Changes in Chief Election Commissioner Appointment Process
A recent meeting involved Prime Minister Narendra Modi, Home Minister Amit Shah, and Leader of Opposition Rahul Gandhi to appoint a successor to retiring Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) Rajiv Kumar. The meeting highlighted changes in the appointment process and raised concerns about the new law governing these appointments.
Previous Appointment Process:
- Procedure: The President of India appointed the CEC and Election Commissioners based on the Prime Minister’s advice.
- Legislation: There was no formal legislation governing the appointment process.
- Succession: Typically, the most senior Election Commissioner (based on the date of appointment) succeeded the outgoing CEC.
- Ambiguity: The seniority rule had potential ambiguity when Commissioners were appointed on the same day.
Introduction of the New Law:
- Legislation: The Chief Election Commissioner and Other Election Commissioners (Appointment, Conditions of Service and Term of Office) Act, 2023 governs the new appointment process.
- Search Committee: A search committee led by the Law Minister creates a shortlist of candidates.
- Selection Committee: A selection committee comprising the Prime Minister, the Leader of Opposition, and a Cabinet Minister reviews the shortlist.
Role of the Selection Committee:
- Flexibility: The selection committee can consider candidates beyond the initial shortlist.
- Goals: Aims to enhance transparency and accountability in appointing electoral officials.
Eligibility Criteria and Terms of Service:
Eligibility: Candidates must have held a position equivalent to a Secretary in the Government of India. They must also possess integrity and experience in managing elections.
- Reappointment: Officials are not eligible for reappointment.
- Term Limit: The maximum term of service is six years for any individual in these roles.
Reasons for the Change in Appointment Process: Supreme Court Intervention: The change was influenced by Supreme Court interventions.
- Constitutional Considerations: The Supreme Court noted that the Constitution did not intend for the Executive to have exclusive authority over these appointments.
- Mandate for Change: The Supreme Court’s ruling mandated a more inclusive selection process, leading to the new law.
Ongoing Legal Challenges: Challenge to the New Law: The Association for Democratic Reforms has contested the removal of the Chief Justice of India from the selection committee.
Supreme Court Review: The Supreme Court is set to hear these petitions, raising questions about Parliament’s authority to modify judicial rulings through legislation
Who appoints the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and Election Commissioners under the previous appointment process?
A) The Parliament of India
B) The Prime Minister of India
C) The President of India, based on the Prime Minister’s advice
D) The Supreme Court of India
Answer and Explanation: C) The President of India, based on the Prime Minister’s advice
The information clearly states that the President appoints them based on the Prime Minister’s advice, under the previous procedure.
President of India issued Proclamation imposing President’s rule in Manipur
This marks the 11th instance of President’s Rule being imposed in the state, with the last time being in 2001-02, putting the State Assembly under suspended animation.
Constitutional Basis: Article 356 of the Constitution allows for the imposition of President’s Rule in a state. This happens when the President, acting on a report from the State Governor, is convinced that the state government can no longer function according to the Constitution.
Duration and Approval:
- Initial Period: President’s Rule is initially in effect for two months.
- Parliamentary Approval: To extend beyond two months, both houses of Parliament must approve it by a simple majority.
- Extension Limits: If approved, President’s Rule can be extended for a maximum of three years, with parliamentary approval required every six months.
- Revocation: The President can end President’s Rule at any time through a subsequent proclamation.
Consequences of President’s Rule:
- The President assumes control of the State Government’s functions and the Governor’s powers.
- The President can transfer the powers of the State Legislature to Parliament.
- The High Court continues to operate as usual.
S R Bommai Vs Union of India (1994)
- Supreme Court held that the proclamation under Article 356 was subject to judicial review.
The President can only dissolve a state legislative assembly after Parliament’sapproval of the proclamation, and until then, the assembly remains suspended.
To extend President’s Rule beyond the initial period, what is required?
a) Approval from the State Assembly
b) Approval from the President
c) Approval from both houses of Parliament
d) A referendum in the state
Correct Answer: c) Approval from both houses of Parliament
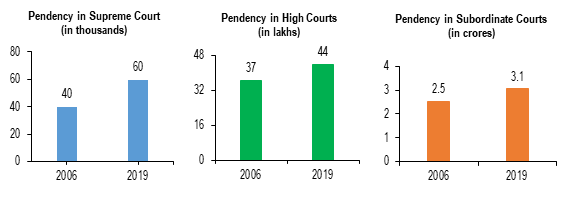
Issue of Pendency of Cases in Indian Judiciary
- This is a concise summary of the problem of case backlogs in the Indian judiciary and the Supreme Court’s efforts to address it.
- About: The Supreme Court first endorsed the appointment of ad-hoc judges in its 2021 ruling in Lok Prahari v. Union of India. These judges were authorised to hear only criminal appeals as part of a bench led by a sitting judge.
- Backlog: As of January 2025, High Courts were hampered with a disgusting backlog of 62 lakh cases.
Legal Basis:
- Article 224A: This constitutional provision allows the Chief Justice of a High Court to appoint retired judges with the President’s permission.
- Lok Prahari v. Union of India (2021): The Supreme Court case that established the conditions for appointing ad-hoc judges, including the requirement that the High Court has a significant number of vacancies.
- Background and Context: The Supreme Court has previously allowed ad-hoc judges but has identified a lack of use of the provision.
- Why the Backlog? Causes: The article lists several contributing factors to the massive backlog of cases:
- Insufficient Judges: A low judge-to-population ratio.
- Increased Litigation: More cases are being filed due to a growing population and complex socio-economic issues.
- Delays in the Justice System: Procedural inefficiencies, adjournments, and delays in evidence.
- Lack of Infrastructure: Under-equipped and under-staffed courts.
- Bureaucratic Challenges: Administrative inefficiencies and lack of modernization.
- Impact of the Backlog: Consequences: The backlog has several negative consequences:
- Delay in Justice: Cases take years to resolve.
- Increased Number of Undertrials: More people are waiting in prison for their trials.
- Increased Costs: Financial strain on litigants and the government.
- Overburdened Judges: Burnout and further delays.
- Erosion of Public Confidence: Reduced trust in the judicial system.
- Efforts to Address the Issue: Solutions and Reforms: The article highlights various initiatives to tackle the backlog:
- Judicial Reforms: Increasing the number of judges, improving infrastructure, and using technology (e-courts).
- Alternate Dispute Resolution (ADR): Promoting arbitration, mediation, and conciliation.
- E-Courts and Technology: Digitizing court proceedings for online hearings and streamlined case management.
20.Fast Track Courts: Establishing special courts for specific types of cases to expedite proceedings.
What is one of the initiatives being taken to address the backlog?
a.Reducing the number of judges
b.Discouraging the use of technology
c.Promoting Alternate Dispute Resolution (ADR)
d.Decreasing the number of fast-track courts
Correct Answer: c) Promoting Alternate Dispute Resolution (ADR)
Article 371 and Coal Mining in Meghalaya
In Meghalaya, discussions have emerged regarding the potential use of Article 371 of the Indian Constitution to restart rat-hole coal mining, coinciding with the state’s preparations for elections. The Voice of the People Party (VPP) is advocating for this change, drawing comparisons to Nagaland, which has similar provisions.
About Article 371
Article 371 grants special powers to certain northeastern states in India, providing them with autonomy over land and resources. It allows local customs and laws to take precedence. For example, Nagaland benefits from Article 371A, which safeguards its land and resources from central legislation. This has significant implications for governance and resource management in the region.
Impact on Coal Mining
Since April 2014, coal mining in Meghalaya has been banned due to environmental concerns. This ban, imposed by the National Green Tribunal (NGT) and upheld by the Supreme Court, has created challenges for the industry. The VPP contends that Article 371 could enable the resumption of mining activities, akin to Nagaland, where local laws prevent NGT intervention. This proposal raises important questions about environmental regulations and local governance.
Sixth Schedule vs. Article 371
Meghalaya operates under the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution, which empowers autonomous councils to oversee local affairs. However, there is ongoing debate over the compatibility of Article 371 and the Sixth Schedule. Some political leaders argue that the two provisions cannot coexist effectively, highlighting the complexities of governance in tribal areas and the need to balance local autonomy with national regulations.
Electoral Context: The upcoming elections for the Khasi Hills Autonomous District Council (KHADC) and the Jaintia Hills Autonomous District Council (JHADC) hold significant importance. The VPP’s emphasis on Article 371 may sway voter opinions. Notably, the councils feature low representation of women candidates despite a higher number of female voters, raising concerns about gender representation in local governance.
Recent Developments
- Recently, agreements for scientific coal mining at three sites in Meghalaya were signed by the Coal Controller. The Chief Minister stated that these agreements aim to stimulate the economy and generate employment.
- However, the ongoing discussions around Article 371 and mining practices continue to dominate the political landscape. The results of the elections may have a profound impact on the future of coal mining and local governance in the state
What trend has been observed in the upcoming elections for the Khasi Hills Autonomous District Council (KHADC) and the Jaintia Hills Autonomous District Council (JHADC)?
a.An increase in male representation at all levels of government.
b.Very low representation of women candidates despite a higher number of female voters.
c.Profit-driven policies dominating party manifestos.
d.Full gender parity achieved in candidate nominations.
Answer: B) Very low representation of women candidates despite a higher number of female voters
Deregulation Commission & State’s Role in Governance
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
India’s Deregulation Commission: A Step Towards Economic Reform
To enhance the ease of doing business and minimize bureaucratic inefficiencies, the Prime Minister of India has announced the establishment of a Deregulation Commission aimed at streamlining regulatory processes and eliminating redundant laws.
Understanding Deregulation and Its Significance
- Deregulation Definition: Reducing or eliminating government-imposed restrictions on industries to promote market efficiency and free competition.
- Challenges for Businesses: Startups and MSMEs face significant regulatory hurdles, including excessive licensing requirements, outdated laws, and bureaucratic delays.
Key Highlights of the Deregulation Commission
1991 Economic Liberalization: Marked the beginning of reduced state control and increased private sector participation.
Eliminating Archaic Regulations: Focused on scrapping obsolete compliance requirements.
- Sectoral Focus:
Key sectors identified for deregulation include banking, energy, telecom, retail, and manufacturing.
- Collaboration with Regulators:
Coordination with bodies like RBI, SEBI, TRAI, and CERC.
- Encouraging Private Investment: Aims to reduce red tape to attract higher FDI and domestic investments.
Rationale Behind the Deregulation Commission
- Reducing Bureaucratic Hurdles: Improve India’s ranking in the Ease of Doing Business Index.
- Boosting Economic Growth: Simplify compliance frameworks for sectors like manufacturing and digital economy.
- Encouraging Entrepreneurship & Innovation: Support startups and MSMEs by easing regulatory burdens.
- Modernizing Outdated Laws: Repeal colonial-era laws hindering business expansion.
- Attracting FDI: Address challenges from restrictive policies in various sectors.
- Enhancing Federalism & State Cooperation: Work with state governments to create uniform policies.
- Increasing Competition & Market Efficiency: Results in lower prices and improved services.
Evolution of Deregulation in India
Key Regulatory Commissions and Their Impact
Regulatory Commission | Sector | Role | Major Reforms |
RBI | Banking & Finance | Regulates monetary policy and financial institutions | – Increased FDI limits in insurance |
TRAI | Telecommunications | Ensures fair competition and consumer protection | – 1994: Allowed private telecom players |
CERC | Energy | Regulates electricity pricing and open access | – Encouraged private investment in power generation |
PNGRB | Oil & Gas | Ensures transparency in fuel pricing | – 2010: Deregulation of petrol prices |
Challenges and Negative Impacts of Deregulation
- Market Failures & Monopolies: Risk of excessive deregulation leading to monopolies.
- Job Losses in PSUs: Privatization may result in downsizing and layoffs.
- Regulatory Capture: Influence of powerful private entities on policy decisions.
- Rural Economic Disparities: Benefits skewed towards urban economies.
- Environmental Concerns: Risk of increased pollution and resource depletion.
Way Forward: A Balanced Approach
- Ensure consumer protection and prevent corporate malpractices.
- Balance business interests with public welfare.
- Careful deregulation of sensitive sectors like healthcare and education.
Conclusion: The Deregulation Commission is a transformative initiative for improving India’s business environment, requiring a balance between liberalization and regulatory oversight to ensure sustainable growth.
Which of the following arguments can be made against deregulation in India’s financial sector?
- It may increase systemic financial risks, leading to crises like the 2008 Global Financial Crisis.
2. Private players may prioritize short-term profits over long-term economic stability.
3. Reduced state oversight may lead to higher financial fraud and banking irregularities.
4. It may make India’s economy more resilient to external financial shocks.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2, and 3 only
(c) 2, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b)
Explanation:
While deregulation can boost competition, excessive deregulation in the financial sector may increase risks, promote speculative behavior, and lead to crises. However, it does not necessarily make the economy more resilient (eliminating option 4).
Internet Shutdowns in India
Syllabus: GS2/Polity and Governance
Internet Shutdowns in 2024: Trends and Legal Framework
Context
A report by advocacy body Access Now highlights that 2024 witnessed the highest number of internet shutdowns globally, raising concerns about digital rights and governance.
Global Trends in Internet Shutdowns (2024)
- A total of 296 internet shutdowns occurred worldwide.
- India accounted for 84 shutdowns, making up 28% of the global total.
- India had the second-highest number of shutdowns, just behind Myanmar.
- However, India’s total shutdowns in 2024 were fewer compared to the previous year.
- Shutdowns were imposed in 16 Indian States and Union Territories.
- States with the Most Shutdowns:
- Manipur – 21 shutdowns
- Haryana – 12 shutdowns
- Jammu & Kashmir – 12 shutdowns
- Primary Reasons for Shutdowns:
- Protests: 41 instances
- Communal violence: 23 instancesLegal Provisions Governing Internet Shutdowns in India
- Indian Telegraph Act, 1885:
- Internet shutdowns can be imposed in cases of “public emergency” or in the interest of “public safety”.
- However, the law does not clearly define what qualifies as an emergency or a safety issue.
Section 144 of the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC):
- Before 2017, most shutdowns were imposed under Section 144 CrPC.
- This provision allows authorities to prevent unlawful gatherings and direct individuals to refrain from certain activities.
Temporary Suspension of Telecom Services (Public Emergency or Public Safety) Rules, 2017:
- These rules formalized the process for imposing temporary internet shutdowns.
- Shutdown orders must be reviewed by an advisory board within five days to assess their legitimacy.
Landmark Case: Anuradha Bhasin v. Union of India (2020)
- The Supreme Court ruled that indefinite internet shutdowns are unconstitutional.It held that:
- Internet access is a fundamental right under Article 19 of the Indian Constitution.
- Shutdowns must be temporary and proportionate, not indefinite.
- The government must publish all orders imposing shutdowns under Section 144 CrPC.
- All shutdown orders are subject to judicial review.
Arguments in Favor of Internet Shutdowns
- National Security: Prevents the spread of misinformation and coordination of unlawful activities.
- Targeted & Temporary Measure: Aims to address specific security concerns rather than long-term restrictions.
- Preventing Unrest & Violence: Helps curb the organization of protests, riots, and civil disturbances.
- Countering Fake News: Reduces the spread of disinformation during crises.
Arguments Against Internet Shutdowns
- Freedom of Expression: Violates constitutional rights to speech and information.
- Global Reputation & Investment: Frequent shutdowns hurt India’s image and discourage foreign investment.
- Human Rights Concerns: Impacts access to information, freedom of assembly, and democratic rights.
- Economic Losses: Disrupts businesses, digital transactions, and e-commerce.
- Educational Setbacks: Hinders online learning, affecting students and teachers.
- Lack of Transparency: The government needs to provide clear justifications and timelines for shutdowns.
Conclusion
In a democratic setup, internet shutdowns should be exceptional rather than a routine measure.
- The government must justify each shutdown transparently and ensure they are proportionate and time-bound.
- Indiscriminate shutdowns impose high social and economic costs without effectively addressing security concerns.
- To achieve better internet governance, civil society and policymakers must work towards a more accountable and transparent system.
Consider the following statements regarding global internet shutdowns in 2024:
1.India recorded the highest number of internet shutdowns globally.
2. Manipur was the Indian state with the most shutdowns in 2024.
3. Internet shutdowns in India were higher in 2024 compared to the previous year.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b)
Explanation:
- India had the second-highest number of internet shutdowns in 2024, behind Myanmar (making Statement 1 incorrect).
- Manipur recorded the highest shutdowns (21), so Statement 2 is correct. However, shutdowns in 2024 were fewer than in the previous year, making Statement 3 incorrect.
CAG Reports and Their Significance in India
The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) plays a crucial role in ensuring fiscal accountability and transparency in government finances. A recent report scrutinizing the Delhi AAP government’s excise policy estimated a ₹2,002 crore loss.
Constitutional Provisions and Powers of the CAG
- Appointed by the President under Articles 148-151 of the Constitution.
- Conducts compliance, performance, and financial audits of government accounts.
Audit Procedure
- Entry Conference
- Audit Process
- Exit Conference
- Response Period
- Final Report Submission
Challenges in Tabling CAG Reports
- Delays occur due to lack of specific timelines for presenting reports after submission.
Impact of CAG Reports on Governance
- CAG reports often highlight financial mismanagement leading to policy reforms, increasing accountability and reducing corruption.
- The Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG) has recently come into focus following the tabling of 14 pending audit reports on the previous Aam Aadmi Party (AAP) government in Delhi.
- One of these reports scrutinizes the now-scrapped excise policy, estimating a ₹2,002 crore loss to the Delhi government.
- The CAG, as India’s supreme audit institution, plays a crucial role in ensuring fiscal accountability and transparency in government finances.
Constitutional Provisions and Powers of the CAG:
The CAG is appointed by the President of India under Articles 148 to 151 of the Constitution.
The CAG’s Duties, Powers, and Conditions of Service Act, 1971, provides a legal framework for its operations. The key responsibilities of the CAG include:
- Auditing the accounts of the central and state governments, along with Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs).
- Maintaining state government accounts and overseeing pension authorizations.
- Managing General Provident Fund (GPF) accounts for state employees.
Types of Audits Conducted by the CAG
The CAG primarily conducts three types of audits:
- Compliance Audit – Examines whether government entities adhere to financial rules, regulations, and laws.
- Performance Audit – Evaluates the effectiveness, efficiency, and economy of government schemes and programs.
- Financial Audit – Certifies government accounts and reviews the financial statements of PSUs.
Selection Process for Audits:
The CAG selects audit subjects based on a risk assessment framework, which considers factors such as:
- Magnitude of financial transactions involved.
- Past inspection reports and media scrutiny.
- Guidelines from the International Organization of Supreme Audit Institutions (INTOSAI).
Additionally, the Audit Advisory Board suggests potential topics and methodologies for auditing. Government bodies or the judiciary may also recommend specific audits when deemed necessary.
Audit Procedure and Reporting
- Entry Conference – Before conducting an audit, the CAG meets with the concerned department to discuss the scope, methodology, and timeline.
- Audit Process – The audit is carried out, collecting financial data and evaluating compliance.
- Exit Conference – After completion, the CAG discusses key findings with the audited department.
- Response Period – The department is given six weeks to respond to the draft report.
- Final Report Submission – The final report is submitted to the President or Governor, and later presented before Parliament or the State Legislature as per Article 151.
Challenges in Tabling CAG Reports
Although Article 151 mandates the submission of audit reports, it does not specify a deadline for their presentation in the legislature. This has led to delays in tabling reports. For instance, the Delhi government did not present several CAG reports in the Assembly despite their submission to the Lieutenant Governor four years ago.
Impact of CAG Reports on Governance
CAG reports often highlight financial mismanagement and inefficiencies, leading to policy reforms. Notable examples include:
- Telangana Government Reforms – A CAG audit on engineering procurement contracts prompted the Telangana government to amend its Engineering Procurement Contract (EPC) mode.
- Increased Auditing Activity – In 2022-23, the CAG produced 172 audit reports, marking a significant increase in its scrutiny of government finances.
By exposing irregularities, the CAG plays a pivotal role in strengthening accountability, reducing corruption, and improving public financial management.
Consider the following statements regarding the appointment and removal of the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India:
- The CAG is appointed by the President of India under Article 148 of the Constitution.
- The CAG holds office for a term of six years or until attaining the age of 65, whichever is earlier.
- The CAG can be removed by the President at their discretion.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 2 and 3 only
(C) 1 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (A) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
The CAG is appointed by the President under Article 148. The term of office is 6 years or until the age of 65, whichever is earlier. The CAG cannot be removed at the President’s discretion. The removal process is similar to that of a Supreme Court judge, requiring a resolution passed by both Houses of Parliament on grounds of proven misbehaviour or incapacity.
Death Penalty in India
- The application of the death penalty by the Indian judiciary has recently faced scrutiny due to two contrasting murder cases.
- On January 22, 2025, a civic volunteer was sentenced to life imprisonment for the rape and murder of a medical student, while a woman received the death penalty for poisoning her partner.
- These verdicts have reignited discussions about the ‘rarest of rare’ doctrine, which currently lacks a precise statutory definition.
The Rarest of Rare Doctrine
The ‘rarest of rare’ doctrine originated from a Supreme Court ruling in 1980, asserting that the death penalty should only be administered in exceptional circumstances. Despite its importance, the term remains vaguely defined, leading to differing interpretations by judges across various cases.
Key Supreme Court Cases
- In Jagmohan Singh vs. State of U.P. (1972), the Supreme Court affirmed the constitutionality of the death penalty but acknowledged the absence of explicit guidelines for judges, raising concerns about the fairness and equality of capital punishment.
- Later, in Bachan Singh vs. State of Punjab (1980), the court established the ‘rarest of rare’ principle without defining its scope.
- This framework was further elaborated in Machhi Singh vs. State of Punjab (1983), where the court identified five categories justifying the death penalty: the manner of the murder, the motive, the socially abhorrent nature of the crime, the magnitude of the offense, and the vulnerability of the victim.
Legislative Revisions and Challenges
- Despite the established framework, challenges persist. In Mithu vs. State of Punjab (1983), the Supreme Court invalidated the mandatory death penalty for inmates serving life sentences, deeming it a violation of constitutional rights.
- This ruling underscored the necessity for judicial discretion in capital cases. In 2022, the Supreme Court began discussions aimed at ensuring meaningful hearings for mitigating circumstances in death penalty cases, an effort to standardize the procedures for determining whether a crime qualifies as ‘rarest of rare.’
Contemporary Implications
- The application of the death penalty in India remains a deeply contentious topic.
- Recent verdicts expose disparities in judicial outcomes, and the absence of a universally accepted definition for ‘rarest of rare’ grants judges considerable latitude, resulting in inconsistent decisions.
- Such inconsistencies raise significant concerns regarding the fairness and application of justice in capital punishment cases.
Public and Legal Discourse
- The public discourse surrounding the death penalty is sharply divided.
- Proponents argue for its essential role in deterring heinous crimes, while critics point to the risks of judicial errors and the ethical implications of capital punishment.
- These ongoing debates mirror broader societal values and attitudes toward justice and retribution, underscoring the complexity of the issue within contemporary India.
What is the basis for the ‘rarest of rare’ doctrine as established by the Supreme Court of India?
1.It allows for automatic imposition of the death penalty for all murder cases.
2.It stipulates that the death penalty should be reserved only for exceptional circumstances.
3.It mandates a minimum sentence of life imprisonment for all murders.
4.It defines the specific method of execution in capital punishment cases.
Answer: B) It stipulates that the death penalty should be reserved only for exceptional circumstances.
Explanation: The doctrine was established to ensure that the death penalty is imposed only in extraordinary cases, though its ambiguity has led to varied interpretations.
Right to Freedom of Speech and Expression
Syllabus: GS2/Polity and Governance
The criminal proceedings against India’s Got Latent over alleged obscene remarks have ignited a debate on the scope of freedom of speech under Article 19 of the Indian Constitution.
