National Safe Motherhood Day 2025, Date, Theme, Significance, Challenges
Syllabus: Important Dates and Themes

National Safe Motherhood Day – April 11
- Observed every year on April 11, National Safe Motherhood Day is a significant campaign in India that highlights the importance of maternal healthcare and safe childbirth practices.
- It commemorates the birth anniversary of Kasturba Gandhi, the wife of Mahatma Gandhi, who devoted her life to women’s welfare and empowerment.
- Despite improvements in maternal health indicators, many women—especially in rural and marginalized communities—continue to face challenges in accessing quality healthcare.
- This day serves as a crucial reminder to prioritize the health, dignity, and rights of every pregnant and lactating woman.
Theme for 2025: “Healthy Beginnings, Hopeful Futures”:
- Focusing on ensuring quality maternal care from the early stages of pregnancy to secure the well-being of both mother and child.
Key Objectives
- Raise Awareness about maternal health, rights, and reproductive care.
- Ensure Access to quality prenatal, delivery, and postnatal healthcare.
- Prevent Maternal Mortality through safe childbirth practices.
- Combat Malnutrition affecting mothers and unborn babies.
- Empower Women through health education and informed decisions.
- Advocate for Skilled Birth Attendance in every delivery.
Historical Background
- Launched in 2003 by the White Ribbon Alliance India (WRAI).
- Honors the 90th birth anniversary of Kasturba Gandhi.
- Highlights the need to reduce maternal mortality and promote women’s reproductive rights.
The 5 Pillars of Safe Motherhood
- Family Planning – Promoting planned pregnancies and access to reproductive health services.
- Prenatal Care – Regular health checkups to monitor the health of both mother and baby.
- Skilled Birth Attendance – Ensuring deliveries are conducted by trained healthcare professionals.
- Emergency Care – Timely intervention in case of pregnancy-related complications.
- Postnatal Care – Essential care after childbirth for the mother’s and newborn’s well-being.
Challenges to Safe Motherhood in India
- Inadequate healthcare infrastructure in remote areas
- Shortage of trained birth attendants
- Widespread poverty and maternal malnutrition
- Cultural and social barriers to healthcare access
- Low awareness of maternal health practices
- Lack of emergency obstetric services
- Neglect of postpartum mental and physical health
Government Initiatives Supporting Maternal Health
- Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY) – Financial support for institutional deliveries
- Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan (PMSMA) – Free antenatal checkups
- Poshan Abhiyaan – Improving maternal and child nutrition
- LaQshya – Enhancing quality in labor rooms and maternity OTs
- National Health Mission (NHM) – Strengthening rural healthcare services
- Mother and Child Tracking System (MCTS) – Monitoring maternal and infant health
The Road Ahead: A Holistic Vision
- Strengthening Primary Health Centers (PHCs) for grassroots care
- Promoting respectful maternity practices through professional training
- Integrating mental health into maternal care services
- Engaging communities and local leaders for awareness
- Leveraging technology like telemedicine and mobile health solutions
- Educating adolescents on reproductive health and early pregnancy prevention
- Adopting data-driven approaches for better healthcare planning
Intersectional Factors Influencing Maternal Health
- Caste and Ethnic Inequality leading to systemic healthcare access issues
- Geographic Isolation limiting transport and facilities in remote areas
- Low Literacy Rates affecting health awareness and decision-making
- Economic Hardship reducing access to quality nutrition and care
- Gender Discrimination affecting reproductive autonomy
- Climate Change disrupting access due to natural disasters
National Safe Motherhood Day (NSMD) is observed annually on April 11 to raise awareness about maternal healthcare. In this context, consider the following statements:
- It is the only country-specific maternal health day officially recognized by the Government of India.
- The initiative was launched by the Ministry of Women and Child Development in 2003.
- The day commemorates the birth anniversary of a prominent woman social reformer who fought for women’s suffrage in India.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1 only
Answer: A. 1 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct. NSMD is indeed unique to India and is officially observed to raise awareness on maternal healthcare.
