Neutral Conditions to Prevail in Pacific Ocean: US Weather Monitor
Syllabus: GS1/Geography
- The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has forecasted that ENSO-neutral conditions will continue to dominate the Pacific Ocean through October 2025. This indicates the absence of El Niño or La Niña phenomena, collectively referred to as the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO).
What is ENSO?
- The El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a natural climate pattern resulting from interactions between the ocean and atmosphere in the equatorial Pacific Ocean, and it influences global weather.
ENSO has three phases:
El Niño:
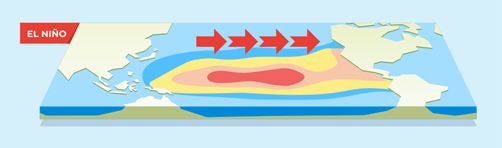
- Warming of central and eastern Pacific Ocean waters.
- Weakens monsoons in India and Australia.
- Brings heavy rains to South America and floods in the southern U.S.
La Niña:
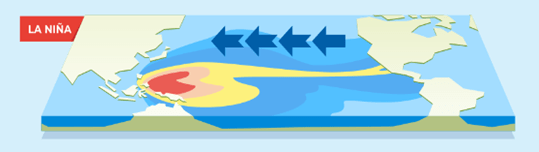
- Cooling of ocean surface temperatures in the same region.
- Strengthens monsoons in South Asia.
- Triggers droughts in the U.S. Southwest and enhances Atlantic hurricane activity.
Neutral:
- Sea surface temperatures remain near the long-term average.
- No dominant El Niño or La Niña conditions.
- Southern Oscillation:
- The atmospheric component of ENSO, measured by the Southern Oscillation Index (SOI), tracks pressure differences between Tahiti and Darwin.
Recent Trends
- A short and weak La Niña earlier in 2025 has transitioned into neutral conditions.
- Sub-surface ocean temperatures have normalized, confirming the end of La Niña.
India’s Monsoon Outlook
- ENSO-neutral conditions are usually associated with normal or above-normal monsoon rainfall in India.
- This is encouraging for Indian agriculture, as nearly 70% of annual rainfall occurs during the June–September monsoon season.
Future Outlook
- NOAA estimates a 50% chance that ENSO-neutral conditions will continue through August–October 2025.
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) will soon release its Long-Range Monsoon Forecast, factoring in these conditions.
- Ongoing monitoring of sea surface temperatures and atmospheric changes is essential for timely detection of El Niño or La Niña developments.
With reference to the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO), consider the following statements:
- El Niño events are generally associated with suppressed Atlantic hurricane activity.
- La Niña strengthens the Walker circulation, leading to intensified trade winds.
- ENSO-neutral conditions always imply the absence of extreme weather events globally.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A. 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct. El Niño suppresses Atlantic hurricane activity by increasing wind shear in the region.
- Statement 2 is correct. La Niña enhances the Walker circulation and strengthens trade winds, pushing warm water westward.
- Statement 3 is incorrect. ENSO-neutral conditions reduce the probability of ENSO-linked extreme events, but do not eliminate the occurrence of other extreme weather events caused by unrelated climatic factors.
Plastic Parks in India
Syllabus: GS 3/Environment
- The Plastic Parks Scheme is gaining prominence as a strategic initiative to promote industrial development and environmental sustainability within India’s plastics sector.
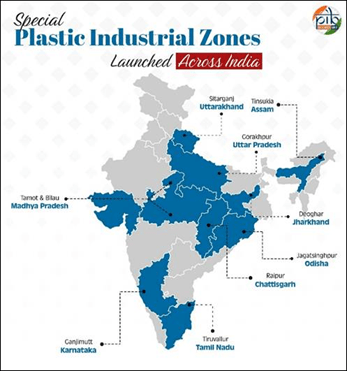
What are Plastic Parks?
- Plastic Parks are dedicated industrial zones developed specifically for plastic processing and allied industries. These parks aim to:
- Consolidate and synergize the fragmented plastic processing sector.