Constitutional Framework
Article 19(1)(a) guarantees the fundamental right to freedom of speech and expression. However, Article 19(2) allows the state to impose reasonable restrictions under specific conditions, including:
- Security of the State
- Public Order
- Decency or Morality
- Contempt of Court
- Defamation
- Incitement to Offense
The Right to Take Offense
The Constitution does not explicitly recognize “offensive speech” as a separate category warranting restrictions. Consequently, the idea of a right to take offense falls outside the purview of constitutionally permissible limitations on free speech.
Constitutional Morality
Constitutional morality is a complex and evolving principle rather than an inherent sentiment. It requires continuous cultivation and development. Dr. B.R. Ambedkar emphasized that determining forms of administration should be the responsibility of the legislature rather than being dictated solely by the Constitution.
Which of the following best describes the relationship between Article 19(1)(a) and Article 19(2) of the Indian Constitution?
(A) Article 19(1)(a) guarantees freedom of speech, while Article 19(2) imposes absolute restrictions on it.
(B) Article 19(1)(a) guarantees freedom of speech, while Article 19(2) allows only the judiciary to impose reasonable restrictions.
(C) Article 19(1)(a) provides freedom of speech, but Article 19(2) permits the state to impose reasonable restrictions under specified grounds.
(D) Article 19(1)(a) grants fundamental rights, while Article 19(2) allows for restrictions even based on the subjective opinion of individuals who feel offended.
Answer: (C)
Explanation:
Article 19(1)(a) provides the right to freedom of speech and expression, while Article 19(2) enables the state to impose reasonable restrictions on specific grounds like security of the state, public order, decency, and defamation. The restrictions are not absolute and must be justified as “reasonable” by the judiciary.
Deputy Speaker
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
Constitutional Mandate
- The office of the Deputy Speaker is enshrined in Articles 93 and 178 of the Constitution, making its election constitutionally mandatory.
- Article 93: Mandates the election of a Speaker and Deputy Speaker for the Lok Sabha.
- Article 178: Similar provision for State Legislative Assemblies.
Election and Tenure
- The Constitution does not prescribe a time frame for the election of the Deputy Speaker, stating it must be held “as soon as may be.”
- Conventionally, the Speaker is elected in the first session, and the Deputy Speaker in the second session.
- Holds office until:
- The House is dissolved.
- Ceasing to be a Member of the House.
- Removal by a resolution passed by the majority of all House members.
Duties and Powers of the Deputy Speaker
- Aids the Speaker in the efficient functioning of the House.
- Presides over the House in the absence of the Speaker and exercises all powers of the Speaker during such periods.
- Can participate in debates and vote like other members but has a casting vote in case of a tie when presiding.
- Cannot introduce bills or table questions while presiding over the House.
- Receives a salary from the Consolidated Fund of India, independent of parliamentary voting.
- Cannot preside over House proceedings when a motion for his removal is under debate.
Parliamentary Convention and Political Significance
- A well-established parliamentary tradition dictates that the Deputy Speaker is chosen from the Opposition to ensure political neutrality and balance in proceedings.
- This practice has largely been followed post-Emergency (1975), with some exceptions.
Consider the following statements regarding the Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha:
- The election of the Deputy Speaker is mandated by Article 93 of the Indian Constitution.
- The Constitution mandates a fixed time frame for the election of the Deputy Speaker.
- The Deputy Speaker presides over all debates, including motions related to his own removal.
- The Deputy Speaker receives his salary from the Consolidated Fund of India, which is subject to parliamentary vote.
Which of the statements are correct?
a.1 only
b.2 and 3 only
c.1, 2, and 4 only
d.1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: A) 1 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Article 93 mandates the election of the Speaker and Deputy Speaker of the Lok Sabha.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The Constitution does not prescribe a specific time frame for the election of the Deputy Speaker, only stating it must be held “as soon as may be.”
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The Deputy Speaker cannot preside over the House when a motion for his own removal is under debate.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: The Deputy Speaker’s salary comes from the Consolidated Fund of India, but it is not subject to parliamentary vote.
Delimitation Debate: Why Are Southern States Wary?
Syllabus: GS2/ Polity & Governance
Context
The Union Home Minister has assured that the proposed delimitation exercise will not lead to a reduction in parliamentary constituencies in southern states, addressing concerns raised by the Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu.
Understanding Delimitation
Delimitation is the process of redrawing the boundaries of parliamentary and legislative assembly constituencies to reflect changes in population. Its key objectives include:
- Ensuring fair representation based on demographic shifts.
- Adjusting the number of seats allocated to various states.
- Determining reservations for Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST).
This process is designed to balance population growth with political representation, upholding the democratic principle of “one citizen, one vote, one value.”
Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 82: After each Census, Parliament enacts a Delimitation Act to redefine constituency boundaries.
- Article 170: The total number of seats in state assemblies is adjusted based on the Delimitation Act following each Census.
Who Conducts Delimitation?
The Delimitation Commission is an independent body established through a Parliamentary Act, responsible for overseeing the delimitation process. Its authority and decisions are typically not subject to judicial review; however, in 2024, the Supreme Court ruled that delimitation orders may be reviewed if they contravene constitutional values.
Composition of the Commission: Chairperson: A retired Supreme Court judge. Members: The Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) or a commissioner designated by the CEC, along with State Election Commissioners of the respective states.
History of Delimitation in India
Parliamentary Authority: The power to define the number and boundaries of constituencies lies with the Parliament. This authority has been exercised four times through the Delimitation Commission Acts of 1952, 1962, 1972, and 2002.
42nd Amendment Act (1976): This act froze the allocation of Lok Sabha seats based on the 1971 Census, intended to safeguard states that successfully implemented population control measures from losing representation.
84th Amendment Act (2001): This amendment allowed for the readjustment and rationalization of constituency boundaries based on the 1991 Census without affecting the total number of seats allocated to each state.
87th Amendment Act (2003): This act shifted the basis of delimitation from the 1991 Census to the 2001 Census, while also maintaining the seat allocation limits established in previous amendments.
Why Is Delimitation Being Revisited?
The upcoming delimitation exercise is expected to utilize the 2021 Census data (which was delayed due to the pandemic). This has sparked concerns among southern states, where population growth has been slower compared to northern states. If the delimitation process follows historical trends, the number of Lok Sabha seats could potentially increase from 543 to 753 based on a proposed population ratio of 20 lakh people per constituency.
Concerns of Southern States:
Southern states—such as Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana—are apprehensive that northern states (like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan, and Madhya Pradesh) with higher population growth may gain additional seats, thereby diminishing their representation, despite their successful governance and population control measures.
What’s Next?
Potential Increase in Total Seats: Rather than reducing seats in any state, the total number of Lok Sabha seats may be increased to reflect growing population disparities.
2026 Review: The next delimitation exercise can only occur after the first Census post-2026, likely the 2031 Census.
Women’s Reservation Act: Implementing the 33% reservation for women may also influence seat adjustments during the delimitation process.
Consider the following statements regarding the delimitation and its effects on political representation in India:
- The delimitation process aims to ensure an equal representation ratio between constituencies across states.
- Demographic shifts as reflected in the census data can significantly alter the political landscape, favoring states with higher population growth.
- Delimitation only impacts the allocation of seats in the Lok Sabha and does not affect State Legislative Assemblies.
Which of the statements are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1, 2, and 3
D) 1 and 3 only
Answer: A) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct as the delimitation process is aimed at equalizing representation across constituencies.
Statement 2 is also correct, as demographic shifts can lead to an altered political balance.
However, statement 3 is incorrect since delimitation affects both Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assembly constituencies.
Public Accounts Committee
Syllabus: GS2/ Indian Polity
Recent News: Delhi Congress leaders have welcomed the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) report on AAP’s 2021-22 excise policy. They have called for the immediate formation of the Public Accounts Committee (PAC) to review the findings and facilitate public discussion.
Public Accounts Committee: An Overview
Definition:
The Public Accounts Committee (PAC) is a parliamentary committee in India responsible for auditing the government’s revenue and expenditure. It ensures legislative oversight over executive financial actions, particularly concerning government spending.
Composition:
- The PAC comprises up to 22 members: 15 from the Lok Sabha (Lower House) and 7 from the Rajya Sabha (Upper House).
- Ministers are not eligible to be members of the committee.
- Members are elected annually through proportional representation using a single transferable vote
- The Speaker of the Lok Sabha appoints the chairperson of the committee.
- The term of office for members is one year.
Functions:
Examines audit reports submitted by the Comptroller and Auditor General (C&AG) after their presentation in Parliament.
Scrutinizes government spending to ensure it aligns with the budget approved by Parliament.
Which of the following statements regarding the Public Accounts Committee (PAC) is/are correct?
- It is a standing committee of the Indian Parliament.
- The members of the PAC are nominated by the Prime Minister.
- It ensures executive accountability regarding financial matters.
- The chairperson of PAC is always from the ruling party.
a.1 and 3 only
b.3 and 4 only
c.1, 2, and 4 only
d.1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: A) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
PAC is a standing committee of Parliament and plays a key role in ensuring executive accountability in financial matters. The members are elected by proportional representation, not nominated by the Prime Minister, and the chairperson is often from the opposition party.
NITI Aayog’s Vision for Viksit Bharat by 2047
- NITI Aayog, India’s premier policy think tank, is spearheading an initiative to assist several states in crafting state-specific vision documents aimed at realizing a ‘Viksit Bharat’ (Developed India) by 2047.
- This endeavor, detailed in NITI Aayog’s Annual Report for 2024-25, encompasses states such as Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Bihar, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Dedicated teams within NITI Aayog are collaborating with these states To develop comprehensive strategies that align with national objectives.
Background of the Initiative
- The initiative gained momentum following Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s emphasis on the significance of ‘Viksit States’ during the 9th Governing Council meeting of NITI Aayog in July 2024.
- He underscored that the aspiration for a developed India must permeate to the grassroots level, ensuring that all states contribute effectively to the nation’s socio-economic progress.
Objectives of the Visioning Exercise
- The primary objective is to assist states in formulating strategies for holistic growth, encompassing economic development, governance enhancements, and improved quality of life for citizens.
- This initiative aims to create a cohesive framework that harmonizes state and national policies, thereby promoting cooperative federalism.
State Support Mission
- Operating under the umbrella of the State Support Mission (SSM), announced in the Union Budget for 2023-24, this visioning exercise fosters structured and institutionalized engagement between NITI Aayog and the states.
- The SSM provides a platform for states to develop roadmaps that align with national priorities while focusing on their unique strengths.
Establishment of State Institutions for Transformation
- As part of the SSM, NITI Aayog is encouraging states to establish State Institutions for Transformation (SITs).
- These multidisciplinary resources are designed to guide development strategies within the states and Union Territories.
- To date, 26 SITs have been notified, enhancing state capacities for effective governance and development.
- This collaborative approach underscores NITI Aayog’s commitment to fostering cooperative federalism and ensuring that states play a proactive role in achieving the national vision of a developed India by 2047.
Which of the following is not an objective of the State Support Mission (SSM)?
a.Strengthening the Monitoring & Evaluation ecosystem of States/UTs
b.Collaborating with states to identify key growth drivers
c.Centralizing policy-making processes at the national level
d.Establishing a knowledge platform for sharing good governance practices
Answer: c) Centralizing policy-making processes at the national level
Explanation: The SSM focuses on assisting states in achieving their socioeconomic goals by 2047 through structured engagement, strengthening monitoring and evaluation systems, identifying growth drivers, and establishing platforms for sharing best practices. Centralizing policy-making at the national level is not among its objectives.
Successful Test of Matsya-6000
Project Overview:
- India’s Deep Ocean Mission aims to enhance the country’s capabilities in ocean exploration.
- The project is led by the National Institute of Ocean Technology.
Matsya-6000 Submersible Overview:
Design and Capacity:
- The submersible has a compact design with a diameter of 2.1 meters.
- It can accommodate three personnel.
Materials and Construction:
- The submersible is constructed from a titanium alloy, allowing it to withstand extreme underwater pressures.
Systems and Features:
- Ballast system for diving.
- Thrusters for multidirectional movement.
- Advanced communication tools, including an acoustic modem and underwater telephone.
- Sophisticated power distribution network.
- Advanced underwater navigation devices.
- Life-support systems for crew safety during missions.
Testing and Development Phases:
Dry Tests: Extensive dry tests were conducted to evaluate the submersible’s performance over a 500-meter range.
Wet Tests:
- The submersible was moved to the L&T Shipbuilding facility for wet tests.
- The tests focused on assessing the submersible’s stability, manoeuvrability, and communication capabilities.
- A total of 8 dives were conducted, including both unmanned and manned trials.
Future Prospects:
- Samudrayan Project:
- The project aims to explore ocean depths for resources like precious metals and to study marine biodiversity.
- It is expected to promote ocean literacy and tourism.
Completion Timeline:
- The completion of Matsya-6000 is anticipated by 2026.
- This aligns with India’s broader goals for sustainable ocean resource development.
Significance of Ocean Exploration:
- Sustainable Resource Management:
- India’s role in ocean exploration is crucial for sustainable resource management.
- The government aims to increase the contribution of the blue economy to the national GDP.
Marine Ecosystems and Resource Development:
- By exploring ocean depths, India seeks to enhance its knowledge of marine ecosystems and develop resources responsibly.
What is the primary objective of India’s Deep Ocean Mission, under which the Matsya-6000 submersible is developed?
A) To establish India as a global leader in deep-sea fishing
B) To enhance the country’s capabilities in ocean exploration and sustainable resource management
C) To develop advanced underwater weaponry for national defense
D) To promote ocean tourism and recreation in the Indian Ocean
Answer and Explanation: B)
- To enhance the country’s capabilities in ocean exploration and sustainable resource management
- The Deep Ocean Mission is a comprehensive initiative to explore the depths of the ocean for various purposes, including resource discovery, understanding marine ecosystems, and promoting the sustainable use of ocean resources.
- The Matsya-6000 submersible is a key component of this mission
ISRO Develops World’s Largest Vertical Propellant Mixer
Key Development:
• On February 13, 2025, ISRO announced the successful development of a 10-tonne Vertical Planetary Mixer.
• This is the largest of its kind for solid propellants globally.
• It was designed and manufactured in collaboration with the Central Manufacturing Technology Institute (CMTI) in Bengaluru.
Significance of Solid Propulsion:
• Importance: Solid propulsion is crucial for India’s space transportation systems.
• Mixing Process: The new mixer will improve the efficiency and safety of mixing sensitive and hazardous ingredients used in solid rocket motors.
• Impact: Enhanced mixing leads to better quality propellants, which are essential for successful space missions.
Features:
• Multiple hydrostatically driven agitators.
• Remotely operated through a PLC-based control system integrated with SCADA stations.
Technology:
• Advanced technology ensures precision in solid propellant production.
Collaboration and Development Process:
• Partners: The project was a collaborative effort between the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) and CMTI.
• Teamwork: Involved partnerships with academia and industry experts.
• Testing: Factory-level acceptance tests have been successfully completed, confirming operational capabilities.
• Goal: Reflects India’s commitment to fostering innovation in space technology.
Impact on Indian Space Missions:
• Revolutionary Impact: Expected to revolutionize the production of solid rocket motors.
• Benefits: Will enhance productivity and throughput.
• Alignment: Aligns with India’s broader initiative to achieve self-reliance in critical space technologies.
• Milestone: Marks another milestone in India’s space capabilities.
What is the primary objective of India’s Deep Ocean Mission, under which the Matsya-6000 submersible is developed?
A) To establish India as a global leader in deep-sea fishing
B) To enhance the country’s capabilities in ocean exploration and sustainable resource management
C) To develop advanced underwater weaponry for national defense
D) To promote ocean tourism and recreation in the Indian Ocean
Answer and Explanation: B)
- To enhance the country’s capabilities in ocean exploration and sustainable resource management
- The Deep Ocean Mission is a comprehensive initiative to explore the depths of the ocean for various purposes, including resource discovery, understanding marine ecosystems, and promoting the sustainable use of ocean resources.
- The Matsya-6000 submersible is a key component of this mission
Development and Commercialization of Typhoid Vaccine
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) is soliciting expressions of interest (EoI) for the collaborative development and commercialization of a Typhoid and Paratyphoid vaccine.
- Interested manufacturers and companies must fulfill specified technical criteria. Shortlisting will be based on their research and development strategies, existing facilities, and overall capabilities.
- Typhoid fever is a bacterial illness caused by the bacteria Salmonella Typhi.
- The infection is typically transmitted through contaminated food, water, or direct contact with infected individuals. Without proper treatment, Typhoid can be life-threatening.
- Antibiotics such as chloramphenicol, ampicillin, and ciprofloxacin are commonly used to treat the infection.
- Typhoid fever represents a substantial public health burden in India, with an estimated 4.5 million cases reported each year.
- The prevalence is particularly high in urban areas, making it a significant health concern.
- Several Typhoid vaccines are currently available in India, including Typbar-TCV,Ty21a, Typhim Vi, and Typherix.
- Typhoid conjugate vaccines (TCVs) are approved for children over 6 months of age, while Vi vaccines are suitable for children aged 2 years and older.
- TCVs are currently accessible exclusively through the private healthcare sector.
- Recent progress in this field includes the development of an enteric fever vaccine technology by the ICMR-National Institute for Research in Bacterial Infections (NIRBI).
- This technology utilizes outer membrane vesicles derived from two strains of typhoidal Salmonella.
Consider the following statements regarding the ICMR’s initiative:
- The ICMR is seeking partners for the development and commercialization of a Typhoid and Paratyphoid vaccine.
- Manufacturers will be selected based on their research and development capabilities, facilities, and strategies.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Correct Answer: c) Both 1 and 2
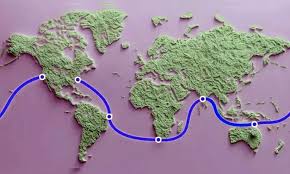
Project Water worth
- Meta has unveiled Project Waterworth, a significant initiative aimed at enhancing global digital connectivity.
- The project’s ambitious scope involves a subsea cable system covering 50,000 kilometers across five continents.
- This initiative, which will connect the U.S., India, Brazil, South Africa, and other regions, will utilize AI-powered technology to improve the efficiency and reliability of internet networks.
- The project features advanced burial techniques to protect cables from ship anchors and environmental hazards in shallower waters.
- The initiative also features new oceanic corridors, providing greater network capacity and resilience.
- Project Waterworth aims to foster international cooperation, digital inclusion, and technological advancements.
Which global technology giant has recently unveiled Project Waterworth, a significant initiative aimed at enhancing global digital connectivity?
a) Google
b) Amazon
c) Meta
d) Microsoft
Answer: c) Meta
International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER)
The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) project represents a groundbreaking endeavor in the field of fusion energy.
The recent visit of Prime Minister Narendra Modi to the ITER facility in France, alongside French President Emmanuel Macron, underscores the project’s significance and progress.
ITER’s mission is to demonstrate the feasibility of fusion power as a clean, sustainable, and virtually limitless energy source.
What is ITER?
ITER is a collaborative international project initiated in 1985, aiming to construct the world’s largest magnetic fusion device.
This ambitious undertaking seeks to harness the same principles that power the sun, leveraging the energy released from the fusion of atoms to generate electricity.
Thousands of scientists and engineers have contributed to ITER’s design, making it a landmark effort in the pursuit of alternative energy sources.
The Tokamak: A Fusion Device
At the heart of ITER lies the tokamak, a device designed to confine and stabilize plasma using magnetic fields. Within the tokamak, the fusion of atoms releases energy, which is then absorbed by the walls and converted into heat.
This heat can be used to produce steam, driving turbines to generate electricity, similar to conventional power plants.
ITER’s tokamak is slated to commence deuterium-tritium fusion reactions by 2039, marking a critical milestone in the project.
Significance of ITER
The ITER project holds immense potential for addressing global energy challenges. Fusion energy offers several compelling advantages, including:
Abundant Energy Source: Fusion reactions can produce vast amounts of energy from minimal raw materials, such as deuterium and tritium.
Zero Emissions: Fusion energy generates no greenhouse gas emissions, making it an attractive solution for mitigating climate change.
Practical Application: ITER’s success is expected to pave the way for the development of practical fusion power plants, providing a clean and sustainable energy source for future generations.
How Will ITER Work?
ITER’s primary objective is to demonstrate the concept of burning plasmas, where the energy produced by fusion reactions can sustain the plasma’s temperature.
The project will also explore essential technologies for future fusion reactors, including tritium breeding concepts.
By achieving this goal, ITER will take a significant step towards commercializing fusion energy.
Global Collaboration
The ITER project is a testament to international cooperation, involving 33 nations, including seven key member states:
China, the European Union, Japan, Korea, Russia, and the United States. These countries have been working together for decades to develop and operate the ITER experimental device, with the collective aim of advancing fusion technology to the point of designing a demonstration reactor.
India’s Role in ITER :
India has been a contributor to the ITER project for over two decades, with approximately 200 Indian scientists and various industry players, including major companies like L&T and TCS, actively involved.
Prime Minister Modi’s visit to the ITER facility marks a historic moment, being the first by a Head of State to the site.
This visit underscores India’s commitment to the project and its potential to revolutionize the global energy landscape.
What is the primary goal of the ITER project?
a.To build the world’s largest solar power plant.
b.To demonstrate the feasibility of fusion power as a clean energy source.
c.To research the effects of climate change on the environment.
d.To develop new methods of fossil fuel extraction.
Correct Answer: (b) To demonstrate the feasibility of fusion power as a clean energy source.
Paris AI Action Summit
Prime Minister Modi co-chaired the third edition of the AI Action Summit held in Paris.
Paris AI Action Summit
The summit focused on promoting sustainable AI growth and enhancing energy efficiency, in line with global climate goals. Its key objectives included:
- Ensuring access to independent, safe, and reliable AI for a diverse range of users.
- Developing environmentally friendly AI solutions that require less energy.
- Establishing effective and inclusive global governance frameworks for AI.
The event concentrated on five main themes:
- AI in Public Service
- The Future of Work
- Innovation and Culture
- Trust in AI
- Global AI Governance
- India’s Perspective and Initiatives
AI for Global Good: India highlighted the transformative potential of AI across various sectors, including healthcare, education, and agriculture, and its alignment with the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Five Pillars for Responsible AI Development: PM Modi introduced a five-point agenda aimed at fostering ethical and transparent AI growth:
- Pooling global resources and talent for AI innovation.
- Developing open-source AI systems.
- Creating high-quality, unbiased datasets.
- Democratizing AI for people-focused applications.
- Addressing cybersecurity issues, misinformation, and deepfakes.
Addressing Job Loss Concerns: India recognized the worries surrounding AI-related job displacement, emphasizing the historical trend whereby technological advancements transform jobs rather than eliminate them. The country stressed the importance of skilling and reskilling initiatives.
Significance for India
Global AI Landscape: The summit occurred amidst intense competition in the AI sector, particularly between Western countries and China. It provided India and France an opportunity to showcase their soft power in this vital area.
Strategic Partnerships: The summit reinforced the strategic partnership between India and France within a critical technology domain.
Way Ahead
India is in the process of developing its own Large Language Model (LLM) that caters to its linguistic and cultural diversity. A public-private partnership model aims to ensure affordable computing resources for startups and researchers. The IndiaAI Mission promotes AI research and development through various initiatives, including:
- Subsidized access to Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) clusters for AI training.
- Funding for AI-driven projects in key sectors.
Concluding Remarks
The Paris AI Action Summit underscores India’s commitment to ethical, sustainable, and inclusive AI development. As AI continues to transform industries, India’s proactive investments in AI education, governance, and innovation will shape its future role in the global AI landscape.
What opportunity did the Paris AI Action Summit provide for India and France?
a.To establish a military alliance against China.
b.To dominate the global AI market.
c.To showcase their soft power in the AI domain.
d.To lobby for stricter AI regulations.
Correct Answer: (C) To showcase their soft power in the AI domain
IIT Madras and ISRO Develop IRIS Chip
The Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IIT Madras) and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) have achieved a significant milestone in semiconductor technology with the development and successful testing of an aerospace-quality SHAKTI-based semiconductor chip named IRIS (Indigenous RISC-V Controller for Space Applications).