- Statement 2 is incorrect. The initiative was launched in 2003 by the White Ribbon Alliance India (WRAI), not the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- Statement 3 is incorrect. It commemorates the birth anniversary of Kasturba Gandhi, not a woman who fought for suffrage; her role was more related to women’s welfare and independence movements.
Khultabad to be Renamed ‘Ratnapur’ A Cultural Reclamation Move by Maharashtra Government
Syllabus:Polity
- Maharashtra Government Renames Khultabad to Ratnapur as Part of Heritage Restoration Efforts
- In a significant move to revive historical and cultural heritage predating the Mughal era, the Maharashtra government has announced the official renaming of Khultabad to its ancient name, Ratnapur.
- The declaration was made on April 8, 2025, by State Social Justice Minister Sanjay Shirsat, as part of an ongoing initiative led by the BJP-Shiv Sena alliance to restore original place names altered during medieval and colonial periods.

Key Highlights of the Announcement
- Official Renaming
- The historic town of Khultabad, located around 25 km from Chhatrapati Sambhaji Nagar (formerly Aurangabad), will now officially be known as Ratnapur.
- The government emphasized that the renaming aims to restore the town’s original identity and is not intended as a politically motivated act.
- Historical and Cultural Significance
- Originally named Ratnapur, the town was renamed during the Mughal period.
- Khultabad is known for its spiritual significance, being home to several Sufi shrines, and is a key site on the Aurangabad–Ellora route.
- Aurangzeb’s Tomb and Controversy
- The town houses the tomb of Mughal emperor Aurangzeb, along with the graves of his son Azam Shah and Asaf Jah I, the founder of the Hyderabad Nizam dynasty.
- Minister Shirsat referred to Aurangzeb as a “tyrant” who persecuted Chhatrapati Sambhaji Maharaj, prompting calls to remove his tomb from the list of protected monuments.
- The site has become a focal point of historical and ideological debate.
- Proposed Developments
- Plans have been proposed to build memorials for Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj and Chhatrapati Sambhaji Maharaj in the area.
- These efforts aim to highlight the legacy of Maratha valour and reinforce regional identity.
Political and Cultural Context
The renaming of Khultabad follows similar moves:
- Aurangabad was renamed Chhatrapati Sambhajinagar.
- Osmanabad was renamed Dharashiv.
- These name changes are part of a broader cultural campaign to reclaim historical narratives, particularly those tied to the Maratha heritage and pre-colonial Indian civilization.
- The campaign reflects a larger political strategy by the state’s ruling coalition to assert regional and cultural pride, especially in the context of rising historical revisionism in public discourse.
Conclusion
- The renaming of Khultabad to Ratnapur represents a symbolic act of cultural revival and historical reclamation, embedded within the larger socio-political discourse of heritage, identity, and memory.
- As the government moves forward with monument construction and heritage reforms, the initiative continues to evoke diverse responses across the political and academic spectrum.
With reference to the renaming of Khultabad to Ratnapur, consider the following statements:
- Khultabad is located in present-day Osmanabad district.
- The renaming initiative is part of a cultural movement to restore pre-Mughal identities.
- Aurangzeb’s tomb in Khultabad is classified as a protected monument under ASI.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 2 only
Answer: B. 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Khultabad is in Chhatrapati Sambhaji Nagar district, not Osmanabad.
- Statement 2 is correct: The renaming is part of a larger cultural strategy to revive pre-Mughal heritage.
- Statement 3 is correct: Aurangzeb’s tomb is currently on the list of protected monuments by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), although there are political demands to remove it.
ADB Projected India Economy Grow By 6.7% in FY2025
Syllabus:Economy
- India’s economy remains on a robust growth trajectory, demonstrating resilience despite mounting global uncertainties.
- The Asian Development Outlook (ADO) April 2025, published by the Asian Development Bank (ADB), forecasts India’s GDP growth at 6.7% in FY2025, propelled by strong domestic demand, improved rural incomes, and easing inflationary pressures.
