Rashtriya Karmayogi Jan Seva Programme
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
Context: The Union Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment successfully launched the first batch of the Rashtriya Karmayogi Jan Seva Programme, aimed at fostering a citizen-centric approach in governance.
About the Programme
- It is an interactive initiative designed to inspire, enlighten, and guide Central Government employees in adopting the Karmayogi Way, which prioritizes Seva-Bhav (a sense of service) and accountability.
- The initiative is spearheaded by the Capacity Building Commission (CBC) to enhance competency-driven governance.
Capacity Building Commission (CBC)
- Established: 2021
- Structure: Three-member body supported by an internal Secretariat led by a Secretary.
- Composition: Members are drawn from diverse backgrounds, including the private sector, academia, public sector, and civil society.
- Objective: Standardizing and improving public sector learning and development initiatives across the country.
Mission Karmayogi
- Launched: 2020
- Type: National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB)
- Objective: Developing a future-ready civil service with the right attitude, skills, and knowledge, in alignment with the vision of New India.
- Governance: Anchored by an apex body, headed by the Prime Minister to ensure effective implementation.
Consider the following statements regarding the Rashtriya Karmayogi Jan Seva Programme:
- It is an initiative launched by the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances, and Pensions.
- The programme emphasizes a citizen-centric approach to governance by fostering Seva-Bhav and accountability.
- The Capacity Building Commission is responsible for implementing this programme.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Explanation:
Incorrect: The Rashtriya Karmayogi Jan Seva Programme is launched by the Union Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, not the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances, and Pensions.
Correct: The programme indeed emphasizes a citizen-centric approach to governance, fostering Seva-Bhav (spirit of service) and accountability among government employees.
Correct: The Capacity Building Commission (CBC), established in 2021, is responsible for implementing and overseeing the programme, aligning it with broader civil service capacity-building initiatives under Mission Karmayogi.
PM’s Scheme for Mentoring Young Authors (PM-YUVA 3.0)
Syllabus: GS2/ Governace
- The Ministry of Education has launched the third edition of the Prime Minister’s Scheme for Mentoring Young Authors (PM-YUVA 3.0) to nurture young literary talent in India.
About the Scheme:
- Aims to mentor aspiring authors under the age of 30, fostering a culture of reading, writing, and publishing.
- Provides mentorship and publishing support to help Indian writers gain recognition on a global platform.
Focuses on three key themes:
- Contribution of Indian Diaspora in Nation Building
- Indian Knowledge System
- Makers of Modern India (1950-2025)
- Aligns with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which emphasizes building a knowledge-driven ecosystem.
- National Book Trust (NBT), India, is responsible for implementing the scheme.
With reference to the Prime Minister’s Scheme for Mentoring Young Authors (PM-YUVA 3.0), consider the following statements:
- It is an initiative of the Ministry of Culture to promote regional literature and folk traditions.
- The scheme aims to train young authors under the age of 35 to foster a reading and writing culture in India.
- National Book Trust (NBT), India, is responsible for implementing the scheme.
- The scheme aligns with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, focusing on creating a knowledge-driven ecosystem.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: PM-YUVA 3.0 is launched by the Ministry of Education, not the Ministry of Culture.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The scheme is designed for authors under the age of 30, not 35.
Statement 3 is correct: National Book Trust (NBT), India is responsible for implementation.
Statement 4 is correct: The scheme aligns with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, promoting a knowledge-driven ecosystem.
Regulating Ultra-Processed Foods - The Need for Stronger Policies
Syllabus: GS2
Introduction
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi has emphasized the urgent need to combat obesity, and the 2025 Economic Survey has proposed a ‘health tax’ on ultra-processed foods (UPFs) to curb their consumption. With one in four Indian adults obese and one in four either diabetic or pre-diabetic (NFHS-5), addressing this health crisis requires bold policy interventions.
Challenges in Food Labelling and Advertising
- Regulatory Gaps
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has struggled to enforce strict food labelling and advertising regulations since 2017.
- Current rules are ambiguous and industry-friendly, failing to implement mandatory front-of-pack warning labels despite the rising health risks of UPFs.
- Flaws in the Indian Nutrition Rating (INR) System
- Introduced in September 2022, the INR system is modeled after Australia’s ineffective ‘health star’ system, which assigns 1 to 5 stars based on nutritional content.
Criticisms include:
- Creates a false health perception: Unhealthy foods appear healthier due to star ratings.
- Lack of scientific scrutiny: The FSSAI relied on an unexamined IIM Ahmedabad study to justify the rating system.
- Industry influence: Key decisions were shaped by food industry representatives, sidelining independent health experts.
Misclassification Examples:
- Soft drinks with high sugar may receive 2 stars instead of a warning label.
- Cornflakes (high in sugar and sodium) are rated 3 stars, misleading consumers about their health impact.
- The FSSAI ignored its own 2021 proposal for mandatory ‘traffic light’ warning labels, favoring an industry-driven approach
Ineffective Advertising Regulations
- India has four different laws regulating HFSS (High Fat, Salt, Sugar) food advertisements, but they lack enforcement:
- Consumer Protection Act, 2019: Defines misleading ads but does not mandate nutritional disclosure.
- National Multisectoral Action Plan (2017): Proposed stricter HFSS ad rules, but no action was taken.
Loopholes in advertising laws:
- No requirement to disclose sugar, salt, or fat content in advertisements.
- Brands continue targeting children with misleading health claims.
Global Best Practices and Lessons for India
- Chile’s ‘High In’ Warning Labels: A policy requiring clear warning labels on UPFs led to a 24% reduction in consumption.
- World Health Organization (WHO) Guidelines: Recommends bold front-of-pack warning labels to help consumers make informed choices.
The Way Forward: Urgent Policy Reforms
- Implement Front-of-Pack Warning Labels
- Abolish the misleading INR system.
- Mandate clear “High in Sugar/Salt/Fat” labels on UPFs.
- Define and Regulate UPFs and HFSS Foods
- Establish strict sugar, salt, and fat limits based on WHO and ICMR-NIN
- Strengthen Advertising Regulations
- Amend laws to ban misleading HFSS advertising.
