PM Modi to Participate in Navkar Mahamantra Divas
Syllabus: Culture
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi will attend Navkar Mahamantra Divas on April 9, 2025, at Vigyan Bhawan in New Delhi.
- Organized on the eve of Mahavir Jayanti, this global spiritual event promotes peace, unity, and inner awakening.
- The Jain International Trade Organization (JITO) is hosting the event, which will see participation from over 1.08 crore devotees across 108 countries.
- Participants will collectively chant the Navkar Mahamantra, a sacred Jain prayer, to inspire universal harmony and self-reflection.
About Navkar Mahamantra
- The Navkar Mahamantra is the most revered chant in Jainism.
- It pays homage to the five supreme beings: Arihants, Siddhas, Acharyas, Upadhyayas, and Sadhus.
- The mantra reflects key Jain values such as non-violence (Ahimsa), humility, truth, and spiritual enlightenment.
- It encourages individuals to practice introspection, self-discipline, and moral transformation.
About Mahavir Jayanti and Lord Mahavir
- Mahavir Jayanti marks the birth anniversary of Lord Mahavir, the 24th Tirthankara in Jainism.
- He was born in 615 BC as Vardhamana into a royal family.
- At the age of 30, he renounced worldly life in search of truth and spiritual liberation.
- After 12 years of deep meditation and penance, he attained Kevala Jnana, or perfect knowledge.
- Lord Mahavir’s teachings, including “Ahimsa Parmo Dharma” (Non-violence is the supreme religion), remain highly relevant in today’s world.
- He emphasized purity, tolerance, and collective welfare through a life of compassion and truth.
- Navkar Mahamantra Divas is a reflection of India’s spiritual heritage and its global influence in promoting peace, harmony, and ethical living.
Consider the following statements regarding the Navkar Mahamantra Divas 2025 and associated Jain philosophical concepts:
- The Navkar Mahamantra is unique among major religious chants in that it does not invoke any deity but instead pays reverence to spiritually elevated beings based on their qualities.
- Lord Mahavir, whose birth is commemorated during Mahavir Jayanti, attained Kevala Jnana before renouncing his royal life, making him the only Tirthankara to do so.
- The 2025 observance of Navkar Mahamantra Divas saw participation from over 108 countries, with global chanting organized on the eve of Mahavir Jayanti.
- The principle of Ahimsa as taught by Mahavir is exclusive to Jainism and finds no mention in other Dharmic traditions like Buddhism or Hinduism.
Which of the above statements are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 1, 2 and 4 only
C. 2 and 4 only
D. 1, 3 and 4 only
Answer: A. 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 – Correct: The Navkar Mahamantra is distinctive as it does not mention any specific deity. Instead, it pays homage to five categories of spiritually perfected beings — Arihants, Siddhas, Acharyas, Upadhyayas, and Sadhus — emphasizing qualities over divine personification. This is a unique feature within major world religions.
Statement 2 – Incorrect: Lord Mahavir renounced his royal life at the age of 30 and then undertook 12 years of asceticism before attaining Kevala Jnana (omniscience). He did not achieve enlightenment before renunciation.
Statement 3 – Correct: The 2025 Navkar Mahamantra Divas was globally significant, with participation from over 108 countries and more than 1.08 crore devotees. It was organized on April 9, the eve of Mahavir Jayanti.
Statement 4 – Incorrect: While Ahimsa is central to Jain philosophy, it is not exclusive to Jainism. Ahimsa is a shared core principle in Buddhism and Hinduism as well — for example, it is a foundational concept in the Yoga Sutras of Patanjali and in Buddhist precepts.
Shingles Vaccine Can Reduce Risk of Dementia
Syllabus: GS 2/Health
- A study conducted in Wales and published in Nature suggests a link between the shingles vaccine and a reduced risk of dementia.
- Individuals who received the shingles vaccine were found to be about 20% less likely to develop dementia over a seven-year period, compared to those who did not receive the vaccine.
- The protective effect appeared stronger in women than in men.
- Shingles, or Herpes Zoster, is caused by the Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV), which also causes chickenpox.
- After an initial infection, the virus can remain dormant in nerve tissue and may reactivate later in life as shingles.