- Looking ahead, GDP is expected to rise further to 6.8% in FY2026, underpinned by supportive fiscal and monetary policies.
- Meanwhile, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has revised its own growth estimate for FY2025 downward from 6.7% to 6.5%, attributing the revision to persisting global trade disruptions and policy uncertainty.
Key Highlights
- Economic Growth Forecasts
ADB Projections:
- FY2025: 6.7%
- FY2026: 6.8%
RBI Projection:
- FY2025: Revised to 6.5%
- Major Growth Drivers
Domestic Demand:
- Stronger household consumption fueled by increased rural incomes
- Urban middle-class and affluent consumers expected to drive spending via higher disposable income
Inflation Trends:
- Inflation is forecasted to ease to 3% in FY2026, and further to 4.0% in FY2027
- Lower inflation likely to bolster consumer confidence and real purchasing power
Policy Stimulus:
- Income tax relief for the middle-income segment
- Monetary easing: The RBI has cut the repo rate by 50 basis points, now at 0%
Sectoral Outlook
- Services Sector: Continues to act as the primary growth engine; driven by exports of business services, and robust performance in education and healthcare
- Agriculture Sector: Strong outlook for FY2025, aided by favorable winter crop output, especially wheat and pulses
- Manufacturing Sector: Set to rebound after subdued performance in FY2024–25, supported by regulatory and structural reforms
Investment and Infrastructure Trends
Urban Infrastructure:
- The central government has launched a dedicated ₹100 billion (approx. USD 1.17 billion) fund for infrastructure modernization and smart city development.
Private Investment:
- Near-term concerns remain due to global instability, but medium-to-long-term prospects are promising due to lower interest rates and an improving regulatory climate
Risks to the Growth Outlook
Global Risks:
- Economic slowdown in the United States
- Imposition of new US tariffs on Indian exports
- Potential surge in commodity prices impacting import bills
Mitigating Factors:
- India’s sound macroeconomic fundamentals
- Adequate monetary and fiscal policy space to cushion external shocks
- ADB Disclaimer: Projections were finalized before April 2, and do not incorporate the impact of newly imposed US tariffs. A regional impact analysis is included to assess possible ramifications on Asia-Pacific economies.
With reference to the Asian Development Outlook (ADO) April 2025, consider the following statements:
- The ADO forecasts India’s GDP to grow at 6.7% in FY2026.
- The ADO attributes India’s growth to robust domestic demand and inflationary trends.
- The Reserve Bank of India has revised its FY2025 growth forecast upward in response to ADO findings.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1 only
D) None
Answer: A) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect – ADO forecasts 6.7% for FY25, not FY26.
- Statement 2 is partially incorrect – growth is attributed to moderating inflation, not inflationary trends.
- Statement 3 is incorrect – RBI revised GDP downward from 6.7% to 6.5%.
First Panchayat Advancement Index (PAI) Report Released – Gujarat & Telangana Lead
Syllabus:Polity
- In a landmark initiative to strengthen evidence-based governance at the grassroots level, the Ministry of Panchayati Raj has launched the first-ever Panchayat Advancement Index (PAI) baseline report for FY 2022–23.
- The PAI introduces a robust data-driven framework to assess the developmental performance of over 2.5 lakh Gram Panchayats (GPs), enabling targeted planning, enhanced accountability, and the advancement of Localized Sustainable Development Goals (LSDGs).
Objectives of the Panchayat Advancement Index
- Provide a quantitative assessment of Panchayat-level development.
- Foster data-informed planning and decision-making at the local level.