- Harmonize regulations across multiple laws to prevent industry loopholes.
Launch Nationwide Awareness Campaigns
Educate consumers in multiple languages on the dangers of UPFs.
Conclusion
The obesity crisis in India is a result of weak policy enforcement, not individual failure. Food industry lobbying has led to lenient labelling and advertising rules, allowing junk food companies to profit at the cost of public health. The Economic Survey has outlined a roadmap, but without decisive regulatory action, India’s health burden will continue to rise. Achieving PM Modi’s vision of a healthy India requires firm, science-backed policies rather than industry-driven compromises.
Consider the following statements regarding the proposed ‘health tax’ on Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs):
- The Economic Survey 2025 recommends imposing a ‘health tax’ on UPFs to reduce their consumption.
- UPFs have been scientifically linked to increased risks of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
- The tax proposal is aligned with the World Health Organization’s (WHO) recommendations on public health policy.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (d) 1, 2, and 3
Explanation:
The Economic Survey 2025 has recommended a ‘health tax’ to curb UPF consumption (Statement 1 is correct).
Scientific studies have linked UPFs to obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular risks (Statement 2 is correct).The WHO has consistently recommended fiscal policies like health taxes to reduce UPF consumption (Statement 3 is correct).
Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK)
Syllabus :GS 2/Governance
Context:
The Ministry of Minority Affairs recently conducted a National Review Meeting to evaluate the progress of the Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK).
About PMJVK:
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme aimed at developing community infrastructure and basic amenities in 1,300 identified areas across India.
- Restructured in May 2018 to bridge socio-economic disparities in targeted regions.
- Implemented through State Governments and Union Territory (UT) Administrations.
- Funding Pattern: Operates on a cost-sharing basis between the Centre and States/UTs.
Key Focus Areas:
Education: Construction of schools, hostels, laboratories, and ITIs.
Health: Establishment of hospitals and healthcare centers.
Skill Development: Promotion of vocational training and employment opportunities.
Women’s Welfare: Building community toilets and welfare centers for women.
Implementation Mechanism:
- State Level Committees (SLCs) recommend project proposals.
- Empowered Committee (EC) within the Ministry of Minority Affairs grants final approval.
This initiative plays a crucial role in reducing socio-economic inequalities and enhancing infrastructure in minority-dominated areas.
Consider the following statements regarding the Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK):
- It is a Central Sector Scheme implemented solely by the Central Government.
- The scheme aims to bridge socio-economic gaps in 1,300 identified areas across India.
- It provides financial assistance for projects related to education, health, and skill development.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect because PMJVK is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, meaning it is implemented through State Governments and UT Administrations with shared funding.
Statement 2 is correct as the scheme targets 1,300 identified areas to reduce socio-economic gaps.
Statement 3 is correct as it funds projects in education, health, skill development, and women’s welfare.
PM’s Visit to Mauritius
Syllabus:IR
- The Prime Minister of India recently paid a state visit to Mauritius, marking his second visit since 2015. He was the Chief Guest at Mauritius’ National Day Celebrations on March 12.
Key Highlights of the Visit
- Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs): Agreements signed in areas such as civil service training, support for small and medium enterprises (SMEs), blue economy development, combating financial crimes, and local currency settlement for trade.
- INR-Based Credit Line: India extended an INR 487.6 crore line of credit for replacing water pipelines in Mauritius, the first-ever INR-denominated credit line.
- White-Shipping Agreement: A maritime security agreement facilitating information exchange between India and Mauritius.
- Award Conferred: The PM received the Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean, becoming the first Indian recipient of this prestigious award.
- Vision MAHASAGAR: The PM introduced the Mutual And Holistic Advancement for Security And Growth Across Regions (MAHASAGAR) vision, expanding upon the existing Vision SAGAR framework.
About Mauritius
Location: A strategically positioned island nation in the western Indian Ocean near India.
Population: Approximately 1.2 million people, with 70% of Indian origin, strengthening historical and cultural ties.
Colonial History: Initially a French colony, later becoming a British possession before gaining independence.
National Day: Celebrated on March 12, coinciding with Mahatma Gandhi’s Dandi March anniversary.
India-Mauritius Bilateral Relations
- Diplomatic and Economic Ties
- Established Relations: India and Mauritius established diplomatic ties in 1948 and have since become key partners in the Asian and Indian Ocean regions.
Bilateral Trade (2022-2023):
- Indian Exports to Mauritius: USD 462.69 million
- Mauritian Exports to India: USD 91.50 million
- Total Trade Volume: USD 554.19 million
- Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA): Signed in 1982 to prevent double taxation for investors and businesses.
- Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA): India’s first trade agreement with an African nation, signed in 2021, promoting trade and investment.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Mauritius is the second-largest source of FDI into India for FY 2023-24, following Singapore.
Defence and Strategic Cooperation
Preferred Defence Partner: India supports Mauritius in acquiring defence platforms, capacity building, and conducting joint patrols in the Indian Ocean.
Key Defence Agreements:
First Agreement: Transfer of a Dornier aircraft and Advanced Light Helicopter (Dhruv) on lease.
Second Agreement: A USD 100 million Line of Credit (LoC) for defence procurement.
Space Cooperation: An MoU signed in November 2023 for the development of a joint satellite, fostering collaboration in space research.
Historical Indian Migration to Mauritius
French Rule (1700s): Indians from Puducherry arrived as artisans and masons.
British Rule (1834–Early 1900s): Around half a million Indian indentured laborers were brought to Mauritius, many of whom settled permanently, shaping its culture and demographics.
Development Assistance
- Infrastructure Projects: India has supported Mauritius in developing the Metro Express project, hospitals, and Agaléga Island infrastructure.
- Humanitarian Aid: India extended cyclone relief assistance during Cyclone Chido (2023), reinforcing its role as a first responder in the region.
Strategic Significance of Mauritius for India
Maritime and Geopolitical Interests
Strategic Location: Mauritius’ position in the Indian Ocean is vital for India’s maritime security and trade routes.