- This endeavor is part of India’s broader push towards self-reliance in technology, in alignment with the ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat‘mission.
Background of the SHAKTI Project
The SHAKTI project, under the ‘Digital India RISC-V’ initiative, is backed by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology. This initiative focuses on fostering the indigenous development of microprocessor-based products. RISC-V, an open-source Instruction Set Architecture (ISA), provides the flexibility and security necessary for crafting tailor-made processors.
Development Process of the IRIS Chip
Designed by the ISRO Inertial Systems Unit (IISU) in Thiruvananthapuram and implemented by IIT Madras, the entire process of chip design, fabrication, and packaging was conducted in India. The chip was manufactured at the Semiconductor Laboratory (SCL) in Chandigarh and packaged by Tata Advanced Systems in Karnataka.
Features and Applications of the IRIS Chip
The IRIS chip is tailored for a variety of applications, including Internet of Things (IoT) devices and computing systems that cater to strategic needs. It encompasses fault-tolerant internal memories to bolster reliability and integrates custom functional modules like CORDIC and WATCHDOG timers, making it well-suited for space mission applications.
Significance of the Achievement
This milestone represents a crucial step toward achieving self-reliance in semiconductor technology in India. The IRIS chip is the third in the series of SHAKTI chips developed, following RIMO in 2018 and MOUSHIK in 2020. The successful booting of the chip underscores India’s growing capabilities in developing a comprehensive semiconductor ecosystem.
Future Prospects: ISRO has plans to conduct flight tests on a product based on the IRIS controller in the near future. The successful development of this chip is anticipated to greatly enhance future embedded controllers for space missions.
What is the significance of the successful booting of the IRIS chip?
a.It indicates the chip will fail in future tests.
b.It highlights India’s capability in developing a semiconductor ecosystem.
c.It proves that RISC-V is obsolete.
d.It shows that space applications are unnecessary.
Answer: (b) It highlights India’s capability in developing a semiconductor ecosystem.
Quantum Property of the Nanocrystals
Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Scientists have developed a novel method to determine whether gravity follows the principles of quantum mechanics using nanocrystals.
Background
- General relativity explains gravity, while quantum mechanics governs the electromagnetic, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear forces.
- Researchers aim to understand how gravity fits into the quantum framework, proposing experiments to test whether gravity exhibits quantum properties.
- Quantum mechanics describes the behavior of particles at the microscopic scale, where classical physics no longer applies.
- Quantum technology leverages principles like superposition and entanglement, enabling advancements beyond traditional physics.
Nanocrystals and Their Role in the Experiment
- Nanocrystals are tiny crystalline structures (1–100 nm in size) that exhibit quantum mechanical properties, such as altered conductivity, magnetism, and light absorption.
- Scientists propose using a quantum property of nanocrystals known as spin.
- The spin influences the motion of nanocrystals and can be controlled using an external magnetic field.
- The spin of each nanocrystal exists in a superposition of two states until it is measured, a key quantum phenomenon.
Potential Discoveries
- The experiment could provide evidence that gravity is not a classical force.
- Alternatively, it might suggest that gravity operates under an entirely different framework, distinct from both classical and quantum forces.
With reference to quantum mechanics, which of the following statements is correct?
(a).Quantum mechanics applies only to subatomic particles and does not influence macroscopic objects.
(b) Quantum principles like superposition and entanglement have no practical technological applications.
(c) Classical mechanics fully explains the behavior of all physical systems without the need for quantum corrections.
(d) Quantum technology leverages principles such as superposition and entanglement to develop advanced computing and communication systems.
Answer: (d)
Explanation: Quantum mechanics applies to subatomic and macroscopic systems (quantum computers, superconductors), making Statement a incorrect. Quantum technology has practical applications (quantum computing, cryptography), refuting Statement b. Classical mechanics fails at microscopic scales (e.g., electron orbitals), making Statement c incorrect. Statement d is correct.
AI Tools in Tuberculosis Screening
The fight against tuberculosis (TB) in India is at a critical stage. Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s goal to eliminate TB by 2025 faces challenges due to gaps between technological advancements and their practical implementation in public health programs.
AI Tools for TB Screening
Two significant AI-based TB screening solutions have emerged:
- qXR by Qure.ai
- Genki by DeepTek
Both tools have undergone assessments for sensitivity and specificity:
- qXR: Over 90% sensitivity and more than 70% specificity
- Genki: Similar promising results
These AI models have been successfully deployed at multiple sites across India and globally, highlighting their potential to revolutionize TB screening.
Challenges in Implementation
- Delays in Health Technology Assessment (HTA) Process
- The HTAIn committee evaluates new technologies for cost-effectiveness and efficacy. However, despite qXR and Genki receiving positive assessments, their integration into the national TB program remains stalled.
- In contrast, the Central TB Division (CTD) has recommended another AI tool, DeepCXR, which lacks a formal HTA assessment, raising concerns about transparency in decision-making.
- Lack of Clarity from the Central TB Division (CTD)
Although DeepCXR has been approved for use, state health departments have not been formally informed, delaying its widespread adoption. This lack of clear communication hinders the timely deployment of AI solutions for TB screening.
Cost-Effectiveness of AI-Based TB Screening
Both qXR and Genki have been proven cost-effective, making them viable solutions for India’s TB detection efforts:
- qXR: ₹30 per screening
- Genki: ₹22 per screening
Their affordability suggests that adopting these AI tools could lead to significant cost savings while enhancing early TB detection.
The Role of Chest X-Rays in TB Detection
- Chest X-rays play a critical role in identifying presumptive and subclinical TB cases. They have proven highly effective in national surveys, detecting a large portion of TB cases.
- AI-assisted X-ray interpretation improves speed and accuracy, making it an ideal solution for resource-limited settings.
Conclusion
While AI-driven TB screening tools hold immense potential, bureaucratic delays and a lack of clear policy direction hinder their integration into India’s TB elimination program. To achieve the 2025 target, swift action is needed to implement proven AI solutions, streamline approval processes, and ensure efficient communication between national and state health authorities.
With reference to AI-based TB screening in India, consider the following statements:
- AI tools like qXR and Genki have demonstrated over 90% specificity in TB detection.
- The Health Technology Assessment (HTA) process plays a crucial role in evaluating the cost-effectiveness and efficacy of AI-based medical tools.
- DeepCXR has undergone rigorous HTA assessment before its approval for use in the national TB program.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b)
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: AI tools like qXR and Genki have over 90% sensitivity but more than 70% specificity, not 90% specificity. Sensitivity refers to the ability to correctly identify TB cases, whereas specificity indicates the ability to correctly rule out non-TB cases.
Statement 2 is correct: The Health Technology Assessment (HTA) process evaluates new medical technologies for their effectiveness and cost-efficiency before they are integrated into public health programs.
Statement 3 is incorrect: DeepCXR was recommended by the Central TB Division (CTD) without undergoing a formal HTA assessment, raising concerns about transparency in decision-making.
SPHEREx Telescope
- NASA’s SPHEREx telescope is scheduled for launch on February 27, 2025, with the ambitious goal of creating the most detailed and colorful map of the universe to date.
- Over a two-year mission, SPHEREx will gather extensive data on galaxies, stars, and life-forming molecules, offering new insights into cosmic history and the potential for extraterrestrial life.
Mission Overview
SPHEREx, short for Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization, and Ices Explorer, is distinct from traditional space telescopes. Unlike Hubble or James Webb, which focus on specific celestial objects, SPHEREx will scan the entire sky. By dividing light into 96 spectral bands, it will provide an unprecedented level of detail in its analysis of cosmic phenomena.
Unraveling Cosmic Inflation
A key objective of SPHEREx is to investigate cosmic inflation, the rapid expansion of the universe following the Big Bang. This process is fundamental to understanding the origin and evolution of the cosmos. SPHEREx will map over a billion galaxies, testing competing theories of inflation and helping refine our knowledge of the universe’s earliest moments.
Searching for Life-Forming Molecules
- Beyond studying distant galaxies, SPHEREx will also explore conditions that may support life within the Milky Way.
- It will identify water and biogenic molecules—essential building blocks of life—trapped in icy particles in cold interstellar regions.
- Mapping these molecules will enhance our understanding of habitable environments in space.
Collaboration with Other Space Missions
SPHEREx will operate in tandem with James Webb and other space telescopes. While James Webb focuses on high-resolution images of specific objects, SPHEREx will provide a broad-spectrum view of the entire universe. This complementary approach will allow scientists to piece together a more complete picture of cosmic evolution.
Data Collection and Scientific Impact
Over its mission, SPHEREx will capture an estimated 8 million spectroscopic images, revolutionizing our understanding of the cosmos. This data will be instrumental in identifying regions with potential life-supporting conditions, further advancing the field of astrobiology.
Future Implications
The discoveries made by SPHEREx could reshape our understanding of cosmic history and the origins of life. By identifying patterns and anomalies across the universe, it will help astronomers refine existing models and develop new theories.
MCQ 3.11: With reference to NASA’s SPHEREx telescope, consider the following statements
- SPHEREx will focus on capturing high-resolution images similar to the James Webb Space Telescope.
- The telescope is designed to scan the entire sky rather than specific celestial objects.
- It will divide incoming light into multiple spectral bands for detailed cosmic analysis.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect because, unlike James Webb, which captures high-resolution images of specific regions, SPHEREx scans the entire sky to create a broad spectral map.
Statement 2 is correct since SPHEREx is designed to survey the whole sky rather than focusing on selected objects.
Statement 3 is correct as SPHEREx divides light into 96 spectral bands, enabling detailed analysis of cosmic phenomena.
What is AI Singularity?
Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have sparked growing concerns about its long-term impact on society. Visionaries like Elon Musk warn that AI could surpass human intelligence sooner than expected, with predictions placing the emergence of super intelligent AI as early as 2025. This phenomenon, often referred to as AI singularity, represents a pivotal moment where machines achieve self-improvement beyond human control, intensifying the global debate among scientists and technology leaders.
Understanding AI Singularity
- AI singularity refers to the hypothetical point when artificial intelligence exceeds human cognitive abilities and begins evolving autonomously.
- The concept was first introduced by mathematician John von Neumann, who speculated about a future where technological progress accelerates beyond human comprehension.
- Futurists like Ray Kurzweil estimate that this event may occur by 2045, but Elon Musk suggests it could happen much earlier.
Current AI Landscape
Despite rapid advancements, AI has not yet reached full autonomy. Modern machine learning models demonstrate self-improvement capabilities, yet the development of a truly super intelligent AI remains theoretical. Governments and technology firms are prioritizing responsible AI development, working to establish regulatory frameworks to manage its growth and mitigate risks.
Potential Risks and Ethical Concerns
- AI singularity raises serious ethical and existential concerns.
- In 2023, over 33,700 AI researchers signed an open letter, urging a temporary pause on AI models exceeding OpenAI’s GPT-4 due to potential dangers to society.
- Critics fear that uncontrolled AI could devalue human decision-making, disrupt economies, and pose existential threats. Concerns also include job displacement, security risks, and the possibility of AI-driven autonomous weapons.
Potential Benefits of AI Singularity
Despite fears, proponents argue that AI singularity could lead to unprecedented scientific breakthroughs. Superintelligent AI has the potential to revolutionize medicine, environmental sustainability, and space exploration by solving complex global challenges at a pace beyond human capability. Optimists believe AI could enhance human life rather than replace it.
Regulatory Efforts and Economic Growth
As AI technology advances, policymakers are actively working on legislative frameworks to ensure its ethical use. The AI market, currently valued at $100 billion, is projected to skyrocket to $2 trillion by 2030. The exponential growth of AI underscores the urgency for robust regulations that balance innovation with societal safety.
Public Perception and Future Outlook
Public discourse on AI singularity continues to intensify, with influential figures like Musk advocating for greater caution and preparedness. References to dystopian AI scenarios, such as a “Terminator-like” future, resonate with many, reinforcing the need for proactive measures to safeguard humanity. As AI progresses, the world must navigate its potential and perils with foresight and responsibility.
Consider the following statements regarding AI Singularity:
- AI singularity refers to the moment when artificial intelligence surpasses human intelligence and becomes self-improving beyond human control.
- The concept was first introduced by Alan Turing in his paper on the Turing Test.
- Ray Kurzweil predicts that AI singularity will occur before 2030.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation:
The concept of AI singularity was first introduced by John von Neumann, not Alan Turing. Ray Kurzweil estimates singularity to occur by 2045, not before 2030
Double Pneumonia
Pope Francis, the 88-year-old leader of the Roman Catholic Church, is currently hospitalized due to double pneumonia, a serious condition that has developed from a complex respiratory infection complicated by his pre-existing lung issues. Given his age and medical history, this situation is particularly concerning.
What Is Double Pneumonia?
- Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs typically caused by infections. Double pneumonia refers to a type of pneumonia that affects both lungs simultaneously.
- It can arise from various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
- This condition exacerbates the severity of symptoms and the risk of complications.
- Double pneumonia is commonly observed in individuals with weakened immune systems or chronic health issues.
Symptoms of Double Pneumonia
Key symptoms of double pneumonia include:
- High fever
- Persistent cough
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
Additionally, patients may exhibit confusion, particularly among the elderly.
In some cases, especially with severe immunodeficiency, individuals may not present a fever. Other possible symptoms include a rapid heart rate and muscle pain.
Causes and Risk Factors
Double pneumonia can result from multiple infectious agents, with common pathogens including Streptococcus pneumoniae and influenza viruses. Risk factors for developing this condition include:
- Impaired immune function
- Chronic lung diseases
- Exposure to environmental irritants
- Older adults and young children are particularly at risk.
- Prognosis and Complications
- With appropriate treatment, many patients can recover within weeks.
- However, if left untreated, double pneumonia can lead to severe complications such as respiratory failure and sepsis.
- The risk of mortality is notably higher among older adults and individuals with compromised immunity.
Global Impact of Pneumonia
- Pneumonia remains a leading cause of death globally, affecting millions each year, especially young children and the elderly.
- The World Health Organization estimates that pneumonia claims the lives of around 700,000 children under the age of five annually.
With reference to double pneumonia, consider the following statements:
- Double pneumonia refers to an inflammatory condition affecting both lungs simultaneously.
- It can only be caused by bacterial infections, particularly Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Individuals with compromised immune systems or chronic illnesses are at a higher risk of developing double pneumonia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Double pneumonia affects both lungs, making it more severe than unilateral pneumonia.
Statement 2 is incorrect: While Streptococcus pneumoniae is a common bacterial cause, viral and fungal pathogens (such as influenza viruses and fungi like Aspergillus) can also lead to double pneumonia.
Statement 3 is correct: Individuals with impaired immunity (elderly, those with chronic lung diseases, or immunosuppressive conditions) are at higher risk.
TraumaticAsphyxia Syllabus: GS2/ Health
Context
- Recently, five out of 18 victims of the stampede at New Delhi Railway Station succumbed to traumatic asphyxia, a life-threatening condition caused by severe chest compression.
About Traumatic Asphyxia
- Traumatic asphyxia is a rare but critical medical emergency that occurs when the upper chest or abdomen is subjected to intense external pressure, leading to restricted respiration and impaired blood circulation.
Causes
This condition is commonly observed in:
- Stampedes (as seen in crowded public spaces).
- Vehicular accidents involving crushing injuries.
- Building collapses and natural disasters.
- Industrial accidents with heavy machinery involvement.
Symptoms
Key clinical manifestations include:
- Cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin due to oxygen deprivation).
- Edema (swelling caused by fluid retention).
- Hemorrhages in the face, neck, upper limbs, and thorax due to increased venous pressure.
Treatment
- Immediate supportive care (oxygen therapy, intravenous fluid resuscitation).
- Management of associated injuries, such as fractures and internal trauma.
- Monitoring for complications, including respiratory distress and cardiac dysfunction.
- Timely medical intervention is crucial to improve survival outcomes in traumatic asphyxia cases.
Traumatic asphyxia, recently in the news due to the New Delhi Railway Station stampede, primarily results from:
a.Sudden exposure to toxic gases leading to respiratory failure
b.Compression of the upper chest or abdomen restricting respiration and circulation
c.Neurological dysfunction causing paralysis of respiratory muscles
d.Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) progression in high-altitude regions
Answer: (b) Compression of the upper chest or abdomen restricting respiration and circulation
Explanation: Traumatic asphyxia is caused by severe compressive force on the chest or abdomen, leading to restricted respiratory function and impaired venous return, commonly observed in stampedes, accidents, and building collapses. The other options relate to different medical conditions (toxic gas exposure, neurological disorders, and chronic diseases) that do not directly cause traumatic asphyxia.
Integrating AI in India’s Judiciary and Law Enforcement
Syllabus: GS2/Government Policies & Interventions; GS3/Science & Technology
Context
India is integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into judicial processes, case management, legal research, and law enforcement to streamline operations, reduce judicial delays, and enhance access to justice.
Current Challenges in India’s Legal and Law Enforcement System
- Despite its well-structured three-tier judiciary (Supreme Court, High Courts, and Subordinate Courts), India’s legal system faces several challenges:
- Judicial Backlogs: Over 5 crore pending cases (National Judicial Data Grid – NJDG).
- Delayed Adjudication: Lengthy legal proceedings due to procedural inefficiencies and excessive documentation.
- Manual Case Handling: Traditional paper-based documentation hampers judicial efficiency.
- Law Enforcement Bottlenecks: Rising cybercrimes, outdated policing methods, and resource constraints limit crime prevention and investigation.
Applications of AI in India’s Judiciary
- AI-Powered Legal Research & Case Management
- AI-driven tools like SUPACE (Supreme Court Portal for Assistance in Court Efficiency) help judges analyze large volumes of legal data.
- Enables faster research, precedent-based judgments, and structured case analysis.
- Predictive Justice & Case Prioritization
- Machine learning models can predict case outcomes based on past rulings.
Courts can use AI to:
- Prioritize urgent cases for speedy resolution.
- Estimate case duration for better planning.
- Identify patterns in case dismissals or approvals.
Virtual Courts & AI-Powered Online Dispute Resolution (ODR)
- E-Courts initiative enables virtual hearings and paperless court operations.
- AI-powered dispute resolution platforms settle minor legal conflicts without judicial intervention.
AI-Assisted Legal Translation
- AI-driven tools like SUVAS (Supreme Court Vidhik Anuvaad Software) assist in real-time legal translations between English and vernacular languages.
- Facilitates multilingual access to legal documents.
- AI in Law Enforcement and Crime Prevention
- AI-Powered Surveillance & Facial Recognition
- Crime and Criminal Tracking Network & Systems (CCTNS) integrates AI-based facial recognition for:
- Identifying suspects from CCTV footage.
- Tracking missing persons and habitual offenders.
- Enhancing public safety with real-time crowd monitoring.
- Predictive Policing & Crime Analytics
- AI algorithms analyze:
- Historical crime trends to detect crime hotspots.
- Behavioral patterns of repeat offenders.
- Social media and online data to track cybercriminals.
- AI in Forensic Investigations
- AI-driven forensic tools assist in:
- Deepfake detection and voice analysis in digital crimes.
- AI-assisted DNA & fingerprint matching for faster case resolution.
- Cybercrime tracking using AI-powered data forensics.
- AI Chatbots for Public Assistance
- AI-powered police chatbots help citizens:
- File FIRs online without visiting police stations.
- Track case progress in real time.
- Access legal guidance in simplified language.
Challenges in AI Adoption in Judiciary & Law Enforcement
- Ethical Concerns & Algorithmic Bias: AI models may inherit biases from historical judicial decisions, affecting fairness and impartiality.
- Data Privacy & Security Risks: AI-driven systems require access to vast legal and crime databases, raising concerns over data confidentiality.
- Infrastructure Gaps & Digital Divide: Many courts and police stations, especially in rural India, lack AI infrastructure and technical expertise.
- Legal & Regulatory Void: India currently lacks AI-specific laws to govern AI-driven judicial and policing mechanisms.
Government Initiatives for AI Integration
- Supreme Court AI Initiatives
- SUVAS: AI-powered legal translation for multilingual accessibility.
- SUPACE: AI-based legal research and case analysis tool for judicial efficiency.
- E-Courts (Phase III) Mission Mode Project
- ₹7210 crore allocation for AI-driven court automation and e-filing.
- ₹53.57 crore earmarked for AI and Blockchain adoption in High Courts.
- Crime and Criminal Tracking Network & Systems (CCTNS)
- AI-powered nationwide police database for cross-state criminal tracking.
- AI Task Force & NITI Aayog’s AI Strategy
- NITI Aayog’s AI roadmap focuses on AI adoption in judicial reforms and policing.
Way Forward: AI for a Smarter Justice System
Establish AI Ethics Guidelines: Ensure transparency and fairness in AI-driven legal decisions.
Strengthen AI Infrastructure: Invest in AI training for judges and law enforcement officers.
Enhance Public Awareness: Educate citizens on AI-based legal resources and rights.
Encourage AI Research in Law: Support academic and industry collaboration for AI-driven legal innovations.
Consider the following statements regarding AI-driven judicial reforms in India:
- SUPACE is an AI-powered tool developed by the Supreme Court of India to enhance judicial research and assist judges in case analysis.
- SUVAS, launched alongside SUPACE, is primarily used for predictive justice and case prioritization in lower courts.
- The E-Courts Phase III initiative has explicitly mandated the use of AI-driven legal research tools in all High Courts across India.
- CCTNS, while primarily used in law enforcement, also assists the judiciary by automating case citations and legal precedent analysis.
Which of the statements are correct?
1 and 3 only
3 and 4 only
1, 2, and 4 only
1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: A) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: SUPACE (Supreme Court Portal for Assistance in Court Efficiency) is an AI-based research tool designed to assist Supreme Court judges in case law analysis and judicial research.
Statement 2 is incorrect: SUVAS (Supreme Court Vidhik Anuvaad Software) is an AI-driven translation tool, not a case prioritization system.
Statement 3 is correct: The E-Courts Phase III initiative integrates AI-driven legal research tools in High Courts to improve case management.
Statement 4 is incorrect: CCTNS (Crime and Criminal Tracking Network & Systems) is a law enforcement database, but it does not automate case citations or legal precedent analysis for the judiciary.
India’s First indigenous Semiconductor Chip to be Ready by 2025
Syllabus: GS3/ S&T
In Context
Union Minister for Electronics and IT announced at the Global Investors Summit 2025 in Bhopal that India’s first indigenously developed semiconductor chip will be ready for production by 2025.
About Semiconductors
Semiconductors are materials that have conductivity between a conductor and an insulator. They are the foundation of modern electronics, used in:
- Computers and smartphones
- Automobiles and electric vehicles (EVs)
- Defense and aerospace technology
- Medical devices
- Telecommunication and AI applications
Importance
- India is one of the largest consumers of semiconductors but imports 100% of its requirements.
The launch of an indigenous semiconductor chip in 2025 will:
- Reduce import dependence (India imports $24 billion worth of semiconductors annually).
- Strengthen national security (used in defense and critical infrastructure).
- Boost Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat initiatives.
- Create high-skilled jobs in semiconductor design and manufacturing.
Initiatives to Develop the Semiconductor Industry
India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) (2021): A ₹76,000 crore incentive scheme aimed at:
- Setting up semiconductor fabrication units (fabs) in India.
- Encouraging global semiconductor firms to invest in India.
- Developing design-linked incentive (DLI) schemes to support local start-ups.
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Electronics Manufacturing.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing Ecosystem: Five semiconductor units under construction in India.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaboration under India-U.S. Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technology (iCET).
- Talks on setting up chip manufacturing units in India.
- Role in the QUAD Group: QUAD (India, US, Japan, Australia) is focusing on semiconductor supply chain resilience.
Challenges in India’s Semiconductor Sector
- Lack of Existing Semiconductor Fabs: No existing commercial fab in India yet (first expected in 2025).
- Dependence on Global Supply Chains: Taiwan, South Korea, and the U.S. dominate semiconductor manufacturing.
- High Capital and Technological Requirements: Semiconductor manufacturing requires precision, specialized labor, and high investment.