- Attract investments and boost production and exports.
- Generate employment and enhance technological innovation.
- Promote environmentally sustainable practices through integrated waste management and recycling systems.
Significance and Progress:
- Plastic Parks form a critical component of India’s broader strategy for plastic waste management and circular economy.
- India is now 12th globally in plastic exports, with figures rising from $8.2 billion in 2014 to $27 billion in 2022, largely due to proactive policy measures like this scheme.
- So far, 10 Plastic Parks have been approved across various states.
Challenges in the Sector:
- The Indian plastics industry, though substantial, is highly fragmented, dominated by micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs).
- These units often lack the infrastructure and scale to compete globally or implement sustainable practices effectively.
Government Interventions:
- The Department of Chemicals and Petrochemicals is implementing the scheme to establish state-of-the-art infrastructure for plastic parks.
- A cluster development approach is used to enable shared common facilities, including recycling and innovation hubs.
- The Government of India provides financial assistance up to 50% of the project cost, subject to a maximum of ₹40 crore per park.
Conclusion:
The Plastic Parks Scheme represents a transformative initiative to bolster India’s plastic processing industry by promoting scale, sustainability, and competitiveness. As India’s share in global plastic trade expands, these parks will be pivotal in ensuring inclusive, innovative, and eco-conscious growth, aligning with national objectives of ‘Make in India’ and sustainable development.
Consider the following statements regarding the Plastic Parks Scheme:
- It is implemented by the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers.
- The scheme provides 100% central assistance for the development of parks.
- It aims to promote cluster development and common infrastructure.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B. 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The scheme is indeed implemented by the Department of Chemicals and Petrochemicals, under the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The GoI provides financial assistance up to 50%, not 100%, with a cap of ₹40 crore per park.
- Statement 3 is correct: It adopts a cluster development approach to build shared infrastructure and common facilities.
Powering India’s Participation in Global Value Chains Report
Syllabus: GS3/Indian Economy
Overview
- NITI Aayog has released a comprehensive report analyzing the status, opportunities, and challenges of India’s automotive industry.
- The document outlines a strategic roadmap to position India as a major contributor to global automotive value chains (GVCs).
Key Highlights
Global Trends in the Automotive Sector
- Shift in Supply Chains: Emergence of battery manufacturing hubs in Europe and the U.S. is reshaping traditional supply chains.
- Industry 4.0 Revolution: Advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Internet of Things (IoT), and robotics are enabling smart factories and connected vehicles, redefining manufacturing paradigms.
- Rising Input Costs: Semiconductor costs per vehicle are projected to increase from $600 to $1,200 by 2030.
- Global Auto Component Market: Estimated at $2 trillion (2022), with $700 billion traded globally.
- Global Automobile Production: Approximately 94 million units manufactured globally, growing at 4–6% annually.
India’s Position
- India ranks as the 4th-largest automobile producer, after China, the U.S., and Japan.
- Annually, India produces nearly 6 million vehicles.
- Stronghold in small cars and utility vehicle segments, with robust domestic and export demand.
- Under the ‘Make in India’ initiative, India is increasingly becoming a global manufacturing hub.
Challenges
- Limited Share in Component Trade: Despite its production strength, India contributes only 3% to the global automotive component trade (valued at ~$20 billion).
- Low Precision Manufacturing Share: India accounts for only 2–4% in high-value segments like engine components and transmission systems.
- Structural Barriers: High operational costs, infrastructural deficiencies, low R&D expenditure, and limited integration with global value chains hinder competitiveness.
Key Recommendations
- Opex and Capex Support: Government support for manufacturing scale-up, especially tooling, infrastructure, and die-making.
- Skill Development: Developing a skilled workforce aligned with technological advances.
- R&D, IP, and Branding: Incentives for R&D, international branding efforts, and IP transfers to support MSMEs and drive innovation.