Agaléga Island: Situated 1,100 km north of Mauritius, the island is strategically important for India’s naval operations.
In 2024, India and Mauritius jointly inaugurated an airstrip and jetty projects to strengthen bilateral cooperation.
Countering China’s Influence: Strengthening ties with Mauritius is crucial for India to counter China’s expanding footprint in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
Geopolitical Competition: The Indian Ocean is witnessing increasing competition from China, Europe, the Gulf nations, Russia, Iran, and Turkey.
Economic and Cultural Importance: Cultural and Diaspora Ties: With 70% of the Mauritian population tracing Indian ancestry, strong cultural and familial bonds exist between both nations.
Blue Economy Partnership: Mauritius plays a critical role in India’s blue economy initiatives, particularly in fisheries, maritime resources, and offshore energy exploration.
Indian Ocean Cooperation: Mauritius is an active member of the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), promoting regional stability and economic integration.
Challenges in India-Mauritius Relations
Economic and Trade Concerns
Tax Treaty Misuse: The DTAA between India and Mauritius has faced criticism for facilitating money laundering and round-tripping of funds.
Trade Imbalance: Despite strong economic ties, Mauritius has significant trade deficits with India, necessitating trade diversification.
Security and Strategic Challenges
Maritime Security: As a key player in the Indo-Pacific strategy, Mauritius’ security concerns align with India’s, yet evolving regional dynamics present new challenges.
Growing Chinese Influence:
- In 2021, China signed a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with Mauritius, helping China expand its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) in Africa.
- This could erode India’s strategic influence in Mauritius.
Way Forward
- Enhanced Defence Cooperation: Strengthening joint training, counterterrorism initiatives, and maritime security collaborations to safeguard regional stability.
- Economic Diversification: Expanding trade relations beyond traditional areas and exploring emerging sectors for bilateral growth.
- People-to-People Ties: Promoting cultural exchanges, educational scholarships, and diaspora engagement to reinforce deep-rooted historical bonds.
- Sustainable Blue Economy Partnership: Leveraging Mauritius’ expertise in ocean resources management to drive mutual economic growth.
- India and Mauritius share a unique, time-tested partnership, and their evolving cooperation will play a crucial role in shaping regional security, economic integration, and strategic alliances in the Indian Ocean region.
Consider the following statements regarding India-Mauritius relations:
- Mauritius is the largest source of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) into India.
- India and Mauritius have signed a Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA), which is India’s first trade agreement with an African nation.
- India has leased the Agaléga Islands from Mauritius for setting up a strategic naval base.
- The White-Shipping Agreement between India and Mauritius facilitates free trade between the two nations without tariff barriers.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (c) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect – While Mauritius has historically been a major source of FDI into India, Singapore overtook Mauritius as the largest FDI contributor in recent years (FY 2023-24). Therefore, this statement is incorrect.
- Statement 2 is correct – India and Mauritius signed CECPA in 2021, which is indeed India’s first-ever trade agreement with an African nation. This statement is correct.
- Statement 3 is incorrect – India has not leased the Agaléga Islands, but developed infrastructure projects there, including an airstrip and a jetty, to enhance maritime security. There is no official declaration of a naval base. This statement is incorrect.
- Statement 4 is incorrect – The White-Shipping Agreement is not about free trade. It is a technical agreement that allows exchange of maritime security data between India and Mauritius to monitor ship movements and counter threats like piracy and smuggling. This statement is incorrect.Thus, only statement 2 is correct, making (c) 2 only the right answer.
PM Modi Receives Mauritius’ Highest Honour
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi has been awarded the Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean by Mauritius.
- This prestigious recognition is the highest civilian honour bestowed by the island nation.
- Modi is the first Indian to receive this honour, reflecting the deep-rooted historical and diplomatic ties between India and Mauritius.
Significance of the Honour
- The Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean is the most distinguished civilian award in Mauritius.
- Since Mauritius became a Republic, this honour has been conferred upon only five foreign dignitaries, including Nelson Mandela.
- The award symbolizes mutual respect, cooperation, and the strong diplomatic relationship between India and Mauritius.
Modi’s Growing List of International Honours
This accolade from Mauritius marks Modi’s 21st international award, adding to a series of global recognitions for his leadership and diplomatic initiatives. Some of the notable awards he has received include:
- Order of Abdulaziz Al Saud (Saudi Arabia, 2016)
- State Order of Ghazi Amir Amanullah Khan (Afghanistan, 2016)
- Grand Collar of the State of Palestine (Palestine, 2018)
- Order of Zayed (UAE, 2019)
- Order of St. Andrew (Russia, 2019)
- Order of the Nile (Egypt, 2023)
- Order of the Druk Gyalpo (Bhutan, 2024)
- Dominica Award of Honour (Dominica, 2024)
India-Mauritius Relations: A Historical Perspective
- The ties between India and Mauritius date back to the 19th century, when Indian indentured labourers were brought to Mauritius. Over time, these historical connections have evolved into a robust economic, cultural, and strategic partnership.
- India is one of Mauritius’ largest trading partners.
- Both countries collaborate extensively in fields such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, and security.
- Mauritius is a key player in India’s diplomatic outreach in the Indian Ocean region, with both nations working closely on maritime security and regional stability.
Conclusion
- The Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean is a testament to India-Mauritius friendship and underscores Modi’s global leadership. This honour further strengthens bilateral ties and reaffirms India’s role as a key partner in Mauritius’ development.
Which of the following statements about the “Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean” is correct?
(a) It is the highest military honour awarded by Mauritius.
(b) It has been awarded to more than 100 foreign dignitaries since Mauritius became a Republic.
(c) Narendra Modi is the first Indian recipient of this honour.
(d) It is an annual award given to prominent global leaders.
Answer: (c)
Explanation:
- The Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean is Mauritius’ highest civilian honour, not a military one. It has been conferred upon only five foreign dignitaries, including Nelson Mandela, since Mauritius became a Republic.
- Modi is the first Indian to receive this honour.
