1. Santhara
Syllabus: GS1/Culture
- A tragic incident involving a three-year-old girl with a brain tumour has sparked a national debate after her parents initiated her into Santhara, a Jain religious ritual of voluntarily embracing death.
What is Santhara?
- Santhara, also called Sallekhana or Samadhi Maran, is an ancient Jain religious vow of gradual fasting unto death.
- It is undertaken with the aim of attaining spiritual purity by detaching from worldly desires and shedding accumulated karma.
- Jain scriptures permit Santhara only under specific circumstances, such as:
- Terminal illness
- Extreme old age
- Severe and unavoidable hardship (e.g., famine or deteriorating health that may lead to unintentional harm to living beings, violating ahimsa).
Ethical and Legal Concerns
- The death of a minor has raised critical questions of consent and legality, as children lack the cognitive maturity to make life-ending decisions.
- Medical professionals and child rights activists argue that the practice, when applied to minors, equates to enforced starvation and violates basic human rights.
Legal Status of Santhara
- In 2015, the Rajasthan High Court ruled that Santhara is akin to suicide, making it punishable under:
- Section 306 – Abetment to suicide
- Section 309 – Attempt to suicide
- The ruling triggered widespread protests from the Jain community, citing infringement on religious freedom.
- Later, the Supreme Court stayed the Rajasthan HC verdict, effectively preserving the status quo and recognizing Santhara as part of Jain religious tradition—pending a final decision.
Consider the following statements regarding the Jain ritual of Santhara and its legal-constitutional implications in India:
- Santhara is explicitly protected under Article 25 of the Constitution as a core religious practice of Jainism, as affirmed by the Supreme Court in a final judgment.
- The Rajasthan High Court, in a 2015 ruling, equated Santhara with suicide and held it punishable under Sections 306 and 309 of the Indian Penal Code.
- Article 21 of the Indian Constitution has been interpreted to include the right to die with dignity in the context of both euthanasia and religious fasting.
- The Supreme Court’s stay on the Rajasthan High Court’s verdict effectively legalizes Santhara in all forms and circumstances, including its use by minors.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 4 only
Correct Answer: B) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: The Supreme Court has stayed the Rajasthan HC judgment but has not delivered a final ruling affirming Santhara as a constitutionally protected religious practice. Thus, legal status is pending adjudication, not fully affirmed.
- Statement 2 – Correct: The Rajasthan HC in 2015 did declare Santhara punishable under IPC Sections 306 and 309, treating it as suicide.
- Statement 3 – Correct: The right to die with dignity has been interpreted under Article 21 by the Supreme Court, especially in the Common Cause v. Union of India (2018) judgment on passive euthanasia.
- Statement 4 – Incorrect: The SC’s interim stay on the HC ruling does not equate to full legalization, especially not for minors who cannot give informed consent, making the recent case ethically and legally controversial.
Mangar Bani
Syllabus: GS1/ Ancient History
- Recent archaeological findings at Mangar Bani, located in the Aravalli ranges along the Delhi-Haryana border, have uncovered prehistoric tools and rock art dating back to the Lower Palaeolithic period (approximately 200,000–500,000 years ago), making it one of the oldest known human habitations in the region.
- Mangar Bani is not only an important archaeological site but also a sacred grove and hill forest, believed to be the only surviving primary forest in the Delhi NCR region. Despite its ecological significance, it is not officially notified as a forest under the Forest (Conservation) Act.
- A primary forest refers to an ecologically mature and naturally regenerated forest, largely untouched by significant human activity, and characterized by the presence of native tree species and high biodiversity.
With reference to Mangar Bani, consider the following statements:
- Mangar Bani is officially classified as a primary forest under the Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980.
- Archaeological evidence from Mangar Bani indicates human habitation dating back to the Upper Palaeolithic period.
- It is located in the Aravalli hills, and represents the last surviving patch of primary forest in the Delhi NCR region.
