World’s Largest Grain Storage Plan in Cooperative Sector
Syllabus: Georaphy/Economy
Why in News?
- On May 31, 2023, the Government approved the World’s Largest Grain Storage Plan in the Cooperative Sector, set to be implemented as a Pilot Project.
- This initiative aims to develop agricultural infrastructure at the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) level, including:
Construction of godowns
- Establishment of custom hiring centers
- Setting up of processing units
The project integrates various existing Government of India (GoI) schemes, such as:
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)
- Agricultural Marketing Infrastructure Scheme (AMI)
- Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM)
- Pradhan Mantri Formalization of Micro Food Processing Enterprises Scheme (PMFME)
Progress of the Pilot Project
- Under the Pilot Project, godowns have been constructed in 11 PACS across 11 States, with a total storage capacity of 9,750 Metric Tons (MT).
State-wise Details of Completed Godowns
|
- Additionally, foundation stones have been laid for 500 additional PACS godowns under the Pilot Project, with a total of 575 PACS identified for implementation across various States/UTs.
Expansion and Future Goals
- The Ministry of Cooperation aims to establish and strengthen 2 lakh multipurpose PACS, Dairy, and Fishery Cooperative Societies across all panchayats and villages in the country.
- To guide this process, a Margdarshika (Standard Operating Procedure) has been introduced.
- In Karnataka, 128 PACS have been established against a target of 218 PACS to be formed by FY 2028-29.
Impact of the World’s Largest Grain Storage Plan
Decentralized Storage Capacity:
- 9,750 MT of storage capacity has been created at the PACS level.
Reduction in Food Grain Wastage:
- Prevents post-harvest losses by ensuring adequate storage facilities.
Strengthening of Food Security:
- Ensures better storage and distribution of food grains to enhance national food security.
Preventing Distress Sales:
- Farmers can store their produce and sell it at better prices rather than being forced into distress sales.
Cost Reduction in Transportation:
- Since PACS can function as both procurement centers and Fair Price Shops (FPS), transportation costs are reduced.
- Avoids the need to transport grains from procurement centers to warehouses and back to FPS.
- This initiative marks a major milestone in strengthening the cooperative sector and enhancing agricultural infrastructure across India.
Consider the following statements regarding the “World’s Largest Grain Storage Plan in the Cooperative Sector”:
- It is being implemented exclusively under the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF).
- The plan aims to develop agri-infrastructure at the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) level.
- One of the objectives of the plan is to enable PACS to operate as procurement centers as well as Fair Price Shops (FPS).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The plan is not implemented exclusively under AIF; rather, it converges multiple schemes like Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF), Agricultural Marketing Infrastructure Scheme (AMI), Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM), and Pradhan Mantri Formalization of Micro Food Processing Enterprises Scheme (PMFME).
- Statement 2 is correct: The plan focuses on strengthening PACS by developing godowns, custom hiring centers, and processing units.
- Statement 3 is correct: The initiative allows PACS to function as procurement centers and Fair Price Shops (FPS), reducing transportation costs and logistical challenges.
3rd Session of India-Uganda Joint Trade Committee held in New Delhi
Syllabus: IR
- The Third Session of the India-Uganda Joint Trade Committee (JTC) was held in New Delhi on 25th-26th March 2025, marking a significant step in reinforcing trade relations between the two nations after a gap of 23 years.
- Both sides conducted a comprehensive review of bilateral trade and acknowledged that the current trade volume does not fully reflect the economic potential of their partnership.
- To address this, both countries committed to enhancing, deepening, and diversifying trade relations.
- A key outcome of the discussions was the proposal to establish an India-Uganda Joint Business Forum to promote direct engagement between business leaders from both nations.

Key Areas of Cooperation
India and Uganda identified priority sectors to expand trade and investment, including:
- Agriculture & Allied Sectors: Coffee, cocoa products, pulses, spices, dairy products, fruits, and vegetables.
- Minerals & Resources: Rare Earth Elements (REE), mining, petrochemicals, and residual chemical products.