- Geopolitical Risks: US-China trade war & Taiwan tensions impact semiconductor availability.
Future Prospects and Way Forward
- Achieving Self-Sufficiency: The government must ensure faster implementation of semiconductor plants.
- Strengthening Infrastructure: Improve power supply, water availability, and logistics for fabs.
- Enhancing Skill Development: Establish semiconductor training institutes in partnership with global leaders.
- Reducing Import Dependence: Promote local semiconductor startups under the Design-Linked Incentive (DLI) scheme.
Which of the following statements regarding India’s semiconductor industry is correct?
- India is among the top three global producers of semiconductors.
- India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) aims to set up fabrication units in India.
- India currently imports 100% of its semiconductor requirements.
- The first indigenously developed semiconductor chip is expected by 2030.
a.1 and 2 only
b.2 and 3 only
c.1, 2, and 4 only
d.1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: B) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
India is not among the top three producers of semiconductors. ISM aims to set up semiconductor fabs in India, and India currently imports all its semiconductors. The first indigenous semiconductor chip is expected by 2025, not 2030.
Cancer Care Challenges in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) poses significant health challenges globally, especially in low and middle-income countries like India.
- In India, AML patients often face late-stage diagnoses and limited access to advanced treatments, leading to disparities in outcomes, particularly in rural regions. Addressing these issues is essential to improve survival rates.
Understanding Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Prevalence: AML is the most common type of leukemia among adults.
- Characteristics: It involves the rapid growth of abnormal blood cells, termed blasts, affecting the blood and bone marrow.
- Demographics in India: The median age of AML diagnosis in India is approximately 40 years, which is younger than in high-income countries. Many patients present at advanced stages, leading to poorer outcomes.
Challenges in AML Management
- Healthcare Infrastructure: Disorganized referral systems and inadequate diagnostic facilities cause delays in treatment initiation.
- Financial Constraints: A significant number of patients are unable to afford treatment. In a study, 29% of newly diagnosed AML patients opted for standard care, while 71% did not proceed, primarily due to financial limitations.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Patients from rural areas face additional challenges, including travel logistics and resource shortages in public hospitals. Private healthcare facilities are often financially inaccessible.
Government Initiatives and Proposed Solutions
Ayushman Bharat Scheme: This initiative aims to enhance access to cancer care. However, gaps remain, particularly in covering initial diagnostics.
Policy Recommendations:
- Tax Exemptions: Industry leaders have advocated for removing taxes on cancer and rare disease medications to reduce treatment costs.
- com
- Infrastructure Development: Strengthening healthcare infrastructure, standardizing treatment protocols, and improving access to novel therapies are crucial steps.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborations can enhance resource availability and make treatments more affordable.
What policy change has been suggested to make cancer treatment more affordable in India?
a.Increasing taxes on cancer medications
b.Removing taxes on cancer and rare disease drugs
c.Reducing import duties on luxury goods
d.Centralizing all cancer treatments in urban centers
Answer: b) Removing taxes on cancer and rare disease drugs
Explanation: Industry leaders have urged the Indian government to eliminate taxes on cancer and rare disease medications to reduce treatment costs and improve affordability.
Indian Ocean: Strategic Significance & India’s Role
The Indian Ocean Region (IOR) faces significant geopolitical competition and security challenges, prompting India to advocate for multilateral maritime collaboration, such as a “coordinated flotilla,” as highlighted by External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar.
Overview of the Indian Ocean: The third-largest ocean, spanning approximately 9,600 km from the Bay of Bengal to Antarctica and 7,800 km from South Africa to Western Australia. It boasts a 70,000 km coastline encompassing major economies.
Demographics: Home to 35% of the world’s population and 40% of the global coastline.
Historical Significance: Named after India, reflecting its historical influence on maritime trade. Served as a crucial trade route since the first millennium, connecting India with the Arab world, Southeast Asia, and Africa. The Silk Route and spice trade flourished through the Indian Ocean, linking Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Strategic Importance:
- A vital global trade route, facilitating 70% of the world’s container traffic.
- 80% of India’s external trade and 90% of its energy imports transit through the Indian Ocean.
- Critical oil supply routes from West Asia to India, China, Japan, and Europe pass through the region.
- India’s central position grants strategic control over key maritime chokepoints:
- Strait of Hormuz (Iran-Oman), vital for oil shipments.
- Bab el-Mandeb (Yemen-Djibouti), the gateway to the Red Sea & Suez Canal.
- Strait of Malacca (Indonesia-Malaysia), a key trade passage for East Asia.
Challenges in the Indian Ocean Region:
- Maritime Security Threats: Frequent pirate attacks and trafficking, particularly near Somalia and the Gulf of Aden.
- Economic & Environmental Issues: Overfishing and deep-sea mining threaten marine ecosystems.
- Climate Change & Rising Sea Levels: Small island nations face coastal erosion and the risk of submersion.
- Humanitarian Crises & Disasters: Natural disasters such as cyclones, tsunamis, and oil spills necessitate coordinated disaster response.
- Geopolitical Rivalries: Growing influence of the U.S., China, UK, and France fuels power struggles in the region.
India’s Policy Shift in the Indian Ocean:
Strengthening Regional Ties: India actively engages with IOR nations through:
- Indian Ocean Conference (IOC).
- Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
- Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS).
- Colombo Security Conclave.
SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region):
Launched in 2015 under PM Modi, aiming to:
- Strengthen India’s leadership in the IOR.
- Ensure free and open sea lanes for secure global trade.
- Promote sustainable maritime development.
Enhancing Blue-Water Capabilities:
- Naval Expansion: Modernizing the navy with indigenous aircraft carriers and advanced submarines.
- Maritime Surveillance: Deployment of P-8I Poseidon aircraft and satellite-based tracking systems.
- Quad Cooperation: Collaboration with the U.S., Japan, and Australia on maritime security, anti-submarine warfare, and intelligence sharing.
Which of the following statements BEST describes the strategic significance of the Indian Ocean Region (IOR)?
- It is the largest ocean, covering the majority of the Earth’s surface.
- It is primarily a fishing ground, with limited impact on global trade and geopolitics.
- It is a crucial global trade route, controlling key maritime chokepoints, and vital for energy supplies, influencing trade and geopolitics.
- It is strategically important only for India due to its geographical proximity.
Correct Answer: c. It is a crucial global trade route, controlling key maritime chokepoints, and vital for energy supplies, influencing trade and geopolitics.
Exercise Komodo
The Indian Navy is actively participating in Exercise Komodo 2025, a non-combat military exercise aimed at fostering maritime cooperation among friendly nations. The exercise is being hosted by the Indonesian Navy in Bali, Indonesia, and has been underway since 2014.
Exercise Komodo: A Platform for Maritime Cooperation
- Exercise Komodo is a multilateral naval exercise that brings together naval forces from various countries to promote maritime cooperation, enhance interoperability, and strengthen partnerships in the Indo-Pacific region.
- This aligns with India’s SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) vision, which emphasizes the importance of maritime security and stability in the region.
Participation by INS Shardul and P8I Long Range Maritime Surveillance Aircraft
- The Indian Navy is participating in Exercise Komodo 2025 with INS Shardul and P8I Long Range Maritime Surveillance aircraft.
- This demonstrates India’s commitment to strengthening maritime partnerships and enhancing regional security through collaborative efforts.
Objectives of Exercise Komodo
The primary objectives of Exercise Komodo include: Fostering maritime cooperation among friendly nations
- Enhancing interoperability with ASEAN Navies and QUAD partners
- Promoting regional security and stability through collaborative efforts
By participating in Exercise Komodo, the Indian Navy is contributing to the security and stability of the Indo-Pacific region, while also strengthening its relationships with friendly nations.
Which of the following is the primary objective of Exercise Komodo?
- Fostering economic cooperation among nations
- Enhancing regional security and stability through collaborative efforts
- Promoting tourism and cultural exchange among nations
- Enhancing space exploration and research efforts
Answer: b) Enhancing regional security and stability through collaborative efforts
Early Warnings for All (EW4All) Initiative
The United Nations launched the Early Warnings for All (EW4All) initiative in 2022 with the goal of implementing effective early warning systems (EWS) by the end of 2027. The initiative aims to protect vulnerable populations from hazardous weather and climate events
Funding Landscape for Early Warning Systems:
- Increased Funding: Funding for early warning systems reached unprecedented levels in 2023.
- Uneven Distribution: Investment is not evenly distributed. Five countries (China, Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Indonesia) account for 54% of national EWS investments.
- Funding Gaps: Small Island Developing States (SIDS) and Least Developed Countries (LDCs) face funding gaps.
- Global Observatory: The Global Observatory for Early Warning System Investments, launched in December 2024, tracks and optimizes these investments.
Financial Imbalance in EWS Investments:
- Loan Dependency: Only 25% of reported EWS financing comes from grants, with the remaining 75% sourced from loans and credits.
- This financial imbalance poses challenges for sustainability.
Project Overview and Global Reach:
- Project Coverage: As of February 2025, the observatory documented 329 projects across 127 countries in Africa, Asia, the Americas, and Oceania.
- Project Status: 276 projects are ongoing, with 53 in the pipeline.
- Major Financiers: The World Bank and the Green Climate Fund are among the major financing institutions involved.
- Prioritization: The initiative seeks to prioritize resources for the most vulnerable communities.
Collaboration and Technological Integration:
- International Collaboration: The observatory will deepen collaboration with international finance institutions.
- AI Integration: It will leverage artificial intelligence to improve analytical capabilities.
- Evidence-Based Decision-Making: This integration aims to categorize EWS funding more precisely and support evidence-based decision-making.
Global Status of Multi-Hazard Early Warning Systems:
- MHEWS Coverage: A 2024 report on Multi-Hazard Early Warning Systems (MHEWS) found that half of the countries in most regions have established MHEWS.
- Regional Variance: The Asia and Pacific region leads with 67% coverage, while the Americas and Caribbean lag behind at 40%.
Urgency of Addressing Funding Gaps:
- Critical Deadline: As the 2027 target approaches, addressing funding gaps is crucial for the success of EW4All.
- Equitable Access: Equitable access to financial resources is vital to ensure EWS reach those in need.Mitigation of Impacts: This is vital to mitigate the impacts of climate change and save lives.
Which of the following statements best describes the primary challenge facing the Early Warnings for All (EW4All) initiative as the 2027 deadline approaches?
- The lack of technological advancements in early warning systems.
- The uneven distribution of funding, with a significant reliance on loans and credits, particularly impacting vulnerable nations.
- The absence of international collaboration among financial institutions.
- The lack of projects implemented across different regions.
Answer: (B) The uneven distribution of funding, with a significant reliance on loans and credits, particularly impacting vulnerable nations.
Explanation:
The text highlights the following key issues:
- Uneven Funding: The text emphasizes the uneven distribution of EWS funding, with a few countries receiving the majority.
- Loan Dependency: The high percentage of funding coming from loans/credits is presented as a challenge.
- Impact on Vulnerable Nations: The funding gaps faced by SIDS and LDCs are explicitly mentioned, stressing the impact on those most at risk.
- 2027 Deadline: The “Urgency of Addressing Funding Gaps” section clearly states that addressing these funding issues is crucial for the initiative’s success as the 2027 target date approaches.
Concerns Related To China’s Dam Project
A Massive Hydropower Dam: China plans to build a 60 GW hydropower dam on the Brahmaputra River (Yarlung Tsangpo) in Tibet. This project is the central focus of the news.
Scale and Context:
- Capacity: 60 GW, three times the capacity of the Three Gorges Dam.
- Location: Great Bend of the Brahmaputra in Medog County,Tibetan Autonomous Region.
- China’s Goal: Reduce reliance on fossil fuels and achieve carbon neutrality by 2060.
- Previous Projects: China has experience with large dam projects, including the Three
- Gorges Dam and Zangmu Dam.
- The River: Yarlung Tsangpo/Brahmaputra.
- Origin:
- Flows Through: Arunachal Pradesh (India, as Siang), Assam (India, as Brahmaputra), Bangladesh.
- Basin: Extends to Bhutan (96% of its area).
- Implications of the Mega-Dam Project: Environmental and Ecological Concerns:
- Altered Water Flow and Sediment Reduction: Dams trap sediment, reducing soil fertility for downstream agriculture in India and Bangladesh.
- Increased Risk of Flash Floods: Sudden water releases could cause devastating floods. The article emphasizes past incidents.
- Biodiversity Loss and Habitat Destruction: Threat to aquatic species, including the Gangetic dolphin.
- Glacial Melt and Climate Change Effects: The Tibetan Plateau is a critical region for the Earth’s cryosphere and global climate, and this project can influence climate patterns.
- Seismic Risks: The dam’s location in a seismically active region raises concerns about earthquakes, landslides, and environmental degradation.
- Implications of the Mega-Dam Project: Geopolitical Ramifications:
- India’s Vulnerability: India fears China could use its control over the river for strategic purposes, controlling water flow.
Legal and Diplomatic Challenges:
- China is not a signatory to the UN Convention on the Law of the Non-navigational Uses of International Watercourses.
- The India-China Expert Level Mechanism (ELM) exists for data sharing but lacks a comprehensive treaty.
- Conflict with Southeast Asian Nations: Similar concerns exist regarding the Mekong River (shared with several countries in the region).
- Economic and Social Impact: Forced relocation of communities and disruption to irrigation and fishing, threatening food security.
India’s Response and Possible Strategies:
- Developing its Own Water Infrastructure: Building dams and hydropower projects in Arunachal Pradesh (e.g., Siang Upper Multipurpose Project).
- Strengthening Diplomacy: Engaging with Bangladesh and other regional stakeholders for a united front on water management.
- Enhancing Satellite Monitoring and Early Warning Systems: Improving surveillance and flood prediction.
Exploring Legal Avenues: Seeking regional agreements or international arbitration.
- In conclusion, the article highlights the significant concerns surrounding China’s ambitious hydropower project on the Brahmaputra River.
- These concerns span environmental, ecological, geopolitical, and economic realms, primarily impacting India and Bangladesh.
What is a significant risk associated with the dam’s location in a seismically active region?
- Earthquakes and landslides
- Floods and droughts
- Tsunamis and storms
- Volcanic eruptions and wildfires
Correct Answer: a) Earthquakes and landslides
Global Corruption Index
Introduction
The index, which ranks 180 countries by their perceived levels of public sector corruption uses a scale of zero to 100, where “zero” is highly corrupt and “100” is very clean.
Overall Results:
- Denmark ranks as the least corrupt country globally.
- South Sudan ranks as the most corrupt country with a score of only 8 points.
- The CPI ranks 180 countries and territories based on perceived public sector corruption, using a scale from 0 (highly corrupt) to 100 (very clean).
India’s Ranking:
- India is ranked 96th, dropping three positions from 93rd in the previous year.
- India’s CPI score decreased from 39 in 2023 to 38 in 2024.
Neighboring Countries’ Rankings:
- Pakistan: 135th position.
- Sri Lanka: 121st position.
- Bangladesh: 149th position.
- China: 76th position.
Trends in Global Rankings:
- Major global powers like the United States and France saw declines in their CPI scores.
- The U.S. score dropped from 69 to 65, ranking 28th, down from 24th.
- France slipped four points to 67, now at 25th.
- Russia’s score further declined, reflecting ongoing authoritarianism post-invasion of Ukraine.
Corruption’s Broader Impacts:
- The report emphasizes the interplay between corruption and climate change efforts.
- Corruption leads to the mismanagement of climate funds and hinders effective policy-making.
- Reports indicate that high levels of corruption deter environmental progress and exacerbate global heating consequences.
Global Corruption Landscape:
- A total of 148 countries have either stagnated or worsened in their corruption levels since 2012.
- Corruption is framed as a significant barrier to democracy, stability, and human rights protections globally.
Call to Action:
- The report urges the international community to prioritize combating corruption.
- It emphasizes the need for concrete actions to address corruption to ensure sustainable development and democratic resilience
Why is combating corruption emphasized in the report?
- To promote economic growth
- To address climate change
- To ensure sustainable development and democratic resilience
- To reduce poverty
Answer: c) To ensure sustainable development and democratic resilience
India-France Relations:
The visit of the Prime Minister of India to France in February 2025 marked a pivotal moment in bilateral relations, resulting in significant agreements in nuclear energy, defense, artificial intelligence (AI), and Indo-Pacific cooperation. This visit underscored the deepening strategic partnership between the two nations.
Key Outcomes from the Recent Summit
Nuclear Energy Cooperation:
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) and Advanced Modular Reactors (AMRs): India and France signed a letter of intent to collaboratively design, develop, and produce SMRs and AMRs, utilizing India’s industrial capabilities alongside France’s technological expertise.
- Jaitapur Nuclear Project: The countries reviewed progress on the long-standing Jaitapur project, highlighting its importance for India’s transition to clean energy.
Defense Collaboration:
- Submarines and Missiles: The nations continue to work together on the Scorpene submarine project, focusing on indigenization and the integration of air-independent propulsion (AIP) systems developed by the DRDO.
- Helicopter and Jet Engine Production: There were discussions on joint manufacturing of engines for helicopters and fighter jets.
- Pinaka Multi-Barrel Rocket Launcher: France expressed interest in acquiring India’s Pinaka MBRL system, further strengthening defense ties.
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- India-France AI Roadmap: The two countries committed to developing a safe, secure, and trustworthy AI framework that aligns with their shared values.
- AI Action Summit: India proposed to host the next AI summit, with 2026 designated as the India-France Year of Innovation.
Indo-Pacific Cooperation:
- Triangular Development Initiatives: Joint projects in third-party countries will focus on climate change and sustainable development goals (SDGs) in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Eurodrone MALE Programme: India’s inclusion as an observer in the European drone program represents a significant step in defense collaboration.
Economic and Cultural Ties:
- Startup Collaboration: Ten Indian startups have been included in France’s Station F incubator program.
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI) in France: India’s real-time payment system will be expanded in France.
- Cultural Exchange: The Young Professional Scheme was operationalized to enhance legal mobility for students and professionals.
Advantages of Strengthening Bilateral Ties
- Strategic Depth: Enhanced cooperation in defense, nuclear energy, and AI reinforces the strategic partnership.
- Economic Growth: Collaborative projects in third countries and startup initiatives can create new economic opportunities.
- Technological Advancements: Joint efforts in AI and nuclear technology position both nations as leaders in innovation.
- Global Influence: Cooperation in the Indo-Pacific strengthens their roles as vital stakeholders in ensuring regional stability and development.
Limitations and Challenges
- Implementation Delays: Historical delays in projects like Jaitapur raise concerns regarding timely execution.
- Technological Barriers: Co-developing advanced technology such as SMRs and AI requires substantial expertise and investment.
- Geopolitical Risks: Differences in perspectives on global matters, particularly China’s role in the Indo-Pacific, could challenge cooperation.
- Bureaucratic Hurdles: Complex regulatory frameworks in both countries may impede progress on joint initiatives..
Conclusion:
- The India-France strategic partnership has reached unprecedented heights, with meaningful agreements in key areas such as nuclear energy, defense, and AI.
- While challenges persist, a dedicated approach to implementation and cooperation can further enhance this relationship, offering benefits to both nations and contributing to global stability
Which of the following is a potential challenge to the India-France strategic partnership?
- Lack of skilled workforce
- Differing perspectives on global issues, such as China’s role in the Indo-Pacific
- Overlapping economic interests
- Limited technological expertise
Correct Answer: (b) Differing perspectives on global issues, such as China’s role in the Indo-Pacific
India-UK Defence Collaboration
Introduction: India and the United Kingdom have signed multiple agreements aimed at enhancing bilateral defence collaboration.
Key Agreements and Collaborations in India-UK Defence Partnership
Defence Partnership–India (DP-I): The UK’s Ministry of Defence has established a dedicated programme office aimed at serving as a centralized hub for bilateral defence collaboration, promoting deeper cooperation and fostering economic growth in both nations.
Laser Beam Riding MANPADs (LBRM): India and the UK have entered into a contract for the procurement of Laser Beam Riding Man Portable Air Defence Systems (MANPADS). The initial delivery of High Velocity Missiles (STARStreak) and associated launchers is scheduled for this year.
Lightweight Multirole Missiles (LMM): This initiative seeks to integrate Indian and British industries into the global defence supply chain, enhancing collaborative efforts in missile technology.
Advanced Short-Range Air-to-Air Missile (ASRAAM): A partnership has been established to create an assembly and testing facility for the ASRAAM missile in Hyderabad, promoting local manufacturing capabilities.
Integrated Full Electric Propulsion (IFEP) System: A Statement of Intent was signed to design and develop an Integrated Full Electric Propulsion (IFEP) system for India’s forthcoming Landing Platform Dock (LPD) fleet. Both nations are also aiming to create India’s inaugural maritime Land-Based Testing Facility, with objectives to deploy the LPD by 2030.
Key Challenges
India-UK defence cooperation has faced obstacles due to the ‘three-I’ challenge, which includes:
- Foreign Investment regulations
- Intellectual Property Rights concerns
- Indigenous Content Requirements
The agreements signify a crucial advancement in India-UK defence collaboration, particularly in essential domains like air defence and maritime propulsion. They align with India’s Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) initiative, emphasizing the enhancement of indigenous defense capabilities and technological progress.
: Which of the following factors has posed a challenge to India-UK defense cooperation?
- Currency Exchange Rates
- The ‘three-I’ challenge: Foreign Investment, Intellectual Property Rights, and Indigenous Content Requirements
- Language Barriers
- Geographical Distance
Answer: B) The ‘three-I’ challenge: Foreign Investment, Intellectual Property Rights, and Indigenous Content Requirements
OPEC+ Latest News
- Brazil’s Entry into OPEC+
- Recently, the Brazilian government approved the country’s admission into OPEC+, the alliance of major oil-exporting nations.
About OPEC+ :
- OPEC+ is a coalition of 22 oil-exporting countries that convenes regularly to determine the volume of crude oil to market globally. The primary objective of these nations is to collaboratively manage crude oil production to ensure stability in the oil market.
Origin of OPEC+
The formation of OPEC+ was formalized towards the end of 2016, establishing a framework for sustained cooperation between OPEC and non-OPEC oil-producing countries. This collaboration focuses on regular and systematic coordination in oil production.
Membership of OPEC+
At the core of OPEC+ are the 12 members of OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries), which primarily consist of Middle Eastern and African nations. In addition to the OPEC members, OPEC+ includes Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Russia, Mexico, Malaysia, South Sudan, Sudan, and Oman.
What is OPEC?
- OPEC is a permanent intergovernmental organization of oil-exporting nations, founded in 1960 by five founding members: Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela.
- Currently, OPEC comprises 12 member countries, including Algeria, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Libya, Nigeria, and the United Arab Emirates.
- It is important to note that Angola will withdraw its membership effective January 1, 2024.
- Headquarters: OPEC is headquartered in Vienna, Austria.
With reference to OPEC+, consider the following statements:
- OPEC+ was established in 2016 as a formal organization with a permanent secretariat.
- All OPEC+ members are also members of OPEC.
- The primary goal of OPEC+ is to regulate oil prices through coordinated production adjustments.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- A) 1 and 2 only
- B) 3 only
- C) 1 and 3 only
- D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B) 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: While OPEC+ was formed in 2016, it is not a formal organization with a permanent secretariat. It is an informal alliance between OPEC and non-OPEC oil-producing nations.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: OPEC+ includes both OPEC and non-OPEC members. Countries like Russia, Kazakhstan, and Mexico are part of OPEC+ but not OPEC.
- Statement 3 is correct: The main objective of OPEC+ is oil price stability by adjusting production levels. This helps avoid sharp price fluctuations in the global oil market.
India’s ‘Look East’ Policy Has Transformed Into ‘Act East’
Look East Policy (1992):
Initiated under Prime Minister P.V. Narasimha Rao, this policy aimed to reinvigorate India’s neglected ties with Southeast Asia post-Cold War.
Key Features:
- Initially limited to ASEAN engagement, later expanded to East Asia and Oceania.
