31,000 per month.
- The revised salary structure applies only to Lok Sabha members and not Rajya Sabha members.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(A) 1 and 4 only
(B) 2 and 3 only
(C) 1, 3, and 4 only
(D) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (B) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: There is no Parliamentary Pay Commission. Instead, salaries are revised under the Salary, Allowances, and Pension of Members of Parliament Act.
- Statement 2 is correct: The increase is linked to the Cost Inflation Index under the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- Statement 3 is correct: The pension for former MPs has been raised from ₹25,000 to ₹31,000 per month.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: The hike applies to both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha members.
Success of Jan Aushadhi Kendras with PACS
Overview
- The Government of India has enabled Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) to establish and operate Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendras (PMBJK) under the Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP).
- This initiative, led by the Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers, seeks to expand access to affordable medicines in rural areas.
Significance of PACS in Rural Healthcare
- With a vast rural network covering over 13 crore small and marginal farmers, PACS are well-positioned to leverage their existing infrastructure, including land, buildings, and storage facilities, to establish Jan Aushadhi Kendras.
- These Kendras will enhance healthcare access in underserved regions, ensuring the availability of quality and affordable medicines.
- The existing trust and rapport that PACS hold within rural communities further contribute to the success of this initiative.
Financial Incentives for PACS-Operated Jan Aushadhi Kendras
- PACS-run Kendras will receive an incentive of 20% of their monthly purchases from the Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Bureau of India (PMBI), subject to a maximum of ₹20,000 per month, based on stock conditions.
- Kendra operators will earn a 20% margin on the Maximum Retail Price (MRP) (excluding taxes) for each medicine sold.
- In addition to generic medicines, these Kendras can also sell allied medical products, similar to conventional pharmacies, ensuring financial sustainability and profitability.
Alignment with National Health Goals
- This initiative is in line with the National Health Policy, which aims to enhance equitable access to quality healthcare. By integrating PACS and Jan Aushadhi Kendras, the government seeks to:
- Ensure availability of affordable medicines in remote areas.
- Reduce medical expenses for small and marginal farmers, allowing them to focus on agricultural investments.
- Generate employment and provide additional revenue streams at the PACS level.
Conclusion
- With its extensive rural reach, PACS is set to play a pivotal role in expanding affordable healthcare access across India. The initiative will strengthen rural healthcare infrastructure, support economic empowerment of farmers, and reduce the burden of medical expenses, thereby contributing to both public health and rural development goals.
- This was stated by the Minister of Cooperation, Shri Amit Shah, in a written reply to a question in the Rajya Sabha.
Consider the following statements regarding the integration of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) with Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendras (PMBJK):
- PACS can utilize their existing infrastructure, such as land, buildings, and storage facilities, to establish and operate Jan Aushadhi Kendras.
- PACS-operated Kendras receive an incentive of 30% of their monthly purchases from Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Bureau of India (PMBI), subject to a ceiling of ₹20,000 per month.
- These Kendras are allowed to sell allied medical products in addition to generic medicines.
- The initiative aligns with the National Health Policy’s goal of equitable access to quality healthcare.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 3, and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (b) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct – PACS can utilize their existing infrastructure to establish Jan Aushadhi Kendras, making healthcare more accessible in rural areas.
- Statement 2 is incorrect – The incentive is 20% of monthly purchases from PMBI, not 30%.
- Statement 3 is correct – Jan Aushadhi Kendras can sell allied medical products, similar to conventional chemist shops.
- Statement 4 is correct – The initiative supports the National Health Policy’s objective of equitable healthcare access.
Multiple Reforms to Enhance Safety and Efficiency in Railway Operations
Indian Railways is undergoing continuous reforms to improve train operations, passenger experience, and network expansion.
- Several key initiatives have been undertaken to expedite project approvals, enhance safety, and modernize railway infrastructure:
Key Reforms and Initiatives:
- Gati Shakti Directorate/Units
- The PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP), launched in October 2021, aims to revolutionize infrastructure planning and execution.
- Indian Railways has established a multi-disciplinary Gati Shakti Directorate at the national level and Gati Shakti Units in Zonal Railways.
- These initiatives ensure faster project approvals by integrating inputs from all stakeholders and infrastructure ministries.
- Enhanced Sanction Powers for GMs and DRMs
- To accelerate project execution, General Managers (GMs) and Divisional Railway Managers (DRMs) have been granted enhanced financial powers for sanctioning projects.
- Streamlined Contract Management
- Full powers have been delegated to General Managers for finalizing tenders.
- Implementation of Works Contract Management System (IRWCMS) and Contractor’s e-MB ensures transparency and efficiency in contract management and billing.
- Kavach: Automatic Train Protection System
- Kavach, India’s indigenous National Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system, has been implemented in mission mode to enhance train safety.
- Elimination of Level Crossings
- All unmanned level crossings on broad-gauge tracks have been eliminated.
- A phased plan is in place to replace manned level crossings with Road Over Bridges (RoBs) and Road Under Bridges (RUBs) to improve safety.
- Station Redevelopment – Amrit Bharat Station Scheme
- The Amrit Bharat Station Scheme focuses on providing world-class passenger amenities and improving operational efficiency.
- 1,337 stations have been taken up for redevelopment under this initiative.
- Modern Trains for Enhanced Passenger Experience
- Introduction of state-of-the-art trains, including:
- Vande Bharat Trains
- Amrit Bharat Trains
- Namo Bharat Rapid Rail
- Bharat Gaurav Trains
- Theme-based tourist circuit trains, launched to showcase India’s rich cultural heritage and historical sites.
- Operated in collaboration with tourism professionals and service providers.
- Digital Transactions at Stations and Trains
- Expansion of digital payment facilities for services like ticketing and catering.
- Freight Transportation Reforms
- To increase freight revenue, Indian Railways has introduced:
- Freight rebates and discounts for assured businesses
- Concessions on short-distance transport
- Mini rake loadings and goods shed development
- General Purpose Wagon Investment Scheme (GPWIS)
- Business Development Portal
- Gati Shakti Cargo Terminals (GCTs)
- Launched to fast-track approvals and simplify cargo terminal setup.
- 95 GCTs have been commissioned so far.
- Railway-India Post Integration for Parcel Services
- A joint initiative between Indian Railways and India Post for seamless parcel delivery.
- Combines first-mile and last-mile connectivity by India Post with station-to-station rail transport.
- Coal Chain Coordination Group
- Formed to coordinate coal transportation among:
- Coal companies
- Mines (captive and commercial)
- Ports, power plants, and industries
- Indian Railways
- Annual Recruitment Calendar
- Indian Railways has introduced an Annual Recruitment Calendar to:
- Minimize uncertainty and waiting time for job aspirants
- Ensure timely filling of vacancies
- Railway Land Leasing Policy
- A long-term land leasing policy has been introduced under PM Gati Shakti to facilitate integrated infrastructure planning and development.
- Introduction of Rolling Blocks
- Rolling Blocks were introduced in 2023 via Gazette Notification.
- This allows pre-scheduled maintenance, repairs, and asset replacement up to 52 weeks in advance for systematic infrastructure upgrades.
- These comprehensive reforms, as outlined by Union Minister of Railways, Information & Broadcasting, and Electronics & IT, Shri Ashwini Vaishnaw, signify a major leap towards modernizing Indian Railways, enhancing safety, and boosting operational efficiency.
The PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP), launched in 2021, aims to integrate infrastructure projects across sectors. Which of the following statements regarding Gati Shakti’s role in Indian Railways is/are correct?
- It ensures multi-modal connectivity by synchronizing railway infrastructure development with roads, ports, and logistics hubs.
- Gati Shakti allows Indian Railways to directly sanction railway projects without requiring inter-ministerial approvals.
- The initiative mandates Project DPRs to be prepared in consultation with stakeholders, leading to expedited approvals.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Gati Shakti focuses on multi-modal connectivity, aligning railway infrastructure with highways, ports, and airports for seamless logistics integration.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: While Gati Shakti expedites approvals, Indian Railways still requires inter-ministerial coordination, but the process has been made more efficient.
- Statement 3 is correct: The Detailed Project Reports (DPRs) are prepared with inputs from multiple stakeholders, ensuring feasibility and alignment with national infrastructure goals.
Amrit Sarovar Scheme

Launched in April 2022, Mission Amrit Sarovar aimed to construct or rejuvenate 75 Amrit Sarovars (ponds) in each district, targeting a total of 50,000 across the country. Each Sarovar was designed to have a pondage area of approximately 1 acre (except in hilly terrain) with a water holding capacity of 10,000 cubic meters.
- As of March 20, 2025, more than 68,000 Amrit Sarovars have been completed across various states and Union Territories, significantly addressing water scarcity and enhancing surface and groundwater availability. This initiative underscores the Government’s commitment to long-term environmental sustainability and community welfare.
Implementation and Funding:
- The initiative has been executed through convergence with multiple schemes, including:
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS)
- 15th Finance Commission Grants
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayi Yojana (PMKSY) sub-schemes like:
- Watershed Development Component
- Har Khet Ko Pani
- State Government Schemes
- Public Contributions such as crowdfunding and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) funds
Key Provisions for Public Participation:
- Laying of Foundation Stone: To be led by a freedom fighter, martyr’s family member, or a Padma awardee. If unavailable, the eldest member of the Gram Panchayat will do the honors.
- Donations & Voluntary Work: Citizens can contribute by donating construction material, benches, or offering Shram Daan (voluntary labor).
- Beautification Efforts: Villagers can mobilize crowdfunding or CSR funds for aesthetic enhancements.
- National Celebrations: On Independence Day & Republic Day, the Tricolour is hoisted at each Sarovar site, with national events being celebrated.
- Utilization for Economic Activities: Encouragement of irrigation, fisheries, and water chestnut cultivation, with user groups managing water structures.
Sustainability and Maintenance:
- Formation of User Groups: Drawn largely from Self-Help Groups (SHGs) for efficient upkeep and management.
- Silt Removal: Conducted voluntarily post-monsoon to maintain Sarovar efficiency.
- Plantation & Green Initiatives: Ongoing afforestation and ecological conservation around Sarovars.
State-Wise Progress (As of March 20, 2025):
- The initiative has been implemented successfully across various States and Union Territories, with notable achievements in:
- Uttar Pradesh: 16,630 Sarovars completed (highest in the country)
- Madhya Pradesh: 5,839
- Karnataka: 4,056
- Maharashtra: 3,055
- Rajasthan: 3,138
- Total Amrit Sarovars completed nationwide: 68,842
Conclusion:
- Mission Amrit Sarovar has played a pivotal role in addressing water challenges and ensuring sustainable water management across the country.
- With Phase II emphasizing community participation, climate resilience, and environmental conservation, the initiative is set to make a lasting impact on India’s water security and rural development.
With reference to Mission Amrit Sarovar, consider the following statements:
- The initiative was launched under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change to conserve wetlands.
- Each Amrit Sarovar is designed to have a pondage area of about 1 acre with a water holding capacity of approximately 10,000 cubic meters, except in hilly terrains.
- The initiative relies exclusively on central government funding, with no provision for state or private sector involvement.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Mission Amrit Sarovar was launched under the Ministry of Rural Development, not the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- Statement 2 is correct: Each Amrit Sarovar is designed to have a pondage area of about 1 acre and a water holding capacity of 10,000 cubic meters, except in hilly terrains where this may vary.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The initiative is implemented through convergence with various schemes (MGNREGS, PMKSY, Finance Commission grants, and state schemes), public crowdfunding, and CSR contributions.
Ministry of Rural Development and United Nations Children’s Fund YuWaah Collaborate to Empower Rural Women and Youth

The Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) and United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) YuWaah have entered into a three-year partnership aimed at empowering rural women and youth across India.
- A Statement of Intent (SOI) was signed to facilitate employment, entrepreneurship, and skill development, thereby increasing female labor force participation in rural areas.
Key Highlights of the Partnership:
- Strengthening Livelihood Opportunities: Women from Self-Help Groups (SHGs) will be connected to jobs, self-employment, and entrepreneurial ventures.
Digital Infrastructure Development:
- Computer Didi Centers and Didi ki Dukan will be set up in five pilot blocks across Andhra Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan.
- Upon successful implementation, the initiative has the potential to scale up to benefit 35 lakh women across 7,000+ blocks.
Youth-Centric Initiatives:
- Youth Hub: A digital aggregator platform for job opportunities, skilling, and volunteering.
- Lakhpati Didi Model: A scalable initiative to promote women entrepreneurship and create thousands of successful rural women entrepreneurs.
Leadership Perspectives:
- Shri T.K. Anil Kumar, Additional Secretary, MoRD, emphasized that the collaboration aligns with the Rural Prosperity and Resilience Programme, announced in Budget 2025-26.
- He highlighted that one-third of the 10 crore SHG members are youth, making them central to this initiative.
- Sharada Thapalia, Deputy Representative (Operations), UNICEF India, acknowledged MoRD’s 10 crore-strong SHG network as a transformative social infrastructure for rural empowerment.
Future Outlook:
- The partnership aims to drive economic self-reliance among rural women and youth while leveraging technology for scalable impact. The signing ceremony was attended by Smriti Sharan (Joint Secretary, MoRD), Dr. Monika (Deputy Secretary, MoRD), and representatives from UNICEF YuWaah and MoRD.
- This initiative marks a significant step towards rural economic transformation, fostering resilience and prosperity through skill-building, employment, and entrepreneurship.
The Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) has signed a Statement of Intent (SoI) with UNICEF YuWaah for a three-year partnership to empower rural women and youth. Which of the following objectives are correct regarding this partnership?
- Connecting SHG women with employment, self-employment, and entrepreneurship.
- Strengthening digital infrastructure through initiatives like Computer Didi Centers and Didi ki Dukan.
- Creating exclusive skilling programs only for male youth in rural areas.
- Establishing Youth Hub, a digital platform for job aggregation, skilling, and volunteering.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2, and 4 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The initiative aims to connect SHG women to job opportunities and self-employment ventures.
- Statement 2 is correct: The establishment of Computer Didi Centers and Didi ki Dukan is part of the digital infrastructure enhancement in five pilot states.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The initiative is not exclusive to male youth but rather focuses on empowering both rural women and youth.
- Statement 4 is correct: The Youth Hub is a job aggregation and skilling platform aimed at improving employment prospects.
RAPID APPROVAL OF HOUSES UNDER PM-JANMAN
The Government has implemented real-time monitoring and accountability measures by transitioning sanctioning mechanisms from the Pradhan Mantri Gati Shakti Portal to the Pradhan Mantri Awaas Portal.
- This initiative aims to streamline the provision of pucca houses to Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTG) households under PM JANMAN, a program spearheaded by the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD).
- To facilitate implementation, the Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA), in collaboration with State Governments/UT Administrations, conducted a habitation-level data collection exercise using the PM Gati Shakti mobile application.
- This data helped estimate the PVTG population and assess infrastructure gaps, including housing shortages. The gathered information is cross-verified by relevant Ministries and State Departments before approval.
Under this system:
- PMAY-G houses are sanctioned via the AwaasSoft portal in alignment with established norms.
- Once approved, data is updated and integrated into PM Gati Shakti, ensuring efficient monitoring of sanctions against identified gaps.
- Implementation and evidence-based monitoring of PMAY-G are executed through an end-to-end transaction-based e-governance model using AwaasSoft and the AwaasApp.
- Key functions, including beneficiary identification, fund release, installment tracking, and completion reporting, are managed digitally.
- Additionally, the physical and financial progress of PMAY-G is publicly accessible through various reports on AwaasSoft.
Grievance Redressal Mechanism
- A structured grievance redressal system operates at multiple levels—Gram Panchayat, Block, District, and State. Complaints from Members of Parliament, State Assemblies, or the general public (including those received via CPGRAMS) are addressed by the State Government to ensure necessary corrective actions.
- This information was provided by Shri Durgadas Uikey, Minister of State for Tribal Affairs, in response to an unstarred question (No: 3019) in the Rajya Sabha.
Consider the following statements regarding the transition of sanctioning mechanisms in housing schemes:
- The shift from the Pradhan Mantri Gati Shakti Portal to the Pradhan Mantri Awaas Portal is aimed at improving real-time monitoring and accountability in the sanctioning of housing schemes.
- PM JANMAN is implemented by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA), whereas housing provisions under the scheme are sanctioned by the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD).
- The AwaasSoft portal functions exclusively as a data collection tool and does not facilitate real-time transactions or beneficiary tracking.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 1 and 3 only
(C) 2 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (A) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The transition from PM Gati Shakti Portal to Pradhan Mantri Awaas Portal aims to enhance real-time monitoring and accountability in housing sanctioning.
- Statement 2 is correct: PM JANMAN is indeed implemented by MoTA, but housing provisions are sanctioned under MoRD through PMAY-G.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: AwaasSoft is not just a data collection tool; it is an end-to-end e-governance platform that facilitates real-time tracking, fund disbursement, and beneficiary verification.
PM-WANI Scheme
The Prime Minister’s Wi-Fi Access Network Interface (PM-WANI) framework is a key initiative aimed at accelerating the expansion of internet services through public Wi-Fi hotspots across the country.
- This initiative aligns with the broader vision of Digital India, fostering increased connectivity and enabling a range of socio-economic benefits.
- Under PM-WANI, Public Data Offices (PDOs) are responsible for establishing, operating, and maintaining WANI-compliant Wi-Fi hotspots based on their techno-commercial considerations.
- These PDOs must collaborate with a Public Data Office Aggregator (PDOA) to facilitate seamless internet services for users.
- As of March 20, 2025, a total of 2,78,439 PM-WANI Wi-Fi hotspots have been deployed across India, significantly enhancing public access to the internet.
- Furthermore, PM-WANI-compliant Wi-Fi hardware is readily available in the market. The Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT) has also contributed by supplying PM-WANI-compliant Wi-Fi hardware through its Transfer of Technology (ToT) partners.
- This information was shared by Pemmasani Chandra Sekhar, Minister of State for Communications and Rural Development, in a written response to a question in the Lok Sabha.
Consider the following statements regarding the Prime Minister’s Wi-Fi Access Network Interface (PM-WANI) framework:
- PM-WANI aims to provide broadband internet connectivity only in rural and backward areas of India.
- Under PM-WANI, Public Data Offices (PDOs) can provide internet services independently without any intermediary.
- The Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT) is responsible for supplying PM-WANI-compliant Wi-Fi hardware.
- PM-WANI requires individuals to obtain a government license before establishing a public Wi-Fi hotspot.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(A) 1 and 3 only
(B) 3 only
(C) 2 and 4 only
(D) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: (B) 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: PM-WANI aims to enhance internet access across both rural and urban areas, not just rural regions.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: PDOs must collaborate with a Public Data Office Aggregator (PDOA) to provide internet services.
- Statement 3 is correct: The Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT) supplies PM-WANI-compliant Wi-Fi hardware through Transfer of Technology (ToT) partners.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: Individuals or entities do not require a government license to set up public Wi-Fi hotspots under PM-WANI, making the initiative highly accessible and scalable.
PM-SHRI Scheme
- A Parliamentary Standing Committee has urged the Education Ministry to release over ₹4,000 crore in pending Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) funds for Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and West Bengal.
- The funds have been withheld due to these st ates not signing the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for the PM SHRI scheme.
- The panel emphasized that SSA predates PM SHRI and plays a crucial role in enforcing the Right to Education (RTE) Act.

Understanding the PM SHRI Scheme
- PM SHRI (PM Schools for Rising India) is a centrally sponsored scheme launched under NEP 2020 to develop 14,500 model schools with a focus on experiential and inquiry-driven learning, 21st-century skill development, eco-friendly infrastructure such as green buildings, water conservation, and waste recycling, and competency-based assessments instead of rote learning.
Key Features of PM SHRI Schools
- Modern infrastructure includes well-equipped labs, libraries, and art rooms. Digital integration ensures smart classrooms and advanced learning tools.
- A holistic learning approach emphasizes play-based and flexible teaching methods. A quality assessment mechanism ensures regular evaluations under the School Quality Assessment Framework (SQAF).
- Schools are selected through a challenge-based process where they must meet performance criteria.
- The scheme has a budget allocation of ₹27,360 crore for five years from 2022-23 to 2026-27, with ₹18,128 crore provided by the central government.
What is Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA)
- SSA is a centrally sponsored scheme designed to ensure universal access to quality education from pre-primary to higher secondary levels.
- It supports state governments in implementing the Right to Education (RTE) Act, which guarantees free and compulsory education for children aged 6-14 years.
Key Focus Areas of SSA
- School infrastructure development includes the construction of classrooms, libraries, and sanitation facilities.
- Teacher training and recruitment aim to enhance teaching quality. The program seeks to improve learning outcomes through curriculum reforms and remedial education.
- Inclusive education initiatives provide support for disadvantaged groups.
- The Parliamentary Panel’s recommendation highlights the critical role of SSA in strengthening India’s education system and ensuring uninterrupted learning opportunities for students.
Consider the following statements regarding the Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA):
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme aimed at ensuring universal access to quality education from pre-primary to higher secondary levels.
- The scheme was launched under the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- SSA is primarily focused on the development of school infrastructure and does not address teacher training or learning outcomes.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation: SSA was launched before NEP 2020 and focuses on multiple aspects of education, including infrastructure, teacher training, and learning outcomes. Statement 2 is incorrect because SSA predates NEP 2020. Statement 3 is incorrect because SSA includes teacher training and learning enhancement measures.
Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY)
The opposition has raised concerns over inadequate implementation of maternity benefits mandated under the National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013, attributing it to insufficient budgetary allocation.

About Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY)
- PMMVY is a maternity benefit program aligned with the provisions of the NFSA, 2013. Since 2022, it has been implemented under Mission Shakti, an umbrella scheme aimed at women’s empowerment.
Eligibility
- The scheme primarily targets socially, economically disadvantaged, and marginalized women.
Benefits
- Financial Assistance: Provides ₹5,000 to pregnant and lactating women to support maternal health and nutrition.
- Supplementary Support: Additional benefits under Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY) raise the total maternity assistance to approximately ₹6,000.
- Nutritional Support: Pregnant and lactating mothers receive free meals through Anganwadi centers during pregnancy and up to six months postpartum to meet essential dietary requirements.
Mission Shakti and Second Child Benefits
- Under Mission Shakti, a maternity benefit of ₹6,000 is provided for the second child, but only if the child is a girl, to encourage positive social attitudes towards female children.
Consider the following statements regarding Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY):
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme implemented under the provisions of the National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013.
- The scheme provides financial assistance for the first two live births, irrespective of gender.
- PMMVY was subsumed under Mission Shakti in 2022 to streamline maternity benefits and women’s empowerment initiatives.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: PMMVY is implemented under NFSA, 2013, making maternity benefits a legal entitlement.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The scheme provides benefits only for the first live birth, except under Mission Shakti, where ₹6,000 is given for the second child only if it is a girl.
- Statement 3 is correct: PMMVY was integrated into Mission Shakti in 2022 to enhance efficiency in women-centric welfare schemes.
Betting and Gambling are State Subjects
Context
- Union Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw has reiterated that betting and gambling fall under the jurisdiction of State governments.
- Between 2022 and 2025, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has issued 1,410 blocking directives for websites associated with online betting, gambling, and gaming.
Regulatory Framework
Finance Act, 2023
- Imposes a 30% income tax on net winnings from online gaming, effective from the assessment year 2024-25.
- Ensures tax compliance for online gaming earnings.
Goods and Services Tax (GST) Regulations
- 28% GST applied to online gaming transactions from October 1, 2023.
- Online gaming platforms must register under the Simplified Registration Scheme of the IGST Act.
- The GST Intelligence Headquarters has the authority to direct the blocking of unregistered platforms violating the IGST Act.
State Jurisdiction Over Betting and Gambling
- Betting and gambling fall under the State List of the Constitution.
- States are responsible for the prevention, investigation, and prosecution of offenses related to betting and gambling.
- The Central Government provides advisories and financial assistance to states for capacity building in enforcement.
Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023
- Introduces legal penalties for unauthorized betting and gambling, with imprisonment ranging from 1 to 7 years along with monetary fines.
Other Initiatives
- Ministry of Education has issued advisories for parents and teachers to address the risks of online gaming addiction.
- Ministry of Information and Broadcasting has implemented guidelines for advertisements related to online gaming, mandating disclaimers on financial risks and addiction potential.
Regarding the taxation of online gaming in India, consider the following statements:
- The Finance Act, 2023 introduced a 30% income tax on net winnings from online gaming, effective from the assessment year 2023-24.
- A uniform GST rate of 18% applies to all forms of online gaming transactions, effective from October 1, 2023.
- Online gaming platforms must register under the Simplified Registration Scheme of the IGST Act.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
Answer: (c) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- The 30% income tax on net winnings applies from the assessment year 2024-25, not 2023-24.
- A 28% GST, not 18%, is imposed on online gaming from October 1, 2023.
- Online gaming platforms must register under the Simplified Registration Scheme of the IGST Act to ensure tax compliance.
India Pitch for UNSC Reforms
India Calls for UNSC Reform to Ensure Lasting Peace
Security of Peacekeepers
UN peacekeepers today face a multitude of threats, including non-state actors, armed groups, and terrorists. India emphasizes the need for enhanced safety measures and security protocols for peacekeepers. Additionally, India advocates for accountability and justice in cases of crimes committed against peacekeeping forces.
Modernization of Peacekeeping Operations
- Recognizing the evolving nature of peacekeeping, India calls for the integration of advanced surveillance, communication, and data analytics in peacekeeping missions. India’s Centre for UN Peacekeeping (CUNPK) offers specialized training programs to equip peacekeepers with modern tools and strategies to meet contemporary challenges effectively.
Funding for Peacekeeping Missions
India underscores the need for well-funded peacekeeping missions. The resources allocated to these missions should be commensurate with their mandates to ensure effective execution and operational success.
Inclusion in Mandate Formation
India advocates for the inclusion of troop-contributing countries in the process of formulating mandates. This approach will enable better adaptation of peacekeeping operations to new realities and ensure that the strategies align with ground-level challenges.
About the United Nations Security Council (UNSC)
The UNSC is one of the principal organs of the United Nations, established in 1945 under the UN Charter to maintain international peace and security. It comprises 15 member states, including five permanent members with veto power—China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States—along with ten non-permanent members elected for two-year terms. The UNSC headquarters is located in New York City.
Need for UNSC Reforms
Current Composition and Representation
The present composition of the UNSC is marked by under-representation and lack of adequate representation of key global regions.
Inability to Address Conflicts
The current structure of the Council has proven ineffective in addressing significant global conflicts, thereby undermining its credibility and primary mandate of upholding international peace and security.
Changing Global Order
Since its inception in 1945, the world order has undergone significant transformations. These new geopolitical realities must be reflected in the permanent membership of the UNSC.
Issue of Veto Power
Only the five permanent members hold veto power, often using it to stall resolutions addressing global crises, such as those in Ukraine and Gaza. The ten non-permanent members, despite being part of the Council, lack veto authority, limiting their influence in decision-making.
Legitimacy Concerns
The concentration of power among the five permanent members creates a perception of inequity, diminishing the legitimacy and effectiveness of the UNSC in addressing contemporary security challenges.
Why India Deserves Permanent Membership in the UNSC
Demographic and Global Representation
India accounts for approximately 18% of the world’s population, making its inclusion in global decision-making bodies like the UNSC a matter of proportional representation.
Economic Strength
India is one of the world’s largest economies, with a significant impact on global stability and development. Its economic contributions align with the UNSC’s objectives of maintaining international peace and security.
Commitment to Peacekeeping
India has consistently been one of the largest contributors to UN peacekeeping missions, demonstrating its strong commitment to global peace and security.
Geopolitical Influence
India’s strategic location in South Asia and the Indo-Pacific region positions it as a crucial player in addressing global security challenges such as terrorism, climate change, and maritime security.
Advocacy for Democratic Values
As the world’s largest democracy, India upholds values of pluralism, tolerance, and inclusivity, which align with the core principles of the UN.
Global Support
India enjoys extensive support from numerous UN member states, including influential nations across different regions, underscoring its potential contribution to strengthening the UNSC’s role in global crisis management.
Challenges in Implementing UNSC Reforms
Veto Power of Permanent Members
- Any proposed reforms require the approval of all five permanent members, who are often reluctant to support changes that might reduce their influence.
Geopolitical and Regional Rivalries
- Regional tensions and geopolitical rivalries further complicate efforts to bring about UNSC reforms.
Complexity of the Reform Process
Reforming the UNSC necessitates an amendment to the UN Charter, which requires a complex and lengthy process involving ratification by a significant number of member states.
Opposition from China
China, as a permanent UNSC member, continues to oppose India’s bid for permanent membership, hindering India’s inclusion in the Council.
Way Forward
Both permanent and non-permanent membership should reflect the present-day global landscape rather than the post-World War II order. Reforms in the UNSC are imperative to maintain its relevance, legitimacy, and effectiveness in addressing contemporary security challenges. However, achieving consensus among UN member states remains a formidable and ongoing process.
Consider the following arguments against the UNSC’s current veto power structure:
- It enables any one of the P5 members to block international consensus.
- It has been used to shield countries from international scrutiny over human rights violations.
- It allows non-permanent members to influence decisions through alliances with P5 nations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation: The veto power enables P5 members to block resolutions, even if the majority supports them (statement 1 is correct). It has been used to prevent action against allies accused of human rights violations (statement 2 is correct). However, non-permanent members do not have veto power and cannot directly influence decisions (statement 3 is incorrect).
Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA)
Context
A Parliamentary Standing Committee has urged the Ministry of Education to resolve the ongoing dispute with West Bengal, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu regarding the non-release of over ₹4,000 crore under the Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA).

Key Issue
- The dispute arises from Tamil Nadu’s refusal to implement the three-language formula under the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and its decision not to sign the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for the PM-SHRI schools
- As a result, SSA funds have been withheld, affecting the state’s education initiatives.
About Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA)
- Implemented by the Department of School Education and Literacy, SSA is a centrally sponsored scheme designed to provide holistic education from pre-primary to Class XII, in alignment with NEP 2020.
- The scheme focuses on ensuring quality, equitable, and inclusive education, catering to students from diverse backgrounds, multilingual needs, and varying academic abilities.
Key Features of SSA
Financial Assistance to States and UTs
- Free uniforms and textbooks for elementary students.
- Reimbursement under the Right to Education (RTE) Act.
- Special training programs and bilingual teaching materials for out-of-school children.
Infrastructure Development
- Construction of school buildings, additional classrooms, and hostels.
- Strengthening of teacher education and ICT-based learning interventions.
Inclusive Education Initiatives
- Establishment and upgradation of schools and hostels in tribal and border areas.
- Support for marginalized communities to ensure universal access to education.
- The resolution of this funding dispute remains crucial for the effective implementation of SSA, ensuring that educational resources reach students without disruption.
Consider the following statements regarding the Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA):
- It is a centrally funded scheme implemented solely by the Ministry of Finance.
- SSA covers education from pre-primary to higher secondary level, aligning with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- The scheme provides financial support to States and UTs for the reimbursement of expenses under the Right to Education (RTE) Act.
- Tamil Nadu’s refusal to sign the MoU for PM SHRI schools has led to the withholding of SSA funds.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3, and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (b) 2, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: SSA is a centrally sponsored scheme, not fully funded by the Centre. It is implemented by the Department of School Education and Literacy, under the Ministry of Education, not the Ministry of Finance.
Statements 2, 3, and 4 are correct: SSA ensures education from pre-primary to higher secondary level, provides financial support for RTE reimbursement, and has faced funding issues due to Tamil Nadu’s refusal to sign the PM SHRI MoU.
Rajneet Kohli Appointed as Executive Director of Foods at HUL
Key Appointment
- Rajneet Kohli to assume role at Hindustan Unilever (HUL) from April 7, 2025
- Succeeds Shiva Krishnamurthy, who is stepping down for an external opportunity
Professional Background
- Former CEO & Executive Director at Britannia Industries (until March 14, 2025)
- Brings 30 years of experience in consumer and retail sectors
- Previously worked with Asian Paints, Coca-Cola, Jubilant FoodWorks, and Britannia
HUL’s Foods & Refreshment Business
- Includes brands like Kissan, Bru, Knorr, Brooke Bond, Horlicks, Lipton, and Hellmann’s
- Contributed ₹15,292 crore in revenue (FY24), 25% of HUL’s total turnover
Kohli’s Impact at Britannia
- Strengthened Britannia’s leadership in the food and bakery segment
- Led product innovation and digital transformation
- Recent Leadership Changes at HUL
- Rohit Jawa – MD & CEO (since June 2023)
- Harman Dhillon – Executive Director, Beauty & Well-being (2023)
- Arun Neelakantan – Executive Director, Customer Development (June 2024)
- Kohli’s leadership is expected to further accelerate HUL’s growth in the foods and refreshment segment
With reference to corporate leadership transitions in FMCG companies, consider the following statements:
- Rajneet Kohli’s appointment as Executive Director – Foods & Refreshment at HUL marks his first leadership role in the FMCG sector.
- The Foods & Refreshment segment contributes over one-third of Hindustan Unilever’s total revenue.
- Kohli’s prior experience includes leadership roles in multinational corporations across multiple consumer-driven industries.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (c) 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Rajneet Kohli has previously held leadership roles in Britannia, Coca-Cola, Jubilant FoodWorks, and Asian Paints, making this not his first leadership role in the FMCG sector.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The Foods & Refreshment segment contributed ₹15,292 crore in FY24, which is 25% of HUL’s total revenue, not over one-third.
- Statement 3 is correct: Kohli has extensive experience across multiple consumer sectors, including food, beverages, paints, and quick-service restaurants.
Cabinet Approves 2% Hike in DA for Government Employees

Key Highlights:
- Increase in DA/DR: Raised from 53% to 55% of Basic Pay/Pension.
- Effective Date: January 1, 2025.
Beneficiaries:
- Central Government Employees:66 lakh.
- Pensioners:55 lakh.
Financial Impact:
- Estimated additional burden on the exchequer: ₹6,614.04 crore per annum.
Background:
- DA is revised twice a year (January and July), based on the All India Consumer Price Index for Industrial Workers (AICPI-IW).
- Last revision: July 2024, when DA increased from 50% to 53%.
- Calculation follows the 7th Central Pay Commission’s
Purpose of DA/DR:
- Designed to offset inflation and preserve the purchasing power of government employees.
- Increasing speculation about the 8th Pay Commission has heightened interest in DA revisions.
With reference to the recent increase in Dearness Allowance (DA) and Dearness Relief (DR) by the Union Government, consider the following statements:
- The DA hike is determined solely based on the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) to account for inflationary trends.
- The increase in DA is applicable only to central government employees and does not extend to pensioners.
- The 7th Central Pay Commission provides the formula for DA calculation, which is revised twice a year.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The DA hike is based on the All India Consumer Price Index for Industrial Workers (AICPI-IW), not the Wholesale Price Index (WPI). The AICPI-IW reflects the cost of living and inflation experienced by government employees.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: DA is applicable to both government employees and pensioners, in the form of DA for serving employees and Dearness Relief (DR) for pensioners.
- Statement 3 is correct: The 7th Central Pay Commission provides the formula for DA revision, which is revised biannually (January and July) based on AICPI-IW.
Panel Recommends Framework for Direct Recruitment in CBI
Key Recommendations
Independent Recruitment Framework:
- Currently, many posts are filled through deputation from various organizations.
- The committee suggests an independent recruitment system for CBI.
- Recruitment could be conducted via SSC, UPSC, or a dedicated CBI examination.
- Lateral entry should be introduced for experts in cybercrime, forensics, financial fraud, and legal fields.
- Deputation should be limited to senior posts only.
- CBI should develop an in-house expertise team to reduce reliance on external specialists.
State Consent for Investigations:
- The committee recommends a new law allowing CBI to investigate cases related to national security and integrity without requiring state government consent.
- The law should include safeguards to maintain neutrality and prevent undue influence.
Permanent Cadre Establishment:
- CBI should create a permanent cadre with structured career growth.
- This would provide stability and reduce dependency on officers from other agencies.
- Challenges Faced by CBI
Lack of Autonomy & Operational Constraints:
- CBI operates under the Delhi Special Police Establishment (DSPE) Act, 1946, which limits its independence.
- Investigations require state government consent, leading to frequent delays and political hurdles.
- Eight states have withdrawn general consent, restricting CBI’s jurisdiction.
Manpower Shortages:
- Nearly 16% of sanctioned positions remain vacant, affecting investigations.
Dependence on Deputation:
- CBI struggles to fill posts below inspector rank due to a shortage of suitable state police officers.
About the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI)
- Established: 1963, based on the Santhanam Committee’s recommendations on corruption prevention.
- Ministry: Operates under the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances, and Pensions.
Jurisdiction:
- Requires state government consent for investigations unless covered under general consent.
Leadership:
- The CBI Director is appointed for a fixed two-year tenure based on recommendations from a three-member Appointment Committee.
- The committee’s recommendations aim to enhance CBI’s independence, efficiency, and expertise, ensuring it remains a robust investigative agency.
Regarding the recruitment process in the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI), consider the following statements:
- The majority of CBI personnel are recruited independently through a dedicated CBI examination.
- Deputation from other government agencies remains the primary mode of filling key posts in CBI.
- The Parliamentary Committee has recommended lateral entry for specialists in cybercrime, forensics, and financial fraud.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: CBI does not have an independent recruitment system; most of its positions are filled through deputation from other agencies such as state police and paramilitary forces.
- Statement 2 is correct: Deputation remains the predominant method of recruitment for CBI personnel.
- Statement 3 is correct: The Parliamentary Committee has recommended lateral entry for specialists in cybercrime, financial fraud, and forensics to enhance expertise.
10th Anniversary of Sagarmala Programme
Sagarmala 2.0
- Building upon the original program, Sagarmala 2.0 focuses on:
- Strengthening stakeholder collaboration for better project execution.
- Enhancing port-led industrial clusters to boost economic output.
- Expanding coastal shipping, inland waterways, and logistics hubs.
Sagarmala Startup Innovation Initiative (S2I2)
- Launched on March 19, 2025, the Sagarmala Startup Innovation Initiative aims to foster innovation and entrepreneurship in India’s maritime sector.
Key Focus Areas:
- Green Shipping – Promoting sustainable and eco-friendly maritime solutions.
- Smart Ports – Integrating artificial intelligence, automation, and digitalization in port operations.
- Maritime Logistics – Improving supply chain efficiency.
- Shipbuilding Technology – Advancing indigenous ship design and manufacturing.
- Sustainable Coastal Development – Ensuring environmental responsibility.
- The initiative follows the guiding principle of Research, Innovation, Startups, and Entrepreneurship.
Challenges and Roadblocks
Despite its progress, the Sagarmala Programme faces several challenges:
- Investment and Budgetary Constraints – Delays in funding allocation hinder timely project completion.
- Land Acquisition and Environmental Concerns – Legal and ecological complexities slow infrastructure development.
- Stakeholder Coordination Issues – Effective implementation requires seamless cooperation among central and state governments, port authorities, and private investors.
- Connectivity Gaps – Limited last-mile connectivity between ports and industrial hubs reduces efficiency.
- Community and Social Impact – Port expansions lead to the displacement of fishing communities, affecting their livelihoods.
Way Forward: Strengthening India’s Maritime Future
- Enhancing Inter-Agency Coordination – Strengthening collaboration across government and private sectors for better execution.
- Sustainable and Green Ports – Developing environmentally friendly ports with a focus on renewable energy and emissions reduction.
- Improving Port-Hinterland Connectivity – Investing in multi-modal transport networks to optimize cargo movement.
- Boosting Indigenous Shipbuilding and Recycling – Strengthening Make in India initiatives in maritime infrastructure and vessel manufacturing.
By addressing these challenges, the Sagarmala Programme will play a critical role in transforming India into a global maritime leader by 2047.
With reference to the Sagarmala Programme, consider the following statements:
- The programme aims to enhance India’s maritime logistics efficiency primarily by expanding port-led infrastructure rather than promoting coastal shipping.
- The Sagarmala Programme is aligned with the Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, which envisions India among the top five shipbuilding nations globally.
- The Sagarmala Development Company Limited (SDCL) was established to execute all port-related projects directly under the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The Sagarmala Programme focuses on shifting from infrastructure-heavy transport models to efficient coastal shipping and inland waterway networks, rather than solely relying on port-led expansion.
- Statement 2 is correct: The programme aligns with the Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, which aims to position India among the top five shipbuilding nations.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The Sagarmala Development Company Limited (SDCL) was created to provide financial support to project Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) but does not execute projects directly under the ministry.
Free Movement Regime between India and Myanmar
Background
- In 2024, the Union Home Minister announced the decision to abolish the Free Movement Regime (FMR) along the Myanmar border. However, no substantial progress has been made in implementing this decision.
Understanding the Free Movement Regime (FMR)
- The Free Movement Regime (FMR) is a bilateral arrangement between India and Myanmar that permits border communities to cross into each other’s territory without a visa.
- Established in 1968, FMR was introduced due to deep familial and ethnic ties shared by tribes living along the border.
- Initially, the regime allowed movement up to 40 km inside the other country’s territory.
- However, in 2004, this limit was reduced to 16 km, followed by additional regulatory measures introduced in 2016.
Rationale Behind Scrapping FMR
Internal Security Concerns
- Myanmar’s ongoing instability, along with the presence of armed groups, has led to an increase in unauthorized migration, creating security challenges for India.
Drug Trafficking
- Myanmar is part of the infamous Golden Triangle, one of the world’s major hubs for illicit drug production and smuggling. The porous border facilitates the influx of narcotics into India, exacerbating drug-related problems in the Northeast.
Insurgent Activities
- Several insurgent groups operate from across the border in Myanmar, using dense forests as a safe haven. The existing FMR enables their movement and logistical support, posing a threat to India’s internal security.
Influx of Refugees
- Escalating violence in Myanmar has led to an increased flow of refugees into India, particularly affecting Manipur and Mizoram. This has resulted in social, economic, and administrative challenges for Indian states.
China’s Expanding Influence
- Following the 2021 military coup in Myanmar, the country has become increasingly dependent on China, which provides diplomatic and economic support. While Myanmar previously sought to diversify its international partnerships, its growing reliance on China raises strategic concerns for India.
India-Myanmar Relations: A Strategic Overview
Geographical Proximity
- India and Myanmar share both a land and maritime boundary in the Bay of Bengal.
- Four northeastern Indian states—Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, and Mizoram—share borders with Myanmar.
Historical and Cultural Linkages
- India and Myanmar share centuries-old historical, religious, and cultural connections, with influences from Buddhism, Hinduism, and ancient trade routes shaping bilateral interactions.
- India and Myanmar signed the Treaty of Friendship in 1951, laying the foundation for their diplomatic relations.
Geopolitical Significance
- Myanmar’s strategic location makes it a vital bridge between South Asia and Southeast Asia.
- India’s Act East Policy and Neighborhood First Policy emphasize strengthening ties with Myanmar to enhance regional connectivity and economic cooperation.
Economic and Trade Relations
- Bilateral trade between India and Myanmar reached USD 1.50 billion in 2023-24.
Trade is conducted under:
- ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA)
- India’s Duty-Free Tariff Preference (DFTP) scheme
Security Cooperation
- India and Myanmar collaborate on border security, counterinsurgency operations, and intelligence sharing.
- Joint patrolling and military operations have been conducted to counter insurgent groups operating across the border.
Connectivity and Infrastructure Initiatives
- India is actively involved in major connectivity projects to enhance trade and infrastructure development:
- Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project (KMMTTP) – A key initiative to improve connectivity between India’s northeastern states and Myanmar via maritime and land routes.
- India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway – A crucial project aimed at bolstering economic integration between the three countries.
- Sittwe Port in Myanmar’s Rakhine State – A strategically significant port under KMMTTP, providing India an alternative trade route bypassing the congested Siliguri Corridor.
Developmental Assistance
- India has extended assistance in multiple sectors, including healthcare, education, skill development, and infrastructure.
- India and Myanmar collaborate under multilateral frameworks such as BIMSTEC and Mekong-Ganga Cooperation (MGC).
Way Forward
Regulated Border Management
- India must develop a structured mechanism to monitor cross-border movement while balancing security and humanitarian considerations.
- Deploying advanced surveillance technologies and strengthening border infrastructure will be crucial.
Public Awareness and Stakeholder Consultation
- It is imperative for the Indian government to educate local communities and stakeholders about the implications of FMR and its potential removal.
- Consultation with northeastern state governments and indigenous communities will help in formulating an inclusive border policy.
Sustainable Refugee Policy
- India needs a well-defined refugee policy to manage the influx of displaced individuals from Myanmar while ensuring national security.
- International collaboration with organizations like UNHCR can aid in managing refugee challenges.
Strategic Engagement with Myanmar
- India must continue engaging diplomatically with Myanmar’s ruling establishment to safeguard strategic and economic interests.
- Diversifying Myanmar’s external partnerships beyond China will be essential for regional stability.
Enhanced Economic and Security Cooperation
- Expanding bilateral trade and connectivity projects will strengthen India’s position in Myanmar.
- Joint counter-insurgency operations and intelligence sharing should be intensified to tackle security threats.
Conclusion
- Given the uncertain political landscape in Myanmar, India must adopt a balanced approach—tightening border security while maintaining people-to-people ties.
- The government should take local communities into confidence, formulate a phased strategy for managing border movement, and enhance cooperation with Myanmar to protect national and regional interests.
Consider the following statements regarding the India-Myanmar border and security cooperation:
- India and Myanmar have conducted joint military operations to target insurgent groups operating along the border.
- The Indo-Myanmar Border Agreement allows the Indian military to cross into Myanmar’s territory in pursuit of insurgents without prior permission.
- Myanmar is part of both the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B. 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct : India and Myanmar have conducted joint military operations such as Operation Sunrise (2019) to neutralize insurgent camps along the border.
- Statement 2 is incorrect : While India has conducted “hot pursuit” strikes against insurgents inside Myanmar (e.g., 2015 strike against NSCN-K militants), such actions require bilateral cooperation and prior coordination, as Myanmar does not permit unilateral military action.
- Statement 3 is correct : Myanmar is a member of both BIMSTEC and ASEAN, playing a strategic role in regional cooperation.
Wage Hike of MGNREGS
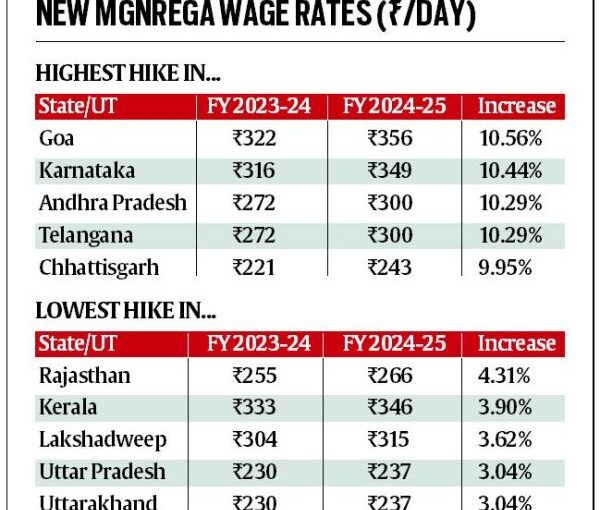
Recent Developments
- The Union government has announced an increase in wages under the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS), ranging from 2% to 7% for the financial year 2025-26.
Key Highlights of Wage Revisions
- The wage hike varies between ₹7 to ₹26 across different states.
- States with the lowest increase (₹7): Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Nagaland, and Telangana.
- Haryana recorded the highest wage increase (₹26), making it the first state to reach ₹400 per day under MGNREGS.
Understanding MGNREGA
Objective & Scope
- Demand-driven wage employment program, where resource allocation from the Centre to states is based on actual employment demand.
- Guarantees 100 days of wage employment per year to rural households whose adult members volunteer for unskilled manual work.
Types of Work Covered
- MGNREGA includes 266 categories of work, primarily focused on:
- Agriculture and allied activities
- Natural resource management (water conservation, afforestation, soil erosion control)
- Rural infrastructure development (roads, irrigation projects, flood control structures)
Wage Calculation Mechanism
- Wages under MGNREGA are linked to the Consumer Price Index for Agricultural Labourers (CPI-AL) to ensure adjustments for inflation in rural areas.
- In FY 2024-25, Goa recorded the highest wage hike (56%), whereas Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand had the lowest (3.04%).
Budgetary Allocation & Financial Trends
- MGNREGA’s budget has seen a significant rise from ₹11,300 crore in 2006-07 to ₹86,000 crore in FY 2024-25.
- A record ₹1,11,000 crore was allocated in FY 2020-21 to address economic distress caused by COVID-19.
Women’s Participation & Digital Reforms
- Women’s participation in MGNREGA has grown from 48% in FY 2013-14 to over 58% in FY 2024-25, reflecting greater financial inclusion.
- Introduction of digital payment systems has improved efficiency and transparency:
- Aadhaar-Based Payment System (ABPS): Ensures targeted wage disbursal, covering 49% of active workers.
- National Mobile Monitoring System (NMMS): Prevents fraudulent attendance and enhances accountability.
- National Electronic Fund Management System (NeFMS): Enables 100% electronic wage disbursement under Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT), making MGNREGA the largest DBT-based scheme in India.
Conclusion
- The recent wage hike under MGNREGS reflects the government’s commitment to strengthening rural employment, ensuring inflation-linked wage adjustments, and enhancing transparency through digital governance.
- However, challenges such as funding delays, timely wage payments, and worksite monitoring need continuous policy attention for improved effectiveness.
With reference to the implementation of MGNREGA, consider the following statements:
- Every rural household in India is entitled to 100 days of guaranteed wage employment per individual per year under MGNREGA.
- The payment of wages under MGNREGA must be completed within 15 days from the date of work completion, failing which the government is liable to pay compensation.
- The National Mobile Monitoring System (NMMS) has been introduced to digitally capture attendance at MGNREGA worksites to reduce fraudulent claims.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 2 and 3 only
(C) 1 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (B) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect → MGNREGA guarantees 100 days of wage employment per household, not per individual. The scheme provides work for adult members of a rural household willing to do unskilled manual labor.
- Statement 2 is correct → As per Section 3 of the MGNREGA Act, 2005, wages must be paid within 15 days of work completion. If delayed, the government is liable to pay compensation as per the Payment of Wages Act, 1936.
- Statement 3 is correct → The National Mobile Monitoring System (NMMS) was introduced in 2021 to ensure real-time digital attendance recording, reducing fake beneficiaries and improving transparency.
Sansad Bhashini Initiative
With reference to the ‘Sansad Bhashini’ initiative, consider the following statements:
- It is a joint initiative of the Lok Sabha Secretariat and the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- The initiative solely focuses on translating parliamentary documents into Hindi and English.
- It incorporates AI-driven chatbots to assist Members of Parliament in retrieving legislative information.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: The Lok Sabha Secretariat and MeitY have collaborated to implement Sansad Bhashini to enhance multilingual accessibility in parliamentary operations.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The initiative does not restrict translations to only Hindi and English but supports multiple languages to promote inclusivity.
Statement 3 is correct: AI-powered chatbots assist MPs and officials in retrieving procedural rules and legislative documents.
With reference to the implementation of MGNREGA, consider the following statements:
- Every rural household in India is entitled to 100 days of guaranteed wage employment per individual per year under MGNREGA.
- The payment of wages under MGNREGA must be completed within 15 days from the date of work completion, failing which the government is liable to pay compensation.
- The National Mobile Monitoring System (NMMS) has been introduced to digitally capture attendance at MGNREGA worksites to reduce fraudulent claims.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 2 and 3 only
(C) 1 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (B) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect → MGNREGA guarantees 100 days of wage employment per household, not per individual. The scheme provides work for adult members of a rural household willing to do unskilled manual labor.
- Statement 2 is correct → As per Section 3 of the MGNREGA Act, 2005, wages must be paid within 15 days of work completion. If delayed, the government is liable to pay compensation as per the Payment of Wages Act, 1936.
- Statement 3 is correct → The National Mobile Monitoring System (NMMS) was introduced in 2021 to ensure real-time digital attendance recording, reducing fake beneficiaries and improving transparency.
PM Internship Scheme
- PM Internship Scheme: Bridging Youth with Industry Experience.
- Union Minister Nirmala Sitharaman recently launched a dedicated mobile application for the Prime Minister Internship Scheme, encouraging more companies to participate in this transformative initiative.
About the PM Internship Scheme
- The PM Internship Scheme is a flagship initiative by the Government of India, designed to equip young individuals with industry exposure and practical experience.
- It focuses on skill development and employment generation, ensuring that youth from economically weaker sections gain valuable insights into real-world professional environments.
Key Features of the Scheme
- Target Beneficiaries: Young individuals aged 21-24 years from low-income households.
- Internship Duration: 12 months in India’s top 500 companies.
- Pilot Phase: Aims to benefit 25 lakh youth.
- Long-Term Goal: Envisions facilitating internships for one crore young individuals over five years.
Sector Coverage: Spans 24 industries, including:
- Oil & Gas
- Energy
- Travel & Hospitality
- Automotive
- Banking & Financial Services
- Eligibility Criteria
Scheme sets the following Eligibility conditions:
Educational Qualifications:
- Passed 10th, 12th, ITI, Polytechnic, or Diploma courses.
- Fresh graduates from non-premier institutions.
Economic & Family Background:
- Belong to a household with an annual income of ₹8 lakh or less (2023-24).
- No family member should hold a government job.
Exclusions:
- Students from IITs, IIMs, National Law Universities (NLUs).
- Individuals holding professional degrees like CA, MBA, MBBS, etc.
Vision & Impact
- This initiative aligns with the government’s broader strategy to bridge the gap between academic learning and professional expertise.
- By focusing on skill enhancement and employment readiness, it paves the way for greater socio-economic mobility among India’s youth.
With reference to the Prime Minister Internship Scheme (PM Internship Scheme), consider the following statements:
- The scheme is open to all young individuals between the ages of 21-30 years.
- It offers internships in only government enterprises to enhance youth participation in public administration.
- The scheme specifically excludes students from IITs, IIMs, and National Law Universities to ensure inclusivity for underrepresented groups.
- The long-term goal of the scheme is to facilitate internships for 5 crore youth over five years.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: (c) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The scheme targets youth aged 21-24 years, not 21-30 years.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Internships are available in both public and private enterprises, covering 24 industries, including energy, automotive, and financial services.
Statement 3 is correct: To promote inclusivity, students from IITs, IIMs, National Law Universities, and professional courses like CA, MBA, MBBS are excluded.
Statement 4 is incorrect: The scheme’s five-year goal is to facilitate internships for 1 crore youth, not 5 crore.
Prime Minister’s Young Authors Mentorship Scheme (YUVA) Scheme
Overview
- The Ministry of Education (MoE) and the National Book Trust (NBT) of India have launched the third edition of the Prime Minister’s Young Authors Mentorship Scheme (PM-YUVA 3.0).
- This initiative aims to identify and nurture young literary talent in India, providing mentorship to aspiring writers under the age of 30.
Previous Editions of the YUVA Scheme YUVA 1.0 (May 2021)
- Launched during the Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav celebrations to commemorate 75 years of India’s independence.
- The central theme focused on the National Movement of India, highlighting unsung heroes, lesser-known facts, and various aspects of the freedom struggle.
- YUVA 2.0 (October 2022)
- Expanded upon the objectives of YUVA 1.0, shifting its theme to Democracy.
- The focus was on nurturing young writers who could explore India’s democratic values, traditions, and governance structures.
PM-YUVA 3.0: Objectives and Themes
- Building on the success of its predecessors, YUVA 3.0 continues the government’s mission to foster literary talent and promote a vibrant reading and writing culture.
- It seeks to provide mentorship and structured guidance to young authors to help them develop their creative writing skills.