- Manufacturing & Industrial Growth: Plastic raw materials, essential oils, and allied products.
- Technology & Infrastructure: Digital infrastructure, banking, MSME growth, solar energy, rural electrification, and electric vehicles.
- Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals: Strengthening cooperation in health services, traditional medicine, and telemedicine.
- Both sides also agreed to explore and formalize Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs) in Public Works, Infrastructure Development, Agriculture, Traditional Medicine, and Standardization.
- Additionally, discussions were held on recognizing the Indian Pharmacopoeia to facilitate pharmaceutical trade.
High-Level Participation
- The Indian delegation was led by Additional Secretary, Department of Commerce, Shri Ajay Bhadoo, who highlighted the strong economic partnership between the two nations and emphasized opportunities in e-commerce, pharmaceuticals, MSME cluster development, and renewable energy.
- The Ugandan delegation was headed by Elly Kamahungye Kafeero, Head of International Political Cooperation Department, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Uganda, accompanied by Amb. Prof. Joyce Kikafunda Kakuramatsi, Uganda’s High Commissioner to India, and a 28-member delegation representing various ministries and Uganda’s Mission in India.
- The discussions were conducted in a cordial and cooperative atmosphere, reflecting the strong and amicable relations between India and Uganda.
Industrial & Export Insights
- As part of their visit, the Ugandan delegation toured the Noida SEZ (Special Economic Zone) to gain first-hand insights into India’s industrial and export ecosystem.
- The deliberations at the 3rd Session of the India-Uganda JTC were forward-looking, setting the stage for increased trade, investment, and mutual growth between the two nations.
Consider the following statements regarding the India-Uganda Joint Trade Committee (JTC) meeting held in March 2025:
- The session was held in Kampala, Uganda, to mark the first bilateral trade summit after a gap of 23 years.
- A major outcome of the meeting was the proposal to establish an India-Uganda Joint Business Forum.
- Discussions included cooperation in agriculture, mining, pharmaceuticals, and digital infrastructure.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation: The session was held in New Delhi, India, not Kampala. However, the discussions did include the proposal for an India-Uganda Joint Business Forum and identified key areas of cooperation such as agriculture, mining, pharmaceuticals, and digital infrastructure.
Success of Jan Aushadhi Kendras with PACS
Syllabus: Govt Policies
Overview
- The Government of India has enabled Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) to establish and operate Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendras (PMBJK) under the Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP).
- This initiative, led by the Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers, seeks to expand access to affordable medicines in rural areas.
Significance of PACS in Rural Healthcare
- With a vast rural network covering over 13 crore small and marginal farmers, PACS are well-positioned to leverage their existing infrastructure, including land, buildings, and storage facilities, to establish Jan Aushadhi Kendras.
- These Kendras will enhance healthcare access in underserved regions, ensuring the availability of quality and affordable medicines.
- The existing trust and rapport that PACS hold within rural communities further contribute to the success of this initiative.
Financial Incentives for PACS-Operated Jan Aushadhi Kendras
- PACS-run Kendras will receive an incentive of 20% of their monthly purchases from the Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Bureau of India (PMBI), subject to a maximum of ₹20,000 per month, based on stock conditions.
- Kendra operators will earn a 20% margin on the Maximum Retail Price (MRP) (excluding taxes) for each medicine sold.
- In addition to generic medicines, these Kendras can also sell allied medical products, similar to conventional pharmacies, ensuring financial sustainability and profitability.
Alignment with National Health Goals
- This initiative is in line with the National Health Policy, which aims to enhance equitable access to quality healthcare. By integrating PACS and Jan Aushadhi Kendras, the government seeks to:
- Ensure availability of affordable medicines in remote areas.
- Reduce medical expenses for small and marginal farmers, allowing them to focus on agricultural investments.
- Generate employment and provide additional revenue streams at the PACS level.
Conclusion
- With its extensive rural reach, PACS is set to play a pivotal role in expanding affordable healthcare access across India. The initiative will strengthen rural healthcare infrastructure, support economic empowerment of farmers, and reduce the burden of medical expenses, thereby contributing to both public health and rural development goals.