- Encourage a competitive and inclusive governance environment among Panchayats
Coverage and Validation
- Total Gram Panchayats (GPs) considered: 2,55,699
- GPs with validated data: 2,16,285
- Excluded States/UTs: Meghalaya, Nagaland, Goa, Puducherry, and West Bengal (pending data validation by respective governments)
- Top Performing States (by Number of Front Runner Panchayats)
- Gujarat – 346 GPs
- Telangana – 270 GPs
- Followed by: Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh
States with Majority in Aspirant Category
- Bihar
- Chhattisgarh
- Andhra Pradesh
- Assessment Framework
- Based on 9 Localized Sustainable Development Goal (LSDG) themes
- Aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the National Indicator Framework (NIF) developed by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) Includes 435 performance indicators
Nine LSDG Themes:
- Poverty-free and Enhanced Livelihoods
- Healthy Panchayat
- Child-Friendly Panchayat
- Water-Sufficient Panchayat
- Clean and Green Panchayat
- Self-Sufficient Infrastructure
- Socially Secured Panchayat
- Good Governance
- Women-Friendly Panchayat
- Data Collection and Technology
Significance of PAI
- Identifies developmental gaps and priorities at the Panchayat level
- Facilitates formulation of Strategic Development Plans (SDPs)
- Promotes a performance-based governance culture
- Aids in state and national-level policy interventions
With reference to the Panchayat Advancement Index (PAI), consider the following statements:
- It is launched by NITI Aayog to track Gram Panchayat performance on Human Development indicators.
- It uses the National Indicator Framework developed by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
- No Gram Panchayat was categorized as an ‘Achiever’ in the first baseline report (FY 2022–23).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B
Explanation: PAI was launched by the Ministry of Panchayati Raj, not NITI Aayog (Statement 1 is incorrect). It does use NIF (Statement 2 correct), and no GP was rated as Achiever (Statement 3 correct).
Cabinet Approves Modernization of Command Area Development and Water Management (M-CADWM)
Syllabus:Environment
- In a significant policy intervention aimed at augmenting agricultural water-use efficiency and productivity, the Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi has approved a new sub-scheme titled Modernization of Command Area Development and Water Management (M-CADWM) under the overarching umbrella of the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY).
- The scheme, with a total outlay of ₹1,600 crore, will be operational during FY 2025–26 and is envisaged as a precursor to a comprehensive national plan aligned with the 16th Finance Commission cycle, set to commence in April 2026.
Key Components and Strategic Objectives
- Sub-scheme under PMKSY, the flagship irrigation and water resource management programme.
- Financial Outlay: ₹1,600 crore for 2025–26.
- Modernize backend irrigation infrastructure, specifically targeting canal-based systems, to ensure seamless water delivery from source to farm gate.
- Emphasis on micro-irrigation compatibility through pressurized underground piping networks, enabling coverage of up to 1 hectare per farmer.
Technological Interventions
- To drive precision and efficiency, the sub-scheme proposes integration of:
- SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems for automated monitoring.
- IoT (Internet of Things) solutions for:
- Real-time water management
- Water accounting
- These technologies aim to optimize Water Use Efficiency (WUE) at the field level.
Implementation Model: Pilots with Innovation Incentives
- Pilot Projects to be implemented across diverse agro-climatic zones to ensure replicability and contextual adaptability.
- Adopted through a Challenge Fund mechanism, encouraging inter-state competitiveness and innovation.
Community Engagement and Institutional Synergy
- Promotes Irrigation Management Transfer (IMT) to Water User Societies (WUS).
- Five-year handholding period, with linkages to:
- Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs)
- Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS)
- This fosters local ownership, accountability, and long-term sustainability.
Youth Participation and Future Orientation
- The scheme aims to incentivize youth involvement in agriculture via technologically enabled irrigation solutions.
- Insights from the pilot phase will inform a National Command Area Development and Water Management Plan beginning April 2026.
Significance
- M-CADWM aligns with the government’s vision of “Per Drop More Crop”, addressing climate resilience, food security, and sustainable resource use.
- It marks a paradigm shift from conventional irrigation models towards smart, tech-driven, and community-led irrigation governance.
Consider the following statements with reference to the M-CADWM sub-scheme:
- It adopts a top-down, centralized implementation strategy.
- It will provide irrigation support up to 5 hectares per farmer through open canal systems.