- The award is not an annual event but is given selectively to leaders who have significantly contributed to Mauritius’ growth and bilateral .
6 Years of POSHAN Abhiyan
Syllabus: GS2/ Welfare Scheme
Context: Launched in 2018, POSHAN Abhiyaan has completed seven years of implementation, marking a significant milestone in India’s commitment to eliminating malnutrition and anemia.
Objectives of POSHAN Abhiyaan: The initiative focuses on a multi-pronged approach to address malnutrition and maternal health, with key objectives:
- Reduction of stunting among children (0-6 years).
- Mitigation of under-nutrition (prevalence of underweight children, 0-6 years).
- Lowering anemia prevalence among women and adolescent girls (15-49 years).
- Reduction of low birth weight (LBW) through enhanced maternal and child healthcare services.
- Strategic Pillars of POSHAN Abhiyaan
Access to Quality Services:
- Strengthening maternal and child health services through flagship programs:
- Integrated Child Development Scheme (ICDS)
- National Health Mission (NHM)
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY)
- Special focus on the first 1,000 days of life, critical for early childhood development.
Cross-Sectoral Convergence:
- Integration with various national programs for a holistic approach:
- Swachh Bharat Mission (sanitation and hygiene)
- National Drinking Water Mission (safe drinking water access)
Leveraging Technology:
- Adoption of digital tools, including the Poshan Tracker application, for real-time monitoring and intervention.
Jan Andolan (People’s Movement):
- Community-led initiatives to raise awareness and encourage behavioral shifts in nutrition and maternal health practices.
- Mission Saksham Anganwadi & POSHAN 2.0
Launched in 2021, integrating multiple nutrition-focused programs under a unified framework, including:
- Supplementary Nutrition Programme (SNP)
- POSHAN Abhiyaan
- Strengthened Anganwadi services, emphasizing:
- Infrastructure development
- Nutritional support
- Capacity-building of frontline workers
Funding Pattern:
- For States & UTs with Legislature: 60:40 (Centre: State)
- For Northeastern & Himalayan States: 90:10 (Centre: State)
Conclusion:
POSHAN Abhiyaan remains a cornerstone initiative in India’s battle against malnutrition, integrating policy, technology, and community engagement to foster a healthier future for children and women.
Consider the following statements regarding POSHAN Abhiyaan:
- It was launched in 2018 with the aim of addressing malnutrition among children and women.
- It exclusively focuses on providing nutritional support to children below five years of age.
- The initiative leverages digital tools like the Poshan Tracker for real-time monitoring.
- It is implemented solely by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
a) 1 and 3 only
b) 2 and 4 only
c) 1, 2, and 3 only
d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
POSHAN Abhiyaan is a multi-sectoral initiative that integrates efforts from different ministries, including the Ministry of Women and Child Development. It does not focus exclusively on children below five years but also addresses adolescent girls and maternal nutrition.
Surat Food Security Saturation Campaign
Syllabus: Government schemes

- Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the Surat Food Security Saturation Campaign Programme in Limbayat, Surat, reinforcing the government’s commitment to ensuring food security for the underprivileged.
- The initiative, aimed at benefiting over 2.3 lakh people, underscores Surat’s collective spirit in supporting the marginalized.
Objectives of the Campaign:
- The campaign is designed to expand the reach of the National Food Security Act (NFSA), ensuring that no eligible individual is left out.
- Over 2.5 lakh new beneficiaries have been identified, including elderly individuals and differently-abled persons.
- The initiative moves beyond political appeasement and focuses on fair and inclusive food distribution.
- Beneficiaries will receive free rations and nutritious food, helping combat hunger and malnutrition.
- Government Initiatives for Food Security:
- The government has implemented several schemes to enhance food security across India: Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana (PMGKY) – Launched during COVID-19 to provide free food grains to the poor.
- PM Poshan Scheme – Ensures nutritious meals for school children, improving their health and learning outcomes.
- Saksham Anganwadi Program – Focuses on maternal and child nutrition, enhancing early childhood development.
- PM Matru Vandana Yojana – Provides financial aid to pregnant women, promoting maternal and infant health.
Emphasis on Nutrition and Hygiene: Eliminating malnutrition and anaemia is a government priority. Surat has set an example in hygiene and cleanliness, complementing the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan. The Har Ghar Jal campaign ensures clean drinking water, improving public health and sanitation.
Financial Inclusion and Support for the Poor: To empower the underprivileged, the government has introduced key financial initiatives: One Nation, One Ration Card (ONORC) – Allows beneficiaries to access rations from anywhere in India, ensuring food security for migrants. Mudra Yojana – Provides collateral-free loans to small businesses and entrepreneurs. PM SVANidhi Yojana – Offers financial support to street vendors, enabling economic self-reliance.
Strengthening the Middle Class: The government recognizes the middle class as a pillar of economic growth. Recent tax relief measures allow middle-class families to retain more income. New tax slabs support financial stability and encourage investment and savings.
Surat’s Economic Growth and Infrastructure Development: Surat is a major hub for textiles, chemicals, and MSMEs. To boost economic activity, the government has invested in MSME-friendly loan schemes, enabling business expansion. Infrastructure projects such as the Surat Metro and the new airport terminal improve connectivity and quality of life.
Women Empowerment Initiatives: Women’s empowerment remains a key focus of the government. Women are encouraged to share their success stories, inspiring greater participation in economic and social development. Special events and programs celebrate women’s contributions across various sectors.
The Surat Food Security Saturation Campaign is a significant milestone in ensuring that every citizen has access to essential nutrition and financial support, fostering growth, inclusivity, and empowerment.
With reference to the Swavalambini Programme, consider the following statements:
1.Swavalambini is a joint initiative of MSDE and NITI Aayog aimed at women entrepreneurship.
2.The programme primarily focuses on providing direct financial assistance to women entrepreneurs for their startups.
3.It includes a Faculty Development Programme (FDP) that trains educators from Higher Education Institutions (HEIs).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct. Swavalambini is a collaborative effort between MSDE and NITI Aayog, aimed at boosting women entrepreneurship.