- This was stated by the Minister of Cooperation, Shri Amit Shah, in a written reply to a question in the Rajya Sabha.
Consider the following statements regarding the integration of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) with Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendras (PMBJK):
- PACS can utilize their existing infrastructure, such as land, buildings, and storage facilities, to establish and operate Jan Aushadhi Kendras.
- PACS-operated Kendras receive an incentive of 30% of their monthly purchases from Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Bureau of India (PMBI), subject to a ceiling of ₹20,000 per month.
- These Kendras are allowed to sell allied medical products in addition to generic medicines.
- The initiative aligns with the National Health Policy’s goal of equitable access to quality healthcare.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 3, and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (b) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct – PACS can utilize their existing infrastructure to establish Jan Aushadhi Kendras, making healthcare more accessible in rural areas.
Statement 2 is incorrect – The incentive is 20% of monthly purchases from PMBI, not 30%.
Statement 3 is correct – Jan Aushadhi Kendras can sell allied medical products, similar to conventional chemist shops.
Statement 4 is correct – The initiative supports the National Health Policy’s objective of equitable healthcare access.
Raksha Rajya Mantri flags-off Mt Everest & Mt Kangchenjunga expeditions from New Delhi
Syllabus: Geography

- Raksha Rajya Mantri Shri Sanjay Seth flagged off two major mountaineering expeditions to Mount Everest and Mount Kangchenjunga from South Block, New Delhi, on March 26, 2025.
- These expeditions, organized under the Ministry of Defence, mark a significant milestone in India’s adventure sports domain and align with Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi’s vision of fostering self-reliance, resilience, and a fearless spirit among the youth.
- The Mount Everest expedition, a collaborative effort between the Himalayan Mountaineering Institute (HMI), Darjeeling, West Bengal, and Jawahar Institute of Mountaineering & Winter Sports (JIM&WS), Jammu & Kashmir, commemorates 60 years of the Nehru Institute of Mountaineering (NIM), Uttarkashi, Uttarakhand.
- Meanwhile, the Mount Kangchenjunga expedition, organized by the National Institute of Mountaineering and Adventure Sports (NIMAS), Dirang, Arunachal Pradesh, is part of the ‘Har Shikhar Tiranga’ initiative.
India’s Growing Leadership in Mountaineering and Adventure Sports
- Speaking at the flag-off event, Shri Sanjay Seth highlighted India’s emergence as a global powerhouse in adventure sports, crediting the mountaineering institutes for playing a crucial role in training and inspiring the next generation of adventurers.
- He emphasized that these expeditions not only test the climbers’ endurance, skill, and teamwork but also serve as a symbol of India’s mountaineering prowess.
Expedition to Mt. Everest
- Team Composition: Seven elite climbers from NIM, HMI, and JIM&WS, all with extensive experience in extreme high-altitude conditions.
- Leader: Col Anshuman Bhadauria, Principal, NIM.
- Route: Traditional South Col Route in Nepal, navigating the treacherous Khumbu Valley, with high-altitude acclimatization camps.
- Objective: To provide invaluable first-hand Everest experience to instructors, enabling them to train and inspire future Indian mountaineers.
- Schedule: Departure on April 2, 2025, with the summit push expected in May 2025.
Expedition to Mt. Kangchenjunga
- Significance: Kangchenjunga is India’s highest and only 8,000-meter peak, posing one of the most formidable challenges in global mountaineering.
- Team Composition: Five skilled climbers and three support staff.
- Leader: Col Ranveer Singh Jamwal, Director, NIMAS, Dirang, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Achievements of NIMAS: Successfully climbed the highest peaks in all 27 Indian states.
- Schedule: Expedition commences on April 7, 2025.
These ambitious expeditions set a new benchmark for India’s mountaineering aspirations, reinforcing the country’s commitment to adventure, resilience, and excellence in extreme sports.
Consider the following statements regarding the recent Indian mountaineering expeditions to Mt. Everest and Mt. Kangchenjunga:
- The expedition to Mt. Everest is being conducted under the Har Shikhar Tiranga initiative by the National Institute of Mountaineering and Adventure Sports (NIMAS).