- It promotes community-level ownership through Water User Societies.
- Learnings from this pilot phase will be used to develop a National Plan from FY 2026 onward.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 and 4 only
C. 2, 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 3 and 4 only
Answer:B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: M-CADWM uses a decentralized, challenge-funding model to promote state innovation.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The irrigation support is up to 1 hectare per farmer, not 5.
Statements 3 and 4 are correct: The scheme promotes Water User Societies and feeds into a national plan starting April 2026.
Launch of the ‘Inter-AIIMS Referral Portal’ for Seamless Healthcare Management
Syllabus: Health
In a significant stride toward transforming India’s public healthcare ecosystem, the Union Minister of Health and Family Welfare, J.P. Nadda, launched the Inter-AIIMS Referral Portal, an indigenously developed digital platform by AIIMS New Delhi. The portal seeks to streamline patient referrals, enhance healthcare delivery, and minimize administrative delays through cutting-edge digital integration.
Core Objectives and Vision
- Purpose: To modernize and digitize the referral mechanism between AIIMS institutions for seamless, secure, and efficient patient transfers.
- Institutional Development: Developed in-house by AIIMS New Delhi as a scalable model for replication across India’s AIIMS network.
- Governance Alignment: Part of the Ministry of Health’s broader digital health transformation agenda.
Key Features and Technological Innovations
- Facial Recognition: Facilitates secure patient identification and automates check-in/out processes.
- Automated Workflows: Minimizes human error and accelerates case management, improving turnaround times for referrals.
- Integrated Communication: Enables authorized medical staff to manage referrals, schedule slots, and communicate across AIIMS centers via a centralized system.
- Patient-Centric Interface: Offers patients real-time clarity on referral status and treatment schedules, improving transparency and trust.
Pilot Implementation and Future Expansion
- Pilot Sites: The initial rollout links AIIMS New Delhi and AIIMS Bilaspur, allowing for protocol testing and system optimization.
- Scalability: Based on pilot feedback, the portal is intended for pan-AIIMS integration, forming a nationwide digital referral network within centrally governed healthcare institutions.
Complementary Facilities and Patient Support
- Vishram Sadan Integration: The portal will connect with the Vishram Sadan system, offering affordable accommodation options for patients and their families during prolonged treatment periods.
- Reduced Waiting Times: Automated referrals and slot allocation systems are expected to substantially reduce patient wait periods, improving clinical outcomes and satisfaction.
Strategic Impact
- Digital Health Infrastructure: Strengthens India’s e-health backbone, especially within the tertiary care network.
- Efficiency and Transparency: Promotes data-driven decision-making, real-time case tracking, and institutional accountability.
- Inclusive Access: Enhances the reach and equity of high-quality medical care through digital innovation, especially for inter-state and rural patients.
With reference to India’s public health digital infrastructure, consider the following statements regarding the Inter-AIIMS Referral Portal:
- It is part of the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
- It enables patient referrals only within states.
- It allows integration with Vishram Sadan to support accommodation for patients.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: C. 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: It is not under ABDM but a standalone initiative by AIIMS and MoHFW.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: It allows inter-state referrals across AIIMS institutions.
- Statement 3 is correct: The portal integrates with Vishram Sadan for patient accommodation.
50 years of India-Portugal diplomatic ties
Syllabus:IR
Context: President Droupadi Murmu engaged in high-level delegation talks with the President of Portugal, marking the 50th anniversary of diplomatic relations between India and Portugal.
Key Highlights:
- This visit was historic as it marked the first official trip by an Indian President to Portugal in over two decades, following President K. R. Narayanan’s visit in 1998.
- In a symbolic gesture of friendship, President Murmu was conferred the ‘City Key of Honour’ by the Mayor of Lisbon.