- The scheme emphasizes three core themes:
- Contribution of the Indian Diaspora in Nation Building
- Indian Knowledge System
- The Makers of Modern India (1950-2025)
Significance of the YUVA Scheme
- Encourages young authors to explore various dimensions of India’s history, culture, and future aspirations.
- Provides a platform for youth to express their perspectives on India’s contributions in different fields, both ancient and contemporary.
- Aligns with the vision of Ek Bharat, Shreshtha Bharat, promoting the documentation and dissemination of India’s rich cultural heritage and intellectual traditions.
- Through this initiative, the government continues to emphasize nation-building through literary excellence, empowering young minds to contribute meaningfully to India’s intellectual and cultural landscape.
With reference to the Prime Minister’s Young Authors Mentorship Scheme (PM-YUVA 3.0), consider the following statements:
- The scheme is jointly implemented by the Ministry of Education (MoE) and the National Book Trust (NBT) of India.
- It exclusively focuses on themes related to the Indian Freedom Struggle.
- PM-YUVA 3.0 aims to mentor young authors under the age of 30.
- The scheme aligns with the vision of Ek Bharat, Shreshtha Bharat.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 3, and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (b) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct. The scheme is implemented by the Ministry of Education (MoE) and the National Book Trust (NBT) of India.
Statement 2 is incorrect. While the first edition (YUVA 1.0) focused on the Indian freedom struggle, PM-YUVA 3.0 includes themes such as Indian Knowledge System, the Contribution of the Indian Diaspora in Nation Building, and the Makers of Modern India (1950-2025).
Statement 3 is correct. The scheme is designed for young authors under 30 years of age.
Statement 4 is correct. The scheme aligns with Ek Bharat, Shreshtha Bharat by fostering a deeper understanding of India’s cultural and intellectual traditions.
Samarth Incubation Programme
- The Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DoT), an autonomous Telecom R&D centre under the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Government of India, has launched the ‘Samarth’ incubation programme to support emerging startups in the telecom sector.
Objectives:
- Foster innovation in telecom software, cybersecurity, 5G and 6G technologies, artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and quantum technologies.
- Promote sustainable and scalable business models by providing access to advanced resources.
- Bridge the gap between ideation and commercialization for startups.
Key Features:
- Implementation Partner: Software Technology Parks of India (STPI) has been selected to execute the programme.
- Mode of Delivery: Hybrid mode with both online and offline engagement.
Cohort Structure:
- Each program will accommodate 18 startups, with a total of 36 startups across two cohorts (each lasting six months).
- Eligibility: Open to DPIIT (Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade) recognized startups.
Support for Startups:
- A grant of up to ₹5 lakh per selected startup.
- Six months of office space at the C-DoT campus.
- Access to C-DoT lab facilities.
- Mentorship from C-DoT technical leaders and industry experts.
Future Prospects: Startups demonstrating significant progress may receive further opportunities under the C-DoT Collaborative Research Program.
Consider the following statements regarding the ‘Samarth’ Incubation Programme launched by the Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DoT):
- It is an initiative to support startups specifically in 5G and 6G technologies, without extending to other domains like cybersecurity or AI.
- The programme is being implemented in collaboration with Software Technology Parks of India (STPI).
- Only startups that have been recognized by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) are eligible for the programme.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Samarth Incubation Programme supports startups not only in 5G and 6G technologies but also in cybersecurity, AI, IoT, and quantum technologies.
Statement 2 is correct: The Software Technology Parks of India (STPI) is the implementation partner for the programme.
Statement 3 is correct: Only DPIIT-recognized startups are eligible for the incubation support.
Modified Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme
- The Government of India has introduced a modified Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme to enhance the operational viability of Cooperative Sugar Mills (CSMs).
- This initiative enables these mills to upgrade their existing sugarcane-based ethanol plants into multi-feedstock facilities, allowing the use of grains such as maize and damaged food grains (DFG) alongside sugarcane.
- The objective is to ensure year-round production, improve efficiency, and strengthen the ethanol industry.
- Ethanol Production in India: Ethanol production in India primarily depends on sugarcane, but its crushing period lasts only 4-5 months annually, limiting production capacity. To address this, the government is promoting the diversification of feedstock’s to ensure consistent ethanol output. The Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme targets a 20% ethanol blend with petrol by 2025, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and enhancing energy security.
- Modified Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme: The scheme offers financial assistance in the form of an interest subvention of 6% per annum or 50% of the bank interest rate, whichever is lower. This support is applicable for loans provided by banks or financial institutions over five years, including a one-year moratorium. By easing financial constraints, the initiative encourages CSMs to expand their ethanol production beyond sugarcane-based operations.
- Benefits of Multi-Feedstock Conversion: The shift to multi-feedstock plants provides several advantages:
- Year-Round Production: Using grains and agricultural residues ensures continuous ethanol output, even outside the sugarcane season.
- Improved Efficiency: Diversified raw materials enhance the mills’ operational flexibility and financial sustainability.
- Economic Growth: Supporting local grain production reduces dependence on sugarcane, strengthening the agricultural economy.
- Impact on Ethanol Production Targets: India has set ambitious ethanol production targets under the EBP Programme. As of February 2025, the blending rate reached 19.6%, indicating significant progress toward the 20% goal. Enhanced production capabilities from CSMs are expected to play a key role in meeting this target.
- Future Prospects for Cooperative Sugar Mills: The modified scheme provides a transformative opportunity for CSMs.
- By embracing a multi-feedstock approach, these mills can ensure long-term sustainability while contributing to India’s renewable energy goals.
- Additionally, leveraging locally available grains promotes self-sufficiency and strengthens the rural economy.
- This strategic shift marks a crucial step in making ethanol production more resilient and efficient in the coming years.
Consider the following statements regarding the Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme:
- It provides an interest subvention of 6% per annum or 50% of the bank interest rate, whichever is lower.
- The scheme allows Cooperative Sugar Mills (CSMs) to upgrade their sugarcane-based ethanol plants into multi-feedstock facilities.
- The financial support under this scheme is provided for a period of ten years, including a two-year moratorium.
- It aims to facilitate year-round ethanol production by diversifying the feedstock to include maize and damaged food grains (DFG).
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1, 2, and 4 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 3, and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Correct: The scheme provides an interest subvention of 6% per annum or 50% of the bank interest rate, whichever is lower.
- Statement 2 – Correct: It allows CSMs to upgrade their sugarcane-based ethanol plants into multi-feedstock facilities.
- Statement 3 – Incorrect: The financial assistance is provided for five years, including a one-year moratorium, not ten years with a two-year moratorium.
Statement 4 – Correct: The scheme encourages the use of maize and damaged food grains (DFG) for ethanol production
Global Free Speech Survey 2024
- The Future of Free Speech report, conducted in October 2024 by an independent think tank, ranks India 24th among 33 countries, highlighting concerns about the protection of controversial speech.
- While many Indians value free speech, their support for government criticism is notably low. The Future of Free Speech Index ranks countries based on public support for free expression.
- The 2024 survey shows a global decline in free speech support since 2021.
- Notably, democratic nations like the United States and Japan have experienced drops, whereas Scandinavian countries, including Norway and Denmark, lead the rankings with the highest scores.
- India scored 62.6, positioned between South Africa and Lebanon. Despite a strong abstract support for free speech, commitment to protecting controversial speech has weakened.
- A concerning 37% of Indian respondents believe the government should restrict criticism of its policies, the highest percentage among surveyed nations, contrasting with just 5% in the UK. The survey indicates a disconnect in India.
- While many claim to support free speech, actual protections are lacking. This trend mirrors patterns seen in Hungary and Venezuela, where public sentiment does not align with government actions, signaling democratic backsliding.
- When asked about changes in their ability to speak freely, Indians expressed a belief in improvement over the past year.
- However, observers suggest the reality has worsened, pointing to a gap between public perception and the actual state of free speech in India.
- The report notes that free speech extends beyond legal rights and requires a culture of open debate and tolerance for dissent.
- The erosion of willingness to defend controversial speech is evident, threatening the essence of free expression.
- Globally, support for free speech tends to correlate with actual freedom of expression. However, India’s situation is atypical.
- Nations with high public support usually enjoy better protections, yet in India, the opposite is true.
- The survey explored various aspects of free speech, including attitudes toward censorship, criticism of the government, and sensitive topics. Support for free speech often declines when it involves offensive content or criticism of religion, reflecting a complex landscape of public opinion.
With reference to the “Future of Free Speech” report, consider the following statements:
- The 2024 survey indicates that support for free speech has increased globally compared to 2021.
- Scandinavian nations, particularly Norway and Denmark, have ranked the highest in the index.
- India’s ranking in the index suggests that public support for free speech correlates directly with actual protections.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The report highlights a decline in free speech support globally since 2021, especially in democratic nations like the US and Japan.
- Statement 2 is correct: Norway and Denmark have consistently scored the highest in the rankings, showing strong public and institutional support for free speech.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The report suggests that while India has public support for free speech, actual protections remain weak. This contradicts the usual correlation seen in other nations.
Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0
- The Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0, introduced by the Union government, aims to overhaul India’s intricate legal system.
- This initiative is part of a broader effort to improve the ease of living by addressing excessive criminalisation and ensuring laws are fair, enforceable, and humane.
- The Vidhi Centre for Legal Policy has highlighted the vast number of criminal provisions in India’s legal framework, many of which impose disproportionate penalties for minor infractions.
India’s Overburdened Legal System
- India currently has 882 central laws, of which 370 contain criminal provisions, covering a staggering 7,305 offences.
- While some laws address serious crimes such as murder and financial fraud, many govern everyday activities like parenting, local community events, and business operations.
- The legal landscape often imposes severe penalties, including life imprisonment and even the death penalty, for offences that may not always warrant such harsh measures.
The Problem of Over-Criminalisation
- A significant issue with India’s current legal system is the criminalisation of minor infractions.
- Citizens can face imprisonment for trivial acts such as failing to report the death of a pet or improper storage of e-cigarettes.
- This overreach blurs the distinction between serious and minor offences, leading to arbitrary enforcement by authorities and increasing the risk of legal exploitation.
Disproportionate Punishments and Legal Inconsistencies
- One of the key concerns is the lack of proportionality in punishments.
- For instance, the Mental Healthcare Act prescribes the same jail term for record-keeping errors as it does for major medical violations.
- Such inconsistencies weaken public trust in the justice system and create a disjointed legal structure that does not align with societal needs.
Social and Economic Impact
- The consequences of harsh legal provisions fall disproportionately on the poor, who often lack access to legal resources.
- With low conviction rates, the judicial process itself becomes a form of punishment, leading to prolonged pretrial detentions.
- Many individuals suffer due to outdated or unjust laws that fail to reflect contemporary realities.
Principles of Legal Reform
The Vidhi Centre for Legal Policy has outlined four key principles for legal reform:
- Preserving Societal Values – Ensuring laws reflect ethical and cultural norms.
- Preventing Justifiable Harm – Criminal laws should address actions that cause significant harm to individuals or society.
- Ensuring Effective Legal Solutions – Laws should provide clear and enforceable
- Proportionality in Punishments – Penalties should correspond to the severity of offences.
Future Legal Reforms
- The Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0 seeks to shift the focus from punitive justice to restorative justice, reducing unnecessary legal burdens and prioritising reforms that benefit citizens.
- A key objective is to decrease the number of undertrial prisoners and streamline judicial procedures to create a more efficient, equitable, and transparent legal system.
- As India moves forward, legal reforms must prioritize justice, fairness, and societal well-being to enhance the quality of life for all citizens.
With reference to the Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0, consider the following statements:
- It aims to reduce excessive criminalisation by eliminating all provisions of imprisonment from central laws.
- The Bill is a step towards prioritising restorative justice over punitive measures.
- It was introduced by the Ministry of Law and Justice to rationalise sentencing in criminal laws.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0 does not eliminate all provisions of imprisonment but seeks to reduce disproportionate criminalisation of minor infractions.
- Statement 2 is correct: The Bill emphasises restorative justice by focusing on proportionality in punishments and rationalising legal penalties.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The Ministry of Law and Justice is not responsible for introducing the Bill; rather, it is a broad government initiative to reform laws across multiple sectors.
India Takes 24th Spot in Free Speech Survey
A global survey by The Future of Free Speech ranked India 24th out of 33 countries on support for free speech.
Constitutional Provisions
- Article 19(1)(a) of the Indian Constitution guarantees every citizen the Right to Freedom of Speech and Expression.
Key Findings:
- Norway and Denmark secured the top positions in the Future of Free Speech Index, with scores of 87.9 and 87.0, respectively.
- Indonesia (56.8), Malaysia (55.4), and Pakistan (57.0) demonstrated the most significant improvements; however, they continued to rank on the lower end of the index.
- Interestingly, some authoritarian-leaning nations, such as Hungary (85.5) and Venezuela (81.8), achieved high scores, indicating a disparity between government-imposed restrictions and public sentiment toward free speech.
The Supreme Court has interpreted this right to include various aspects, such as:
- Right to propagate one’s own views as well as those of others.
- Freedom to remain silent.
- Freedom of the press.
- Right against the imposition of pre-censorship on newspapers.
- Freedom to publish commercial advertisements.
- Right to protection from unlawful telephone tapping.
- Reasonable Restrictions (Article 19(2))
The Right to Freedom of Speech and Expression is not absolute and is subject to reasonable restrictions imposed by the State on the following grounds:
- Security of the State
- Sovereignty and Integrity of India
- Public Order
- Friendly Relations with Foreign States
- Decency and Morality
- Contempt of Court
- Defamation
- Incitement to an Offense
- These restrictions ensure that freedom of speech is exercised responsibly while balancing individual rights with national security and social harmony.
Consider the following statements regarding the Right to Freedom of Speech and Expression under the Indian Constitution:
- The right includes the freedom to propagate both one’s own views as well as those of others.
- Commercial advertisements are not covered under the ambit of Article 19(1)(a).
- The right to remain silent has been recognized as part of the freedom of speech by the Supreme Court of India.
- The state can impose restrictions on free speech on grounds of public interest and economic justice.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 1, 2, and 3 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Supreme Court has ruled that the freedom of speech includes the right to propagate both one’s own views and those of others.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: Commercial advertisements are protected under Article 19(1)(a). However, they can be restricted under reasonable limitations.
- Statement 3 is correct: The right to remain silent was upheld in the Bijoe Emmanuel Case (1986), where students refusing to sing the national anthem were protected under freedom of speech.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: Restrictions under Article 19(2) are limited to sovereignty, integrity, security, friendly relations, public order, decency, morality, contempt of court, defamation, and incitement to an offense. Public interest and economic justice are not valid grounds for restriction.
Finance Commission
- The Finance Commission (FC) is a constitutional body established under Article 280 of the Indian Constitution.
- It is formed every five years by the President of India to recommend the financial distribution between the Centre and States.
Composition:
- Chairman: An expert in public affairs.
- Four Members: Experts in finance, economics, and administration.
Functions:
- Vertical Devolution: Determines the state’s share in the central divisible pool of taxes (e.g., GST, income tax).
- Horizontal Distribution: Allocates funds among states based on factors like fiscal needs, revenue-generating capacity, and developmental performance.
- Grants-in-Aid: Recommends grants to revenue-deficient states and specific sectors in need of financial assistance.
16th Finance Commission
- Constituted in 2023, it will recommend financial distribution for the period April 1, 2026 – March 31, 2031.
- Expected to address states’ financial concerns, including demands for Special Category Status (SCS).
Special Category Status (SCS): Understanding the Demand
What is SCS?
- Special Category Status (SCS) is a classification granted to states facing severe economic and geographical disadvantages to provide them with additional central assistance.
- It was introduced in 1969 based on the Gadgil Formula, recommended by the 5th Finance Commission (Mahavir Tyagi).
- Initially granted to Assam, Jammu & Kashmir, and Nagaland.
Criteria for Special Category Status (As per Gadgil Formula):
A state must meet the following conditions:
- Hilly and difficult terrain.
- Low population density and/or a significant tribal population.
- Strategic location along international borders.
- Economic and infrastructural backwardness.
- Non-viable state finances.
Evolution and States with SCS
Initially granted to three states (1969), later expanded.
Currently, 11 states hold SCS:
- Northeast states: Assam, Nagaland, Manipur, Meghalaya, Tripura, Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, and Sikkim.
- Hilly states: Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
- Telangana: Granted due to bifurcation from Andhra Pradesh.
States Demanding SCS:
- Andhra Pradesh (Due to bifurcation).
- Bihar (Citing economic backwardness).
- Odisha (Due to natural disaster vulnerability and underdevelopment).
Benefits of Special Category Status (SCS):
Higher Central Assistance:
- 90% of funds as grants and 10% as loans for Centrally Sponsored Schemes (CSS).
- Non-SCS states receive only 30% grants and 70% loans.
Special Plan Assistance:
- Dedicated funding for state-specific projects of strategic importance.
Non-Lapsable Funds:
- Unused funds do not lapse at the end of the financial year, ensuring continuity in funding.
Tax Concessions:
- Special tax incentives (many now subsumed under GST).
Conclusion
- The demand for Special Category Status remains a contentious issue, especially for states like Bihar, which seek additional financial support due to economic underdevelopment.
- With the 16th Finance Commission’s recommendations expected in the coming years, the debate on SCS is likely to gain momentum.
With reference to the Finance Commission of India, consider the following statements:
- The Finance Commission is a statutory body established by an Act of Parliament.
- It is responsible for recommending the allocation of financial resources between the Centre and States.
- The recommendations of the Finance Commission are binding on the government.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- The Finance Commission is a constitutional body, not a statutory body, as it is established under Article 280 of the Indian Constitution. Hence, Statement 1 is incorrect.
- Its primary function is to recommend how financial resources should be distributed between the Centre and States. Hence, Statement 2 is correct.
- The recommendations of the Finance Commission are not binding on the government. They are only advisory in nature. Hence, Statement 3 is incorrect.
Vice-President Criticised Freebies Culture
What Are Freebies?
- Freebies refer to goods, services, or financial incentives provided by political parties, often during elections, to attract voters.
- While there is no formal definition, they commonly include free electricity, LPG connections, bicycles, loan waivers, and direct cash transfers.
Challenges and Concerns
Fiscal Burden:
- Excessive spending on freebies strains state finances, leading to fiscal deficits and rising public debt, which can weaken long-term economic stability.
Resource Allocation Issues:
- Prioritizing freebies diverts funds from essential sectors like infrastructure, education, and healthcare, affecting sustainable development.
Economic Inefficiency and Dependency:
- Freebies may encourage inefficient resource utilization and foster dependency, rather than addressing structural issues like poverty and unemployment.
Competitive Populism:
- Political parties engage in a race to outdo each other in offering freebies, often at the cost of sound economic policy and governance reforms.
Impact on Policy Reforms:
- Over-reliance on freebies shifts focus from essential governance measures, such as skill development, employment generation, and education reforms.
Constitutional Perspective:
- While Article 38 of the Indian Constitution mandates the State to promote social welfare and reduce inequalities, unchecked freebies can threaten financial sustainability.
Supreme Court’s Observations
- The Supreme Court has criticized the practice of pre-election freebies, noting that they:
- Distort electoral fairness by influencing voter preferences.
- Undermine work ethic, discouraging economic participation.
Views of Experts
- Former RBI Governor Duvvuri Subbarao warned against freebies’ detrimental impact on state finances.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi has termed the practice of offering freebies as distributing “revris” (sweets) for votes, calling it short-term populism over long-term progress.
- Suggestions & Way Forward
National Policy on Freebies:
- Establish clear guidelines on government expenditures to ensure they contribute to sustainable development.
Code of Conduct & National Dialogue:
- A collective effort, led by the Centre, to regulate and rationalize the distribution of freebies.
Targeted Welfare Programs:
Instead of blanket freebies, focus on data-driven welfare measures that cater to genuinely needy populations, improving long-term outcomes
With reference to the economic impact of freebies, consider the following statements:
- Freebies contribute to long-term economic growth by increasing aggregate demand in the economy.
- Competitive populism associated with freebies can lead to fiscal imprudence and higher public debt.
- The opportunity cost of freebies often results in underfunding of critical sectors like healthcare and education.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation: Statement 1 is incorrect: While freebies may temporarily boost aggregate demand, they do not necessarily contribute to long-term economic growth as they often fail to create productive assets.
- Statement 2 is correct: Competitive populism escalates fiscal deficits as states compete to provide more benefits without considering fiscal sustainability.
- Statement 3 is correct: The opportunity cost of excessive freebie spending leads to underinvestment in critical infrastructure and social sectors, affecting long-term development.
Rashtriya Karmayogi Jan Seva Programme
Context: The Union Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment successfully launched the first batch of the Rashtriya Karmayogi Jan Seva Programme, aimed at fostering a citizen-centric approach in governance.
About the Programme
- It is an interactive initiative designed to inspire, enlighten, and guide Central Government employees in adopting the Karmayogi Way, which prioritizes Seva-Bhav (a sense of service) and accountability.
- The initiative is spearheaded by the Capacity Building Commission (CBC) to enhance competency-driven governance.
Capacity Building Commission (CBC)
- Established: 2021
- Structure: Three-member body supported by an internal Secretariat led by a Secretary.
- Composition: Members are drawn from diverse backgrounds, including the private sector, academia, public sector, and civil society.
- Objective: Standardizing and improving public sector learning and development initiatives across the country.
Mission Karmayogi
- Launched: 2020
- Type: National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB)
- Objective: Developing a future-ready civil service with the right attitude, skills, and knowledge, in alignment with the vision of New India.
- Governance: Anchored by an apex body, headed by the Prime Minister to ensure effective implementation.
Consider the following statements regarding the Rashtriya Karmayogi Jan Seva Programme:
- It is an initiative launched by the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances, and Pensions.
- The programme emphasizes a citizen-centric approach to governance by fostering Seva-Bhav and accountability.
- The Capacity Building Commission is responsible for implementing this programme.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Explanation:
- Incorrect: The Rashtriya Karmayogi Jan Seva Programme is launched by the Union Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, not the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances, and Pensions.
- Correct: The programme indeed emphasizes a citizen-centric approach to governance, fostering Seva-Bhav (spirit of service) and accountability among government employees.
- Correct: The Capacity Building Commission (CBC), established in 2021, is responsible for implementing and overseeing the programme, aligning it with broader civil service capacity-building initiatives under Mission Karmayogi.
PM’s Scheme for Mentoring Young Authors (PM-YUVA 3.0)
- The Ministry of Education has launched the third edition of the Prime Minister’s Scheme for Mentoring Young Authors (PM-YUVA 3.0) to nurture young literary talent in India.
About the Scheme:
- Aims to mentor aspiring authors under the age of 30, fostering a culture of reading, writing, and publishing.
- Provides mentorship and publishing support to help Indian writers gain recognition on a global platform.
Focuses on three key themes:
- Contribution of Indian Diaspora in Nation Building
- Indian Knowledge System
- Makers of Modern India (1950-2025)
- Aligns with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which emphasizes building a knowledge-driven ecosystem.
- National Book Trust (NBT), India, is responsible for implementing the scheme.
With reference to the Prime Minister’s Scheme for Mentoring Young Authors (PM-YUVA 3.0), consider the following statements:
- It is an initiative of the Ministry of Culture to promote regional literature and folk traditions.
- The scheme aims to train young authors under the age of 35 to foster a reading and writing culture in India.
- National Book Trust (NBT), India, is responsible for implementing the scheme.
- The scheme aligns with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, focusing on creating a knowledge-driven ecosystem.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: PM-YUVA 3.0 is launched by the Ministry of Education, not the Ministry of Culture.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The scheme is designed for authors under the age of 30, not 35.
- Statement 3 is correct: National Book Trust (NBT), India is responsible for implementation.
- Statement 4 is correct: The scheme aligns with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, promoting a knowledge-driven ecosystem.
Quantum Property of the Nanocrystals Regulating Ultra-Processed Foods - The Need for Stronger Policies
Introduction
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi has emphasized the urgent need to combat obesity, and the 2025 Economic Survey has proposed a ‘health tax’ on ultra-processed foods (UPFs) to curb their consumption. With one in four Indian adults obese and one in four either diabetic or pre-diabetic (NFHS-5), addressing this health crisis requires bold policy interventions.
Challenges in Food Labelling and Advertising
- Regulatory Gaps
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has struggled to enforce strict food labelling and advertising regulations since 2017.
- Current rules are ambiguous and industry-friendly, failing to implement mandatory front-of-pack warning labels despite the rising health risks of UPFs.
- Flaws in the Indian Nutrition Rating (INR) System
- Introduced in September 2022, the INR system is modeled after Australia’s ineffective ‘health star’ system, which assigns 1 to 5 stars based on nutritional content.
Criticisms include:
- Creates a false health perception: Unhealthy foods appear healthier due to star ratings.
- Lack of scientific scrutiny: The FSSAI relied on an unexamined IIM Ahmedabad study to justify the rating system.
- Industry influence: Key decisions were shaped by food industry representatives, sidelining independent health experts.
Misclassification Examples:
- Soft drinks with high sugar may receive 2 stars instead of a warning label.
- Cornflakes (high in sugar and sodium) are rated 3 stars, misleading consumers about their health impact.
- The FSSAI ignored its own 2021 proposal for mandatory ‘traffic light’ warning labels, favoring an industry-driven approach
Ineffective Advertising Regulations
- India has four different laws regulating HFSS (High Fat, Salt, Sugar) food advertisements, but they lack enforcement:
- Consumer Protection Act, 2019: Defines misleading ads but does not mandate nutritional disclosure.
- National Multisectoral Action Plan (2017): Proposed stricter HFSS ad rules, but no action was taken.
Loopholes in advertising laws:
- No requirement to disclose sugar, salt, or fat content in advertisements.
- Brands continue targeting children with misleading health claims.
Global Best Practices and Lessons for India
- Chile’s ‘High In’ Warning Labels: A policy requiring clear warning labels on UPFs led to a 24% reduction in consumption.
- World Health Organization (WHO) Guidelines: Recommends bold front-of-pack warning labels to help consumers make informed choices.
The Way Forward: Urgent Policy Reforms
- Implement Front-of-Pack Warning Labels
- Abolish the misleading INR system.
- Mandate clear “High in Sugar/Salt/Fat” labels on UPFs.
- Define and Regulate UPFs and HFSS Foods
- Establish strict sugar, salt, and fat limits based on WHO and ICMR-NIN
- Strengthen Advertising Regulations
- Amend laws to ban misleading HFSS advertising.
- Harmonize regulations across multiple laws to prevent industry loopholes.
Launch Nationwide Awareness Campaigns
Educate consumers in multiple languages on the dangers of UPFs.
Conclusion
- The obesity crisis in India is a result of weak policy enforcement, not individual failure. Food industry lobbying has led to lenient labelling and advertising rules, allowing junk food companies to profit at the cost of public health. The Economic Survey has outlined a roadmap, but without decisive regulatory action, India’s health burden will continue to rise. Achieving PM Modi’s vision of a healthy India requires firm, science-backed policies rather than industry-driven compromises.
Consider the following statements regarding the proposed ‘health tax’ on Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs):
- The Economic Survey 2025 recommends imposing a ‘health tax’ on UPFs to reduce their consumption.
- UPFs have been scientifically linked to increased risks of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
- The tax proposal is aligned with the World Health Organization’s (WHO) recommendations on public health policy.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (d) 1, 2, and 3
Explanation:
- The Economic Survey 2025 has recommended a ‘health tax’ to curb UPF consumption (Statement 1 is correct).
- Scientific studies have linked UPFs to obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular risks (Statement 2 is correct).The WHO has consistently recommended fiscal policies like health taxes to reduce UPF consumption (Statement 3 is correct).
Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK)
Context:
The Ministry of Minority Affairs recently conducted a National Review Meeting to evaluate the progress of the Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK).
About PMJVK:
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme aimed at developing community infrastructure and basic amenities in 1,300 identified areas across India.
- Restructured in May 2018 to bridge socio-economic disparities in targeted regions.
- Implemented through State Governments and Union Territory (UT) Administrations.
- Funding Pattern: Operates on a cost-sharing basis between the Centre and States/UTs.
Key Focus Areas:
Education: Construction of schools, hostels, laboratories, and ITIs.
Health: Establishment of hospitals and healthcare centers.
Skill Development: Promotion of vocational training and employment opportunities.
Women’s Welfare: Building community toilets and welfare centers for women.
Implementation Mechanism:
- State Level Committees (SLCs) recommend project proposals.
- Empowered Committee (EC) within the Ministry of Minority Affairs grants final approval.
- This initiative plays a crucial role in reducing socio-economic inequalities and enhancing infrastructure in minority-dominated areas.
Consider the following statements regarding the Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK):
- It is a Central Sector Scheme implemented solely by the Central Government.
- The scheme aims to bridge socio-economic gaps in 1,300 identified areas across India.
- It provides financial assistance for projects related to education, health, and skill development.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect because PMJVK is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, meaning it is implemented through State Governments and UT Administrations with shared funding.
Statement 2 is correct as the scheme targets 1,300 identified areas to reduce socio-economic gaps.
Statement 3 is correct as it funds projects in education, health, skill development, and women’s welfare.
Poverty Estimation in India
Overview:
- A study by economists Surjit S Bhalla and Karan Bhasin highlights a significant decline in poverty and inequality in India over the past decade. The findings are based on government household expenditure data from 2022-23 and 2023-24.
Key Findings
- Poverty Reduction: The poverty rate at the $3.65 PPP threshold has dropped from 52% in 2011-12 to 15.1% in 2023-24, while extreme poverty (below $1.90 PPP) is now under 1%.
- Consumption Growth: The greatest improvements have been observed in the bottom three deciles of the population, reflecting record increases in consumption.
- Declining Inequality: The Gini coefficient, a measure of income inequality, has decreased from 37.5 in 2011-12 to 29.1 in 2023-24, indicating a more equitable distribution of resources.
- Global Comparison: Among large, fast-growing economies, India’s reduction in inequality stands out. Only Bhutan and the Dominican Republic have demonstrated better performance, albeit with smaller populations.
- Need for a New Poverty Line: Existing poverty lines are outdated. The study suggests adopting a benchmark based on the bottom 33rd percentile or relative poverty measures similar to those used in Europe.
- Official Poverty Estimates: NITI Aayog has not yet revised poverty estimates, which were last set by the Tendulkar and Rangarajan committees.
Poverty Line Estimation in India
- Tendulkar Committee (2009): Defined the poverty line based on monthly per capita expenditure—₹33 per day in urban areas and ₹27 per day in rural areas. The national poverty threshold for 2011-12 was ₹816 per capita per month for rural areas and ₹1,000 for urban areas.
- Rangarajan Committee (2014): Suggested higher thresholds—₹47 per day in urban areas and ₹30 per day in rural areas—but the government did not adopt this methodology, continuing to use the Tendulkar poverty line.
- International Benchmark: The World Bank defines extreme poverty as living on less than $2.15 per day, adjusted for inflation and price differences across countries.
Challenges in India’s Poverty Measurement
- Inadequate Thresholds: Current poverty lines—₹965 per month in urban areas and ₹781 in rural areas—are considered too low to reflect essential living standards.
- Outdated Methodology: The approach relies on calorie intake rather than modern consumption patterns and living costs.
- Limited Consideration of Essential Needs: The poverty line does not adequately account for increasing private expenditures on health, education, and housing.
- State-Level Disparities: A uniform poverty line across states does not consider variations in the cost of living, leading to inaccurate assessments.
- Lack of Periodic Updates: The official poverty line has not been revised to align with inflation and changing economic conditions, reducing its relevance.
Recommendations for Improvement
- Regular Revisions: Update the poverty line periodically to reflect inflation and evolving consumption patterns.
- Broader Criteria: Expand the definition of poverty to include essential non-food expenditures such as healthcare, education, and housing.
- Regional Adjustments: Implement state-specific poverty lines to better account for regional cost-of-living variations.
- Modernized Approach: Shift from outdated calorie-based metrics to holistic indicators that consider nutrition, well-being, and overall living standards.
A revised and comprehensive approach to poverty measurement will ensure that social welfare policies are more effective and inclusive, addressing the actual needs of India’s population.
Consider the following statements regarding the recent study on poverty and inequality in India:
- The study indicates that India’s extreme poverty (below $1.90 PPP) is currently estimated to be around 5%.
- The Gini coefficient has increased from 29.1 in 2011-12 to 37.5 in 2023-24, reflecting rising inequality.
- The study suggests a new poverty benchmark based on the bottom 33rd percentile of the population.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1 and 2 only
Answer: (c) 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The study finds that extreme poverty (below $1.90 PPP) is now under 1%, not 5%.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The Gini coefficient has actually decreased from 37.5 in 2011-12 to 29.1 in 2023-24, indicating a reduction in inequality.
Statement 3 is correct: The study suggests a new poverty line based on the bottom 33rd percentile, recognizing the outdated nature of existing poverty lines.
National Waterways (Construction of Jetties / Terminals) Regulations, 2025
The Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways (MoPSW) has introduced a new set of regulations, formulated by the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI), aimed at streamlining the development and operation of India’s inland waterways network.
Key Highlights of the National Waterways (Construction of Jetties/Terminals) Regulations, 2025
- These regulations are designed to enhance private sector participation in the development of inland waterway terminals.
- Any entity, including private players, seeking to develop or operate an inland waterway terminal must obtain a No Objection Certificate (NoC) from IWAI.
- The regulations apply to both new and existing terminals, covering both permanent and temporary
- Permanent terminals can be operated for their entire lifetime by the developer.
- Temporary terminals will be granted an initial five-year operational term, with an option for extensions.
- Developers and operators bear full responsibility for technical design, construction, and ensuring adequate access to the terminal, aligning with their business objectives.
Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI): A Brief Overview
- Established: 1986 under the Inland Waterways Authority of India Act, 1985.
- Primary Role: Development, maintenance, and regulation of National Waterways under the National Waterways Act, 2016.
- Headquarters: Noida, Uttar Pradesh.
Significance of Inland Waterways
- Reducing Logistics Costs
- India’s logistics costs account for 14% of GDP, significantly higher than the global average of 8-10%.
- Enhancing waterway infrastructure will help bring these costs down, making trade more competitive.
- Decongestion of Transport Networks
- Shifting cargo movement to inland waterways will ease congestion on road and rail networks, reducing traffic bottlenecks.
- Eco-Friendly Mode of Transport
- Lower fuel consumption and reduced emissions make inland waterways a more sustainable transport solution.
- This aligns with India’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and climate action commitments.
- Economic Growth & Trade Expansion
- The volume of cargo transported via National Waterways has increased from 18 million tonnes to 133 million tonnes in FY 2023-24.
- Improved inland waterway infrastructure will boost trade, especially in regions near National Waterways.
Government Initiatives for Inland Waterways Development
- Jalvahak Scheme
- Provides direct incentives to cargo owners using inland waterways for distances exceeding 300 km.
- Offers reimbursement of up to 35% of total operating costs incurred during cargo transportation.
- Jal Marg Vikas Project (JMVP)
- Aims to develop National Waterway-1 (NW-1) with modern infrastructure and terminals.
- Sagarmala Project
- Focuses on the integration of inland waterways with coastal shipping and major ports.
- Freight Village Development
- Establishes logistics hubs near key waterways to enhance multimodal transport connectivity.
Conclusion
The National Waterways (Construction of Jetties/Terminals) Regulations, 2025 represent a significant policy shift aimed at boosting private sector participation, reducing logistics costs, and promoting eco-friendly cargo transport. With the rapid digitization of waterway operations and strong government policy support, these reforms will play a crucial role in making India’s inland waterways a viable and competitive transport network.
Consider the following statements regarding the National Waterways (Construction of Jetties/Terminals) Regulations, 2025:
- Private players are required to obtain a license from the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways (MoPSW) to develop inland waterway terminals.
- Permanent terminals are granted operational rights for a maximum of 20 years.
- Temporary terminals are granted an initial operational period of five years, with a possibility of extension.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 2 and 3 only
(C) 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (C) 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Private players need to obtain a No Objection Certificate (NoC) from IWAI, not a license from MoPSW.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: Permanent terminals can be operated for their entire lifetime without a fixed limit like 20 years.
- Statement 3 is correct: Temporary terminals are granted an initial five-year term with an option for extension.
Impact of GeM on India’s Economy
- The Government e-Marketplace (GeM) has transformed public procurement in India, benefiting both government buyers and small businesses.
What is GeM?
- The Government e-Marketplace (GeM) is an online platform established for public procurement in India.
- Launched in 2016 by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, its goal is to improve transparency, efficiency, and speed in government procurement processes.
- Objective
GeM’s primary objective is to create an open and transparent procurement platform for government buyers.
Core Principles of GeM
- The platform is based on several key principles, ensuring streamlined, fair, and effective procurement.
Key Features of GeM
SWAYATT: This initiative aims to enhance ease of doing business by providing direct market linkages for startups, women entrepreneurs, Micro & Small Enterprises (MSEs), Self Help Groups (SHGs), and youth to participate in public procurement.
Startup Runway 2.0: This feature offers startups a chance to showcase their innovative products and services to government buyers, facilitating their engagement in public procurement.
Dedicated Marketplace for Startups: GeM has created a specific marketplace category for startups, allowing them to list products and services, regardless of their DPIIT (Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade) certification.
Womaniya: This initiative highlights products made by women entrepreneurs and women self-help groups (WSHGs), empowering women-led businesses in the procurement process.
Collaboration with MSMEs: GeM works closely with stakeholders from the MSME sector, with a particular focus on promoting entrepreneurs from Scheduled Caste (SC) and Scheduled Tribe (ST) communities.
SARAS Collection: The SARAS Collection showcases a curated range of handcrafted goods, including handicrafts, handloom textiles, office décor, and personal care products, all sourced from SHGs across India.
Impact of GeM
- Cost Savings: By promoting competitive pricing, GeM has contributed to significant reductions in procurement costs for the government.
- Wider Market Access: The platform has opened up opportunities for vendors from all corners of the country, including rural areas, to participate in government procurement.
- Boost to MSMEs & Startups: Around 50% of GeM orders come from MSMEs, supporting the growth of small businesses and fostering a more inclusive economy.
- Conclusion
GeM’s strategic initiatives have greatly contributed to improving the ease of doing business and boosting participation in government procurement. As it continues to evolve, GeM remains dedicated to its vision of creating a sustainable, transparent, and competitive marketplace, advancing India’s progress toward inclusive and effective public procurement practices.
The Womaniya initiative on Government e-Marketplace (GeM) is primarily aimed at:
- A) Enabling direct procurement of goods and services exclusively from women entrepreneurs without competitive bidding.
- B) Establishing a dedicated procurement quota for women-led enterprises across all government departments.
- C) Facilitating the showcasing and procurement of products crafted by women entrepreneurs and Self-Help Groups (SHGs) to enhance their market access.
D) Offering subsidized loans and financial incentives to women entrepreneurs participating in public procurement.
Answer: C
Explanation:
- The Womaniya initiative under the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) is designed to promote the participation of women entrepreneurs and women-led SHGs by facilitating the listing and procurement of their products and services on the platform.
- This initiative aims to bridge the gender gap in public procurement but does not involve exclusive tenders, mandatory procurement quotas, or financial grants.
- The focus is on market linkage and visibility rather than providing direct financial support or bypassing competitive processes.
- This question tests the aspirant’s ability to grasp the nuanced objectives of government initiatives and distinguish between affirmative action policies and preferential financial assistance—a common area of confusion in public policy.
India’s Path to a High-Income Economy
- A recent World Bank report titled “Becoming a High-Income Economy in a Generation” highlights that India needs an average annual growth rate of 7.8% over the next 22 years to achieve high-income country (HIC) status by 2047.
- The report emphasizes the need for ambitious reforms and their effective implementation to meet this goal.
Key Highlights of the Report
- India’s Economic Growth Journey
- India’s share in the global economy has doubled from 6% in 2000 to 3.4% in 2023, making it the 5th largest economy.
- Before the pandemic, India’s economy grew at an average annual rate of 6.7%, second only to China among major economies.
- Target: High-Income Status by 2047
- Current Status: India is classified as a lower-middle-income country, with a GNI per capita of USD 2,540 (2023).
- Goal: To reach HIC status, India’s GNI per capita must increase 8 times by 2047.
- In 2023, the World Bank classified high-income countries as those with a GNI per capita above USD 14,005, while upper-middle-income nations fall between USD 4,516 – 14,005.
Growth Scenarios for India
Scenario | Growth Rate (Real GDP) | Outcome |
Slow Reforms | Below 6% | India remains upper-middle income, falling short of HIC status. |
Business as Usual | 6.6% | India improves but does not reach high-income status. |
Accelerated Reforms | 7.8% | India achieves high-income status by 2047. |
- Only a few countries—Chile, Romania, Poland, Czech Republic, and Slovakia—have transitioned to high-income status within 20 years. In contrast, Brazil, Mexico, and Turkey remain stuck in the upper-middle-income category, making India’s goal ambitious yet achievable.
- Challenges to Achieving High-Income Status
Declining Investment Rate
- Investment-to-GDP ratio peaked at 8% in 2008 but has fallen to 27.5% in 2024.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Challenges
- India’s FDI-to-GDP ratio is 6%, much lower than Vietnam (5%) and China (3.1%).
- Low Labor Force Participation
- India’s Labor Force Participation Rate (LFPR) is 55% (2023), lower than China (65.8%).
- Female Labor Force Participation (FLFP) has risen to 7% in 2023-24, but remains below the global benchmark of over 50%.
Challenges in Job Creation
- 45% of India’s workforce is still in agriculture, a sector with low productivity (disguised unemployment).
- The share of manufacturing in total employment is just 11%, and modern market services account for only 7%—far lower than East Asian economies.
- 73% of India’s workforce is in informal jobs (compared to 7% in other emerging economies).
Declining Trade Openness
- Exports and imports account for 46% of GDP (2023), down from 56% in 2012.
- High tariffs and non-tariff barriers restrict trade expansion.
- Weak Integration into Global Value Chains (GVCs)
- While India has made gains in mobile phone exports, its overall manufacturing sector lags behind other economies.
- Services sector (IT & BPO) remains strong, but manufacturing needs significant improvements.
- Key Reforms Needed to Achieve HIC Status
Boosting Investment
- Increase investment rate from 33.5% to 40% of GDP by 2035.
- Strengthen financial sector regulations to improve credit flow.
- Enhance MSME access to formal credit.
- Improve bankruptcy resolution and bad debt recovery mechanisms.
Creating More and Better Jobs
- Raise labor force participation to match economies like Vietnam (73%) and the Philippines (60%).
- Encourage private sector investment in job-rich sectors like agro-processing, hospitality, transportation, and care economy.
- Expand skilled workforce and improve access to finance.
- Strengthen modern manufacturing and high-value services.
- Boosting Global Trade Competitiveness
- Invest in export-oriented sectors and integrate into GVCs.
- Formalizing the Workforce
- Simplify labor laws to reduce informal employment and promote better wage conditions.
- Strengthening Human Capital and Innovation
- Improve secondary school enrollment and vocational training to meet industry demands.
- Expand R&D investments in Artificial Intelligence (AI), Biotechnology, and Clean Energy.
- Understanding the Middle-Income Trap
- What is the Middle-Income Trap?
- A concept introduced by the World Bank (2007), referring to economies that grow rapidly but fail to reach high-income status.
- It applies to countries with a GNI per capita between USD 1,000 – USD 12,000 (2011 prices).
- Countries in this trap face challenges such as rising labor costs, weak innovation, income inequality, and overreliance on specific industries.
- Is India at Risk of Falling into the Middle-Income Trap?
- Income Inequality: The top 10% of India’s population holds 57% of national income, while the bottom 50% holds just 13%.
- Tax Structure: High GST and corporate tax cuts disproportionately benefit the wealthy, widening the income gap.
- Stagnant Wages & Inflation: Declining or stagnant wages, high household debt, and low savings make India vulnerable to this trap.
- Conclusion
- India’s goal of becoming a high-income country by 2047 is ambitious but achievable. To meet this target, the country must accelerate reforms in investment, job creation, trade competitiveness, and innovation while addressing income inequality and labor market challenges. Without significant reforms, India risks remaining in the upper-middle-income category, like Brazil, Mexico, and Turkey.
Which of the following statements regarding India’s growth trajectory, as per the World Bank report “Becoming a High-Income Economy in a Generation,” is/are correct?
- India’s Gross National Income (GNI) per capita must increase by nearly six times by 2047 to achieve high-income country (HIC) status.
- Among major economies, India had the fastest economic growth in the two decades before the pandemic.
- The “Accelerated Reforms” scenario predicts that India must sustain a GDP growth rate of at least 8% to reach HIC status by 2047.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
- a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 only
d) None of the above
Answer: c) 1 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: India’s GNI per capita must increase nearly 8 times (not six) from USD 2,540 (2023) to cross the USD 14,005 threshold for high-income status.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: India had the second-fastest economic growth before the pandemic, not the fastest. China had the highest growth rate.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The report states that 8% GDP growth is required, not at least 8%.
Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA)
- The Supreme Court has criticized the functioning of the Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA), remarking that it has become a “rehabilitation centre for former bureaucrats.”
- The statement reflects concerns over inefficiency, bureaucratic inertia, and lack of enforcement in ensuring transparency and protection for homebuyers.
About the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016 (RERA)
- Legislative Domain: While land and colonization fall under the State List (Entry 18 of List II, Schedule VII), real estate regulation was brought under the purview of the Union Parliament to ensure consumer protection and industry transparency.
Objective: RERA is a landmark reform in India’s real estate sector, aimed at eliminating project delays, financial mismanagement, and consumer exploitation.
Regulatory Mechanism: The Act established State Real Estate Regulatory Authorities (S-RERA) for overseeing registration, compliance, and dispute resolution.
Key Provisions of RERA
- Establishment of Regulatory Bodies
State Real Estate Regulatory Authority (S-RERA):
- Mandated to register all real estate projects and maintain a public database for consumer transparency.
- Ensures developers, homebuyers, and agents adhere to statutory norms.
- Promotes sustainable and affordable housing by enforcing compliance.
Real Estate Appellate Tribunal:
- Functions as an adjudicating authority for appeals against RERA decisions.
- Ensures expeditious dispute resolution in the real estate sector.
- Financial Safeguards for Homebuyers
Escrow Account Provision:
- Developers are required to deposit 70% of buyers’ payments in an escrow account, ensuring funds are used exclusively for project construction.
Advance Payment Restriction:
- Builders cannot collect more than 10% of the total property cost as an advance payment without a legally binding written agreement.
- Protection Mechanisms for Homebuyers
Carpet Area-Based Pricing:
- Property prices are determined only on the basis of the net usable floor area (carpet area), eliminating misleading pricing based on the super built-up area.
Mandatory Timely Completion of Projects:
- Developers must adhere to project timelines, with penalties imposed for any unjustified delays.
Structural Defect Liability:
- Builders are legally accountable for five years to fix any structural defects in the property post-handover.
- Penal Provisions & Legal Compliance
Equal Penal Interest:
- Both developers and homebuyers are subject to equal penal interest for delays in payment or possession.
Stringent Penal Action:
- Developers face up to 3 years imprisonment for violations.
- Real estate agents and homebuyers may face up to 1 year imprisonment for non-compliance with tribunal rulings.
The regulation of land and colonization falls under the State List in the Indian Constitution. However, Parliament enacted the RERA Act, 2016. Under which of the following Constitutional provisions was the Act justified?
- Article 246 (Seventh Schedule): It allows Parliament to legislate on matters related to interstate trade and commerce that may affect real estate transactions.
- Article 254: Parliament can enact laws on a State subject if it believes uniformity is necessary for national economic growth and consumer protection.
- Entry 6 of the Union List: It provides Parliament with the authority to regulate “Industries declared by law to be under Union control.”
- Doctrine of Repugnancy: If a Central law conflicts with a State law, the Central law prevails under certain conditions.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
- a) 1 and 2 only
b) 1, 2, and 4 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: b) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Article 246 and the Seventh Schedule allow Parliament to regulate commercial activities with inter-state implications, justifying RERA’s applicability.
- Statement 2 is correct: Article 254(2) permits Parliament to legislate on a State subject for national uniformity in consumer protection.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: Real estate is not an industry under Entry 6 of the Union List.
- Statement 4 is correct: Doctrine of Repugnancy ensures that if a State law conflicts with a Central law, the Central law prevails.
Production Linked Incentive Scheme
- The government has decided not to extend the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme beyond the existing 14 sectors due to underperformance in some areas and delays in incentive payouts.
Key Developments
- Out of the $23 billion allocated, only $1.73 billion (8%) has been disbursed as of October 2024.
- The scheme has generated $151.93 billion worth of goods—just 37% of the original target.
- Major firms, including Foxconn, Reliance, and Adani, faced delays, unmet targets, or non-compliance.
- The government has rejected requests to extend deadlines or include new sectors.
- About the PLI Scheme
- Launch: Introduced in 2020 under the Ministry of Commerce & Industry with an outlay of ₹1.97 lakh crore.
- Sectors Covered: 14 sectors, including Mobile Manufacturing, Pharmaceuticals, Automotive, ACC Battery, Telecom, White Goods, and Solar.
Objectives:
- Provide incentives on incremental sales for five years under the Make in India
- Reduce dependence on foreign imports, particularly from China.
- Boost employment, particularly in labor-intensive sectors.
- Increase manufacturing’s share of GDP to 25% by 2025.
Incentive Mechanism:
- 4–6% incentives on incremental sales over a base year.
- Available to both domestic and foreign companies registered in India.
Benefits of the PLI Scheme
- Electronics Manufacturing: India produced $49 billion worth of mobile phones in FY 2023–24; Apple now manufactures high-end models in India.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Exports nearly doubled to $27.85 billion compared to a decade ago.
- FDI Inflows: Attracted foreign investments and supported India’s ‘China Plus One’ strategy.
- Strategic Growth: Encouraged production in key sectors like semiconductors and solar modules.
Challenges and Concerns
- Low Incentive Disbursement: Only 8% of allocated funds disbursed despite achieving production targets.
- Delayed Subsidy Payments: Slow disbursement affects cash flow for participating firms.
- Unmet Production Targets: Many companies failed to start or expand operations.
- Bureaucratic Hurdles: Rigid compliance norms and administrative delays hinder implementation.
- Manufacturing Growth Decline: Manufacturing’s share in GDP dropped from 15.4% (2020) to 14.3% (2024).
Consider the following statements regarding the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme:
- The scheme provides incentives based on absolute production rather than incremental sales.
- It was launched in 2020 to promote domestic manufacturing and reduce import dependency.
- The PLI scheme covers more than 20 sectors, including semiconductors and medical devices.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The scheme provides incentives on incremental sales, not absolute production. Companies must show an increase over the base year’s output to qualify for benefits.
Statement 2 is correct: The scheme was launched in 2020 under the Ministry of Commerce & Industry to boost domestic manufacturing and reduce reliance on imports, particularly from China.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The scheme covers 14 sectors, not more than 20. These include electronics, pharmaceuticals, automobiles, telecom, and solar modules, but not semiconductors (which fall under a separate incentive program).
What is Hawala?
- The use of hawala networks has witnessed a significant rise in recent years, particularly in facilitating illicit activities such as poaching, money laundering, and terrorism financing.
- Investigations have uncovered that illegal wildlife trafficking rings, especially those involved in tiger poaching in central India, are increasingly exploiting these informal financial systems to conduct their operations.
Understanding Hawala
- Hawala is an unregulated, informal system of money transfer that enables transactions without the movement of physical cash.
- It relies on a trust-based network of brokers known as hawaladars, who facilitate financial transfers through verbal or token-based agreements.
- Despite lacking regulatory oversight, hawala remains widely used due to its speed, simplicity, and anonymity.
Mechanism of Hawala Transactions
- A typical hawala transaction follows a structured but informal process:
- Deposit & Token Generation: The sender deposits money with a hawaladar in one location.
- Code Sharing: The sender receives a token, code, or reference, which is communicated to the recipient.
- Collection of Funds: The recipient presents the token to a hawaladar in their location and collects the funds.
- This system avoids conventional banking channels, making it attractive for users who seek discreet financial transactions.
Who Uses Hawala?
Hawala is utilized by both legitimate and illicit actors:
- Migrant Workers: Often use hawala to send remittances due to its lower costs and efficiency compared to formal banking systems.
- Undocumented Individuals: Those without access to official banking prefer hawala for financial transactions.
- Organized Crime & Terrorist Networks: Drug traffickers, smugglers, and terrorist groups leverage hawala’s anonymity to move illicit funds.
- Integration of Cryptocurrency into Hawala: With the evolution of financial technology, cryptocurrencies like USDT (Tether) have become an integral part of modern hawala networks.
Why USDT?
- Stablecoin Advantage: Unlike volatile cryptocurrencies, USDT is pegged to the US dollar, making it a stable medium for illicit financial transfers.
- Bypassing Banking Systems: Transactions occur without relying on traditional financial institutions, enabling cross-border money laundering.
- Anonymity & Evasion of Scrutiny: Cryptocurrency transactions in crypto-friendly regions allow seamless transfers without regulatory oversight.
- Legal and Regulatory Implications
- Although hawala is not inherently illegal, it is increasingly associated with criminal activities, leading to global scrutiny and crackdowns:
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Laws: Many countries have banned hawala transactions due to their role in money laundering and terrorism financing.
- Regulatory Adaptation: Authorities are enhancing surveillance of cryptocurrency-based hawala transactions to curb illicit financial flows.
- Continued Evolution: Despite legal restrictions, hawala networks persist, adapting to new technologies such as blockchain and decentralized finance (DeFi).
Conclusion
- Hawala remains a double-edged financial system—serving both legitimate users and criminal enterprises.
- The rise of cryptocurrency-based hawala transactions presents new challenges for law enforcement agencies.
- Strengthening regulatory frameworks, increasing financial transparency, and leveraging technological solutions are crucial to mitigating the risks associated with hawala networks.
With reference to the “Hawala” system, consider the following statements:
- Hawala transactions require the physical movement of cash between different locations.
- It operates outside the formal banking system and is largely unregulated.
- The term “hawala” is derived from an Arabic word meaning “trust” or “transfer.”
- It is only used for illicit financial transactions and has no legitimate applications.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2, and 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: In a hawala transaction, physical cash is not transferred—instead, funds are settled through informal networks of brokers.
- Statement 2 is correct: Hawala operates outside the formal banking system, making it difficult for authorities to track.
- Statement 3 is correct: The term “hawala” originates from Arabic, meaning “trust” or “transfer.”
- Statement 4 is incorrect: While hawala is often misused for illegal activities, it is also widely used for legitimate purposes, such as migrant remittances.
What is Dx-EDGE Initiative?
Overview
- India has launched the ‘Digital Excellence for Growth and Enterprise’ (Dx-EDGE) initiative to empower micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) with digital tools and skills. This initiative is a collaborative effort between the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), NITI Aayog, and the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE). It aims to enhance the competitiveness and resilience of MSMEs through
Objectives of Dx-EDGE
- The initiative is designed to future-proof MSMEs by providing access to advanced technologies, digital skills, and innovation. It aligns with India’s vision of Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by ensuring widespread digital adoption across the sector.
Key Challenges Faced by MSMEs
- Despite their critical role in India’s economy, MSMEs face several challenges, including:
- Limited technology adoption affecting efficiency and productivity.
- Lack of a skilled workforce to leverage digital tools.
- Difficulties in obtaining quality certifications, impacting market access.
- Addressing these challenges is essential for improving operational efficiency and global competitiveness.
Public-Private-Academia Partnership (PPAP)
- Dx-EDGE adopts a Public-Private-Academia Partnership (PPAP) model, integrating expertise from private enterprises, government agencies, and academic institutions. This multi-stakeholder approach is crucial for driving MSMEs’ digital transformation.
Establishment of Digital Excellence Centres
- A key component of Dx-EDGE is the creation of Digital Excellence Centres, which will:
- Assist MSMEs in formulating digital transformation strategies.
- Provide training and resources to ensure effective technology adoption.
- Serve as innovation hubs to bridge knowledge gaps in digitalisation.
Role of Education and Skill Development
- The initiative emphasises workforce upskilling to align with global manufacturing standards. This focus on education and skill development ensures that MSMEs can effectively integrate Industry 4.0 technologies.
Future Impact
- Dx-EDGE is expected to:
- Enhance MSME competitiveness in domestic and global markets.
- Drive economic growth by boosting productivity and efficiency.
- Strengthen India’s digital ecosystem, accelerating the transition to a digitally advanced economy.
- By fostering digital excellence, this initiative positions India’s MSMEs as key drivers of economic resilience and technological innovation.
Consider the following statements regarding the ‘Digital Excellence for Growth and Enterprise’ (Dx-EDGE) initiative:
- It is a joint initiative of the Ministry of MSME, NITI Aayog, and the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII).
- The initiative focuses solely on providing financial assistance to MSMEs for digital adoption.
- Digital Excellence Centres established under Dx-EDGE will play a role in formulating digital transformation strategies for MSMEs.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
Answer: (c) 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect because the Dx-EDGE initiative is a collaboration between NITI Aayog, CII, and AICTE, not the Ministry of MSME.
- Statement 2 is incorrect as Dx-EDGE focuses on digital capacity building, innovation, and skill development, rather than just financial assistance.
- Statement 3 is correct as Digital Excellence Centres will guide MSMEs in identifying tailored digital transformation paths.
India becomes World’s 2nd-largest Exporter of Tea in 2024