- The shingles vaccine is recommended for older adults to prevent this reactivation.
- Dementia refers to a group of disorders that result in progressive cognitive decline, impacting memory, reasoning, behavior, and the ability to perform daily activities.
- Common types of dementia include Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, dementia with Lewy bodies, and frontotemporal dementia.
- Risk factors for dementia include advancing age, hypertension, diabetes, obesity, smoking, alcohol misuse, physical inactivity, social isolation, depression, strokes, infections, and brain injury.
- The condition places a significant burden on individuals, caregivers, and society. While there is no cure for dementia, management strategies include medication (such as cholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA antagonists), physical and cognitive activities, and controlling associated medical conditions.
- The recent study’s design allowed researchers to compare dementia rates between groups eligible and ineligible for the shingles vaccine based on birth dates.
- The findings support the theory that reducing the occurrence of viral infections may contribute to lowering the risk of developing dementia.
With reference to a recent population-based cohort study published in Nature, which examined the association between shingles (Herpes Zoster) vaccination and reduced dementia incidence, consider the following statements:
- The use of birth-date-based eligibility in the study strengthens causal inference by minimizing selection bias.
- The observed reduction in dementia risk among vaccinated individuals supports the hypothesis that latent viral reactivation may contribute to neurodegeneration.
- The findings conclusively establish that shingles vaccination can prevent all forms of dementia across demographic groups.
- The effect observed was sex-neutral, indicating similar vaccine efficacy across genders.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1, 2, and 4 only
D) 1, 3, and 4 only
Correct Answer: A) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1: Correct :The study design used birth-date-based eligibility to determine who received the vaccine. This is a form of a quasi-experimental design that can reduce selection bias, as eligibility is externally assigned and not based on individual choice, helping approximate causal inference.
Statement 2: Correct: The study suggests a plausible biological mechanism: latent VZV reactivation may contribute to chronic neuroinflammation, which is a known contributor to neurodegenerative conditions like dementia. Preventing shingles reactivation could therefore have indirect neuroprotective effects.
Statement 3: Incorrect:The study does not conclusively establish prevention of all dementia types. It’s observational, shows association not causation, and was based on a specific demographic (those eligible for the vaccine by age). Dementia is multifactorial, and no vaccine offers universal protection.
Statement 4: Incorrect: The findings were more pronounced in women than in men, suggesting gender differences in response to vaccination or in baseline dementia risk—possibly due to differences in immunity, behavior, or reporting.
Time Use Survey
Syllabus :GS 2/Governance/GS3/Economy
- The Time Use Survey (TUS) 2024, conducted by the National Statistics Office (NSO) under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI), provides a comprehensive analysis of how individuals in India allocate their time across various daily activities.
- The first all-India TUS was conducted in 2019, while the latest edition was released in February 2025.
Purpose and Objectives:
- Assess the distribution of time spent on paid and unpaid work, including caregiving, domestic chores, and voluntary services.
- Enable evidence-based policymaking in gender equity, labor, education, and welfare.
- Analyze gender-based disparities in time allocation, particularly in unpaid domestic and care work.
- Support international data harmonization by aligning with global practices, similar to surveys in countries like Australia, Japan, and the USA.
Key Findings from TUS 2024:
Work-Related Activities:
- Delhi leads the country with an average of 563 minutes/day spent on work-related activities.
- Goa follows with 536 minutes/day, a marked increase from 2019.
- The national average stands at 440 minutes/day.
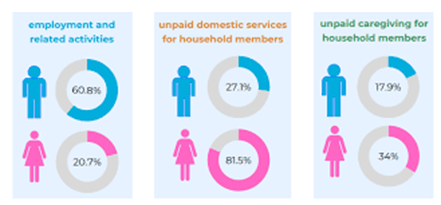
Unpaid Domestic Services:
- A significant gender disparity persists:
- Women: 289 minutes/day
- Men: 88 minutes/day
Learning Activities:
- Slight national decline: 424 minutes/day (2019) to 414 minutes/day (2024).
- Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu continue to rank high in time dedicated to learning.
Socializing & Community Participation:
- Nagaland shows an increase in social engagement.
- Patterns vary widely across states.