- Cluster-Based Development: Creating automotive clusters with shared R&D and testing infrastructure to strengthen the supply chain ecosystem.
- Adoption of Industry 4.0: Promoting digitalization, smart manufacturing, and compliance with international standards.
- International Collaboration: Fostering joint ventures, foreign direct investment, and leveraging Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) for market expansion.
- Ease of Doing Business: Streamlining regulatory mechanisms, promoting flexible labour norms, and enhancing supplier networks.
Way Forward
Production and Export Targets:
- Auto component production expected to grow to $145 billion.
- Exports projected to triple to $60 billion, leading to a trade surplus of $25 billion.
- Employment Generation: Estimated to create 2–2.5 million jobs.
- GVC Integration: India aims to enhance its global value chain participation from 3% to 8%.
Conclusion
- India stands at a critical juncture with the potential to become a global leader in the automotive industry. Strategic interventions, collaborative policymaking, and technology adoption are essential to overcome structural constraints.
- By capitalizing on global trends and domestic strengths, India can drive inclusive, sustainable, and innovation-led growth in the automotive sector.
With reference to India’s automotive sector, consider the following statements:
- India is the third-largest global automobile producer, just behind China and the United States.
- India’s share in the global automotive component trade is significantly higher than its share in complete automobile exports.
- The majority of India’s automotive exports are in the heavy commercial vehicles and luxury sedan categories.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. None
D. 1 and 2 only
Answer: C. None
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: India is the fourth-largest automobile producer after China, USA, and Japan.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: India has a modest share (~3%) in the global component trade, whereas it performs better in complete vehicle exports, especially in small cars and utility vehicles.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: India’s strengths lie in small cars and utility vehicles, not in heavy commercial or luxury segments.
India Ends Transshipment for Bangladesh Exports
Syllabus: GS2/IR
Context
- India has officially withdrawn the transshipment facility that previously allowed Bangladesh to export goods to third countries via Indian land customs stations, ports, and airports, marking a significant development in regional trade logistics.
About the Transshipment Agreement
- Introduced in 2020 by India’s Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC).
- Aimed at enhancing regional trade cooperation and logistics efficiency for Bangladesh by enabling its cargo to transit through Indian infrastructure.
- Facilitated seamless Bangladeshi exports to Europe, West Asia, and other global destinations via India’s multimodal transport network.
Why Was It Revoked?
- Primary Concern: Rising logistical congestion at Indian airports and ports.
Resulted in:
- Delays in India’s own export consignments.
- Backlogs in cargo handling.
- Escalation in operational costs for Indian exporters.
- Decision aligns with India’s need to prioritize domestic trade efficiency amidst increasing global trade competitiveness.
Implications for Bangladesh
- Expected to increase logistics costs and transit time for Bangladeshi exports, especially to Western markets.
- Could potentially divert Bangladesh’s trade alignment toward alternate regional corridors, possibly involving Chinese infrastructure partnerships.
India-Bangladesh Relations: A Comprehensive Overview
Historical Foundations
- 1971 Liberation War: India’s support for the Bengali nationalist movement laid the groundwork for robust bilateral ties.
- Land Boundary Agreement (2015): Resolved a 70-year-old dispute by exchanging enclaves and streamlining borders.
- Connectivity Milestones
Rail Connectivity:
- Revival of five pre-1965 rail links.
- Operational trains: Maitri Express, Bandhan Express, Mitali Express.
Cross-Border Infrastructure:
- Inauguration of Akhaura–Agartala rail link improves access to Northeast India.
- Economic Interdependence
Trade Volume (FY 2023–24):
- Total Bilateral Trade: US$ 12.90 billion
- Indian Exports to Bangladesh: US$ 11.06 billion
- Bangladesh is India’s largest trading partner in South Asia; India is Bangladesh’s second largest partner in Asia.
- Trade Frameworks
Multilateral Trade Agreements:
- Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA)
- SAARC Preferential Trade Agreement (SAPTA)
- South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA)
- Regional and Strategic Cooperation
- Active participation in SAARC and BIMSTEC.