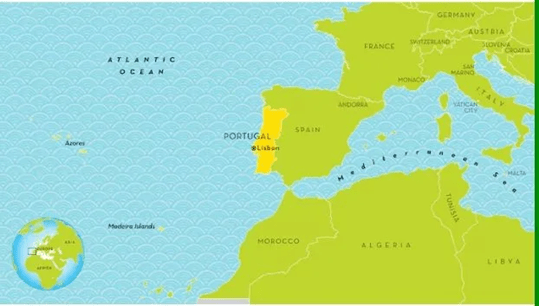
About Portugal:
- Geographical Location: Portugal occupies the westernmost edge of mainland Europe, situated on the Iberian Peninsula.
Borders:
- East and North: Spain
- West and South: Atlantic Ocean
Portugal: Historical and Geopolitical Overview
- TerritorialComposition: Portugal comprises not only the mainland territory on the Iberian Peninsula but also includes the autonomous archipelagos of Azores and Madeira in the Atlantic Ocean.
- Capital and Urban Centre: Lisbon, the capital city, is also the largest urban and economic hub of the country, playing a central role in its political, cultural, and maritime legacy.
- Pioneer of the Age of Exploration:In the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal emerged as a leading maritime and navigational power, spearheading the Age of Exploration. Legendary explorers such as Vasco da Gama, who discovered the sea route to India, and Ferdinand Magellan, the first to circumnavigate the globe, were Portuguese.
- ColonialExpansion: Portugal established a vast colonial empire with territories in South America (Brazil), Africa (Angola, Mozambique), and Asia (including Goa in India). This made Portugal one of the earliest and longest-standing colonial powers.
- Modern International Standing:Portugal is a member of the European Union (EU) and plays an active role in regional cooperation, multilateral diplomacy, and development partnerships, particularly within the Lusophone (Portuguese-speaking) world.
With reference to recent India–Portugal diplomatic developments, consider the following:
- President Droupadi Murmu is the first-ever Indian President to visit Portugal.
- The year 2025 marks the 50th anniversary of India–Portugal diplomatic relations.
- President Murmu was conferred the “City Key of Honour” during the visit.
Which of the statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 2 and 3
D. 3 only
Answer: B
Explanation: Statement 1 is incorrect – President K.R. Narayanan visited Portugal in 1998.
Statement 2 is correct – 2025 marks the 50th anniversary.
Statement 3 is correct – The City Key of Honour was conferred upon President Murmu.
Niveshak Didi Initiative
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
About the Niveshak Didi Initiative
- Objective:
To promote financial awareness among rural populations by leveraging trained women postal workers and community leaders as financial literacy ambassadors.
Phase 1 Highlights (2018 Onward):
- Conducted by IPPB across various states.
- Beneficiaries: Over 55,000 individuals, with 60% women participants.
- Focused on rural financial empowerment through literacy camps.
Phase 2 Goals:
- Rollout of over 4,000 financial literacy camps nationwide.
- Participation of nearly 40,000 women postal workers, designated as “Niveshak Didis.”
- Curriculum includes:
- Responsible investing
- Fraud prevention and awareness
- Saving habits
- Use of digital banking tools
Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA)
- Established: 2016
- Statutory Authority under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
Mandate:
- Promote financial literacy.
- Empower citizens to make informed decisions regarding personal finance.
- Educate investors about their rights and responsibilities.
- Special emphasis on outreach in rural and underserved communities.
India Post Payments Bank (IPPB)
- Established: 2018
- Under: Department of Posts, Ministry of Communications
- Vision: To deliver inclusive, affordable, and accessible banking services, particularly to the unbanked and underbanked sections of society.
Operational Model:
- Leverages the extensive postal network.
- Focuses on paperless, cashless, and presence-less banking using smartphones and biometric devices.
With reference to the Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA), consider the following:
- It is a statutory body under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
- It was established under the Companies Act, 2013.
- It manages unclaimed dividends and matured deposits.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 1, 2 and 3
D. 2 and 3 only
Answer: C
Explanation: All statements are correct. IEPFA is a statutory body under MCA, created under Section 125 of the Companies Act, 2013. It manages unclaimed dividends, matured deposits, and promotes financial literacy.