Leisure Activities:
- Nationwide increase observed.
- Uttarakhand reports a substantial rise in time spent on leisure.
Self-Care (Sleep, Hygiene, etc.):
- A general decline in self-care time nationwide.
- However, Meghalaya and Jammu & Kashmir show upward trends in this category.
With reference to the Time Use Survey (TUS) 2024 conducted by the National Statistics Office (NSO), consider the following statements:
- The primary objective of the TUS is to generate Gross Domestic Product (GDP) estimates by accounting for unpaid domestic work.
- The survey revealed that while work-related activity time increased in urban regions like Delhi and Goa, the national average remained below 450 minutes per day.
- The decline in time spent on learning activities was uniform across all Indian states, indicating a nationwide reduction in educational engagement.
- TUS data can aid in addressing the “invisible work” often performed by women and is aligned with global statistical practices.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 2 and 3 only
B) 1 and 4 only
C) 2 and 4 only
D) 1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: C) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 Incorrect:
While TUS data can support economic valuation of unpaid work, its primary objective is not to calculate GDP directly but to assess time allocation across various activities, particularly gender-disaggregated participation in paid and unpaid work. GDP estimates traditionally do not include unpaid domestic services.
Statement 2 – Correct:
According to TUS 2024, Delhi and Goa showed significant increases in time spent on work-related activities (563 mins and 536 mins, respectively), whereas the national average was 440 minutes, which is below 450 mins/day.
Statement 3 – Incorrect:
The decline in learning activities was not uniform across states. Some states like Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu remained high in educational engagement, indicating regional variance.
Statement 4 – Correct:
One of the key policy utilities of TUS is highlighting the “invisible” unpaid work largely done by women, contributing to policy discourse on gender equality. India conducts TUS in line with international statistical standards, placing it alongside countries like USA, Japan, and Australia.
NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement)
Syllabus: GS2/ International, GS3/ Economy
Context
- To accelerate progress on a potential trade agreement with the United States and avert the imposition of 26% reciprocal tariffs, India’s Ministry of Commerce and Industry has expanded its NAFTA division.
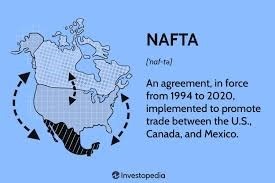
North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
- The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) was a trilateral trade pact between the United States, Canada, and Mexico, in effect from 1994 to 2020.
- It created one of the world’s largest free trade areas by eliminating tariffs and reducing trade barriers to foster deeper economic integration.
- In 2020, NAFTA was replaced by the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), which introduced updated provisions, particularly in digital trade, labor standards, and environmental protection.
Key Challenges in India-US Trade Negotiations
Data Localisation Requirements
- The S. Trade Representative (USTR) has raised concerns over India’s data localisation norms, which require financial institutions and payment service providers to store data exclusively within India’s borders—a policy seen as restrictive by U.S. tech and financial companies.
Intellectual Property (IP) Issues
India remains on the USTR’s Priority Watch List due to multiple IP-related concerns, including:
- Absence of a dedicated trade secrets law.
Delays in patent approvals.
- Inconsistent enforcement of IP protections across jurisdictions.
- Labour and Environmental Standards
India has not finalized a comprehensive trade agreement with any Western country, largely due to divergent stances on:
- Labor rights, particularly regarding enforcement mechanisms.
- Environmental regulations, where developed countries demand more stringent commitments than India is currently prepared to adopt.
The replacement of NAFTA by USMCA in 2020 primarily aimed to address which of the following gaps in the original agreement?
- Outdated digital trade provisions
- Weak labor and environmental commitments
- Absence of an investment dispute resolution mechanism
- Tariff barriers among member states
Select the correct answer using the code below:
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1, 2, and 3 only
D) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: A
Explanation:
- USMCA modernized NAFTA by adding provisions on digital trade, enhancing labor protections, and strengthening environmental standards.
- NAFTA already had dispute resolution and tariff elimination mechanisms.
Statement 3 is incorrect—both NAFTA and USMCA contain dispute mechanisms; the change was not their introduction but refinement. - Statement 4 is incorrect—NAFTA had already removed most tariffs.