- The Mt. Kangchenjunga expedition marks the 60th anniversary of the Nehru Institute of Mountaineering (NIM).
- The expeditions are being conducted under the aegis of the Ministry of Defence.
- The traditional North Col Route in Tibet has been chosen for the Everest expedition.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Har Shikhar Tiranga initiative is associated with the Mt. Kangchenjunga expedition, not Mt. Everest.
Statement 2 is correct: The Mt. Everest expedition commemorates 60 years of the Nehru Institute of Mountaineering (NIM), Uttarkashi.
Statement 3 is correct: The expeditions are organized under the Ministry of Defence.
Statement 4 is incorrect: The South Col Route in Nepal, not the North Col Route in Tibet, has been chosen for the Everest expedition.
Multiple Reforms to Enhance Safety and Efficiency in Railway Operations
Syllabus: Govt Policies
- Indian Railways is undergoing continuous reforms to improve train operations, passenger experience, and network expansion.
- Several key initiatives have been undertaken to expedite project approvals, enhance safety, and modernize railway infrastructure:
Key Reforms and Initiatives:
- Gati Shakti Directorate/Units
- The PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP), launched in October 2021, aims to revolutionize infrastructure planning and execution.
- Indian Railways has established a multi-disciplinary Gati Shakti Directorate at the national level and Gati Shakti Units in Zonal Railways.
- These initiatives ensure faster project approvals by integrating inputs from all stakeholders and infrastructure ministries.
- Enhanced Sanction Powers for GMs and DRMs
- To accelerate project execution, General Managers (GMs) and Divisional Railway Managers (DRMs) have been granted enhanced financial powers for sanctioning projects.
- Streamlined Contract Management
- Full powers have been delegated to General Managers for finalizing tenders.
- Implementation of Works Contract Management System (IRWCMS) and Contractor’s e-MB ensures transparency and efficiency in contract management and billing.
- Kavach: Automatic Train Protection System
- Kavach, India’s indigenous National Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system, has been implemented in mission mode to enhance train safety.
- Elimination of Level Crossings
- All unmanned level crossings on broad-gauge tracks have been eliminated.
- A phased plan is in place to replace manned level crossings with Road Over Bridges (RoBs) and Road Under Bridges (RUBs) to improve safety.
- Station Redevelopment – Amrit Bharat Station Scheme
- The Amrit Bharat Station Scheme focuses on providing world-class passenger amenities and improving operational efficiency.
- 1,337 stations have been taken up for redevelopment under this initiative.
- Modern Trains for Enhanced Passenger Experience
- Introduction of state-of-the-art trains, including:
- Vande Bharat Trains
- Amrit Bharat Trains
- Namo Bharat Rapid Rail
- Bharat Gaurav Trains
- Theme-based tourist circuit trains, launched to showcase India’s rich cultural heritage and historical sites.
- Operated in collaboration with tourism professionals and service providers.
- Digital Transactions at Stations and Trains
- Expansion of digital payment facilities for services like ticketing and catering.
- Freight Transportation Reforms
- To increase freight revenue, Indian Railways has introduced:
- Freight rebates and discounts for assured businesses
- Concessions on short-distance transport
- Mini rake loadings and goods shed development
- General Purpose Wagon Investment Scheme (GPWIS)
- Business Development Portal
- Gati Shakti Cargo Terminals (GCTs)
- Launched to fast-track approvals and simplify cargo terminal setup.
- 95 GCTs have been commissioned so far.
- Railway-India Post Integration for Parcel Services
- A joint initiative between Indian Railways and India Post for seamless parcel delivery.
- Combines first-mile and last-mile connectivity by India Post with station-to-station rail transport.
- Coal Chain Coordination Group
- Formed to coordinate coal transportation among:
- Coal companies
- Mines (captive and commercial)
- Ports, power plants, and industries
- Indian Railways
- Annual Recruitment Calendar
- Indian Railways has introduced an Annual Recruitment Calendar to:
- Minimize uncertainty and waiting time for job aspirants
- Ensure timely filling of vacancies
- Railway Land Leasing Policy
- A long-term land leasing policy has been introduced under PM Gati Shakti to facilitate integrated infrastructure planning and development.