Statement 2 is incorrect. The programme does not provide direct financial aid but facilitates access to funding through various government and private schemes.
Statement 3 is correct. The Faculty Development Programme (FDP) is a crucial component, training faculty members from HEIs to mentor women entrepreneurs.
Modified Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme
syllabus: Government schemes
- The Government of India has introduced a modified Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme to enhance the operational viability of Cooperative Sugar Mills (CSMs).
- This initiative enables these mills to upgrade their existing sugarcane-based ethanol plants into multi-feedstock facilities, allowing the use of grains such as maize and damaged food grains (DFG) alongside sugarcane.
- The objective is to ensure year-round production, improve efficiency, and strengthen the ethanol industry.
- Ethanol Production in India: Ethanol production in India primarily depends on sugarcane, but its crushing period lasts only 4-5 months annually, limiting production capacity. To address this, the government is promoting the diversification of feedstock’s to ensure consistent ethanol output. The Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme targets a 20% ethanol blend with petrol by 2025, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and enhancing energy security.
- Modified Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme: The scheme offers financial assistance in the form of an interest subvention of 6% per annum or 50% of the bank interest rate, whichever is lower. This support is applicable for loans provided by banks or financial institutions over five years, including a one-year moratorium. By easing financial constraints, the initiative encourages CSMs to expand their ethanol production beyond sugarcane-based operations.
- Benefits of Multi-Feedstock Conversion: The shift to multi-feedstock plants provides several advantages:
- Year-Round Production: Using grains and agricultural residues ensures continuous ethanol output, even outside the sugarcane season.
- Improved Efficiency: Diversified raw materials enhance the mills’ operational flexibility and financial sustainability.
- Economic Growth: Supporting local grain production reduces dependence on sugarcane, strengthening the agricultural economy.
- Impact on Ethanol Production Targets: India has set ambitious ethanol production targets under the EBP Programme. As of February 2025, the blending rate reached 19.6%, indicating significant progress toward the 20% goal. Enhanced production capabilities from CSMs are expected to play a key role in meeting this target.
- Future Prospects for Cooperative Sugar Mills: The modified scheme provides a transformative opportunity for CSMs.
- By embracing a multi-feedstock approach, these mills can ensure long-term sustainability while contributing to India’s renewable energy goals.
- Additionally, leveraging locally available grains promotes self-sufficiency and strengthens the rural economy.
- This strategic shift marks a crucial step in making ethanol production more resilient and efficient in the coming years.
Consider the following statements regarding the Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme:
- It provides an interest subvention of 6% per annum or 50% of the bank interest rate, whichever is lower.
- The scheme allows Cooperative Sugar Mills (CSMs) to upgrade their sugarcane-based ethanol plants into multi-feedstock facilities.
- The financial support under this scheme is provided for a period of ten years, including a two-year moratorium.
- It aims to facilitate year-round ethanol production by diversifying the feedstock to include maize and damaged food grains (DFG).
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1, 2, and 4 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 3, and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 – Correct: The scheme provides an interest subvention of 6% per annum or 50% of the bank interest rate, whichever is lower.
Statement 2 – Correct: It allows CSMs to upgrade their sugarcane-based ethanol plants into multi-feedstock facilities.
Statement 3 – Incorrect: The financial assistance is provided for five years, including a one-year moratorium, not ten years with a two-year moratorium.
Statement 4 – Correct: The scheme encourages the use of maize and damaged food grains (DFG) for ethanol production.
Implementation of Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY)
Launched: Kharif 2016 season
Voluntary: For States/UTs and farmers
Objective: Affordable, comprehensive, and technology-driven crop insurance
Key Features
Affordable Premiums:
2% for Kharif food & oilseed crops
1.5% for Rabi food & oilseed crops
5% for annual commercial & horticultural crops
Government subsidizes remaining premium
Comprehensive Coverage:
Covers natural disasters (droughts, floods), pest attacks, disease outbreaks
Covers post-harvest losses due to hailstorms, landslides
Timely Compensation:
Claims processed within two months of harvest
Technology-Driven Implementation:
Uses satellite imaging, drones, mobile apps for precise crop loss estimation
Post-Harvest Loss Coverage:
Covers losses for up to 14 days for crops stored in cut & spread condition
Did You Know?
Restructured Weather-Based Crop Insurance Scheme (RWBCIS) was introduced alongside PMFBY
Key Difference:
PMFBY: Compensates based on actual crop losses
RWBCIS: Provides payouts based on predefined weather parameters (rainfall, temperature, humidity)
Consider the following statements regarding the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY):
- The scheme was launched in the Kharif 2016 season and is mandatory for all States and farmers.
- The government provides a subsidy on the premium amount to ensure affordability for farmers.
- PMFBY covers post-harvest losses for up to 30 days for crops stored in a “cut and spread” condition.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: PMFBY was launched in Kharif 2016, but it is voluntary for both States/UTs and farmers since the 2020 revamp.
Statement 2 is correct: The government subsidizes the remaining premium after the farmers pay their share.
Statement 3 is incorrect: PMFBY provides post-harvest loss coverage for up to 14 days, not 30 days.
Soil Fertility Mapping
Syllabus: GS 3/Economy
In News
- Soil fertility maps have been developed for 351 villages across 34 districts in Maharashtra, enhancing precision in fertilizer application and soil management.
What is Soil Fertility Mapping?
- Soil fertility maps provide location-specific data, enabling optimal fertilizer use to prevent overuse or deficiency.
- Soil & Land Use Survey of India (SLUSI) generates digital soil fertility maps using geospatial techniques and Soil Health Card (SHC) data.
- These maps help farmers apply fertilizers and soil amendments efficiently, reducing wastage and enhancing economic benefits.
Technological Integration in Soil Mapping
- Geospatial techniques, including remote sensing and AI-based tools, are used in soil fertility mapping.
- GPS-based geo-coding assigns a unique QR code to each soil sample, ensuring seamless tracking and analysis in soil testing laboratories.
Challenges in Implementation
- Logistical, technical, and infrastructure limitations in remote and hilly regions hinder effective soil testing.