- Primary forests are typically younger forests subjected to reforestation and managed silviculture practices.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 3 only
C) 1, 3, and 4 only
D) 2 and 4 only
Answer: B) 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Mangar Bani is not officially notified as a forest under the Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980, despite functioning ecologically as one.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The evidence dates back to the Lower Palaeolithic period, not Upper Palaeolithic.
- Statement 3 is correct: Mangar Bani is indeed located in the Aravalli hills and is considered the last remaining primary forest in the Delhi NCR.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: Primary forests are ecologically mature and minimally disturbed, unlike reforested or managed forests.
Rules for Obtaining Voter ID in India
Syllabus: GS2/ Governance
Context
- In the aftermath of the recent terrorist attack in Pahalgam, investigations revealed that several deported Pakistani nationals were in possession of Indian identity documents, including voter ID cards, raising concerns about loopholes in the electoral registration system.
Constitutional and Legal Framework
- Article 326 of the Indian Constitution guarantees the right to vote to every Indian citizen aged 18 years or above for elections to the Lok Sabha and State/Union Territory Legislative Assemblies.
Section 16 of the Representation of the People Act, 1950 disqualifies individuals from being registered in electoral rolls if they:
- Are not citizens of India,
- Have been declared to be of unsound mind by a competent court,
- Are disqualified due to corrupt practices or offences under election laws.
Voter Registration Procedure
- The Election Commission of India (ECI) requires new applicants to use Form 6 for enrolment.
Required documents include:
- Self-attested proof of age and address (e.g., utility bills, Aadhaar, driving license),
- A signed declaration of Indian citizenship.
- Proof of citizenship (e.g., birth certificate, passport) is not mandatory by default unless the Electoral Registration Officer (ERO) suspects the authenticity of the applicant’s claim.
Verification Process involves:
- Preliminary scrutiny by Booth Level Officers (BLOs),
- Document verification,
- Public hearings to consider claims or objections,
- Final approval or rejection by the ERO.
Penal Provisions
- Section 31 of the Representation of the People Act, 1950, criminalizes false declarations in voter applications and prescribes penalties for offenders.
With reference to the legal framework governing electoral registration in India, consider the following statements:
- Article 326 of the Constitution provides that only Indian citizens aged 21 and above are eligible to vote in Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections.
- Proof of Indian citizenship is always mandatory for voter registration under Form 6.
- Section 16 of the Representation of the People Act, 1950 disqualifies a person from electoral rolls if they are of unsound mind or are not citizens of India.
- False declarations made in voter applications are punishable under Section 31 of the Representation of the People Act, 1950.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 and 4 only
C. 2 and 4 only
D. 1, 3 and 4 only
Answer: B. 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The minimum voting age under Article 326 is 18 years, not 21.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: Proof of citizenship is not always mandatory unless specifically required by the ERO.
- Statement 3 is correct: Section 16 disqualifies non-citizens and persons of unsound mind (as declared by a competent court).
- Statement 4 is correct: Section 31 penalizes false declarations in electoral applications.
OPEC and OPEC+
Syllabus: GS2/Important International Institutions
Context:
- Global oil prices have plummeted to multi-year lows following OPEC+’s decision to fast-track production increases, raising concerns over market stability.
About OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries):
- Establishment: Founded in 1960 at the Baghdad Conference by five countries—Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, and Venezuela.
- Current Membership: Comprises 12 oil-exporting nations — Algeria, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Venezuela.
- Headquarters: Vienna, Austria (not a member state).
- Objective: To coordinate and unify petroleum production policies among member states to ensure price stability, a regular supply to consumers, and a fair return for producers.
About OPEC+:
- Formation: Established in 2016 following the ‘Algiers Accord’ and the ‘Vienna Agreement’, in response to drastic price declines due to oversupply and rising U.S. shale oil output.
- Composition: Includes 10 non-OPEC oil-producing countries—Russia, Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan, Brunei, Bahrain, Mexico, Oman, South Sudan, Sudan, and Malaysia—alongside the 12 OPEC members.