- Introduction of Rolling Blocks
- Rolling Blocks were introduced in 2023 via Gazette Notification.
- This allows pre-scheduled maintenance, repairs, and asset replacement up to 52 weeks in advance for systematic infrastructure upgrades.
- These comprehensive reforms, as outlined by Union Minister of Railways, Information & Broadcasting, and Electronics & IT, Shri Ashwini Vaishnaw, signify a major leap towards modernizing Indian Railways, enhancing safety, and boosting operational efficiency.
The PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP), launched in 2021, aims to integrate infrastructure projects across sectors. Which of the following statements regarding Gati Shakti’s role in Indian Railways is/are correct?
- It ensures multi-modal connectivity by synchronizing railway infrastructure development with roads, ports, and logistics hubs.
- Gati Shakti allows Indian Railways to directly sanction railway projects without requiring inter-ministerial approvals.
- The initiative mandates Project DPRs to be prepared in consultation with stakeholders, leading to expedited approvals.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Gati Shakti focuses on multi-modal connectivity, aligning railway infrastructure with highways, ports, and airports for seamless logistics integration.
Statement 2 is incorrect: While Gati Shakti expedites approvals, Indian Railways still requires inter-ministerial coordination, but the process has been made more efficient.
Statement 3 is correct: The Detailed Project Reports (DPRs) are prepared with inputs from multiple stakeholders, ensuring feasibility and alignment with national infrastructure goals.
Amrit Sarovar Scheme
Syllabus:Govt Policies
Overview

- Launched in April 2022, Mission Amrit Sarovar aimed to construct or rejuvenate 75 Amrit Sarovars (ponds) in each district, targeting a total of 50,000 across the country. Each Sarovar was designed to have a pondage area of approximately 1 acre (except in hilly terrain) with a water holding capacity of 10,000 cubic meters.
- As of March 20, 2025, more than 68,000 Amrit Sarovars have been completed across various states and Union Territories, significantly addressing water scarcity and enhancing surface and groundwater availability. This initiative underscores the Government’s commitment to long-term environmental sustainability and community welfare.
Implementation and Funding:
- The initiative has been executed through convergence with multiple schemes, including:
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS)
- 15th Finance Commission Grants
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayi Yojana (PMKSY) sub-schemes like:
- Watershed Development Component
- Har Khet Ko Pani
- State Government Schemes
- Public Contributions such as crowdfunding and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) funds
Key Provisions for Public Participation:
- Laying of Foundation Stone: To be led by a freedom fighter, martyr’s family member, or a Padma awardee. If unavailable, the eldest member of the Gram Panchayat will do the honors.
- Donations & Voluntary Work: Citizens can contribute by donating construction material, benches, or offering Shram Daan (voluntary labor).
- Beautification Efforts: Villagers can mobilize crowdfunding or CSR funds for aesthetic enhancements.
- National Celebrations: On Independence Day & Republic Day, the Tricolour is hoisted at each Sarovar site, with national events being celebrated.
- Utilization for Economic Activities: Encouragement of irrigation, fisheries, and water chestnut cultivation, with user groups managing water structures.
Sustainability and Maintenance:
- Formation of User Groups: Drawn largely from Self-Help Groups (SHGs) for efficient upkeep and management.
- Silt Removal: Conducted voluntarily post-monsoon to maintain Sarovar efficiency.
- Plantation & Green Initiatives: Ongoing afforestation and ecological conservation around Sarovars.
State-Wise Progress (As of March 20, 2025):
- The initiative has been implemented successfully across various States and Union Territories, with notable achievements in:
- Uttar Pradesh: 16,630 Sarovars completed (highest in the country)
- Madhya Pradesh: 5,839
- Karnataka: 4,056
- Maharashtra: 3,055
- Rajasthan: 3,138
- Total Amrit Sarovars completed nationwide: 68,842
Conclusion:
- Mission Amrit Sarovar has played a pivotal role in addressing water challenges and ensuring sustainable water management across the country.