22nd Amendment to the U.S. Constitution state
Syllabus: GS2/ International issues
Context: The 22nd Amendment to the U.S. Constitution has resurfaced in public discourse following former President Donald Trump’s comments regarding the two-term limit for U.S. Presidents.
About the 22nd Amendment:
The 22nd Amendment imposes a restriction on the number of terms an individual can serve as President of the United States.
Key Provision:
It states that no person shall be elected to the office of the President more than twice.
Historical Background:
Ratified in 1951, the amendment was introduced in response to President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s unprecedented four-term presidency (1932–1944), which broke the longstanding tradition of a two-term limit.
Successor Clause: If a person assumes the presidency and serves more than two years of a term to which another was elected (e.g., a Vice President succeeding a President), they may be elected only once more.
Maximum Possible Tenure:
- A person may thus serve as President for a maximum of 10 years (2 years as a successor + 2 full 4-year terms).
- The amendment reflects a constitutional safeguard aimed at preventing the concentration of power and reinforcing the principle of democratic rotation in office.
With reference to the 22nd Amendment to the U.S. Constitution, consider the following statements:
- It was introduced in response to Franklin D. Roosevelt’s decision to serve more than two terms as President.
- The amendment completely bars any individual from holding the office of the U.S. President for more than eight years under all circumstances.
- A Vice President who succeeds to the presidency and serves less than two years of the predecessor’s term may be elected to the presidency for two additional terms.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The 22nd Amendment was indeed passed following FDR’s four-term presidency, breaking the informal two-term precedent.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: A person can serve up to 10 years—if they succeed to the presidency and serve less than two years, they can still be elected twice.
- Statement 3 is correct: This clause explicitly allows a Vice President or successor to complete less than two years of a term and still be elected twice.
MoSPI Released “Women and Men in India 2024” Report
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context:
- The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has released the 26th edition of its annual publication titled “Women and Men in India 2024: Selected Indicators and Data”, providing a statistical snapshot of gender-based progress and disparities across the country.
Overview
- The publication compiles gender-disaggregated data across critical sectors such as population, education, health, labour, finance, entrepreneurship, political participation, and gender-based violence, drawing from diverse government and institutional sources.
Key Findings
Education
- The Gender Parity Index (GPI) for both primary and higher secondary enrolments has improved in FY 2024 compared to the two previous years, suggesting rising female participation in formal education.
- Enrolment rates at upper primary and elementary levels are now nearly equal between boys and girls.
Labour Force Participation
The Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) for women aged 15 and above has significantly risen from 49.8% in 2017–18 to 60.1% in 2023–24, highlighting greater integration of women into the workforce and formal economy.
Financial Inclusion
- Women account holders now comprise 2% of all bank accounts nationwide.
- They contribute 7% of total deposits, with rural women accounting for 42.2% of all rural account holders—indicating increased financial agency in rural India.
Entrepreneurship and Economic Independence
- Female-headed proprietary establishments in manufacturing, trade, and services sectors have shown consistent growth from 2021–22 through 2023–24.
- Startups with at least one woman director (DPIIT-recognized) grew from 1,943 in 2017 to 17,405 in 2024—an over 800% increase in just seven years.
Political Participation
- Female voter turnout peaked at 2% in 2019, followed by a slight dip to 65.8% in 2024, yet remaining comparable to male turnout—indicating sustained political engagement among women.
Violence Against Women
- 9% of married women aged 18–49 report having experienced spousal violence.
States with the highest reported prevalence include:
- Karnataka:4%
- Bihar:5%
- Manipur:6%
With reference to the trends presented in the “Women and Men in India 2024” report, consider the following statements:
- The Gender Parity Index (GPI) at the primary and higher secondary levels showed a declining trend from FY22 to FY24.
- Female Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) for women aged 15+ has exceeded 60% as of FY 2023–24.
- Rural women constitute a majority of India’s total bank deposit holders.
- Startups with at least one woman director have grown more than 700% between 2017 and 2024.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 2 and 4 only
B. 1, 2, and 3 only
C. 2, 3, and 4 only
D. 1 and 4 only
Answer: A. 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 – Incorrect: GPI has shown an increasing trend at both primary and higher secondary levels, not declining.