- Mandate: Jointly manages oil output levels to stabilize global crude markets and protect the interests of both producers and consumers.
With reference to OPEC and OPEC+, consider the following statements:
- OPEC was established in response to the 1973 oil crisis and originally included only three Middle Eastern countries.
- Austria is a founding member of OPEC and hosts its headquarters in Vienna.
- OPEC+ was created to include non-OPEC oil-producing countries in coordinated production decisions.
- The ‘Algiers Accord’ and the ‘Vienna Agreement’ laid the foundation for the formation of OPEC+.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 and 4 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 3 and 4 only
Answer: B. 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: OPEC was formed in 1960, not in response to the 1973 oil crisis. The founding members included five countries—Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, and Venezuela—not just three from the Middle East.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: Austria is not a member of OPEC, though Vienna hosts OPEC’s headquarters.
- Statement 3 is correct: OPEC+ includes non-OPEC countries to coordinate oil production and manage prices.
- Statement 4 is correct: The Algiers Accord (2016) and Vienna Agreement (2016) were foundational in establishing OPEC+.
NAMASTE (National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem) Scheme
Syllabus :GS 2/Social Justice
- A NAMASTE scheme event was recently held in Budaun, Uttar Pradesh, where sanitation workers were honored.
About the NAMASTE Scheme:
- The National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) scheme was launched in July 2023 by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, in collaboration with the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- Type: Central Sector Scheme
- Objective: The scheme aims to ensure the safety, dignity, and rehabilitation of sanitation workers by eliminating hazardous manual cleaning of sewers and septic tanks. It focuses on promoting mechanized and safe sanitation practices.
Key Components:
- Profiling of Sewer and Septic Tank Workers (SSWs)
- Health insurance coverage under AB-PMJAY
- Occupational safety training for SSWs
- Upfront capital subsidy for sanitation vehicles/equipment
- Distribution of PPE kits and safety devices
- Emergency Response Sanitation Units (ERSUs)
- IEC Campaign to raise awareness of the safety and dignity of sanitation workers
- 2024 Addition: The scheme was expanded to include waste pickers, supporting their access to safe, dignified, and sustainable livelihoods.
Which of the following statements regarding the NAMASTE (National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem) scheme is/are correct?
- The scheme includes a provision for the financial support of sanitation workers’ children’s education.
- The scheme is primarily focused on the manual scavenger rehabilitation process, emphasizing social integration through skills development.
- It aims to eliminate manual scavenging by mechanizing the cleaning of sewers and septic tanks while promoting dignity for sanitation workers.
- The scheme provides for the setting up of Emergency Response Sanitation Units (ERSUs) for rapid deployment in times of sanitation emergencies.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2, and 4 only
(b) 2, 3, and 4 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
The correct answer is (b) 2, 3, and 4 only.
Explanation:
- The scheme includes a provision for the financial support of sanitation workers’ children’s education.
- This statement is incorrect. The NAMASTE scheme focuses on ensuring the safety, dignity, and rehabilitation of sanitation workers, with a primary focus on mechanizing sewer and septic tank cleaning processes. However, there is no direct provision in the scheme specifically for the financial support of children’s education of sanitation workers. This might be part of future government policies but is not a direct feature of NAMASTE.
- The scheme is primarily focused on the manual scavenger rehabilitation process, emphasizing social integration through skills development.
- This statement is correct. While the NAMASTE scheme is focused on eliminating hazardous manual scavenging, it also emphasizes rehabilitation through skill development and social integration. The scheme aims to rehabilitate manual scavengers by providing them with training and support to ensure their dignified inclusion into society.
- It aims to eliminate manual scavenging by mechanizing the cleaning of sewers and septic tanks while promoting dignity for sanitation workers.
- This statement is correct. The NAMASTE scheme’s primary objective is to eliminate manual scavenging by mechanizing the cleaning of sewers and septic tanks, thereby ensuring the safety and dignity of sanitation workers. This is the core objective of the scheme.