- Village-Level Soil Testing Labs and mini-labs are being set up to address these challenges and improve accessibility.
Importance of Soil Fertility Mapping
- Identifies soil degradation and nutrient deficiencies.
- Facilitates balanced fertilizer application, enhancing soil health and agricultural productivity.
Key Government Initiatives
- Soil Health & Fertility Scheme
- Promotes Integrated Nutrient Management (INM) by combining:
- Chemical fertilizers
- Organic manures
- Bio-fertilizers
- Aims to enhance soil health and agricultural productivity.
Soil Health Card (SHC)
- Provides soil nutrient status (categorized as low, medium, or high).
- Recommends nutrient application strategies to improve soil health.
Parameters tested include:
- pH, electrical conductivity, organic carbon
- Macronutrients: Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur
- Micronutrients: Zinc, iron, copper, manganese, and boron
- Farmers can download their SHC by entering their registered mobile number.
- The Soil Health & Fertility Scheme is implemented across all States and UTs in India.
With reference to Soil Fertility Mapping, consider the following statements:
- The Soil & Land Use Survey of India (SLUSI) is responsible for generating digital soil fertility maps using satellite imaging and AI-based techniques.
- The process of soil fertility mapping involves assigning a unique QR code to each soil sample for precise tracking and analysis.
- Soil fertility maps primarily focus on macronutrients like Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium, and do not include micronutrients such as Zinc and Boron.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: SLUSI generates digital soil fertility maps using geospatial techniques, including remote sensing and AI-based tools.
Statement 2 is correct: Each soil sample is assigned a unique QR code, which is retained during analysis in soil testing labs.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Soil fertility mapping includes both macronutrients and micronutrients, such as Zinc, Iron, Copper, Manganese, and Boron, making it a comprehensive assessment tool.
Hantavirus
Syllabus Science and Technology
Context:
- The recent tragic deaths of actor Gene Hackman and his wife Betsy Arakawa have drawn attention to hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS), a rare but severe rodent-borne disease.
- Arakawa’s death, linked to HPS, has highlighted the risks associated with this virus and the need for greater public awareness.
What is Hantavirus?
- Hantavirus refers to a group of viruses carried by rodents.
- Transmission to humans occurs through contact with rodent urine, feces, or saliva, primarily from deer mice in the United States.
- Unlike many infectious diseases, hantavirus does not spread between humans.
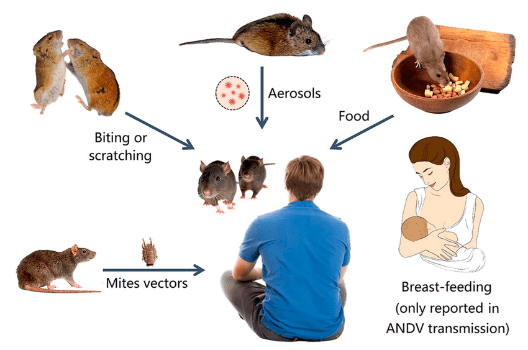
Types of Hantavirus Diseases
- The impact of hantavirus varies by region, with two major diseases associated with it:
- Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) – Primarily found in the Americas, this severe respiratory disease can be fatal.
- Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS) – More common in Europe and Asia, this disease primarily affects the kidneys.
- Each hantavirus strain is associated with specific rodent hosts, making regional awareness crucial.
Symptoms of Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS)
Symptoms typically develop between one to eight weeks after exposure.
Early signs resemble flu-like symptoms, including fatigue, fever, and muscle aches.
As the disease progresses, severe respiratory distress occurs, leading to shortness of breath and chest tightness.
Fatality Rate: Approximately 38% of individuals who develop respiratory complications succumb to HPS.
Treatment and Prevention
No Cure Available: There is currently no antiviral treatment for HPS.
Early Detection is Crucial: Supportive care, including oxygen therapy and intensive respiratory support, may improve survival chances.
Preventive Measures:
Avoid exposure to rodent-infested environments.
Use disinfectants to clean areas with possible rodent activity.
Refrain from sweeping or vacuuming dry rodent droppings, as this can aerosolize the virus.
Wear protective masks and gloves when cleaning contaminated areas.
Public Health Awareness and Safety Measures
Public health officials recommend heightened awareness in regions where rodents are common.
Using protective gear while cleaning rodent droppings can significantly reduce the risk of exposure.
Educational initiatives on hantavirus risks and safe hygiene practices can help prevent infections and protect communities.
With no specific cure available, prevention and early detection remain the most effective strategies against hantavirus infections.
Consider the following statements regarding Hantavirus:
- Hantavirus is primarily transmitted through direct human-to-human contact.
- The disease caused by Hantavirus in the Americas is known as Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS).
- The primary rodent carrier of Hantavirus in the United States is the deer mouse.
- Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) has a fatality rate of over 50%.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 4 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: (c) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 – Incorrect: Hantavirus does not spread through human-to-human contact. It is transmitted to humans primarily through exposure to rodent urine, feces, or saliva.
Statement 2 – Incorrect: Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) is found in the Americas, while Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS) is more common in Europe and Asia.
Statement 3 – Correct: The deer mouse (Peromyscus maniculatus) is the primary reservoir of Hantavirus in the United States.
Statement 4 – Incorrect: The fatality rate of HPS is approximately 38%, not over 50%.
Vitiligo and Gut Bacteria
syllabus Science and Technology
- Recent studies have highlighted a potential breakthrough in the treatment of vitiligo, a chronic autoimmune disorder that leads to skin depigmentation.
- This condition, which affects a significant portion of the global population, has both cosmetic and psychological impacts.
- Emerging research suggests that gut-friendly bacteria may play a key role in slowing its progression, opening new possibilities for treatment.

Understanding Vitiligo
- Vitiligo occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing skin pigment.
- This results in white patches on the skin, which can appear anywhere on the body but are most noticeable on the face, hands, and arms.
- While often perceived as a cosmetic issue, vitiligo can lead to social stigma and emotional distress, especially in individuals with darker skin tones.