Overview
- According to the Indian Tea Board, India has emerged as the second-largest tea exporter globally, surpassing Sri Lanka and trailing only Kenya.
India’s Tea Exports (2024)
- Total Exports: 255 million kg
- Growth: Export value surged by 15%, from ₹6,161 crore in 2023 to ₹7,111 crore in 2024
- Tea Varieties Exported:
- Black Tea – Dominates exports (96%)
- Other varieties include regular, green, herbal, masala, and lemon tea
Key Factors Driving Growth
- Increased demand from West Asia, with Iraq now constituting 20% of India’s tea exports
- Projected Imports by Iraq: Expected to reach 40-50 million kg in FY 2024-25
- Expansion into over 25 markets, including UAE, Iraq, Iran, Russia, US, and UK
- Branding efforts and improved tea workers’ welfare have strengthened India’s global position
- Major Tea-Producing Regions
- Assam: Assam Valley, Cachar
- West Bengal: Dooars, Terai, Darjeeling
- Other notable varieties: Assam, Darjeeling, and Nilgiri teas, recognized for their superior quality
Tea Board of India
- Established: 1954 under the Tea Act, 1953
- Purpose: Regulates the Indian tea industry and safeguards the interests of producers
Governing Body:
- Comprises 32 members, including the Chairman and Deputy Chairman, appointed by the Government of India
- Headquarters: Kolkata
- Authority: Administers all tea-producing regions across India
- India’s tea industry continues to flourish, bolstered by strategic market expansion, quality branding, and increased global demand
With reference to India’s tea exports, consider the following statements:
- India has overtaken both Sri Lanka and Kenya to become the largest tea exporter in the world.
- Iraq has emerged as a key importer of Indian tea, accounting for nearly 20% of India’s total tea exports.
- The majority of India’s tea exports comprise green tea due to rising global health consciousness.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: India is the second-largest tea exporter, having surpassed Sri Lanka but not Kenya, which remains the largest.
- Statement 2 is correct: Iraq has become a major importer, accounting for 20% of India’s tea exports in 2024.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: Black tea constitutes 96% of India’s exports, not green tea.
Implementation of Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY)
- Launched: Kharif 2016 season
- Voluntary: For States/UTs and farmers
- Objective: Affordable, comprehensive, and technology-driven crop insurance
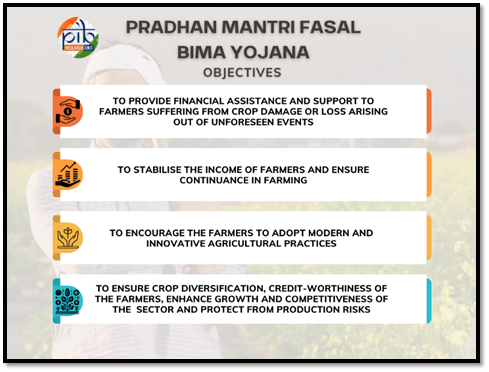
Key Features
Affordable Premiums:
- 2% for Kharif food & oilseed crops
- 5% for Rabi food & oilseed crops
- 5% for annual commercial & horticultural crops
- Government subsidizes remaining premium
Comprehensive Coverage:
- Covers natural disasters (droughts, floods), pest attacks, disease outbreaks
- Covers post-harvest losses due to hailstorms, landslides
Timely Compensation:
- Claims processed within two months of harvest
Technology-Driven Implementation:
- Uses satellite imaging, drones, mobile apps for precise crop loss estimation
Post-Harvest Loss Coverage:
- Covers losses for up to 14 days for crops stored in cut & spread condition
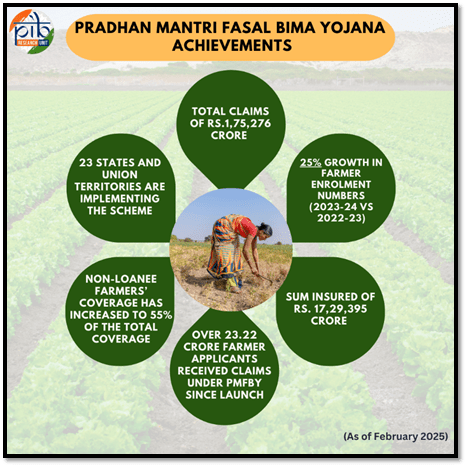
Did You Know?
- Restructured Weather-Based Crop Insurance Scheme (RWBCIS) was introduced alongside PMFBY
Key Difference:
- PMFBY: Compensates based on actual crop losses
- RWBCIS: Provides payouts based on predefined weather parameters (rainfall, temperature, humidity)
Consider the following statements regarding the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY):
- The scheme was launched in the Kharif 2016 season and is mandatory for all States and farmers.
- The government provides a subsidy on the premium amount to ensure affordability for farmers.
- PMFBY covers post-harvest losses for up to 30 days for crops stored in a “cut and spread” condition.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: PMFBY was launched in Kharif 2016, but it is voluntary for both States/UTs and farmers since the 2020 revamp.
- Statement 2 is correct: The government subsidizes the remaining premium after the farmers pay their share.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: PMFBY provides post-harvest loss coverage for up to 14 days, not 30 days.
Bose Metal
Recent Discovery: A team of researchers from China and Japan has identified strong indications that niobium diselenide (NbSe₂) can exhibit properties characteristic of a Bose metal.
Understanding Bose Metals:
- Bose metals are materials that, below a critical temperature, form Cooper pairs electron pairs bound by attractive forces without transitioning into a superconducting state.
- Unlike conventional metals, which either become insulators or superconductors at absolute zero, Bose metals maintain conductivity between these two extremes.
Key Characteristics
- Formation of Cooper Pairs: Electrons in Bose metals pair up but do not form a superconducting long-range coherence.
- Intermediate Conductivity: Their electrical resistance lies between that of superconductors (zero resistance) and insulators (infinite resistance).
- Challenge to Traditional Theories: Existing models suggest disordered metals should either lose conductivity (becoming insulators) or exhibit superconductivity, but Bose metals defy this expectation.
Potential Applications
- Quantum Computing: Bose metals could aid in exploring novel quantum states and contribute to the development of qubits.
- Condensed Matter Physics: Offers insights into quantum phase transitions and disordered metallic states.
- Advanced Electronics: May lead to innovations in electronic devices with unique conductive properties.
- Superconductivity Research: Helps in understanding the transition mechanisms
Challenges and Limitations
- Lack of Practical Applications: Currently remains a theoretical concept with no direct industrial implementation.
- Experimental Difficulties: Requires precise control over temperature, material thickness, and external magnetic fields for observation.
- Unclear Classification: Ongoing debate on whether Bose metals represent a distinct quantum state or merely a transitional phase between superconductors and insulators.
- This discovery contributes to the broader understanding of quantum materials and their unconventional conductive behaviours, potentially paving the way for future ad advancements in material science and electronics.
Consider the following statements regarding Bose metals:
- They exhibit zero electrical resistance below a critical temperature.
- They form Cooper pairs but do not achieve long-range superconducting coherence.
- Bose metals challenge the traditional classification of disordered metals into either superconductors or insulators.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect. Unlike superconductors, Bose metals do not exhibit zero electrical resistance. Instead, they maintain conductivity but do not transition into a fully superconducting state.
- Statement 2 is correct. They form Cooper pairs, but these pairs do not achieve coherence over long distances, preventing superconductivity.
- Statement 3 is correct. Bose metals defy traditional theories that suggest a disordered metal should either become an insulator or a superconductor at absolute zero.
Giloy
- Research on Giloy (Tinospora cordifolia) has surged by 376.5% in the last decade, with a notable rise in interest post-COVID-19 due to its immune-boosting, antiviral, and adaptogenic properties.
- Giloy: The Ayurvedic Wonder Herb
- Botanical Name: Tinospora cordifolia.
- Common Name:
Traditional Significance:
- In Sanskrit, called “Amrita”, meaning “herb of immortality”.
- Used extensively in Ayurveda, Siddha, and Unani medicine.
Habitat & Cultivation:
- A native tropical plant of India.
- Thrives in plains, foothills, and semi-arid regions.
- Major cultivating states: Bihar, West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh.
Bioactive Compounds:
- Contains alkaloids, steroids, glycosides, and flavonoids.
- Medicinal properties exist in its stem, root, and whole plant.
Medicinal Benefits & Therapeutic Uses
- Immunomodulatory Effects: Enhances white blood cell (WBC) production, boosting immune response.
- Antiviral Properties: Studied for its potential in combating COVID-19 and viral infections.
- Anti-diabetic Action: Helps regulate blood glucose levels, beneficial for Type-2 diabetes.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Useful in treating arthritis, joint pain, and chronic inflammatory diseases.
- HepatoprotectiveBenefits: Supports liver health by reducing oxidative stress.
- Antioxidant & Stress-Relieving Properties: Functions as an adaptogen, reducing mental and physical stress.
- Gastroprotective Effects: Aids in treating gastritis, acidity, and digestive disorders.
Consider the following pairs related to the bioactive compounds in Giloy and their effects:
Compound | Effect |
Alkaloids | Anti-inflammatory properties |
Glycosides | Regulate blood sugar levels |
Steroids | Enhance immune function |
Flavonoids | Increase cholesterol levels |
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1, 2, and 3 only
(b) 1 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1, 2, and 3 only
Explanation:
- Alkaloids (Correctly matched) → Exhibit anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
- Glycosides (Correctly matched) → Contribute to blood sugar regulation, beneficial for diabetes management.
- Steroids (Correctly matched) → Play a role in immune enhancement and anti-cancer properties.
- Flavonoids (Incorrectly matched) → Instead of increasing cholesterol, they act as antioxidants, reducing oxidative stress.
Tiangong Space Station
- China and Pakistan have signed a cooperation agreement to train Pakistani astronauts for missions aboard the Tiangong Space Station.
- This marks a significant milestone in Pakistan’s space ambitions as it strengthens bilateral space cooperation with China.
- Pakistan’s Space Collaboration with China
- Pakistan has historically maintained close strategic ties with China and has sought to enhance its space capabilities by aligning with Chinese space initiatives.
- This agreement is expected to increase Pakistan’s participation in space exploration and human spaceflight.
- Tiangong Space Station – China’s Orbital Outpost
Key Features:
- Completion Year: 2022
- Orbital Altitude: Up to 450 km (280 miles) above Earth.
- Capacity: Can house a maximum of three astronauts for extended durations.
- Designed Operational Lifespan: At least 15 years.
- Significance of Tiangong:
- China’s first long-term space station, intended to rival the International Space Station (ISS).
- Advances scientific research in microgravity, material sciences, and life sciences.
- Enhances China’s self-reliance in space exploration after exclusion from the ISS program (led by the US and its allies).
- What is a Space Station?
- Definition & Functionality:
- A space station is a large, habitable spacecraft that orbits Earth and serves as a research laboratory in microgravity conditions.
- It allows for long-duration human space missions without returning to Earth.
- Space stations are typically modular, meaning they can be expanded or upgraded over time.
Notable Space Stations:
- International Space Station (ISS):
- A joint project involving NASA, Roscosmos, ESA, JAXA, and CSA.
- Conducts biological, physical, and technological research in microgravity.
- Tiangong Space Station:
- China’s independent space station, expanding China’s role in global space research.
Consider the following statements regarding the Tiangong Space Station:
- Tiangong was completed in 2020 and has an operational lifespan of 10 years.
- It is designed to accommodate a maximum of six astronauts at a time.
- Unlike the ISS, which is multinational, Tiangong is operated solely by China.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect. Tiangong was completed in 2022, not 2020, and has a lifespan of at least 15 years.
- Statement 2 is incorrect. It can house only three astronauts, not six.
- Statement 3 is correct. Unlike the multinational ISS, Tiangong is entirely operated by China.
Amazon Unveils ‘Ocelot’ Quantum Computing Prototype Chip
Context:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) has introduced ‘Ocelot’, its first prototype quantum computing chip, with claims of reducing quantum error correction costs by up to 90%. This development marks a significant step toward addressing the long-standing challenge of quantum error instability.
Ocelot Chip: Key Features
- The Ocelot chip incorporates a two-layer integrated silicon architecture, optimizing coherence and computational efficiency. The major components include:
- Five Data Qubits (Cat Qubits): These qubits store quantum states essential for computation and are designed to mitigate error propagation.
- Five Buffer Circuits: Integrated stabilization mechanisms that enhance qubit coherence and prevent quantum state degradation.
- Four Additional Qubits: Dedicated to error detection and correction, ensuring computational fidelity.
Tantalum-based Oscillators:
- Utilization of superconducting Tantalum improves performance, reducing quantum decoherence.
Quantum Error Correction: Addressing Qubit Instability
- Unlike classical computing, which operates on binary bits (0s and 1s), quantum computing relies on qubits, which leverage quantum superposition to exist in multiple states simultaneously.
- However, qubits are highly prone to environmental perturbations, including:
- Thermal fluctuations
- Vibrational disturbances
- Electromagnetic interference
- To counter these issues, AWS’s Cat qubits, inspired by Schrödinger’s cat thought experiment, intrinsically stabilize quantum states. This innovation reduces computational overhead required for traditional quantum error correction.
With reference to AWS’s Ocelot chip, consider the following statements:
- The Ocelot chip employs a three-layer integrated silicon design for enhanced qubit coherence.
- Cat qubits in Ocelot function by leveraging quantum superposition and error resilience mechanisms.
- The oscillators in the Ocelot chip are made from Niobium, a common superconducting material in quantum processors.
- AWS’s approach to quantum error correction in Ocelot eliminates the need for external error detection circuits.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 3, and 4
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- The Ocelot chip uses a two-layer (not three-layer) silicon design for optimizing qubit stability. Cat qubits leverage quantum superposition and intrinsic error correction mechanisms to improve computational efficiency. The oscillators in Ocelot are made from Tantalum, not Niobium. The Ocelot chip still requires external qubits for error detection, although its design significantly reduces computational costs.
Link of High levels of Selenium in Wheat to Hair Loss
- A joint investigation by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) identified elevated selenium levels in the blood and hair of affected individuals.
- The contamination was traced to wheat supplied through Public Distribution System (PDS) outlets.
- Selenium: An Essential Yet Potentially Toxic Element
Nature & Occurrence:
- Selenium is an essential trace mineral found in various foods and dietary supplements.
- It does not occur in pure elemental form but is a byproduct of metal sulfide ore refining.
- Exists in soil and groundwater in inorganic forms, which plants absorb and convert into organic compounds like selenocysteine and selenium methionine.
Biological Role:
- Selenium is crucial for human health, being a key component of 25 selenoproteins, including:
- Thioredoxin reductases (involved in cell growth and DNA repair).
- Glutathione peroxidases (protects against oxidative damage).
- It plays a vital role in thyroid hormone metabolism, DNA synthesis, reproduction, and immune defense.
Industrial Applications of Selenium
- Glassmaking: Used to remove color from glass and create red-colored glass and enamels.
- Electronics: Previously used in photocells, light meters, and solar cells (now largely replaced by silicon-based devices).
- Pigments: Adds a red hue to ceramics, paints, and plastics.
- Rubber Industry: Enhances rubber’s durability and resistance through vulcanization.
- Selenium Toxicity (Selenosis): A Growing Concern
Causes:
- Excessive selenium intake via diet, supplements, or environmental exposure.
- Contaminated food or water sources can lead to high selenium levels in the body.
Symptoms:
- Hair loss, a key symptom of selenium toxicity, was observed in individuals from Shegaon Taluka, where foodborne exposure is suspected as the primary cause.
- The findings underscore the need for strict quality monitoring in PDS supplies to prevent toxic exposure and safeguard public health.
Consider the following statements regarding selenium:
- It is primarily found in its pure elemental form in nature.
- It is an essential trace mineral required for human biological functions.
- Selenium compounds play a role in thyroid hormone metabolism and oxidative stress regulation.
- The human body can synthesize selenium independently without dietary intake.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer:(b)
Explanation: Selenium is not found in pure elemental form in nature but as a byproduct of metal sulfide ore refining. It is essential for human health, contributing to thyroid hormone metabolism and oxidative stress regulation. However, the body cannot synthesize selenium independently and must obtain it through diet.
Gene Therapy for Maple Syrup Urine Disease
- Understanding Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD) MSUD is a rare genetic metabolic disorder caused by a deficiency in the Branched-Chain Alpha-Keto Acid Dehydrogenase (BCKDH) enzyme complex.
This enzyme complex is essential for the breakdown of three branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs):
- Leucine
- Isoleucine
- Valine
- A malfunction or absence of the BCKDH complex results in the accumulation of toxic metabolites, leading to severe neurological impairment and, in extreme cases, death.
Key Features of MSUD:
- Distinctive Odor: The disorder is named after the characteristic sweet, maple syrup-like smell in the urine of affected individuals.
Current Treatment Options:
- Strict Dietary Management (low BCAA intake).
- Liver Transplantation, which provides a permanent enzymatic source for BCAA metabolism.
Breakthrough in Gene Therapy
- Scientists have developed a gene replacement therapy to target two forms of classic MSUD using an adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector. This technique delivers functional copies of the BCKDHA and BCKDHB genes to correct the enzyme deficiency.
Key Outcomes of the Therapy:
- Successfully restored metabolic function in knockout cell models.
- Offers a potential curative approach, reducing dependency on strict dietary restrictions and liver transplants.
Which of the following statements correctly describes Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)?
- It is a metabolic disorder caused by an enzyme deficiency in the breakdown of branched-chain amino acids.
- It results in a characteristic sweet odor in urine due to toxic metabolite accumulation.
- The condition can be completely cured through strict dietary management alone.
- It primarily affects the metabolism of essential fatty acids.
Which is the Correct Option?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2, and 3 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer:(a)
Explanation: MSUD is a disorder of branched-chain amino acid metabolism, not essential fatty acids. While dietary management helps control the condition, it does not cure MSUD—severe cases may require liver transplantation or gene therapy.
Ethical Guidelines for Integrative Medicine Research in India
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has introduced an addendum to its existing ethical guidelines for biomedical research, focusing on Research in Integrative Medicine (RIM).
- This initiative seeks to harmonize traditional Ayush systems with contemporary medical science under a structured ethical framework.
- The primary goal is to ensure scientific rigor, patient safety, and credibility in integrative medical practices while advancing holistic healthcare solutions.
Understanding Integrative Medicine (IM)
- Integrative Medicine (IM) is a comprehensive medical approach that synthesizes conventional medical treatments with evidence-based traditional therapies.
- It emphasizes personalized patient care, targeting overall well-being rather than disease-specific interventions.
- With growing global interest in such multidisciplinary approaches, a well-defined ethical and regulatory structure is imperative to ensure scientific validation and acceptance.
Significance of Ethical Guidelines in RIM
The new ethical framework introduced by ICMR is intended to:
- Encourage evidence-based research in Integrative Medicine while maintaining scientific integrity.
- Uphold patient rights by ensuring ethical research practices and informed consent mechanisms.
- Standardize clinical investigations integrating Ayush and allopathic medicine to prevent pseudoscientific claims.
Key Measures Under the Addendum
The addendum incorporates several structural modifications to enhance the ethical governance of RIM:
- Ethics Committees (ECs) must now mandatorily include two Ayush experts, with at least one being external to the institution.
- Strengthened informed consent protocols ensure participants are explicitly informed about the nature and scope of Integrative Medicine interventions.
- Regulatory adherence to existing laws such as the Drugs & Cosmetics Act (1940) and the New Drugs & Clinical Trial Rules (2019) is required.
- Ayush-approved medicines will be exempt from additional safety trials, while non-codified traditional formulations must undergo rigorous regulatory scrutiny before clinical use.
Oversight by Ethics Committees
- Ethics Committees are entrusted with ensuring compliance with ethical norms in Integrative Medicine research.
- Their role extends beyond regulatory enforcement to critical evaluation of scientific merit in RIM studies.
- The inclusion of Ayush experts fortifies the multidisciplinary assessment process, ensuring a balanced scientific and traditional knowledge-based review.
Future Implications for Healthcare
- The integration of modern and traditional medicine under a structured ethical framework could transform personalized treatment methodologies.
By fostering scientifically validated interdisciplinary approaches, the initiative could:
- Improve treatment outcomes while minimizing adverse effects.
- Strengthen global credibility of India’s traditional medical systems.
- Establish a precedent for ethical governance in multi-system healthcare research.
- The ICMR’s revised ethical framework is a critical step toward institutionalizing Integrative Medicine, ensuring its scientific legitimacy while protecting patient interests.

Which of the following statements correctly describes Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)?
- It is a metabolic disorder caused by an enzyme deficiency in the breakdown of branched-chain amino acids.
- It results in a characteristic sweet odor in urine due to toxic metabolite accumulation.
- The condition can be completely cured through strict dietary management alone.
- It primarily affects the metabolism of essential fatty acids.
Which is the Correct Option?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2, and 3 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer:(a)
Explanation: MSUD is a disorder of branched-chain amino acid metabolism, not essential fatty acids. While dietary management helps control the condition, it does not cure MSUD—severe cases may require liver transplantation or gene therapy.
Gut Health and Multiple Sclerosis
Understanding Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a multifaceted neuroinflammatory disorder wherein aberrant immune responses target the central nervous system (CNS), leading to demyelination and neuronal degeneration.
- Epidemiological data reveal that MS affects approximately one million individuals in the United States and over 2.8 million globally.
- Clinical manifestations are heterogeneous, encompassing fatigue, motor dysfunction, and cognitive impairment.
- While the precise etiology remains elusive, a confluence of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers orchestrates disease onset and progression.
Genetic and Environmental Contributions
- Twin studies provide compelling evidence of the genetic-environmental nexus in MS pathogenesis.
- The concordance rate among monozygotic twins stands at 25%, whereas dizygotic twins exhibit a mere 2% risk.
- This disparity underscores the substantial role of environmental determinants, such as viral infections, vitamin D levels, and gut microbiota composition, in modulating disease susceptibility.
The Gut Microbiota’s Role in MS
- Emerging research underscores the pivotal role of the gut microbiome in neuroimmunological dynamics.
- Dysbiosis—perturbation of microbial homeostasis—has been implicated in immune dysregulation and neuroinflammation.
- Comparative metagenomic analyses reveal distinct microbial signatures in MS patients relative to healthy counterparts, illuminating potential mechanistic links.
Microbial Signatures and Disease Modulation
- Studies indicate an increased prevalence of Blautia species in MS patients, juxtaposed with a diminished presence of Prevotella, a genus associated with mucosal integrity and immunomodulation.
- Murine models elucidate a critical interplay between Bifidobacterium and Akkermansia; an imbalance between these bacterial populations appears to correlate with disease severity.
- Experimental paradigms employing antibiotic-treated mice further substantiate these findings.
- Mice colonized with Blautia exhibit exacerbated MS-like symptoms,
- whereas those administered Bifid bacterium demonstrate attenuated neuroinflammatory responses, reinforcing the hypothesis that gut microbiota composition critically influences disease pathophysiology.
Clinical Implications and Future Directions
- The Bifidobacterium-to-Akkermansia ratio emerges as a potential biomarker for disease severity, offering a novel avenue for diagnostic refinement.
- Moreover, therapeutic strategies targeting microbial modulation—such as probiotics, fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), and dietary interventions—may hold promise in ameliorating disease burden.
- Understanding the nuanced mechanisms through which commensal bacteria transition from beneficial to pathogenic states remains imperative for developing precision medicine approaches in MS management
Consider the following statements regarding Multiple Sclerosis (MS):
- MS is solely a genetically inherited disorder with negligible environmental influence.
- The disease is characterized by demyelination of neurons in the central nervous system.
- MS symptoms are uniform across all affected individuals.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- MS is not solely a genetic disorder, as evidenced by twin studies indicating environmental contributions. Symptoms vary widely among individuals, disproving statement 3.
Solar Maximum
- NASA has launched the Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere (PUNCH) Mission, strategically aligning with the solar maximum phase of the Sun’s 11-year cycle.
- The mission aims to enhance our understanding of how the Sun’s outer atmosphere (corona) transitions into the solar wind—a phenomenon crucial for space weather forecasting.
What is the Solar Cycle?
- The Sun’s magnetic field behaves like a giant bar magnet with defined north and south poles.
- This magnetic field is generated by the movement of electrically charged particles within the Sun’s plasma.
- Every ~11 years, the Sun undergoes a complete magnetic pole reversal, switching its north and south poles.
- This phenomenon is termed the solar cycle and is a fundamental driver of solar activity, sunspots, and space weather phenomena.
Solar Maximum: The Peak of Solar Activity
Characteristics of Solar Maximum:
- Represents the most active phase of the solar cycle.
- Marked by increased solar radiation, enhanced energy emissions, and a surge in sunspot numbers.
- Occurs when the Sun’s magnetic field completely flips, initiating significant geomagnetic and atmospheric changes.
Duration of Solar Maximum:
- Typically lasts between 1 to 2 years.
- The time between two consecutive solar maxima can vary between 9 to 13 years.
Impacts of Solar Maximum on Earth
- Solar Flares & Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs):
- The Sun releases bursts of magnetic energy, triggering large-scale solar storms.
- CMEs can send high-energy particles and radiation towards Earth, disrupting space-based and terrestrial systems.
- Disruptions to Electrical Infrastructure:
- Intense geomagnetic storms can induce voltage surges in power grids, potentially leading to large-scale blackouts.
- Satellite & Communication Failures:
- Heightened solar radiation affects satellite electronics, causing malfunctions in communication, navigation, and GPS systems.
- Spacecraft operating in low Earth orbit become more vulnerable to drag and radiation damage.
NASA’s PUNCH Mission: A Step Toward Solar Wind Understanding
What is the PUNCH Mission?
- PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) is a NASA Small Explorer (SMEX) mission.
- It aims to study how the Sun’s corona evolves into the solar wind that pervades the heliosphere.
Key Features of the PUNCH Mission:
- Utilizes a constellation of four small satellites in Sun-synchronous, low Earth orbit.
- Captures continuous, deep-field, 3D imagery of the solar corona to track the origins and dynamics of the solar wind.
- Helps improve space weather forecasting, crucial for protecting astronauts, satellites, and power grids from solar disturbances.
Which of the following statements regarding the solar cycle is/are correct?
- The solar cycle is driven by the reversal of the Sun’s magnetic field approximately every 11 years.
- The solar maximum phase is characterized by a decrease in sunspot activity and lower solar energy output.
- The magnetic field of the Sun is generated by the movement of charged particles in its plasma.
- The time interval between two consecutive solar maxima is precisely 11 years and never varies.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
- a) 1 and 3 only
b) 2 and 4 only
c) 1, 3, and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Correct Answer: a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Sun’s magnetic poles reverse every ~11 years, defining the solar cycle.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: Solar maximum is a phase of high sunspot activity and increased solar emissions.
- Statement 3 is correct: The Sun’s magnetic field originates from the motion of electrically charged particles in its plasma.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: The duration of the solar cycle is not fixed and can range between 9 to 13 years.
Rise in India’s R&D Spending
- India’s Gross Expenditure on Research and Development (GERD) has witnessed a 2x increase over the last decade, escalating from ₹60,196 crore (2013-14) to ₹1,27,381 crore.
- However, despite this growth, India’s GERD-to-GDP ratio (~0.7%) remains significantly lower than that of China (2.4%) and the United States (3.1%), highlighting the need for greater investment, policy reforms, and private sector involvement.
DISHA Program: A Catalyst for Technological Advancement
- The DISHA Program (Developing Innovations, Successful Harnessing, and Adoption) aims to position India as a knowledge-driven economy by promoting disruptive technologies across multiple disciplines.
- It fosters a synergistic ecosystem where faculty members, researchers, and students contribute to cutting-edge innovations.
- In alignment with this vision, the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) was introduced to bridge the gap between science, humanities, and social sciences, ensuring a holistic research environment that drives interdisciplinary collaboration.
Major Government Initiatives to Strengthen R&D
- National Research Foundation (NRF):
- Objective: To increase research funding, facilitate public-private partnerships, and boost scientific and technological progress.
- Atal Innovation Mission (AIM):
- Encourages entrepreneurship and grassroots-level innovation, particularly among students, startups, and professionals.
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme:
- Provides financial incentives to industries investing in high-tech manufacturing and R&D-driven sectors.
- Startup India & Make in India:
- Strengthen India’s startup ecosystem by offering policy incentives, financial support, and regulatory ease for homegrown innovations.
Challenges in India’s R&D Ecosystem
- Low Private Sector Participation
- In India, the private sector accounts for only ~36% of GERD.
- In contrast, developed economies have a private sector R&D contribution exceeding 60-70%.
- Lack of risk appetite, high capital costs, and weak industry-academia collaboration impede private R&D investment.
- Insufficient R&D Funding
- While GERD has grown in absolute terms, its percentage of GDP (~0.7%) remains low compared to:
- China (2.4%)
- United States (3.1%)
- South Korea (4.5%)
- Low public expenditure on fundamental research limits India’s global scientific output and patent filings.
- Weak University-Industry Collaboration
- Limited commercialization of academic research due to:
- Bureaucratic delays in funding approvals.
- Lack of robust technology-transfer mechanisms.
- Minimal industry-driven R&D initiatives in universities.
Which of the following statements regarding India’s Gross Expenditure on Research and Development (GERD) is/are correct?
- India’s GERD has more than doubled in the last decade but remains below 1% of GDP.
- India’s private sector accounts for over 60% of GERD, aligning with developed nations.
- China and the United States invest a higher percentage of GDP in R&D compared to India.
- India’s public sector remains the dominant contributor to research funding.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
- a) 1 and 2 only
b) 1, 3, and 4 only
c) 2, 3, and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: b) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: India’s GERD doubled but remains ~0.7% of GDP, much lower than global leaders.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: India’s private sector contributes only ~36%, far lower than in developed economies (60-70%).
- Statement 3 is correct: China (4% of GDP) and the USA (3.1% of GDP) invest significantly more in R&D than India.
Statement 4 is correct: Public sector entities dominate R&D funding in India due to limited private participation.
Hantavirus
Context:
- The recent tragic deaths of actor Gene Hackman and his wife Betsy Arakawa have drawn attention to hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS), a rare but severe rodent-borne disease.
- Arakawa’s death, linked to HPS, has highlighted the risks associated with this virus and the need for greater public awareness.
What is Hantavirus?
- Hantavirus refers to a group of viruses carried by rodents.
- Transmission to humans occurs through contact with rodent urine, feces, or saliva, primarily from deer mice in the United States.
- Unlike many infectious diseases, hantavirus does not spread between humans.
Types of Hantavirus Diseases
- The impact of hantavirus varies by region, with two major diseases associated with it:
- Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) – Primarily found in the Americas, this severe respiratory disease can be fatal.
- Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS) – More common in Europe and Asia, this disease primarily affects the kidneys.
- Each hantavirus strain is associated with specific rodent hosts, making regional awareness crucial.
Symptoms of Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS)
- Symptoms typically develop between one to eight weeks after exposure.
- Early signs resemble flu-like symptoms, including fatigue, fever, and muscle aches.
- As the disease progresses, severe respiratory distress occurs, leading to shortness of breath and chest tightness.
- Fatality Rate: Approximately 38% of individuals who develop respiratory complications succumb to HPS.
Treatment and Prevention
- No Cure Available: There is currently no antiviral treatment for HPS.
- Early Detection is Crucial: Supportive care, including oxygen therapy and intensive respiratory support, may improve survival chances.
Preventive Measures:
- Avoid exposure to rodent-infested environments.
- Use disinfectants to clean areas with possible rodent activity.
- Refrain from sweeping or vacuuming dry rodent droppings, as this can aerosolize the virus.
- Wear protective masks and gloves when cleaning contaminated areas.
Public Health Awareness and Safety Measures
- Public health officials recommend heightened awareness in regions where rodents are common.
- Using protective gear while cleaning rodent droppings can significantly reduce the risk of exposure.
- Educational initiatives on hantavirus risks and safe hygiene practices can help prevent infections and protect communities.
- With no specific cure available, prevention and early detection remain the most effective strategies against hantavirus infections.
Consider the following statements regarding Hantavirus:
- Hantavirus is primarily transmitted through direct human-to-human contact.
- The disease caused by Hantavirus in the Americas is known as Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS).
- The primary rodent carrier of Hantavirus in the United States is the deer mouse.
- Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) has a fatality rate of over 50%.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 4 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: (c) 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: Hantavirus does not spread through human-to-human contact. It is transmitted to humans primarily through exposure to rodent urine, feces, or saliva.
- Statement 2 – Incorrect: Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) is found in the Americas, while Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS) is more common in Europe and Asia.
- Statement 3 – Correct: The deer mouse (Peromyscus maniculatus) is the primary reservoir of Hantavirus in the United States.
- Statement 4 – Incorrect: The fatality rate of HPS is approximately 38%, not over 50%.
Vitiligo and Gut Bacteria
syllabus Science and Technology
- Recent studies have highlighted a potential breakthrough in the treatment of vitiligo, a chronic autoimmune disorder that leads to skin depigmentation.
- This condition, which affects a significant portion of the global population, has both cosmetic and psychological impacts.
- Emerging research suggests that gut-friendly bacteria may play a key role in slowing its progression, opening new possibilities for treatment.