Joint Military Exercises:
- Sampriti (Army)
- Milan (Navy)
Energy Security:
- Bangladesh imports ~2,000 MW of electricity from India.
Challenges in Bilateral Engagement
Border Security Issues:
- Despite LBA, illegal crossings, smuggling, and occasional border skirmishes
Teesta Water Dispute:
- Long-pending issue causing political tension and water stress.
Trade Imbalance:
- Heavy tilt in favor of India triggers economic anxieties in Bangladesh.
Cross-border Migration:
- Sensitive issue in Indian domestic politics, especially in Assam and West Bengal.
Security Threats:
- Extremist groups and cross-border smuggling require continuous vigilance.
China’s Expanding Footprint:
- Strategic investments in Bangladesh’s infrastructure and defense seen as a challenge to India’s traditional sphere of influence.
Way Forward
- India must balance national logistics interests with its commitment to regional cooperation.
- Bangladesh remains a critical strategic ally in South Asia:
- Shares the longest land boundary with India.
- Acts as a gateway to the Northeast.
Strategic roadmap should include:
- Revitalizing dialogue on water sharing and trade.
- Collaborating on green logistics and port infrastructure.
- Enhancing people-to-people ties and cultural diplomacy.
Conclusion
- India-Bangladesh relations are a blend of shared history, economic interdependence, and strategic cooperation.
- While the revocation of the transshipment facility signals logistical recalibration, sustained diplomatic engagement and policy innovation are essential to ensure that the bilateral relationship continues to evolve on the pillars of mutual respect, economic pragmatism, and regional integration.
Consider the following statements regarding the transshipment facility extended by India to Bangladesh:
- It allowed Bangladeshi goods to transit through Indian ports and airports for export to third countries.
- It was introduced by India’s Ministry of External Affairs in 2020.
- The facility was revoked primarily due to strategic concerns over China’s growing influence in Bangladesh.
Which of the statements is/are correct?
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 2 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A) 1 only
- Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct – the facility allowed Bangladeshi cargo to transit through Indian infrastructure to reach global markets. - Statement 2 is incorrect – the scheme was introduced by the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC), not the Ministry of External Affairs.
- Statement 3 is incorrect – the facility was revoked due to logistical congestion, not directly because of geopolitical concerns.
The Magic of Indian Silk
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
India’s Silk Sector: An Introduction
- India’s raw silk production has witnessed a consistent upward trajectory, increasing from 31,906 metric tonnes (MT) in 2017–18 to 38,913 MT in 2023–24, reflecting strategic interventions and government support.
What is Sericulture?
- Sericulture refers to the cultivation of silkworms for silk production. The process involves:
- Rearing silkworms primarily on mulberry, oak, castor, and arjun
- Within a month, the worms spin cocoons.
- The cocoons are harvested, boiled to loosen the threads, and silk fibers are reeled, twisted into yarn, and woven into fabrics.
Lifecycle of the Silkworm Moth:
- Egg →
- Larva (caterpillar/silkworm) →
- Pupa (inside cocoon) →
- Moth (adult stage)
India’s Position in the Global Silk Industry
- India is the second-largest producer and consumer of silk
- Despite this, silk comprises only 2% of total global textile production.
- India produces four varieties of natural silk:
- Mulberry (dominant)
- Eri
- Tasar
- Muga
- Major Silk-Producing States
- Karnataka (largest producer)
- Followed by: Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh
Silk Production & Export Trends
- Exports of silk and silk goods increased from ₹1,649.48 crore in 2017–18 to ₹2,027.56 crore in 2023–24.
- In 2023–24, India exported 3,348 MT of silk waste, which includes leftover or imperfect silk such as broken fibers and cocoon fragments.
Key Government Initiatives
- Silk Samagra Scheme
- Launched to enhance silk production and quality, while empowering underprivileged and rural families through sericulture.