- With Phase II emphasizing community participation, climate resilience, and environmental conservation, the initiative is set to make a lasting impact on India’s water security and rural development.
With reference to Mission Amrit Sarovar, consider the following statements:
- The initiative was launched under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change to conserve wetlands.
- Each Amrit Sarovar is designed to have a pondage area of about 1 acre with a water holding capacity of approximately 10,000 cubic meters, except in hilly terrains.
- The initiative relies exclusively on central government funding, with no provision for state or private sector involvement.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Mission Amrit Sarovar was launched under the Ministry of Rural Development, not the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- Statement 2 is correct: Each Amrit Sarovar is designed to have a pondage area of about 1 acre and a water holding capacity of 10,000 cubic meters, except in hilly terrains where this may vary.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The initiative is implemented through convergence with various schemes (MGNREGS, PMKSY, Finance Commission grants, and state schemes), public crowdfunding, and CSR contributions.
Ministry of Rural Development and United Nations Children’s Fund YuWaah Collaborate to Empower Rural Women and Youth
Syllabus:Govt Policies

- The Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) and United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) YuWaah have entered into a three-year partnership aimed at empowering rural women and youth across India.
- A Statement of Intent (SOI) was signed to facilitate employment, entrepreneurship, and skill development, thereby increasing female labor force participation in rural areas.
Key Highlights of the Partnership:
- Strengthening Livelihood Opportunities: Women from Self-Help Groups (SHGs) will be connected to jobs, self-employment, and entrepreneurial ventures.
Digital Infrastructure Development:
- Computer Didi Centers and Didi ki Dukan will be set up in five pilot blocks across Andhra Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan.
- Upon successful implementation, the initiative has the potential to scale up to benefit 35 lakh women across 7,000+ blocks.
Youth-Centric Initiatives:
- Youth Hub: A digital aggregator platform for job opportunities, skilling, and volunteering.
- Lakhpati Didi Model: A scalable initiative to promote women entrepreneurship and create thousands of successful rural women entrepreneurs.
Leadership Perspectives:
- Shri T.K. Anil Kumar, Additional Secretary, MoRD, emphasized that the collaboration aligns with the Rural Prosperity and Resilience Programme, announced in Budget 2025-26.
- He highlighted that one-third of the 10 crore SHG members are youth, making them central to this initiative.
- Sharada Thapalia, Deputy Representative (Operations), UNICEF India, acknowledged MoRD’s 10 crore-strong SHG network as a transformative social infrastructure for rural empowerment.
Future Outlook:
- The partnership aims to drive economic self-reliance among rural women and youth while leveraging technology for scalable impact. The signing ceremony was attended by Smriti Sharan (Joint Secretary, MoRD), Dr. Monika (Deputy Secretary, MoRD), and representatives from UNICEF YuWaah and MoRD.
- This initiative marks a significant step towards rural economic transformation, fostering resilience and prosperity through skill-building, employment, and entrepreneurship.
The Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) has signed a Statement of Intent (SoI) with UNICEF YuWaah for a three-year partnership to empower rural women and youth. Which of the following objectives are correct regarding this partnership?
- Connecting SHG women with employment, self-employment, and entrepreneurship.
- Strengthening digital infrastructure through initiatives like Computer Didi Centers and Didi ki Dukan.
- Creating exclusive skilling programs only for male youth in rural areas.
- Establishing Youth Hub, a digital platform for job aggregation, skilling, and volunteering.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2, and 4 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: The initiative aims to connect SHG women to job opportunities and self-employment ventures.
Statement 2 is correct: The establishment of Computer Didi Centers and Didi ki Dukan is part of the digital infrastructure enhancement in five pilot states.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The initiative is not exclusive to male youth but rather focuses on empowering both rural women and youth.
Statement 4 is correct: The Youth Hub is a job aggregation and skilling platform aimed at improving employment prospects.