Understanding Vitiligo
- Vitiligo occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing skin pigment.
- This results in white patches on the skin, which can appear anywhere on the body but are most noticeable on the face, hands, and arms.
- While often perceived as a cosmetic issue, vitiligo can lead to social stigma and emotional distress, especially in individuals with darker skin tones.
- The condition affects 5% to 2% of the global population, with higher prevalence reported in regions like Gujarat and Rajasthan in India.
New Research Findings
- Recent studies from Northwestern University have discovered a natural compound derived from gut-friendly bacteria that could slow vitiligo progression.
- Pre-clinical trials in mice showed that this microbial compound reduced pigment loss by 74%.
- The compound works by reducing harmful killer T cells while increasing protective regulatory T cells, helping to restore immune balance.
- These findings suggest that modifying the gut microbiome could become a novel therapeutic approach for vitiligo.
Importance of Early Intervention
- Vitiligo often appears during adolescence or between the ages of 40 and 50.
- The condition is more pronounced in individuals with darker skin, leading to greater emotional and social distress.
- Early intervention can help stabilize pigment loss, improving treatment outcomes and quality of life for patients.
Future Treatment Possibilities
- Researchers are now exploring ways to translate these findings into human treatments:
- Current options include weekly injections, but more accessible alternatives like topical ointments or food additives are also being considered.
- Further studies are needed to determine the optimal dosage, duration, and long-term effectiveness of these treatments.
Broader Implications
- This research could have applications beyond vitiligo, potentially benefiting other autoimmune diseases with similar immune system dysfunction.
- Collaboration among scientists will be essential to refine the microbial compound and assess its compatibility with existing vitiligo treatments.
- By leveraging the power of the gut microbiome, researchers may unlock new, non-invasive therapies that could revolutionize the treatment of vitiligo and other immune-related conditions.
Consider the following statements regarding vitiligo:
- Vitiligo is an autoimmune disorder that leads to the destruction of keratinocytes, resulting in depigmented patches on the skin.
- The condition has a higher prevalence in regions like Gujarat and Rajasthan in India.
- The emotional and social impact of vitiligo is more pronounced in individuals with darker skin tones.
- The disease primarily manifests in childhood and is rarely observed after the age of 30.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 4 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 2, and 4 only
d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: Vitiligo results from the destruction of melanocytes, not keratinocytes.
- Statement 2 – Correct: Studies indicate that vitiligo has a higher prevalence in regions like Gujarat and Rajasthan in India.
- Statement 3 – Correct: Since vitiligo causes visible depigmentation, individuals with darker skin tones often experience greater emotional and social distress.
- Statement 4 – Incorrect: Vitiligo commonly appears during adolescence or between ages 40-50, but it is not strictly confined to childhood.
H1N1 Virus
- Delhi is experiencing a notable surge in seasonal flu cases, with H1N1 (Swine Flu) and Influenza B emerging as dominant strains.
- These infections are leading to persistent high fevers and prolonged upper respiratory symptoms, raising concerns among healthcare professionals.
Understanding the H1N1 Virus
Overview
- H1N1, commonly known as Swine Influenza (Swine Flu), is a respiratory infection caused by Type A influenza viruses, which primarily affect pigs.
- While human infections are rare, sporadic cases do occur, and in some instances, limited human-to-human transmission has been observed.
H1N1 in India
- The first confirmed case of H1N1 in India was reported in May 2009. Since then, the virus has caused multiple outbreaks, with significant surges recorded in 2021, 2022, 2023, and now again in 2024, making it a recurring public health challenge.
- Modes of Transmission
H1N1 primarily spreads through:
- Respiratory droplets released when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
Direct contact with contaminated surfaces, followed by touching the eyes, nose, or mouth.
Symptoms of H1N1 Infection
- H1N1 symptoms are similar to seasonal influenza and may include:
- High fever
- Cough and sore throat
- Body aches and headaches
- Chills and fatigue
- Some cases may experience diarrhea and vomiting
- Severe cases can lead to pneumonia, respiratory failure, and even death
Treatment and Prevention
- Currently, no specific vaccine is available for H1N1 prevention.
However, adopting preventive measures can help curb the spread:
- Frequent handwashing with soap and water.
- Avoiding close contact with infected individuals.
- Wearing masks in crowded areas to prevent airborne transmission.
- Seeking medical attention at the onset of flu-like symptoms.
With rising cases, public awareness and timely precautions remain key in managing the spread of H1N1 and safeguarding public health.
Consider the following statements regarding H1N1 (Swine Flu):
- H1N1 is caused by a Type B influenza virus.
- The first confirmed case of H1N1 in India was reported in 2009.
- Human-to-human transmission of H1N1 has never been reported.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- The correct option is (b) 2 only, as statement 2 is correct, while statements 1 and 3 are incorrect. Initially, H1N1 was believed to spread only from pigs to humans, but scientific studies confirmed human-to-human transmission soon after the 2009 outbreak.
- The virus spreads primarily through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes, similar to seasonal flu.
- Studies and epidemiological data confirm sustained human-to-human transmission of H1N1, making it capable of spreading within communities.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have documented multiple cases of human-to-human transmission, particularly in crowded and enclosed environments.
- This statement is incorrect as H1N1 has been proven to spread from person to person, which is why it led to a pandemic in 2009.
Shingles Disease
Understanding Shingles Disease
- Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, is a viral infection that causes a painful rash or blisters on the skin.
- The rash often appears in a band-like pattern in a specific area of the body but can occur anywhere.
- The risk of developing shingles increases with age, making it most common in individuals above 50 years.
Cause of Shingles
- It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus—the same virus responsible for chickenpox.
- After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in the body, residing in nerve tissues.
- In later life, reactivation of the virus can lead to shingles, often triggered by weakened immunity, stress, or aging.
Is Shingles Contagious?
- Shingles itself is not contagious, meaning it cannot spread directly from person to person.
- However, the varicella-zoster virus can spread to individuals who have never had chickenpox or not been vaccinated, causing chickenpox, not shingles.
- Symptoms of Shingles
Common symptoms include:
- Pain, itching, tingling, and numbness in the affected area.
- Fever, headache, chills, and fatigue may also occur.
- While shingles is not life-threatening, it can be extremely painful.
Complications
- The most common complication is postherpetic neuralgia (PHN)—a condition where shingles pain persists long after the blisters heal.
- Other complications may include vision problems (if it affects the eyes) and neurological issues in severe cases.
Prevention and Treatment
- Prevention:
- Shingrix is a vaccine that helps prevent shingles and its long-term complications.
- Treatment:
- There is no cure for shingles.
- Antiviral medications can help reduce severity and duration, especially when started early in the infection.
With reference to Shingles (Herpes Zoster), consider the following statements:
- Shingles is caused by the same virus responsible for measles.
- A person who has never had chickenpox cannot develop shingles.
- Shingles is highly contagious and spreads through direct contact with an infected person’s blisters.
- Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a common complication of shingles.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer :(c) 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Shingles is caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), which is also responsible for chickenpox, not measles (which is caused by the measles virus).
- Statement 2 is incorrect: Shingles can only occur in individuals who have previously had chickenpox because the varicella-zoster virus remains dormant in the body. However, a person who has never had chickenpox can contract chickenpox if exposed to the virus from a person with shingles.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: Shingles is not highly contagious. While the virus can spread, it does so only through direct contact with fluid from the blisters, and even then, it causes chickenpox, not shingles in those who have never had chickenpox before.
- Statement 4 is correct: Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a painful condition where shingles pain persists for months or even years after the rash disappears, making it the most common complication of shingles.
Chandrayaan-3
Overview of Chandrayaan-3
- Chandrayaan-3 is the Indian Space Research Organisation’s (ISRO) second attempt at achieving a successful lunar landing and rover operation, following Chandrayaan-2.
- The mission was launched aboard ISRO’s LVM3 rocket, an advanced three-stage launch vehicle designed for cost-effective placement of payloads into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO).
- The LVM3 M4 launcher successfully deployed the integrated modules into an elliptical parking orbit (170 x 36,500 km) before its lunar journey.
Mission Objectives
The primary objectives of Chandrayaan-3 include:
- Achieving a safe and soft landing on the Moon.
- Deploying a rover to conduct surface exploration.
- Performing in-situ scientific experiments to analyze lunar composition and thermal properties.
- Investigating the presence of water ice, which could support future lunar habitation and interplanetary travel.
Mission Components Chandrayaan-3 consists of:
- Lander Module (LM): Responsible for soft-landing and conducting surface experiments.
- Rover: Designed to explore and analyze the lunar surface.
- Propulsion Module (PM): Provides necessary thrust for trans-lunar injection and payload support.
Recent Scientific Findings
- New data from Chandrayaan-3 suggests that water ice deposits may exist beyond the Moon’s polar regions.
- The Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Ahmedabad, conducted a study based on data from the Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE)
Key Findings from ChaSTE:
- A 60°C temperature difference was recorded between the lunar surface and 10 cm beneath it.
- This suggests that the Moon’s surface layer is highly non-conductive, offering crucial insights into its thermal properties and composition.
- The discovery strengthens the possibility of water ice being more widespread than previously believed, impacting future lunar missions and resource utilization strategies.
With reference to Shingles (Herpes Zoster), consider the following statements:
- Shingles is caused by the same virus responsible for measles.
- A person who has never had chickenpox cannot develop shingles.
- Shingles is highly contagious and spreads through direct contact with an infected person’s blisters.
- Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a common complication of shingles.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer :(c) 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Shingles is caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), which is also responsible for chickenpox, not measles (which is caused by the measles virus).
- Statement 2 is incorrect: Shingles can only occur in individuals who have previously had chickenpox because the varicella-zoster virus remains dormant in the body. However, a person who has never had chickenpox can contract chickenpox if exposed to the virus from a person with shingles.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: Shingles is not highly contagious. While the virus can spread, it does so only through direct contact with fluid from the blisters, and even then, it causes chickenpox, not shingles in those who have never had chickenpox before.
- Statement 4 is correct: Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a painful condition where shingles pain persists for months or even years after the rash disappears, making it the most common complication of shingles.
Thalassemia
Context
- The Andhra Pradesh government is considering increasing the monthly pension for thalassemia patients and extending financial support to those above the poverty line (APL) due to the high cost of treatment. Currently, patients below the poverty line (BPL) receive treatment under the NTR Vaidya Seva scheme.
What is Thalassemia?
- Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder inherited from parents, where the body fails to produce sufficient hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells (RBCs) responsible for carrying oxygen.
- Each RBC contains 240 to 300 million hemoglobin molecules, and a deficiency results in severe anemia, requiring blood transfusions every 2-3 weeks for survival.
Symptoms of Thalassemia
- Beyond anemia,
- patients may experience
- Weak bones
- Delayed or stunted growth
- Iron overload (from frequent transfusions)
- Poor appetite
- Enlarged spleen or live
- Pale skin
Consider the following statements regarding Thalassemia:
- Thalassemia is an acquired blood disorder caused by iron deficiency.
- It leads to severe anemia due to the body’s inability to produce sufficient hemoglobin.
- Blood transfusions are required only in the early stages of the disease.
- Thalassemia is recognized as a benchmark disability under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Thalassemia is not an acquired disorder; it is a genetic disorder inherited from parents.
- Statement 2 is correct: The disorder prevents sufficient hemoglobin production, leading to severe anemia.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: Blood transfusions are lifelong and not limited to early stages. Patients require transfusions every 2-3 weeks.
- Statement 4 is correct: Thalassemia is classified as a benchmark disability under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016.
Building Compassion into the Health-Care Structure
- On February 7, 2025, the World Health Organization (WHO) released a significant report titled ‘Compassion and Primary Health Care,’ emphasizing compassion as a transformative force in global health.
- The report highlights the necessity of integrating compassion into health-care services to enhance patient outcomes and improve provider well-being.
- WHO’s Director-General underscored the importance of compassion in strengthening primary care and advancing quality health services.
The Benefits of Compassionate Health Care
- Compassion in health care extends beyond ethical considerations, offering tangible benefits for both patients and medical professionals.
- For Patients:
- Research from Stanford University’s Centre for Compassion and Altruism Research and Education (CCARE) shows that compassionate care accelerates recovery and reduces hospital stays.
- A Johns Hopkins Hospital study found that simple gestures—such as doctors spending an additional 40 seconds reassuring patients—significantly reduce anxiety and improve healing.
For Medical Professionals:
- Practicing compassion alleviates stress, enhances job satisfaction, and fosters stronger patient-provider relationships.
- Maintaining a balance between emotional involvement and professional detachment prevents burnout, allowing for sustained high-quality care.
- Compassion vs. Empathy and Sympathy
- Compassion is often misinterpreted as empathy, sympathy, or kindness, but these concepts have distinct meanings:
- Sympathy: A temporary feeling of pity for someone’s suffering without deeper emotional involvement.
- Empathy: Feeling and internalizing another person’s pain, which can lead to emotional exhaustion in medical professionals.
- Compassion: A sustainable approach where health-care providers acknowledge suffering and act to alleviate it without becoming overwhelmed.
- By fostering compassion rather than excessive empathy, health professionals can make rational, well-informed decisions while maintaining emotional stability.
The Role of Compassion in Mental Health Care
- Mental health disorders, particularly depression and anxiety, have reached alarming levels globally due to factors such as social isolation, economic uncertainty, and trauma. Unlike physical illnesses, mental health conditions are often stigmatized, discouraging individuals from seeking help.
Compassion in Mental Health Treatment:
- Provides a safe space where patients feel understood and valued.
- Encourages open communication, reducing feelings of shame and self-doubt.
- Helps individuals adhere to treatment plans and develop long-term coping mechanisms.
Compassion in Mental Health Recovery
- Compassionate care is particularly vital for individuals who have endured trauma, abuse, or neglect. Survivors of war, violence, and human trafficking require not only medical intervention but also emotional support, patience, and human connection to facilitate recovery.
- Case Study: The Transformation of Pradeep
- Pradeep, a rescued child suffering from severe trauma, was abandoned due to superstitious beliefs.
- At Bal Ashram, a rehabilitation center, caregivers adopted a compassionate approach, allowing him to heal at his own pace rather than forcing him to relive his past.
- Over time, with emotional support and a nurturing environment, he regained his ability to communicate and formed meaningful relationships.
- His recovery highlights the transformative power of compassion in mental health rehabilitation.
Strategies for Implementing Compassionate Health Care
- Raising Awareness:
- Health-care institutions, policy-makers, and industry leaders must prioritize compassion as a core principle in decision-making.
- Training Health-Care Providers:
- Medical professionals should undergo experiential learning and specialized training in compassionate care to integrate it effectively into practice.
- Ensuring Equitable and Accessible Health Care:
- A truly compassionate system must be inclusive, ensuring high-quality treatment for individuals regardless of their socio-economic status, gender, or background.
Conclusion
- Health care is not just about curing diseases; it is about promoting overall well-being. Compassion should be at the heart of medical practice, influencing patient interactions and health-care policies.
- By raising awareness, training professionals, and ensuring accessibility, the global medical community can create a people-centric health-care system rooted in compassion.
- Now is the time to embrace and globalize compassionate care, ensuring that every patient receives dignity, respect, and the quality treatment they deserve.
Consider the following statements regarding the WHO’s report on ‘Compassion and Primary Health Care’:
- The report highlights the role of compassion as a transformative force in global health.
- It primarily focuses on the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in primary health care to enhance patient outcomes.
- The report underscores the importance of emotional involvement over professional detachment for health-care providers.
- It was released by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2025.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The WHO report emphasizes the role of compassion as a transformative force in health care.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: While technology and AI are being integrated into health care, this report does not primarily focus on AI but on the human aspect of compassionate care.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The report highlights that excessive emotional involvement can lead to burnout, and instead, it promotes a balance between compassion and professional detachment.
- Statement 4 is correct: The report was released by WHO in 2025.
WHO Report on Maternal Mortality
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has released a recent study shedding light on the urgent issue of maternal mortality.
- According to the 2020 data, approximately 287,000 women lost their lives due to preventable causes associated with pregnancy and childbirth, translating to nearly 800 deaths per day.
- This report underscores the critical gaps in maternal healthcare and calls for immediate global action.
Primary Causes of Maternal Mortality
- The WHO study identifies haemorrhage and hypertensive disorders as the leading causes of maternal deaths:
- Haemorrhage (27%) – The most common cause, often occurring during or immediately after childbirth.
- Hypertensive disorders (16%) – Conditions such as pre-eclampsia significantly contribute to maternal deaths.
- The prevalence of these causes varies across regions, with sub-Saharan Africa and Western Asia reporting the highest mortality rates.
Regional Disparities in Maternal Mortality
- Maternal mortality rates show stark regional variations, revealing the unequal healthcare challenges across the world:
- Western Asia & Northern Africa: Haemorrhage accounts for 29% of maternal deaths.
- Sub-Saharan Africa: Haemorrhage contributes to 28% of fatalities.
- Australia & New Zealand: A significantly lower rate of 15%.
- Latin America & the Caribbean: Hypertensive disorders are more prevalent in this region.
- These disparities highlight the urgent need for region-specific interventions and improved healthcare systems.
Postpartum Complications and Mortality Risks
- A significant proportion of maternal deaths due to haemorrhage and sepsis occur during the postpartum period, which extends up to 42 days after childbirth.
- In 2020, at least 111 countries reported maternal deaths within this critical window, underscoring the necessity for enhanced postnatal care and continuous monitoring.
Global Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) and SDG Progress
- The global Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) stood at 223 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2020.
- Despite international efforts, this figure signals a stagnation in progress since the adoption of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in 2015.
- The WHO warns that at the current pace, the world is unlikely to meet the SDG target of reducing MMR to below 70 by 2030.
The Need for Strengthened Maternity Care
- The study emphasizes the critical role of high-quality maternity care in reducing maternal deaths. Key priorities include:
- Enhanced antenatal services to identify risks early.
- Rapid emergency interventions to manage complications.
- Stronger postnatal care to monitor and address health risks after childbirth.
WHO’s Global Roadmap for Maternal Health
- Recognizing the urgent need for action, the WHO launched a global roadmap in 2024 to combat postpartum haemorrhage, a leading cause of maternal mortality. Developed in collaboration with over 130 global experts, this roadmap sets priorities for intervention and policy changes.
- The WHO continues to advocate for high-quality, respectful, and accessible maternal healthcare services throughout pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period. Addressing maternal mortality requires global commitment, strategic policies, and enhanced healthcare systems to ensure that no woman dies from preventable pregnancy-related causes.
Consider the following statements regarding the recent WHO report on maternal mortality:
- The report states that approximately 500,000 women died from preventable pregnancy-related causes in 2020.
- Haemorrhage and hypertensive disorders are the leading causes of maternal mortality.
- The Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) target aims to reduce the global maternal mortality ratio (MMR) to below 100 per 100,000 live births by 2030.
- The highest rates of maternal mortality are reported in sub-Saharan Africa and Western Asia.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
1 and 3 only
2 and 4 only
1, 2, and 3 only
2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The WHO report states that 287,000 women died in 2020 due to preventable maternal causes, not 500,000.
- Statement 2 is correct: Haemorrhage (27%) and hypertensive disorders (16%) are the leading causes of maternal mortality.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The SDG target aims to reduce MMR to below 70 per 100,000 live births, not 100.
- Statement 4 is correct: The highest maternal mortality rates are observed in sub-Saharan Africa and Western Asia.
Genetically Engineered Non-Browning Bananas
- Introduction: A UK-based biotech company, Tropic, has developed a genetically-engineered banana that resists browning.
- This innovation aims to reduce food waste and environmental impact, addressing the significant spoilage rate of bananas, which leads to nearly 50% of global banana crop wastage annually.
- By extending the fruit’s freshness, this advancement contributes to sustainability and efficient resource utilization.
The Science Behind Banana Ripening:
- Bananas undergo a natural ripening process, transitioning from green to yellow and eventually brown due to the presence of ethylene, a plant hormone.
- Even after harvest, bananas continue to produce ethylene, which activates genes responsible for the production of polyphenol oxidase (PPO)—an enzyme that reacts with oxygen, causing browning.
- Physical damage or bruising accelerates this process by increasing ethylene production, leading to faster spoilage.
Development of Non-Browning Bananas:
- Tropic’s genetic modification technique alters the banana’s PPO-producing gene, effectively silencing it.
- This does not stop the ripening process but prevents enzymatic browning, maintaining the fruit’s visual appeal for a longer duration.
- A similar approach has been applied to Arctic apples, which also resist browning.
- This breakthrough in fruit preservation technology could revolutionize post-harvest management, reducing waste and enhancing shelf life.
Environmental Impact of Food Waste:
- Food waste contributes significantly to global carbon emissions.
- In the UK alone, approximately 1.4 million edible bananas are discarded daily, adding to landfill waste and greenhouse gas emissions.
- The introduction of non-browning bananas encourages prolonged consumption, potentially reducing food wastage.
- According to Tropic, widespread adoption of this technology could result in CO₂ reductions equivalent to removing 2 million cars from roads annually, marking a major step toward environmental sustainability.
Implications for the Future of Agriculture:
- The success of genetically-engineered bananas could pave the way for similar advancements in other crops.
- Scientists have already applied these techniques to tomatoes, melons, kiwifruits, and mushrooms, enhancing their shelf life and reducing spoilage.
- This innovation signals a new era in agricultural biotechnology, improving crop resilience, sustainability, and global food security.
Conclusion:
- Tropic’s non-browning banana represents a significant milestone in food science and sustainability.
- By tackling spoilage issues, this breakthrough contributes to waste reduction, environmental conservation, and efficient agricultural practices.
- As biotechnology advances, such innovations could play a crucial role in addressing global food security challenges while minimizing environmental impact.
Consider the following statements regarding Tropic’s genetically-engineered banana:
- It prevents ripening entirely to enhance shelf life.
- The modification targets the polyphenol oxidase (PPO) enzyme to reduce browning.
- This technique has previously been applied to other fruits like Arctic apples.
- The primary goal of this innovation is to increase banana production.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation: The genetic modification does not stop ripening but prevents browning by silencing the PPO enzyme. The same technique has been used for Arctic apples. The goal is not to increase production but to reduce food waste and environmental impact.
Viral Meningitis
- Viral Meningitis Cases in Kerala: A Public Health Concern: Recent reports indicate that five students from a private school in Kalamassery, Kerala, have exhibited symptoms of viral meningitis.
- Their samples have been sent to the National Institute of Virology (NIV) for testing.
- This incident highlights the need for awareness regarding viral meningitis, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
What Is Meningitis?
Meningitis is the inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It can be caused by bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections. Among these, viral meningitis is the most common and is generally less severe than bacterial meningitis.
Severity of Viral Meningitis
Viral meningitis is usually self-limiting and mild, often resolving without long-term complications. However, bacterial meningitis is a medical emergency that requires immediate antibiotic treatment. If untreated, bacterial meningitis can lead to hearing loss, neurological damage, and even death.
Symptoms of Viral Meningitis
Common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Photophobia (sensitivity to light)
In young children, symptoms may be non-specific, such as irritability, poor feeding, and lethargy. Early recognition is essential for prompt medical intervention.
Diagnosis of Viral Meningitis
The gold standard for diagnosing meningitis is a lumbar puncture, which involves collecting cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF analysis helps differentiate viral from bacterial meningitis. If viral meningitis is suspected, RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction) is used to detect specific viruses.
Treatment Approaches
Since viral meningitis is caused by viruses, antibiotics are ineffective. Treatment is primarily supportive, focusing on:
- Pain relief (using analgesics)
- Hydration
- Nutritional support
- Most patients recover fully within one to two weeks.
Recovery and Risks
- Viral meningitis has a high recovery rate with no long-term complications in most cases.
- In contrast, bacterial meningitis can be fatal or cause permanent disabilities if not treated promptly.
Causes of Viral Meningitis
- The most common viruses causing viral meningitis include:
- Enteroviruses (most frequent cause)
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
- Varicella-zoster virus (VZV)
- Mumps virus
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Transmission of Enteroviruses
Enteroviruses spread through:
- Direct contact with an infected person
- Respiratory secretions (coughing, sneezing)
- Fecal-oral contamination
- These viruses are resilient and can survive on surfaces for extended periods. Disinfecting with bleach is an effective way to eliminate them.
Preventive Measures
- Maintaining hygiene (frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with sick individuals)
- Not sharing personal items (such as water bottles and utensils)
- Keeping infected children at home to prevent outbreaks
- Proper sanitation and disinfection
Role of Vaccination in Prevention
Vaccines against bacterial meningitis include those for pneumococcus and meningococcal.
Vaccination against mumps and chickenpox reduces the risk of viral meningitis.
Immunization programs play a crucial role in controlling outbreaks of meningitis.
Consider the following statements regarding viral meningitis:
- It is more severe than bacterial meningitis and requires immediate antibiotic treatment.
- Enteroviruses are the most common cause of viral meningitis.
- Lumbar puncture is the primary diagnostic test for meningitis.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect because viral meningitis is usually mild, whereas bacterial meningitis is more severe and requires urgent antibiotics.
Statement 2 is correct as enteroviruses are the leading cause of viral meningitis.
Statement 3 is correct since lumbar puncture (CSF analysis) is the standard test for diagnosing meningitis.
Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE)
- Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE) Poses Health Concerns in Uttar Pradesh
- Despite being a rare disease globally, Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE) remains a significant health concern in Lucknow and Uttar Pradesh, primarily due to low measles vaccination coverage.
What is Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE)?
- SSPE is a progressive and typically fatal brain disorder associated with measles (rubeola) infection.
- It usually develops several years after a person has seemingly recovered from measles.
- Though SSPE has been reported worldwide, it is rare in Western countries.
- Males are more commonly affected than females.
- The disease primarily impacts children and adolescents.
Causes of SSPE
- Normally, the measles virus does not cause brain damage.
- However, in some cases, an abnormal immune response or a variant form of the virus leads to severe brain inflammation.
- This inflammation may persist for years, causing progressive neurological damage.
Symptoms of SSPE
SSPE symptoms appear in stages and progressively worsen over time.
Early Symptoms:
- Declining school performance
- Forgetfulness
- Sudden mood swings (temper outbursts, irritability)
- Distractibility and hallucinations
Progressive Symptoms:
- Sudden muscular jerks in the arms, head, or body
- Seizures
- Uncontrollable muscle movements
- Speech and intellectual deterioration
Severe and Final Stages:
- Increasing muscle rigidity
- Difficulty in swallowing, leading to choking risks and pneumonia
- Blindness
- Abnormal blood pressure and pulse
- Fever in the final phase
Treatment and Prognosis
- High mortality rates are associated with SSPE, and there is no known cure.
- Treatment focuses on symptom management.
- Antiviral drugs and immune-boosting medications may help slow disease progression.
- Given the lack of a cure, the most effective strategy against SSPE remains preventing measles through vaccination.
1Consider the following statements regarding Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE):
- SSPE is a progressive brain disorder that occurs due to a previous measles infection.
- The disease primarily affects adults above the age of 40.
- SSPE is more commonly found in developing countries due to lower measles vaccination rates.
- It is caused by a bacterial infection that affects the nervous system.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation: SSPE is a progressive and fatal brain disorder caused by a measles virus infection that usually affects children and adolescents. It is more prevalent in developing countries due to low vaccination rates. The disease is caused by a virus, not bacteria.
Uniyala Keralensis

Overview
- Researchers have recently confirmed the existence of a new plant species, Uniyala keralensis, within the Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve in Kerala.
- This discovery highlights the remarkable biodiversity of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Although the species was originally collected 27 years ago, its classification was only recently finalized, underscoring the importance of continuous botanical research.
Taxonomy and Classification
- Family: Asteraceae
- Initially misidentified as Vernonia multibracteata, Uniyala keralensis was later recognized as a distinct species.
- The genus Uniyala was formally established following in-depth studies and comparisons with herbarium specimens, leading to its separation from Vernonia.
Morphological Characteristics
- Growth Form: Shrub, reaching 1 to 3 meters in height.
- Flowers: Light purple, blooming between August and April.
Leaves:
- Larger compared to closely related species.
- Possess long petioles.
- Feature fewer lateral veins, aiding in species identification.
Habitat and Distribution
- Endemic to southwest India, specifically in the Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve.
- Prefers open landscapes on the western slopes of the region.
- Found at elevations ranging from 700 to 1,400 metres above sea level.
- The estimated population consists of nearly 5,000 individuals, distributed across four subpopulations, covering an area of 250 square kilometres.
Conservation Status
- Classified as Data Deficient (DD) under the IUCN Red List Criteria.
- Due to limited ecological data, its extinction risk remains undetermined.
- Further research is essential to assess its population trends, threats, and conservation requirements.
Significance of the Discovery
- Reinforces the biodiversity richness of the Western Ghats.
- Highlights the need for continued exploration and conservation efforts in this global biodiversity hotspot.
- Enhances scientific knowledge of regional flora, contributing to broader ecological and environmental research.
- This discovery serves as a reminder of the hidden botanical treasures yet to be explored and the urgent need for conservation measures in ecologically sensitive regions like the Western Ghats.
Consider the following statements regarding Uniyala keralensis:
- It belongs to the Fabaceae family and was first classified in 2024.
- It is endemic to the Eastern Ghats and found in tropical lowlands.
- The species was previously misidentified as Vernonia multibracteata.
- It is classified as Critically Endangered under the IUCN Red List.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Uniyala keralensis belongs to the Asteraceae family, not Fabaceae.
Statement 2 is incorrect: It is endemic to the Western Ghats, not the Eastern Ghats. Additionally, it is found at elevations of 700-1,400 metres, not in tropical lowlands.
Statement 3 is correct: The species was originally misidentified as Vernonia multibracteata.
Statement 4 is incorrect: Uniyala keralensis is classified as Data Deficient (DD), not Critically Endangered.
Melioidosis in Odisha
- Recent studies have underscored the increasing concern surrounding melioidosis, particularly in Odisha.
- Research suggests that South Asia accounts for a significant proportion of global melioidosis cases.
- A multidisciplinary collaboration between microbiologists and climate scientists aims to analyze the environmental conditions that drive the transmission of this disease.
Understanding Melioidosis
- Causative Agent: Melioidosis is caused by the bacterium Burkholderia pseudomallei.
- Mode of Transmission: Infection occurs primarily through direct contact with contaminated soil or water, inhalation of aerosols, or ingestion.
- Clinical Manifestations: The disease presents in a spectrum of forms, ranging from localized skin infections to severe pneumonia and septicemia.
- Mortality Risk: In severe cases, the fatality rate can reach up to 50%, making early diagnosis and treatment crucial.
Environmental Factors Influencing Melioidosis
- The incidence of melioidosis is strongly linked to environmental conditions. Key contributing factors include:
- Rainfall Patterns: The disease shows a seasonal peak, particularly during and after the monsoon, due to increased bacterial growth and dispersal in wet soil.
- Temperature Variations: Higher temperatures enhance bacterial survival and transmission dynamics.
Research Collaboration and Findings
- A joint study conducted by AIIMS Bhubaneswar and IIT Bhubaneswar focused on tracking melioidosis cases in Odisha over a nine-year period. The research involved:
- Analyzing meteorological data to identify environmental conditions that correlate with disease outbreaks.
- Establishing a geospatial disease risk map highlighting districts with the highest vulnerability.
High-Risk Regions in Odisha
- The study identified several high-risk districts, particularly those with dense populations and favorable environmental conditions for bacterial growth. These include:
- Cuttack
- Balasore
- Khordha
- Jajpur
- The clustering of cases in these regions suggests increased human exposure to the bacteria, necessitating targeted public health interventions.
Climate Change and Its Role in Disease Dynamics:
- The ongoing shifts in climate patterns pose a significant challenge by altering rainfall distribution and intensifying extreme weather events. These changes may:
- Expand the geographical range of Burkholderia pseudomallei.
- Increase the frequency and severity of melioidosis outbreaks.
- Overburden public health infrastructure, necessitating climate-adaptive disease surveillance.
Broader Implications for Global Disease Modelling
- The insights from Odisha’s research offer a framework for other regions affected by melioidosis. The integration of climate analytics into disease prediction models can:
- Enhance early warning systems for melioidosis and similar infections.
- Improve public health preparedness against emerging climate-driven diseases.
- Provide data-driven policy recommendations for mitigation strategies.
Future Research Directions
- While current studies have provided significant insights, further research is essential to understand additional factors influencing melioidosis, such as:
- Land use changes and their impact on bacterial reservoirs.
- Soil composition and microbial ecology in affected regions.
- Long-term climate projections to anticipate disease expansion patterns.
By integrating climate science, microbiology, and epidemiology, future research can enhance our ability to combat melioidosis and mitigate its impact on public health.
Consider the following statements regarding Melioidosis:
- It is caused by Burkholderia mallei and primarily affects livestock.
- The bacterium thrives in wet soil and can be transmitted through inhalation, ingestion, or direct skin contact.
- The disease has a high fatality rate and peaks during dry seasons when soil dispersal is at its maximum.
- The recent research in Odisha identified monsoon patterns as a key factor in disease outbreaks.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Burkholderia mallei causes glanders, not melioidosis. Melioidosis is caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei.
- The bacteria can infect humans through inhalation, ingestion, or direct contact with contaminated soil/water.
- The disease peaks during and after the monsoon, not in dry seasons, due to increased bacterial dispersal.
- The Odisha study correlated monsoon patterns with outbreaks, confirming the seasonal link.
Update on elimination of Trachoma and Malaria
- India has been officially declared trauma-free as a public health problem by the World Health Organization (WHO) on October 8, 2024.
- This milestone makes India the third country in the WHO Southeast Asia Region to achieve this status.
- The elimination of Trachoma, a leading cause of preventable blindness, highlights significant advancements in public health, hygiene, and sanitation practices.
Government Initiatives for Trachoma Elimination
- The National Programme for Control of Blindness and Visual Impairment (NPCBVI) played a key role in controlling Trachoma.
India followed the WHO-SAFE Strategy, which includes:
- Surgery for trachomatous trichiasis
- Antibiotics to treat infection
- Facial hygiene promotion
- Environmental cleanliness improvement
- A National Trachomatous Trichiasis (TT-only) survey was conducted in 200 endemic districts between 2021-2024 under WHO guidelines, confirming a decline in prevalence below elimination thresholds.
National Quality Assurance Standards (NQAS)
- The Indian government has implemented the National Quality Assurance Standards (NQAS) to ensure the safety, efficiency, and reliability of public healthcare services.
- Initially developed for District Hospitals, it was later extended to:
- Sub-District Hospitals (SDHs)
- Community Health Centers (CHCs)
- Ayushman Arogya Mandir – Urban & Rural Health Centers (AAM-UPHCs, AAM-PHCs, AAM-SHCs)
- Integrated Public Health Laboratories (IPHLs) (launched on June 28, 2024)
- A Virtual Assessment for NQAS certification was introduced to facilitate compliance. As of December 31, 2024, a total of 22,786 health facilities had received NQAS certification.
Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS)
- The Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS) were introduced in 2007 and revised in 2012 and 2022 to define minimum essential services for:
- District & Sub-District Hospitals
- Community Health Centers (CHCs)
- Primary Health Centers (PHCs)
- Sub-Health Centers (SHCs)
- These standards ensure better healthcare delivery, patient safety, and public trust in the system.
- India’s Exit from the High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) Group for Malaria
- India has exited the High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) group, indicating a major reduction in Malaria prevalence.
- The Government of India adopted a comprehensive, multi-pronged approach under the National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme (NVBDCP).
Key Strategies for Malaria Reduction
- Disease Management
- Early case detection through active, passive, and sentinel surveillance
- Complete and effective treatment for all detected cases
- Strengthening referral services for severe malaria cases
- Rapid response mechanisms for malaria outbreaks
- Integrated Vector Management (IVM)
- Indoor Residual Spraying (IRS) in high-risk regions
- Long-Lasting Insecticidal Nets (LLINs) in endemic zones
- Use of larvivorous fish & bio-larvicides in urban malaria-prone areas
- Environmental engineering & source reduction measures to eliminate breeding sites
- Supportive Interventions
- Behavior Change Communication (BCC) to educate communities
- Inter-Sectoral Convergence for coordinated disease control efforts
- Capacity building of health workers and field staff
These strategic efforts have significantly reduced malaria transmission, paving the way for India’s goal of Malaria elimination by 2030
With reference to India’s elimination of Trachoma as a public health problem, consider the following statements:
- India followed the SAFE strategy recommended by WHO, which includes measures like surgery, antibiotics, face washing, and environmental improvement.
- The National Trachomatous Trichiasis (TT-only) survey was conducted under the National Programme for Control of Blindness and Visual Impairment (NPCBVI) to assess prevalence.
- India is the first country in the WHO Southeast Asia Region to eliminate Trachoma as a public health problem.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: WHO’s SAFE strategy (Surgery, Antibiotics, Facial cleanliness, Environmental improvement) was implemented in India.
Statement 2 is correct: The TT-only survey was conducted across 200 endemic districts to determine prevalence.
Statement 3 is incorrect: India is the third country in the WHO Southeast Asia Region (not the first) to eliminate Trachoma as a public health problem.
NBRI Develops GM Cotton Resistant to Pink Bollworm
Development by CSIR-NBRI
- Scientists at the CSIR-National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI) in Lucknow have claimed to develop the world’s first genetically modified (GM) cotton that is completely resistant to the Pink Bollworm (PBW).
Background on GM Cotton in India
- Since the introduction of GM cotton in India in 2002, varieties such as Bollgard 1 and Bollgard 2, developed in collaboration with Monsanto, have been effective against certain bollworm species. However, these varieties have not maintained strong resistance against the Pink Bollworm.
- The CSIR-National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI) is a leading research institution in India that focuses on botanical research and conservation.
Pink Bollworm (PBW): The Pink Bollworm, also known as gulabi sundhi, is a pest that damages the cotton crop by burrowing its larvae into the cotton bolls. This infestation cuts and stains the lint, making it unsuitable for use.
- The Pink Bollworm primarily spreads through the air. Residual infected crops left by farmers in the fields as fuel sources can also harbour PBW larvae, which may later infect future crops.
- To prevent further infestation, farmers are advised not to plant cotton in fields where PBW has been detected for at least one season. Burning crop residues at the earliest and ensuring no mixing between healthy and infected seeds are recommended preventive measures.
Genetically Modified (GM) Crops
- Genetically modified crops are plants that have undergone genetic engineering to alter their DNA. This process is carried out to introduce desirable traits such as pest resistance, herbicide tolerance, improved nutritional content, or increased yield.
- The creation of GM crops involves several steps, including the identification of desired traits, isolation of genes, insertion into the crop genome, and the expression of the trait.
- Techniques used in genetic modification include gene guns, electroporation, microinjection, and agrobacterium-mediated transformation.
- There are different types of genetic modifications, including transgenic (genes introduced from unrelated species), cis-genic (genes transferred within the same species), subgenic (genome editing without foreign gene insertion), and multiple trait integration (combining multiple modifications).
- The main genetically engineered traits in crops include herbicide tolerance (HT), insect resistance (IR), and stacked traits that combine multiple beneficial features.
Genetically Modified Crops in India
- Bt cotton was the first and, to date, the only GM crop to receive commercial approval in India. The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) approved its commercial release in 2002.
- Bt cotton contains two alien genes from the soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), which help the crop develop a protein toxic to the Pink Bollworm.
- Several other GM crops are currently in different stages of development in India, including Bt brinjal and DMH-11 mustard.
Regulatory Framework for GM Crops in India
- The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC), which functions under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC), is responsible for assessing proposals related to the commercial release of GM crops in India.
There are multiple acts and rules that regulate GM crops in India. These include:
- The Environment Protection Act, 1986
- The Biological Diversity Act, 2002
- The Plant Quarantine Order, 2003
- GM policy under the Foreign Trade Policy
- The Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006
- The Drugs and Cosmetics Rule (8th Amendment), 1988
- The development of PBW-resistant GM cotton by CSIR-NBRI marks an important step in India’s agricultural biotechnology sector. It represents a potential solution to a major pest problem while highlighting the ongoing debate over the role of GM crops in India’s agriculture.
Consider the following statements regarding the Pink Bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella):
- It primarily spreads through seed contamination rather than air transmission.
- The infestation damages the cotton lint, making it unfit for use.
- Burning crop residues is a recommended preventive measure against its infestation.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation: The Pink Bollworm primarily spreads through air transmission and through infected crop residues left on fields, not just through seed contamination. The damage to cotton lint and the recommendation to burn infected crop residues are correct
Vikram and Kalpana: ISRO Develops High-speed Microprocessors0
Overview:The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Semiconductor Laboratory (SCL), Chandigarh, have collaboratively developed two state-of-the-art 32-bit microprocessors—Vikram 3201 and Kalpana 3201.
Key Features and Specifications
Vikram 3201
- India’s first fully indigenous 32-bit microprocessor designed for space applications.
- Optimized to function under harsh conditions encountered in launch vehicles.
- Capable of processing 32 bits of data at a time.
- Supports floating-point computations, enhancing its efficiency in numerical and scientific calculations.
- Offers high-level language compatibility, ensuring ease of programming and integration into complex space systems.
Kalpana 3201
- A 32-bit SPARC V8 RISC microprocessor, adhering to the IEEE 1754 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA).
- Designed to be compatible with open-source software toolsets, increasing its adaptability for various applications.
- Successfully tested with flight software, demonstrating its reliability in mission-critical operations.
These indigenous microprocessors mark a significant step towards self-reliance in semiconductor technology, particularly for aerospace and defense applications
: With reference to ISRO’s newly developed Vikram 3201 microprocessor, consider the following statements:
- It is India’s first fully indigenous 64-bit microprocessor designed for space applications.
- It is specifically designed to function in the harsh conditions of launch vehicles.
- It supports floating-point computations, which enhances its numerical processing capabilities.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect because Vikram 3201 is a 32-bit microprocessor, not 64-bit.
- Statement 2 is correct as Vikram 3201 is optimized for harsh launch vehicle conditions.
- Statement 3 is correct since the microprocessor supports floating-point computations, which improve its efficiency in numerical processing.
Progress on GM Food Crops: DBT Official
- India’s bio-economy has seen remarkable growth, playing a crucial role in biotech research, including GM crops.
Key Statistics (as per India Bioeconomy Report 2025):
- Grew 16-fold from $10 billion in 2014 to $165.7 billion in 2024.
- Contributes 4.25% to India’s GDP.
- Achieved a CAGR of 17.9% over the last four years.
Major Sectors in the Bio-Economy:
- Bio-Industry (Enzymes, Biofuels, Bioplastics): 47%
- Biopharma (Medicines, Diagnostics): 35%
- Bio IT & Research Services (Clinical Trials, Contract Research): 9%
- Bio-Agriculture (Including GM crops): 8.1%
State-wise Contribution:
- Maharashtra – $35 billion (21%)
- Karnataka – $32 billion (19%)
- Telangana – $19 billion (12%)
Biotech Startups & Future Growth:
- 10,075 biotech startups in 2024, expected to grow to 22,500 by 2030.
- Estimated to create 35 million jobs by 2030.
Advantages of GM Crops
- Higher Yields – Helps improve agricultural productivity and food security.
- Reduced Pesticide Use – Pest-resistant crops like Bt Cotton lower pesticide dependency.
- Climate Resilience – GM crops with drought and salinity tolerance can withstand extreme conditions.
- Nutritional Enhancement – Biofortified crops like Golden Rice help combat malnutrition.
Challenges & Concerns
- Environmental Impact – GM crops may affect biodiversity, soil health, and pollinators.
- Health Risks – Long-term health effects remain a topic of debate.
- Farmer Dependency – GM seeds are patented, increasing reliance on multinational corporations.
- Ethical & Religious Issues – Some communities oppose genetic modification for cultural reasons.
Regulatory Framework & Policies in India
- Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) – The primary regulatory body for GM crops.
- Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) – Regulates GM food imports.
- Environment Protection Act, 1986 – Covers rules on GM organisms and hazardous microorganisms.
- BioE3 Policy – Aims to enhance biotech applications in agriculture, including GM mustard.
- BioSaarthi Program – Connects biotech startups with international mentors to drive innovation.
Global Perspective on GM Crops
- Countries like the USA, Brazil, and China – Have widely adopted GM crops.
- EU and India – Maintain a cautious approach due to public concerns and regulatory hurdles.
- Scientific Community vs. Activists – While scientists highlight potential benefits, activists warn of risks.
Conclusion
GM crops represent a significant step in agricultural biotechnology, with potential benefits in food security and climate resilience. However, environmental, health, and socio-economic concerns necessitate a balanced regulatory approach. As India advances in its bio-economy, a well-defined policy framework is crucial for sustainable GM crop adoption.
With reference to Genetically Modified (GM) crops, consider the following statements:
- GM crops can be designed to exhibit drought and salinity tolerance through genetic modification.
- Golden Rice is a genetically modified crop that contains enhanced levels of Vitamin D.
- India has commercially approved both Bt Cotton and Bt Brinjal for large-scale cultivation.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation:
- GM crops can indeed be engineered for drought and salinity resistance (Statement 1 is correct).
- Golden Rice is fortified with Vitamin A, not Vitamin D (Statement 2 is incorrect).
- Bt Brinjal was approved in 2010 but later banned, while Bt Cotton remains the only commercially cultivated GM crop in India (Statement 3 is incorrect).
Rise in Tobacco Exports
Context:
- India’s tobacco exports have doubled in the past four years due to increasing global demand and rising prices, driven by declining production in key tobacco-producing nations such as Brazil and Zimbabwe.
Overview of Tobacco Cultivation in India:
- Tobacco is a significant commercial crop cultivated under diverse agro-ecological conditions across India.
- It is a drought-tolerant, hardy, and short-duration crop, making it suitable for cultivation even on marginal lands where other crops may not be profitable.
- Despite occupying only 24% to 0.3% of India’s total arable land, tobacco farming remains a highly labour-intensive and economically rewarding activity compared to food crops.
Major Tobacco-Producing States:
- Andhra Pradesh
- Karnataka
- Gujarat
- Uttar Pradesh
- Tamil Nadu
- Bihar
- West Bengal
Types of Tobacco Grown in India:
- Flue-Cured Virginia (FCV) – Used primarily in cigarettes.
- Bidi Tobacco – Used in the production of bidis.
- Cigar Filler Tobacco – Used for making cigars.
- Hookah and Chewing Tobacco – Consumed in various forms, including gutkha and khaini.
Production and Global Standing:
- India is the second-largest producer of tobacco globally, following China.
- It is also the third-largest exporter, after Brazil and China, playing a crucial role in the global tobacco trade.
With reference to tobacco cultivation in India, consider the following statements:
- Tobacco is a highly water-intensive crop and requires heavy irrigation for optimal growth.
- India is the largest producer and exporter of tobacco in the world.
- The cultivation of Flue-Cured Virginia (FCV) tobacco is primarily concentrated in Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (c) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Tobacco is a drought-tolerant crop, meaning it does not require heavy irrigation. It can grow even in marginal lands where other crops may not thrive.
Statement 2 is incorrect: While India is the second-largest producer of tobacco after China, it is the third-largest exporter, following Brazil and China.
Statement 3 is correct: Flue-Cured Virginia (FCV) tobacco, which is used in cigarettes, is predominantly cultivated in Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka.
Gujarat Achieves 95% of NITI Aayog’s TB-Free Target
Key Achievements
- Gujarat was assigned a target of 145,000 TB patient registrations and successfully registered 137,929 cases.
- A total of 124,581 patients completed treatment, achieving a 90.52% treatment completion rate.
- Treatment facilities were provided to 131,501 registered TB patients.
- Financial Assistance – Nikshay Poshan Yojana (NPY)
- Each notified TB patient receives ₹1,000 per month during treatment.
- Assistance is provided in cash or in-kind to ease the financial burden.
Nutritional Support Initiatives
- A total of 10,682 Nikshay Mitras have been registered on the Nikshay portal.
- A total of 349,534 nutrition kits have been distributed to TB patients to ensure proper dietary support.
100-Day Intensive TB Eradication Campaign
- Launched in December 2024 to enhance early detection and treatment.
- Covers 16 districts and four municipal corporations.
- As of March 20, 2025, 35.75 lakh individuals have been screened, leading to the detection of 16,758 new TB patients.
Conclusion
Gujarat’s initiatives in early detection, financial support, and nutritional assistance are significantly contributing to TB elimination.
Consider the following statements regarding the Nikshay Poshan Yojana (NPY):
- It provides direct financial assistance to tuberculosis (TB) patients for their nutritional support.
- The financial assistance under the scheme is ₹500 per month for every TB patient.
- It is part of the National Tuberculosis Elimination Program (NTEP).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 1 and 3 only
(C) 2 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (B) 1 and 3 onlyExplanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Nikshay Poshan Yojana (NPY) provides financial assistance to TB patients to help meet their nutritional requirements.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The financial assistance provided is ₹1,000 per month, not ₹500.
- Statement 3 is correct: The scheme is part of the National Tuberculosis Elimination Program (NTEP).
What is Noma?
- Noma, also known as cancrum oris, is a severe gangrenous disease that primarily affects children between the ages of 2 to 6 years.
- In December 2023, the World Health Organization (WHO) officially classified it as a neglected tropical disease (NTD) due to its high fatality rate and lack of global attention.
- While noma is most prevalent in sub-Saharan Africa, cases have also been reported in parts of Asia and the Americas.
- The disease progresses rapidly, leading to severe facial disfigurement, lifelong disabilities, and profound social stigma.
Pathogenesis and Risk Factors
- Noma is caused by a non-specific polymicrobial infection, involving a combination of bacteria and fungi. It typically develops in malnourished children living in extreme poverty, particularly in areas with poor sanitation and inadequate healthcare access. The major risk factors include:
- Severe malnutrition, especially during vulnerable periods such as weaning.
- Poor oral hygiene, which allows bacteria to thrive.
- Underlying infections, including measles, malaria, and HIV, that weaken the immune system.
- Environmental factors, such as overcrowding, poor living conditions, and lack of clean water.
- Due to these conditions, children with compromised immunity are particularly susceptible to noma.
Clinical Stages of Noma
The WHO categorizes noma into five progressive clinical stages:
- Stage 0 – Simple gingivitis: Early gum inflammation without visible ulcers.
- Stage 1 – Acute necrotising gingivitis: Rapid bacterial infection causing gum tissue destruction.
- Stage 2 – Oedema: Swelling of the face and mouth, leading to increased tissue damage.
- Stage 3 – Gangrene: Severe tissue necrosis with facial disintegration.
- Stage 4 – Scarring: Healing process begins but results in severe disfigurement.
- Stage 5 – Sequelae: Long-term complications, including difficulty in eating, speaking, and social exclusion.
The disease typically begins with a minor oral ulcer but can escalate rapidly, causing irreversible damage within days if untreated.
Treatment and Management
- Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for saving lives. Treatment strategies include:
- Antibiotic therapy (e.g., penicillin and metronidazole) to combat bacterial infection.
- Nutritional support to address severe malnutrition.
- Oral hygiene improvement through antiseptic mouth rinses.
- Reconstructive surgery for survivors with facial disfigurements.
- Despite treatment, mortality rates remain alarmingly high, with only 15% of affected children surviving the acute phase. Survivors require extensive surgical reconstruction and long-term rehabilitation to regain basic functions like eating and speaking.
Global Response and Challenges
Estimating the true burden of noma is difficult due to:
- High case fatality rates before medical intervention.
- Weak healthcare infrastructure in affected regions.
- Social stigma, which discourages families from seeking medical help.
- WHO’s last recorded estimate (1998) suggested 140,000 cases per year, but the actual prevalence remains unknown. In 2012, the United Nations Human Rights Council recognized the neglect of noma as a potential violation of children’s rights, highlighting the need for global action.
Efforts to combat noma focus on:
- Food security and malnutrition prevention.
- Vaccination programs against measles and other infections.
- Early detection and community education on oral hygiene and sanitation.
- Future Strategies for Eradication
- The WHO aims to integrate noma into existing healthcare frameworks, ensuring:
- Stronger health systems for early detection and treatment.
- Training programs for healthcare workers in affected regions.
- Community awareness campaigns to reduce stigma and promote hygiene.
Noma remains a critical public health challenge, particularly in poverty-stricken regions. Addressing it requires global advocacy, increased funding, and policy-level interventions. Only through sustained efforts can this preventable yet deadly disease be effectively managed and ultimately eliminated.
Consider the following statements regarding Noma (Cancrum Oris):
- It is a viral disease that primarily affects children between the ages of 5 to 10 years.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) classified it as a neglected tropical disease in December 2023.
- It predominantly affects individuals in high-income countries with access to advanced healthcare.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Noma is not a viral disease; it is a polymicrobial bacterial infection that rapidly destroys facial tissues. It primarily affects children between 2 to 6 years of age, not 5 to 10 years.
- Statement 2 is correct: The WHO classified Noma as a neglected tropical disease (NTD) in December 2023, highlighting its severity and lack of global attention.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: Noma is not prevalent in high-income countries. It primarily affects sub-Saharan Africa, parts of Asia, and the Americas, where malnutrition, poor hygiene, and weak healthcare infrastructure contribute to its spread.
AIIMS New Delhi and SAMEER sign landmark MOU to enhance innovation in medical electronics and healthcare technology
Consider the following statements regarding the MoU between SAMEER and AIIMS, New Delhi:
- SAMEER is an autonomous institution under the Ministry of Science and Technology.
- The MoU focuses on developing high-field and low-field MRI/NMR systems for medical applications.
- The Indigenous Magnetic Resonance Imaging (IMRI) mission is being implemented under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- One of the key objectives of the MoU is to facilitate clinical validation of an indigenous 1.5 Tesla MRI system.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 4 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- SAMEER is an autonomous institution under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), not the Ministry of Science and Technology. (Statement 1 is incorrect)
- The MoU focuses on developing high-field/low-field MRI/NMR systems for medical applications. (Statement 2 is correct)
- The IMRI mission is sponsored by MeitY, not the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. (Statement 3 is incorrect)
- A key objective of the MoU is clinical validation of the indigenous 1.5 Tesla MRI system. (Statement 4 is correct)
Consider the following statements regarding Noma (Cancrum Oris):
- It is a viral disease that primarily affects children between the ages of 5 to 10 years.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) classified it as a neglected tropical disease in December 2023.
- It predominantly affects individuals in high-income countries with access to advanced healthcare.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Noma is not a viral disease; it is a polymicrobial bacterial infection that rapidly destroys facial tissues. It primarily affects children between 2 to 6 years of age, not 5 to 10 years.
- Statement 2 is correct: The WHO classified Noma as a neglected tropical disease (NTD) in December 2023, highlighting its severity and lack of global attention.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: Noma is not prevalent in high-income countries. It primarily affects sub-Saharan Africa, parts of Asia, and the Americas, where malnutrition, poor hygiene, and weak healthcare infrastructure contribute to its spread.
MRI Technology
In News
- India has successfully developed its first indigenously manufactured MRI machine, which will undergo trial runs at AIIMS Delhi.
About MRI Technology
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive medical imaging technique that provides highly detailed images of internal organs, tissues, and structures, particularly the brain, spinal cord, muscles, and joints.
Key Features of MRI Technology
- Radiation-Free Imaging: Unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it safer for repeated diagnostic use.
- High-Resolution Scanning: Utilizes powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to generate precise anatomical images.
- Wide Medical Applications: Essential for detecting neurological disorders, musculoskeletal conditions, and cardiovascular diseases.
Consider the following statements about the applications of MRI technology:
- Functional MRI (fMRI) measures changes in blood oxygenation in the brain.
- MRI is ineffective in imaging soft tissues and is primarily used for bone scans.
- MRI contrast agents enhance the visibility of certain tissues by altering their magnetic properties.
- MRI is widely used for early detection of neurodegenerative disorders.
Which of the above statements are correct?
- A) 1 and 3 only
B) 2 and 4 only
C) 1, 3, and 4 only
D) All of the above
Answer: C) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Functional MRI (fMRI) detects changes in blood oxygenation levels, making it useful for studying brain activity.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: MRI is highly effective for imaging soft tissues (brain, muscles, spinal cord) but less effective for bones due to low hydrogen content.
- Statement 3 is correct: MRI contrast agents, like Gadolinium-based compounds, improve visibility by affecting magnetic properties.
- Statement 4 is correct: MRI is widely used for diagnosing Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and multiple sclerosis at early stages.
Lyme Disease Treatment Breakthrough
- Scientists have identified a critical enzyme, BbLDH (Borrelia burgdorferi lactate dehydrogenase), as a key factor in the survival and infectivity of Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacterium responsible for Lyme disease.
- This discovery presents a promising avenue for developing targeted treatments against Lyme disease and other tick-borne infections.
About Lyme Disease
- Lyme disease, or Lyme borreliosis, is a bacterial infection caused by Borrelia burgdorferi.
- It is transmitted to humans via bites from infected blacklegged ticks (Ixodes scapularis in North America and Ixodes ricinus in Europe).
- The disease is prevalent in the northeastern and midwestern United States, as well as parts of Europe and Asia.
- Symptoms include a bull’s-eye rash (erythema migrans), fever, fatigue, and headaches. If untreated, it can lead to severe complications, affecting the joints, heart, and nervous system.
Role of BbLDH in Borrelia burgdorferi
- BbLDH (lactate dehydrogenase) is an essential enzyme that facilitates the bacterium’s metabolic processes.
- Unlike most organisms, B. burgdorferi does not require thiamin (vitamin B1) for metabolism. Instead, BbLDH is critical for converting pyruvate to lactate, which helps maintain the NADH/NAD+ balance—a process vital for bacterial growth and infectivity.
Research Findings & Implications
- Scientists employed genetic, biochemical, and structural analyses, including X-ray crystallography, to determine BbLDH’s function.
- Loss-of-function studies demonstrated that disrupting BbLDH impairs the bacterium’s ability to survive and infect hosts, confirming its indispensable role in B. burgdorferi’s life cycle.
Therapeutic Potential of BbLDH Inhibitors
- High-throughput screening has identified several promising BbLDH inhibitors that could form the basis of genus-specific treatments.
- Unlike broad-spectrum antibiotics, these inhibitors specifically target Borrelia burgdorferi, reducing the risk of disrupting beneficial microbiota.
- The lead researcher, Chunhao Li, emphasized that BbLDH’s unique biochemical properties make it an optimal drug target for Lyme disease therapeutics.
Broader Applications & Future Research
- The study not only enhances our understanding of Lyme disease but also provides insights into LDH-dependent metabolic pathways in other tick-borne pathogens.
- This could pave the way for innovative treatments for a range of vector-borne diseases, strengthening global public health efforts against tick-borne infections.
With reference to Lyme disease, consider the following statements:
- It is caused by a virus and transmitted through mosquito bites.
- The disease is endemic only to North America and has no reported cases in Europe or Asia.
- If left untreated, Lyme disease can affect multiple organ systems, including the nervous system and heart.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Lyme disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, not a virus. It is transmitted through infected blacklegged tick bites, not mosquitoes.
Statement 2 is incorrect: While Lyme disease is prevalent in North America, it is also reported in Europe and parts of Asia.
Statement 3 is correct: If left untreated, the disease can lead to complications affecting the nervous system, joints, and cardiovascular system.
The Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) in India
Concerns Among Medical Professionals
- Some doctors experience ethical discomfort in performing abortions, particularly in later stages of pregnancy.
- The debate over fetal viability becomes more intense as gestation advances, raising legal and moral dilemmas.
Understanding Fetal Viability
- Fetal viability refers to the stage at which a fetus can survive outside the womb.
- There is no universally agreed-upon moment of viability, making it a contentious issue in ethical and legal discussions.
- As pregnancy progresses, the fetus’s right to life is perceived to strengthen, intensifying debates on abortion laws.
India’s Legal Framework on Abortion
Evolution of Abortion Laws
- Before 1971, abortion was regulated under the Indian Penal Code (IPC), primarily criminalizing the procedure, except when performed in good faith to save the woman’s life.
- The IPC did not distinguish between wanted and unwanted pregnancies, creating significant barriers to safe abortion access.
The Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act, 1971
- Enacted as a health measure to decriminalize abortion in specific cases under the supervision of registered medical practitioners.
Key provisions:
- Abortions permitted up to 20 weeks under defined conditions.
- Up to 12 weeks: Requires approval from one doctor.
- 12 to 20 weeks: Requires approval from two doctors.
- The MTP (Amendment) Act, 2021
- Extended abortion limit to 24 weeks for specific categories, including:
- Survivors of rape and incest.
- Women experiencing a change in marital status during pregnancy.
- Other vulnerable women (e.g., minors, differently-abled women).
- The term “any married woman or her husband” was replaced with “any woman or her partner”, recognizing pregnancies outside marriage.
Beyond 24 weeks:
- Requires approval from a medical board in each district.
- Permitted only in cases of substantial fetal abnormalities.
Arguments Supporting the MTP Act
- Bodily Autonomy & Reproductive Rights
- Women should have the right to make decisions regarding their own bodies.
- The Supreme Court has upheld reproductive rights as part of personal liberty under Article 21.
Protection of Physical Health
- Abortion may be essential if continuing the pregnancy threatens the woman’s life or health (e.g., gestational diabetes, eclampsia).
Mental Health Considerations
- Pregnancy may worsen pre-existing mental health conditions like depression, anxiety, or postpartum psychosis.
- Access to abortion can prevent psychological distress.
Non-Viable Fetuses
- Abortion may be justified when fetal congenital abnormalities are incompatible with life, preventing prolonged suffering.
Unplanned Pregnancies
- Women facing economic hardships or social challenges should have the choice to terminate an unintended pregnancy.
Reduction in Unsafe Abortions
- Legal abortion access minimizes unsafe procedures that pose serious health risks, reducing maternal mortality.
Arguments Against the MTP Act
Right to Life of the Fetus
- The fetus’s right to life is considered to strengthen with gestational age, making abortion ethically contentious.
Psychological Consequences for Women
- Some women experience long-term emotional distress, including guilt, regret, and trauma post-abortion.
Concerns Over Non-Medical Abortions
- Fear that abortion may be used as a form of contraception, rather than a medically necessary intervention.
Risk of Misuse
- Potential for sex-selective abortions, despite laws prohibiting the practice.
- Loopholes may allow abortion for reasons unrelated to medical necessity.
Impact on Societal and Cultural Norms
- Widespread abortion may alter societal values regarding family and life.
- Many cultures consider abortion morally unacceptable and contrary to religious beliefs.
Way Forward
- Enhancing Access to Safe Abortion Services
- Increase availability of MTP pills and reduce administrative hurdles.
- Ensure that abortion is treated as a healthcare service rather than an exceptional legal provision.
- Strengthening Sex Education & Awareness
- Comprehensive sexual education can help reduce unwanted pregnancies.
- Address stigma surrounding abortion and reproductive rights.
- Empathy in Medical Decision-Making
- Healthcare professionals should be encouraged to approach abortion cases with compassion and understanding.
- Particularly important in late-term abortions, where ethical conflicts intensify.
- By balancing women’s reproductive rights, fetal viability concerns, and ethical considerations, India can move towards a more inclusive and comprehensive approach to abortion laws.
Consider the following statements regarding the concept of fetal viability:
- It refers to the stage at which a fetus can survive outside the mother’s womb.
- It has a universally accepted gestational threshold.
- It plays a significant role in determining the legality of abortion in many countries.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Fetal viability refers to the ability of a fetus to survive outside the womb, usually considered to be around 24-28 weeks of gestation, but this varies with medical advancements.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: There is no universally accepted gestational threshold for viability, as it depends on medical technology and healthcare access.
- Statement 3 is correct: The concept of fetal viability significantly influences legal abortion frameworks, as seen in India’s MTP Act and global
1st Glacier Declared Dead from Climate Change
- Satellite imagery spanning more than three decades has confirmed the disappearance of Iceland’s Okjökull Glacier. It was the first glacier to be officially declared dead due to human-induced climate change in 2014.