It includes four key components:
- Research & Development, Training, Technology Transfer, and IT Initiatives
- Seed Production and Supply Chains
- Market Coordination and Infrastructure Development
- Quality Certification, Export Branding, and Technology Upgradation
- North East Region Textile Promotion Scheme (NERTPS)
- Specifically targets sericulture development in North-Eastern States.
- Focus on promoting Eri and Muga silk, which are indigenous to the region.
- Aims to revive, diversify, and expand silk-based livelihoods in the region.
- Indian Silk Export Promotion Council (ISEPC)
- Sponsored by the Ministry of Textiles.
- Apex body for exporters, manufacturers, and traders of silk.
Functions:
- Explore international markets
- Organize trade fairs, buyer-seller meets
- Resolve trade disputes
- Strengthen export competitiveness
Conclusion
- Sericulture in India is more than an industry—it’s a source of sustainable rural livelihood, cultural heritage, and economic growth. Through dedicated schemes like Silk Samagra and institutional support via ISEPC, India continues to boost its silk production, quality, and global outreach, with a strong focus on inclusive development and traditional skills.
Consider the following statements regarding the varieties of silk produced in India:
- Eri and Muga silks are exclusively reared on mulberry leaves.
- Mulberry silk accounts for the majority share in India’s overall silk output.
- Muga silk is traditionally associated with Assam and is known for its golden sheen.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 2 and 3 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 3 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Eri and Muga silkworms are non-mulberry varieties. Mulberry leaves are specific to Mulberry silk.
- Statement 2 is correct: Mulberry is the dominant variety produced in India.
- Statement 3 is correct: Muga silk, native to Assam, is noted for its natural golden luster and is culturally significant in the region.
Naxalmukt Bharat Abhiyan: From Red Zones to Growth Corridors
Syllabus: GS3/ Internal Security
Genesis of the Naxalite Movement
- The Naxalite movement traces its roots to Naxalbari village in West Bengal (1967), where a radical leftist uprising emerged advocating land redistribution and tribal rights.
- Drawing ideological inspiration from Maoist doctrines, it rapidly transformed into an armed insurgency targeting the Indian state.
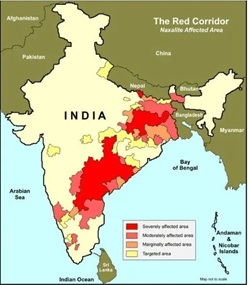
Geographical Spread: The Red Corridor
- The insurgency expanded across the “Red Corridor”, encompassing parts of:
- Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, Maharashtra
- West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana
- Madhya Pradesh, Kerala
This region has historically been marked by socio-economic backwardness, poor governance, and tribal marginalization—fertile ground for extremist ideologies.
Nature and Modus Operandi
Naxalite groups engage in:
- Guerrilla warfare and ambushes targeting state forces and infrastructure
- Extortion and taxation of local populations
- Child recruitment and radicalization
- Sabotage of developmental initiatives to maintain control
While projecting themselves as protectors of the oppressed, their methods often perpetuate fear and lawlessness.