Statement 2 – Correct: The LFPR for women 15+ rose to 60.1% in 2023–24, a significant improvement.
Statement 3 – Incorrect: While rural women account for 42.2% of bank accounts, this doesn’t imply they form the majority of total deposit holders.
Statement 4 – Correct: Startups with at least one woman director increased from 1,943 (2017) to 17,405 (2024), i.e., over 800% growth.
Exercise INDRA 2025
Syllabus: GS3/Defence
Context:
The 14th edition of the India–Russia bilateral naval exercise, INDRA 2025, was recently concluded.
Overview:
The exercise featured complex maritime drills aimed at enhancing operational synergy between the navies of India and Russia. It focused on strengthening interoperability for addressing shared maritime security challenges.
Background:
Initiated in 2003, the INDRA series has evolved into a pivotal component of India–Russia defence cooperation. The exercise underscores the strategic commitment of both nations to safeguard maritime domains through joint preparedness and collaborative frameworks against emerging threats at sea.
With reference to the India–Russia bilateral naval exercise INDRA, consider the following statements:
- The INDRA exercises began as army-only exercises and later expanded to include naval and air components.
- One of the core objectives of the INDRA series is to enhance interoperability between India and Russia for countering asymmetric threats in maritime domains.
- The INDRA exercises are conducted annually with alternating host nations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: The INDRA exercises initially began as army-level drills and were later expanded to include tri-services, i.e., naval and air components, reflecting a comprehensive security approach.
Statement 2 is correct: The key focus of INDRA exercises includes countering common threats, including asymmetric and non-traditional threats like piracy, terrorism, and smuggling in maritime spaces.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The exercise is not held annually with strict alternation of host nations. The frequency and venue have varied depending on diplomatic and logistical considerations.
President Murmu Receives City Key of Honour
Syllabus: IR
- President of India, Smt. Droupadi Murmu, undertook a significant state visit to Portugal on April 7, 2025, marking the golden jubilee of diplomatic relations between India and Portugal.
- The visit underscored the shared aspirations of both nations to advance as knowledge-based, innovation-driven economies, while further consolidating historical and cultural bonds.
Key Outcomes and Strategic Engagements
- Symbolic Recognition: City Key of Honour
President Murmu was conferred the prestigious ‘City Key of Honour’ by the Mayor of Lisbon at City Hall.
In her address, she lauded Lisbon’s values of:
- Cultural openness and diversity
- Democratic tolerance
- Progressiveness in digital transformation and innovation ecosystems
- Techno-Digital Partnership
Lisbon was acknowledged as an emerging European hub for digital innovation, notably in:
- Digital public infrastructure
- Smart city solutions
- Startup accelerators
President Murmu identified these sectors as high-potential areas for India–Portugal cooperation, aligning with India’s Digital India and Start-up India missions.
- State Banquet at Palacio da Ajuda
- Hosted by Portuguese President H.E. Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa, the banquet reflected the warmth of bilateral relations.
President Murmu reiterated the countries’ deep-rooted cultural connections, referencing:
- Architectural influences
- Historical maritime linkages
- Culinary and linguistic imprints
- Commemorating 50 Years of Diplomatic Relations (1975–2025)
The visit served as a platform to transform historical ties into a visionary partnership, expanding into modern sectors such as:
- Science and technology
- Defence cooperation
- Education and research collaboration
- Information Technology and innovation ecosystems
- Cultural and academic exchange
India’s Aspirational Identity as a Knowledge Economy
President Murmu emphasized India’s focus on:
- Innovation-led growth
- Robust digital infrastructure
- Inclusive and sustainable development
Portugal was identified as a strategic and like-minded partner in achieving this vision, particularly through collaboration in emerging tech sectors.
Portugal’s Role in India–EU Engagement
Acknowledged Portugal’s leadership in fostering India–EU relations, citing:
- 2000: Hosting of the first India–EU Summit under Portugal’s EU Presidency.
- 2021: Facilitation of the “India–EU Plus 27” Leaders’ Meeting, a landmark multilateral engagement.
Vision for the Future
President Murmu expressed optimism regarding:
- A broadened bilateral agenda, encompassing global challenges.