About Okjökull Glacier
Okjökull Glacier was located around the summit crater of Ok, a 1,200-meter-high shield volcano, approximately 71 kilometers northwest of Reykjavík, Iceland. Historically, it was a dome-shaped glacier, but climate change has led to its complete disappearance.
Global Efforts to Memorialize Vanishing Glaciers
- In 2023, Iceland established the world’s first iceberg graveyard, commemorating 15 glaciers listed as either dead or critically endangered on the Global Glacier Casualty List. This list includes Anderson Glacier in Washington State, USA, which was declared dead in 2015, making it the first such glacier loss in the United States.
United Nations Initiatives
- Recognizing the urgent need for action, the United Nations declared 2025 as the International Year of Glaciers’ Preservation. March 21st was designated as World Day for Glaciers, starting from 2025.
- The Cryosphere: Earth’s Frozen Reservoir
- The cryosphere refers to all frozen water on Earth. The term derives from the Greek word kryos, meaning frost or ice cold. It includes glaciers, ice sheets, ice shelves, icebergs, sea ice, lake ice, river ice, permafrost, snow cover, and solid precipitation.
Major Ice Sheets on Earth
- The Greenland Ice Sheet and the Antarctic Ice Sheet contain more than 70 percent of the world’s freshwater ice. Ice on these sheets exceeds two kilometers in thickness.
Key Facts About the Cryosphere
- Seventy percent of Earth’s freshwater exists as snow or ice. Ten percent of the Earth’s land area is covered by glaciers or ice sheets.
- Hindu Kush Himalaya:The Water Tower of Asia
- The Hindu Kush Himalayan region spans approximately 3,500 kilometers across Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Nepal, Myanmar, and Pakistan. It is known as the Water Tower of Asia because it is the source of ten major river systems, including the Ganga, Brahmaputra, Indus, Yangtze, and Mekong.
- These rivers provide freshwater to 240 million people directly in the region and support one-fourth of the world’s population through their basins.
- Melting Crisis in the Hindu Kush Himalaya
- The Hindu Kush Himalayan cryosphere is warming at twice the global average rate. This increases the risk of glacial lake outburst floods, which pose severe hazards to downstream communities.
Role of the Cryosphere in Climate and Ecology
The cryosphere reflects sunlight through the albedo effect, helping regulate Earth’s temperature. It stores freshwater in glaciers and ice sheets, controlling sea levels. It plays a vital role in the global water cycle by feeding rivers and groundwater through seasonal melting. It provides a habitat for unique species such as polar bears, penguins, and snow leopards. It acts as an indicator of climate change, as it is highly sensitive to temperature variations.
Threats to the Cryosphere and Global Consequences
Global warming is causing widespread ice loss, accelerating the melting of glaciers, ice caps, and sea ice. Melting ice is contributing to rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities worldwide. Habitat loss is affecting marine ecosystems dependent on sea ice.
Permafrost thawing is releasing stored methane and carbon dioxide, worsening global warming. Changing snow and ice patterns are disrupting water availability for agriculture, hydropower, and human consumption.
Global Efforts to Protect the Cryosphere
- The Paris Agreement of 2015 aims to limit global temperature rise to below two degrees Celsius, preferably 1.5 degrees Celsius, to prevent further cryosphere degradation. The International Cryosphere Climate Initiative was formed during COP-15 in 2009 to work with governments and scientists to preserve the cryosphere.
- The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change highlights the urgent need for mitigation and adaptation strategies. The National Mission for Sustaining the Himalayan Ecosystem is part of India’s National Action Plan on Climate Change and aims to protect the Himalayan ecosystem.
- The World Meteorological Organization’s CryoNet is a global monitoring system tracking ice mass loss and cryosphere changes. The Arctic Council is a collaborative forum for Arctic nations to address climate-related issues in the polar region. Global ice monitoring programs such as the Global Cryosphere Watch and the European Space Agency’s CryoSat Mission provide data on ice loss.
Conclusion
The cryosphere plays a critical role in regulating global climate, providing freshwater, and sustaining biodiversity. Its rapid degradation due to climate change poses severe threats to ecosystems, human populations, and global stability. Preserving the cryosphere is essential for ensuring a sustainable future for all life on Earth.
Consider the following statements regarding the Okjökull Glacier:
- It was the first glacier in the world to be officially declared dead due to anthropogenic climate change.
- It was a part of the Greenland Ice Sheet before completely melting in 2014.
- The disappearance of Okjökull led to the formation of the world’s first iceberg graveyard in Iceland.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (c) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct. Okjökull was the first glacier to be officially declared dead due to climate change in 2014.
Statement 2 is incorrect. It was not part of the Greenland Ice Sheet but was a small glacier in Iceland, located on the Ok volcano.
Statement 3 is correct. Iceland created the world’s first iceberg graveyard in 2023 to memorialize glaciers that have vanished or are critically endangered.
UN World Water Development Report 2025 – Mountains and Glaciers
Key Findings
Accelerated Glacier Melt:
- Glaciers are melting at an unprecedented rate, with significant mass loss in recent years.
- Over 9,000 billion tonnes of ice have been lost since 1975—equivalent to an ice block the size of Germany.
- Impurities like black carbon from wildfires and dust storms are intensifying the melting process by absorbing more solar radiation.
Permafrost Thawing:
- Rising temperatures are causing permafrost to melt, releasing organic carbon into the atmosphere and worsening climate change.
- Destabilized slopes increase the risk of landslides and other natural disasters.
Decline in Snow Cover:
- Snow cover in mountain regions has decreased, particularly during spring and summer.
- Between 1979 and 2022, there has been a 79% global declinein snow cover.
Impacts & Concerns
Erratic Water Flow & Flooding Risks:
- Increased risk of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs)—responsible for over 12,000 deaths in the past 200 years.
Sea Level Rise Contribution:
- Glacier melt accounts for 25-30% of global sea level rise, threatening millions worldwide.
Way Forward & Recommendations
Mountains as Water Towers:
- Covering 33 million sq km, mountain regions sustain nearly 2 billion peopleby providing freshwater.
Policy & Awareness:
- Urgent need for resource mobilizationand strong policy frameworks to mitigate climate impacts.
- Increased awareness and proactive action required to protect mountain ecosystemsand downstream communities.
With reference to the United Nations World Water Development Report 2025, consider the following statements:
- The report states that glaciers have lost over 9,000 billion tonnes of ice since 1950.
- Black carbon from wildfires and dust storms can accelerate glacier melting by increasing solar radiation absorption.
- The report highlights that permafrost thawing is reducing atmospheric carbon levels, thereby mitigating climate change.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The report highlights that glaciers have lost over 9,000 billion tonnes of ice since 1975, not 1950.
Statement 2 is correct: Black carbon and dust can accelerate glacier melting by increasing the absorption of solar radiation.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Permafrost thawing releases organic carbon into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change rather than mitigating it.
Eucalyptus
Background
- Eucalyptus, a fast-growing tree native to Australia, was introduced to India by the British in the 1840sfor timber production.
- In Karnataka, large-scale eucalyptus plantations were established between the 1960s and 1980sto support the timber and paper industries.
- However, environmental concerns led to a ban on eucalyptus cultivation in 2017, though a 2019 court staytemporarily halted its enforcement.

Environmental Concerns
- Groundwater Depletion– Eucalyptus has a high water demand, which disrupts local hydrological cycles and depletes groundwater levels.
- Soil Degradation & Loss of Biodiversity– The tree exhibits allelopathy (chemical suppression of other plant growth), reducing soil fertility and harming native vegetation.
- Impact on Grassland Ecosystems– Large-scale plantations encroach upon natural grasslands, threatening species such as:
- Blackbucks(Antilope cervicapra)
- Lesser Floricans(Sypheotides indicus)
- Great Indian Bustards(Ardeotis nigriceps)
Future Outlook
- Grasslands and savannah ecosystemsplay a crucial role in biodiversity conservation and rural livelihoods.
- Karnataka aims to balance economic developmentwith environmental sustainability, serving as a model for sustainable ecological practices in India.
Consider the following statements regarding Eucalyptus cultivation in Karnataka:
- The British introduced eucalyptus to India in the 19th century primarily for its medicinal properties.
- Karnataka banned eucalyptus plantations in 2017 due to their adverse environmental effects.
- Eucalyptus trees contribute significantly to groundwater recharge due to their deep-rooted structure.
- Eucalyptus exhibits allelopathy, which negatively impacts soil fertility and biodiversity.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect – The British introduced eucalyptus in the 1840s for timber production, not for medicinal purposes.
Statement 2 is correct – Karnataka banned eucalyptus cultivation in 2017 due to environmental concerns.
Statement 3 is incorrect – Eucalyptus is known for high water consumption rather than contributing to groundwater recharge.
Statement 4 is correct – The tree releases chemical compounds that inhibit the growth of other plants (allelopathy), reducing soil fertility and biodiversity.
Anthurium Flowers
In News
- Mizoram marked a significant milestone in agro-based exports from the North Eastern Region (NER) by exporting its first consignment of Anthurium flowersto Singapore.

About Anthurium Flowers
- Scientific Name:Anthurium
- Geographical Distribution:
- Native to the Americas, spanning from northern Mexico to northern Argentina, including the Caribbean.
- In India, it thrives in the Northeastern states, particularly Mizoram, due to its favorable climate.
- Other key cultivation regions include Tamil Nadu (21%), Karnataka (16%), Madhya Pradesh (14%), and West Bengal (12%).
Botanical & Morphological Features
- A herbaceousplant that grows as an epiphyte (on other plants) or terrestrially.
- Recognized by its spadix(central spike) and a colorful spathe (leaf-like bract) in shades of red, pink, orange, and more.
- Contains calcium oxalate crystals, making its sap an irritantto skin and eyes.
Economic & Cultural Significance
Exports:
- Contributes to India’s floriculture exports, valued at USD 86.62 million in FY 2023–24.
- Major importers include the USA, Netherlands, UAE, UK, and Canada.
Tourism & Cultural Promotion:
- Mizoram hosts the annual “Anthurium Festival”, which promotes tourism, local enterprises, and the commercial value of the flower.
Livelihood Support:
- A crucial source of rural income, particularly benefiting women farmersand cooperative societies in the Northeast.
Consider the following statements regarding Anthurium flowers:
- Anthurium is a species native to Southeast Asia and is widely cultivated in the Indian subcontinent.
- In India, Mizoram is the leading producer of Anthurium flowers due to its suitable climatic conditions.
- Anthurium plants grow exclusively as terrestrial plants and do not exhibit epiphytic characteristics.
- The sap of Anthurium contains calcium oxalate crystals, which can be an irritant to human skin and eyes.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect – Anthurium is native to the Americas (from northern Mexico to northern Argentina), not Southeast Asia.
Statement 2 is correct – Mizoram is a major cultivator of Anthurium in India, supported by its favorable climatic conditions.
Statement 3 is incorrect – Anthurium plants can grow both terrestrially and epiphytically.
Statement 4 is correct – The plant contains calcium oxalate crystals, which can cause skin and eye irritation.
Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary
Context:
- The Punjab government recently informed the Supreme Court (SC) that the Eco-Sensitive Zone (ESZ) around Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary would be limited to 100 meters for the Nayagaon municipal committee instead of the previously. proposed 1 to 3 km.

About Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Location: Situated in Chandigarh, near the renowned Sukhna Lake, at the foothills of the Shivalik range.
- Origin of Sukhna Lake:
- Created in 1958 by the famous architect Le Corbusier.
- Formed by diverting the Sukhna Choe, a seasonal stream originating from the Shivalik hills.
Establishment:
- The sanctuary was officially notified in 1998.
- Developed as part of afforestation efforts for soil conservation around Sukhna Lake.
- Geography & Soil Characteristics:
- Covers 2,600 hectares.
- Comprises sandy soil from the Shivalik hills, interspersed with clay pockets.
- Geographically unstable and prone to soil erosion, particularly during the monsoon season.
- The sanctuary has around 150 small and large water bodies, including Sukhna Lake, forming its catchment area.
Ecological Features:
- Vegetation & Ecosystem
- The sanctuary comprises a mosaic of forests, grasslands, and wetlands, with Sukhna Lake serving as a vital component of its ecosystem.
- Flora
Notable tree species:
- Khair (Acacia catechu)
- Phulai (Acacia modesta)
- Kikar (Acacia nilotica)
- Shisham (Dalbergia sissoo)
Other species:
- Moonj (Saccharum munja) – A grass species.
- Amaltas (Cassia fistula) – Indian Laburnum with medicinal and ornamental value.
- Jhingan (Lannea coromandelica) – Used in traditional medicine.
- Amla (Phyllanthus emblica) – Indian Gooseberry.
- Rati, Vasaka – Medicinal plants contributing to the region’s biodiversity.
Fauna
Mammals:
- Squirrel
- Common Mongoose
- Indian Hare
- Porcupine
- Jungle Cat
- Jackal
- Wild Boar
- Avian Diversity:
- Peacock
- Hill Myna
- Jungle Crow
- Black Drongo
- Parrots
- Doves
- Seasonal migratory birds also visit the sanctuary.
Significance & Concerns:
Eco-Sensitive Zone (ESZ) Reduction:
- The Punjab government’s decision to limit the ESZ to 100 meters in Nayagaon raises concerns about urban encroachment and its impact on the sanctuary’s ecosystem.
- Originally, an ESZ of 1 to 3 km was proposed to buffer the sanctuary from human activities.
Environmental Challenges:
- Soil erosion and runoff threaten the stability of the area.
- Increasing urbanization and deforestation pose risks to water bodies and wildlife habitats.
Conservation Outlook:
- Need for balanced urban planning while ensuring habitat protection.
- Strengthening afforestation and soil conservation measures to maintain ecological integrity.
- The Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary plays a critical role in maintaining regional biodiversity, and decisions regarding its Eco-Sensitive Zone should prioritize long-term environmental sustainability over short-term urban expansion.
With reference to the Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary, consider the following statements:
- It was established in 1958 as a protected area for wetland conservation.
- The sanctuary is located at the foothills of the Shivalik range and is prone to soil erosion.
- Sukhna Lake was artificially created by diverting a seasonal stream.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- The sanctuary was established in 1998, not 1958(Statement 1 is incorrect).
- It is located in the Shivalik foothills, prone to soil erosion(Statement 2 is correct).
- Sukhna Lake was artificially createdin 1958 by diverting Sukhna Choe, a seasonal stream (Statement 3 is correct).
Urban Heat Island (UHI)
- The Telangana Socio-Economic Outlook 2025report highlights that Hyderabad is experiencing intensified nighttime heat stress due to the Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect.
Understanding the Urban Heat Island Effect
- The Urban Heat Island (UHI) effectis a climatic phenomenon where urban areas experience significantly higher temperatures compared to their surrounding rural regions. This temperature disparity is primarily driven by human activities and urban development that modify land surfaces and atmospheric conditions.
Key Causes of the UHI Effect:
- Loss of Green Spaces & Natural Soils
- Urbanization reduces vegetation cover(trees, parks, and grasslands), leading to diminished shading and evapotranspiration, a natural cooling process.
- Building & Infrastructure Density
- Materials like concrete, asphalt, and metalabsorb and store more heat than natural surfaces, retaining warmth for longer durations.
Urban Layout & Street Design
- Narrow streets and high-rise buildingscreate “urban canyons” where heat is trapped and less effectively dissipated, exacerbating localized warming.
- Heat Emissions from Human Activities
- Vehicles, air conditioners, industrial operations, and power generationcontribute to increased heat output.
- Greenhouse gases (e.g., CO₂)trap this heat, further amplifying the warming effect.
Consequences of the UHI Effect:
- Increased nighttime temperatures—urban areas cool down more slowly than rural surroundings.
- Temperature differentials can reach up to 12°C at night, intensifying heat stressand impacting public health.
- Exacerbates global warming, making cities even hotter.
Why is it Called an “Urban Heat Island”?
- The term originates from temperature distribution maps, where urban zones appear as “hot islands”amid cooler rural surroundings, resembling an island of heat in a “sea” of lower temperatures.
- The UHI effect, when combined with climate change, contributes to rising global temperaturesand urban microclimates, making sustainable urban planning crucial for mitigating heat stress in cities.
Consider the following statements regarding the Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect:
- It is caused solely by industrial emissions and vehicular pollution.
- Urban areas tend to remain warmer than rural areas, especially at night.
- The phenomenon is exclusive to tropical and subtropical cities.
- Evapotranspiration plays a crucial role in mitigating UHI effects.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: UHI is caused by multiple factors including reduced green cover, heat-retaining infrastructure, and human activitieslike air conditioning, industrial emissions, and vehicular heat emissions. It is not solely due to pollution.
- Statement 2 is correct: Urban areas absorb and retain heatduring the day and release it slowly at night, leading to higher nighttime temperatures compared to rural areas.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: UHI is not limited to tropical regions; it can occur in temperate, arid, and even cold regions, depending on urbanization patterns.
- Statement 4 is correct: Evapotranspiration (moisture loss from plants and soil)cools the air, helping to mitigate UHI intensity.
Blue Flag Tag
In News:
- Rushikonda Beach in Visakhapatnamhas regained its prestigious Blue Flag certification, reaffirming its status as an environmentally sustainable and well-maintained coastal destination. With this, India now has 13 Blue Flag-certified beaches.
About the Blue Flag Certification:
- The Blue Flagis a globally recognized eco-label awarded to beaches, marinas, and sustainable boating tourism operators that meet stringent environmental, safety, and cleanliness standards.
Key Facts:
- Administered by:Foundation for Environmental Education (FEE), headquartered in Copenhagen, Denmark.
- Significance:Recognized as a symbol of environmental excellence, ensuring cleanliness, safety, and sustainability.
- Criteria for Certification:
A beach or marina must comply with 33 strict parametersacross four major categories: - Environmental Education and Information– Spreading awareness about coastal conservation.
- Water Quality– Ensuring clean and pollution-free seawater.
- Environmental Management– Sustainable waste disposal and biodiversity conservation.
- Safety and Services– Adequate infrastructure, lifeguards, and emergency response systems.
This achievement reinforces India’s commitment to promoting sustainable coastal tourism and preserving its natural marine ecosystems.
With reference to the Blue Flag Certification, consider the following statements:
- It is an international eco-label awarded exclusively to marine protected areas.
- The certification is administered by the International Maritime Organization (IMO).
- A beach must meet 33 criteria across multiple categories to receive this certification.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Blue Flag is awarded to beaches, marinas, and sustainable boating tourism operators, not just marine protected areas.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The certification is administered by the Foundation for Environmental Education (FEE), headquartered in Denmark, not by the IMO.
Statement 3 is correct: To qualify for the Blue Flag, a beach/marina must satisfy 33 environmental, safety, and management criteria.
Permafrost Thawing in Kashmir Himalaya
Context
- A recent study has highlighted the escalating environmental risks associated with the melting permafrost in the Kashmir Himalaya, raising concerns over its impact on infrastructure, water resources, and natural hazards.
What is Permafrost?
- Permafrost refers to ground that remains completely frozen (≤ 0°C) for at least two consecutive years.
- It is predominantly found in high-altitude regionsand Earth’s polar latitudes (near the North and South Poles).
Major Concerns
- Infrastructure Damage: Thawing permafrost can weaken foundationsof roads, hydropower projects, and other built structures.
Increased Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs):
- In Jammu & Kashmir, 332 proglacial lakeshave been identified.
- Of these, 65 pose significant GLOF risks, which could worsen with permafrost degradation.
- Potential Impacts
Human Activities as a Catalyst:
- Deforestation, land-use changes, and infrastructure expansion(roads, dams, and tourism) can accelerate permafrost degradation.
Water Cycle Disruptions:
- Permafrost plays a key role in maintaining groundwater and river base flow.
- Its thawing could significantly alter water availability, though research on this remains limited.
Recommendations for Mitigation
- Infrastructure Planning: Future development projects should incorporate permafrost vulnerability assessments.
- Enhanced Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA): Greater focus on cryospheric hazardslike GLOFs.
- Advanced Monitoring Systems:
- Increased use of satellite imagery and in-situ data loggersfor real-time permafrost tracking.
- Comprehensive Research:
- More in-depth studies on permafrost degradation’s long-term impacton water resources and infrastructure stability.
As the Kashmir Himalaya faces intensifying climate challenges, proactive strategies are essential to mitigate risks and adapt to a rapidly changing environment
Consider the following statements regarding permafrost:
- Permafrost refers to any ground that remains frozen at or below -5°C for a minimum of five consecutive years.
- It is found only in the Arctic and Antarctic regions and does not exist in high-altitude mountain ranges.
- The thawing of permafrost contributes to increased methane emissions, which can accelerate climate change.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (c) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Permafrost is defined as ground that remains frozen at ≤0°C for at least two consecutive years (not -5°C for five years).
Statement 2 is incorrect: While permafrost is common in polar regions, it is also found in high-altitude mountain ranges such as the Himalayas, Alps, and Andes.
Statement 3 is correct: Thawing permafrost releases methane (CH₄) and carbon dioxide (CO₂), intensifying global warming.
India’s Heat Action Plans
- A recent study has found that most Indian cities’ Heat Action Plans (HAPs)lack effective long-term strategies to combat extreme heat, and those with such measures have failed in their implementation.
What are Heat Action Plans (HAPs)?
- HAPs are early warning systems and preparedness strategiesdesigned to minimize the health impacts of extreme heat, particularly for vulnerable populations.
About the Study
- Title:“Is India Ready for a Warming World?”
- Conducted by:Sustainable Futures Collaborative (SFC) and international universities (King’s College London, Harvard, Princeton, and UC Berkeley).
- Focus:Cities with over 1 million people expected to face increasing dangerous heat index values.
Key Findings
- Short-term measureslike access to water and adjusted work schedules are widely implemented.
- Long-term strategiessuch as cooling infrastructure, insurance for heat-related job losses, fire management, and electricity grid upgrades are either absent or poorly enforced.
- Urban cooling efforts(e.g., increasing green cover and shaded areas) do not effectively target the most heat-vulnerable populations.
- Planning gaps pose a significant risk, potentially leading to a rise in heat-related deathsas heatwaves become more frequent, intense, and prolonged.
- The study underscores the urgent need for comprehensive and well-executed heat mitigation strategiesto safeguard urban populations in an era of rising temperatures.
Consider the following statements regarding Heat Action Plans (HAPs) in India:
- HAPs serve as early warning systems and preparedness strategies to mitigate the impact of extreme heat.
- They are implemented exclusively by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Long-term measures such as insurance for heat-related job losses and urban cooling infrastructure are widely implemented in Indian cities.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: HAPs are early warning and preparedness strategies to protect vulnerable populations from extreme heat.
Statement 2 is incorrect: HAPs are implemented at state and city levels, often under disaster management authorities in coordination with various ministries, not exclusively by MoEFCC.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The study highlighted that long-term measures are either absent or poorly implemented, making Indian cities highly vulnerable to heat-related disasters.
Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary
Location & Significance
- Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary is situated in the Chikkamagaluru and Shivamogga districts of Karnatakaand derives its name from the Bhadra River, which flows through the region.
Designation & Conservation Status
- Declared a Wildlife Sanctuary in 1951.
- Upgraded to a Project Tiger Reserve in 1998.
- First tiger reserve in India to complete a village relocation program by 2002.
- Geographical Features
- Core area:16 sq. km.
- Buffer zone:84 sq. km.
- Terrain:Includes hills and valleys, notably Mullayanagiri (the highest peak in Karnataka), Baba Budangiri, and Muthodi ranges.
- Flora of Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary
The sanctuary hosts diverse forest types:
- Southern Moist Mixed Deciduous Forests– Characterized by Teak, Terminalia, and Lagerstroemia
- Dry Deciduous Forests– Includes Pterocarpus (Honne), Grewia (Tadasalu), and Bamboo
- Shola Forests– Supports species such as Cinnamon, Mimusops, and Strobilanthes (Neelakurinji), known for its rare blooming cycle.
Fauna of Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary
- Mammals:Includes Tigers, Leopards, Dholes (Wild Dogs), Gaurs, Sambar Deer, Barking Deer, and Elephants.
- Birds:Over 250 species, including Grey Junglefowl, Malabar Parakeet, Hill Myna, Malabar Trogon, and Hornbills.
- Reptiles:Features King Cobra, Russell’s Viper, Indian Monitor Lizard, and Marsh Crocodiles.
- Butterflies:Hosts rare species like Yamfly, Baronet, Crimson Rose, Southern Birdwing, and Great Orange Tip.
Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary remains a crucial site for biodiversity conservation, playing a vital role in Karnataka’s ecological balance.
Consider the following statements regarding the geographical features of Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Mullayanagiri, the highest peak in Karnataka, is located within the sanctuary.
- The sanctuary has both core and buffer zones, with a total area exceeding 1,000 square kilometers.
- The Bhadra River, which originates in the Eastern Ghats, flows through the sanctuary.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Mullayanagiri (1,930 meters), the highest peak in Karnataka, is part of the Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary region.
Statement 2 is correct: The sanctuary consists of a 500.16 sq. km core zone and a 571.84 sq. km buffer zone, making a total area of 1,072 sq. km.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The Bhadra River originates in the Western Ghats, not the Eastern Ghats, and it flows through the sanctuary before joining the Tungabhadra River.
Coral Bleaching Devastates Western Australia’s Ningaloo Reef
Context
- A severe mass coral bleaching event, described as unprecedented, is currently unfolding along Australia’s western coast, severely impacting the Ningaloo Reef, a UNESCO World Heritage site. This event is part of the fourth global coral bleaching episode, which has been ongoing since 2023.
Global Impact of Coral Bleaching
- The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) reports that nearly 84% of the world’s reef areas have experienced bleaching-level heat stress, affecting over 80 countries and territories.
- Rising global sea surface temperatures, overfishing, and pollution have exacerbated the crisis, with climate change being a primary driver.
Coral Reefs: An Overview
What Are Coral Reefs?
- Coral reefs are complex underwater ecosystems built by reef-building corals.
- Composed of colonies of coral polyps bound by calcium carbonate.
- Coral polyps live in a mutualistic relationship with algae known as zooxanthellae, which provide them with nutrients through photosynthesis.
Favorable Conditions for Coral Growth
- Temperature: 20°C–35°C
- Salinity: 27%–40%
- Depth: Prefer shallow waters (less than 50 meters) for optimal sunlight exposure.
- Major Coral Reefs Around the World
- Global Coral Reefs
- Great Barrier Reef (Australia) – UNESCO World Heritage Site
- Caribbean Reefs – Florida, Belize, and Bahamas
- Coral Triangle (Southeast Asia) – Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines
- Coral Reefs in India
- Gulf of Kutch (Gujarat)
- Gulf of Mannar (Tamil Nadu)
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands
- Lakshadweep Islands
- Malvan (Maharashtra)
- Significance of Coral Reefs
- Biodiversity Hotspot – Support 25% of all marine species.
- Coastal Protection – Act as natural barriers against storms and erosion.
- Climate Mitigation – Aid in carbon sequestration.
- Blue Economy – Sustain livelihoods through fishing and tourism.
- Biomedical Resources – Source of antiviral and anticancer compounds.
- Threats to Coral Reefs
Climate-Related Threats
- Coral Bleaching – Caused by rising ocean temperatures.
- Ocean Acidification – Weakens coral skeletons due to increasing CO₂
- Algal Blooms – Triggered by nutrient pollution, suffocating corals.
Human-Induced Threats
- Overfishing – Disrupts marine food chains.
- Pollution – Plastic waste, oil spills, and chemical runoff degrade reef health.
- Coral Mining – Unsustainable extraction for construction materials.
- Coastal Development – Leads to habitat destruction and sedimentation.
The Way Forward
- Climate Action
- Strengthen efforts to limit global warming to well below 2°C, in line with the Paris Agreement.
- Policy & Governance
- Implement Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly:
- SDG 8 (Sustainable Economic Growth)
- SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption & Production)
- Global Collaboration
- Strengthen international partnerships to combat overfishing and marine pollution.
- Scientific Innovation
- Invest in R&D for climate-resilient coral species to enhance reef restoration efforts.
- By integrating policy, conservation, and innovation, proactive measures can help protect the world’s coral reefs from irreversible decline.
With reference to coral bleaching, consider the following statements:
- Coral bleaching occurs when corals expel their symbiotic algae due to increased ocean salinity.
- Ocean acidification can exacerbate coral bleaching by weakening coral skeletons.
- The Great Barrier Reefis the only coral reef system listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect– Coral bleaching occurs due to rising sea surface temperatures, not increased salinity. The stress forces corals to expel zooxanthellae algae, leading to their white appearance.
- Statement 2 is correct– Ocean acidification, caused by increased CO₂ absorption in seawater, weakens coral skeletons and makes them more vulnerable to bleaching and erosion.
- Statement 3 is incorrect– The Great Barrier Reef is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, but other coral reefs like Ningaloo Reef (Australia) and Belize Barrier Reef (Caribbean) are also listed.
India Secures Copper Exploration Block in Zambia
Context
- India has secured a 9,000 sq. km exploration block in Zambia for copper and cobalt mining, marking a significant step in securing critical minerals.
- Zambia is the 7th largest copper producer globally and a key supplier in the international market.
Recent Trends in the Global Copper Market
- Shrinking Global Supply: According to Bloomberg, the supply of copper ore is tightening, leading to an intense competition for resources.
- China’s Dominance: China controls 50% of the world’s copper smelting and refining capacity, giving it strategic leverage in the global copper supply chain.
- Rising Demand: Copper demand is increasing due to its essential role in EV batteries, renewable energy, and clean technologies.
- Leading Copper Producers: Chile, Peru, China, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), and the United States dominate global copper production.
- Geopolitical Competition: Major economies like India, China, and the U.S. are aggressively securing copper resources, leading to intensified geopolitical tensions over mineral supply chains.
India’s Copper Situation
- Declining Domestic Production: In 2023-24, India’s copper ore production was 78 million tonnes, an 8% decline from 2018-19 levels.
- Major Copper-Producing States:
- Madhya Pradesh (largest producer)
- Rajasthan (second-largest producer)
- Surge in Copper Imports: India’s copper concentrate imports have doubled in value to ₹26,000 crore in 2023-24 compared to 2018-19.
Challenges in Domestic Copper Mining:
- India possesses significant copper deposits, but extensive exploration is required before mining can commence.
- The global average time to operationalize a new copper mine is 17 years, making long-term planning essential.
India’s Overseas Copper Strategy
- Investment in Foreign Copper Assets: India is securing copper mines in Zambia, Chile, and the DRC to meet short-term demand.
- Geopolitical Risks: While overseas investments help address supply shortages, they come with political and economic risks, including resource nationalism and regulatory uncertainties.
Africa’s Growing Role in Critical Minerals
- Major Supplier: Africa contributes 70% of global cobalt and 16% of global copper
- DRC’s Expansion: The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is set to become the world’s second-largest copper producer by 2030.
India’s Engagement in Africa:
- The Ministry of Mines is actively working to acquire mineral assets in the DRC, Tanzania, Mozambique, and Rwanda to secure long-term supply chains.
Consider the following statements regarding the global copper market:
- China accounts for more than half of the world’s copper smelting and refining capacity.
- The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is projected to become the world’s largest copper producer by 2030.
- The time required to operationalize a new copper mine globally averages around 17 years.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct. China holds 50% of the global copper smelting and refining capacity, giving it control over supply chains.
- Statement 2 is incorrect. While the DRC is projected to become the world’s second-largest copper producer by 2030, it is unlikely to surpass Chile, which remains the largest producer.
- Statement 3 is correct. The global average time to operationalize a copper mine is 17 years, making long-term investments crucial.
Avalanche
Context:
- A devastating avalanche struck a Border Roads Organisation (BRO) project in Mana, Chamoli, Uttarakhand.
- The incident highlights the hazards of working in high-altitude terrain and the vulnerability of critical infrastructure in Himalayan regions.
Avalanche: Understanding the Phenomenon
Definition:
- An avalanche is a sudden, rapid descent of snow, ice, rock, and debris down a steep mountainside.
- Snow avalanches are the most common type and can reach speeds exceeding 320 km/h (200 mph).
Causes of Avalanches:
- Avalanches occur when an unstable snowpack collapses, often due to:
- Weak Layer Formation: Poor bonding between snow layers (e.g., ice sheets, fresh snowfall, or melting layers).
External Triggers:
- Sudden weight addition (e.g., snowfall, human activity).
- Vibrations (e.g., earthquakes, explosions, or movement of heavy vehicles).
- Weather Conditions:
- Heavy snowfall increases snow weight.
- Wind erosion deposits snow unevenly.
- Spring thaw reduces friction between layers.
Terrain Factors:
- Slope steepness (30°–45°) is ideal for avalanches.
- Loose rock formations increase instability.
Types of Avalanches:
- Sluffs (Loose Snow Avalanches):
- Composed of dry, powdery snow.
- Small, less destructive but can trap climbers.
Slab Avalanches:
- Larger and deadlier, caused when a weak layer collapses under a thick slab of snow.
- Fast-moving and highly destructive.
- Can bury entire settlements and infrastructure.
Consider the following statements regarding Avalanches:
- Avalanches can only occur in snow-covered regions with an altitude above 3,000 meters.
- Slab avalanches are generally more dangerous than sluff avalanches.
- Earthquakes and explosions can act as triggers for avalanches.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Avalanches can occur at lower altitudes if conditions are unstable.
- Statement 2 is correct: Slab avalanches involve large snow masses and are more destructive than sluffs.
- Statement 3 is correct: Vibrations from earthquakes and explosions can trigger avalanches.
Ganga Water Treaty
The Ganga Water Treaty: Challenges and the Path Ahead
- The Ganga Water Treaty, signed in 1996, is set to expire in 2026, making the upcoming negotiations between India and Bangladesh crucial for future water-sharing agreements. Bangladesh is pushing for a larger share of dry-season water due to severe shortages affecting agriculture. However, these talks unfold against a backdrop of rising tensions following political shifts in Bangladesh and unresolved disputes, particularly over the Teesta River.
Background of the Ganga Water Treaty
- The Ganga River has long been a point of contention between India and Bangladesh. The Farakka Barrage, operational since 1975, was built to regulate water flow but intensified disputes. The treaty established a framework for water-sharing, recognizing Bangladesh as a lower riparian state and attempting to balance the needs of both nations while addressing historical grievances.
Key Provisions of the Treaty
- The treaty outlines a water-sharing formula based on the Ganga’s flow at the Farakka Barrage during the dry season:
- If the flow is 70,000 cusecs or less, both countries receive equal shares.
- It guarantees a minimum water flow for both nations during critical periods.
- A Joint Rivers Commission was established to monitor compliance and resolve disputes
Importance of the Upcoming Talks
- The upcoming negotiations mark the 86th round of discussions between India and Bangladesh. Bangladesh has advocated for a comprehensive water-sharing framework covering all transboundary rivers. Currently, the Ganga Water Treaty remains the only operational agreement between the two nations. The outcome of these talks could shape future water-sharing pacts, particularly for the Teesta River.
Challenges and Future Considerations
- The treaty faces increasing challenges due to climate change and shifting water patterns. Experts warn that if the treaty expires without renewal, India may not be obligated to share water, potentially escalating tensions and threatening the ecologically fragile Sundarbans delta. A holistic and climate-resilient agreement is necessary to ensure sustainable water management.
Geographical and Ecological Impact
- The Ganga River traverses diverse landscapes before forming a delta and flowing into the Bay of Bengal. This region is ecologically critical, supporting rich biodiversity, fisheries, and agriculture. Any disruption in water flow can have far-reaching consequences, impacting livelihoods and the fragile ecosystem of the Sundarbans.
- With the 2026 deadline approaching, India and Bangladesh must navigate these challenges to forge a fair, long-term, and environmentally sustainable water-sharing agreement.
Consider the following statements regarding the Ganga Water Treaty:
- The treaty was signed between India and Bangladesh in 1996 for a duration of 50 years.
- The treaty allows India unilateral control over water flow at the Farakka Barrage.
- The agreement provides for an equal share of water if the flow at Farakka Barrage is 70,000 cusecs or less.
- A Joint Rivers Commission was set up under the treaty to ensure compliance and dispute resolution.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (c) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation: The treaty was signed in 1996 but for 30 years, not 50 years (expires in 2026). While India operates the Farakka Barrage, it does not have unilateral control—water-sharing is based on a formula. The treaty ensures equal sharing of water if flow is 70,000 cusecs or less, and a Joint Rivers Commission exists for oversight.
Uttara hand Ropeway Projects
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) has sanctioned two significant ropeway projects to bolster pilgrimage accessibility and tourism in Uttarakhand.
- These ropeways will connect Sonprayag to Kedarnath and Govindghat to Hemkund Sahib Ji, leveraging state-of-the-art technology to ensure efficient, eco-friendly, and sustainable transportation for thousands of pilgrims annually.
Kedarnath Ropeway: A Paradigm Shift in Pilgrimage Transport
- The Kedarnath ropeway, spanning 12.9 km, will be executed under the Design, Build, Finance, Operate, and Transfer (DBFOT) model with an estimated investment of ₹4,081.28 crore.
- Incorporating Tri-cable Detachable Gondola (3S) technology, it will facilitate the movement of 1,800 passengers per hour per direction, translating to a daily carrying capacity of 18,000 passengers.
- This project will drastically reduce travel time from the current 8-9 hours to approximately 36 minutes, significantly enhancing the pilgrim experience.
Religious and Logistical Significance
- Kedarnath, one of the 12 sacred Jyotirlingas, witnesses an annual footfall of approximately 20 lakh devotees.
- Presently, the journey to the temple is undertaken via trekking, ponies, palanquins, or helicopters.
- The introduction of the ropeway ensures all-weather connectivity, augmenting pilgrimage efficiency and accessibility.
Hemkund Sahib Ji Ropeway: Strengthening Accessibility to a High-Altitude Pilgrimage Site
- The second ropeway project spans 4 km from Govindghat to Hemkund Sahib Ji, with an investment of ₹2,730.13 crore.
- This project integrates Monocable Detachable Gondola (MDG) technology for the initial segment and Tri-cable Detachable Gondola (3S) technology for the latter, ensuring optimal safety and efficiency.
- With a capacity of 1,100 passengers per hour per direction, it can accommodate 11,000 passengers daily.
Cultural and Ecotourism Impact
- Situated at an altitude of 15,000 feet, Hemkund Sahib Ji is a revered Sikh pilgrimage site that remains accessible for only five months a year, attracting 5 to 2 lakh devotees annually.
- The ropeway will not only ease the arduous journey but also promote tourism in the adjacent Valley of Flowers, a UNESCO World Heritage site known for its diverse alpine flora and ecological significance.
Economic and Environmental Considerations
- Employment Generation and Socio-Economic Growth
- The implementation of these ropeways is anticipated to generate substantial employment across multiple sectors, including construction, operations, hospitality, travel, and food services.
- The resultant economic boost aligns with the broader objective of balanced socio-economic development in hilly regions of Uttarakhand.
- Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Transit Solutions
- Both projects are meticulously designed to minimize environmental impact, offering low-emission transport alternatives that reduce the carbon footprint associated with traditional pilgrimage routes.
- The initiative embodies the commitment to sustainable tourism, ensuring that development harmonizes with ecological preservation.
Consider the following statements regarding the Kedarnath ropeway project:
- It will operate using the Monocable Detachable Gondola (MDG) technology.
- It will be developed under the Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) model.
- The project aims to reduce the travel time to approximately 36 minutes.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (c) 3 only
Explanation:
The Kedarnath ropeway employs Tri-cable Detachable Gondola (3S) technology, not MDG (eliminating statement 1). It follows the DBFOT model, not BOT (eliminating statement 2). Statement 3 is correct.
Gum Arabic (Acacia Gum)
Context:
- The illegal smuggling of gum Arabic (Acacia Gum) from war-torn Sudan is significantly affecting global supply chains. Sudan accounts for 80% of the world’s production, followed by Chad, Nigeria, and other Sahelian nations.
What is Gum Arabic?
- Gum Arabic is a natural resin obtained from Acacia trees, primarily Acacia senegal and Acacia seyal.
- It is a complex polysaccharide with exceptional emulsifying, stabilizing, and thickening properties.
Major Applications:
- Food Industry: Functions as an emulsifier, stabilizer, and thickener in soft drinks, baked goods, and confectionery.
- Cosmetics: Enhances texture and stability in skincare products and lipsticks.
- Pharmaceuticals: Used in syrups, capsules, and tablet coatings due to its binding properties.
- The ongoing conflict in Sudan has exacerbated disruptions in supply chains, impacting industries reliant on gum Arabic worldwide.
Which of the following best explains why the smuggling of Gum Arabic from Sudan is disrupting global supply chains?
- Sudan is the world’s largest producer, supplying over 80% of the total global demand.
- Gum Arabic is classified as a strategic commodity, critical for the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic
- The conflict in Sudan has led to the involvement of non-state actors, who control trade routes and manipulate prices.
- Major global industries depend on Sudanese gum Arabic due to the lack of viable synthetic alternatives.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
- a) 1, 2, and 3 only
b) 2 and 4 only
c) 1, 3, and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Sudan contributes over 80% of the world’s gum Arabic supply, making disruptions in its production and trade highly consequential.
- Statement 2 is correct: Due to its essential role in multiple industries, gum Arabic is considered a strategic commodity, much like rare earth metals in technology.
- Statement 3 is correct: Armed groups in Sudan control smuggling routes, using gum Arabic as a source of illicit funding, further disrupting legal supply chains.
- Statement 4 is correct: There are no widely used synthetic substitutes for gum Arabic, making industries heavily reliant on natural production.
Wallace Line
- The Wallace Line is a fundamental biogeographical demarcation that explains the stark differences in species distribution between the Asian and Australasian ecozones.
- Identified by Alfred Russel Wallace in the 19th century, this hypothetical boundary delineates Southeast Asia from Wallacea, a transitional region where species exhibit mixed evolutionary traits of both Asian and Australian
Geographical Extent of the Wallace Line:
- It traverses the Lombok Strait between Bali and Lombok, despite the relatively short 35 km distance between them.
- It extends through the Makassar Strait, demarcating Borneo and Sulawesi.
- Further, it runs eastward beyond the Philippines, south of Mindanao Island into the Philippine Sea.
Ecological and Evolutionary Implications:
- The Wallace Line is a consequence of deep oceanic trenches formed during the Pleistocene glaciations, which prevented species migration even when sea levels were lower.
- On the western side of the Wallace Line, faunal species exhibit characteristics of the Indo-Malayan realm (Asiatic origins).
- On the eastern side, species exhibit traits of Australasian descent, reflecting Gondwanan evolutionary lineage.
Findings on Sulawesi Island:
- Sulawesi’s fauna shows affinities with diverse biogeographic regions, including Africa, India, Java, Maluku Islands, New Guinea, and the Philippines.
- It serves as an ecological transition zone, housing species that do not conform strictly to either Asian or Australian lineages.
Examples of Sulawesi’s Unique Fauna:
- Asiatic Influence:
- Tarsiers (Tarsiidae), a type of primate.
- Lowland Anoa (Bubalus depressicornis) and Mountain Anoa (Bubalus quarlesi), small bovid species.
- Australasian Influence:
- Dwarf Cuscus (Strigocuscus celebensis), a marsupial species unique to Sulawesi.
Biogeographical Significance of the Wallace Line Which of the following best explains why the Wallace Line is considered a critical concept in biogeography?
- It represents a sharp faunal divide between Asiatic and Australasian species despite geographic proximity.
- It is caused by deep-sea trenches, which have historically prevented the migration of land-based fauna.
- The Wallace Line runs parallel to tectonic plate boundaries, which influence the speciation process through geological separation.
- It marks a zone of convergent evolution, where species from Asia and Australia have independently evolved similar traits.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
- a) 1 and 2 only
b) 1, 2, and 3 only
c) 1, 3, and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: b) 1, 2, and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Wallace Line separates Asiatic fauna on the west from Australasian species on the east, despite short geographic distances.
- Statement 2 is correct: Deep-sea trenches (like those in the Lombok Strait) acted as natural barriers preventing the intermingling of species.
- Statement 3 is correct: The Wallace Line is influenced by plate tectonics, as it runs along an ancient boundary separating the Sunda Shelf (Eurasian Plate) from the Sahul Shelf (Australian Plate).
- Statement 4 is incorrect: The Wallace Line does not mark convergent evolution; rather, it signifies biogeographic isolation where species did not evolve shared traits.
Thorium Reserves
- Chinese geologists have discovered one million tonnes of thorium in the Inner Mongolia region, marking a significant development in the global nuclear energy sector.
- The discovery aligns with China’s long-term nuclear energy diversification strategy, with a focus on Thorium Molten-Salt Reactors (TMSRs) as a viable alternative to conventional uranium-based reactors.
Thorium’s Strategic Potential as a Nuclear Fuel
- High Energy Yield: Thorium is capable of generating 200 times more energy than uranium, making it a superior nuclear fuel.
- Enhanced Safety Features: Unlike traditional uranium-based reactors, thorium reactors do not pose a meltdown risk, require no water cooling, and produce minimal radioactive waste.
- TMSRs as a Game-Changer: Thorium molten-salt reactors (TMSRs), which dissolve thorium in liquid salts, have the potential to revolutionize clean energy production.
China’s Ambitious Thorium Energy Projects
- China has approved the world’s first TMSR power plant, expected to generate 10 megawatts by 2029.
- The country is also exploring thorium-powered ships and lunar reactors for future moon-based energy solutions.
- India’s Thorium Reserves & Nuclear Strategy
- India possesses one of the world’s largest thorium reserves, making it a critical player in thorium-based nuclear energy development.
Major Deposits:
- Kerala and Odisha account for over 70% of India’s total thorium deposits.
- Additional reserves are located in Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh.
- India’s Three-Stage Nuclear Program:
- Thorium utilization is central to Stage III of India’s nuclear power strategy, focusing on breeder reactors capable of converting thorium into Uranium-233, a fissile material for sustained energy production.
Challenges in Thorium Utilization
- Technological Barriers: Extracting thorium from its ores is energy-intensive and generates significant waste, necessitating advanced reactor designs.
- Economic Viability: Despite abundant reserves, the high cost of thorium reactor technology has slowed commercial-scale adoption.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies: India requires enhanced research and industrial capabilities to transition from uranium-dependent reactors to a thorium-based nuclear program.
: Why is thorium considered a superior alternative to uranium for nuclear energy production?
- Thorium produces 200 times more energy per unit compared to uranium.
- Thorium-based reactors are inherently safer, with no risk of meltdown and minimal radioactive waste.
- Unlike uranium, thorium does not require enrichment, making it more economically viable for energy production.
- Thorium can be directly used as a fuel in conventional nuclear reactors without requiring transformation into fissile material.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
- a) 1 and 2 only
b) 1, 2, and 3 only
c) 1, 3, and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: b) 1, 2, and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Thorium’s energy density is significantly higher than uranium, making it a more efficient nuclear fuel.
- Statement 2 is correct: Thorium reactors do not require water cooling, eliminating meltdown risks, and produce less long-lived nuclear waste.
- Statement 3 is correct: Unlike uranium, thorium does not need enrichment, reducing processing costs.
Statement 4 is incorrect: Thorium is not naturally fissile and requires conversion into Uranium-233 before it can sustain a chain reaction in nuclear reactors
Golden Passport Program of Vanuatu
Context:
Former IPL chief Lalit Modi has renounced his Indian passport and obtained citizenship in Vanuatu, an island nation in the South Pacific Ocean that offers a “golden passport” program through its Citizenship by Investment (CBI) scheme.
Vanuatu: Geographical & Strategic Overview
Location: Situated in the South Pacific Ocean, approximately 800 km west of Fiji and 1,770 km east of Australia.
Tectonic Activity: Lies within the Pacific Ring of Fire, a region known for high seismic and volcanic activity, making it prone to earthquakes and tsunamis.
Golden Passport Program: Citizenship by Investment (CBI) Scheme
- Overview & Process
- Vanuatu’s CBI program allows individuals to acquire citizenship through financial contributions.
- Investment Requirement: Citizenship costs between $135,500 to $155,500, with additional provisions for a family of four.
- Processing Time: Citizenship is typically granted within 30 to 60 days after submission of the application.
- Key Benefits of Vanuatu Citizenship
- Passport Strength: Ranked 51st in the Henley Passport Index, ahead of Saudi Arabia, China, India, and Indonesia.
- Tax Haven Status: No personal income tax, capital gains tax, inheritance tax, or wealth tax, making it attractive for high-net-worth individuals.
- Economic Reliance: Offshore financial services form a crucial component of Vanuatu’s revenue generation strategy.
- Scandals & Criticism
Security Concerns: Individuals with criminal backgrounds have been granted citizenship, raising concerns about the potential misuse of the program.
EU & UK Backdoor Entry Risk: The scheme is viewed as a loophole for accessing European markets, triggering scrutiny from global regulators.
Money Laundering Risks: Vanuatu’s lax taxation and financial regulations pose concerns over potential illicit financial activities.
With reference to Vanuatu’s Citizenship by Investment (CBI) program, consider the following statements:
- Vanuatu is an island nation located in the Indian Ocean, known for its rich biodiversity.
- The Citizenship by Investment (CBI) program allows individuals to obtain Vanuatu’s citizenship by purchasing real estate in the country.
- Vanuatu ranks higher than India in the Henley Passport Index and is considered a tax haven due to the absence of personal income tax.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect. Vanuatu is located in the South Pacific Ocean, not the Indian Ocean.
- Statement 2 is incorrect. Vanuatu’s CBI program does not require real estate purchases; instead, it grants citizenship in exchange for financial contributions to the government.
- Statement 3 is correct. Vanuatu ranks 51st in the Henley Passport Index, higher than India, and has no personal income tax, capital gains tax, or inheritance tax, making it a tax heaven.
Chagos Archipelago
About Chagos Archipelago
- The Chagos Archipelago is a group of 58 islands located approximately 500 km south of the Maldives in the Indian Ocean.
- The islands remained uninhabited until the late 18th century, when the French brought laborers from Africa and India to work on newly established coconut plantations.
- In 1814, France ceded the islands to Britain as part of a colonial agreement.
British Control and Mauritius’ Claim
- In 1965, the United Kingdom established the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT), with the Chagos Islands as a central part.
- Chagos was historically administered as part of Mauritius, another British colony, but when Mauritius gained independence in 1968, the Chagos Islands remained under British control.
- Mauritius asserts sovereignty over Chagos, citing its historical ties predating British colonial rule.
Strategic Importance
The largest atoll, Diego Garcia, is home to a major U.S. military base, making the region geopolitically significant.
Consider the following statements regarding the Chagos Archipelago:
- The Chagos Archipelago consists of 58 islands located approximately 500 km south of the Maldives in the Indian Ocean.
- The islands were uninhabited until the late 18th century, when the British brought laborers from Africa and India.
- In 1814, the Chagos Islands were ceded to Britain by France as part of a colonial agreement.
- Diego Garcia, the largest atoll in the Chagos Archipelago, hosts a French naval base.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Chagos Archipelago is a group of 58 islands located 500 km south of the Maldives in the Indian Ocean.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The French, not the British, brought laborers from Africa and India to work on coconut plantations.
- Statement 3 is correct: France ceded the Chagos Islands to Britain in 1814.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: Diego Garcia hosts a S. military base, not a French naval base.
Parvatmala Pariyojana
: Consider the following statements regarding the Parvatmala Pariyojana:
- It was launched in the Union Budget 2022 under the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) mode.
- It is implemented by the National Highway Logistics Management Limited (NHLML) under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH).
- The project aims to develop 500+ ropeway projects covering 2,500 km within five years.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Parvatmala Pariyojana was announced in the Union Budget 2022 under the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) mode to improve connectivity in hilly and remote areas through ropeway projects.
- Statement 2 is correct: The implementation of this project is being carried out by National Highway Logistics Management Limited (NHLML), which operates under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH).
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The project aims to develop 250+ ropeway projects covering approximately 1,200 km within five years, not 500+ projects covering 2,500 km. Therefore, this statement is factually incorrect.
Which of the following statements regarding India’s Gross Expenditure on Research and Development (GERD) is/are correct?
- India’s GERD has more than doubled in the last decade but remains below 1% of GDP.
- India’s private sector accounts for over 60% of GERD, aligning with developed nations.
- China and the United States invest a higher percentage of GDP in R&D compared to India.
- India’s public sector remains the dominant contributor to research funding.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
- a) 1 and 2 only
b) 1, 3, and 4 only
c) 2, 3, and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: b) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: India’s GERD doubled but remains ~0.7% of GDP, much lower than global leaders.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: India’s private sector contributes only ~36%, far lower than in developed economies (60-70%).
- Statement 3 is correct: China (4% of GDP) and the USA (3.1% of GDP) invest significantly more in R&D than India.
Statement 4 is correct: Public sector entities dominate R&D funding in India due to limited private participation.
Parvatmala Pariyojana
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA), chaired by the Prime Minister, has approved two significant ropeway projects in Uttarakhand under the National Ropeways Development Programme – Parvatmala Pariyojana.
About Parvatmala Pariyojana
- Launched in the Union Budget 2022 under the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) mode.
- Implemented by the National Highway Logistics Management Limited (NHLML) under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH).
- Aims to develop over 250 ropeway projects, covering 1,200 km within five years.
Significance of Ropeways:
- Enhanced Connectivity: Facilitates transportation in remote and hilly regions, improving accessibility.
- Tourism & Economic Growth: Promotes tourism and generates employment opportunities.
- Efficient Transport: Offers a direct aerial route, reducing travel time and overcoming difficult terrains.
- Eco-Friendly Approach: Minimizes deforestation and land degradation, making it a sustainable infrastructure solution.
Consider the following statements regarding the Parvatmala Pariyojana:
- It was announced in the Union Budget 2022 under the Viability Gap Funding (VGF) mode.
- The programme is implemented by the National Highway Logistics Management Limited (NHLML) under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH).
- It aims to develop over 500 ropeway projects covering 2,500 km within five years.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The Parvatmala Pariyojana was announced in the Union Budget 2022, but it follows the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) mode, not the Viability Gap Funding (VGF) mode.
- Statement 2 is correct: The programme is implemented by NHLML, which is a subsidiary of the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) under MoRTH.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The actual target is to develop 250+ ropeway projects covering 1,200 km in five years, not 500 projects covering 2,500 km.
La Nina
- La Niña is a climatic phenomenon characterized by the cooling of surface ocean waters along the tropical west coast of South America.
- It is the opposite phase of El Niño, which is associated with unusually warm ocean temperatures in the equatorial Pacific.
- Together, these events form the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle, influencing global weather patterns.
- La Niña is identified when sea surface temperatures decrease by more than 0.5°C (0.9°F) for at least five consecutive three-month seasons.
Causes of La Niña
- La Niña occurs due to the accumulation of cooler-than-normal waters in the tropical Pacific, a region between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
- This cooling is driven by unusually strong trade winds and ocean currents, which push warm surface waters westward, allowing cold, deep ocean water to rise to the surface—a process known as upwelling.
- This significant drop in sea-surface temperature alters global atmospheric circulation patterns.
Effects of La Niña
Impact on Air Pressure and Rainfall
- La Niña reduces air pressure over the western Pacific, leading to increased rainfall.
- Southeast Asia experiences stronger summer monsoons, benefiting agriculture in regions like northwest India and Bangladesh.
Risk of Flooding in Australia
- While La Niña enhances rainfall for agriculture in South Asia, severe events can lead to excessive precipitation and flooding in northern Australia.
Global Rainfall Patterns
- Increased rainfall occurs in southeastern Africa and northern Brazil.
- Conversely, La Niña raises air pressure over the central and eastern Pacific, causing drier conditions in those regions.
Drier Conditions in Certain Areas
- The west coast of tropical South America, the Gulf Coast of the United States, and the pampas of South America experience reduced rainfall and prolonged dry spells.
Boost to the Fishing Industry
- The upwelling effect brings cold, nutrient-rich waters to the surface, fostering plankton growth.
- This supports marine ecosystems, benefiting fish populations and the fishing industry, particularly in regions like the eastern Pacific.
Duration and Seasonal Trends:
- La Niña events typically last between one and three years, whereas El Niño events are usually shorter, lasting less than a year. Both phenomena tend to peak during the Northern Hemisphere winter, significantly influencing global weather patterns.
- By shaping rainfall distribution, ocean currents, and atmospheric circulation, La Niña plays a crucial role in global climate variability, impacting agriculture, economies, and ecosystems worldwide.
Consider the following statements regarding La Niña:
- It is associated with the cooling of sea surface temperatures in the eastern and central Pacific Ocean.
- It leads to an increase in air pressure over the western Pacific, resulting in reduced monsoon activity in South Asia.
- It enhances upwelling, which benefits marine ecosystems and fisheries in the eastern Pacific.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: La Niña is characterized by cooler-than-normal sea surface temperatures in the eastern and central Pacific.
Statement 2 is incorrect: La Niña lowers air pressure over the western Pacific, leading to stronger monsoons in South Asia, not weaker ones.
Statement 3 is correct: Upwelling caused by La Niña brings nutrient-rich cold water to the surface, which boosts marine productivity and benefits fisheries.
Karnataka’s Controversial Sharavathi Hydroelectric Project
Project Overview
- Located in Karnataka, the project aims to generate 2,000 MW of electricity.
- It also seeks to supply drinking water to Bengaluru.
- Consists of upper and lower reservoirs with a pumped storage mechanism.
- Modeled after Telangana’s Kaleshwaram project.
- Requires five tunnels and eight pumping stations.
- Estimated cost: ₹8,000 crore.
Environmental Concerns
- Threatens the Sharavathi Valley, a biodiversity hotspot in the Western Ghats.
- Home to endangered species like the Lion-tailed Macaque and Great Indian Hornbill.
- Requires clearing 360 acres of protected forest land within a wildlife sanctuary.
- Karnataka’s forest cover is only 20%, below the national target of 33%.
- Potential violations of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
Technical and Economic Viability
- Consumes more electricity than it generates (Deficit project).
- Expected to generate 12,000 MWh annually, but requires 14,833 MWh for pumping.
- Raises concerns about economic feasibility due to increased energy demand.
- May require additional costly energy projects to compensate for the shortfall.
Legal and Procedural Challenges
- The Karnataka High Court has issued a stay order on the bidding process.
- Allegations of corruption and favoritism in awarding the contract to MEIL.
- Karnataka Power Corporation Limited (KPCL) under scrutiny for irregularities.
- Critics highlight lack of transparency and rushed bidding process.
Political and Public Reactions
- Opposition parties accuse the Congress-led state government of benefiting vested interests.
- Environmental activists and local communities mobilizing protests and legal challenges.
- Reflects the larger conflict between energy expansion and conservation.
Broader National Implications
- Raises concerns over India’s renewable energy goals vs. ecological sustainability.
- Could set a precedent for balancing development and conservation.
- The future of the Western Ghats’ biodiversity remains uncertain.
Consider the following statements regarding the Sharavathi Pumped Storage Hydroelectric Project (PSHP):
- It is designed to generate electricity by utilizing the natural flow of the Sharavathi River without requiring water pumping.
- The project is modeled after Telangana’s Kaleshwaram project.
- The project is located in the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The project requires water pumping uphill during off-peak hours, making it a pumped storage system rather than a conventional hydropower project.
- Statement 2 is correct: The project is modeled after Telangana’s Kaleshwaram project, which also involves water pumping infrastructure.
- Statement 3 is correct: The Western Ghats is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and the project is located within this ecologically sensitive region.
Kursk Region
Russian Offensive in the Kursk Region
- Russian forces have launched a large-scale counteroffensive to reclaim western parts of the Kursk region from Ukrainian troops.
- This development marks a significant escalation in the ongoing conflict, with strategic and historical implications.
About the Kursk Region
Geographical Significance:
- Kursk is a city and the administrative center of Kursk Oblast, located along Russia’s southwestern border.
- It lies approximately 450 km south of Moscow, along the upper Seym River.
- The region is part of the Black Earth Belt, known for its exceptionally fertile soil.
- Kursk has a moderately continental climate, characterized by significant seasonal variations.
Historical Importance:
- Kursk is one of Russia’s oldest cities, first recorded in 1032.
- In 1240, the city was destroyed by the Tatars and remained in ruins until 1586, when it was rebuilt as a military outpost.
Battle of Kursk (July–August 1943):
- The city was a key battleground during World War II, witnessing the largest tank battle in history.
- The German defeat in Kursk marked a turning point in the Eastern Front.
Economic and Industrial Landscape:
- Kursk has a diverse industrial base, with key sectors including:
- Machine building
- Food processing
- Electronic equipment production
- Synthetic fiber manufacturing
- These industries contribute significantly to the region’s economic growth.
Recent Developments & Ongoing Conflict
- In the summer of 2024, Ukrainian forces launched a surprise lightning offensive, capturing parts of Russia’s Kursk region.
- However, Ukraine’s hold on Kursk has weakened, as Russia intensifies its counteroffensive to reclaim lost territory.
- The Russian advance threatens Kyiv’s sole territorial bargaining chip, making this battle crucial for both sides at a critical juncture in the war.
Consider the following statements regarding the Kursk region:
- Kursk is located in the Black Earth Belt, known for its highly fertile soil.
- The Battle of Kursk in World War II was the largest naval battle in history.
- The city of Kursk was first mentioned in historical records in the 13th century.
- Kursk has a continental climate with distinct seasonal variations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3, and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Kursk is part of Russia’s Black Earth Belt, known for its highly fertile soil, making it agriculturally significant.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The Battle of Kursk (1943) was the largest tank battle in history, not a naval battle.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: Kursk was first mentioned in 1032, which is in the 11th century, not the 13th century.
- Statement 4 is correct: Kursk has a moderately continental climate with distinct seasonal variations.
Chagos Archipelago
- The Chagos Archipelago, situated in the Indian Ocean, has been at the center of a long-standing territorial dispute between Mauritius and the United Kingdom.
- Although Mauritius gained independence in 1968, the UK retained control over Chagos.
- In recent years, the UK has formally acknowledged Mauritius’ claims to the archipelago, but tensions persist, particularly regarding Diego Garcia, a strategically significant military base.
Historical Background
- The Chagos Archipelago consists of over 60 islands, with Diego Garcia being the largest and most strategically vital. Initially uninhabited, Chagos saw its first permanent settlements in the 18th century.
- The French claimed the islands in the 1700s, but following the Napoleonic Wars, the British took control.
- Over time, the islands became plantation hubs, heavily reliant on slave and indentured labor.
Creation of the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT):
- In 1965, the UK established the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT), incorporating Chagos as part of a broader Cold War strategy to maintain military influence in the Indian Ocean.
- The UK paid Mauritius £3 million for the separation of Chagos from its territory.
Strategic Importance of Diego Garcia
- By the 1970s, the United States constructed a military base on Diego Garcia, leading to the forced displacement of the Chagossian population to Mauritius and Seychelles.
- The base became fully operational in 1986 and has since played a pivotal role in US military operations across the region.
International Legal Rulings
Mauritius has long contested UK sovereignty over Chagos:
- 2017: The UN General Assembly sought an advisory opinion from the International Court of Justice (ICJ) regarding Chagos’ legal status.
- 2019: The ICJ ruled that the UK’s administration over Chagos was unlawful and that it should return the islands to Mauritius.
- The UN General Assembly subsequently urged the UK to withdraw from Chagos.
Recent Developments
- In 2024, the UK and Mauritius signed a landmark agreement, formally recognizing Mauritius’ sovereignty over Chagos while allowing the UK to maintain control over Diego Garcia for 99 years.
- However, this deal has drawn criticism, particularly from the Chagossians, who were excluded from negotiations and remain uncertain about their right to resettlement.
Geopolitical Implications and Future Challenges
- The agreement has heightened concerns over China’s expanding influence in the Indian Ocean, as Mauritius strengthens its strategic ties with Beijing.
- Analysts warn that the deal may disrupt the regional balance of power, with potential implications for security and military strategy.
- Meanwhile, the Chagossians’ future remains uncertain, with ongoing discussions regarding resettlement and compensation.
- The Chagos dispute continues to be a significant geopolitical issue, influencing regional diplomacy, legal debates, and military strategy in the Indian Ocean region.
Which of the following international organizations has been involved in the Chagos sovereignty dispute?
- International Court of Justice (ICJ)
- United Nations General Assembly (UNGA)
- European Union (EU)
- African Union (AU)
- a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 2, and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: c) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- The International Court of Justice (ICJ) and the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) played key roles in ruling against UK sovereignty over Chagos.
- The African Union (AU) has also supported Mauritius’ claim. However, the European Union (EU) has not been directly involved in the dispute.
Kyushu Island
Kyushu Island: Strategic & Geographical Significance
Latest Developments:
- The Japanese government has proposed deploying long-range missiles on Kyushu Island, underscoring its increasing strategic military importance in the Indo-Pacific region.
Geographical Overview of Kyushu Island
Location & Borders:
- Kyushu is the southernmost and third-largest of Japan’s four main islands.
- It spans an area of 35,640 sq. km.
- Bordering water bodies:
- West: East China Sea.
- East: Pacific Ocean.
Northwestern Separation:
- The Tsushima Strait (Eastern Channel) separates Kyushu from the Korean Peninsula.
Topography & Climate:
- Characterized by volcanic mountain ranges, including:
- Mount Aso – The largest active volcanic crater in the world.
- Mount Kuju (1,794 m) – The highest peak on the island.
- The island experiences a subtropical climate with high rainfall, supporting dense subtropical vegetation.
- Rivers & Economy:
- Chikugo River (142 km) – Longest river on Kyushu.
- Agriculture:
- Major crops: Rice, tea, tobacco, sweet potatoes, citrus fruits.
- Industries:
- Northern Kyushu is a major industrial hub, particularly for:
- Iron & steel production.
- Chemical industries.
- Saga Prefecture is renowned for porcelain and pottery.
Key Cities:
- Kita-Kyushu: Major industrial complex in the north.
- Fukuoka: Commercial center of the island.
- Nagasaki: Historically significant port city.
Consider the following statements regarding Kyushu Island:
- It is the largest of Japan’s four main islands.
- It is located to the east of the Pacific Ocean and west of the East China Sea.
- Mount Aso, located in Kyushu, is the world’s largest dormant volcanic crater.
- The Tsushima Strait separates Kyushu from China.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 3 and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Kyushu is not the largest; it is the third-largest of Japan’s four main islands.
- Statement 2 is correct – Kyushu is bordered by the Pacific Ocean (east) and the East China Sea (west).
- Mount Aso is active, not dormant, making Statement 3 incorrect.
- The Tsushima Strait separates Kyushu from the Korean Peninsula, not China.
Yemen
Geopolitical Importance of Yemen
- Bordering Nations: Saudi Arabia (north) and Oman (east).
Coastal & Strategic Significance:
- Yemen has coastlines along the Red Sea (west), Gulf of Aden, Arabian Sea, and Guardafui Channel (south).
- It controls the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, a crucial maritime chokepoint linking the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea via the Gulf of Aden.
- The strait is vital for global oil transportation and international shipping routes, making it strategically significant for global trade.
Who are the Houthis?
- Religious & Ethnic Background: The Houthis belong to the Zaidi Shia sect, primarily concentrated in Sa’dah province, northwestern Yemen.
Origins:
- The Houthi movement began in the 1990s as an uprising against the dictatorship of then-Yemeni President Ali Abdullah Saleh.
Role in the Yemen Civil War:
- The Houthis are one of the dominant factions in Yemen’s ongoing civil war.
- They currently control large portions of western and northwestern Yemen, including Sana’a, the capital.
Key Factions in the Yemen Conflict
- Apart from the Houthis, other significant groups involved in the war include:
- Yemeni Government – Backed by Saudi Arabia and the U.S., it seeks to regain control over Houthi-occupied territories.
- Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) – A Sunni extremist organization operating in Yemen.
- Ansar al-Sharia – A terrorist group linked to AQAP.
- Iranian Backing & Anti-Israel Stance
- The Houthis are a key member of “The Axis of Resistance”, a regional alliance led by Iran that opposes Israel and Western influence in the Middle East.
- They receive military, financial, and logistical support from Iran, aligning their ideology and actions with Iran’s broader strategic objectives.
Consider the following statements regarding the geopolitical significance of Yemen:
- Yemen shares its land borders with Saudi Arabia, Oman, and the United Arab Emirates.
- The Bab-el-Mandeb Strait connects the Red Sea with the Persian Gulf.
- Yemen’s control over the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait makes it crucial for global maritime trade.
- The Gulf of Aden, bordering Yemen, is a key route for global oil transportation.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Yemen shares its borders with Saudi Arabia (north) and Oman (east) but not with the UAE.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The Bab-el-Mandeb Strait connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden, NOT the Persian Gulf.
- Statement 3 is correct: Yemen’s control over Bab-el-Mandeb gives it strategic importance in global maritime trade.
- Statement 4 is correct: The Gulf of Aden is a crucial oil shipping route linking the Indian Ocean, Middle East, and Europe.
Mount Fuji
- Japan has announced the introduction of a climbing fee of US$27 for Mount Fuji’s four main trails starting this summer.
- This initiative aims to control overcrowding and enhance safety measures for tourists visiting the iconic peak.
About Mount Fuji
- Tallest Mountain in Japan: Mount Fuji, also known as Fuji-san, stands at 3,776 meters (12,389 feet), making it Japan’s highest peak.
- Location: It is situated on Honshu Island, spanning Yamanashi and Shizuoka prefectures, approximately 100 km southwest of the Tokyo-Yokohama metropolitan area.
- Volcanic Chain: Mount Fuji is part of the Fuji Volcanic Zone, an extensive volcanic chain that stretches from the Mariana Islands and Izu Islands through the Izu Peninsula to northern Honshu.
- Volcanic Status: It is a stratovolcano that has remained dormant since its last eruption in 1707, but it is still classified as active by geologists.
- Cultural Significance: Recognized as one of Japan’s “Three Holy Mountains” alongside Mount Tate and Mount Haku, Fuji holds spiritual and cultural importance.
- UNESCO World Heritage Status: It is a central feature of the Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park, established in 1936, and was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2013.
Formation and Geological History of Mount Fuji
- Traditional Belief: According to legend, Mount Fuji was formed in 286 BCE following a massive earthquake.
Scientific Formation:
- The actual formation is more complex and is estimated to have occurred over the last 2.6 million years on a base that dates back 65 million years.
- First eruptions and initial peaks likely appeared after 700,000 years ago.
Evolution of Mount Fuji:
- Komitake (North slope) and Ashitaka-yama (Southeast) were the earliest formations.
- Stratovolcanic activity led to the rise of Fuji’s main structure after 400,000 years ago.
- Three successive volcanic formations shaped present-day Mount Fuji:
- Komitake (Oldest, forms the base)
- Ko Fuji (“Old Fuji”) – Formed around 100,000 years ago
- Shin Fuji (“New Fuji”) – The most recent formation, completing Fuji’s modern structure.
- The implementation of climbing fees reflects Japan’s ongoing efforts to preserve Mount Fuji’s ecosystem and ensure sustainable tourism, balancing its natural, cultural, and geological significance.
Which of the following rivers and water bodies are geographically closest to Mount Fuji?
- Sagami River
- Fuji River
- Lake Biwa
- Suruga Bay
Which one is the Correct Answer?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2, and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: C) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Mount Fuji is surrounded by key water bodies and rivers:
- Fuji River (flows near the mountain)
- Sagami River (located close to the eastern side of Mount Fuji)
- Suruga Bay (near the southern coastline of Honshu, close to Mount Fuji)
- Lake Biwa, however, is Japan’s largest freshwater lake but is located in Shiga Prefecture, far from Mount Fuji.
River Betwa
- The Betwa River, once a lifeline of the Vindhyas, has nurtured civilizations, sustained kingdoms, and echoed the footsteps of sages and warriors.
- However, today, it struggles for survival—its waters dwindling, its flow fading.
About River Betwa
- Historical Significance: Known in ancient texts as Vetravati, the Betwa River holds deep cultural and spiritual significance, being mentioned in the Vedas and revered in the Mahabharata as a symbol of penance and purity.
Origin & Course:
- It originates from Jhiri village in Raisen district, Madhya Pradesh, within the Vindhya Range, near Narmadapuram (formerly Hoshangabad).
- The river follows a northeastern trajectory, coursing through Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh before merging with the Yamuna River east of Hamirpur, spanning 610 km.
- Almost half of its journey traverses the rugged Malwa Plateau, before descending into the Bundelkhand uplands.
- Major Tributaries: The Jamni and Dhasan rivers contribute significantly to its flow.
- Dams & Water Management: The Betwa is dammed at Dukwan and Deogarh, serving irrigation and hydrological regulation purposes.
Cultural & Strategic Importance:
- The Indian Navy honored the river by naming a frigate INS Betwa after it.
- It plays a crucial role in the Ken-Betwa Link Project, an ambitious interlinking initiative to address water scarcity in Bundelkhand.
- Ken-Betwa Link Project (KBLP)
Objective:
- The KBLP aims to transfer surplus water from the Ken River to the Betwa River, mitigating drought conditions in Bundelkhand.
Historical Context:
- It is the first project under the National Perspective Plan (1980) for interlinking rivers.
- Project Phases:
- Phase I: Involves the construction of the Daudhan Dam Complex, including:
- Low-Level Tunnel
- High-Level Tunnel
- Ken-Betwa Link Canal
- Hydropower facilities
- Phase II: Focuses on three major developments:
- Lower Orr Dam
- Bina Complex Project
Kotha Barrage
- The Betwa River stands at a crossroads—either rejuvenated through conservation and interlinking efforts or left to fade into history as a forgotten relic of the past.
Consider the following statements regarding the Betwa River:
- It originates in the Vindhya Range of Uttar Pradesh.
- The river is a major tributary of the Ganga.
- It flows through both Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
- The Indian Navy has named a warship after this river.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The Betwa River originates in Jhiri village, Raisen district, Madhya Pradesh, not Uttar Pradesh.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: It is a tributary of the Yamuna, not the Ganga.
- Statement 3 is correct: It flows through Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh before merging with the Yamuna.
- Statement 4 is correct: The INS Betwa, a frigate in the Indian Navy, is named after the river.
Ana Sagar Lake
- Supreme Court Orders Removal of Replica Structures from Seven Wonders Park in Ana Sagar Lake Wetland
- The Supreme Court has directed the state government to remove replica structures from the ‘Seven Wonders’ park located in the wetland area of Ana Sagar Lake within six months.
About Ana Sagar Lake
- Ana Sagar Lake, an artificial water body in Ajmer, Rajasthan, was created by constructing a dam across the Luni (Lavanavari) River. Built between 1135 and 1150 AD by Arnoraja Chauhan, the grandfather of Prithviraj Chauhan, the lake is named after its founder.
Spanning 13 km, the lake features several historical structures, including:
- Baradari (pavilions) built by Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan in 1637 AD.
- Daulat Bagh Gardens, designed by Emperor Jehangir, located along the lake’s banks.
- A central island, accessible by boat.
- A circuit house, formerly the British Residency, situated on a nearby hill.
- A significant feature of Ana Sagar Lake is that it typically dries up during the summer months.
Consider the following statements regarding Ana Sagar Lake:
- It is a natural lake formed due to tectonic activity.
- The lake was constructed by a Chauhan ruler in the 12th century.
- The Baradari pavilions on the lake’s banks were built by Emperor Akbar.
- The lake remains filled with water throughout the year due to perennial inflow from the Luni River.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Ana Sagar is an artificial lake, not a natural one. It was constructed by raising a dam across the Luni (Lavanavari) River.
- Statement 2 is correct: The lake was built between 1135-1150 AD by Arnoraja Chauhan, the grandfather of Prithviraj Chauhan.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The Baradari (pavilions) were constructed by Shah Jahan, not Akbar.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: The lake dries up every summer, indicating that it does not receive a perennial water supply.
Farm Distress Index
- A pilot study titled “Agrarian Distress and PM Fasal Bima Yojana: An Analysis of Rainfed Agriculture” was conducted in Telangana and Andhra Pradesh during 2020-21 and 2021-22 to assess farmer distress. However, a systematic national-level assessment of the Farmers’ Distress Index (FDI) is currently unavailable.
Farmers’ Distress Index (FDI):
- FDI is a comprehensive assessment tool designed to identify and address the root causes of agrarian distress, including climate variability, price volatility, and farmers’ risk-bearing capacity.
Objective:
- To develop a user-friendly predictive tool that helps policymakers, researchers, and farmers anticipate and mitigate agrarian distress.
Key Parameters of FDI:
- Exposure to Risk: Climate shocks, pest attacks, droughts, floods, and market fluctuations.
- Adaptive Capacity: Farmers’ ability to cope with adverse conditions through technology, financial resources, and knowledge.
- Sensitivity: The vulnerability of different farming communities based on socio-economic and geographical factors.
- Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies: Government policies, crop insurance schemes, irrigation systems, and community-based support.
- Triggers: Sudden economic or environmental changes that lead to distress.
- Psychological Factors: Mental health and financial stress experienced by farmers.
- Impacts: The long-term consequences on livelihoods, food security, and migration patterns.
- Purpose and Significance:
- Targeted Government Intervention: Helps ensure that relief measures reach the most affected regions.
- Early Warning System: Provides alerts three months in advance, allowing proactive measures to be taken.
- Planning Tool: Assists policymakers in developing localized solutions to mitigate distress.
- The Farmers’ Distress Index is a crucial step towards improving agricultural resilience and rural well-being, ensuring timely intervention and sustainable farming practices.
Consider the following statements regarding the Farmers’ Distress Index (FDI):
- It is a tool developed to assess farmer distress based on parameters such as climate variability, price fluctuations, and psychological factors.
- The index is designed to provide real-time intervention measures at the national level.
- It includes parameters like adaptive capacity, mitigation strategies, and sensitivity to external shocks.
- The Farmers’ Distress Index is officially integrated into India’s agricultural policy and implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct. The Farmers’ Distress Index (FDI) is designed to assess distress based on multiple parameters such as climate risks, market fluctuations, and psychological factors.
- Statement 2 is incorrect. The index is not a real-time intervention tool, but rather a predictive model aimed at early warning and proactive policy planning.
- Statement 3 is correct. It incorporates adaptive capacity, mitigation strategies, and sensitivity as key indicators.
- Statement 4 is incorrect. While FDI is being studied and piloted, it has not yet been officially integrated into national agricultural policy.
Lapis Lazuli
Overview
- Lapis Lazuli is a highly valued semi-precious rock known for its deep blue color, often streaked with golden flecks.
Composition
- The intense blue hue of lapis lazuli is due to lazurite (25-40%), with its shade influenced by sulfur content.
- The golden shimmer comes from the presence of pyrite, while diopside and sodalite occur in minor quantities.
Global Distribution
- Found in several countries, including Chile, Russia, and the United States.
- The finest quality lapis lazuli originates from Badakhshan province in Afghanistan, where it has been mined for over 6,000 years.
Historical Significance
- Ancient India: Lapis lazuli was imported from Badakhshan as early as 1000 BCE.
- Indus Valley Civilization: Archaeologists have discovered lapis lazuli ornaments in sites like Mohenjo-daro and Harappa.
- Ancient Egypt: Used extensively in jewelry and ground into powder for eye makeup.
- Renaissance Europe: Artists ground lapis lazuli into ultramarine pigment, which was one of the most expensive colors used in paintings.
- Lapis lazuli remains a gemstone of historical, artistic, and cultural significance, valued for both its beauty and its enduring legacy.
With reference to Lapis Lazuli, consider the following statements:
- It derives its blue color primarily from the presence of the mineral azurite.
- Pyrite inclusions in lapis lazuli are responsible for its characteristic golden specks.
- The Indus Valley Civilization had no known trade connections for acquiring lapis lazuli.
- The Badakhshan region in Afghanistan is historically known for high-quality lapis lazuli deposits.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect – The blue color of lapis lazuli comes from lazurite, not azurite.
- Statement 2 is correct – The golden specks in lapis lazuli are due to pyrite
- Statement 3 is incorrect – The Indus Valley Civilization did trade for lapis lazuli, as evidenced by findings in Mohenjo-daro and Harappa.
- Statement 4 is correct – Badakhshan (Afghanistan) has been a primary source of high-quality lapis lazuli for over 6,000 years.
Strait of Hormuz
Latest News
- Amid escalating tensions with the United States, Iran has deployed missile systems on the three disputed islands—Greater Tunb, Lesser Tunb, and Abu Musa—located near the Strait of Hormuz.
- This move highlights Iran’s strategic control over this critical maritime passage and raises concerns over regional security and global energy supply disruptions.
Key Facts About the Strait of Hormuz
Geographical Significance:
- The Strait of Hormuz is a narrow yet strategically vital waterway that lies between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula, specifically the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Oman’s Musandam Peninsula.
- It serves as a critical maritime route connecting the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Oman and further to the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean.
Geopolitical Boundaries:
- Northern Coast: Iran
- Southern Coast: United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Oman
- Western End: Persian Gulf
- Eastern End: Gulf of Oman
- Dimensions & Navigability:
- The Strait of Hormuz stretches for 167 kilometers in length.
- The width varies from 95 kilometers at its broadest point to just 39 kilometers at its narrowest.
- Despite its narrowing towards the north, it remains deep enough for the passage of large oil tankers and cargo vessels.
Islands in the Strait of Hormuz:
- Hengam Island
- Hormuz Island
- Qishm Island
- Greater Tunb, Lesser Tunb, and Abu Musa (disputed between Iran and UAE)
Economic & Strategic Importance:
- It is one of the world’s most critical choke points for global energy trade.
- Approximately 25% of the world’s crude oil and 30% of the world’s liquefied natural gas (LNG) pass through this waterway.
- Disruptions in the Strait of Hormuz can significantly impact global oil prices and energy security.
Consider the following statements regarding the Strait of Hormuz:
- It connects the Persian Gulf to the Arabian Sea.
- It is the narrowest maritime chokepoint for global oil transportation.
- The United States maintains a permanent naval base on Abu Musa Island to secure energy trade.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Strait of Hormuz connects the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Oman, which in turn leads to the Arabian Sea.
- Statement 2 is correct: It is one of the narrowest and most critical maritime chokepoints for global oil transportation, with a width narrowing to 39 km at its tightest point.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The United States does not maintain a permanent naval base on Abu Musa Island. The island is disputed between Iran and the UAE, and Iran has control over it. The S. does, however, maintain a strong naval presence in the region through its 5th Fleet, headquartered in Bahrain.
World’s Largest Grain Storage Plan in Cooperative Sector
Why in News?
- On May 31, 2023, the Government approved the World’s Largest Grain Storage Plan in the Cooperative Sector, set to be implemented as a Pilot Project.
- This initiative aims to develop agricultural infrastructure at the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) level, including:
Construction of godowns
- Establishment of custom hiring centers
- Setting up of processing units
The project integrates various existing Government of India (GoI) schemes, such as:
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)
- Agricultural Marketing Infrastructure Scheme (AMI)
- Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM)
- Pradhan Mantri Formalization of Micro Food Processing Enterprises Scheme (PMFME)
Progress of the Pilot Project
- Under the Pilot Project, godowns have been constructed in 11 PACS across 11 States, with a total storage capacity of 9,750 Metric Tons (MT).
State-wise Details of Completed Godowns
|
- Additionally, foundation stones have been laid for 500 additional PACS godowns under the Pilot Project, with a total of 575 PACS identified for implementation across various States/UTs.
Expansion and Future Goals
- The Ministry of Cooperation aims to establish and strengthen 2 lakh multipurpose PACS, Dairy, and Fishery Cooperative Societies across all panchayats and villages in the country.
- To guide this process, a Margdarshika (Standard Operating Procedure) has been introduced.
- In Karnataka, 128 PACS have been established against a target of 218 PACS to be formed by FY 2028-29.
Impact of the World’s Largest Grain Storage Plan
Decentralized Storage Capacity:
- 9,750 MT of storage capacity has been created at the PACS level.
Reduction in Food Grain Wastage:
- Prevents post-harvest losses by ensuring adequate storage facilities.
Strengthening of Food Security:
- Ensures better storage and distribution of food grains to enhance national food security.
Preventing Distress Sales:
- Farmers can store their produce and sell it at better prices rather than being forced into distress sales.
Cost Reduction in Transportation:
- Since PACS can function as both procurement centers and Fair Price Shops (FPS), transportation costs are reduced.
- Avoids the need to transport grains from procurement centers to warehouses and back to FPS.
- This initiative marks a major milestone in strengthening the cooperative sector and enhancing agricultural infrastructure across India.
Consider the following statements regarding the “World’s Largest Grain Storage Plan in the Cooperative Sector”:
- It is being implemented exclusively under the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF).
- The plan aims to develop agri-infrastructure at the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) level.
- One of the objectives of the plan is to enable PACS to operate as procurement centers as well as Fair Price Shops (FPS).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The plan is not implemented exclusively under AIF; rather, it converges multiple schemes like Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF), Agricultural Marketing Infrastructure Scheme (AMI), Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM), and Pradhan Mantri Formalization of Micro Food Processing Enterprises Scheme (PMFME).
- Statement 2 is correct: The plan focuses on strengthening PACS by developing godowns, custom hiring centers, and processing units.
- Statement 3 is correct: The initiative allows PACS to function as procurement centers and Fair Price Shops (FPS), reducing transportation costs and logistical challenges.
Raksha Rajya Mantri flags-off Mt Everest & Mt Kangchenjunga expeditions from New Delhi