Consequences of Naxalism
- Political Impacts
- Erodes state authority and weakens democratic institutions
- Creates governance vacuums, making administration ineffective
- Economic Impacts
- Disrupts agriculture, mining, and infrastructure projects
- Escalates public expenditure on security, crowding out development
- Deters private investment in high-risk regions
- Social Impacts
- Fuels alienation and mistrust among tribal and rural communities
- Hampers access to healthcare, education, and public services
- Undermines human development indices in affected zones
India’s Progress Against LWE
Significant Improvements (2010–2024):
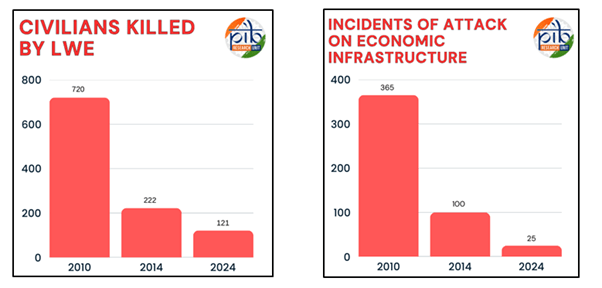
- Reduction in LWE-affected districts: From 126 in 2010 to 38 in 2024
- Violence down by 81%: From 1,936 incidents in 2010 to 374 in 2024
- Over 8,000 cadre surrenders in the last decade
Enhanced developmental outreach, with visible improvements in:
- Connectivity
- Healthcare and education
- Governance and administrative presence
Key Government Initiatives
- Security Related Expenditure (SRE) Scheme
- Sub-scheme under the Modernization of Police Forces (MPF)
- Reimbursement of security-related costs for LWE-affected districts
- SAMADHAN Strategy
- A multi-pronged approach:
- Smart Leadership
- Aggressive Strategy
- Motivation and Training
- Actionable Intelligence
- Dashboard-based Monitoring (KPIs/KRAs)
- Harnessing Technology
- Localized Action Plans
- Financial Deprivation of Extremist Networks
- Fortified Police Stations
- 612 stations built in high-risk zones to enhance security and outreach
- Aspirational Districts Programme
- The Ministry of Home Affairs oversees 35 LWE-affected districts
- Focus on health, education, infrastructure, and livelihood generation
- Special Central Assistance (SCA)
- ₹30 crore/year to most-affected districts
- ₹10 crore/year to “Districts of Concern”
- Aimed at bridging infrastructure gaps and accelerating development
Way Forward
- Community Engagement
- Empower tribal institutions and promote participatory governance
- Initiate confidence-building measures with local populations
- Education and Employment
- Provide skill development, education, and employment avenues
- Target youth populations to prevent radicalization and recruitment
- Technological Integration
- Deploy advanced surveillance, communication systems, and intelligence tools
- Promote e-governance and digital inclusion
Conclusion: Towards a Naxal-Free India
- The Government of India aims to eliminate Left-Wing Extremism by March 31, 2026, recognizing it as a key barrier to inclusive growth in tribal and remote regions.
- The success of the “Naxalmukt Bharat Abhiyan” rests on a balanced strategy that combines:
- Robust security operations
- Sustainable development
- Empowered local governance
- With sustained political will, administrative coordination, and local participation, the vision of a LWE-free India is well within reach.
Which of the following elements of the Government’s SAMADHAN Strategy directly aim at dismantling the financial and operational capacity of Naxalite groups?
- Actionable Intelligence
- Harnessing Technology
- No Access to Financing
- Action Plans for Each Theatre
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 4 only
C) 3 and 4 only
D) 1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: D) 1, 2, and 3 only
Explanation: Actionable intelligence helps in intercepting extortion networks, while harnessing technology enables tracking of financial channels and movements. “No Access to Financing” explicitly targets the economic backbone of LWE. “Action Plans for Each Theatre” is operational, not financial.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC)
Syllabus:Summits
Why in News?
- India and Italy have reaffirmed their commitment to enhancing strategic cooperation across critical sectors, following a high-level meeting in April 2025 between External Affairs Minister Dr. S. Jaishankar and Italian Deputy Prime Minister Antonio Tajani.
- The dialogue centered around the Joint Strategic Action Plan (JSAP) 2025–2029, a comprehensive roadmap unveiled during the bilateral meeting between Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Italian Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni in November 2024, on the sidelines of the G20 Summit in Rio de Janeiro.
Key Pillars of India–Italy Cooperation under JSAP (2025–2029)
The strategic agenda aims to diversify and deepen collaboration in the following domains:
- Trade and Investment
- Defence and Security
- Clean Energy Transition
- High-Technology and Digital Infrastructure
- Space and Scientific Research
- People-to-People and Educational Exchanges
- Emerging sectors for enhanced synergy include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Cybersecurity and Telecommunications
- Renewable Energy and Biofuels
- Higher Education and Youth Mobility
India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC)
- The India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC) is a landmark multimodal connectivity initiative aimed at enhancing trade and transport infrastructure between India, the Middle East, and Europe.