AIIMS New Delhi and SAMEER sign landmark MOU to enhance innovation in medical electronics and healthcare technology
Syllabus:Health
MoU to Strengthen Indigenous Medical Imaging Technology
- The Society for Applied Microwave Electronics Engineering & Research (SAMEER) and All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to advance research and development in medical imaging and radio frequency (RF) technologies.
- The agreement was formalized on the 32nd Foundation Day of the Department of NMR at AIIMS, New Delhi and marks a significant step toward strengthening India’s self-reliance in medical imaging technology.
Key Focus Areas of the MoU:
The MoU outlines collaboration between SAMEER and AIIMS across five major areas:
- Collaborative Research in Medical Devices Development
- Clinical Validation of the Indigenous 1.5 Tesla MRI System developed by SAMEER, Mumbai
- Research in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) for Image Enhancement and Accelerated Imaging
- Design and Development of Subsystems for High/Low Field MRI Scanners
- Development of RF Subsystems for High Field Animal MRI Scanners
- Strengthening India’s Self-Reliance in MRI Technology
The Indigenous Magnetic Resonance Imaging (IMRI) – A National Mission, sponsored by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), is being executed by SAMEER, Mumbai, in collaboration with:
- C-DAC Trivandrum & Kolkata
- Inter-University Accelerator Centre (IUAC), New Delhi
- DSI-MIRC, Bangalore
The goal of this initiative is to design, develop, and test an indigenous 1.5 Tesla MRI system for medical imaging applications. Significant progress has been achieved, including the development and integration of critical MRI subsystems such as:
Conclusion
The MoU between SAMEER and AIIMS represents a major milestone in India’s journey toward self-reliant healthcare technology. By combining expertise in electronics, AI, and medical research, this partnership is set to revolutionize medical imaging, improve healthcare accessibility, and boost indigenous innovation in medical technology.
Consider the following statements regarding the MoU between SAMEER and AIIMS, New Delhi:
- SAMEER is an autonomous institution under the Ministry of Science and Technology.
- The MoU focuses on developing high-field and low-field MRI/NMR systems for medical applications.
- The Indigenous Magnetic Resonance Imaging (IMRI) mission is being implemented under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- One of the key objectives of the MoU is to facilitate clinical validation of an indigenous 1.5 Tesla MRI system.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 4 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- SAMEER is an autonomous institution under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), not the Ministry of Science and Technology. (Statement 1 is incorrect)
- The MoU focuses on developing high-field/low-field MRI/NMR systems for medical applications. (Statement 2 is correct)
- The IMRI mission is sponsored by MeitY, not the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. (Statement 3 is incorrect)
- A key objective of the MoU is clinical validation of the indigenous 1.5 Tesla MRI system. (Statement 4 is correct)
RAPID APPROVAL OF HOUSES UNDER PM-JANMAN
Syllabus: Govt Policies
- The Government has implemented real-time monitoring and accountability measures by transitioning sanctioning mechanisms from the Pradhan Mantri Gati Shakti Portal to the Pradhan Mantri Awaas Portal.
- This initiative aims to streamline the provision of pucca houses to Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTG) households under PM JANMAN, a program spearheaded by the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD).
- To facilitate implementation, the Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA), in collaboration with State Governments/UT Administrations, conducted a habitation-level data collection exercise using the PM Gati Shakti mobile application.
- This data helped estimate the PVTG population and assess infrastructure gaps, including housing shortages. The gathered information is cross-verified by relevant Ministries and State Departments before approval.
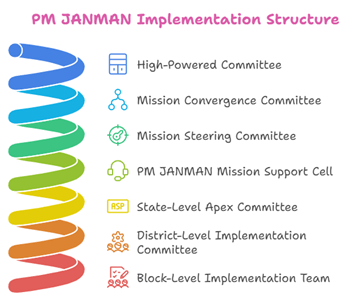
Under this system:
- PMAY-G houses are sanctioned via the AwaasSoft portal in alignment with established norms.
- Once approved, data is updated and integrated into PM Gati Shakti, ensuring efficient monitoring of sanctions against identified gaps.