- Raksha Rajya Mantri Shri Sanjay Seth flagged off two major mountaineering expeditions to Mount Everest and Mount Kangchenjunga from South Block, New Delhi, on March 26, 2025.
- These expeditions, organized under the Ministry of Defence, mark a significant milestone in India’s adventure sports domain and align with Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi’s vision of fostering self-reliance, resilience, and a fearless spirit among the youth.
- The Mount Everest expedition, a collaborative effort between the Himalayan Mountaineering Institute (HMI), Darjeeling, West Bengal, and Jawahar Institute of Mountaineering & Winter Sports (JIM&WS), Jammu & Kashmir, commemorates 60 years of the Nehru Institute of Mountaineering (NIM), Uttarkashi, Uttarakhand.
- Meanwhile, the Mount Kangchenjunga expedition, organized by the National Institute of Mountaineering and Adventure Sports (NIMAS), Dirang, Arunachal Pradesh, is part of the ‘Har Shikhar Tiranga’ initiative.
India’s Growing Leadership in Mountaineering and Adventure Sports
- Speaking at the flag-off event, Shri Sanjay Seth highlighted India’s emergence as a global powerhouse in adventure sports, crediting the mountaineering institutes for playing a crucial role in training and inspiring the next generation of adventurers.
- He emphasized that these expeditions not only test the climbers’ endurance, skill, and teamwork but also serve as a symbol of India’s mountaineering prowess.
Expedition to Mt. Everest
- Team Composition: Seven elite climbers from NIM, HMI, and JIM&WS, all with extensive experience in extreme high-altitude conditions.
- Leader: Col Anshuman Bhadauria, Principal, NIM.
- Route: Traditional South Col Route in Nepal, navigating the treacherous Khumbu Valley, with high-altitude acclimatization camps.
- Objective: To provide invaluable first-hand Everest experience to instructors, enabling them to train and inspire future Indian mountaineers.
- Schedule: Departure on April 2, 2025, with the summit push expected in May 2025.
Expedition to Mt. Kangchenjunga
- Significance: Kangchenjunga is India’s highest and only 8,000-meter peak, posing one of the most formidable challenges in global mountaineering.
- Team Composition: Five skilled climbers and three support staff.
- Leader: Col Ranveer Singh Jamwal, Director, NIMAS, Dirang, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Achievements of NIMAS: Successfully climbed the highest peaks in all 27 Indian states.
- Schedule: Expedition commences on April 7, 2025.
These ambitious expeditions set a new benchmark for India’s mountaineering aspirations, reinforcing the country’s commitment to adventure, resilience, and excellence in extreme sports.
Consider the following statements regarding the recent Indian mountaineering expeditions to Mt. Everest and Mt. Kangchenjunga:
- The expedition to Mt. Everest is being conducted under the Har Shikhar Tiranga initiative by the National Institute of Mountaineering and Adventure Sports (NIMAS).
- The Mt. Kangchenjunga expedition marks the 60th anniversary of the Nehru Institute of Mountaineering (NIM).
- The expeditions are being conducted under the aegis of the Ministry of Defence.
- The traditional North Col Route in Tibet has been chosen for the Everest expedition.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The Har Shikhar Tiranga initiative is associated with the Kangchenjunga expedition, not Mt. Everest.
- Statement 2 is correct: The Mt. Everest expedition commemorates 60 years of the Nehru Institute of Mountaineering (NIM), Uttarkashi.
- Statement 3 is correct: The expeditions are organized under the Ministry of Defence.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: The South Col Route in Nepal, not the North Col Route in Tibet, has been chosen for the Everest expedition.
New Pamban Bridge
KeyHighlights:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi will inaugurate the New Pamban Bridge in Rameshwaram, Tamil Nadu, on April 6, 2025.- The event, coinciding with Ram Navami, marks a major milestone in India’s infrastructure development.
- Spanning 2.5 kilometers, the bridge significantly improves connectivity between mainland India and Rameshwaram Island, reducing train travel time from 25-30 minutes to under five minutes.
Engineering Marvel
- The New Pamban Bridge is Asia’s first vertical lift bridge, replacing the century-old structure built in 1914, which was decommissioned in December 2022 due to severe corrosion.
- Constructed by Rail Vikas Nigam Limited (RVNL) at a cost of ₹535 crore, the bridge is designed to accommodate faster trains and increased traffic.
Advanced Features & Challenges
- Electromechanical Lift System: Allows the bridge to be lifted in just five minutes to facilitate maritime movement, operated by a single person.
- Speed Limit: Trains can run at a maximum speed of 75 km/h, except on the vertical lift section, where safety regulations limit speed to 50 km/h.
- Weather Sensitivity: The lifting mechanism is affected by wind speeds exceeding 58 km/h, a frequent occurrence from October to February, potentially impacting operations.
Historical Significance & Connectivity
- The old Pamban Bridge was the sole railway link to Rameswaram until the construction of a road bridge in 1988.
- The new bridge restores a vital rail connection, crucial for local commuters and the influx of pilgrims visiting Rameswaram.
Inauguration & Future Developments
- The inauguration ceremony will include the launch of a new train service between Tambaram and Rameswaram.
- Additionally, the Rameswaram railway station is undergoing redevelopment, with completion expected by September 2025.
Consider the following statements regarding the New Pamban Bridge:
- It is the first vertical lift bridge in Asia.
- The bridge was constructed by the Indian Railways at a cost exceeding ₹700 crore.
- It is designed to accommodate both railway and vehicular traffic.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation:
- The New Pamban Bridge is Asia’s first vertical lift railway bridge (Statement 1 is correct).
- It was constructed by Rail Vikas Nigam Limited (RVNL) at a cost of ₹535 crore, not ₹700 crore (Statement 2 is incorrect).
- The bridge is exclusively for railway traffic and does not accommodate vehicular movement (Statement 3 is incorrect).
3rd Session of India-Uganda Joint Trade Committee held in New Delhi
- The Third Session of the India-Uganda Joint Trade Committee (JTC)was held in New Delhi on 25th-26th March 2025, marking a significant step in reinforcing trade relations between the two nations after a gap of 23 years.
- Both sides conducted a comprehensive review of bilateral trade and acknowledged that the current trade volume does not fully reflect the economic potential of their partnership.
- To address this, both countries committed to enhancing, deepening, and diversifying trade relations.
- A key outcome of the discussions was the proposal to establish an India-Uganda Joint Business Forumto promote direct engagement between business leaders from both nations.