Launch and Strategic Significance
- Officially launched during the G20 Summit in New Delhi (2023) through a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) involving:
India, UAE, Saudi Arabia, France, Germany, Italy, the European Union, and the United States. - IMEEC is embedded within the broader Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII), an initiative introduced at the G7 Summit 2021 (UK).
- It is widely perceived as a strategic alternative to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), offering a transparent and rules-based infrastructure framework.
Structure of IMEEC
- The Corridor is divided into two major components:
- Eastern Corridor – Linking India with the Gulf region via maritime and railway routes.
- Northern Corridor – Connecting Gulf countries to Europe, primarily through land and port infrastructure.
Conclusion
- The deepening of India–Italy relations and the operationalization of IMEEC underscore India’s proactive approach to multilateral connectivity, strategic autonomy, and global trade realignment.
- Together, these developments reflect India’s evolving role in shaping a multipolar, rules-based international order anchored in inclusive growth and sustainable infrastructure.
With reference to the India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC), consider the following statements:
- It is a transcontinental connectivity initiative announced at the G20 Summit in New Delhi.
- The United States is a signatory and full infrastructure partner in the IMEEC.
- The corridor aims to link India to Europe via Central Asia and Afghanistan.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 2 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A) 1 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct – IMEEC was announced during the G20 Summit in New Delhi in 2023.
- Statement 2 is incorrect – The US is a strategic partner in the initiative, not a full infrastructure partner.
- Statement 3 is incorrect – IMEEC connects India to Europe via the Middle East (UAE, Saudi Arabia), not through Central Asia or Afghanistan.
rt-LAMP Assay
Syllabus:Science
Overview
- Researchers from the Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST), Thiruvananthapuram, have developed a novel indigenous molecular diagnostic tool—the real-time Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (rt-LAMP) assay—to enable early and accurate detection of Tuberculosis (TB).
What is the rt-LAMP Assay?
- The rt-LAMP assay is a rapid, sensitive, and specific diagnostic technique, comparable to advanced platforms like GeneXpert and Truenat.
- It can detect as few as 10 DNA copies per microlitre, allowing for diagnosis even at early stages of infection.
- Unlike RT-PCR, which requires three thermal cycling steps, rt-LAMP functions at a constant temperature, making the process simpler and more cost-effective.
Key Features:
- Uses six primers for DNA amplification (RT-PCR uses only two), enhancing both speed and specificity.
- Employs the fluorescent dye Syto 16, which does not inhibit the reaction, overcoming the challenge of false negatives associated with older LAMP methods.
- Diagnostic results are available within 10–20 minutes, significantly faster than conventional methods.
Regulatory and Validation Status
- The assay has been licensed for industrial production.
- It has received approval from the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO).
- Validation by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) is currently underway.
- The test is also under review by the WHO’s Health Technology Access Pool (HTAP).
Strategic Significance for TB Control in India
- Despite efforts to scale molecular diagnostics, India continues to rely heavily on sputum smear microscopy—used in 79% of presumptive TB cases as of 2023.
Although molecular testing labs increased from 5,090 in 2022 to 6,496 in 2023, progress remains below targets set under the National Strategic Plan (2017–2025). - The indigenous rt-LAMP assay offers a low-cost, rapid, scalable, and accurate alternative, well-suited for resource-limited settings.
Its implementation could:
- Accelerate TB case detection
- Reduce transmission rates
- Improve the efficacy of the National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP)
- Advance India’s goal of TB elimination by 2025
The rt-LAMP assay developed for TB detection holds which of the following advantages over conventional RT-PCR techniques?
- Capability to detect DNA at extremely low concentrations
- Requirement of isothermal (single-temperature) conditions
- Shorter diagnostic turnaround time
- Reduced dependence on expensive thermal cyclers
Select the correct answer using the code below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Explanation:.