- The condition affects 5% to 2% of the global population, with higher prevalence reported in regions like Gujarat and Rajasthan in India.
New Research Findings
- Recent studies from Northwestern University have discovered a natural compound derived from gut-friendly bacteria that could slow vitiligo progression.
- Pre-clinical trials in mice showed that this microbial compound reduced pigment loss by 74%.
- The compound works by reducing harmful killer T cells while increasing protective regulatory T cells, helping to restore immune balance.
- These findings suggest that modifying the gut microbiome could become a novel therapeutic approach for vitiligo.
Importance of Early Intervention
- Vitiligo often appears during adolescence or between the ages of 40 and 50.
- The condition is more pronounced in individuals with darker skin, leading to greater emotional and social distress.
- Early intervention can help stabilize pigment loss, improving treatment outcomes and quality of life for patients.
Future Treatment Possibilities
- Researchers are now exploring ways to translate these findings into human treatments:
- Current options include weekly injections, but more accessible alternatives like topical ointments or food additives are also being considered.
- Further studies are needed to determine the optimal dosage, duration, and long-term effectiveness of these treatments.
Broader Implications
- This research could have applications beyond vitiligo, potentially benefiting other autoimmune diseases with similar immune system dysfunction.
- Collaboration among scientists will be essential to refine the microbial compound and assess its compatibility with existing vitiligo treatments.
- By leveraging the power of the gut microbiome, researchers may unlock new, non-invasive therapies that could revolutionize the treatment of vitiligo and other immune-related conditions.
Consider the following statements regarding vitiligo:
- Vitiligo is an autoimmune disorder that leads to the destruction of keratinocytes, resulting in depigmented patches on the skin.
- The condition has a higher prevalence in regions like Gujarat and Rajasthan in India.
- The emotional and social impact of vitiligo is more pronounced in individuals with darker skin tones.
- The disease primarily manifests in childhood and is rarely observed after the age of 30.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 4 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 2, and 4 only
d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 – Incorrect: Vitiligo results from the destruction of melanocytes, not keratinocytes.
Statement 2 – Correct: Studies indicate that vitiligo has a higher prevalence in regions like Gujarat and Rajasthan in India.
Statement 3 – Correct: Since vitiligo causes visible depigmentation, individuals with darker skin tones often experience greater emotional and social distress.
Statement 4 – Incorrect: Vitiligo commonly appears during adolescence or between ages 40-50, but it is not strictly confined to childhood.
H1N1 Virus:
- Delhi is experiencing a notable surge in seasonal flu cases, with H1N1 (Swine Flu) and Influenza B emerging as dominant strains.
- These infections are leading to persistent high fevers and prolonged upper respiratory symptoms, raising concerns among healthcare professionals.
Understanding the H1N1 Virus
Overview
- H1N1, commonly known as Swine Influenza (Swine Flu), is a respiratory infection caused by Type A influenza viruses, which primarily affect pigs.
- While human infections are rare, sporadic cases do occur, and in some instances, limited human-to-human transmission has been observed.
H1N1 in India
- The first confirmed case of H1N1 in India was reported in May 2009. Since then, the virus has caused multiple outbreaks, with significant surges recorded in 2021, 2022, 2023, and now again in 2024, making it a recurring public health challenge.
- Modes of Transmission
H1N1 primarily spreads through:
- Respiratory droplets released when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
Direct contact with contaminated surfaces, followed by touching the eyes, nose, or mouth.
Symptoms of H1N1 Infection
- H1N1 symptoms are similar to seasonal influenza and may include:
- High fever
- Cough and sore throat
- Body aches and headaches
- Chills and fatigue
- Some cases may experience diarrhea and vomiting
- Severe cases can lead to pneumonia, respiratory failure, and even death
Treatment and Prevention
Currently, no specific vaccine is available for H1N1 prevention.
However, adopting preventive measures can help curb the spread:
Frequent handwashing with soap and water.
Avoiding close contact with infected individuals.
Wearing masks in crowded areas to prevent airborne transmission.
Seeking medical attention at the onset of flu-like symptoms.
With rising cases, public awareness and timely precautions remain key in managing the spread of H1N1 and safeguarding public health.
Consider the following statements regarding H1N1 (Swine Flu):
- H1N1 is caused by a Type B influenza virus.
- The first confirmed case of H1N1 in India was reported in 2009.
- Human-to-human transmission of H1N1 has never been reported.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- The correct option is (b) 2 only, as statement 2 is correct, while statements 1 and 3 are incorrect. Initially, H1N1 was believed to spread only from pigs to humans, but scientific studies confirmed human-to-human transmission soon after the 2009 outbreak.
- The virus spreads primarily through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes, similar to seasonal flu.
- Studies and epidemiological data confirm sustained human-to-human transmission of H1N1, making it capable of spreading within communities.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have documented multiple cases of human-to-human transmission, particularly in crowded and enclosed environments.
- This statement is incorrect as H1N1 has been proven to spread from person to person, which is why it led to a pandemic in 2009.
Shingles Disease
Understanding Shingles Disease
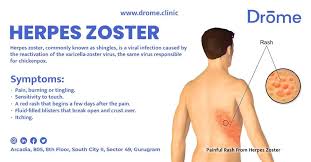
- Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, is a viral infection that causes a painful rash or blisters on the skin.
- The rash often appears in a band-like pattern in a specific area of the body but can occur anywhere.
- The risk of developing shingles increases with age, making it most common in individuals above 50 years.
Cause of Shingles
- It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus—the same virus responsible for chickenpox.
- After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in the body, residing in nerve tissues.
- In later life, reactivation of the virus can lead to shingles, often triggered by weakened immunity, stress, or aging.
Is Shingles Contagious?
- Shingles itself is not contagious, meaning it cannot spread directly from person to person.
- However, the varicella-zoster virus can spread to individuals who have never had chickenpox or not been vaccinated, causing chickenpox, not shingles.
- Symptoms of Shingles
Common symptoms include:
- Pain, itching, tingling, and numbness in the affected area.
- Fever, headache, chills, and fatigue may also occur.