Key Areas of Cooperation
- India and Uganda identified priority sectors to expand trade and investment, including:
- Agriculture & Allied Sectors: Coffee, cocoa products, pulses, spices, dairy products, fruits, and vegetables.
- Minerals & Resources: Rare Earth Elements (REE), mining, petrochemicals, and residual chemical products.
- Manufacturing & Industrial Growth: Plastic raw materials, essential oils, and allied products.
- Technology & Infrastructure: Digital infrastructure, banking, MSME growth, solar energy, rural electrification, and electric vehicles.
- Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals: Strengthening cooperation in health services, traditional medicine, and telemedicine.
- Both sides also agreed to explore and formalize Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs)in Public Works, Infrastructure Development, Agriculture, Traditional Medicine, and Standardization.
- Additionally, discussions were held on recognizing the Indian Pharmacopoeiato facilitate pharmaceutical trade.
High-Level Participation
- The Indian delegationwas led by Additional Secretary, Department of Commerce, Shri Ajay Bhadoo, who highlighted the strong economic partnership between the two nations and emphasized opportunities in e-commerce, pharmaceuticals, MSME cluster development, and renewable energy.
- The Ugandan delegationwas headed by Elly Kamahungye Kafeero, Head of International Political Cooperation Department, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Uganda, accompanied by Amb. Prof. Joyce Kikafunda Kakuramatsi, Uganda’s High Commissioner to India, and a 28-member delegation representing various ministries and Uganda’s Mission in India.
- The discussions were conducted in a cordial and cooperative atmosphere, reflecting the strong and amicable relations between India and Uganda.
Industrial & Export Insights
- As part of their visit, the Ugandan delegation toured the Noida SEZ (Special Economic Zone)to gain first-hand insights into India’s industrial and export ecosystem.
- The deliberations at the 3rd Session of the India-Uganda JTCwere forward-looking, setting the stage for increased trade, investment, and mutual growth between the two nations.
Consider the following statements regarding the India-Uganda Joint Trade Committee (JTC) meeting held in March 2025:
- The session was held in Kampala, Uganda, to mark the first bilateral trade summit after a gap of 23 years.
- A major outcome of the meeting was the proposal to establish an India-Uganda Joint Business Forum.
- Discussions included cooperation in agriculture, mining, pharmaceuticals, and digital infrastructure.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation: The session was held in New Delhi, India, not Kampala. However, the discussions did include the proposal for an India-Uganda Joint Business Forum and identified key areas of cooperation such as agriculture, mining, pharmaceuticals, and digital infrastructure.
Free Movement Regime between India and Myanmar
Background
- In 2024, the Union Home Minister announced the decision to abolish the Free Movement Regime (FMR) along the Myanmar border. However, no substantial progress has been made in implementing this decision.
Understanding the Free Movement Regime (FMR)
- The Free Movement Regime (FMR) is a bilateral arrangement between India and Myanmar that permits border communities to cross into each other’s territory without a visa.
- Established in 1968, FMR was introduced due to deep familial and ethnic ties shared by tribes living along the border.
- Initially, the regime allowed movement up to 40 km inside the other country’s territory.
- However, in 2004, this limit was reduced to 16 km, followed by additional regulatory measures introduced in 2016.
Rationale Behind Scrapping FMR
Internal Security Concerns
- Myanmar’s ongoing instability, along with the presence of armed groups, has led to an increase in unauthorized migration, creating security challenges for India.
Drug Trafficking
- Myanmar is part of the infamous Golden Triangle, one of the world’s major hubs for illicit drug production and smuggling. The porous border facilitates the influx of narcotics into India, exacerbating drug-related problems in the Northeast.
Insurgent Activities
- Several insurgent groups operate from across the border in Myanmar, using dense forests as a safe haven. The existing FMR enables their movement and logistical support, posing a threat to India’s internal security.
Influx of Refugees
- Escalating violence in Myanmar has led to an increased flow of refugees into India, particularly affecting Manipur and Mizoram. This has resulted in social, economic, and administrative challenges for Indian states.
China’s Expanding Influence
- Following the 2021 military coup in Myanmar, the country has become increasingly dependent on China, which provides diplomatic and economic support. While Myanmar previously sought to diversify its international partnerships, its growing reliance on China raises strategic concerns for India.
India-Myanmar Relations: A Strategic Overview
Geographical Proximity
- India and Myanmar share both a land and maritime boundary in the Bay of Bengal.
- Four northeastern Indian states—Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, and Mizoram—share borders with Myanmar.
Historical and Cultural Linkages
- India and Myanmar share centuries-old historical, religious, and cultural connections, with influences from Buddhism, Hinduism, and ancient trade routes shaping bilateral interactions.
- India and Myanmar signed the Treaty of Friendship in 1951, laying the foundation for their diplomatic relations.
Geopolitical Significance
- Myanmar’s strategic location makes it a vital bridge between South Asia and Southeast Asia.
- India’s Act East Policy and Neighborhood First Policy emphasize strengthening ties with Myanmar to enhance regional connectivity and economic cooperation.
Economic and Trade Relations
- Bilateral trade between India and Myanmar reached USD 1.50 billion in 2023-24.
Trade is conducted under:
- ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA)
- India’s Duty-Free Tariff Preference (DFTP) scheme
Security Cooperation
- India and Myanmar collaborate on border security, counterinsurgency operations, and intelligence sharing.
- Joint patrolling and military operations have been conducted to counter insurgent groups operating across the border.
Connectivity and Infrastructure Initiatives
- India is actively involved in major connectivity projects to enhance trade and infrastructure development:
- Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project (KMMTTP) – A key initiative to improve connectivity between India’s northeastern states and Myanmar via maritime and land routes.
- India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway – A crucial project aimed at bolstering economic integration between the three countries.
- Sittwe Port in Myanmar’s Rakhine State – A strategically significant port under KMMTTP, providing India an alternative trade route bypassing the congested Siliguri Corridor.
Developmental Assistance
- India has extended assistance in multiple sectors, including healthcare, education, skill development, and infrastructure.
- India and Myanmar collaborate under multilateral frameworks such as BIMSTEC and Mekong-Ganga Cooperation (MGC).
Way Forward
Regulated Border Management
- India must develop a structured mechanism to monitor cross-border movement while balancing security and humanitarian considerations.
- Deploying advanced surveillance technologies and strengthening border infrastructure will be crucial.
Public Awareness and Stakeholder Consultation
- It is imperative for the Indian government to educate local communities and stakeholders about the implications of FMR and its potential removal.
- Consultation with northeastern state governments and indigenous communities will help in formulating an inclusive border policy.
Sustainable Refugee Policy
- India needs a well-defined refugee policy to manage the influx of displaced individuals from Myanmar while ensuring national security.
- International collaboration with organizations like UNHCR can aid in managing refugee challenges.
Strategic Engagement with Myanmar
- India must continue engaging diplomatically with Myanmar’s ruling establishment to safeguard strategic and economic interests.
- Diversifying Myanmar’s external partnerships beyond China will be essential for regional stability.
Enhanced Economic and Security Cooperation
- Expanding bilateral trade and connectivity projects will strengthen India’s position in Myanmar.
- Joint counter-insurgency operations and intelligence sharing should be intensified to tackle security threats.
Conclusion
- Given the uncertain political landscape in Myanmar, India must adopt a balanced approach—tightening border security while maintaining people-to-people ties.
- The government should take local communities into confidence, formulate a phased strategy for managing border movement, and enhance cooperation with Myanmar to protect national and regional interests.
Consider the following statements regarding the India-Myanmar border and security cooperation:
- India and Myanmar have conducted joint military operations to target insurgent groups operating along the border.
- The Indo-Myanmar Border Agreement allows the Indian military to cross into Myanmar’s territory in pursuit of insurgents without prior permission.
- Myanmar is part of both the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B. 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct : India and Myanmar have conducted joint military operations such as Operation Sunrise (2019) to neutralize insurgent camps along the border.
- Statement 2 is incorrect : While India has conducted “hot pursuit” strikes against insurgents inside Myanmar (e.g., 2015 strike against NSCN-K militants), such actions require bilateral cooperation and prior coordination, as Myanmar does not permit unilateral military action.
- Statement 3 is correct : Myanmar is a member of both BIMSTEC and ASEAN, playing a strategic role in regional cooperation.
PM’s Visit to Mauritius
- The Prime Minister of India recently paid a state visit to Mauritius, marking his second visit since 2015. He was the Chief Guest at Mauritius’ National Day Celebrations on March 12.
Key Highlights of the Visit
- Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs): Agreements signed in areas such as civil service training, support for small and medium enterprises (SMEs), blue economy development, combating financial crimes, and local currency settlement for trade.
- INR-Based Credit Line:India extended an INR 487.6 crore line of credit for replacing water pipelines in Mauritius, the first-ever INR-denominated credit line.
- White-Shipping Agreement:A maritime security agreement facilitating information exchange between India and Mauritius.
- Award Conferred:The PM received the Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean, becoming the first Indian recipient of this prestigious award.
- Vision MAHASAGAR:The PM introduced the Mutual And Holistic Advancement for Security And Growth Across Regions (MAHASAGAR) vision, expanding upon the existing Vision SAGAR framework.
About Mauritius
Location: A strategically positioned island nation in the western Indian Ocean near India.
Population: Approximately 1.2 million people, with 70% of Indian origin, strengthening historical and cultural ties.
Colonial History: Initially a French colony, later becoming a British possession before gaining independence.
National Day: Celebrated on March 12, coinciding with Mahatma Gandhi’s Dandi March anniversary.
India-Mauritius Bilateral Relations
- Diplomatic and Economic Ties
- Established Relations: India and Mauritius established diplomatic ties in 1948 and have since become key partners in the Asian and Indian Ocean regions.
Bilateral Trade (2022-2023):
- Indian Exports to Mauritius: USD 462.69 million
- Mauritian Exports to India: USD 91.50 million
- Total Trade Volume: USD 554.19 million
- Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA): Signed in 1982 to prevent double taxation for investors and businesses.
- Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA): India’s first trade agreement with an African nation, signed in 2021, promoting trade and investment.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Mauritius is the second-largest source of FDI into India for FY 2023-24, following Singapore.
Defence and Strategic Cooperation
Preferred Defence Partner: India supports Mauritius in acquiring defence platforms, capacity building, and conducting joint patrols in the Indian Ocean.
Key Defence Agreements:
First Agreement: Transfer of a Dornier aircraft and Advanced Light Helicopter (Dhruv) on lease.
Second Agreement: A USD 100 million Line of Credit (LoC) for defence procurement.
Space Cooperation: An MoU signed in November 2023 for the development of a joint satellite, fostering collaboration in space research.
Historical Indian Migration to Mauritius
French Rule (1700s): Indians from Puducherry arrived as artisans and masons.
British Rule (1834–Early 1900s): Around half a million Indian indentured laborers were brought to Mauritius, many of whom settled permanently, shaping its culture and demographics.
Development Assistance
- Infrastructure Projects: India has supported Mauritius in developing the Metro Express project, hospitals, and Agaléga Island infrastructure.
- Humanitarian Aid: India extended cyclone relief assistance during Cyclone Chido (2023), reinforcing its role as a first responder in the region.
Strategic Significance of Mauritius for India
Maritime and Geopolitical Interests
Strategic Location: Mauritius’ position in the Indian Ocean is vital for India’s maritime security and trade routes.
Agaléga Island: Situated 1,100 km north of Mauritius, the island is strategically important for India’s naval operations.
In 2024, India and Mauritius jointly inaugurated an airstrip and jetty projects to strengthen bilateral cooperation.
Countering China’s Influence: Strengthening ties with Mauritius is crucial for India to counter China’s expanding footprint in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
Geopolitical Competition: The Indian Ocean is witnessing increasing competition from China, Europe, the Gulf nations, Russia, Iran, and Turkey.
Economic and Cultural Importance: Cultural and Diaspora Ties: With 70% of the Mauritian population tracing Indian ancestry, strong cultural and familial bonds exist between both nations.
Blue Economy Partnership: Mauritius plays a critical role in India’s blue economy initiatives, particularly in fisheries, maritime resources, and offshore energy exploration.
Indian Ocean Cooperation: Mauritius is an active member of the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), promoting regional stability and economic integration.
Challenges in India-Mauritius Relations
Economic and Trade Concerns
Tax Treaty Misuse: The DTAA between India and Mauritius has faced criticism for facilitating money laundering and round-tripping of funds.
Trade Imbalance: Despite strong economic ties, Mauritius has significant trade deficits with India, necessitating trade diversification.
Security and Strategic Challenges
Maritime Security: As a key player in the Indo-Pacific strategy, Mauritius’ security concerns align with India’s, yet evolving regional dynamics present new challenges.
Growing Chinese Influence:
- In 2021, China signed a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with Mauritius, helping China expand its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) in Africa.
- This could erode India’s strategic influence in Mauritius.
Way Forward
- Enhanced Defence Cooperation: Strengthening joint training, counterterrorism initiatives, and maritime security collaborations to safeguard regional stability.
- Economic Diversification: Expanding trade relations beyond traditional areas and exploring emerging sectors for bilateral growth.
- People-to-People Ties: Promoting cultural exchanges, educational scholarships, and diaspora engagement to reinforce deep-rooted historical bonds.
- Sustainable Blue Economy Partnership: Leveraging Mauritius’ expertise in ocean resources management to drive mutual economic growth.
India and Mauritius share a unique, time-tested partnership, and their evolving cooperation will play a crucial role in shaping regional security, economic integration, and strategic alliances in the Indian Ocean region.
Consider the following statements regarding India-Mauritius relations:
- Mauritius is the largest source of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) into India.
- India and Mauritius have signed a Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA), which is India’s first trade agreement with an African nation.
- India has leased the Agaléga Islands from Mauritius for setting up a strategic naval base.
- The White-Shipping Agreement between India and Mauritius facilitates free trade between the two nations without tariff barriers.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (c) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect – While Mauritius has historically been a major source of FDI into India, Singapore overtook Mauritius as the largest FDI contributor in recent years (FY 2023-24). Therefore, this statement is incorrect.
- Statement 2 is correct – India and Mauritius signed CECPA in 2021, which is indeed India’s first-ever trade agreement with an African nation. This statement is correct.
- Statement 3 is incorrect – India has not leased the Agaléga Islands, but developed infrastructure projects there, including an airstrip and a jetty, to enhance maritime security. There is no official declaration of a naval base. This statement is incorrect.
- Statement 4 is incorrect – The White-Shipping Agreement is not about free trade. It is a technical agreement that allows exchange of maritime security data between India and Mauritius to monitor ship movements and counter threats like piracy and smuggling. This statement is incorrect.Thus, only statement 2 is correct, making (c) 2 only the right answer.
PM Modi Receives Mauritius’ Highest Honour
- Prime Minister Narendra Modihas been awarded the Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean by Mauritius.
- This prestigious recognition is the highest civilian honour bestowed by the island nation.
- Modi is the first Indian to receive this honour, reflecting the deep-rooted historical and diplomatic ties between India and Mauritius.
Significance of the Honour
- The Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Oceanis the most distinguished civilian award in Mauritius.
- Since Mauritius became a Republic, this honour has been conferred upon only five foreign dignitaries, including Nelson Mandela.
- The award symbolizes mutual respect, cooperation, and the strong diplomatic relationshipbetween India and Mauritius.
Modi’s Growing List of International Honours
This accolade from Mauritius marks Modi’s 21st international award, adding to a series of global recognitions for his leadership and diplomatic initiatives. Some of the notable awards he has received include:
- Order of Abdulaziz Al Saud(Saudi Arabia, 2016)
- State Order of Ghazi Amir Amanullah Khan(Afghanistan, 2016)
- Grand Collar of the State of Palestine(Palestine, 2018)
- Order of Zayed(UAE, 2019)
- Order of St. Andrew(Russia, 2019)
- Order of the Nile(Egypt, 2023)
- Order of the Druk Gyalpo(Bhutan, 2024)
- Dominica Award of Honour(Dominica, 2024)
India-Mauritius Relations: A Historical Perspective
- The ties between India and Mauritiusdate back to the 19th century, when Indian indentured labourers were brought to Mauritius. Over time, these historical connections have evolved into a robust economic, cultural, and strategic partnership.
- India is one of Mauritius’ largest trading partners.
- Both countries collaborate extensivelyin fields such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, and security.
- Mauritius is a key player in India’s diplomatic outreachin the Indian Ocean region, with both nations working closely on maritime security and regional stability.
Conclusion
- The Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Oceanis a testament to India-Mauritius friendship and underscores Modi’s global leadership. This honour further strengthens bilateral ties and reaffirms India’s role as a key partner in Mauritius’ development.
Which of the following statements about the “Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean” is correct?
(a) It is the highest military honour awarded by Mauritius.
(b) It has been awarded to more than 100 foreign dignitaries since Mauritius became a Republic.
(c) Narendra Modi is the first Indian recipient of this honour.
(d) It is an annual award given to prominent global leaders.
Answer: (c)
Explanation:
- The Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Oceanis Mauritius’ highest civilian honour, not a military one. It has been conferred upon only five foreign dignitaries, including Nelson Mandela, since Mauritius became a Republic.
- Modi is the first Indian to receive this honour.
- The award is not an annual event but is given selectively to leaders who have significantly contributed to Mauritius’ growth and bilateral .
National Board for Wildlife
- The Prime Minister chaired the 7th meeting of the National Board for Wildlife (NBWL) at Gir National Park, Gujarat, focusing on wildlife conservation strategies, dolphin population estimation, and human-wildlife conflict mitigation.
- India’s first riverine dolphin population estimation was released, recording 6,327 river dolphins across 28 rivers in 8 states. Uttar Pradesh had the highest population, followed by Bihar, West Bengal, and Assam.
- Key wildlife conservation initiatives included the foundation stone laying of the National Referral Centre for Wildlife in Junagadh, Gujarat, to serve as a hub for wildlife health and disease management.
- To address human-wildlife conflicts, a Centre of Excellence will be established at the Wildlife Institute of India’s SACON (Salim Ali Centre for Ornithology and Natural History) in Coimbatore.
- Rapid Response Teams will be equipped with advanced technology for conflict mitigation.
- Cheetah reintroduction plans were also discussed, with new sites proposed in Gandhisagar Sanctuary, Madhya Pradesh, and Banni Grasslands, Gujarat, aiming to strengthen reintroduction and habitat restoration efforts.
- The National Board for Wildlife (NBWL) was originally established as the Indian Board for Wildlife in 1952 and later reconstituted in 2022.
- The Prime Minister serves as the Chairperson (Ex-officio), and the Minister of Environment, Forest & Climate Change (MoEFCC) is the Vice-Chairperson.
- The 47-member committee comprises government officials, conservationists, ecologists, environmentalists, and military personnel.
- NBWL’s approval is required for construction of tourist lodges in protected areas, alteration of Protected Area (PA) boundaries, destruction or diversion of wildlife habitats, and de-notification of Tiger Reserves.
- Gir National Park, located in the Saurashtra region of Gujarat, was declared a sanctuary in 1965 and upgraded to a national park in 1975.
- It is the only place outside Africa where lions exist in the wild. The Asiatic lion population has increased from fewer than 200 in the late 1960s to 674 as per the 2020 Census.
- The park is home to 40 species of mammals and 425 species of birds.
- Regarding India’s first riverine dolphin estimation, a multiple-choice question was posed.
- The study recorded over 6,000 river dolphins, conducted across 28 rivers spanning 8 states. The initiative aligns with Project Dolphin, which aims to conserve freshwater and marine dolphins in India.
- The correct answer is that Uttar Pradesh has the highest river dolphin population, making the correct statements the estimation being across 28 rivers in 8 states and alignment with Project Dolphin.
With reference to India’s first riverine dolphin estimation, consider the following statements:
- The study recorded over 6,000 river dolphins across multiple states, with Bihar having the highest population.
- The estimation was conducted across 28 rivers spanning 8 states.
- The initiative aligns with the conservation efforts under ‘Project Dolphin’ launched by the Government of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect. Uttar Pradesh, not Bihar, has the highest river dolphin population.
Statement 2 is correct. The study covered 28 rivers across 8 states.
Statement 3 is correct. The estimation aligns with Project Dolphin, which aims at conserving freshwater and marine dolphins in India
Gharials (Gavialis Gangeticus)
Why in News?
- The Madhya Pradesh government released 10 gharials into the Chambal River at the National Chambal Gharial Sanctuary in Morena as part of conservation efforts.
About Gharials (Gavialis gangeticus)
- Etymology:The name “Gharial” is derived from the Hindi word “Ghara” (pot), referring to the bulbous nasal protuberance (narial excrescence) found exclusively in adult males.
Sexual Dimorphism:
- Males and females differ significantly in size and appearance.
- Only males possess the distinctive nasal growth.
- Dietary Specialization:
- Unlike crocodiles, gharials feed exclusively on fish, making them piscivorous.
- They lack the jaw strength to attack large mammals or humans, rendering them non-man-eaters.
Habitat & Distribution:
- Gharials are strictly riverine species, requiring:
- Deep, clear, fast-flowing waters.
- Steep, sandy riverbanks for basking and nesting.
Major River Systems Supporting Gharials:
- Chambal River (Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh).
- Girwa River (Uttar Pradesh).
- Ken River (Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh).
- Yamuna River (Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Delhi).
- Brahmaputra River (Assam, Arunachal Pradesh).
- Ghaghara River (Uttar Pradesh, Bihar).
- Bhagirathi-Hooghly River (West Bengal).
- Conservation Status & Efforts
Legal & International Protection:
- IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered 🛑
- Wildlife Protection Act (1972): Schedule I (Highest Protection)
- CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species): Appendix I (Prohibits commercial trade).
Key Conservation Initiatives:
- Project Crocodile (1975):
- Launched with UNDP & FAO assistance.
- Focused on captive breeding and reintroduction programs.
- Gharial Reserves in India:
- Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan are the main states with dedicated gharial reserves.
Notable Protected Areas:
- National Chambal Sanctuary (MP, UP, Rajasthan).
- Katarniaghat Wildlife Sanctuary (UP).
- Chambal River – Geographical & Ecological Significance
- Origin & Course:
- Source: Janapav Hills, Vindhyan Range, Madhya Pradesh.
- Flow: Passes through Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh, ultimately joining the Yamuna River.
Major Tributaries:
- Right Bank Tributaries: Banas, Parvati, Kali Sindh.
- Left Bank Tributaries: Shipra.
- Dams on the Chambal River:
- Gandhi Sagar Dam
- Rana Pratap Sagar Dam
- Jawahar Sagar Dam
Geological & Ecological Importance:
Ravine Formation:
- Chambal basin is prone to severe soil erosion, leading to deep ravines in Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan.
- These ravines serve as natural habitats for endangered species.
- Keoladeo National Park (Rajasthan):
- Receives water supply from the Chambal River Irrigation Project.
Supports migratory birds like Siberian Cranes.
Consider the following statements regarding gharials
- Unlike crocodiles, gharials primarily feed on fish and do not attack large mammals.
- Males and females exhibit no significant difference in physical characteristics.
- The Chambal River is one of the last remaining strongholds of wild gharial populations in India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct. Gharials are piscivorous and not man-eaters.
Statement 2 is incorrect. They show sexual dimorphism (males have a bulbous snout).
Statement 3 is correct. Chambal River hosts one of the largest wild gharial populations.
PM2.5 Pollution Sources in Northern India
- The Prime Minister of India recently paid a state visit to Mauritius, marking his second visit since 2015. He was the Chief Guest at Mauritius’ National Day Celebrations on March 12.
Key Highlights of the Visit
- Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs): Agreements signed in areas such as civil service training, support for small and medium enterprises (SMEs), blue economy development, combating financial crimes, and local currency settlement for trade.
- INR-Based Credit Line:India extended an INR 487.6 crore line of credit for replacing water pipelines in Mauritius, the first-ever INR-denominated credit line.
- White-Shipping Agreement:A maritime security agreement facilitating information exchange between India and Mauritius.
- Award Conferred:The PM received the Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean, becoming the first Indian recipient of this prestigious award.
- Vision MAHASAGAR:The PM introduced the Mutual And Holistic Advancement for Security And Growth Across Regions (MAHASAGAR) vision, expanding upon the existing Vision SAGAR framework.
About Mauritius
Location: A strategically positioned island nation in the western Indian Ocean near India.
Population: Approximately 1.2 million people, with 70% of Indian origin, strengthening historical and cultural ties.
Colonial History: Initially a French colony, later becoming a British possession before gaining independence.
National Day: Celebrated on March 12, coinciding with Mahatma Gandhi’s Dandi March anniversary.
India-Mauritius Bilateral Relations
- Diplomatic and Economic Ties
- Established Relations: India and Mauritius established diplomatic ties in 1948 and have since become key partners in the Asian and Indian Ocean regions.
Bilateral Trade (2022-2023):
- Indian Exports to Mauritius: USD 462.69 million
- Mauritian Exports to India: USD 91.50 million
- Total Trade Volume: USD 554.19 million
- Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA): Signed in 1982 to prevent double taxation for investors and businesses.
- Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA): India’s first trade agreement with an African nation, signed in 2021, promoting trade and investment.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Mauritius is the second-largest source of FDI into India for FY 2023-24, following Singapore.
Defence and Strategic Cooperation
Preferred Defence Partner: India supports Mauritius in acquiring defence platforms, capacity building, and conducting joint patrols in the Indian Ocean.
Key Defence Agreements:
First Agreement: Transfer of a Dornier aircraft and Advanced Light Helicopter (Dhruv) on lease.
Second Agreement: A USD 100 million Line of Credit (LoC) for defence procurement.
Space Cooperation: An MoU signed in November 2023 for the development of a joint satellite, fostering collaboration in space research.
Historical Indian Migration to Mauritius
French Rule (1700s): Indians from Puducherry arrived as artisans and masons.
British Rule (1834–Early 1900s): Around half a million Indian indentured laborers were brought to Mauritius, many of whom settled permanently, shaping its culture and demographics.
Development Assistance
- Infrastructure Projects: India has supported Mauritius in developing the Metro Express project, hospitals, and Agaléga Island infrastructure.
- Humanitarian Aid: India extended cyclone relief assistance during Cyclone Chido (2023), reinforcing its role as a first responder in the region.
Strategic Significance of Mauritius for India
Maritime and Geopolitical Interests
Strategic Location: Mauritius’ position in the Indian Ocean is vital for India’s maritime security and trade routes.
Agaléga Island: Situated 1,100 km north of Mauritius, the island is strategically important for India’s naval operations.
In 2024, India and Mauritius jointly inaugurated an airstrip and jetty projects to strengthen bilateral cooperation.
Countering China’s Influence: Strengthening ties with Mauritius is crucial for India to counter China’s expanding footprint in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
Geopolitical Competition: The Indian Ocean is witnessing increasing competition from China, Europe, the Gulf nations, Russia, Iran, and Turkey.
Economic and Cultural Importance: Cultural and Diaspora Ties: With 70% of the Mauritian population tracing Indian ancestry, strong cultural and familial bonds exist between both nations.
Blue Economy Partnership: Mauritius plays a critical role in India’s blue economy initiatives, particularly in fisheries, maritime resources, and offshore energy exploration.
Indian Ocean Cooperation: Mauritius is an active member of the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), promoting regional stability and economic integration.
Challenges in India-Mauritius Relations
Economic and Trade Concerns
Tax Treaty Misuse: The DTAA between India and Mauritius has faced criticism for facilitating money laundering and round-tripping of funds.
Trade Imbalance: Despite strong economic ties, Mauritius has significant trade deficits with India, necessitating trade diversification.
Security and Strategic Challenges
Maritime Security: As a key player in the Indo-Pacific strategy, Mauritius’ security concerns align with India’s, yet evolving regional dynamics present new challenges.
Growing Chinese Influence:
- In 2021, China signed a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with Mauritius, helping China expand its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) in Africa.
- This could erode India’s strategic influence in Mauritius.
Way Forward
- Enhanced Defence Cooperation: Strengthening joint training, counterterrorism initiatives, and maritime security collaborations to safeguard regional stability.
- Economic Diversification: Expanding trade relations beyond traditional areas and exploring emerging sectors for bilateral growth.
- People-to-People Ties: Promoting cultural exchanges, educational scholarships, and diaspora engagement to reinforce deep-rooted historical bonds.
- Sustainable Blue Economy Partnership: Leveraging Mauritius’ expertise in ocean resources management to drive mutual economic growth.
India and Mauritius share a unique, time-tested partnership, and their evolving cooperation will play a crucial role in shaping regional security, economic integration, and strategic alliances in the Indian Ocean region.
Consider the following statements regarding India-Mauritius relations:
- Mauritius is the largest source of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) into India.
- India and Mauritius have signed a Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA), which is India’s first trade agreement with an African nation.
- India has leased the Agaléga Islands from Mauritius for setting up a strategic naval base.
- The White-Shipping Agreement between India and Mauritius facilitates free trade between the two nations without tariff barriers.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (c) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect – While Mauritius has historically been a major source of FDI into India, Singapore overtook Mauritius as the largest FDI contributor in recent years (FY 2023-24). Therefore, this statement is incorrect.
- Statement 2 is correct – India and Mauritius signed CECPA in 2021, which is indeed India’s first-ever trade agreement with an African nation. This statement is correct.
- Statement 3 is incorrect – India has not leased the Agaléga Islands, but developed infrastructure projects there, including an airstrip and a jetty, to enhance maritime security. There is no official declaration of a naval base. This statement is incorrect.
- Statement 4 is incorrect – The White-Shipping Agreement is not about free trade. It is a technical agreement that allows exchange of maritime security data between India and Mauritius to monitor ship movements and counter threats like piracy and smuggling. This statement is incorrect.Thus, only statement 2 is correct, making (c) 2 only the right answer.
SC’s Directive on Forest Conservation Efforts
- In a landmark directive issued in March 2025, the Supreme Court of Indiamandated that Chief Secretaries of States and Administrators of Union Territories establish expert committees to systematically identify forested areas within their jurisdictions.
- This ruling underscores the judicial oversight of environmental governanceand reaffirms the significance of scientific forest classification for policy implementation.
- The ruling aligns with the historic Supreme Court judgment of December 1996, which provided an expansive definition of “forests”—encompassing all areas meeting the dictionary definition of a forest, regardless of ownership, classification, or legal status.
- This precedent set a broad conservation frameworkaimed at ecological balance and sustainable resource management.
Evolution of Forest Conservation Laws in India
- The Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980
- Enacted to regulate deforestationand protect ecologically sensitive areas from unsustainable exploitation.
- Established the requirement of Central government approvalfor any diversion of forest land for non-forest purposes.
- T.N. Godavarman Case (1996): The Expanded Definition of ‘Forest’
- In December 1996, the Supreme Court, in N. Godavarman Thirumulpad v. Union of India, ruled that:
- The term “forest”should be interpreted broadly to include all lands that exhibit forest characteristics, irrespective of ownership, classification, or legal designation.
- This widenedthe scope of forest conservation laws to cover unclassified forests, private forests, and community forests.
- This ruling laid the foundation for judicial monitoringof forest governance in India.
Recent Supreme Court Orders and Their Implications
- Reiteration of Compliance with 1996 Ruling
- The Supreme Court, in November 2023 and February 2024, reaffirmed that States and UTs must strictly adhereto the 1996 ruling.
- In its March 2025 directive, the court warned that officials failing to complywould face personal liability, strengthening institutional accountability in forest governance.
- Formation of Expert Committees for Forest Identification
- The Supreme Court directed the constitution of expert committeesat the State and UT levels.
Their responsibilities include:
- Identifying all forested areas, including degraded, deforested, and encroached lands.
- Assessing private plantationsand their ecological contributions.
- Ensuring data accuracy for conservation planning.
- Impact of the 2023 Amendments to the Forest (Conservation) Act
- The Forest (Conservation) Amendment Act, 2023, introduced significant changes, sparking controversy among environmentalists.
Key concerns raised by critics:
- The amendments narrowed the definition of “forest,”potentially excluding certain ecologically significant areas from protection.
- This could lead to increased commercial exploitationand ecological disruptions.
- Petitioners in the Supreme Court argue that such legislative dilutioncontradicts the judicially established forest definition from the 1996 ruling.
Data Consolidation and Compliance Mechanisms
- The Supreme Court mandated States and UTsto submit comprehensive records of forest lands.
This is crucial for:
- Accurate assessment of India’s forest cover.
- Ensuring compliancewith conservation policies.
- Monitoring deforestation trends.
- Future Roadmap for Forest Governance: Timely completion of forest identificationby expert committees.
- Submission of reportsto the Union government, followed by review by the Supreme Court.
Enhanced accountability through judicial scrutiny and legal oversight. - This directive signifies a watershed momentin India’s environmental jurisprudence, ensuring scientifically sound, legally robust, and ecologically sustainable forest conservation measures.
With reference to the Supreme Court’s March 2025 directive on forest identification, consider the following statements:
- It mandates the formation of expert committeesat the State and Union Territory levels.
- The directive is based on a long-standing legal precedent established in 1980under the Forest (Conservation) Act.
- The ruling warns that officials failing to comply will face personal liability.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Supreme Court ordered the formation of expert committeesto identify all forest lands in each State and UT.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The directive is based on the 1996 Supreme Court rulingin the N. Godavarman case, not the 1980 Act.
- Statement 3 is correct: The Court explicitly warned officials of personal liabilityfor non-compliance.
Vantara
- Prime Minister Narendra Modihas inaugurated Vantara, a groundbreaking initiative aimed at wildlife conservation, rescue, and rehabilitation.
- Situated in Jamnagar, Gujarat, Vantara represents a monumental stepin India’s conservation efforts, integrating scientific rehabilitation methods with traditional animal care.
Vantara: A Global Benchmark in Wildlife Conservation
World’s Largest Wildlife Rehabilitation Centre:
- Encompasses thousands of acresdedicated to the care of rescued and endangered species.
- Currently shelters over 1.5 lakh animals, including endangered and threatened species, offering them a second chance at survival.
Rescue and Rehabilitation:
- Provides advanced veterinary care, nutritional support, and naturalistic enclosuresfor animal well-being.
- Focuses on long-term conservation strategies, particularly for elephants, big cats, primates, and exotic species.
Awards & Recognitions:
- ‘Prani Mitra’ National Award (Corporate Category):Conferred by the Central Government to Radhe Krishna Temple Elephant Welfare Trust (RKTEWT) for exceptional contributions to elephant rescue, treatment, and care.
Which of the following statements regarding Vantara is/are correct?
- Vantara is the largest wildlife rehabilitation centre in the world, providing care for over 5 lakh rescued animals.
- It has been developed as a government-led initiativeunder the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change.
- The Radhe Krishna Temple Elephant Welfare Trust (RKTEWT), associated with Vantara, has been awarded the ‘Prani Mitra’ National Awardfor elephant conservation.
- Vantara is exclusively dedicated to elephant rehabilitationand does not house other endangered species.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
- a) 1 and 3 only
b) 2 and 4 only
c) 1, 2, and 3 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct:Vantara is the world’s largest wildlife rehabilitation centre, housing 5 lakh+ rescued animals.
- Statement 2 is incorrect:It is a privately managed initiative, not directly under the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change.
- Statement 3 is correct:RKTEWT received the ‘Prani Mitra’ National Award for elephant conservation efforts.
- Statement 4 is incorrect:While it prioritizes elephant rescue, it also rehabilitates various endangered species, including big cats, primates, and exotic wildlife.
Butterflies have been declining the last 20 years
Context:
- A recent study has revealed a 22% decline in butterfly populationsacross the United States since the year 2000, attributing the loss to insecticide use, climate change, and habitat destruction.
- Monarch butterflies, in particular, have experienced a drastic reductionin numbers.
About Butterflies:
- Scientific Classification:Butterflies belong to the superfamily Papilionoidea within the insect order Lepidoptera, which also includes moths and skippers.
- Global Distribution:They are found worldwide, thriving in diverse ecosystems.
- Thermoregulation:Being cold-blooded, butterflies are unable to regulate their body temperature, making them highly sensitive to environmental conditions.
Life Cycle: Their life cycle consists of four distinct stages:
Egg
Larva (Caterpillar)
Pupa (Chrysalis)
Adult (Imago)
Ecological Importance of Butterflies:
Indicators of Environmental Health:
Butterflies serve as bio-indicators, reflecting changes in climate, pollution levels, and ecological balance.
Crucial to the Food Chain:
They provide sustenance for birds, bats, and insectivorous animals while also serving as hosts for parasitic species.
Vital Pollinators:
Ranking just after bees, wasps, and flies, butterflies significantly contribute to plant
reproduction and biodiversity.
Threats to Butterfly Populations:
- Habitat Loss:Driven by urbanization, deforestation, and land-use changes.
- Climate Change:Alters migration patterns and disrupts breeding cycles.
- Pesticide Use:Insecticides and herbicides negatively impact butterfly populations by poisoning larvae and reducing host plant availability.
Interesting Facts:
- Monarch Butterfliesundertake an extraordinary migratory journey, covering distances between 1,200 and 2,800 miles, traveling from the northeastern U.S. and southeastern Canada to central Mexico.
- Marbled Map Butterflyis endemic to the Eastern Ghats and Odisha, making it a unique species of ecological significance.
- Common Birdwing Butterfly, listed under CITES, is frequently found in illegal wildlife tradedue to its striking appearance.
- Nymphalidae Familyrepresents the most dominant butterfly group, comprising 58% of species, likely due to their adaptability to host plants and ecological conditions.
Consider the following statements regarding butterflies:
- Butterflies belong to the order Hemiptera, which also includes moths and dragonflies.
- They are cold-blooded organisms, making them highly sensitive to environmental changes.
- Butterflies undergo incomplete metamorphosis, with only three stages in their life cycle.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Butterflies belong to the order Lepidoptera, not Hemiptera (which includes true bugs like cicadas and aphids). They undergo complete metamorphosis, consisting of four stages (egg, larva, pupa, adult).
Modified Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme
In News : The Government of India has introduced a revised Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme to strengthen Cooperative Sugar Mills (CSMs) and enhance ethanol production capacity.
About the Modified Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme
- The scheme aims to convert existing sugarcane-based ethanol plants into multi-feedstock facilities, enabling them to utilize alternative sources such as maize and damaged food grains (DFG) for ethanol production.
- It provides interest subvention at 6% per annum or 50% of the bank interest rate, whichever is lower, on loans extended to entrepreneurs.
- The subvention is applicable for five years, including a one-year moratorium period.
- The initiative is aligned with the Government’s Ethanol Blended with Petrol (EBP) Programme, which seeks to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and promote sustainable energy alternatives.
Need for the Scheme
- To promote ethanol production from diverse feedstocks and reduce reliance on sugarcane.
- To enhance financial viability of ethanol distilleries by lowering borrowing costs.
- To support the government’s commitment to clean energy and environmental sustainability.
Did You Know?
- The Government of India has been implementing the Ethanol Blended with Petrol (EBP) Programme nationwide to promote biofuels.
- The EBP Programme aims for 20% ethanol blending with petrol by 2025.
- Various ethanol interest subvention schemes have been introduced from July 2018 to April 2022 to encourage ethanol production and reduce crude oil imports.
- This scheme is a strategic step towards energy security, rural development, and environmental sustainability while supporting the economic interests of sugar mills and grain-based ethanol producers.
Consider the following statements regarding the Modified Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme:
- The scheme allows sugar mills to produce ethanol only from sugarcane-based sources.
- It provides an interest subvention of 6% per annum or 50% of the bank interest rate, whichever is lower.
- The subvention period under this scheme is five years, including a one-year moratorium.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
The scheme allows ethanol production from multiple feedstocks, including maize and damaged food grains, not just sugarcane.
Seagrass Conservation Key to Global Biodiversity
Context
A recent review published in Nature Reviews Earth & Environment highlights the alarming decline of seagrass ecosystems globally, with losses occurring at a rate of 1-2% per year due to human activities.
About Seagrasses
- Seagrasses are submerged flowering plants that form dense underwater meadows and have evolved from terrestrial plants to adapt to marine environments.
- Unlike seaweed (algae), seagrasses possess roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and seeds, enabling them to reproduce and sustain ecosystems.
Importance of Seagrass Ecosystems
- Carbon Sequestration & Climate Action
- Often referred to as the “lungs of the sea”, seagrasses sequester carbon up to 35 times faster than tropical rainforests, making them crucial in mitigating climate change.
Biodiversity and Marine Life Protection
- They serve as nurseries for fish species and provide shelter for endangered marine species, supporting ocean biodiversity.
Coastal Protection : Seagrasses act as natural barriers, protecting coastal areas from storms, erosion, and disaster risks.
Economic Significance
- Seagrass meadows provide an estimated economic value of $6.4 trillion annually by sustaining fisheries and boosting coastal tourism.
- Seagrass Distribution in India
India, with a recalculated coastline of 11,098 km (2023-24), has extensive seagrass meadows in:
Gulf of Mannar
Palk Bay
Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Lakshadweep Islands
Gulf of Kutch
Threats to Seagrass Ecosystems
Anthropogenic Activities – Urbanization, pollution, and agricultural runoff.
Weak Law Enforcement – Limited implementation of policies protecting coastal biodiversity.
Biodiversity Loss – Unregulated fishing, boating, and habitat destruction leading to ecosystem degradation.
Global & Indian Restoration Efforts
Global Initiatives
- Seagrass Watch – A citizen science program training volunteers, NGOs, and research organizations to monitor and conserve seagrass habitats worldwide.
- Blue Carbon Initiative – Focuses on carbon sequestration in coastal ecosystems, including mangroves, salt marshes, and seagrasses.
Indian Conservation Initiatives
- National Policy on Marine Fisheries (2017) – Recognizes seagrass meadows as essential coastal ecosystems alongside mangroves and coral reefs.
- Climate Resilience Project – Implemented in Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Odisha, supported by the Global Climate Fund (GCF).
- Seagrass Restoration – Ongoing efforts in Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay to restore degraded seagrass meadows.
Consider the following statements regarding seagrasses:
- Seagrasses are a type of algae that lack roots, stems, and flowers.
- They sequester carbon at a rate much slower than tropical rainforests.
- Seagrass meadows act as natural barriers, protecting coastal areas from erosion and storms.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Explanation:
Incorrect – Seagrasses are not algae; they are flowering plants that evolved from terrestrial plants and adapted to marine environments. Unlike algae, seagrasses have roots, stems, and leaves, and they can produce flowers and seeds.
Incorrect – Seagrasses sequester carbon up to 35 times faster than tropical rainforests, making them one of the most efficient carbon sinks in the world. This ability helps mitigate climate change by reducing atmospheric carbon dioxide.
Correct – Seagrass meadows act as natural barriers, reducing the impact of coastal erosion and storms. Their dense root systems stabilize the seabed, preventing sediment displacement, and their presence helps dissipate wave energy, protecting coastal communities from storm surges.
Madhav National Park
Context:
- Madhav National Park in Madhya Pradesh has been officially designated as India’s 58th tiger reserve, marking a significant milestone in the country’s wildlife conservation efforts.
- The announcement was made by Union Environment Minister Bhupender Yadav. This designation makes it the ninth tiger reserve in Madhya Pradesh, reaffirming the state’s commitment to protecting its rich biodiversity.
- Currently, the reserve is home to five tigers, including two recently born cubs, with plans to introduce two more tigers to strengthen the population.
Significance of Tiger Reserves:
- Tiger reserves play a crucial role in wildlife conservation and ecological balance by providing a protected habitat for tigers and other species.
- These reserves are essential components of India’s broader strategy to preserve biodiversity, prevent poaching, and mitigate human-wildlife conflict.
- The establishment of new tiger reserves reflects the government’s continued commitment to environmental protection and sustainable ecosystem management.
Madhav National Park: Location and Features
Location: Shivpuri district, Madhya Pradesh
Ecosystem: Features a mix of dry deciduous forests, grasslands, and water bodies, making it an ideal habitat for various wildlife species, including tigers.
Biodiversity: Home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, contributing to the state’s rich natural heritage.
Tiger Reintroduction Projects in Madhav National Park
- Madhav National Park’s designation as a tiger reserve follows successful tiger reintroduction efforts.
- In 2023, three tigerswere introduced as part of a larger initiative to restore tiger populations in Madhya Pradesh.
- Similar projects have been successfully implemented in Panna and Nauradehi reserves, contributing to the revival of tiger populations in the region.
Government Support and Conservation Initiatives
- Prime Minister Narendra Modiwelcomed the declaration, emphasizing India’s commitment to wildlife conservation and biodiversity protection.
- Madhya Pradesh Chief Minister Mohan Yadavhighlighted the state’s leadership in tiger conservation and expressed gratitude for the recognition.
- The government is focusing on habitat restoration, anti-poaching measures, and community involvementto ensure long-term success.
Future Prospects for Madhav Tiger Reserve
- The reserve is expected to grow in importance as more tigers are introducedthrough planned conservation initiatives.
- Efforts are being made to enhance tiger habitats, ensure prey availability, and engage local communities in conservation efforts.
- The Madhav Tiger Reserve aims to become a model for sustainable wildlife conservation in India.
Challenges in Wildlife Conservation
Despite positive developments, several challenges persist in tiger conservation:
- Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade:A major threat to tiger populations.
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation:Due to urbanization, deforestation, and human encroachment.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict:Increased encounters between tigers and local communities.
- Need for Stronger Law Enforcement:Effective monitoring, patrolling, and stricter penalties for wildlife crimes are essential.
- Community Participation:Sustainable conservation requires involvement of local communities in protecting tiger habitats.
With ongoing conservation efforts and government support, Madhav Tiger Reserve is poised to become a thriving sanctuary for tigers and other wildlife, reinforcing India’s status as a global leader in tiger conservation.
Which of the following statements regarding Madhav Tiger Reserve is correct?
- It was originally a hunting ground for the Gwalior royal family.
- It is part of the Bundelkhand Plateau region.
- The park has a significant population of swamp deer (Barasingha).
- It has been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 3, and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- It was originally a hunting ground for the Gwalior royal family – Correct. Madhav National Park, now Madhav Tiger Reserve, was historically used as a hunting ground by the Scindia rulers of Gwalior. The park was later designated as a protected area.
- It is part of the Bundelkhand Plateau region – Correct. Madhav Tiger Reserve is located in the Shivpuri district of Madhya Pradesh, which is geologically part of the Bundelkhand Plateau. The region consists of dry deciduous forests and grasslands, making it suitable for various wildlife species, including tigers.
- The park has a significant population of swamp deer (Barasingha) – Incorrect. Swamp deer (Barasingha) are not found in Madhav Tiger Reserve in significant numbers. Instead, they are primarily found in Kanha National Park in Madhya Pradesh, where conservation efforts have been successful in reviving their population.
- It has been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site – Incorrect. Madhav Tiger Reserve is not a UNESCO World Heritage Site. While India has several UNESCO-listed natural sites (such as Kaziranga, Sundarbans, and Keoladeo National Parks), Madhav Tiger Reserve has not received this designation.
Amrut Biodiversity Park
Introduction
- The Amrut Biodiversity Park, inaugurated by Lieutenant Governor V.K. Saxena in 2025, is a major environmental initiative in Delhi.
- Spread across 90 hectares along NH-24 in the Yamuna floodplains, the park is part of the Delhi Development Authority’s (DDA) efforts to restore and rejuvenate the region’s ecosystem.
- It aims to enhance urban green spaces while fostering environmental awareness.

Ecosystem Restoration
- Previously used for agriculture and settlements, the park underwent a major transformation to revive the floodplain ecosystem.
Water Management:
- Six new water bodieswere created with a combined capacity of 225 million litres.
- These help store stormwaterand reduce flood risks during monsoons.
- The park features jute-reinforced slopesand riverine grass communities to stabilize the land and improve groundwater recharge.
Biodiversity and Green Cover
A key aspect of the park is its diverse plantation, aimed at enhancing biodiversity.
Trees Planted: Around 14,500 trees, including Neem, Peepal, and Mango.
Shrubs and Grasses: 18,000 shrubs and over 3.21 lakh riverine grasses have been introduced.
Bird Habitat Creation: The rich biodiversity is expected to attract bird species, contributing to a vibrant ecosystem.
Public Engagement and Recreational Spaces
- To promote community involvement, the park features designated public spacesalong NH-24.
- Thematic Walking Tracks:Inspired by India’s freedom struggle, pathways are named after key events like the Dandi March and the First War of Independence.
- Nature Interaction Areas:Visitors can explore and connect with Delhi’s ecological heritage.
Hydrology and Water Conservation
- The park’s hydrologyhas been carefully restored through sustainable measures.
- Dredging and Water Flow Management:Existing catchments were deepened to enhance water retention and flow regulation during monsoon seasons.
- Sustainable Water Bodies:Efforts are in place to ensure that these remain functional year-round, contributing to floodplain health.
Environmental Concerns and Challenges
While the park has been praised for its green initiative, it has also faced criticism from environmentalists.
- Flood Risk:Some experts argue that the area remains prone to seasonal inundation.
- Financial Feasibility:Concerns have been raised about the long-term sustainability of maintaining the park.
- DDA’s Response:The authorities remain optimistic, emphasizing the park’s ecological benefits and its role in urban reforestation.
Future Plans and Development
- The DDA plans to further enhance the visitor experiencewith additional facilities:
- Café Establishment:A proposed eco-friendly café will provide refreshments for visitors.
- Recreational Spaces:The park is envisioned as a relaxation hub for joggers, nature enthusiasts, and families.
Conclusion
The Amrut Biodiversity Park represents a significant step in Delhi’s environmental restoration efforts. While challenges persist, its focus on biodiversity, water conservation, and public engagement makes it a valuable addition to the city’s green infrastructure.
Which of the following statements regarding Madhav Tiger Reserve is correct?
- It was originally a hunting ground for the Gwalior royal family.
- It is part of the Bundelkhand Plateau region.
- The park has a significant population of swamp deer (Barasingha).
- It has been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 3, and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- It was originally a hunting ground for the Gwalior royal family – Correct. Madhav National Park, now Madhav Tiger Reserve, was historically used as a hunting ground by the Scindia rulers of Gwalior. The park was later designated as a protected area.
- It is part of the Bundelkhand Plateau region – Correct. Madhav Tiger Reserve is located in the Shivpuri district of Madhya Pradesh, which is geologically part of the Bundelkhand Plateau. The region consists of dry deciduous forests and grasslands, making it suitable for various wildlife species, including tigers.
- The park has a significant population of swamp deer (Barasingha) – Incorrect. Swamp deer (Barasingha) are not found in Madhav Tiger Reserve in significant numbers. Instead, they are primarily found in Kanha National Park in Madhya Pradesh, where conservation efforts have been successful in reviving their population.
- It has been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site – Incorrect. Madhav Tiger Reserve is not a UNESCO World Heritage Site. While India has several UNESCO-listed natural sites (such as Kaziranga, Sundarbans, and Keoladeo National Parks), Madhav Tiger Reserve has not received this designation.
World Air Quality Report 2024
Key Findings of the Report
- India ranks as the fifth most polluted country globally, with an average PM2.5 concentration of 50.6 μg/m³, which is 10 times higher than the WHO’s annual guideline of 5 μg/m³.
- In 2023, India was the third most polluted country.
- Delhi remains the most polluted capital city, recording an average PM2.5 level of 91.8 μg/m³, making it the world’s worst capital in terms of air quality.
- Among the 20 most polluted cities worldwide, 13 are in India, with Byrnihat (Assam-Meghalaya border) being the worst affected.
- 3% of countries (126 out of 138) exceeded WHO’s PM2.5 annual safety limits.
- Only 17% of global cities met WHO’s air pollution standards.
- 5 concentrations declined in Southeast Asian countries, but transboundary haze and El Niño effects remain significant air pollution challenges.
Understanding Air Pollution & Its Impact
What is Air Pollution?
- Air pollution occurs when harmful substances such as particulate matter (PM), toxic gases, and chemical compounds are released into the atmosphere, degrading air quality and harming living beings.
Major Air Pollutants
Particulate Matter (PM10 & PM2.5): Fine particles from industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and construction dust.
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO₂): Emitted from vehicles and industries, contributes to acid rain and respiratory diseases.
Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂): A byproduct of burning fossil fuels, causes lung irritation and acid rain.
Ozone (O₃): A major urban smog component, damages lung function.
Carbon Monoxide (CO): Produced by incomplete combustion, leads to oxygen deprivation in the bloodstream.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) & Lead: Harmful industrial emissions affecting neurological and respiratory health.
Concerns Associated with Air Pollution
Health Implications
- Increased cases of respiratory diseases, lung infections, and cardiovascular disorders.
- Children, elderly, and people with pre-existing conditions are most vulnerable.
Environmental Damage
- Contributes to climate change, biodiversity loss, and soil & water contamination.
- Leads to crop damage and reduced agricultural productivity.
- Economic & Social Costs
- Increased healthcare expenses due to pollution-related diseases.
- Economic losses due to workforce inefficiency and reduced productivity.
Government Initiatives to Combat Air Pollution in India
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) – 2019
- Aims to reduce PM2.5 and PM10 levels by 20-30% by 2024 in targeted cities.
- Focuses on air quality monitoring, stricter emission regulations, and public awareness campaigns.
- Bharat Stage VI (BS-VI) Emission Standards – 2020
- Stricter vehicle fuel norms to cut vehicular pollution.
- Introduction of low-sulfur fuels and advanced emission control technologies.
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY)
- Provides subsidized LPG connections to reduce dependence on biomass and firewood, preventing indoor pollution.
- FAME Scheme (Faster Adoption & Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles)
- Promotes electric and hybrid vehicles to cut vehicular emissions.
- Encourages investment in EV charging infrastructure and subsidies for EV adoption.
- Green Initiatives for Sustainable Habitat (GRIHA)
- Promotes eco-friendly construction and energy-efficient buildings.
- Encourages use of solar power, rainwater harvesting, and green architecture.
- Waste Management & Cleanliness Programs
- Swachh Bharat Abhiyan focuses on urban cleanliness and solid waste management.
- Stricter regulations on plastic waste reduction and clean disposal practices.
- Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM)
- Regulates air pollution control measures in the Delhi-NCR region.
- Ensures better coordination and enforcement of environmental laws.
- Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP)
- Emergency pollution control measures based on air quality levels.
- Includes odd-even vehicle schemes, construction bans, and strict emission regulations in Delhi-NCR.
- Promotion of Public Transport & Green Mobility
- Expansion of metro networks, electric buses, and carpooling initiatives.
- Encouragement of non-motorized transport like cycling & pedestrian-friendly zones.
Way Forward
- Strengthen nationwide air quality monitoring and enforce stricter emissions control.
- Promote green energy solutions such as solar and wind power to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Enhance industrial pollution regulations and implement carbon pricing mechanisms.
- Encourage community participation through awareness campaigns and eco-friendly initiatives.
- India’s battle against air pollution demands a multi-sectoral approach involving policy reforms, technological advancements, and active citizen participation to ensure a cleaner and healthier environment.
Regarding the World Air Quality Report 2024, consider the following statements:
- India is ranked as the third most polluted country
- Byrnihat, a town on the Assam-Meghalaya border, is the most polluted city in India.
- Delhi is the second most polluted capital cityin the world in terms of PM2.5 concentration.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer:(b)
Explanation: India is the fifth most polluted country (not third). Delhi remains the most polluted capital city, not the second.
Sarus Crane
A rare sighting of the Sarus Crane (Grus antigone)has been reported in the Saikhowa region of Tinsukia, Assam, drawing the attention of birdwatchers and wildlife enthusiasts.

About the Sarus Crane
Tallest Flying Bird: The Sarus Crane holds the distinction of being the tallest flying bird in the world.
Scientific Name: Grus Antigone
Distribution
- Found in Southeast Asia, northern India, and northern Australia.
- In India, their population is densely distributed along the Gangetic plainsand eastern Rajasthan, with lower densities further south.
- Unlike many other crane species, the Sarus Crane is non-migratory.
Habitat
- Prefers wetlands, including canals, marshes, and ponds.
- Often found in proximity to human habitation.
Distinctive Features of the Sarus Crane
- Height: 152-156 cm, making it the tallest of all flying birds.
- Wingspan: Can reach up to 5 meters.
- Weight: Ranges from 5 to 12 kg.
- Plumage: Mostly greywith a naked red head, upper neck, and pale red legs.
White Markings: A white patch on the top of the head and a small white spot behind the eye.
Social Behavior:
- Considered the least social of all cranes, usually seen in pairs or small groups of three to four.
- Monogamous species—pairs bond for life.
- Nesting:
- Nests are built in wetlandsor flooded paddy fields.
- Lifespan:
- Generally 30 to 40 years, though some crane species have been recorded to live up to 80 years.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Listed in Appendix II
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule IV
- The Sarus Crane population faces threats from habitat destruction, wetland degradation, and human disturbances. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensuring the survival of this iconic species.
Consider the following statements regarding the Sarus Crane (Grus antigone):
- It is the tallest non-flying bird in the world.
- Sarus Cranes are migratory birds that travel across different regions based on seasonal changes.
- In India, they are predominantly found in the Gangetic plains and eastern Rajasthan.
- The Sarus Crane is listed as “Endangered” on the IUCN Red List.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
- The Sarus Crane is the tallest flying bird, not a non-flying bird. (Statement 1 is incorrect)
- Unlike many other crane species, the Sarus Crane is non-migratoryand remains in its habitat throughout the year. (Statement 2 is incorrect)
- In India, its population is densely distributed along the Gangetic plains and eastern Rajasthan, with lower densities in the south. (Statement 3 is correct)
- The Sarus Crane is classified as “Vulnerable”on the IUCN Red List, not “Endangered.” (Statement 4 is incorrect.
WMO’s State of Climate 2024 Report
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has released the State of Climate 2024 report, revealing alarming trends in greenhouse gas concentrations, global temperatures, and environmental changes.
Greenhouse Gas Concentration
- In 2023, carbon dioxide (CO₂) levels reached 420 parts per million (ppm)—the highest recorded in 800,000 years.
- Alongside CO₂, concentrations of methane (CH₄) and nitrous oxide (N₂O) also surged to record levels, intensifying the greenhouse effect and contributing to unprecedented temperature rises.
Global Temperature Milestone
- The year 2024 marked a critical threshold in global warming.
- The global mean near-surface temperature was 1.55°C above pre-industrial levels, exceeding the 1.5°C limit set by the Paris Agreement for the first time in a single year.
- While this does not necessarily mean a permanent breach of the target, it signals increased risks to ecosystems and human societies.
Long-Term Warming Trends
- The WMO estimates long-term warming to be between 1.34°C and 1.41°C above pre-industrial levels (1850–1900).
- Climate projections indicate that, if current trends persist, the 1.5°C threshold could be permanently exceeded by 2029, pushing the planet closer to critical climate tipping points.
Ocean Heat and Sea Level Rise
- The past eight years have recorded the highest ocean heat content, with 90% of excess heat from greenhouse gases absorbed by the oceans.
- Sea levels continue to rise at an accelerated pace, doubling since satellite measurements began. The primary contributors to this rise are the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers.
Intensified Extreme Weather Events
- The increase in greenhouse gas levels has fueled more frequent and severe extreme weather events, including tropical cyclones, heavy rainfall, floods, and droughts.
- In 2024, climate-related displacements reached their highest levels since 2008, highlighting the worsening humanitarian impact of climate change.
Cryosphere Changes and Ice Loss
- The cryosphere is undergoing dramatic transformations, with glaciers retreating at an alarming rate.
- Antarctic sea ice has recorded its second-lowest extent ever, while seven of the last ten years have witnessed the highest negative mass balance of glaciers, indicating substantial ice loss.
- These trends threaten global sea levels, freshwater availability, and ecosystems dependent on frozen water reserves.
With reference to the WMO’s State of Climate 2024 report, consider the following statements:
- The global mean near-surface temperature in 2024 was recorded at 1.55°C above pre-industrial levels, marking the first instance of exceeding the Paris Agreement threshold of 1.5°C for an entire decade.
- The rise in greenhouse gases, including CO₂, CH₄, and N₂O, has led to ocean heat content reaching its highest levels in recorded history.
- The report indicates that the melting of glaciers and polar ice caps is solely responsible for rising sea levels worldwide.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is partially correct; the 1.55°C rise was recorded in a single year, not over a decade. However, it does indicate growing climate instability.
Statement 2 is correct; 90% of excess heat is absorbed by oceans, increasing ocean heat content.
Statement 3 is incorrect; while glacier and ice cap melting contributes significantly to rising sea levels, thermal expansion of seawater due to global warming is another major factor.
Phansad Wildlife Sanctuary
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has released the State of Climate 2024 report, revealing alarming trends in greenhouse gas concentrations, global temperatures, and environmental changes.
Greenhouse Gas Concentration
- In 2023, carbon dioxide (CO₂) levels reached 420 parts per million (ppm)—the highest recorded in 800,000 years.
- Alongside CO₂, concentrations of methane (CH₄) and nitrous oxide (N₂O) also surged to record levels, intensifying the greenhouse effect and contributing to unprecedented temperature rises.
Global Temperature Milestone
- The year 2024 marked a critical threshold in global warming.
- The global mean near-surface temperature was 1.55°C above pre-industrial levels, exceeding the 1.5°C limit set by the Paris Agreement for the first time in a single year.
- While this does not necessarily mean a permanent breach of the target, it signals increased risks to ecosystems and human societies.
Long-Term Warming Trends
- The WMO estimates long-term warming to be between 1.34°C and 1.41°C above pre-industrial levels (1850–1900).
- Climate projections indicate that, if current trends persist, the 1.5°C threshold could be permanently exceeded by 2029, pushing the planet closer to critical climate tipping points.
Ocean Heat and Sea Level Rise
- The past eight years have recorded the highest ocean heat content, with 90% of excess heat from greenhouse gases absorbed by the oceans.
- Sea levels continue to rise at an accelerated pace, doubling since satellite measurements began. The primary contributors to this rise are the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers.
Intensified Extreme Weather Events
- The increase in greenhouse gas levels has fueled more frequent and severe extreme weather events, including tropical cyclones, heavy rainfall, floods, and droughts.
- In 2024, climate-related displacements reached their highest levels since 2008, highlighting the worsening humanitarian impact of climate change.
Cryosphere Changes and Ice Loss
- The cryosphere is undergoing dramatic transformations, with glaciers retreating at an alarming rate.
- Antarctic sea ice has recorded its second-lowest extent ever, while seven of the last ten years have witnessed the highest negative mass balance of glaciers, indicating substantial ice loss.
- These trends threaten global sea levels, freshwater availability, and ecosystems dependent on frozen water reserves.
Consider the following statements regarding Phansad Wildlife Sanctuary:
- It is located in the Sindhudurg district of Maharashtra.
- The sanctuary was historically a hunting reserve of the princely state of Murud-Janjira.
- It is part of the Western Ghats and protects a unique coastal woodland ecosystem.
- The White-rumped Vulture, a critically endangered species, is found in the sanctuary.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3, and 4 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect – The sanctuary is in Raigad district, not Sindhudurg.
Statement 2 is correct – The princely state of Murud-Janjira used this area as a hunting reserve.
Statement 3 is correct – The sanctuary is part of the Western Ghats’ coastal woodland ecosystem.
Statement 4 is correct – The White-rumped Vulture (Gyps bengalensis), a critically endangered species, is found in the sanctuary.
Kanger Valley National Park
- Kanger Valley National Park (KVNP), situated in the formerly Maoist-affected region of Bastar district in Chhattisgarh, has recently been added to UNESCO’s tentative list of World Heritage Sites under the ‘Natural’ category.
- This recognition highlights the park’s ecological significance and rich biodiversity.
Overview of Kanger Valley National Park
Location & Geography
- KVNP is located in Jagdalpur, Bastar district, Chhattisgarh.
- The park is named after the Kanger River, which flows from Northwest to Southeastthrough the valley.
- The Kanger River is a tributary of the Kolab River, which eventually merges with the Godavari River.
- The terrain consists of flatlands, gentle slopes, steep inclines, plateaus, deep gorges, valleys, and winding streams.
- The Tirathgarh Waterfall, formed by the Kanger River, cascades from a height of 150 feet, offering a spectacular sight.
- The park houses over 15 limestone caves, including the Kotumsar, Kailash, and Dandak caves, known for their geological formations and underground ecosystems.
Flora
- KVNP exhibits a mixed moist deciduous forest, with dominant species such as Sal, Teak, and Bamboo.
Fauna
- Mammals: The park is home to tigers, leopards, mouse deer, wildcats, sambar, chital, barking deer, langurs, jackals, rhesus macaques, and flying squirrels.
- Avian Species: The aerial biodiversity includes common hill mynas, red jungle fowls, spotted owlets, racket-tailed drongos, and various species of parrots.
- The inclusion of Kanger Valley National Parkin UNESCO’s tentative list underscores its ecological importance, unique geological formations, and diverse wildlife, making it a crucial conservation site in central India.
Consider the following statements regarding Kanger Valley National Park (KVNP):
- It is located in the Durg districtof Chhattisgarh.
- The Kanger River, after flowing through the park, directly merges with the Godavari River.
- KVNP is characterized by the presence of limestone caves, plateaus, deep gorges, and waterfalls.
- It has been included in the tentative list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites under the ‘Cultural’ category.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: (c) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: KVNP is located in Bastar district, not Durg district.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The Kanger River is a tributary of the Kolab River, which eventually joins the Godavari River, but it does not merge directly with the Godavari.
Statement 3 is correct: The park is known for limestone caves, deep gorges, plateaus, waterfalls (Tirathgarh Falls), and diverse topography.
Statement 4 is incorrect: KVNP has been added to UNESCO’s tentative list under the ‘Natural’ category, not the ‘Cultural’ category.
Caracal
- A rare caracalhas been recently sighted in Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve, Rajasthan, generating excitement among wildlife enthusiasts.
About Caracal
- The caracalis a medium-sized, nocturnal wildcat known for its agility and striking black-tipped ears.
- Indian Name:Siya Gosh (Persian: “Black Ear”).
- Scientific Name:Caracal caracal
Distribution & Habitat
- Found in Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia.
- In India, their population is critically low, with an estimated 50 individuals, primarily in Rajasthan and Gujarat.
- They inhabit rocky hills, grasslands, savannas, scrublands, and forests, showcasing high adaptabilityto various environments.
Physical Features
- Slender body, long legs, and largest among small African cats.
- Size: 8–18 kgin weight, up to 1 meter in length.
- Fur: Short, dense, and varies from tawny-brown to reddish-tan, with whitish underparts.
- Facial markings:Dark lines and white spots around the eyes.
- Distinctive black-tipped earswith tufts, aiding in communication.
Unique Abilities
- Renowned for leaping over 2 metersto catch birds mid-air.
- Can sprint at speeds of up to 80 km/h (50 mph).
- Solitary by nature, but may occasionally form small groups.
- Shy and elusive, making sightings in the wild extremely rare.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List:Least Concern (globally), but faces severe population decline in India.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972:Schedule I (providing the highest level of legal protection in India).
- The recent sighting in Mukundra Hills Tiger Reservehighlights the need for focused conservation efforts to protect this elusive species in India.
With reference to the Caracal (Caracal caracal) in India, consider the following statements:
- The caracal is listed as Critically Endangered under the IUCN Red List in India.
- It is known for its ability to leap several meters into the air to catch birds in flight.
- In India, its population is mainly found in Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Madhya Pradesh.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The caracal is listed as “Least Concern” globally on the IUCN Red List, though its population in India is highly threatened.
Statement 2 is correct: Caracals are exceptional jumpers and can leap over 2 meters to catch birds in mid-air.
Statement 3 is incorrect: In India, the caracal is primarily found in Rajasthan and Gujarat, but not significantly in Madhya Pradesh.
Sustainable Development vs. Environmental Protection
- The Supreme Court recently overturned the National Green Tribunal (NGT) order that had halted the Auroville Foundation’s township project in Puducherry due to the absence of environmental clearance.
Key Aspects of the Judgment
- The Supreme Court reaffirmed the precautionary principleand the polluter pays principle as integral components of India’s environmental law.
- It recognized the right to a clean environmentas a fundamental right under Articles 14 (equality) and 21 (right to life) of the Constitution.
- Simultaneously, the Court acknowledged that the right to developmentthrough industrialization is also a fundamental right, deriving its legitimacy from Articles 14, 19 (right to practice any profession, trade, or business), and 21 of the Constitution.
- The judgment emphasized the necessity of maintaining a “golden balance”between environmental protection and economic development.
Which of the following principles were recognized by the Supreme Court as part of India’s environmental law in the Auroville case?
- Polluter Pays Principle
2. Precautionary Principle
3. Sustainable Development Principle
4. Intergenerational Equity Principle
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2, and 3 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation: The Supreme Court explicitly cited the Polluter Pays Principle and Precautionary Principle as fundamental to India’s environmental jurisprudence. While the Sustainable Development Principle and Intergenerational Equity Principle are also important in environmental law, they were not explicitly highlighted in this judgment.
Corbett Tiger Reserve
Recent Developments
The Supreme Court recently criticized the Uttarakhand government for its slow action against senior officials accused of illegal constructions within the Corbett Tiger Reserve.
About Corbett Tiger Reserve
Location: Situated in the foothills of the Himalayas in Uttarakhand.
Establishment:
- Established in 1936as Hailey National Park, making it India’s first national park.
- Renamed Corbett National Parkin 1957 to honor Jim Corbett, a renowned conservationist and naturalist.
Area:
- Initially designated as a national park, later expanded to cover 1,288.31 sq. kmas a Tiger Reserve.
Topography:
- Characterized by an undulating terrainwith multiple valleys.
- Major rivers: Ramganga, Pallaen, and Sonanadi.
- Predominantly located in the Bhabarand lower Shivalik regions, featuring porous soil, boulder deposits, and a deep water table.
Flora
Dominated by Sal forests, along with Sheesham and Kanju trees, particularly along ridges.
Grasslands (locally called ‘Chaur’) are remnants of abandoned settlements and clearings.
- Riparian vegetationthrives along riverbanks.
- Invasive species:Lantana, an aggressive weed, poses a significant ecological challenge.
Fauna
- Flagship species:Tigers and elephants.
- Other carnivores:Leopards, small carnivores.
- Herbivores:Sambar, hog deer, spotted deer.
- Avifauna:A diverse range of bird species.
- Reptiles:Gharials, crocodiles.
- Aquatic life:Rich fish diversity in reserve rivers.
Which of the following principles were recognized by the Supreme Court as part of India’s environmental law in the Auroville case?
- Polluter Pays Principle
2. Precautionary Principle
3. Sustainable Development Principle
4. Intergenerational Equity Principle
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2, and 3 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation: The Supreme Court explicitly cited the Polluter Pays Principle and Precautionary Principle as fundamental to India’s environmental jurisprudence. While the Sustainable Development Principle and Intergenerational Equity Principle are also important in environmental law, they were not explicitly highlighted in this judgment.
Global Forest Vision 2030
About the Forest Declaration Assessment (FDA)
- Initially launched in 2015as the New York Declaration on Forests (NYDF) Progress Assessment.
- The NYDF, adopted in 2014at the UN Climate Summit, is a voluntary, non-binding