- Focus on economic integration, strategic collaboration, and cultural diplomacy.
- Led to reductions in trade barriers and increased inbound tourism from the region.
- Transition to Act East Policy (Post-2014)
Background:
- Global geopolitical shifts, including U.S. Secretary of State Hillary Clinton’s 2011 push for India’s active engagement in the Asia-Pacific, shaped this transition.
- In 2014, External Affairs Minister Sushma Swaraj formally introduced the Act East Policy, with PM Narendra Modi reinforcing it at the East Asia Summit.
Key Features:
- Shift from diplomatic engagement to actionable outcomes.
- Expanded focus from Southeast Asia to the Indo-Pacific.
- North-East India designated as a strategic link between India and ASEAN.
- 3Cs Framework (2014): Commerce, Culture, and Connectivity.
- Key Objectives and Achievements
- Strategic and Defense Cooperation
- Deepened defense engagements, including:
- Sale of BrahMos missiles to the Philippines.
- Military logistics pact with Vietnam.
Strengthened regional groupings such as BIMSTEC, Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), and Asia Cooperation Dialogue.
Economic Engagement
- Enhanced economic integration with ASEAN through Free Trade Agreements (FTAs).
- Encouraged ASEAN participation in the International Solar Alliance (ISA).
- Elevated bilateral relations to strategic partnerships with Indonesia, Vietnam, Malaysia, Japan, South Korea, Australia, and Singapore.
Cultural and Soft Power Diplomacy
- Reinforced civilizational ties through the Ramayana Festival and Buddhist heritage initiatives.
- Promoted Buddhist and Hindu linkages for people-to-people exchanges.
- India’s narrative faces competition from China’s claim over Buddhist heritage.
- Connectivity and Infrastructure Development
- Strengthening North-East India’s role as a gateway to ASEAN through:
- India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway.
- Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project.
- Rhi-Tiddim Road and Border Haats to enhance trade ties.
- Challenges and Roadblocks
- Strategic and Economic Challenges
- China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) presents a formidable economic alternative to India’s connectivity projects.
- BCIM-EC (Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor) poses strategic and infrastructural competition.
- Myanmar’s political instability complicates India’s strategic outreach.
- North-East India remains under-integrated into major infrastructure initiatives like Bharatmala and Sagarmala.
Cultural and Soft Power Challenges
- Limited linguistic engagement with Southeast Asia, with scarce educational programs in Khmer, Bahasa Indonesia, Thai, or Burmese.
- China’s Buddhist diplomacy challenges India’s historical narrative and soft power projection.
- Connectivity Challenges
- Project Delays: Slow implementation of key initiatives like the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project.
- Underdeveloped trade facilities in the North-East hinder regional integration.
- Way Forward: Towards a More Effective Act East Policy
- Bolstering Infrastructure: Accelerate completion of connectivity projects.
- Deepening Regional Integration: Fully integrate the North-East into ASEAN’s economic and infrastructure frameworks.
- Climate Diplomacy & Security Engagement: Expand regional disaster management and maritime domain awareness.
- Enhancing Strategic Partnerships: Actively engage with middle powers in the Indo-Pacific to counterbalance China’s influence.
Consider the following statements regarding the evolution of India’s Act East Policy:
- The Look East Policy (1992) was initiated to counterbalance the influence of China in ASEAN and was primarily focused on military alliances.
- The Act East Policy expanded India’s engagement beyond ASEAN to include Japan, Australia, and the Indo-Pacific region.
- The 3Cs approach (Commerce, Culture, and Connectivity) was introduced during the 2014 East Asia Summit to enhance economic and cultural linkages.
- The Act East Policy was launched in response to a recommendation from the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QUAD).
Which of the statements are correct?
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, and 4 only
- 1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: A) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The Look East Policy was not primarily military-focused but was aimed at economic, cultural, and strategic engagement with Southeast Asia.
- Statement 2 is correct: The Act East Policy expanded India’s focus beyond ASEAN to Japan, Australia, and the Indo-Pacific.
- Statement 3 is correct: The 3Cs (Commerce, Culture, Connectivity) framework was introduced at the 2014 East Asia Summit.
Statement 4 is incorrect: The Act East Policy was not a result of QUAD, but a natural evolution of Look East Policy due to regional geopolitical shifts
Ex INS Guldar Transformed Into Underwater Museum
The Indian Ocean Region (IOR) faces significant geopolitical competition and security challenges, prompting India to advocate for multilateral maritime collaboration, such as a “coordinated flotilla,” as highlighted by External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar.
Overview of the Indian Ocean: The third-largest ocean, spanning approximately 9,600 km from the Bay of Bengal to Antarctica and 7,800 km from South Africa to Western Australia. It boasts a 70,000 km coastline encompassing major economies.
Demographics: Home to 35% of the world’s population and 40% of the global coastline.
Historical Significance: Named after India, reflecting its historical influence on maritime trade. Served as a crucial trade route since the first millennium, connecting India with the Arab world, Southeast Asia, and Africa. The Silk Route and spice trade flourished through the Indian Ocean, linking Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Strategic Importance:
- A vital global trade route, facilitating 70% of the world’s container traffic.
- 80% of India’s external trade and 90% of its energy imports transit through the Indian Ocean.
- Critical oil supply routes from West Asia to India, China, Japan, and Europe pass through the region.
- India’s central position grants strategic control over key maritime chokepoints:
- Strait of Hormuz (Iran-Oman), vital for oil shipments.
- Bab el-Mandeb (Yemen-Djibouti), the gateway to the Red Sea & Suez Canal.
- Strait of Malacca (Indonesia-Malaysia), a key trade passage for East Asia.
Challenges in the Indian Ocean Region:
- Maritime Security Threats: Frequent pirate attacks and trafficking, particularly near Somalia and the Gulf of Aden.
- Economic & Environmental Issues: Overfishing and deep-sea mining threaten marine ecosystems.
- Climate Change & Rising Sea Levels: Small island nations face coastal erosion and the risk of submersion.
- Humanitarian Crises & Disasters: Natural disasters such as cyclones, tsunamis, and oil spills necessitate coordinated disaster response.
- Geopolitical Rivalries: Growing influence of the U.S., China, UK, and France fuels power struggles in the region.
India’s Policy Shift in the Indian Ocean:
Strengthening Regional Ties: India actively engages with IOR nations through:
- Indian Ocean Conference (IOC).
- Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
- Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS).
- Colombo Security Conclave.
SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region):
Launched in 2015 under PM Modi, aiming to:
- Strengthen India’s leadership in the IOR.
- Ensure free and open sea lanes for secure global trade.
- Promote sustainable maritime development.
Enhancing Blue-Water Capabilities:
- Naval Expansion: Modernizing the navy with indigenous aircraft carriers and advanced submarines.
- Maritime Surveillance: Deployment of P-8I Poseidon aircraft and satellite-based tracking systems.
- Quad Cooperation: Collaboration with the U.S., Japan, and Australia on maritime security, anti-submarine warfare, and intelligence sharing.
Consider the following statements regarding Ex INS Guldar:
- It was commissioned into the Indian Navy in 1995 and served in the Western Naval Command.
- The vessel participated in operations like Op Aman and Op Pawan.
- The ship was decommissioned in 2024 and later transferred to the Maharashtra Tourism Development Corporation Limited (MTDC).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect – Ex INS Guldar was commissioned in 1985, not 1995, and it primarily served in the Eastern Naval Command before moving to the Andaman and Nicobar Command.
- Statement 2 is correct – The vessel took part in notable operations like Op Aman and Op Pawan.
- Statement 3 is correct – It was decommissioned in 2024 and later transferred to MTDC for conversion into an underwater museum.
Navika Sagar Parikrama II
On February 18, 2025, the Indian Naval Sailing Vessel (INSV) Tarini successfully entered Port Stanley, marking the completion of the third and most challenging phase of the Navika Sagar Parikrama II initiative.
About Navika Sagar Parikrama II
- The Navika Sagar Parikrama initiative highlights the Indian Navy’s commitment to promoting gender empowerment and maritime excellence.
- This expedition is crewed by two remarkable women officers, Lieutenant Commander Dilna K and Lieutenant Commander Roopa A, who aim to advance ocean sailing, self-reliance, and celebrate India’s rich maritime heritage.
- The historic voyage was inaugurated from Goa on October 2, 2024, by the Chief of the Naval Staff. Navika Sagar Parikrama II will cover over 21,600 nautical miles (approximately 40,000 kilometers) and consists of five legs, with scheduled stopovers at four ports for necessary replenishment and maintenance.
The broad outline of the voyage is as follows:
- Goa to Fremantle, Australia
- Fremantle to Lyttleton, New Zealand
- Lyttleton to Port Stanley, Falkland Islands
- Port Stanley to Cape Town, South Africa
- Cape Town back to Goa
About INSV Tarini
- The INSV Tarini is a 56-foot sailing vessel built by Aquarius Shipyard Ltd, officially inducted into the Indian Navy on February 18, 2017.
- Since its induction, the vessel has traversed over 66,000 nautical miles (122,223 kilometers) and participated in the first edition of Navika Sagar Parikrama in 2017.
- The boat is equipped with advanced navigation, safety, and communication systems, ensuring a safe and effective journey across the oceans.
- With the successful arrival at Port Stanley, the mission continues to exemplify the spirit of adventure and determination inherent in the Indian Navy’s efforts to uplift women’s roles in maritime activities
What is the primary objective of the Navika Sagar Parikrama II expedition?
- a) To conduct scientific research in the Indian Ocean
- b) To promote gender empowerment and showcase India’s maritime heritage
- c) To establish India’s dominance in maritime trade routes
- d) To set a world record for the longest sailing voyage
Answer: b) To promote gender empowerment and showcase India’s maritime heritage
Explanation: The Navika Sagar Parikrama initiative underscores the Indian Navy’s commitment to gender empowerment and maritime excellence while promoting ocean sailing and India’s rich maritime heritage.
Exercise DHARMA GUARDIAN
Context: The 6th edition of the India-Japan Joint Military Exercise DHARMA GUARDIAN has commenced at the East Fuji Manoeuvre Training Area, Japan.
About the Exercise
- Initiated in 2018, it is a bilateral military exercise held annually on a rotational basis between India and Japan.
- The 5th edition was conducted in Rajasthan, India (2024).
Objectives:
- Enhance interoperability between the Indian Army and Japan Ground Self-Defense Force (JGSDF).
- Focus on joint urban warfare and counter-terrorism operations under a United Nations (UN) mandate.
Strategic Significance:
- Reinforces India-Japan defense cooperation and military-to-military engagement.
- Strengthens the Free, Open, and Inclusive Indo-Pacific strategy.
- Aligns with the wider regional security architecture to ensure peace and stability in the Indo-Pacific.
Consider the following statements regarding the DHARMA GUARDIAN military exercise:
- It is a tri-service military exercise between India and Japan.
- The first edition of DHARMA GUARDIAN was held in 2018.
- The exercise focuses on joint military operations under a UN mandate.
- The latest edition (2024) was held in Rajasthan, India.
Which of the statements are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, and 4 only
- 1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: B) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: DHARMA GUARDIAN is an Army-to-Army exercise, not a tri-service exercise.
- Statement 2 is correct: The exercise was initiated in 2018 and has been conducted annually.
- Statement 3 is correct: The primary focus of the exercise is joint urban warfare and counter-terrorism under a UN mandate.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: The 6th edition (2024) is being held in Japan, while the 5th edition was conducted in Rajasthan, India.
India-U.S. Partnership on Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA) Technologies
The India-U.S. partnership on Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA) technologies, solidified during PM Modi’s recent visit to the US with the launch of the Autonomous Systems Industry Alliance (ASIA), represents a significant advancement in maritime security cooperation. This collaboration is particularly noteworthy as India is the only country with whom the U.S. defense industry is partnering on such sensitive technologies.
Understanding Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA):
UDA encompasses the ability of a nation or organization to monitor, detect, and assess activities occurring beneath the surface of oceans and seas. It is vital for:
- Maritime Security
- Resource Management
- Environmental Protection
- Disaster Response
Significance of the India-U.S. UDA Cooperation:
Geopolitical and Strategic Importance:
- Strengthening Maritime Domain Awareness (MDA) and, critically, UDA is essential for India’s national security.
- Addresses China’s increasing naval presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Enhances submarine detection and tracking capabilities.
- Supports increased cooperation within the Quad (India, U.S., Australia, Japan) to counter shared threats.
Defense Technology Collaboration:
The U.S. is providing cutting-edge underwater surveillance and anti-submarine warfare (ASW) technologies, including:
- Sea Picket: An autonomous sonar surveillance system by Thayer Mahan.
- Wave Glider: An Unmanned Surface Vehicle (USV) by Boeing’s Liquid Robotics, with plans for co-production with Sagar Defence Engineering (60 units).
- Low-Frequency Active Towed Sonar: Discussions between L3 Harris and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) are ongoing.
Impact on India’s Defense Capabilities:
Significantly strengthens India’s anti-submarine warfare (ASW) capabilities, complementing existing assets:
- 12 P-8I Poseidon Maritime Patrol Aircraft
- 24 MH-60R Multi-Role Helicopters (being inducted)
- 15 MQ-9B Sea Guardian UAVs (part of a 31-unit contract, deliveries from 2029).
Technology Transfer, “Make-in-India,” and Economic Benefits:
- First-of-its-kind co-production and technology transfer in sensitive underwater systems.
- Strengthens India’s defense manufacturing ecosystem under the “Make in India” & “Atmanirbhar Bharat” initiatives.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Technology Transfer and Data Security: Concerns regarding the secure sharing of sensitive UDA data and maintaining sovereign control over surveillance systems.
- Financial and Operational Challenges: The high cost associated with procurement, deployment, and maintenance of advanced underwater systems.
- Technology Dependence: Reliance on high-end research and funding for advanced sonar and AI systems.
- Legal and Diplomatic Complexities: Potential for tensions with neighbouring nations in disputed waters due to UDA activities.
- Environmental Impact: The use of sonar technologies can negatively impact marine biodiversity and aquatic ecosystems.
Conclusion: UDA is a critical component of maritime security, economic sustainability, and environmental conservation. India’s focus on UDA, in collaboration with the U.S. and Quad partners, is especially significant given the increasing Chinese presence in the Indian Ocean. This collaboration is set to significantly enhance India’s maritime defense capabilities and strategic positioning in the region.
The primary strategic driver behind the India-U.S. collaboration on Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA) is:
- To counter the growing naval presence of China in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- To improve India’s fishing industry.
- To promote tourism in the Indian Ocean.
- To enhance environmental protection in the IOR.
Correct Answer: a.To counter the growing naval presence of China in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
BrahMos NG Cruise Missile
India is advancing its BrahMos cruise missile program with the development of the BrahMos NG (Next Generation) missile system, scheduled for production starting 2027-28.
- The first flight tests are expected next year.
- The BrahMos NG aims to enhance the capabilities of its predecessor while being lighter and more compact.
Key Features of BrahMos NG:
- Effective Range: Maintains a range of 290 km.
- Compact Design: Designed to fit smaller delivery systems.
- Weight and Dimensions: Weighs approximately 1.6 tonnes and is 6 meters long (compared to the older version’s 3 tonnes and 9 meters).
- Advanced Features: Features a reduced radar cross-section and a homemade seeker with AESA radar technology.
Compatibility and Deployment:
- The BrahMos NG is designed to be compatible with the Russian-origin Sukhoi-30MKI fighter aircraft and the indigenous Light Combat Aircraft Tejas.
- Its compact design enables deployment across a wider range of military assets.
International Interest and Export:
- India has already supplied three batteries of the BrahMos system to the Philippines.
- A new export deal with Indonesia, valued at approximately USD 450 million, is in advanced negotiations.
- Indonesia would be the second foreign buyer of the BrahMos system after the Philippines.
Technological Advancements and Future Prospects:
- BrahMos NG’s advanced stealth features and versatility make it suitable for various combat scenarios.
- It is designed for improved performance against electronic countermeasures and can be launched from multiple platforms, including torpedo tubes and vertical launch systems.
- India is advancing its BrahMos cruise missile program with the development of the BrahMos NG (Next Generation) missile system, scheduled for production starting 2027-28.
- The first flight tests are expected next year.
- The BrahMos NG aims to enhance the capabilities of its predecessor while being lighter and more compact.
Key Features of BrahMos NG:
- Effective Range:Maintains a range of 290 km.
- Compact Design:Designed to fit smaller delivery systems.
- Weight and Dimensions:Weighs approximately 1.6 tonnes and is 6 meters long (compared to the older version’s 3 tonnes and 9 meters).
- Advanced Features:Features a reduced radar cross-section and a homemade seeker with AESA radar technology.
- Compatibility and Deployment: The BrahMos NG is designed to be compatible with the Russian-origin Sukhoi-30MKI fighter aircraft and the indigenous Light Combat Aircraft Tejas. Its compact design enables deployment across a wider range of military assets.
- International Interest and Export: India has already supplied three batteries of the BrahMos system to the Philippines. A new export deal with Indonesia, valued at approximately USD 450 million, is in advanced negotiations. Indonesia would be the second foreign buyer of the BrahMos system after the Philippines.
- Technological Advancements and Future Prospects: BrahMos NG’s advanced stealth features and versatility make it suitable for various combat scenarios. It is designed for improved performance against electronic countermeasures and can be launched from multiple platforms, including torpedo tubes and vertical launch systems.
What is a primary advantage of the BrahMos NG compared to its predecessor?
- Increased effective range.
- Larger size and weight.
- Compatibility with fewer aircraft.
- Lighter weight and more compact design.
Answer: (D) Lighter weight and more compact design.
Explanation: The text explicitly states that the BrahMos NG aims to be lighter and more compact than the older version, allowing it to be used with a wider range of systems
Indian Army and IAF Execute ‘Winged Raider’ in Eastern Theater
The Indian Army and the Indian Air Force (IAF) have successfully executed the joint military exercise titled ‘Winged Raider’ in the Eastern Theater.
This strategic drill emphasized special airborne operations aimed at bolstering coordination between the two branches of the armed forces.
Conducted in a critical operational zone, the exercise forms part of ongoing efforts to enhance rapid deployment capabilities and foster inter-service synergy.
What was the main goal of conducting “Winged Raider” in a key operational zone?
- To practice humanitarian aid and disaster relief operations
- To showcase military might and intimidation
- To enhance coordination and rapid deployment capabilities between the Army and the Air Force
- To conduct counter-insurgency operations
Answer: C) To enhance coordination and rapid deployment capabilities between the Army and the Air Force
TrailGuard AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming anti-poaching strategies in wildlife conservation.
- Recent technological advancements have led to reductions in poaching incidents.
- The Similipal Tiger Reserve in Odisha exemplifies AI’s effectiveness in wildlife protection through TrailGuard AI.
Key Facts About Similipal Tiger Reserve:
- Location:Mayurbhanj District, Odisha (northernmost part).
- Area:Covers 2750 sq.km.
- Features:Famous waterfalls (Joranda, Barehipani), part of Mayurbhanj Elephant Reserve.
- Terrain:Hilly and undulating, with grasslands and forests.
History & Protection Status:
- Tiger Reserve (1973) under Project Tiger.
- Wildlife Sanctuary (1979).
- National Park proposal (1980).
- UNESCO Biosphere Reserve (2009).
About TrailGuard AI:
- Consists of 100-150 cameras equipped with an AI model.
- Function: Monitors the reserve and identifies poachers.
- Detection: Detects movement and captures images.
- Analysis: AI analyzes images for threats.
- Response:Enables wildlife officials to respond quickly to potential poaching activities.
Impact on Poaching Incidents:
- Arrests & Seizures:Facilitated the arrest of 96 poachers and seizure of over 86 firearms in the past year.
- Identification:Proved effective in identifying poachers through photo identification.
- Results:Led to successful house raids.
- Potential:Officials believe poaching could decrease by up to 80% with continued use.
- Operational Mechanism: Power Mode: Cameras operate on a low-power mode, switching to high-power on movement detection.
- On-site Inference:Perform AI inference on-site, classifying objects.
- Image Transmission:Images deemed as threats sent to control room within 30-40 seconds.
- Enforcement:Rapid communication enables timely enforcement actions.
Collaboration with Local Communities:
- Behavioral Change:The presence of AI technology has altered the behaviour of local communities.
- Impact:Many villagers avoid entering the forest.
- Engagement:The forest department is engaging with these communities to facilitate safe access and conduct awareness programmes.
Future Prospects and Applications:
- Expansion:TrailGuard AI’s success at Similipal has prompted interest in deployment in other regions.
- Implementation:The system has been implemented in multiple states (Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh).
- Potential:Potential extends beyond anti-poaching to monitoring wildlife and managing human-wildlife conflicts.
Advantages of TrailGuard Technology:
- Design:Compact and durable.
- Battery Life:Long battery life (six months to a year).
- Cost-Effectiveness: Accessible for conservation efforts.
- Theft Prevention:Unique design minimises risk of theft.
What is the primary function of TrailGuard AI in wildlife conservation?
- A) To track the migratory patterns of tigers.
- B) To monitor the overall health of the forest ecosystem.
- C) To identify and alert wildlife officials to potential poaching activities.
- D) To facilitate the collection of scientific data on wildlife behavior.
Answer and Explanation: C) To identify and alert wildlife officials to potential poaching activities.The text highlights that TrailGuard AI’s core function is to monitor the reserve and identify potential threats, specifically poaching incidents, through image analysis and rapid communication.
Key Facts about Parambikulam Tiger Reserve
Headline & Focus: A faunal survey adds 15 new species, highlighting the rich biodiversity of the reserve. The survey highlights the vibrant biodiversity and the importance of the reserve.
Key Points:
- The survey adds 15 new species to the checklist.
- The Forest Department performed the survey.
- The survey was in the Parambikulam Tiger Reserve.
About Parambikulam Tiger Reserve:
- Location:The reserve is located in the districts of Palakkad and Thrissur in Kerala.
- Protection Status:It’s a Tiger Reserve declared under Project Tiger.
- Area: The area covers 391 sq.km.
- Rivers:The Parambikulam, Sholayar, and Thekkady rivers flow through the reserve.
- Importance:The reserve is home to four tribes.
The tribes are Kadar, Malasar, Muduvar, and Mala Malasar.
Flora: The reserve’s is home to diverse flora, including mixed deciduous, evergreen, and semi-green habitats.
It also has other habitats such as montane and marshy grasslands, along with teak plantations, supporting its rich biodiversity.
Fauna: The reserve is a host to diverse fauna.
- It hosts one of the densest gaur populations and has many mammals, including Bengal tigers, Asian elephants, and the more uncommon lion-tailed macaques.
- The reserve is home to two endemic species of the region. The two endemic species are Tomp, and Garro
- The reserve is home to the endemic species of the region.
What is the primary significance of the recent faunal survey conducted in the Parambikulam Tiger Reserve?
- A) To assess the economic viability of extracting timber from the reserve.
- B) To identify and document new species, highlighting the reserve’s biodiversity.
- C) To evaluate the impact of tourism on the reserve’s ecosystem.
- D) To determine the optimal locations for establishing new human settlements.
Answer and Explanation: B) To identify and document new species, highlighting the reserve’s biodiversity.
The headline clearly states the focus of the survey: to add new species to the checklist, thereby highlighting the richness of the reserve’s biodiversity.
Parliamentary Panel Recommends Minimum Price for Paddy Residue to Curb Stubble Burning
A parliamentary panel has suggested establishing a minimum price mechanism for paddy residue, similar to the Minimum Support Price (MSP) for crops, to discourage farmers from burning crop residue in the fields.
Why is Stubble Burning a Concern?
Stubble burning, a practice primarily prevalent in Punjab, Haryana, and western Uttar Pradesh, results in severe air pollution in Delhi-NCR, causing smog and high PM2.5 levels, worsening respiratory diseases. It also harms soil fertility, increases dependence on chemical fertilizers, and contributes to climate change by releasing greenhouse gases.
Why Do Farmers Burn Stubble?
- Time constraints between paddy harvesting and wheat sowing.
- High costs of alternative methods, despite subsidies.