- The scheme provides for the setting up of Emergency Response Sanitation Units (ERSUs) for rapid deployment in times of sanitation emergencies.
- This statement is correct. One of the components of the NAMASTE scheme is the provision of Emergency Response Sanitation Units (ERSUs), which are designed to be deployed during sanitation emergencies. These units help in rapid response to sanitation-related crises, ensuring quick and safe management of waste disposal.
Israel Cabinet Approves Plan for Gaza Conquest
Syllabus :GS2/IR
- Israel’s Security Cabinet has approved an expansion of military operations in Gaza, which may include the potential conquest and occupation of the territory. As part of the offensive, the Israeli army has mobilized tens of thousands of reservists.
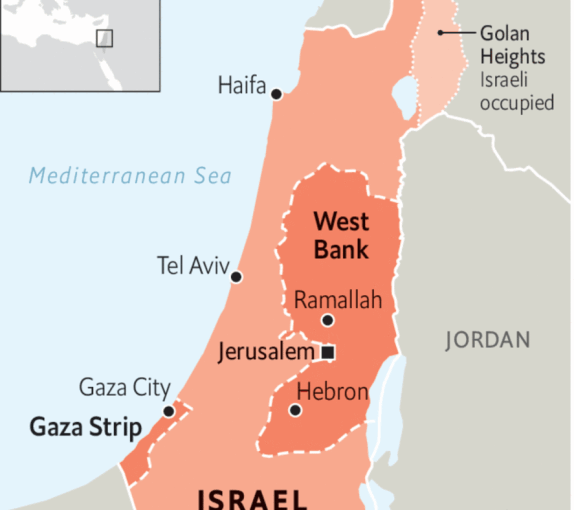
The Gaza Strip:
- The Gaza Strip is a small territory located in the Middle East, bordered by Israel to the north and east, Egypt to the southwest, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west.
- It spans 25 miles (40 kilometers) in length and 4–5 miles (6–8 kilometers) in width.
- The region is named after the ancient city of Gaza, which is situated near the northeastern end of the strip.
- Over the years, the Gaza Strip has been a focal point of conflict, with ongoing tensions and disputes over its governance and territory.
Consider the following statements regarding the Gaza Strip:
- The Gaza Strip has been a point of contention primarily between Israel and Egypt.
- The Gaza Strip is a narrow coastal area that spans approximately 25 miles in length and is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea, Israel, and Egypt.
- The region derives its name from the ancient city of Gaza, located near its northeastern end, and has historically been a site of numerous territorial conflicts.
- Israel’s recent military expansion in Gaza aims for a permanent occupation of the region, a stance that has not received significant support from the international community.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2, and 3 only
(b) 2, 3, and 4 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
correct answer: 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: This statement is partially correct as the Gaza Strip has indeed been a point of conflict primarily between Israel and Palestine, and Egypt has also been involved historically but in a lesser direct role in the conflict. Hence, this statement is misleading.
- Statement 2: This statement is correct. The Gaza Strip is a narrow territory, spanning approximately 25 miles in length and bordered by Israel, Egypt, and the Mediterranean Sea.
- Statement 3: This statement is correct. The Gaza Strip is named after the ancient city of Gaza and has been a long-standing area of territorial dispute, especially between Israel and Palestine.
- Statement 4: This statement is partially misleading. While Israel’s military expansion has been criticized, the aim to permanently occupy the region has not been explicitly endorsed in official policies or statements. The international community remains divided on this issue, with strong criticism from multiple entities.
Civil Defence Drills
Syllabus :GS2/Governance/GS 3/Internal Security
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has instructed states across India to conduct nationwide mock drills aimed at enhancing civil defense readiness, particularly in response to the heightened tensions with Pakistan after the terrorist attack in Pahalgam.
Civil Defence Drills:
- The drills are a part of India’s passive defense strategy, focusing on preparedness amidst ongoing cross-border firing and rising geopolitical tensions. These exercises will take place across 244 identified districts, including operations at the village level.