Statement 1: Capability to detect DNA at extremely low concentrations
- The rt-LAMP assay developed by SCTIMST can detect TB DNA even at as low as 10 copies per microlitre, which makes it highly sensitive—often better than RT-PCR for early-stage detection
Statement 2: Requirement of isothermal (single-temperature) conditions
- Unlike RT-PCR, which requires thermal cycling (denaturation, annealing, and extension phases), rt-LAMP operates at a constant temperature, making it simpler and faster to perform.
Statement 3: Shorter diagnostic turnaround time
- The rt-LAMP assay delivers results in 10–20 minutes, whereas RT-PCR usually takes several hours due to its temperature cycling requirements.
Statement 4: Reduced dependence on expensive thermal cyclers
- Because it runs at a single temperature, the rt-LAMP assay does not require complex, costly thermal cyclers, making it ideal for low-resource or peripheral healthcare settings.
Kathak
Syllabus: Art /Culture
- Renowned Kathak Dancer Kumudini Lakhia Passes Away at 94

About Kathak
- Etymology: The term Kathak is derived from the Sanskrit word Katha, which means story.
- Nature of Performance: Initially performed as a temple dance, Kathak evolved into a court dance during the Mughal period, with stories from scriptures being portrayed through intricate movements.
- Major Gharanas: Prominent Kathak schools or gharanas include the Lucknow, Jaipur, and Benaras gharanas.
- Dance Style: The focus in Kathak lies on footwork (Tatkaar), pirouettes (Chakkars), mudras, and facial expressions. Dancers traditionally wear ankle bells (ghungroos) to accentuate their rhythmic footwork.
Musical Association
- Kathak is the only classical dance form directly associated with Hindustani (North Indian) music.
- Mughal Influence: Under the patronage of the Mughal court, Kathak transformed into a refined art form, focusing on grace and intricate rhythmic patterns.
Patronage
- The dance form received immense support from Wajid Ali Shah, the last Nawab of Awadh, who played a key role in its development.
- Prominent Exponents
- Birju Maharaj, Sitara Devi, Shovana Narayan, and Aditi Mangaldas are among the renowned exponents of Kathak.
Kumudini Lakhia’s Contributions to Kathak
- Kumudini Lakhia was a revolutionary figure in the world of Kathak. She defied traditional norms by moving away from the classical focus on mythological narratives like Radha-Krishna and Shiva-Parvati.
- She believed in “art for art’s sake,” emphasizing movement, rhythm, and form rather than relying on storytelling.
- Transformation of the Art: Over a distinguished career spanning seven decades, she played a crucial role in transforming Kathak from a solo, narrative-based performance to a group ensemble format, exploring contemporary and abstract themes.
- Awards and Recognition: Kumudini Lakhia’s exceptional contribution to the dance world earned her the Padma Shri in 1987, Padma Bhushan in 2010, and Padma Vibhushan in 2024, making her one of the most highly regarded figures in Indian classical dance.
Which of the following statements about Kathak dance and its evolution are correct?
- Kathak originated as a temple performance, depicting stories from scriptures, and later evolved into a court dance during the Mughal period.
- The dance form primarily focuses on storytelling through narrative content like Radha-Krishna or Shiva-Parvati.
- Kumudini Lakhia’s contribution to Kathak involved transforming the dance from a solo, narrative-based form to a group ensemble format.
- Kathak is exclusively associated with Hindustani (North Indian) music and has no ties to the Mughal courts.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct because Kathak originated as a temple performance and evolved under the Mughal influence into a court dance.
- Statement 2 is incorrect because Kumudini Lakhia challenged the classical focus on narrative themes and emphasized movement, rhythm, and form.
- Statement 3 is correct as Kumudini Lakhia revolutionized Kathak by transforming it into a group ensemble form.
- Statement 4 is incorrect as Kathak is deeply associated with both Hindustani music and Mughal influence, particularly during the Mughal court period.