It establishes 10 goals, including:
- Halting deforestation by 2030.
- Restoring 350 million hectaresof degraded landscapes.
- India is not a signatoryto the NYDF.
Key Findings of the 2023 FDA Report
- Alarming Forest Loss
- 37 million hectaresof forest lost in 2023 alone (equivalent to 9 million soccer fields).
- Major drivers of deforestation:
- Palm oil
- Soy production
- Beef cattle ranching
- Timber harvesting
- Affected regions: Amazon, Southeast Asia, Africa.
- Impact on Biodiversity
- Amazon:Cattle ranching causes 80% of deforestation across all Amazonian countries.
- Southeast Asia:Palm oil plantations threaten species like orangutans and Sumatran tigers.
- Palm oil alone contributes 5%to global tropical deforestation.
- Key Recommendations of the Report
- Align national policieswith global forest conservation goals under UNFCCC COP30 (to be held in Brazil, 2025).
- Strengthen deforestation-free trade agreementsand ban imports of products linked to forest destruction.
Increase financial incentives, such as:
- Results-based paymentsfor forest conservation.
- Forest carbon finance mechanisms.
- Protect Indigenous Peoples and Local Communities (IPs & LCs)by securing land and resource rights.
- Ensure financial institutionsintegrate forest-related risks into investment decisions.
- Redirect harmful subsidiestoward sustainable land-use practices.
- Improve forest governanceby strengthening environmental commitments.
- Integrate forest natural capitalinto national debt management frameworks.
India’s Role: Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges:
- High dependencyon imported palm oil and timber.
- Lack of trade restrictionson products linked to deforestation.
- Small farmersmay struggle to prove deforestation-free production due to limited access to technology.
Opportunities:
- Introduce deforestation-free import lawsto regulate trade practices.
- Support small farmersthrough capacity building, financial aid, and technological advancements.
- Lead South-South cooperationon sustainable agriculture and responsible trade practices.
- Integrate deforestation-free strategieswith existing initiatives such as:
- Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA)
- National Agroforestry Policy
- National Bio-Energy Mission
With reference to the Forest Declaration Assessment (FDA) Report 2023, consider the following statements:
- The FDA was originally launched as the New York Declaration on Forests (NYDF) Progress Assessment in 2015.
- India is a signatory to the NYDF, committing to halt deforestation by 2030.
- The FDA report highlights that palm oil is responsible for nearly 50% of global tropical deforestation.
- The Amazon rainforest is primarily affected by illegal mining and urban expansion, rather than cattle ranching.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4
Answer: (c) 1 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: The FDA was launched in 2015 as a continuation of the New York Declaration on Forests (NYDF) Progress Assessment.
Statement 2 is incorrect: India is not a signatory to the NYDF.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Palm oil contributes 5%, not 50%, to global tropical deforestation.
Statement 4 is incorrect: Cattle ranching, not illegal mining or urban expansion, is the largest cause (80%) of deforestation in the Amazon.
Iguana
- Iguanas are large, robust lizards predominantly found in the tropical regions of the Americas.
- Characterized by scaly skin adorned with warts and spines along their backs, they also possess a distinctive dewlap (flap of flesh) under their necks.
- These herbivorous reptiles exhibit a variety of color morphs, including green, blue, and grey, adapting to diverse environments ranging from arid deserts to dense rainforests.

Geographic Distribution
- Native Habitat:Found across Central and South America, spanning from Mexico to Paraguay and Brazil.
- Introduced Regions:Established populations in Florida, Hawaii, and Caribbean islands.
- Largest Lizard in the USA:The green iguana holds the title of the largest lizard species within U.S. borders.
- Arboreal Nature:Primarily tree-dwelling, descending only for nesting.
- Preferred Habitats
- Terrestrial Biomes:Forests & rainforests
- Aquatic Biomes:Rivers, lakes, and coastal waters
- Wetlands:Swamps
- Urban & Agricultural Areas:Display adaptability to suburban environments
Conservation Status & Threats
- IUCN Red List:Currently not threatened.
- CITES Listing:Appendix II, meaning trade is regulated to prevent overexploitation.
Major Threats:
- Overexploitation due to demand in the pet trade and leather industry.
- Habitat destructionresulting from deforestation and urban expansion.
How Did Iguanas Reach Fiji?
- A recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciencessuggests that the ancestors of Fijian iguanas undertook an extraordinary 8,000 km journey across the Pacific Ocean from the Americas, using rafts of floating vegetation.
The Rafting Hypothesis
- Rafting:A process where animals travel across oceans by drifting on natural floating debris.
- Common among:Small invertebrates such as insects, but rare for large vertebrates due to survival challenges.
Previous Evidence of Iguana Rafting
- 1995 Caribbean Observation:Scientists observed 15 green iguanas rafting 300 km across the ocean on hurricane debris.
- Galápagos Iguanas:Likely rafted 1,000 km from South America to the Galápagos Islands.
- Fijian Iguana Migration:The 8,000 km voyage remains one of the longest known instances of vertebrate rafting, making it an exceptional biological phenomenon.
Consider the following statements regarding iguanas:
- Iguanas are exclusively carnivorous and thrive in desert ecosystems.
- They possess a dewlap, a flap of flesh under their neck, which helps in thermoregulation and communication.
- The largest lizard found within U.S. borders is the Komodo dragon.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: b) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Iguanas are primarily herbivorous, feeding on leaves, flowers, and fruits. While they are adaptable to different environments, they are not exclusive desert dwellers and are more commonly found in tropical forests and wetlands.
Statement 2 is correct: The dewlap helps in communication, thermoregulation, and dominance displays among iguanas.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The largest lizard within U.S. borders is the green iguana (Iguana iguana), not the Komodo dragon, which is native to Indonesia.
Tavasya
Tavasya, the second frigate under Project 1135.6 Additional Follow-on Ships, was launched by Goa Shipyard Limited (GSL).
This follows the launch of Triputin 2024, with both frigates expected to be delivered to the Indian Navy by 2026 and 2027.

Background
In 2016, India and Russiasigned an agreement for four additional Krivak-class stealth frigates.
Two were imported from Russia, while two were built in Indiaunder technology transfer.
Tavasyais the second of the two indigenously built follow-on Krivak-class frigates.
Key Features
Symbolism: Named after Bhima’s mace, representing naval strength.
Multi-Role Capability: Designed for surface, sub-surface, and air combat operations.
Specifications:
Length: 124.8 meters
Width: 15.2 meters
Draught: 4.5 meters
Displacement: ~3,600 tonnes
Speed: Maximum 28 knots
Indigenous Contributions
Triput and Tavasyaincorporate indigenous equipment, weapons, and sensors, enhancing India’s naval self-reliance.
Tavasya marks a significant milestone, likely signaling the end of license-built warshipsas India advances toward self-designed and self-constructed naval vessels.
With reference to India’s Project 1135.6, consider the following statements:
- The project involves the construction of four additional Krivak-class frigates, two of which were built in India under a technology transfer agreement.
- The Krivak-class frigates are primarily designed for amphibious assault operations.
- Tavasya is the first of the two follow-on stealth frigates built by Goa Shipyard Limited under this project.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct. India signed an agreement with Russia in 2016for four additional Krivak-class stealth frigates, with two built in Russia and two in India under technology transfer.
- Statement 2 is incorrect. Krivak-class frigates are designed for anti-surface, anti-submarine, and anti-air warfare, not amphibious assault operations.
- Statement 3 is incorrect. Tavasya is the secondof the two follow-on stealth frigates built by Goa Shipyard Limited (GSL) under this project, not the first.
Sea Dragon 2025
- The Sea Dragon 2025is a multilateral naval exercise focused on anti-submarine warfare (ASW).
- Hosted by the United States Navy’s 7th Fleet, it commenced on March 4, 2025, off the coast of Guam.
- This annual drill brings together key naval forces from the United States, Japan, Australia, South Korea, and India to enhance maritime security coordination in the Indo-Pacific region.

Historical Evolution of Sea Dragon
- The Sea Dragonexercise originated in 2019 as a bilateral initiative between the United States Navy and the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF).
- In 2020, it expanded to include Japan, South Korea, and New Zealand, broadening its scope.
- Indiajoined in 2021, marking a strategic shift in its participation. By 2024, the exercise evolved into a Quad + South Korea collaboration, with Canada being excluded.
Participants in Sea Dragon 2025
- The 2025 editionof the exercise features key naval forces, including the United States Navy (USN), Indian Navy (IN), Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force (JMSDF), Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), and Republic of Korea Navy (ROKN).
- Each nation deploys advanced Maritime Patrol and Reconnaissance Aircraft (MPRA)for joint ASW training, enhancing operational coordination.
Objectives of Sea Dragon 2025
- The primary objectives of the exercise are to enhance tactical coordinationamong participating navies and strengthen anti-submarine warfare capabilities.
- It aims to improve maritime securityin the Indo-Pacific region by conducting simulated submarine-hunting exercises.
- The drill also focuses on promoting military cooperationamong allied forces, ensuring seamless interoperability in maritime operations.
Nature of the Exercise
- Designed specifically for anti-submarine warfare, Sea Dragon involves MPRA deploymentsequipped with advanced sensors for real-world submarine detection training.
- The exercise consists of mock drillsthat simulate underwater threats, allowing pilots to exchange strategies and refine their submarine-tracking techniques.
Grading System and Awards
- The performance of participating nations is assessed based on submarine detection efficiency.
- The nation that achieves the highest score is awarded the Dragon Belt Award. Since 2022, the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force (JMSDF)has consistently won this prestigious recognition.
Significance for India and the Indo-Pacific
- For India, Sea Dragon 2025 enhances anti-submarine warfare skills, strengthens defence cooperationwith Quad nations, and prepares the country for future joint naval operations.
- In the Indo-Pacific region, the exercise plays a crucial role in ensuring stability, promoting freedom of navigation, and reinforcing regional defence collaboration.
Consider the following statements regarding the Sea Dragon 2025 exercise:
- It is hosted by the United States Indo-Pacific Command (INDOPACOM) to enhance surface warfare capabilities.
- The exercise is primarily focused on anti-submarine warfare (ASW).
- India has been a participant in the exercise since its inception in 2019.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The exercise is hosted by the U.S. 7th Fleet, not INDOPACOM. Additionally, it focuses on anti-submarine warfare, not surface warfare.
Statement 2 is correct: Sea Dragon 2025 is explicitly designed for ASW, enhancing submarine detection and tracking.
Statement 3 is incorrect: India joined the exercise in 2021, not 2019. The exercise initially started as a bilateral drill between the U.S. and Australia.
AIKEYME and IOS Sagar
- The Indian Navyis set to launch two pioneering initiatives—AIKEYME and IOS Sagar—to enhance India’s role as the ‘Preferred Security Partner’ and ‘First Responder’ in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- These initiatives reflect India’s commitment to regional maritime security and cooperative engagement with African and IOR nations.
AIKEYME (Africa India Key Maritime Engagement)
- Meaning:‘AIKEYME’ derives from Sanskrit, meaning ‘Unity’.
- Nature:A large-scale multilateral maritime exercise involving African nations.
- Co-hosts:Indian Navy and the Tanzania Peoples’ Defence Force (TPDF).
- Location:Off the coast of Dar-es-Salaam, Tanzania.
- Duration:Six days, scheduled for mid-April 2025.
Participating Nations:
- Comoros, Djibouti, Eritrea, Kenya, Madagascar, Mauritius, Mozambique, Seychelles, and South Africa, along with India and Tanzania.
- Objective:Strengthening maritime cooperation, security, and interoperability among participating nations.
Indian Ocean Ship (IOS) Sagar
- Concept:A naval deployment initiative under which INS Sunayna will operate in the Southwest IOR.
- Crew Composition:A combined crew from India and nine Friendly Foreign Countries (FFCs).
Participating Nations:
- Comoros, Kenya, Madagascar, Maldives, Mauritius, Mozambique, Seychelles, Sri Lanka, and South Africa.
- Objective:Enhancing regional maritime security, fostering defense cooperation, and building naval interoperability.
These initiatives underscore India’s growing strategic engagement in the IOR, reinforcing its position as a maritime security leader and strengthening partnerships with African and island nations.
With reference to the Indian Navy’s AIKEYME initiative, consider the following statements:
- AIKEYME is a maritime exercise between India and ASEAN countries aimed at enhancing blue economy collaboration.
- The first edition of AIKEYME will be co-hosted by the Indian Navy and the Tanzania Peoples’ Defence Force (TPDF).
- AIKEYME focuses on maritime security and involves participation from African nations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: AIKEYME is not associated with ASEAN but with African nations.
Statement 2 is correct: The first edition will be jointly hosted by India and Tanzania.
Statement 3 is correct: AIKEYME is designed to enhance maritime security and foster cooperation among African coastal nations.
Vikram 3201 and Kalpana 3201 Microprocessor
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)has recently announced the development of two advanced 32-bit microprocessors, Vikram 3201 and Kalpana 3201, specifically designed for space applications.
- These microprocessors represent a major leap in India’s indigenous technology developmentand were developed in collaboration with the Semiconductor Laboratory (SCL), Chandigarh.
Evolution of ISRO’s Microprocessor Technology
- ISRO has been actively involved in the development of microprocessorsfor its launch vehicles and space missions. The Vikram 1601, a 16-bit microprocessor, has been operational since 2009.
- As part of the continuous technological evolution, ISRO has now developed Vikram 3201, an upgraded 32-bit processor, fabricated using 180nm CMOS technologyat SCL, Chandigarh.
- This development aligns with India’s “Make in India” initiative, fostering self-reliance in critical semiconductor technology.
Vikram 3201: Features & Capabilities
- India’s first fully indigenous 32-bit microprocessor.
- Designed to withstand harsh space environments(radiation-hardened).
- Supports floating-point computations, enhancing its capability for complex mathematical operationsin space missions.
- Compatible with high-level programming languages, especially Ada, which is widely used in safety-critical systems.
- Indigenously developed software toolsfurther enhance its efficiency and adaptability.
Kalpana 3201: Features & Capabilities
- Based on the SPARC V8 architecture, a widely used RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) microprocessor
- Designed for high performance and energy efficiency, making it ideal for mission-critical applications.
- Compatible with open-source software, facilitating easy integration with various software development tools.
- Offers scalability for multiple applications, including satellite and avionics systems.
Testing and Validation
- The Vikram 3201 microprocessorhas undergone extensive testing for reliability in space conditions.
- It was validated during the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module (POEM-4) mission, demonstrating its suitability for operational deployment.
- This successful validation marks a crucial milestonein the indigenous development of space-grade microprocessors.
- Additional Semiconductor Innovations by ISRO & SCL
- In addition to microprocessors, ISRO and SCL have developed critical semiconductor devices, including:
- Reconfigurable Data Acquisition System– Enhances data collection and processing in space missions.
- Multi-Channel Low Drop-out (LDO) Regulator Integrated Circuit– Enables power efficiency and miniaturization of avionics systems in launch vehicles.
Future Prospects & Strategic Importance
- The successful development of Vikram 3201 and Kalpana 3201represents a significant step towards Atmanirbharata (self-reliance) in high-reliability microprocessor technology.
- These microprocessors are expected to enhance the performance of India’s space missions, reducing dependence on foreign semiconductor technology.
- The initiative strengthens India’s position in the global space sectorand lays the foundation for future advancements in indigenous microchip development.
- This achievement underscores India’s growing capabilities in semiconductor fabrication, paving the way for technological sovereignty in space exploration and beyond.
Consider the following statements regarding Vikram 3201 and Kalpana 3201 microprocessors:
- Vikram 3201 is based on the ARM architecture, while Kalpana 3201 is based on the SPARC V8 architecture.
- Both microprocessors are developed using 180nm CMOS technology.
- Vikram 3201 is designed to be radiation-hardened, whereas Kalpana 3201 is not.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 3 only
D) 2 only
Answer: D) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Vikram 3201 does not use ARM; Kalpana 3201 is based on SPARC V8 architecture, while Vikram 3201 has its independent architecture.
Statement 2 is correct: Both microprocessors are fabricated using 180nm CMOS technology at SCL, Chandigarh.
Statement 3 is incorrect: While Vikram 3201 is radiation-hardened, no official statement confirms that Kalpana 3201 lacks this feature.
NAVAL EXERCISE - VARUNA 2025
- The 23rd edition of the bilateral naval exercise VARUNA, a symbol of the robust Indo-French maritime partnership, is scheduled to take place from March 19 to 22, 2025.
- Since its inception in 2001, VARUNA has grown into a pivotal naval collaboration, enhancing interoperability and operational synergybetween the two nations.
- This year’s edition will witness an impressive array of complex maritime drills, spanning sub-surface, surface, and aerial domains.
- The exercise will be marked by the joint participation of aircraft carriers INS Vikrant and FS Charles de Gaulle, supported by their respective fighter aircraft, destroyers, frigates, and an Indian Scorpene-class submarine—reflecting the formidable naval capabilities of both countries.
Key Features of VARUNA 2025
Advanced Air Defence Drills & Fighter Exercises
- Simulated air-to-air combatfeaturing the French Rafale-M and Indian MiG-29K, enhancing tactical proficiency.
Anti-Submarine Warfare Operations
- Focus on underwater domain awarenessthrough rigorous submarine-hunting and detection exercises.
Surface Warfare Operations
- Coordinated fleet manoeuvresand combat engagements to refine operational synchronisation.
Maritime Patrol and Surveillance
- Deployment of maritime patrol aircraftto bolster situational awareness and intelligence gathering.
Replenishment-at-Sea Exercises
- Strengthening of logistical cooperationand sustainment capabilities for extended maritime operations.
- By facilitating mutual learning and best practice exchanges, VARUNA 2025 reinforces the ability of both navies to operate seamlessly, even in highly complex maritime scenarios.
- This exercise reaffirms the shared commitment of India and Franceto ensuring a free, open, and secure maritime domain, further solidifying their strategic partnership in global maritime security.
With reference to the bilateral naval exercise VARUNA, consider the following statements:
- It is conducted exclusively in the Indian Ocean region.
- The exercise involves the participation of aircraft carriers from both India and France.
- Anti-submarine warfare is a key component of the exercise.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: While VARUNA is frequently conducted in the Indian Ocean region, it has also been held in the Mediterranean Seain certain editions.
- Statement 2 is correct: The 2025 editionfeatures the participation of INS Vikrant and FS Charles de Gaulle, showcasing both nations’ naval capabilities.
- Statement 3 is correct: Anti-submarine warfareis a major focus area, enhancing underwater domain awareness.
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)
- The Director of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)recently praised India’s growing nuclear sector, describing it as one of the most dynamic in Asia and globally.
About the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)
- The IAEAis the leading international organization dedicated to scientific and technical cooperation in the nuclear field.
- It promotes the safe, secure, and peacefulapplication of nuclear science and technology
- As an autonomous entity within the United Nations (UN) system, it seeks to maximize the societal benefitsof nuclear technology while ensuring its exclusively peaceful use.
- Often referred to as the “Atoms for Peace and Development”organization, the IAEA reports to both the United Nations General Assembly and the United Nations Security Council.
IAEA – Statute and Membership
- The Statute of the IAEAwas formally approved on October 23, 1956, at a conference held at the United Nations Headquarters.
- The IAEA officially came into existenceon July 29, 1957.
- Headquarters: Vienna, Austria.
- Membership: The IAEA currently has 178 member states.
Structure of the IAEA
General Conference
- Composed of all member states, it convenes annually to approve budgets, review programs, and discuss general policies.
Board of Governors
- Consists of 35 member statesthat meet approximately five times a year.
- Responsible for implementing statutory functions, approving safeguards agreements, and appointing the Director General.
Secretariat
- Oversees the day-to-day operationsof the IAEA.
- Headed by the Director General.
Functions of the IAEA
- Ensures the peaceful use of nuclear energyby working with member states and global partners.
- Implements nuclear safeguardsthrough monitoring, inspections, and data analysis to detect and deter the misuse of nuclear materials, including for weapons development.
- Upholds comprehensive safeguards agreementsunder the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), serving as a first line of defense against nuclear weapons proliferation.
- Supports scientific and technical cooperationby facilitating knowledge exchange among member states.
- Strengthens global preparednessfor nuclear and radiological emergencies, ensuring a swift and effective response to minimize risks and damage.
With reference to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), consider the following statements:
- The IAEA is an autonomous body within the United Nations (UN) system but reports only to the UN General Assembly.
- It was established under the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT) in 1957.
- The IAEA’s primary mandate includes ensuring the safe, secure, and peaceful use of nuclear technology.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (c) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- The IAEA reports to both the UN General Assembly and the UN Security Council, making Statement 1 correct.
- The IAEA was not established under the NPT; it was founded under its own statute in 1957, making Statement 2 incorrect.
- The IAEA’s primary roleis to ensure that nuclear energy is used for peaceful purposes, making Statement 3 correct.
ASTRA MK-III Renamed Gandiva
- In News: India’s latest and most advanced beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air missile, Astra MK-III, has been officially renamed Gandiva.
Key Features of Gandiva Missile
- Extended Operational Range
- Capable of striking aerial targets at 340 kmwhen launched from an altitude of 20 km.
- Effective up to 190 kmwhen engaging enemy aircraft at 8 km altitude.
- Cutting-Edge Propulsion System
- Powered by a dual-fuel ducted ramjet engine, an advanced propulsion system that utilizes atmospheric oxygenfor sustained high-speed flight.
- Operates within a launch speed range of 0.8 to 2.2 Machand can engage enemy aircraft moving at speeds between 0 and 3.6 Mach.
Advanced Target Neutralization
- Designed to effectively engage and destroya variety of aerial threats, including fighter jets, bombers, and military transport aircraft.
- The Gandiva missilesignificantly enhances India’s aerial combat capabilities, offering a superior beyond-visual-range interception system to counter modern aerial threats.
Consider the following statements regarding the Gandiva missile (Astra MK-III):
- It is India’s latest beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air missile.
- It is powered by a solid-fuel rocket engine for sustained high-speed flight.
- It has a maximum operational range of 340 km when launched from an altitude of 8 km.
- It is capable of engaging enemy aircraft moving at speeds between 2.0 and 3.6 Mach.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Correct Answer: (a) 1 and 4 only
Explanation:
Correct – The Gandiva missile is India’s latest beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air missile, enhancing aerial combat capabilities.
Incorrect – It is not powered by a solid-fuel rocket engine but by a dual-fuel ducted ramjet engine, which utilizes atmospheric oxygen for sustained high-speed flight.
Incorrect – The missile has a maximum operational range of 340 km when launched from an altitude of 20 km, not 8 km. At 8 km altitude, it has an effective range of 190 km.
Correct – It is capable of engaging enemy aircraft moving at speeds between 2.0 and 3.6 Mach.
TROPEX-2025
Context
The Theatre-Level Operational Readiness Exercise (TROPEX) 25 is being conducted over a span of three months, from January to March 2025.
About TROPEX 25
- Largest Biennial Maritime Exerciseorganized by the Indian Navy, with significant participation from the Indian Army, Indian Air Force, and Coast Guard.
- Executed in multiple phases, both in Harbour and at Sea, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of operational preparedness.
Encompasses various dimensions of modern naval warfare, including:
- Cyber and Electronic Warfare Operations
- Live Weapon Firingsduring the Joint Work-Up Phase
- Amphibious Exercise (AMPHEX)focusing on integrated land-sea operations
- TROPEX 25 serves as a crucial platform for enhancing combat readiness, interoperability, and joint operational synergyamong India’s armed forces.
Consider the following statements regarding TROPEX 25:
- It is an annual maritime exercise conducted by the Indian Navy.
- It involves participation from the Indian Army, Indian Air Force, and the Coast Guard.
- The exercise includes cyber and electronic warfare, live weapon firings, and an amphibious exercise.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
TROPEX is a biennial (not annual) maritime exercise organized by the Indian Navy. It features participation from multiple branches of the armed forces and includes cyber warfare, live weapon firings, and amphibious operations.
Exercise Khanjar-XII
Context:
- The 12th edition of the India-Kyrgyzstan Joint Special Forces Exercise, Khanjar-XII, is scheduled to take place from March 10 to March 23, 2025, in Kyrgyzstan.
- This annual exercise, which began in 2011, alternates between the two countries.
- The Indian contingentconsists of troops from the Parachute Regiment (Special Forces), while the Kyrgyzstan contingent includes the Kyrgyz Scorpion Brigade.
- The primary focus of the exercise is to enhance cooperation in counter-terrorism and special operations, particularly in urban and mountainous terrains.
Objectives of Khanjar-XII
The main aim of the exercise is to exchange expertise and best practices in counter-terrorism operations. Key focus areas include:
Sniping techniques
- Complex building interventions
- Mountain warfare training
- These skills are vital for both nations in tackling modern security threats, terrorism, and insurgency.
Cultural Exchange and Diplomatic Relations
- Beyond military training, Khanjar-XII also serves as a platform for cultural exchange. Participants will engage in cultural activities, including the celebration of Nowruz, a significant Kyrgyz festival.
- This fosters stronger diplomatic ties, mutual respect, and understanding between the two nations.
Strategic Importance
- The exercise underscores the deepening strategic ties between India and Kyrgyzstan.
- It reflects their shared commitment to regional security, counter-terrorism cooperation, and military preparedness.
- By jointly addressing transnational threats, both countries aim to contribute to peace and stability in the region.
Previous Editions of Khanjar Exercise
- Since its inception, the Khanjar series has continuously evolved, enhancing interoperability and operational readiness.
- The 11th edition was held in India in January 2024, building upon past experiences to strengthen counter-terrorism strategies.
India’s Broader Defence Cooperation
- In addition to Khanjar-XII, India is actively expanding its defence partnerships. Recently, India and Japanconducted the 7th Army-to-Army Staff Talks in New Delhi, focusing on:
- Military education
- Technological collaborations
- Operational training
- These initiatives highlight India’s growing defence cooperationwith global partners, reinforcing its role in regional security and stability.
With reference to the India-Kyrgyzstan Joint Special Forces Exercise ‘Khanjar-XII,’ consider the following statements:
- The exercise has been conducted annually since 2011 and is held exclusively in Kyrgyzstan.
- The Indian contingent primarily consists of personnel from the Ghatak Platoon of the Indian Army.
- The Kyrgyzstan contingent in Khanjar-XII includes the Kyrgyz Scorpion Brigade.
- The exercise mainly focuses on naval warfare and maritime security cooperation.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 3 only
c) 1, 3, and 4 only
d) 2 and 4 only
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 – Incorrect: While the exercise began in 2011, it is not exclusively held in Kyrgyzstan. It alternates between India and Kyrgyzstan.
Statement 2 – Incorrect: The Indian contingent consists of troops from the Parachute Regiment (Special Forces), not the Ghatak Platoon.
Statement 3 – Correct: The Kyrgyz Scorpion Brigade is the designated unit from Kyrgyzstan participating in the exercise.
Statement 4 – Incorrect: The exercise focuses on counter-terrorism, special operations, and mountain warfare, not naval warfare or maritime security.
Exercise Desert Hunt 2025
- The Indian Air Force conducted Exercise Desert Hunt 2025, a Tri-Service Special Forces exercise, at Air Force Station Jodhpur, Rajasthan.
Participating Special Forces Units
- Para (Special Forces) – Indian Army
- Marine Commandos (MARCOS) – Indian Navy
- Garud (Special Forces) – Indian Air Force
Objective & Strategic Importance:
- Theexercise aimed to enhance interoperability, coordination, and synergy among the three elite forces, ensuring swift and effective responses to emerging security threats.
- It focused on joint operational preparedness, fostering seamless collaboration in multi-domain warfare
Key Operations & Tactical Drills
- The participating forces engaged in high-intensity combat drills, including:
- Airborne insertionbehind enemy lines for rapid force deployment.
- Precision strikeson high-value targets.
- Hostage rescueoperations under simulated conflict conditions.
- Counter-terrorism operationsin complex terrains.
- Combat free fallsdemonstrating stealth and infiltration capabilities.
- Urban warfare scenariosreplicating real-time threats in built-up areas.
- The exercise rigorously tested the combat readinessof the Special Forces under realistic battlefield conditions, reinforcing their ability to operate in hostile environments.
Consider the following statements regarding Exercise Desert Hunt 2025:
- It was conducted as a bilateral military exercise between India and France.
- It focused on enhancing joint operational capabilityamong Special Forces of the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- The exercise involved counter-terrorism, hostage rescue, and precision strike operations.
- It was hosted at the Indian Air Force’s frontline base in Rajasthan.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2, and 3 only
(b) 2, 3, and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer:(b)
Explanation: Exercise Desert Hunt 2025 was a domestic tri-service exercise and not a bilateral military drill (eliminating Statement 1). The exercise focused on joint operations among Indian Special Forces and was conducted at Air Force Station Jodhpur, Rajasthan.
EU Mobilises €800 Billion for Defence and Ukraine
- In a landmark policy shift, European Commission President Ursula von der Leyenunveiled a comprehensive €800 billion defence initiative, reflecting Europe’s evolving security doctrine amidst geopolitical volatility.
- This announcement follows the United States’ suspension of military aid to Ukraine, signaling a potential recalibration of Washington’s foreign policy prioritiesand necessitating a more self-reliant European defence architecture.
- This initiative underscores the European Union’s (EU) strategic imperativeto mitigate vulnerabilities exposed by the Ukraine-Russia war, while concurrently addressing long-standing concerns over its military preparedness.
- The plan is scheduled for deliberation at the March 7, 2025, Brussels Summit, where EU member states will assess its feasibility, financial structuring, and geopolitical ramifications.
Structural Framework: Key Components of the Defence Initiative
The proposal is structured around five pivotal elements, each designed to strengthen European defence capabilities while ensuring fiscal sustainability and financial cohesion within the EU framework.
- Revision of Fiscal Rules for Defence Expenditure
- The plan proposes relaxing EU fiscal constraints, allowing member states to surpass the existing 3% GDP defence expenditure cap.
- This amendment could potentially liberate up to €650 billion, significantly bolstering military budgets.
- Establishment of a €150 Billion Defence Loan Facility
- A dedicated loan mechanismwill be introduced to finance targeted military investments, facilitating defence-industrial expansion and technological advancements.
- Reallocation of Cohesion Funds for Defence Initiatives
- The plan permits repurposing EU cohesion funds—originally allocated for socioeconomic development in less-developed regions—towards military infrastructure and capability enhancement.
- This reallocation reflects a strategic pivot in EU financial planning, prioritizing security over traditional developmental imperatives.
- Creation of a Savings and Investment Union for Defence
- A unified financial ecosystemwill be developed to streamline capital inflows into the European defence-industrial sector, fostering cross-border defence collaborations.
- Expansion of the European Investment Bank’s (EIB) Mandate
- The EIB will be empowered to finance military and police equipment investments, ensuring greater fiscal support for security-related procurements.
However, direct funding for offensive weaponry and ammunition remains prohibited, reflecting EU’s normative constraints on military financing.
Implementation Bottlenecks and Strategic Challenges
- Despite its ambitious scope, the practical realization of the initiative remains uncertain, due to multiple institutional and geopolitical constraints:
- Approval Complexities– The plan requires consensus among EU member states, necessitating extensive diplomatic negotiations and legislative approvals.
- Delayed Battlefield Impact– Given the bureaucratic intricacies of EU policymaking, immediate military support for Ukraine is unlikely, raising concerns over short-term defence gaps.
- Divergent National Interests– While countries like Germany, Italy, and Greece endorse the proposal, some Nordic and Eastern European states remain cautious about its long-term efficacy.
Strategic Implications and the Future of European Defence
- Shift Towards Strategic Autonomy– The initiative signals a long-term EU trajectory towards defence self-sufficiency, reducing its dependence on NATO and U.S. security guarantees.
- Potential Geopolitical Realignment– If successfully implemented, this framework could reshape Europe’s defence posture, impacting transatlantic security dynamics and EU’s global strategic standing.
- Outcome of the Brussels Summit– The March 7, 2025, Brussels Summit will serve as a litmus test for the initiative’s viability, determining the extent of European unity on defence modernization.
With reference to the European Commission’s €800 billion defence initiative, consider the following statements:
- It proposes an exemption from existing fiscal constraints, allowing defence spending beyond the 3% GDP limit.
- The plan enables redirection of EU cohesion fundstowards military expenditure.
- The European Investment Bank (EIB) will be permitted to finance weapon and ammunition procurements.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct – The plan relaxes fiscal rules, allowing EU nations to surpass the existing 3% GDP defence expenditure ceiling.
Statement 2 is correct – It authorizes repurposing EU cohesion funds for military objectives, deviating from their traditional socioeconomic development focus.
Statement 3 is incorrect – While the EIB’s mandate is expanded to include defence and security investments, direct funding for weapons and ammunition remains restricted.
World Happiness Report 2025
- The World Happiness Report 2025, recently released by the Wellbeing Research Centre at the University of Oxford, evaluates global happiness levels based on citizens’ self-assessed life satisfaction.
Methodology of the Report
- The rankings are derived from global surveys measuring individuals’ perceptions of their lives.
- The study is a collaboration between the Wellbeing Research Centre, Gallup, and the United Nations Sustainable Development Solutions Network.
- Key factors influencing happiness include GDP per capita, healthy life expectancy, social support, freedom, generosity, and perceptions of corruption.
Key Insights on Happiness Determinants
- The report highlights that happiness is influenced by more than just economic wealth. Strong social bonds, trust, and acts of kindness play a critical role in determining life satisfaction.
- Individuals who regularly share meals and have reliable social support networks report higher happiness levels. Interestingly, people underestimate the kindness of others—studies show that actual rates of returning lost items are significantly higher than expected.
Global Rankings and Trends
- In 2025, Finland continues to hold the top position, followed by Denmark, Iceland, and Sweden.
- Israel secures the eighth spot despite ongoing conflicts. Costa Rica and Mexico enter the top ten for the first time, ranking sixth and tenth, respectively.
- Meanwhile, the United States drops to its lowest position at 24, and the United Kingdom ranks 23rd.
- Afghanistan remains the least happy nation, followed by Sierra Leone and Lebanon.
Rising Loneliness Among Young Adults
- A troubling trend observed in the report is the increasing loneliness among young adults.
- Since 2006, there has been a rise in social isolation, with 19% of young people reporting they lack social support.
- This lack of human connection significantly reduces happiness levels, emphasizing the need to foster stronger community ties for overall well-being.
India’s Position in the Happiness Index
- India is ranked 118 out of 147 countries in the 2025 report.
- Despite strong social support structures, the country faces challenges with perceptions of freedom.
- Among its neighbors, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Nepal, and China rank lower than anticipated, with China at 68.
The Role of Kindness and Community in Happiness
- The report underscores the reciprocal benefits of caring and sharing, where both the giver and receiver experience an uplift in well-being.
- Encouraging community participation, trust, and generosity could significantly improve happiness levels across societies.
Consider the following factors used in the World Happiness Report to rank countries:
- GDP per capita
- Social support
- Military expenditure as a percentage of GDP
- Perceptions of corruption
- Healthy life expectancy
Which of the above factors are considered in the report’s methodology?
a.1, 2, 3, and 5
b.1, 2, 4, and 5
c.2, 3, 4, and 5
d.1, 3, 4, and 5
Answer: (b) 1, 2, 4, and 5
Explanation:
- The World Happiness Report considers GDP per capita, social support, perceptions of corruption, and healthy life expectancy as key determinants.
- However, military expenditure is not included as a ranking factor. The report primarily focuses on factors influencing individual well-being rather than national security metrics.
World Puppetry Day
About World Puppetry Day
- World Puppetry Day is observed annually on March 21st to celebrate puppetry as a global art form and to honor puppeteers worldwide.
- This day highlights the significance of puppetry in cultural storytelling, entertainment, and artistic expression across various mediums, including stage, television, and film.
Understanding Puppetry
- Puppetry is an ancient performing art that involves crafting and manipulating puppets—figures representing humans, animals, or abstract forms—without mechanical aid.
- Puppets are controlled manually to create theatrical performances that engage audiences through storytelling and social commentary.
Puppetry in India
- India has a rich tradition of puppetry, deeply rooted in folklore, mythology, and artistic expression.
- The art has been used for centuries to narrate historical epics, moral tales, and social issues.

Major Types of Puppetry in India
- String Puppets (Kathputli): Predominantly found in Rajasthan and Gujarat, these puppets are manipulated using strings and often depict folk tales and traditional narratives.
- Shadow Puppets: Crafted from leather, these puppets are used to cast shadows on a screen. This form is especially popular in Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala.
- Rod Puppets: Controlled with rods, these puppets are commonly used in West Bengal and Assam, often portraying mythological stories.
- Glove Puppets: Worn on the puppeteer’s hands, these puppets are particularly known in Kerala (Pavakathakali), blending elements of classical dance with puppetry.
The celebration of World Puppetry Day emphasizes the cultural importance of puppetry and encourages the preservation and promotion of this unique art form.
With reference to puppetry in India, consider the following statements:
- The Kathputli form of puppetry, primarily found in Rajasthan, is a type of rod puppetry.
- Shadow puppetry is practiced in states such as Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Pavakathakali, a type of glove puppetry, is influenced by Kathakali dance traditions.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Kathputli is not rod puppetry but a string puppetry form, primarily found in Rajasthan and Gujarat. (Statement 1 is incorrect.)
- Shadow puppetry is a traditional art form seen in Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh, where leather puppets cast shadows on a screen. (Statement 2 is correct.)
- Pavakathakali, a glove puppet tradition from Kerala, is inspired by Kathakali dance, incorporating similar costume styles and expressions. (Statement 3 is correct.)
Rang Panchami
Rang Panchami is celebrated five days after Holi, serving as the grand conclusion to the festive revelries.
Significance and Meaning
- The term “Rang Panchami” is derived from two words—”Rang” (color) and “Panchami” (fifth day)—indicating its occurrence on the fifth day after Holi.
Regional Observance
- This vibrant festival is predominantly celebrated in Maharashtra, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and parts of Rajasthan with great enthusiasm.
Traditions and Festivities
- Rang Panchami signifies the arrival of spring, bringing communities together to rejoice in the spirit of color.
- People mark the occasion by throwing and applying colored powders (gulal) on each other, creating an atmosphere of joy and togetherness.
Consider the following statements regarding Rangpanchami:
- It is celebrated on the full moon day of the Hindu month of Phalguna.
- The festival marks the end of Holi celebrations and is observed primarily in western and central India.
- Unlike Holi, Rangpanchami is associated with invoking spiritual and cosmic energies through colors.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Rangpanchami is celebrated five days after Holi, not on the full moon day (Purnima) of Phalguna.
Statement 2 is correct: It is mainly observed in Maharashtra, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
Statement 3 is correct: Unlike Holi, which is more social and playful, Rangpanchami has a spiritual aspect, where colors are believed to activate cosmic energies.
Project Pari
Public Art of India (PARI) Project
- The PARI project is an initiative launched by the Ministry of Culture to promote and enrich India’s public art landscape. It is implemented by the Lalit Kala Akademi and the National Gallery of Modern Art (NGMA).
- The project showcases the country’s diverse regional art forms, including Phad, Thangka, Gond, and Warli, featuring the work of over 200 artists.
- Currently, the PARI project is operational only in Delhi, where it aims to foster public engagement through artistic expression. It encourages dialogue and reflection by integrating India’s rich cultural heritage with contemporary themes.
- As part of the government’s broader efforts, the initiative provides incentives to talented artists, ensuring the preservation and promotion of India’s artistic traditions in modern public spaces.

With reference to the “Public Art of India (PARI) Project”, consider the following statements:
- The project is implemented by the Ministry of Culture in collaboration with private institutions.
- It primarily focuses on integrating India’s ancient art traditions with modern artistic expressions.
- As of now, the project has been implemented in multiple cities across India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The project is implemented by the Ministry of Culture but executed through Lalit Kala Akademi and the National Gallery of Modern Art (NGMA), not private institutions.
Statement 2 is correct: PARI aims to blend India’s rich cultural heritage with contemporary themes, making it a fusion of traditional and modern art.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Currently, the project is limited to Delhi and has not yet been expanded to other cities.
Indo-U.S. Cultural Property Agreement
Context:
- India has signed the Cultural Property Agreement (CPA) with the United States of America (USA) to prevent the smuggling of Indian antiquities.
Key Highlights of the Indo-U.S. Cultural Property Agreement:
Objective: Aims to prevent the illicit trafficking of Indian cultural artifacts and antiquities.
Legal Framework:
- Aligns with Article 9 of the 1970 UNESCO Convention, which allows countries facing threats to their cultural heritage to seek international assistance.
- Focuses on preventive measures rather than specific timelines or numerical targets.
Impact:
- A total of 588 antiquities have been repatriated from the USA, with 297 returned in 2024 alone.
- Strengthens cooperation in areas of technical assistance, combating illicit trade, and addressing the looting of cultural property.
International Collaboration:
- India engages with UNESCO, INTERPOL, and other global bodies to protect and repatriate cultural heritage.
Consider the following statements regarding the Indo-U.S. Cultural Property Agreement (CPA):
- The agreement is time-bound and aims to repatriate a minimum number of artifacts per year.
- It is focused only on the repatriation of stolen artifacts and does not involve broader cooperation in cultural heritage protection.
- India collaborates with international agencies like UNESCO and INTERPOL to combat illicit trafficking of cultural property.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A.1 only
B. 2 only
C. 3 only
D. 2 and 3 only
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The CPA is preventive in nature and does not have specific timelines or a target number for repatriations.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The agreement includes technical cooperation and measures to prevent illicit trade, not just repatriation.
Statement 3 is correct: India collaborates with UNESCO, INTERPOL, and other global organizations to combat the trafficking
International Women’s Day
Syllabus: GS1/Society
About International Women’s Day (IWD):
- Celebrated annually on March 8 to honor women’s contributions and advocate for gender equality.
Historical Background:
- Declared as International Women’s Day by Vladimir Lenin in 1922 to recognize women’s role in the 1917 Russian Revolution.
- Officially recognized by the United Nations in 1977.
Themes for 2025:
- United Nations (UN) Theme: “For All Women and Girls: Rights. Equality. Empowerment.”
- Official IWD Theme: “Accelerate Action.”
2025 Significance:
- Marks 30 years since the adoption of the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action, a global framework for advancing women’s rights.
Legal Framework for Women Empowerment in India:
Constitutional Provisions:
Article 14: Ensures equality before the law.
Article 15: Prohibits discrimination based on sex.
Article 51A(e): Encourages citizens to renounce practices that violate women’s dignity.
Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP):
Article 39: Advocates equal livelihood opportunities and equal pay.
Article 42: Ensures maternity relief.
Challenges Faced by Women in India:
- Gender Discrimination: Social and cultural biases limiting opportunities.
- Limited Access to Education: Especially in rural areas, restricting future prospects.
- Economic Inequality: Wage disparity, job limitations, and financial dependence.
- Safety Concerns: High rates of gender-based violence, harassment, and trafficking.
- Health & Reproductive Rights: Limited access to quality healthcare and maternal services.
- Child Marriage: Affects health, education, and independence.
- Political Underrepresentation: Low participation in decision-making roles.
- Social Norms & Expectations: Rigid gender roles restricting freedom.
- Workplace Harassment: Insufficient protective measures.
India’s Commitment to International Women’s Rights:
- India is a signatory to key global treaties and agreements, including:
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948)
- International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR, 1966)
- Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW, 1979)
- Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action (1995)
- United Nations Convention Against Corruption (2003)
- Agenda 2030 for Sustainable Development
Key Achievements in Women Empowerment in India:
- Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam, 2023: Reserves one-third of seats for women in Lok Sabha, State Legislative Assemblies, and Delhi Assembly.
- National Sex Ratio: Improved to 1020 females per 1000 males (NFHS-5).
- Maternity Leave: Extended to 26 weeks.
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana:2 crore accounts opened.
- PM Awas Yojana Gramin: 72% of houses are owned by women.
- Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR): Reduced to 97 per lakh live births (2018-20) from 130 per lakh (2014-16).
- Abolition of Triple Talaq: Strengthening legal rights for Muslim women.
- Women in Armed Forces:
- Permanent commission granted in 12 Arms and Services.
- Agniveer recruitment for women in all three defense services.
- Women in STEM: 43% of STEM graduates in India are women—the highest in the world.
Government Initiatives for Women Empowerment:
- Mission Shakti (2021-2025): Focuses on women’s welfare, safety, and empowerment.
- Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao: Aims to improve female child survival and education.
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana: Encourages savings for girl children.
- Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram: Ensures free maternity healthcare.
- PM Matru Vandana Yojana: Provides financial support for pregnant women.
- Mission Saksham Anganwadi & Poshan 2.0: Focuses on improving women’s health through better nutrition.
- WISE-KIRAN (Women in Science & Engineering): Supported 1,962 women scientists (2018-2023).
- Nari Shakti Puraskar: Recognizes outstanding contributions of women.
- Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2017: Extends paid maternity leave to 26 weeks.
This comprehensive framework ensures a holistic approach to gender equality and women’s empowerment in India.
Consider the following statements regarding International Women’s Day (IWD):
- It was first declared as International Women’s Day by the United Nations in 1922.
- The year 2025 marks 30 years since the adoption of the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action.
- The official United Nations (UN) theme for IWD 2025 is “Accelerate Action.”
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 2 only
Explanation: Vladimir Lenin, not the UN, declared March 8 as International Women’s Day in 1922.The UN theme for IWD 2025 is “For All Women and Girls: Rights. Equality. Empowerment.”, while “Accelerate Action.” is the official IWD theme.