- Implementation and evidence-based monitoring of PMAY-G are executed through an end-to-end transaction-based e-governance model using AwaasSoft and the AwaasApp.
- Key functions, including beneficiary identification, fund release, installment tracking, and completion reporting, are managed digitally.
- Additionally, the physical and financial progress of PMAY-G is publicly accessible through various reports on AwaasSoft.
Grievance Redressal Mechanism
- A structured grievance redressal system operates at multiple levels—Gram Panchayat, Block, District, and State. Complaints from Members of Parliament, State Assemblies, or the general public (including those received via CPGRAMS) are addressed by the State Government to ensure necessary corrective actions.
- This information was provided by Shri Durgadas Uikey, Minister of State for Tribal Affairs, in response to an unstarred question (No: 3019) in the Rajya Sabha.
Consider the following statements regarding the transition of sanctioning mechanisms in housing schemes:
- The shift from the Pradhan Mantri Gati Shakti Portal to the Pradhan Mantri Awaas Portal is aimed at improving real-time monitoring and accountability in the sanctioning of housing schemes.
- PM JANMAN is implemented by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA), whereas housing provisions under the scheme are sanctioned by the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD).
- The AwaasSoft portal functions exclusively as a data collection tool and does not facilitate real-time transactions or beneficiary tracking.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 1 and 3 only
(C) 2 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (A) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The transition from PM Gati Shakti Portal to Pradhan Mantri Awaas Portal aims to enhance real-time monitoring and accountability in housing sanctioning.
- Statement 2 is correct: PM JANMAN is indeed implemented by MoTA, but housing provisions are sanctioned under MoRD through PMAY-G.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: AwaasSoft is not just a data collection tool; it is an end-to-end e-governance platform that facilitates real-time tracking, fund disbursement, and beneficiary verification.
PM-WANI Scheme
Syllabus: Govt Policies
- The Prime Minister’s Wi-Fi Access Network Interface (PM-WANI) framework is a key initiative aimed at accelerating the expansion of internet services through public Wi-Fi hotspots across the country.
- This initiative aligns with the broader vision of Digital India, fostering increased connectivity and enabling a range of socio-economic benefits.
- Under PM-WANI, Public Data Offices (PDOs) are responsible for establishing, operating, and maintaining WANI-compliant Wi-Fi hotspots based on their techno-commercial considerations.
- These PDOs must collaborate with a Public Data Office Aggregator (PDOA) to facilitate seamless internet services for users.

- As of March 20, 2025, a total of 2,78,439 PM-WANI Wi-Fi hotspots have been deployed across India, significantly enhancing public access to the internet.
- Furthermore, PM-WANI-compliant Wi-Fi hardware is readily available in the market. The Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT) has also contributed by supplying PM-WANI-compliant Wi-Fi hardware through its Transfer of Technology (ToT) partners.
- This information was shared by Pemmasani Chandra Sekhar, Minister of State for Communications and Rural Development, in a written response to a question in the Lok Sabha.
Consider the following statements regarding the Prime Minister’s Wi-Fi Access Network Interface (PM-WANI) framework:
- PM-WANI aims to provide broadband internet connectivity only in rural and backward areas of India.
- Under PM-WANI, Public Data Offices (PDOs) can provide internet services independently without any intermediary.
- The Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT) is responsible for supplying PM-WANI-compliant Wi-Fi hardware.
- PM-WANI requires individuals to obtain a government license before establishing a public Wi-Fi hotspot.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(A) 1 and 3 only
(B) 3 only
(C) 2 and 4 only
(D) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: (B) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: PM-WANI aims to enhance internet access across both rural and urban areas, not just rural regions.
Statement 2 is incorrect: PDOs must collaborate with a Public Data Office Aggregator (PDOA) to provide internet services.
Statement 3 is correct: The Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT) supplies PM-WANI-compliant Wi-Fi hardware through Transfer of Technology (ToT) partners.
Statement 4 is incorrect: Individuals or entities do not require a government license to set up public Wi-Fi hotspots under PM-WANI, making the initiative highly accessible and scalable.