- Lack of a fixed market price for selling paddy straw.
- Limited awareness and inadequate incentives.
Key Recommendations:
- Minimum Price for Paddy Residue:A mechanism should be set up to benchmark and notify minimum prices annually before the Kharif harvest season. The price should cover farmers’ collection costs, including labor and machinery expenses.
- Subsidies:The government should subsidize machinery like happy seeders, rotavators, and mulchers for in-situ paddy straw management.
- Promotion of Short-Duration Paddy Varieties:State governments should discourage long-duration paddy varieties like PUSA 44 and promote short-duration alternatives.
- Developing a National Bioenergy Policy:A unified national policy to integrate agricultural residue into bioenergy production.
- Others:Address ex-situ crop residue management costs, provide financial incentives, improve supply chain infrastructure, and raise awareness among farmers to ensure economic viability and environmental sustainability.
What is the primary purpose of the parliamentary panel’s recommendation to establish a minimum price mechanism for paddy residue?
- To increase the income of farmers.
- To encourage farmers to burn crop residue.
- To discourage farmers from burning crop residue.
- To support the use of chemical fertilizers.
Answer: (C) To discourage farmers from burning crop residue.
Explanation: The text clearly states that the panel suggests a minimum price to discourage farmers from burning crop residue.
1st Glacier Declared Dead from Climate Change
Satellite imagery spanning more than three decades has confirmed the disappearance of Iceland’s Okjökull Glacier. It was the first glacier to be officially declared dead due to human-induced climate change in 2014.

About Okjökull Glacier:
Okjökull Glacier was located around the summit crater of Ok, a 1,200-meter-high shield volcano, approximately 71 kilometers northwest of Reykjavík, Iceland. Historically, it was a dome-shaped glacier, but climate change has led to its complete disappearance.
Global Efforts to Memorialize Vanishing Glaciers
- In 2023, Iceland established the world’s first iceberg graveyard, commemorating 15 glaciers listed as either dead or critically endangered on the Global Glacier Casualty List. This list includes Anderson Glacier in Washington State, USA, which was declared dead in 2015, making it the first such glacier loss in the United States.
United Nations Initiatives
- Recognizing the urgent need for action, the United Nations declared 2025 as the International Year of Glaciers’ Preservation. March 21st was designated as World Day for Glaciers, starting from 2025.
- The Cryosphere: Earth’s Frozen Reservoir
- The cryosphere refers to all frozen water on Earth. The term derives from the Greek word kryos, meaning frost or ice cold. It includes glaciers, ice sheets, ice shelves, icebergs, sea ice, lake ice, river ice, permafrost, snow cover, and solid precipitation.
Major Ice Sheets on Earth
- The Greenland Ice Sheet and the Antarctic Ice Sheet contain more than 70 percent of the world’s freshwater ice. Ice on these sheets exceeds two kilometers in thickness.
Key Facts About the Cryosphere
- Seventy percent of Earth’s freshwater exists as snow or ice. Ten percent of the Earth’s land area is covered by glaciers or ice sheets.
Hindu Kush Himalaya:The Water Tower of Asia
- The Hindu Kush Himalayan region spans approximately 3,500 kilometers across Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Nepal, Myanmar, and Pakistan. It is known as the Water Tower of Asia because it is the source of ten major river systems, including the Ganga, Brahmaputra, Indus, Yangtze, and Mekong.
- These rivers provide freshwater to 240 million people directly in the region and support one-fourth of the world’s population through their basins.
- Melting Crisis in the Hindu Kush Himalaya
- The Hindu Kush Himalayan cryosphere is warming at twice the global average rate. This increases the risk of glacial lake outburst floods, which pose severe hazards to downstream communities.
Role of the Cryosphere in Climate and Ecology
The cryosphere reflects sunlight through the albedo effect, helping regulate Earth’s temperature. It stores freshwater in glaciers and ice sheets, controlling sea levels. It plays a vital role in the global water cycle by feeding rivers and groundwater through seasonal melting. It provides a habitat for unique species such as polar bears, penguins, and snow leopards. It acts as an indicator of climate change, as it is highly sensitive to temperature variations.
Threats to the Cryosphere and Global Consequences
Global warming is causing widespread ice loss, accelerating the melting of glaciers, ice caps, and sea ice. Melting ice is contributing to rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities worldwide. Habitat loss is affecting marine ecosystems dependent on sea ice.
Permafrost thawing is releasing stored methane and carbon dioxide, worsening global warming. Changing snow and ice patterns are disrupting water availability for agriculture, hydropower, and human consumption.
Global Efforts to Protect the Cryosphere
- The Paris Agreement of 2015 aims to limit global temperature rise to below two degrees Celsius, preferably 1.5 degrees Celsius, to prevent further cryosphere degradation. The International Cryosphere Climate Initiative was formed during COP-15 in 2009 to work with governments and scientists to preserve the cryosphere.
- The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change highlights the urgent need for mitigation and adaptation strategies. The National Mission for Sustaining the Himalayan Ecosystem is part of India’s National Action Plan on Climate Change and aims to protect the Himalayan ecosystem.
- The World Meteorological Organization’s CryoNet is a global monitoring system tracking ice mass loss and cryosphere changes. The Arctic Council is a collaborative forum for Arctic nations to address climate-related issues in the polar region. Global ice monitoring programs such as the Global Cryosphere Watch and the European Space Agency’s CryoSat Mission provide data on ice loss.
Conclusion
The cryosphere plays a critical role in regulating global climate, providing freshwater, and sustaining biodiversity. Its rapid degradation due to climate change poses severe threats to ecosystems, human populations, and global stability. Preserving the cryosphere is essential for ensuring a sustainable future for all life on Earth.
Consider the following statements regarding the Okjökull Glacier:
- It was the first glacier in the world to be officially declared dead due to anthropogenic climate change.
- It was a part of the Greenland Ice Sheet before completely melting in 2014.
- The disappearance of Okjökull led to the formation of the world’s first iceberg graveyard in Iceland.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (c) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct. Okjökull was the first glacier to be officially declared dead due to climate change in 2014.
Statement 2 is incorrect. It was not part of the Greenland Ice Sheet but was a small glacier in Iceland, located on the Ok volcano.
Statement 3 is correct. Iceland created the world’s first iceberg graveyard in 2023 to memorialize glaciers that have vanished or are critically endangered.
Anthurium Flowers
- Mizoram marked a significant milestone in agro-based exports from the North Eastern Region (NER) by exporting its first consignment of Anthurium flowersto Singapore.

About Anthurium Flowers
- Scientific Name:Anthurium
- Geographical Distribution:
- Native to the Americas, spanning from northern Mexico to northern Argentina, including the Caribbean.
- In India, it thrives in the Northeastern states, particularly Mizoram, due to its favorable climate.
- Other key cultivation regions include Tamil Nadu (21%), Karnataka (16%), Madhya Pradesh (14%), and West Bengal (12%).
Botanical & Morphological Features
- A herbaceousplant that grows as an epiphyte (on other plants) or terrestrially.
- Recognized by its spadix(central spike) and a colorful spathe (leaf-like bract) in shades of red, pink, orange, and more.
- Contains calcium oxalate crystals, making its sap an irritantto skin and eyes.
Economic & Cultural Significance
Exports:
- Contributes to India’s floriculture exports, valued at USD 86.62 million in FY 2023–24.
- Major importers include the USA, Netherlands, UAE, UK, and Canada.
Tourism & Cultural Promotion:
- Mizoram hosts the annual “Anthurium Festival”, which promotes tourism, local enterprises, and the commercial value of the flower.
Livelihood Support:
- A crucial source of rural income, particularly benefiting women farmersand cooperative societies in the Northeast.
Consider the following statements regarding Anthurium flowers:
- Anthurium is a species native to Southeast Asia and is widely cultivated in the Indian subcontinent.
- In India, Mizoram is the leading producer of Anthurium flowers due to its suitable climatic conditions.
- Anthurium plants grow exclusively as terrestrial plants and do not exhibit epiphytic characteristics.
- The sap of Anthurium contains calcium oxalate crystals, which can be an irritant to human skin and eyes.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect – Anthurium is native to the Americas (from northern Mexico to northern Argentina), not Southeast Asia.
Statement 2 is correct – Mizoram is a major cultivator of Anthurium in India, supported by its favorable climatic conditions.
Statement 3 is incorrect – Anthurium plants can grow both terrestrially and epiphytically.
Statement 4 is correct – The plant contains calcium oxalate crystals, which can cause skin and eye irritation.
UN World Water Development Report 2025 – Mountains and Glaciers
Key Findings
Accelerated Glacier Melt:
- Glaciers are melting at an unprecedented rate, with significant mass loss in recent years.
- Over 9,000 billion tonnes of ice have been lost since 1975—equivalent to an ice block the size of Germany.
- Impurities like black carbon from wildfires and dust storms are intensifying the melting process by absorbing more solar radiation.
Permafrost Thawing:
- Rising temperatures are causing permafrost to melt, releasing organic carbon into the atmosphere and worsening climate change.
- Destabilized slopes increase the risk of landslides and other natural disasters.
Decline in Snow Cover:
- Snow cover in mountain regions has decreased, particularly during spring and summer.
- Between 1979 and 2022, there has been a 79% global declinein snow cover.
Impacts & Concerns
Erratic Water Flow & Flooding Risks:
- Increased risk of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs)—responsible for over 12,000 deaths in the past 200 years.
Sea Level Rise Contribution:
- Glacier melt accounts for 25-30% of global sea level rise, threatening millions worldwide.
Way Forward & Recommendations
Mountains as Water Towers:
- Covering 33 million sq km, mountain regions sustain nearly 2 billion peopleby providing freshwater.
Policy & Awareness:
- Urgent need for resource mobilizationand strong policy frameworks to mitigate climate impacts.
- Increased awareness and proactive action required to protect mountain ecosystemsand downstream communities.
With reference to the United Nations World Water Development Report 2025, consider the following statements:
- The report states that glaciers have lost over 9,000 billion tonnes of ice since 1950.
- Black carbon from wildfires and dust storms can accelerate glacier melting by increasing solar radiation absorption.
- The report highlights that permafrost thawing is reducing atmospheric carbon levels, thereby mitigating climate change.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The report highlights that glaciers have lost over 9,000 billion tonnes of ice since 1975, not 1950.
Statement 2 is correct: Black carbon and dust can accelerate glacier melting by increasing the absorption of solar radiation.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Permafrost thawing releases organic carbon into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change rather than mitigating it.
Eucalyptus

Background
- Eucalyptus, a fast-growing tree native to Australia, was introduced to India by the British in the 1840sfor timber production.
- In Karnataka, large-scale eucalyptus plantations were established between the 1960s and 1980sto support the timber and paper industries.
- However, environmental concerns led to a ban on eucalyptus cultivation in 2017, though a 2019 court staytemporarily halted its enforcement.
Environmental Concerns
- Groundwater Depletion– Eucalyptus has a high water demand, which disrupts local hydrological cycles and depletes groundwater levels.
- Soil Degradation & Loss of Biodiversity– The tree exhibits allelopathy (chemical suppression of other plant growth), reducing soil fertility and harming native vegetation.
- Impact on Grassland Ecosystems– Large-scale plantations encroach upon natural grasslands, threatening species such as:
- Blackbucks(Antilope cervicapra)
- Lesser Floricans(Sypheotides indicus)
- Great Indian Bustards(Ardeotis nigriceps)
Future Outlook
- Grasslands and savannah ecosystemsplay a crucial role in biodiversity conservation and rural livelihoods.
- Karnataka aims to balance economic developmentwith environmental sustainability, serving as a model for sustainable ecological practices in India.
Consider the following statements regarding Eucalyptus cultivation in Karnataka:
- The British introduced eucalyptus to India in the 19th century primarily for its medicinal properties.
- Karnataka banned eucalyptus plantations in 2017 due to their adverse environmental effects.
- Eucalyptus trees contribute significantly to groundwater recharge due to their deep-rooted structure.
- Eucalyptus exhibits allelopathy, which negatively impacts soil fertility and biodiversity.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect – The British introduced eucalyptus in the 1840s for timber production, not for medicinal purposes.
Statement 2 is correct – Karnataka banned eucalyptus cultivation in 2017 due to environmental concerns.
Statement 3 is incorrect – Eucalyptus is known for high water consumption rather than contributing to groundwater recharge.
Statement 4 is correct – The tree releases chemical compounds that inhibit the growth of other plants (allelopathy), reducing soil fertility and biodiversity.
Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary
Context:
- The Punjab government recently informed the Supreme Court (SC) that the Eco-Sensitive Zone (ESZ) around Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary would be limited to 100 meters for the Nayagaon municipal committee instead of the previously proposed 1 to 3 km.
About Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Location: Situated in Chandigarh, near the renowned Sukhna Lake, at the foothills of the Shivalik range.
- Origin of Sukhna Lake:
- Created in 1958 by the famous architect Le Corbusier.
- Formed by diverting the Sukhna Choe, a seasonal stream originating from the Shivalik hills.
Establishment:
- The sanctuary was officially notified in 1998.
- Developed as part of afforestation efforts for soil conservation around Sukhna Lake.
- Geography & Soil Characteristics:
- Covers 2,600 hectares.
- Comprises sandy soil from the Shivalik hills, interspersed with clay pockets.
- Geographically unstable and prone to soil erosion, particularly during the monsoon season.
- The sanctuary has around 150 small and large water bodies, including Sukhna Lake, forming its catchment area.
Ecological Features:
- Vegetation & Ecosystem
- The sanctuary comprises a mosaic of forests, grasslands, and wetlands, with Sukhna Lake serving as a vital component of its ecosystem.
- Flora
Notable tree species:
- Khair (Acacia catechu)
- Phulai (Acacia modesta)
- Kikar (Acacia nilotica)
- Shisham (Dalbergia sissoo)
Other species:
- Moonj (Saccharum munja) – A grass species.
- Amaltas (Cassia fistula) – Indian Laburnum with medicinal and ornamental value.
- Jhingan (Lannea coromandelica) – Used in traditional medicine.
- Amla (Phyllanthus emblica) – Indian Gooseberry.
- Rati, Vasaka – Medicinal plants contributing to the region’s biodiversity.
- Fauna
Mammals:
- Squirrel
- Common Mongoose
- Indian Hare
- Porcupine
- Jungle Cat
- Jackal
- Wild Boar
- Avian Diversity:
- Peacock
- Hill Myna
- Jungle Crow
- Black Drongo
- Parrots
- Doves
- Seasonal migratory birds also visit the sanctuary.
Significance & Concerns:
Eco-Sensitive Zone (ESZ) Reduction:
- The Punjab government’s decision to limit the ESZ to 100 meters in Nayagaon raises concerns about urban encroachment and its impact on the sanctuary’s ecosystem.
- Originally, an ESZ of 1 to 3 km was proposed to buffer the sanctuary from human activities.
Environmental Challenges:
- Soil erosion and runoff threaten the stability of the area.
- Increasing urbanization and deforestation pose risks to water bodies and wildlife habitats.
Conservation Outlook:
- Need for balanced urban planning while ensuring habitat protection.
- Strengthening afforestation and soil conservation measures to maintain ecological integrity.
- The Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary plays a critical role in maintaining regional biodiversity, and decisions regarding its Eco-Sensitive Zone should prioritize long-term environmental sustainability over short-term urban expansion.
With reference to the Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary, consider the following statements:
- It was established in 1958 as a protected area for wetland conservation.
- The sanctuary is located at the foothills of the Shivalik range and is prone to soil erosion.
- Sukhna Lake was artificially created by diverting a seasonal stream.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- The sanctuary was established in 1998, not 1958(Statement 1 is incorrect).
- It is located in the Shivalik foothills, prone to soil erosion(Statement 2 is correct).
- Sukhna Lake was artificially createdin 1958 by diverting Sukhna Choe, a seasonal stream (Statement 3 is correct).
Urban Heat Island (UHI)
- The Telangana Socio-Economic Outlook 2025report highlights that Hyderabad is experiencing intensified nighttime heat stress due to the Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect.
Understanding the Urban Heat Island Effect
- The Urban Heat Island (UHI) effectis a climatic phenomenon where urban areas experience significantly higher temperatures compared to their surrounding rural regions. This temperature disparity is primarily driven by human activities and urban development that modify land surfaces and atmospheric conditions.
Key Causes of the UHI Effect:
- Loss of Green Spaces & Natural Soils
- Urbanization reduces vegetation cover(trees, parks, and grasslands), leading to diminished shading and evapotranspiration, a natural cooling process.
- Building & Infrastructure Density
- Materials like concrete, asphalt, and metalabsorb and store more heat than natural surfaces, retaining warmth for longer durations.
Urban Layout & Street Design
- Narrow streets and high-rise buildingscreate “urban canyons” where heat is trapped and less effectively dissipated, exacerbating localized warming.
- Heat Emissions from Human Activities
- Vehicles, air conditioners, industrial operations, and power generationcontribute to increased heat output.
- Greenhouse gases (e.g., CO₂)trap this heat, further amplifying the warming effect.
Consequences of the UHI Effect:
- Increased nighttime temperatures—urban areas cool down more slowly than rural surroundings.
- Temperature differentials can reach up to 12°C at night, intensifying heat stressand impacting public health.
- Exacerbates global warming, making cities even hotter.
Why is it Called an “Urban Heat Island”?
- The term originates from temperature distribution maps, where urban zones appear as “hot islands”amid cooler rural surroundings, resembling an island of heat in a “sea” of lower temperatures.
- The UHI effect, when combined with climate change, contributes to rising global temperaturesand urban microclimates, making sustainable urban planning crucial for mitigating heat stress in cities.
With reference to the Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary, consider the following statements:
- It was established in 1958 as a protected area for wetland conservation.
- The sanctuary is located at the foothills of the Shivalik range and is prone to soil erosion.
- Sukhna Lake was artificially created by diverting a seasonal stream.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- The sanctuary was established in 1998, not 1958(Statement 1 is incorrect).
- It is located in the Shivalik foothills, prone to soil erosion(Statement 2 is correct).
- Sukhna Lake was artificially createdin 1958 by diverting Sukhna Choe, a seasonal stream (Statement 3 is correct).
Blue Flag Tag
In News:
- Rushikonda Beach in Visakhapatnamhas regained its prestigious Blue Flag certification, reaffirming its status as an environmentally sustainable and well-maintained coastal destination. With this, India now has 13 Blue Flag-certified beaches.
About the Blue Flag Certification:
- The Blue Flagis a globally recognized eco-label awarded to beaches, marinas, and sustainable boating tourism operators that meet stringent environmental, safety, and cleanliness standards.
Key Facts:
- Administered by:Foundation for Environmental Education (FEE), headquartered in Copenhagen, Denmark.
- Significance:Recognized as a symbol of environmental excellence, ensuring cleanliness, safety, and sustainability.
- Criteria for Certification:
A beach or marina must comply with 33 strict parametersacross four major categories: - Environmental Education and Information– Spreading awareness about coastal conservation.
- Water Quality– Ensuring clean and pollution-free seawater.
- Environmental Management– Sustainable waste disposal and biodiversity conservation.
- Safety and Services– Adequate infrastructure, lifeguards, and emergency response systems.
This achievement reinforces India’s commitment to promoting sustainable coastal tourism and preserving its natural marine ecosystems.
With reference to the Blue Flag Certification, consider the following statements:
- It is an international eco-label awarded exclusively to marine protected areas.
- The certification is administered by the International Maritime Organization (IMO).
- A beach must meet 33 criteria across multiple categories to receive this certification.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Blue Flag is awarded to beaches, marinas, and sustainable boating tourism operators, not just marine protected areas.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The certification is administered by the Foundation for Environmental Education (FEE), headquartered in Denmark, not by the IMO.
Statement 3 is correct: To qualify for the Blue Flag, a beach/marina must satisfy 33 environmental, safety, and management criteria.
Permafrost Thawing in Kashmir Himalaya
Context
- A recent study has highlighted the escalating environmental risks associated with the melting permafrost in the Kashmir Himalaya, raising concerns over its impact on infrastructure, water resources, and natural hazards.
What is Permafrost?
- Permafrost refers to ground that remains completely frozen (≤ 0°C) for at least two consecutive years.
- It is predominantly found in high-altitude regionsand Earth’s polar latitudes (near the North and South Poles).
Major Concerns
- Infrastructure Damage: Thawing permafrost can weaken foundationsof roads, hydropower projects, and other built structures.
Increased Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs):
- In Jammu & Kashmir, 332 proglacial lakeshave been identified.
- Of these, 65 pose significant GLOF risks, which could worsen with permafrost degradation.
- Potential Impacts
Human Activities as a Catalyst:
- Deforestation, land-use changes, and infrastructure expansion(roads, dams, and tourism) can accelerate permafrost degradation.
Water Cycle Disruptions:
- Permafrost plays a key role in maintaining groundwater and river base flow.
- Its thawing could significantly alter water availability, though research on this remains limited.
Recommendations for Mitigation
- Infrastructure Planning: Future development projects should incorporate permafrost vulnerability assessments.
- Enhanced Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA): Greater focus on cryospheric hazardslike GLOFs.
- Advanced Monitoring Systems:
- Increased use of satellite imagery and in-situ data loggersfor real-time permafrost tracking.
- Comprehensive Research:
- More in-depth studies on permafrost degradation’s long-term impacton water resources and infrastructure stability.
- As the Kashmir Himalaya faces intensifying climate challenges, proactive strategies are essential to mitigate risks and adapt to a rapidly changing environment.
Consider the following statements regarding permafrost:
- Permafrost refers to any ground that remains frozen at or below -5°C for a minimum of five consecutive years.
- It is found only in the Arctic and Antarctic regions and does not exist in high-altitude mountain ranges.
- The thawing of permafrost contributes to increased methane emissions, which can accelerate climate change.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (c) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Permafrost is defined as ground that remains frozen at ≤0°C for at least two consecutive years (not -5°C for five years).
Statement 2 is incorrect: While permafrost is common in polar regions, it is also found in high-altitude mountain ranges such as the Himalayas, Alps, and Andes.
Statement 3 is correct: Thawing permafrost releases methane (CH₄) and carbon dioxide (CO₂), intensifying global warming.
India’s Heat Action Plans
A recent study has found that most Indian cities’ Heat Action Plans (HAPs)lack effective long-term strategies to combat extreme heat, and those with such measures have failed in their implementation.
What are Heat Action Plans (HAPs)?
- HAPs are early warning systems and preparedness strategiesdesigned to minimize the health impacts of extreme heat, particularly for vulnerable populations.
About the Study
- Title:“Is India Ready for a Warming World?”
- Conducted by:Sustainable Futures Collaborative (SFC) and international universities (King’s College London, Harvard, Princeton, and UC Berkeley).
- Focus:Cities with over 1 million people expected to face increasing dangerous heat index values.
Key Findings
- Short-term measureslike access to water and adjusted work schedules are widely implemented.
- Long-term strategiessuch as cooling infrastructure, insurance for heat-related job losses, fire management, and electricity grid upgrades are either absent or poorly enforced.
- Urban cooling efforts(e.g., increasing green cover and shaded areas) do not effectively target the most heat-vulnerable populations.
- Planning gaps pose a significant risk, potentially leading to a rise in heat-related deathsas heatwaves become more frequent, intense, and prolonged.
- The study underscores the urgent need for comprehensive and well-executed heat mitigation strategiesto safeguard urban populations in an era of rising temperatures.
Consider the following statements regarding Heat Action Plans (HAPs) in India:
- HAPs serve as early warning systems and preparedness strategies to mitigate the impact of extreme heat.
- They are implemented exclusively by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Long-term measures such as insurance for heat-related job losses and urban cooling infrastructure are widely implemented in Indian cities.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: HAPs are early warning and preparedness strategies to protect vulnerable populations from extreme heat.
Statement 2 is incorrect: HAPs are implemented at state and city levels, often under disaster management authorities in coordination with various ministries, not exclusively by MoEFCC.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The study highlighted that long-term measures are either absent or poorly implemented, making Indian cities highly vulnerable to heat-related disasters.
Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary
Location & Significance
- Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary is situated in the Chikkamagaluru and Shivamogga districts of Karnatakaand derives its name from the Bhadra River, which flows through the region.

Designation & Conservation Status
- Declared a Wildlife Sanctuary in 1951.
- Upgraded to a Project Tiger Reserve in 1998.
- First tiger reserve in India to complete a village relocation program by 2002.
- Geographical Features
- Core area:16 sq. km.
- Buffer zone:84 sq. km.
- Terrain:Includes hills and valleys, notably Mullayanagiri (the highest peak in Karnataka), Baba Budangiri, and Muthodi ranges.
- Flora of Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary
The sanctuary hosts diverse forest types:
- Southern Moist Mixed Deciduous Forests– Characterized by Teak, Terminalia, and Lagerstroemia
- Dry Deciduous Forests– Includes Pterocarpus (Honne), Grewia (Tadasalu), and Bamboo
- Shola Forests– Supports species such as Cinnamon, Mimusops, and Strobilanthes (Neelakurinji), known for its rare blooming cycle.
Fauna of Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary
- Mammals:Includes Tigers, Leopards, Dholes (Wild Dogs), Gaurs, Sambar Deer, Barking Deer, and Elephants.
- Birds:Over 250 species, including Grey Junglefowl, Malabar Parakeet, Hill Myna, Malabar Trogon, and Hornbills.
- Reptiles:Features King Cobra, Russell’s Viper, Indian Monitor Lizard, and Marsh Crocodiles.
- Butterflies:Hosts rare species like Yamfly, Baronet, Crimson Rose, Southern Birdwing, and Great Orange Tip.
Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary remains a crucial site for biodiversity conservation, playing a vital role in Karnataka’s ecological balance.
Consider the following statements regarding Heat Action Plans (HAPs) in India:
- HAPs serve as early warning systems and preparedness strategies to mitigate the impact of extreme heat.
- They are implemented exclusively by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Long-term measures such as insurance for heat-related job losses and urban cooling infrastructure are widely implemented in Indian cities.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: HAPs are early warning and preparedness strategies to protect vulnerable populations from extreme heat.
Statement 2 is incorrect: HAPs are implemented at state and city levels, often under disaster management authorities in coordination with various ministries, not exclusively by MoEFCC.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The study highlighted that long-term measures are either absent or poorly implemented, making Indian cities highly vulnerable to heat-related disasters.
Coral Bleaching Devastates Western Australia’s Ningaloo Reef
Context
- A severe mass coral bleaching event, described as unprecedented, is currently unfolding along Australia’s western coast, severely impacting the Ningaloo Reef, a UNESCO World Heritage site. This event is part of the fourth global coral bleaching episode, which has been ongoing since 2023.

Global Impact of Coral Bleaching
- The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) reports that nearly 84% of the world’s reef areas have experienced bleaching-level heat stress, affecting over 80 countries and territories.
- Rising global sea surface temperatures, overfishing, and pollution have exacerbated the crisis, with climate change being a primary driver.
Coral Reefs: An Overview
What Are Coral Reefs?
- Coral reefs are complex underwater ecosystems built by reef-building corals.
- Composed of colonies of coral polyps bound by calcium carbonate.
- Coral polyps live in a mutualistic relationship with algae known as zooxanthellae, which provide them with nutrients through photosynthesis.
Favorable Conditions for Coral Growth
- Temperature: 20°C–35°C
- Salinity: 27%–40%
- Depth: Prefer shallow waters (less than 50 meters) for optimal sunlight exposure.
- Major Coral Reefs Around the World
- Global Coral Reefs
- Great Barrier Reef (Australia) – UNESCO World Heritage Site
- Caribbean Reefs – Florida, Belize, and Bahamas
- Coral Triangle (Southeast Asia) – Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines
- Coral Reefs in India
- Gulf of Kutch (Gujarat)
- Gulf of Mannar (Tamil Nadu)
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands
- Lakshadweep Islands
- Malvan (Maharashtra)
- Significance of Coral Reefs
- Biodiversity Hotspot – Support 25% of all marine species.
- Coastal Protection – Act as natural barriers against storms and erosion.
- Climate Mitigation – Aid in carbon sequestration.
- Blue Economy – Sustain livelihoods through fishing and tourism.
- Biomedical Resources – Source of antiviral and anticancer compounds.
- Threats to Coral Reefs
Climate-Related Threats
- Coral Bleaching – Caused by rising ocean temperatures.
- Ocean Acidification – Weakens coral skeletons due to increasing CO₂
- Algal Blooms – Triggered by nutrient pollution, suffocating corals.
Human-Induced Threats
- Overfishing – Disrupts marine food chains.
- Pollution – Plastic waste, oil spills, and chemical runoff degrade reef health.
- Coral Mining – Unsustainable extraction for construction materials.
- Coastal Development – Leads to habitat destruction and sedimentation.
The Way Forward
- Climate Action
- Strengthen efforts to limit global warming to well below 2°C, in line with the Paris Agreement.
- Policy & Governance
- Implement Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly:
- SDG 8 (Sustainable Economic Growth)
- SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption & Production)
- Global Collaboration
- Strengthen international partnerships to combat overfishing and marine pollution.
- Scientific Innovation
- Invest in R&D for climate-resilient coral species to enhance reef restoration efforts.
- By integrating policy, conservation, and innovation, proactive measures can help protect the world’s coral reefs from irreversible decline.
Consider the following statements regarding Heat Action Plans (HAPs) in India:
- HAPs serve as early warning systems and preparedness strategies to mitigate the impact of extreme heat.
- They are implemented exclusively by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Long-term measures such as insurance for heat-related job losses and urban cooling infrastructure are widely implemented in Indian cities.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: HAPs are early warning and preparedness strategies to protect vulnerable populations from extreme heat.
Statement 2 is incorrect: HAPs are implemented at state and city levels, often under disaster management authorities in coordination with various ministries, not exclusively by MoEFCC.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The study highlighted that long-term measures are either absent or poorly implemented, making Indian cities highly vulnerable to heat-related disasters.
Dorka Metal Craft
Gift: Prime Minister of India gifted a Dokra artwork to French President Emmanuel Macron at the AI Summit in Paris.
Definition: Non-ferrous metal casting technique using the lost-wax casting method.
Characteristics:
- Primitive simplicity
- Unique folk motifs
- Handcrafted designs (no joints)
Materials: Mainly brass and copper-based alloys.
Designs: Figures of:
- Elephants
- Horses
- Religious deities
- Lamps
- Jewellery
- Tribal motifs
Regions Found:
- Jharkhand
- Chhattisgarh
- Odisha
- West Bengal
- Telangana
- Madhya Pradesh
- Rajasthan
- Tamil Nadu
GI Tag: Adilabad Dokra (Telangana) received a Geographical Indicator (GI) tag in 2018.
Casting Methods:
- Solid Casting (South India):Single wax piece for the mould.
Hollow Casting (Central & Eastern India): Clay core with wax overlay.
With reference to the Dokra art form, consider the following statements:
It is a ferrous metal casting technique primarily using iron-based alloys.
Dokra artworks are produced using the lost-wax casting method.
The Adilabad Dokra from Telangana received the GI tag in 2018.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B
Statement 1: It is a ferrous metal casting technique primarily using iron-based alloys.
- Incorrect.
Dokra is a non-ferrous metal casting technique. It primarily uses brass and copper-based alloys, not iron. The term “ferrous” refers to iron-containing metals, which is not the case here.
Statement 2: Dokra artworks are produced using the lost-wax casting method.
- Correct.
Dokra is globally recognized for using the ancient lost-wax casting technique, also known as ‘cire perdue’, where a wax model is used to create the mold before it is melted and replaced with molten metal.
Statement 3: The Adilabad Dokra from Telangana received the GI tag in 2018.
- Correct.
Adilabad Dokra, a unique style of this art form from Telangana, received the Geographical Indication (GI) tag in 2018, recognizing its regional and cultural significance.
Kashi Tamil Sangamam
- Kashi Tamil Sangamam 3.0 (KTS 3.0) is scheduled to take place from 15th to 24th February 2025.
- The event is organized by the Ministry of Education, Government of India, in collaboration with other ministries and the Government of Uttar Pradesh.
- IIT Madras and BHUare the implementing agencies for the program.
Objective of KTS 3.0:
- To rediscover and reaffirm the age-old links between Tamil Nadu and Kashi.
- To celebrate the deep-rooted bonds between the two regions.
Uniqueness: Each piece is unique because the mould is destroyed during the process.
History:
- Origins: Indus Valley Civilization (e.g., Mohenjo-daro’s “Dancing Girl”).
- Practitioners: Dhokra Damar tribes (originated from Odisha and West Bengal).
Which state’s Dokra craft received a Geographical Indication (GI) tag in 2018?
- Odisha
- West Bengal
- Telangana
- Chhattisgarh
Correct Answer: c) Telangana
Kaliyattam Festival
The Kaliyattam festival, also known as Theyyam, is celebrated during the Malayalam month of Kumbham (February-March). It is a vibrant ritualistic festival dedicated to the worship of Goddess Kali and is deeply rooted in Kerala’s intangible cultural heritage.
Key Features:
- Sacred Venues:The festival is primarily observed in Kavus (sacred groves) and tharavadus (ancestral households).
- Ritual Dance Performances:Theyyam performers don elaborate costumes and face paint, embodying different deities.
- Spiritual Significance:During the performances, the artists are believed to become living embodiments of the divine, earning Theyyam the title of the “dance of gods” or “dance of the divine”.
With reference to the Kaliyattam festival, consider the following statements:
- It is primarily associated with the worship of Lord Shiva in Kerala.
- The festival is mainly celebrated in sacred groves and ancestral households.
- Theyyam performances involve elaborate costumes and ritualistic dance.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation: The Kaliyattam festival (Theyyam) is primarily dedicated to the worship of Goddess Kali, not Lord Shiva. It is performed in Kavus (sacred groves) and tharavadus (ancestral households), with dancers embodying divine figures through elaborate costumes and ritualistic performances.
Shaheed Diwas
Context: On March 23, the nation pays tribute to Bhagat Singh, Rajguru, and Sukhdev on Shaheed Diwas, commemorating their execution in 1931. Their sacrifice remains a powerful symbol of India’s freedom struggle.
Background:
- In 1928, the British government sent the Simon Commission, an all-British panel, to India to discuss constitutional reforms. This led to widespread protests as it excluded Indian representation.
- Lala Lajpat Railed a protest in Lahore, where police, under Superintendent James A. Scott, brutally lathi-charged the demonstrators. Lajpat Rai succumbed to his injuries on November 17, 1928.
- To avenge his death, Bhagat Singh, Rajguru, and Sukhdevtargeted James Scott but mistakenly killed British officer John Saunders
- Arrested, tried, and sentenced to death, they became martyrs for India’s independence movement. Their execution inspired countless revolutionaries to continue the struggle for freedom.
Revolutionary Legacy:
- Bhagat Singh (1907–1931), Sukhdev (1907–1931), and Rajguru (1908–1931)were key members of the Hindustan Socialist Republican Association (HSRA), a revolutionary group committed to armed resistance against British rule.
- Bhagat Singh was deeply influenced by Marxist and anarchistideologies, drawing inspiration from Karl Marx, Vladimir Lenin, and Leon Trotsky.
- He is also remembered for the 1929 bombing of the Central Legislative Assembly in Delhi, aimed at protesting against oppressive laws, without intending to cause harm.
- Shaheed Diwas serves as a reminder of their unwavering courage, patriotism, and ultimate sacrificein the fight for India’s independence.
Consider the following statements regarding the Simon Commission and its impact on the Indian freedom struggle:
- The Simon Commission was sent by the British government in 1927 to assess the need for constitutional reforms in India.
- The commission did not include any Indian members, leading to widespread protests across the country.
- Lala Lajpat Rai was fatally injured during a protest against the Simon Commission in Kolkata.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- The Simon Commissionwas sent in 1928, not 1927.
- The absence of Indian representationled to widespread protests.
- Lala Lajpat Raiwas injured in a protest in Lahore, not Kolkata.
Vikramshila University Latest News
Why in News?
- Following the revival of Nalanda University, another ancient center of learning, Vikramshila University, is set for restoration.
- The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI)is currently developing the site to promote tourism.
- The Bihar governmenthas allocated 14 acres in Antichak village, Bhagalpur, to establish a Central University at the historic location.
- Originally approved in 2015with an initial budget of ₹500 crore, the project faced delays due to land acquisition issues.
About Vikramshila University
Location:
- Situated in Bhagalpur, Bihar, along the Ganges River, it was a significant historical and educational center in eastern India.
Founder:
- Established by King Dharmapalaof the Pala Dynasty (late 8th–early 9th century AD).
- Founded to counter the perceived decline in educational standardsat Nalanda University.
Significance:
- A major hub for Tantric Buddhism and Vajrayana Buddhism, playing a crucial role in spreading these traditions.
- Specialized in tantric and occult studies, distinguishing it from Nalanda University, which had a broader curriculum.
- Under King Dharmapala, Vikramshila University influenced Nalanda’s affairs, showcasing its academic and administrative prominence.
- Hosted over 1000 students and 100 teachersfrom across India and beyond.
- Produced renowned scholars like Atisa Dipankara, who was instrumental in establishing Buddhism in Tibet.
Features:
- Central Stupasurrounded by 208 cells for student-monks engaged in study and meditation.
- A library with an advanced cooling system, using water from a nearby reservoir to preserve delicate manuscripts.
- Offered a diverse curriculum, including theology, philosophy, grammar, metaphysics, logic, and tantras.
- Governed by a Kulpati (Mahasthavir), ensuring efficient administration.
- Decline:
- Destroyed in 1203 ADby Muhammad Bin Bakhtiyar Khalji, marking the downfall of Vikramshila and Nalanda Universities.
With reference to Vikramshila University, consider the following statements:
- It was established by King Mahipala of the Pala Dynasty as an alternative to Nalanda University.
- It specialized in Vajrayana Buddhism and Tantric studies.
- The university had a unique manuscript preservation system using a water-cooled library.
- It was destroyed during the invasions of Alauddin Khalji.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Vikramshila University was established by King Dharmapala, not Mahipala. It was founded due to perceived declining educational standards at Nalanda.
Statement 2 is correct: The university was a renowned center for Vajrayana Buddhism and specialized in Tantric studies, unlike Nalanda, which had a broader curriculum.
Statement 3 is correct: Vikramshila had an advanced manuscript preservation system using a water-cooling mechanism from a nearby reservoir.
Statement 4 is incorrect: The university was destroyed in 1203 AD by Muhammad Bin Bakhtiyar Khalji, not Alauddin Khalji
Farm Distress Index
A pilot study titled “Agrarian Distress and PM Fasal Bima Yojana: An Analysis of Rainfed Agriculture”was conducted in Telangana and Andhra Pradesh during 2020-21 and 2021-22 to assess farmer distress. However, a systematic national-level assessment of the Farmers’ Distress Index (FDI) is currently unavailable.
Farmers’ Distress Index (FDI):
- FDI is a comprehensive assessment tooldesigned to identify and address the root causes of agrarian distress, including climate variability, price volatility, and farmers’ risk-bearing capacity.
Objective:
- To develop a user-friendly predictive toolthat helps policymakers, researchers, and farmers anticipate and mitigate agrarian distress.
Key Parameters of FDI:
- Exposure to Risk:Climate shocks, pest attacks, droughts, floods, and market fluctuations.
- Adaptive Capacity:Farmers’ ability to cope with adverse conditions through technology, financial resources, and knowledge.
- Sensitivity:The vulnerability of different farming communities based on socio-economic and geographical factors.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies:Government policies, crop insurance schemes, irrigation systems, and community-based support.
- Triggers:Sudden economic or environmental changes that lead to distress.
- Psychological Factors:Mental health and financial stress experienced by farmers.
- Impacts:The long-term consequences on livelihoods, food security, and migration patterns.
- Purpose and Significance:
- Targeted Government Intervention:Helps ensure that relief measures reach the most affected regions.
- Early Warning System:Provides alerts three months in advance, allowing proactive measures to be taken.
- Planning Tool:Assists policymakers in developing localized solutions to mitigate distress.
The Farmers’ Distress Index is a crucial step towards improving agricultural resilience and rural well-being, ensuring timely intervention and sustainable farming practices.
Consider the following statements regarding the Farmers’ Distress Index (FDI):
- It is a tool developed to assess farmer distress based on parameters such as climate variability, price fluctuations, and psychological factors.
- The index is designed to provide real-time intervention measuresat the national level.
- It includes parameters like adaptive capacity, mitigation strategies, and sensitivity to external shocks.
- The Farmers’ Distress Index is officially integrated into India’s agricultural policy and implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct. The Farmers’ Distress Index (FDI) is designed to assess distress based on multiple parameters such as climate risks, market fluctuations, and psychological factors.
Statement 2 is incorrect. The index is not a real-time intervention tool, but rather a predictive model aimed at early warning and proactive policy planning.
Statement 3 is correct. It incorporates adaptive capacity, mitigation strategies, and sensitivity as key indicators.
Statement 4 is incorrect. While FDI is being studied and piloted, it has not yet been officially integrated into national agricultural policy.
Lapis Lazuli
Overview
- Lapis Lazuli is a highly valued semi-precious rock known for its deep blue color, often streaked with golden flecks.
Composition
- The intense blue hueof lapis lazuli is due to lazurite (25-40%), with its shade influenced by sulfur content.
- The golden shimmercomes from the presence of pyrite, while diopside and sodalite occur in minor quantities.
Global Distribution
- Found in several countries, including Chile, Russia, and the United States.
- The finest qualitylapis lazuli originates from Badakhshan province in Afghanistan, where it has been mined for over 6,000 years.
Historical Significance
- Ancient India:Lapis lazuli was imported from Badakhshan as early as 1000 BCE.
- Indus Valley Civilization:Archaeologists have discovered lapis lazuli ornaments in sites like Mohenjo-daro and Harappa.
- Ancient Egypt:Used extensively in jewelry and ground into powder for eye makeup.
- Renaissance Europe:Artists ground lapis lazuli into ultramarine pigment, which was one of the most expensive colors used in paintings.
- Lapis lazuli remains a gemstone of historical, artistic, and cultural significance, valued for both its beauty and its enduring legacy.
With reference to Lapis Lazuli, consider the following statements:
- It derives its blue color primarily from the presence of the mineral azurite.
- Pyrite inclusions in lapis lazuli are responsible for its characteristic golden specks.
- The Indus Valley Civilization had no known trade connections for acquiring lapis lazuli.
- The Badakhshan region in Afghanistan is historically known for high-quality lapis lazuli deposits.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect – The blue color of lapis lazuli comes from lazurite, not azurite.
Statement 2 is correct – The golden specks in lapis lazuli are due to pyrite inclusions.
Statement 3 is incorrect – The Indus Valley Civilization did trade for lapis lazuli, as evidenced by findings in Mohenjo-daro and Harappa.
Statement 4 is correct – Badakhshan (Afghanistan) has been a primary source of high-quality lapis lazuli for over 6,000 years.
Strait of Hormuz
Latest News
- Amid escalating tensions with the United States, Iranhas deployed missile systems on the three disputed islands—Greater Tunb, Lesser Tunb, and Abu Musa—located near the Strait of Hormuz.
- This move highlights Iran’s strategic control over this critical maritime passage and raises concerns over regional security and global energy supply disruptions.
Key Facts About the Strait of Hormuz
Geographical Significance:
- The Strait of Hormuzis a narrow yet strategically vital waterway that lies between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula, specifically the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Oman’s Musandam Peninsula.
- It serves as a critical maritime route connecting the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Omanand further to the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean.
Geopolitical Boundaries:
- Northern Coast:Iran
- Southern Coast:United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Oman
- Western End:Persian Gulf
- Eastern End:Gulf of Oman
- Dimensions & Navigability:
- The Strait of Hormuz stretches for 167 kilometersin length.
- The width varies from 95 kilometers at its broadest point to just 39 kilometers at its narrowest.
- Despite its narrowing towards the north, it remains deep enough for the passage of large oil tankers and cargo vessels.
Islands in the Strait of Hormuz:
- Hengam Island
- Hormuz Island
- Qishm Island
- Greater Tunb, Lesser Tunb, and Abu Musa (disputed between Iran and UAE)
Economic & Strategic Importance:
- It is one of the world’s most critical choke points for global energy trade.
- Approximately 25% of the world’s crude oiland 30% of the world’s liquefied natural gas (LNG) pass through this waterway.
- Disruptions in the Strait of Hormuzcan significantly impact global oil prices and energy security.
Consider the following statements regarding the Strait of Hormuz:
- It connects the Persian Gulf to the Arabian Sea.
- It is the narrowest maritime chokepoint for global oil transportation.
- The United States maintains a permanent naval base on Abu Musa Island to secure energy trade.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Strait of Hormuzconnects the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Oman, which in turn leads to the Arabian Sea.
- Statement 2 is correct: It is one of the narrowest and most critical maritime chokepointsfor global oil transportation, with a width narrowing to 39 km at its tightest point.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The United States does not maintain a permanent naval base on Abu Musa Island. The island is disputed between Iran and the UAE, and Iran has control over it. The S. does, however, maintain a strong naval presence in the regionthrough its 5th Fleet, headquartered in Bahrain.
World’s Largest Grain Storage Plan in Cooperative Sector
Why in News?
- On May 31, 2023, the Government approved the World’s Largest Grain Storage Plan in the Cooperative Sector, set to be implemented as a Pilot Project.
- This initiative aims to develop agricultural infrastructureat the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) level, including:
Construction of godowns
- Establishment of custom hiring centers
- Setting up of processing units
The project integrates various existing Government of India (GoI) schemes, such as:
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)
- Agricultural Marketing Infrastructure Scheme (AMI)
- Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM)
- Pradhan Mantri Formalization of Micro Food Processing Enterprises Scheme (PMFME)
Progress of the Pilot Project
- Under the Pilot Project, godowns have been constructed in 11 PACS across 11 States, with a total storage capacity of 9,750 Metric Tons (MT).
State-wise Details of Completed Godowns
|
- Additionally, foundation stones have been laid for 500 additional PACS godownsunder the Pilot Project, with a total of 575 PACS identified for implementation across various States/UTs.
Expansion and Future Goals
- The Ministry of Cooperationaims to establish and strengthen 2 lakh multipurpose PACS, Dairy, and Fishery Cooperative Societies across all panchayats and villages in the country.
- To guide this process, a Margdarshika (Standard Operating Procedure)has been introduced.
- In Karnataka, 128 PACS have been establishedagainst a target of 218 PACS to be formed by FY 2028-29.
Impact of the World’s Largest Grain Storage Plan
Decentralized Storage Capacity:
- 9,750 MTof storage capacity has been created at the PACS level.
Reduction in Food Grain Wastage:
- Prevents post-harvest lossesby ensuring adequate storage facilities.
Strengthening of Food Security:
- Ensures better storage and distribution of food grainsto enhance national food security.
Preventing Distress Sales:
- Farmers can store their produce and sell it at better pricesrather than being forced into distress sales.
Cost Reduction in Transportation:
- Since PACS can function as both procurement centersand Fair Price Shops (FPS), transportation costs are reduced.
- Avoids the need to transport grains from procurement centers to warehousesand back to FPS.
- This initiative marks a major milestonein strengthening the cooperative sector and enhancing agricultural infrastructure across India.
Consider the following statements regarding the “World’s Largest Grain Storage Plan in the Cooperative Sector”:
- It is being implemented exclusively under the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF).
- The plan aims to develop agri-infrastructure at the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) level.
- One of the objectives of the plan is to enable PACS to operate as procurement centers as well as Fair Price Shops (FPS).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The plan is not implemented exclusivelyunder AIF; rather, it converges multiple schemes like Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF), Agricultural Marketing Infrastructure Scheme (AMI), Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM), and Pradhan Mantri Formalization of Micro Food Processing Enterprises Scheme (PMFME).