Key components of the drills include:
- Activation of air-raid warning signals.
- Implementation of crash blackout measures.
- Camouflaging critical infrastructure.
- Evacuation plans for civilians.
- Establishing a direct communication line with the Indian Air Force.
- Training civilians on various civil defense protocols in case of hostile attacks.
- Additionally, states have been directed to activate control rooms, organize firefighting and warden services, and undertake maintenance activities for bunkers and trenches. Bunkers are particularly common in border areas like Jammu and Kashmir, offering civilians protection against cross-border firing.
Civil Defence Framework in India:
- The Civil Defence Act, 1968, was enacted following the 1962 India-China war and the 1965 India-Pakistan war. The Act aims to safeguard people, property, and infrastructure from hostile attacks by air, land, or sea. It also empowers the creation of a Civil Defence Corps to carry out relief and support during wars or disasters.
- The Civil Defence Corps is made up of trained civilian volunteers, who can be mobilized during emergencies. The drills will also involve students from schools and colleges, National Cadet Corps (NCC) members, and volunteers from the Nehru Yuva Kendra Sangathan (NYKS).
With reference to Civil Defence in India, consider the following statements:
- The Civil Defence Act, 1968 was enacted in the immediate aftermath of the Kargil War to bolster border preparedness.
- Civil Defence Corps, as per the Act, is composed of only ex-servicemen trained in emergency protocols.
- Under current guidelines, mock drills for civil defence preparedness may include blackout measures, evacuation planning, and civilian training.
- Bunkers in India are constructed only along the India-Pakistan International Border (IB), specifically in Rajasthan and Gujarat.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Correct Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: The Civil Defence Act, 1968 was enacted post the 1962 India-China War and 1965 India-Pakistan War, not after the Kargil War (which occurred in 1999).
- Statement 2 – Incorrect: The Civil Defence Corps is not limited to ex-servicemen. It consists of trained civilian volunteers, including students and members of organizations like NCC and NYKS.
- Statement 3 – Correct: The Ministry of Home Affairs has directed that mock drills include blackout measures, camouflaging installations, evacuation planning, and training civilians.
- Statement 4 – Incorrect: Bunkers are built in border areas prone to cross-border firing, especially in Jammu & Kashmir. The statement wrongly restricts it to Rajasthan and Gujarat.
Executive Director of IMF
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
- Parameswaran Iyer, former CEO of NITI Aayog and currently serving as a director at the World Bank, has assumed interim charge as India’s Executive Director at the International Monetary Fund (IMF), following the early departure of K. V. Subramanian.
About the IMF Executive Board:
- The Executive Board of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) functions as the primary decision-making body overseeing the institution’s day-to-day operations. It comprises 25 Executive Directors, who are either elected by individual countries with significant financial quotas or by multi-country constituencies.
Key Functions:
- Approving IMF lending to member countries facing temporary balance of payments difficulties,
- Ensuring global macroeconomic and financial stability,
- Preventing potential spillover effects across the international financial system.
Consider the following statements regarding the Executive Board of the International Monetary Fund (IMF):
- Every Executive Director on the Board represents only one country, regardless of the size of its financial quota.
- The Executive Board plays a role in approving lending arrangements to countries experiencing long-term structural economic crises.
- The Executive Board consists of members who are responsible for the IMF’s daily operations and policy implementation.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer:B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect—some Directors represent multi-country constituencies.
- Statement 2 is incorrect—IMF lending typically addresses temporary balance of payments difficulties, not long-term structural crises.
- Statement 3 is correct.
India becomes 1st country in world to develop genome-edited rice varieties
Syllabus:Science
- India has achieved a significant milestone by becoming the first country globally to develop genome-edited rice varieties. Agriculture Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan recently launched the first two genome-edited rice varieties, developed by institutions under the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- During the event in New Delhi, the Minister expressed his congratulations to the agricultural scientists involved, highlighting the nation’s confidence in their capabilities.