- A mutually beneficial partnership that contributes to regional and international peace, prosperity, and innovation.
Consider the following statements regarding India–Portugal bilateral relations in the context of the 2025 Presidential visit:
- The conferment of the ‘City Key of Honour’ on President Murmu was a symbolic act representing civic appreciation for India’s leadership in smart city governance.
- Portugal’s role in hosting both the first India–EU Summit in 2000 and the India–EU Plus 27 Summit in 2021 indicates its centrality in fostering multilateral EU engagements with India.
- Lisbon’s emergence as a hub of digital public infrastructure and startup accelerators was explicitly recognized as complementary to India’s goals under Digital India and Start-up India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 2 and 3 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: While the ‘City Key of Honour’ symbolized mutual respect and strong ties, it wasn’t awarded for India’s smart city governance specifically.
- Statement 2 is correct: Portugal hosted the first India–EU Summit (2000) and the India–EU Plus 27 Summit (2021).
- Statement 3 is correct: Lisbon’s innovation ecosystem aligns with India’s flagship missions — Digital India and Start-up India.
Brazil’s Proposal for a UN-Backed Global Climate Action Council
Syllabus: Environment
Context:
In a bid to catalyze global climate governance, Brazil has proposed the establishment of a Global Climate Action Council under the aegis of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). This initiative is expected to take center stage at the upcoming 30th Conference of the Parties (COP30), scheduled to be held in Belém, Brazil, in November 2025.
Key Features of the Proposal:
- Objective and Vision:
- The proposed Global Climate Action Council is envisioned as a streamlined, agile mechanism to complement existing UNFCCC structures.
- It aims to simplify decision-making, accelerate implementation, and enhance coordination among nations for climate action.
- The council is intended to reduce bureaucratic inertia, often criticized in the current multilateral negotiation process.
- Core Functions:
- Expedite Climate Implementation: Bridge the gap between climate commitments made at COPs and their ground-level execution.
- Global Coordination Hub: Serve as a platform for synchronizing national efforts, aligning them with global climate targets.
- Monitoring and Accountability: Facilitate transparent review of climate pledges and their progress through periodic assessments.
- Minimize Procedural Complexity: Create a more result-oriented and responsive institutional framework within the UNFCCC ecosystem.
Strategic Significance of COP30:
- Brazil’s proposal gains particular salience as it prepares to host COP30—an opportunity to showcase its leadership in climate diplomacy.
- The Belém summit is expected to deliberate extensively on the feasibility, structure, and potential mandate of the council.
Global Response and Emerging Divergences:
Supportive Positions:
- Countries like Germany, the Netherlands, and Sweden have shown support, citing the need to reform and expedite climate governance mechanisms.
- These countries see the council as a corrective step to overcome the sluggish pace of existing frameworks.
Cautious Voices:
- Several developed nations have expressed measured interest, voicing concern over the creation of a parallel institutional structure.
- There are apprehensions that such a council could dilute the authority of the UNFCCC or create institutional overlap, adding more complexity rather than resolving it.
Current Status and Way Forward:
- As of now, Brazil’s proposal remains informal and under exploratory discussion.
- It is expected to feature prominently in COP30 deliberations, where its structure, legitimacy, and compatibility with existing frameworks will be critically assessed.
Broader Implications:
- The proposal underscores the growing urgency of climate action amidst increasing global climate crises.
- It also highlights Brazil’s aspiration to reposition itself as a climate leader, especially from the Global South, advocating for a more agile and responsive global climate architecture.
With reference to Brazil’s proposal for a Global Climate Action Council under the UNFCCC, consider the following statements:
- The council, if created, would function as a legally binding body parallel to the COP structure.
- One of its primary objectives is to ensure time-bound implementation of climate decisions made during COP meetings.
- The proposal has received universal support among developed countries due to its efficiency-oriented focus.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 2 and 3 only
Answer: B. 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The proposal is currently informal and not legally binding. It aims to complement, not replace or parallel, the COP.
- Statement 2 is correct: The core aim is to speed up implementation of COP decisions, enhancing global response efficiency.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: While some developed nations support the initiative (e.g., Germany, Sweden), others have expressed concerns over redundancy and bureaucratic overlap.