- Statement 2 is correct: The plan focuses on strengthening PACSby developing godowns, custom hiring centers, and processing units.
- Statement 3 is correct: The initiative allows PACS to function as procurement centers and Fair Price Shops (FPS), reducing transportation costs and logistical challenges.
Lake Sapanca
Lake Sapanca in Türkiye is facing severe environmental degradation due to urbanization, industrial expansion, and agricultural runoff, leading to increased pollution and habitat destruction.
About Lake Sapanca:
Location:
Situated in northwestern Türkiye, between the Gulf of İzmit and Adapazarı Meadow.
Lies in a tectonic depression, running parallel to Iznik Lake.
Bordering Nations:
Türkiye’s Sakarya Province is home to the lake.
The catchment area is 251 km², surrounded by mountains in the south and small hills in the north.
River Inflows: The lake has multiple inflows from small streams originating from surrounding mountains. It serves as a primary freshwater source for domestic and industrial purposes.
Key Issues:
- High nutrient loads (Nitrogen & Phosphorus) due to agricultural runoff & wastewater discharge, leading to eutrophication.
- Urban expansion & deforestation reducing water retention capacity.
- Seasonal pollution peaks observed in summer due to low water flow.
During which season are seasonal pollution peaks typically observed in Lake Sapanca, and why?
(a) Winter, due to increased snow melt
(b) Spring, due to heavy rainfall
(c) Summer, due to low water flow
(d) Autumn, due to leaf decomposition
Correct Answer: Summer, due to low water flow
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act
Indian Abortion Laws: A Historical Overview
Prior to 1971, abortions were largely criminalized under the Indian Penal Code (IPC), with exceptions only for procedures performed to save a woman’s life. The IPC did not differentiate between desired and unwanted pregnancies, making safe abortion access extremely difficult.
The Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act of 1971:
- The MTP Act was enacted to decriminalize abortion in specific circumstances, recognizing it as a “health” measure.
- Initially, the Act allowed termination up to 20 weeks of pregnancy. A single doctor’s opinion was required for terminations within 12 weeks, and the opinion of two doctors was needed for terminations between 12 and 20 weeks.
The 2021 Amendment to the MTP Act:
Extended Gestational Limit: Rule 3B allowed abortion up to 24 weeks for specific categories of women, including those who experienced a change in marital status during pregnancy, survivors of rape or incest, and other vulnerable women.
Inclusive Language: The amendment broadened the legal scope by replacing “married woman or her husband” with “any woman or her partner,” encompassing pregnancies outside of marriage.
Post-24 Weeks: For pregnancies beyond 24 weeks, a medical board of expert doctors, established by the state government, assesses cases involving substantial fetal abnormalities to determine if termination is permissible.
Current Case: The Bombay High Court recently allowed a 25-week pregnancy termination in a private hospital, illustrating how the legal framework is applied in specific situations.
Which of the following accurately describes the legal status of abortion in India prior to the Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act of 1971?
- Abortion was legal and widely accessible, with no gestational limits.
- Abortion was largely criminalized under the Indian Penal Code (IPC), with exceptions only to save a woman’s life.
- Abortion was legal up to 12 weeks of gestation, with a single doctor’s approval required.
- Abortion was regulated by the MTP Act from the beginning, albeit with more stringent rules than present.
Correct Answer: b) Abortion was largely criminalized under the Indian Penal Code (IPC), with exceptions only to save a woman’s life.
Marital Rape in India
Legal Ambiguity and Ongoing Debate: The core reason the topic is in the news is the ongoing legal debate and lack of clarity regarding marital rape in India.
Chhattisgarh High Court Ruling: The Gorakhnath Sharma case highlights the existing legal framework that protects husbands from rape charges for sex with wives over 15. This underscores the current legal immunity.
Supreme Court Petitions: The news mentions that the Supreme Court is actively hearing petitions to criminalize marital rape. This directly reflects the push for legal reform and the desire to challenge the existing status quo.
Contrasting Legal Stances: The news emphasizes the conflict between different legal perspectives:
Existing Law: The Indian Penal Code (IPC) and the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) currently offer immunity to husbands in cases of marital rape (with the exception of those involving wives under 18).
Judicial Rulings: While the law grants immunity, various court rulings (e.g., Independent Thought and KS Puttaswamy) have affirmed the importance of consent, sexual autonomy, and the rights of women. These rulings create a tension with the existing law.
Government’s Stance: The Ministry of Home Affairs’ statement shows reluctance to criminalize marital rape fully, highlighting a differing view from women’s rights advocates and potentially some within the judiciary.
Impact and Relevance of the Law:
- A fundamental Human Rights Issue:The criminalization of marital rape directly impacts women’s rights to personal autonomy, equality, and freedom from violence.
- Comparison to Global Standards:The article highlights that marital rape is criminalized in a majority of countries around the world, and the news of the SC hearing petitions to criminalize marital rape is an indicator of the desire to align with these international standards.
- Recent Judicial Pronouncements: the text highlights that the text highlights that in 2023, the Bombay HC ruled that consensual sex with a minor wife is rape, rejecting the defense of consent in such cases. In 2024, the Madhya Pradesh HC ruled that unnatural sex with a wife is not rape and that a wife’s consent is irrelevant in such matters. These rulings create a tension with the existing law.
- Potential Solutions and Reforms:The article outlines possible actions, such as raising the marriage age, legislative amendments, alternative legal frameworks and reviewing global best practices. These underscore the recognition that changes are needed and highlight the importance of the debate.
- In essence, the news is centered on the ongoing legal and social debate in India about whether or not to criminalize marital rape. The differing legal stances, judicial pronouncements, and the desire for reform are all major factors as to why this issue has gained prominence in the news cycle.
What potential solutions are outlined in the article to address the issue of marital rape?
- Raising the marriage age, legislative amendments, alternative legal frameworks, and reviewing global best practices
- Only raising the marriage age
- Only legislative amendments
- Only alternative legal frameworks
Correct Answer: a) Raising the marriage age, legislative amendments, alternative legal frameworks, and reviewing global best practices
Strait of Hormuz
Latest News
- Amid escalating tensions with the United States, Iranhas deployed missile systems on the three disputed islands—Greater Tunb, Lesser Tunb, and Abu Musa—located near the Strait of Hormuz.
- This move highlights Iran’s strategic control over this critical maritime passage and raises concerns over regional security and global energy supply disruptions.

Key Facts About the Strait of Hormuz
Geographical Significance:
- The Strait of Hormuzis a narrow yet strategically vital waterway that lies between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula, specifically the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Oman’s Musandam Peninsula.
- It serves as a critical maritime route connecting the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Omanand further to the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean.
Geopolitical Boundaries:
- Northern Coast:Iran
- Southern Coast:United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Oman
- Western End:Persian Gulf
- Eastern End:Gulf of Oman
- Dimensions & Navigability:
- The Strait of Hormuz stretches for 167 kilometersin length.
- The width varies from 95 kilometers at its broadest point to just 39 kilometers at its narrowest.
- Despite its narrowing towards the north, it remains deep enough for the passage of large oil tankers and cargo vessels.
Islands in the Strait of Hormuz:
- Hengam Island
- Hormuz Island
- Qishm Island
- Greater Tunb, Lesser Tunb, and Abu Musa (disputed between Iran and UAE)
Economic & Strategic Importance:
- It is one of the world’s most critical choke points for global energy trade.
- Approximately 25% of the world’s crude oiland 30% of the world’s liquefied natural gas (LNG) pass through this waterway.
- Disruptions in the Strait of Hormuzcan significantly impact global oil prices and energy security.
Consider the following statements regarding the Strait of Hormuz:
- It connects the Persian Gulf to the Arabian Sea.
- It is the narrowest maritime chokepoint for global oil transportation.
- The United States maintains a permanent naval base on Abu Musa Island to secure energy trade.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Strait of Hormuzconnects the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Oman, which in turn leads to the Arabian Sea.
- Statement 2 is correct: It is one of the narrowest and most critical maritime chokepointsfor global oil transportation, with a width narrowing to 39 km at its tightest point.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The United States does not maintain a permanent naval base on Abu Musa Island. The island is disputed between Iran and the UAE, and Iran has control over it. The S. does, however, maintain a strong naval presence in the regionthrough its 5th Fleet, headquartered in Bahrain.
World’s Largest Grain Storage Plan in Cooperative Sector
Why in News?
- On May 31, 2023, the Government approved the World’s Largest Grain Storage Plan in the Cooperative Sector, set to be implemented as a Pilot Project.
- This initiative aims to develop agricultural infrastructureat the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) level, including:
Construction of godowns
- Establishment of custom hiring centers
- Setting up of processing units
The project integrates various existing Government of India (GoI) schemes, such as:
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)
- Agricultural Marketing Infrastructure Scheme (AMI)
- Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM)
- Pradhan Mantri Formalization of Micro Food Processing Enterprises Scheme (PMFME)
Progress of the Pilot Project
- Under the Pilot Project, godowns have been constructed in 11 PACS across 11 States, with a total storage capacity of 9,750 Metric Tons (MT).
State-wise Details of Completed Godowns
|
- Additionally, foundation stones have been laid for 500 additional PACS godownsunder the Pilot Project, with a total of 575 PACS identified for implementation across various States/UTs.
Expansion and Future Goals
- The Ministry of Cooperationaims to establish and strengthen 2 lakh multipurpose PACS, Dairy, and Fishery Cooperative Societies across all panchayats and villages in the country.
- To guide this process, a Margdarshika (Standard Operating Procedure)has been introduced.
- In Karnataka, 128 PACS have been establishedagainst a target of 218 PACS to be formed by FY 2028-29.
Impact of the World’s Largest Grain Storage Plan
Decentralized Storage Capacity:
- 9,750 MTof storage capacity has been created at the PACS level.
Reduction in Food Grain Wastage:
- Prevents post-harvest lossesby ensuring adequate storage facilities.
Strengthening of Food Security:
- Ensures better storage and distribution of food grainsto enhance national food security.
Preventing Distress Sales:
- Farmers can store their produce and sell it at better pricesrather than being forced into distress sales.
Cost Reduction in Transportation:
- Since PACS can function as both procurement centersand Fair Price Shops (FPS), transportation costs are reduced.
- Avoids the need to transport grains from procurement centers to warehousesand back to FPS.
- This initiative marks a major milestonein strengthening the cooperative sector and enhancing agricultural infrastructure across India.
Consider the following statements regarding the “World’s Largest Grain Storage Plan in the Cooperative Sector”:
- It is being implemented exclusively under the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF).
- The plan aims to develop agri-infrastructure at the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) level.
- One of the objectives of the plan is to enable PACS to operate as procurement centers as well as Fair Price Shops (FPS).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The plan is not implemented exclusivelyunder AIF; rather, it converges multiple schemes like Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF), Agricultural Marketing Infrastructure Scheme (AMI), Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM), and Pradhan Mantri Formalization of Micro Food Processing Enterprises Scheme (PMFME).
- Statement 2 is correct: The plan focuses on strengthening PACSby developing godowns, custom hiring centers, and processing units.
- Statement 3 is correct: The initiative allows PACS to function as procurement centers and Fair Price Shops (FPS), reducing transportation costs and logistical challenges.
Lake Sapanca
Lake Sapanca in Türkiye is facing severe environmental degradation due to urbanization, industrial expansion, and agricultural runoff, leading to increased pollution and habitat destruction.

About Lake Sapanca:
Location:
Situated in northwestern Türkiye, between the Gulf of İzmit and Adapazarı Meadow.
Lies in a tectonic depression, running parallel to Iznik Lake.
Bordering Nations:
Türkiye’s Sakarya Province is home to the lake.
The catchment area is 251 km², surrounded by mountains in the south and small hills in the north.
River Inflows: The lake has multiple inflows from small streams originating from surrounding mountains. It serves as a primary freshwater source for domestic and industrial purposes.
Key Issues:
- High nutrient loads (Nitrogen & Phosphorus) due to agricultural runoff & wastewater discharge, leading to eutrophication.
- Urban expansion & deforestation reducing water retention capacity.
- Seasonal pollution peaks observed in summer due to low water flow.
During which season are seasonal pollution peaks typically observed in Lake Sapanca, and why?
(a) Winter, due to increased snow melt
(b) Spring, due to heavy rainfall
(c) Summer, due to low water flow
(d) Autumn, due to leaf decomposition
Correct Answer: Summer, due to low water flow
Sovereign Green Bonds
India, like many emerging markets, is employing sovereign green bonds (SGrBs) to fund its transition to a low-carbon economy. Despite this, investor demand for these bonds has remained weak.
India’s Green Bond Efforts
Since 2022-23, India has issued SGrBs eight times, raising approximately Rs 53,000 crore. However, these issues have struggled to gain traction due to a lack of investor interest, making it challenging for the government to secure a greenium.
Greenium and Bond Yields
Globally, greeniums have reached 7-8 basis points, while in India, it is often at just 2–3 basis points. Greeniums reflect the difference in yield between green bonds and conventional bonds. A higher greenium indicates a lower yield and, therefore, a cost advantage for the issuer.
Green Bonds:
Green bonds are debt instruments issued by governments, corporations, and multilateral banks to raise funds for projects that reduce emissions or enhance climate resilience. These bonds are typically offered at lower yields than conventional bonds, assuring investors that the proceeds will be used exclusively for green investments.
Sovereign Green Bonds (SGrBs)
Sovereign green bonds (SGrBs) are issued by sovereign entities, such as the Government of India. India formulated a framework for issuing these bonds in 2022, defining “green projects” as those that promote:
* Energy efficiency in resource utilization
* Reduced carbon emissions
* Climate resilience
* Improved natural ecosystem
What is the primary purpose of India’s sovereign green bonds (SGrBs)?
- a) To raise funds for infrastructure development
- b) To promote foreign direct investment
- c) To fund the transition to a low-carbon economy
- d) To stimulate economic growth
Answer: c) To fund the transition to a low-carbon economy
New Income Tax Bill 2025 Highlights
- It replaces terms like ‘previous year’ with ‘tax year’ and does away with ‘assessment year.’
- Streamlined to 566 pages (proposed) from over 800 pages (existing).
Modernization: The bill aims to modernize India’s tax system.
Key Goals (Finance Ministry):
- Enhance readability by eliminating intricate language.
- Improve navigation by removing redundant provisions.
- Facilitate ease of reference by reorganizing sections logically.
Tax Slabs (New Regime):
- 0 – ₹4 lakh: 0%
- ₹4-8 lakh: 5%
- ₹8-12 lakh: 10%
- ₹12-16 lakh: 15%
- ₹16-20 lakh: 20%
- ₹20-24 lakh: 25%
- Above ₹24 lakh: 30%
Relief for Middle Class: The exemption limit has been raised, and slabs have been rejigged. For salaried employees, the nil tax limit will be ₹12.75 lakh per annum, after taking into account a standard deduction of ₹75,000.
Access to Data: Tax authorities will have access to email servers, online investment accounts, trading and bank accounts, social media accounts, and digital application servers during searches.
Bill Stats:
- The number of chapters has been halved from 47 to 23.
- There are 57 tables (vs. 18 in the existing Act).
- It removes 1,200 provisions and 900 explanations.
- The word count is 2.6 lakh (vs. 5.12 lakh in the existing Act).
Tax Certainty: The bill aims to minimize litigation and fresh interpretation.
Support for Key Sectors: The bill includes new provisions to support startups, digital businesses, and renewable energy investments (Clauses 11-154).
Dispute Resolution: The bill specifies that the Dispute Resolution Panel will need to pass speaking orders with reasons to decide on objections taken by taxpayers.
Detailed Framework for Non-profits: The bill establishes a more detailed framework for non-profit organizations (Clauses 332-355).
Cryptocurrency Provisions: The bill introduces provisions for virtual digital assets and updates tax rates (Clauses 67-91).
Updated Return Timeline: The time frame for filing updated returns is extended from two to four years.
Reduced Sections: The bill aims to reduce the number of sections by 25-30%.
Largely Unchanged Concepts: Concepts like indirect transfers, GAAR, capital gains, SEP, taxation of royalty/FTS, tax rates, and residential status remain largely unchanged.
Modernization: Restructuring transforms 298 sections (effectively 819 sections) into 536 clauses.
Backlogs: A time limit has been set for disposing of appeals at the first appellate authority level.
Simpler Language: The bill attempts to simplify the language of the legislation.
Tax Year: The bill will replace terms such as “assessment year” and “previous year” with “tax year.”
Taxpayer-Centered Reforms: FM Sitharaman listed the new bill among the center’s taxpayer-centered reforms.
Suggestions: The income tax portal is still inviting suggestions from people with regards to the new tax bill under the section ‘new.’
The New Income Tax Bill extends the timeframe for filing updated returns from:
- 1year to 3 years
- 2 years to 4 years
- 3 years to 5 years
- There is no change in the timeframe.
Answer: b) 2 years to 4 years
Devolution Index Report
The recently published Devolution Index Report represents a significant milestone for rural local self-governance in India. This detailed document evaluates the state of decentralization across various states and Union Territories, with the goal of empowering Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) and fulfilling the vision of “Local Self Government” as outlined in the 73rd Constitutional Amendment.
About the Devolution Index
The Devolution Index is the product of extensive research and analysis, assessing India’s progress in decentralisation by focusing on six essential dimensions: Framework, Functions, Finances, Functionaries, Capacity Building, and Accountability. Each of these dimensions is crucial for determining the effectiveness of Panchayati Raj Institutions.
Key Dimensions of the Index
- Evaluates the legal and institutional structures that support Panchayati Raj.
- Functions:Examines the range of responsibilities assigned to Panchayats.
- Finances:Assesses the financial autonomy and resource allocation for local bodies.
- Functionaries:Reviews the human resources available and their capacity to perform their duties effectively.
- Capacity Building:Focuses on training and development opportunities for Panchayat members.
- Accountability:Evaluates the mechanisms ensuring transparency and responsibility within local governance.
Empowerment of Panchayats
The Index specifically investigates the autonomy that Panchayats possess in decision-making, reflecting the essence of Article 243G of the Constitution of India, which empowers state legislatures to devolve powers to Panchayats over 29 subjects listed in the Eleventh Schedule.
Utility for Multiple Stakeholders
- The Devolution Index serves a diverse range of stakeholders:
- Citizens benefit from increased transparency regarding Panchayat operations and resource distribution.
- Elected representatives gain data-driven insights for advocating necessary reforms.
- Government officials receive a roadmap for implementing effective decentralisation policies.
- Policymakers can assess the health of local governance and identify areas that require urgent reform.
- Alignment with Viksit Bharat Vision
- This initiative is in line with the Viksit Bharat vision, wherein developed and empowered Panchayats serve as the backbone for rural transformation. The Index aims to promote inclusive growth and sustainable development at the grassroots level
Future Implications
- The Devolution Index is poised to strengthen cooperative federalism in India. It encourages states to identify areas for improvement and adopt best practices for enhancing the effectiveness of Panchayati Raj Institutions. This initiative is crucial for improving local self-governance and ensuring responsive governance in rural areas.
How can citizens benefit from the Devolution Index?
- A) By receiving monetary compensation
- B) By increased transparency regarding Panchayat operations and resource distribution
- C) By direct involvement in legislative processes
- D) By obtaining employment in government offices
Answer: B) By increased transparency regarding Panchayat operations and resource distribution
Tobin Tax
The U.S. President Donald Trump’s administration is contemplating implementing a Tobin Tax on capital flows, a decision that could potentially disrupt global financial markets.
About the Tobin Tax: Definition: The Tobin Tax is a levy on foreign exchange transactions designed to discourage short-term speculative trading. Typically, it involves a small tax rate (0.1%-0.5%) applied to currency conversions to reduce volatility in financial markets.
Origin and Theory: Proposed in 1972 by Nobel laureate James Tobin, the tax was conceived as a response to currency market instability following the collapse of the Bretton Woods system. Tobin’s objective was to “throw sand in the wheels” of currency speculation, thereby stabilizing exchange rates.
Key Features:
- Application to currency transactions to discourage short-term speculation.
- A low tax rate intended to prevent market disruption.
- Potential revenue generation for public welfare or development projects.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
Market Stability | Reduces speculative trading and market volatility. | May reduce market liquidity. |
Revenue Generation | Can generate substantial revenue for governments. | Difficult to implement uniformly across nations. |
Currency Protection | Helps protect weaker currencies from speculative attacks. | May increase transaction costs for businesses and investors. |
Fairer Global Economy | Limits the financial power of hedge funds and large investors. | Could incentivize financial transactions to move to tax-free zones or offshore havens. |
What is the typical tax rate associated with a Tobin Tax on currency conversions?
(a) 5%-10%
(b) 1%-2%
(c) 0.1%-0.5%
(d) 10%-20%
Correct Answer: 0.1%-0.5%
India’s Pharmaceutical Exports Set for 10x Growth
- Capabilities, solidifying its position as a vital component of the global pharmaceutical value chain.
Current Global Market Status
- India stands as the largest global supplier of generic drugs, contributing 20% to worldwide sales.
- India ranks third in terms of drug and pharmaceutical production by volume.
- Exports span approximately 200 countries and territories.
- The primary export destinations include the USA, Belgium, South Africa, the UK, and Brazil.
- Despite being a key global player in generics, India ranks 11th in terms of pharmaceutical export value.
- The total annual turnover of pharmaceuticals in FY24 was ₹4.17 lakh crore, reflecting an average growth rate of 10.1% over the past five years.
Export Projections
India’s pharmaceutical exports are expected to rise from $27 billion in 2023 to $65 billion by 2030. This growth is anticipated to shift from volume-based to value-driven strategies, focusing on key areas such as Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs), biosimilars, and specialty generics.
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API):
India’s API exports are projected to grow from $5 billion to $80-90 billion by 2047.Global supply chain diversification, particularly in light of the U.S. Biosecure Act, presents an opportunity for India to bolster API production.
Biosimilars:
- Current biosimilar exports are valued at $0.8 billion, with expectations to increase fivefold to $4.2 billion by 2030, and to $30-35 billion by 2047.
- This growth will be supported by enhanced R&D, regulatory simplifications, and capacity expansions.
- Biosimilars are medications that closely resemble biologic drugs created through living systems, showcasing comparable structure and functionality.
Generic Formulations:
- Accounting for 70% of India’s pharmaceutical exports, generic formulations are valued at $19 billion.
- These exports are projected to grow to $180-190 billion by 2047, with a notable shift towards higher-margin specialty generics.
Policy and Strategic Measures
The Indian government has initiated several programs to promote the pharmaceutical sector and stimulate investment:
- In September 2020, the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme was introduced for the pharmaceutical sector as part of the Self-Reliant India initiative, with a budget of ₹15,000 crore allocated from 2020-2021 to 2028-29.
- Targeted policy measures are vital, including strengthening the API industry, addressing export barriers, and developing country-specific export strategies.
- India supplies 55-60% of UNICEF’s vaccines but should aim to expand its presence in high-value markets through clinical trials and manufacturing investments.
- Key enablers for growth include regulatory harmonization, expansion of PLI, and R&D incentives.
Challenges
India faces several obstacles, including issues related to intellectual property rights and limited R&D capabilities. It is crucial to understand the political, economic, sociocultural, technological, environmental, and legal factors when assessing the opportunities and challenges within the Indian pharmaceutical market.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
As a global leader in generic drug supply, India aims to ascend the value chain by focusing on specialty generics, biosimilars, and innovative products. This strategic shift could position India among the top five nations in export value by 2047. With aspirations to become the “healthcare custodian of the world,” the nation is prioritizing innovation, R&D, and regulatory improvements. Collaboration between academia, industry, and government will be essential in establishing a robust, globally competitive pharmaceutical sector.
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding India’s position in the global pharmaceutical market?
- India ranks first in terms of pharmaceutical export value.
- India is the largest global supplier of generic drugs, accounting for 20% of global sales.
- India does not export pharmaceuticals to many countries.
- India ranks fourth in drug production by volume.
Answer: B) India is the largest global supplier of generic drugs, accounting for 20% of global sales.