- He emphasized that this groundbreaking research will contribute significantly to Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision of a “Viksit Bharat.”
- Minister Chouhan further noted that to meet the growing nutritional demands of India’s increasing population, the country must enhance its agricultural production.
- These new rice varieties are designed not only to benefit farmers but also the general public.
- They have been specifically developed for cultivation in multiple states, including Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, West Bengal, and Madhya Pradesh.
- The first variety, DRR Dhan 100 Kamala, is derived from the popular Samba Mahsuri rice.
- This variety matures 15 to 20 days earlier than conventional varieties and yields 25% more produce
- The second variety, Pusa DST Rice 1, is highly tolerant to salinity and alkalinity, making it suitable for cultivation in saline conditions.
- This variety also offers a 30% higher yield in such environments.
- The widespread cultivation of these two varieties, covering approximately 5 million hectares, is projected to produce an additional 4.5 million tons of paddy.
- Minister Chouhan described the launch of these varieties as a historic event, noting that they will reduce production costs while increasing overall yield.
- These innovations are expected to play a vital role in addressing the nutritional needs of India’s growing population.
- ICAR has stated that these varieties represent a major step forward in creating climate-resilient, high-yield agricultural practices.
- The organization also affirmed that they will play a leading role in driving the second green revolution in India.
India has recently become the first country in the world to develop genome-edited rice varieties. These varieties were launched by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR). Which of the following statements regarding the two genome-edited rice varieties developed by ICAR is/are correct?
- DRR Dhan 100 Kamala is derived from Samba Mahsuri, matures 15-20 days earlier, and yields 25% more production.
- Pusa DST Rice 1 is salinity and alkalinity-tolerant, with a 30% higher yield under saline conditions.
- These varieties are primarily developed for the states of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Maharashtra.
- The cultivation of these varieties in 5 million hectares is expected to produce 4.5 million tons of additional paddy.
Select the correct answer:
- A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1, 2, and 4 only
C) 1, 2, and 3 only
D) 2 and 4 only
Answer: B) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: DRR Dhan 100 Kamala is derived from Samba Mahsuri, matures 15-20 days earlier, and yields 25% more production. (Correct)
- Statement 2: Pusa DST Rice 1 is salinity and alkalinity-tolerant, with a 30% higher yield under saline conditions. (Correct)
- Statement 3: These varieties are developed for multiple states, not just Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Maharashtra. (Incorrect)
- Statement 4: Cultivation in 5 million hectares is expected to produce 4.5 million tons of additional paddy. (Correct)
Multi-Influence Ground Mine (MIGM)
Syllabus:Defence
- India has marked a significant achievement by successfully test-firing the Multi Influence Ground Mine (MIGM), a cutting-edge indigenously developed underwater weapon system.
About Multi Influence Ground Mine (MIGM):
- The MIGM is a sophisticated underwater naval mine designed to detect and neutralize advanced stealth ships and submarines. It employs multi-influence sensing technology, allowing it to track and respond to various threat signatures—acoustic, magnetic, and pressure—making it highly versatile and effective in diverse maritime combat scenarios.
- Technologically, the MIGM incorporates Fibre Reinforced Plastic (FRP) composites, state-of-the-art electronics, high-density power packs, and advanced software algorithms, enhancing its durability, precision, and operational efficiency.
- The system has been developed by the Naval Science and Technological Laboratory (NSTL) in Visakhapatnam, with collaborative support from other laboratories under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
With reference to the Multi Influence Ground Mine (MIGM), consider the following statements:
- It is designed exclusively to detect magnetic signatures of submarines.
- It uses composite materials such as Fibre Reinforced Plastic (FRP) in its construction.
- The system has been developed solely by the Indian Navy without DRDO involvement.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 1 and 2 only
D. 2 and 3 only
Answer:A
Explanation: Statement 1 is incorrect—MIGM detects acoustic, magnetic, and pressure signatures. Statement 3 is incorrect—MIGM is developed by NSTL, a DRDO lab, not solely by the Navy.