Project Varsha
Syllabus:Defence
Context
- India is set to enhance its maritime security and strategic deterrence by establishing a new naval base under Project Varsha to host nuclear submarines and warships on the eastern coast.
About the Project Varsha Naval Base
- Location: The base is being developed near Rambilli village in Andhra Pradesh, about 50 km from the Eastern Naval Command (ENC) headquarters in Visakhapatnam.
- Timeline: Expected to be operational by 2026.
Strategic Significance:
- Designed to host nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs) and other warships.
- Includes underground tunnels and pens to ensure stealth operations in the Bay of Bengal.
- Enhances survivability and concealment during long-duration patrols.
Complementary Western Base: Project Seabird
- India’s western seaboard is secured through the Karwar Naval Base in Karnataka, being developed under Project Seabird.
- Together, the eastern (Varsha) and western (Seabird) bases will bolster India’s two-front maritime security architecture.
India’s Nuclear Submarine Fleet
- The Indian Navy currently operates two SSBNs:
- INS Arihant (commissioned)
- INS Arighaat (sea trials)
- INS Aridhaman:
- The third SSBN, expected to be commissioned soon.
- It will be larger (7,000 tonnes) and more advanced than its predecessors.
- Designed to enhance India’s second-strike nuclear capability under its nuclear triad.
Which of the following statements regarding Project Varsha is/are correct?
- It is being developed on the western coast of India near Karwar.
- The project includes underground facilities for nuclear submarines.
- It will serve as a base for India’s nuclear-powered aircraft carriers.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 2 and 3 only
Answer: B. 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Project Varsha is being developed near Rambilli, Andhra Pradesh on the eastern coast, not western.
- Statement 2 is correct: It includes underground tunnels/pens for nuclear submarines.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: No nuclear-powered aircraft carriers are planned yet; focus is on submarines (SSBNs).
Ozone Pollution
Syllabus:Environment
Context: A recent study by IIT Kharagpur has revealed that surface ozone pollution is significantly harming major food crops in central India and the Indo-Gangetic Plain, posing a threat to national food security.
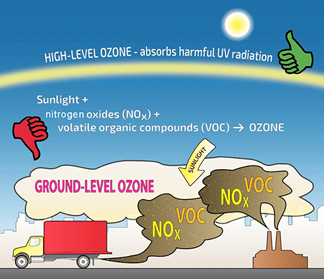
What is Ozone Pollution?
- Ozone (O₃) is a gas made up of three oxygen atoms.
- It exists in two layers of the atmosphere:
- Stratosphere (Upper Atmosphere): Beneficial – forms the ozone layer that protects life from harmful UV radiation.
- Troposphere (Ground level): Harmful – acts as an air pollutant and a greenhouse gas.
- Formation: Tropospheric ozone is not directly emitted. It forms through a reaction between:
- Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
- In the presence of sunlight.
- WHO Safe Limit: 100 µg/m³ (8-hour average)
Impact on Crops
- Ozone enters plants via stomata, causing oxidative stress.
Leads to:
- Reduced photosynthesis
- Cellular damage
- Yield loss
- Findings of the IIT Kharagpur Study:
- Wheat yields may decline by up to 20% under high-emission scenarios.
- Rice and maize yields may reduce by ~7%.
- Ozone exposure in affected regions exceeds safe limits by up to 6 times.
Wider Implications
Directly threatens India’s food security.
Undermines efforts to achieve UN SDGs:
- Goal 1: No Poverty
- Goal 2: Zero Hunger
Consider the following statements:
- Stratospheric ozone contributes to climate change and causes harm to crops.
- Surface-level ozone is a greenhouse gas and can negatively affect agricultural productivity.
- Ozone pollution aligns with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) on zero hunger and no poverty.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1 and 2 only
Answer: B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Stratospheric ozone is protective, not harmful.
- Statement 2 is correct: Tropospheric ozone is a greenhouse gas and affects crops.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: Ozone pollution hinders, not aligns with, SDGs.