- While shingles is not life-threatening, it can be extremely painful.
Complications
- The most common complication is postherpetic neuralgia (PHN)—a condition where shingles pain persists long after the blisters heal.
- Other complications may include vision problems (if it affects the eyes) and neurological issues in severe cases.
Prevention and Treatment
- Prevention:
- Shingrix is a vaccine that helps prevent shingles and its long-term complications.
- Treatment:
- There is no cure for shingles.
- Antiviral medications can help reduce severity and duration, especially when started early in the infection.
With reference to Shingles (Herpes Zoster), consider the following statements:
- Shingles is caused by the same virus responsible for measles.
- A person who has never had chickenpox cannot develop shingles.
- Shingles is highly contagious and spreads through direct contact with an infected person’s blisters.
- Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a common complication of shingles.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer :(c) 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Shingles is caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), which is also responsible for chickenpox, not measles (which is caused by the measles virus).
Statement 2 is incorrect: Shingles can only occur in individuals who have previously had chickenpox because the varicella-zoster virus remains dormant in the body. However, a person who has never had chickenpox can contract chickenpox if exposed to the virus from a person with shingles.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Shingles is not highly contagious. While the virus can spread, it does so only through direct contact with fluid from the blisters, and even then, it causes chickenpox, not shingles in those who have never had chickenpox before.
Statement 4 is correct: Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a painful condition where shingles pain persists for months or even years after the rash disappears, making it the most common complication of shingles.
Chandrayaan-3
Overview of Chandrayaan-3
Chandrayaan-3 is the Indian Space Research Organisation’s (ISRO) second attempt at achieving a successful lunar landing and rover operation, following Chandrayaan-2.
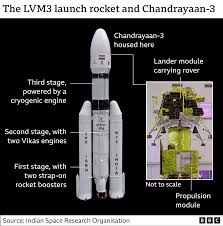
- The mission was launched aboard ISRO’s LVM3 rocket, an advanced three-stage launch vehicle designed for cost-effective placement of payloads into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO).
- The LVM3 M4 launcher successfully deployed the integrated modules into an elliptical parking orbit (170 x 36,500 km) before its lunar journey.
Mission Objectives
The primary objectives of Chandrayaan-3 include:
- Achieving a safe and soft landing on the Moon.
- Deploying a rover to conduct surface exploration.
- Performing in-situ scientific experiments to analyze lunar composition and thermal properties.
- Investigating the presence of water ice, which could support future lunar habitation and interplanetary travel.
Mission Components Chandrayaan-3 consists of:
- Lander Module (LM): Responsible for soft-landing and conducting surface experiments.
- Rover: Designed to explore and analyze the lunar surface.
- Propulsion Module (PM): Provides necessary thrust for trans-lunar injection and payload support.
Recent Scientific Findings
- New data from Chandrayaan-3 suggests that water ice deposits may exist beyond the Moon’s polar regions.
- The Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Ahmedabad, conducted a study based on data from the Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE)
Key Findings from ChaSTE:
- A 60°C temperature difference was recorded between the lunar surface and 10 cm beneath it.
- This suggests that the Moon’s surface layer is highly non-conductive, offering crucial insights into its thermal properties and composition.
- The discovery strengthens the possibility of water ice being more widespread than previously believed, impacting future lunar missions and resource utilization strategies.
With reference to Chandrayaan-3 and its recent findings, consider the following statements:
- Chandrayaan-3 was launched using the PSLV rocket, which is specifically designed for interplanetary missions.
- The Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE) instrument provided evidence of uniform thermal conductivity across the Moon’s surface.
- New findings suggest that water ice may exist beyond the Moon’s polar regions, altering previous assumptions about lunar resource distribution.
- The primary objective of Chandrayaan-3 was to conduct orbital mapping of lunar water ice without deploying a lander or rover.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2, and 4 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
Incorrect: Chandrayaan-3 was launched using the LVM3 (Launch Vehicle Mark-3), not PSLV. LVM3 is a heavy-lift rocket capable of placing payloads in Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO). PSLV, on the other hand, is primarily used for Earth observation satellites and deep-space probes but is not designed for carrying heavy payloads like Chandrayaan-3.
Incorrect: The ChaSTE instrument revealed a significant 60°C temperature difference between the lunar surface and 10 cm below, suggesting that the Moon’s surface is highly non-conductive. This contradicts the idea of uniform thermal conductivity.
Correct: New findings based on data from ChaSTE and PRL Ahmedabad suggest that water ice may be present beyond the Moon’s polar regions, expanding the potential resource availability for future lunar exploration and human settlement.
Incorrect: Chandrayaan-3 included a lander (Vikram) and a rover (Pragyan) to conduct in-situ experiments on the Moon’s surface. Orbital mapping of lunar ice was not the mission’s primary goal; instead, the lander-rover system was designed for surface-based scientific exploration.
Thalassemia
Syllabus: GS2-Health/GS3-Science and Tech
Context
- The Andhra Pradesh government is considering increasing the monthly pension for thalassemia patients and extending financial support to those above the poverty line (APL) due to the high cost of treatment. Currently, patients below the poverty line (BPL) receive treatment under the NTR Vaidya Seva scheme.
What is Thalassemia?
- Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder inherited from parents, where the body fails to produce sufficient hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells (RBCs) responsible for carrying oxygen.
- Each RBC contains 240 to 300 million hemoglobin molecules, and a deficiency results in severe anemia, requiring blood transfusions every 2-3 weeks for survival.
Symptoms of Thalassemia
- Beyond anemia,
- patients may experience
- Weak bones
- Delayed or stunted growth
- Iron overload (from frequent transfusions)
- Poor appetite
- Enlarged spleen or live
- Pale skin
Consider the following statements regarding Thalassemia:
- Thalassemia is an acquired blood disorder caused by iron deficiency.
- It leads to severe anemia due to the body’s inability to produce sufficient hemoglobin.
- Blood transfusions are required only in the early stages of the disease.
- Thalassemia is recognized as a benchmark disability under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Thalassemia is not an acquired disorder; it is a genetic disorder inherited from parents.
Statement 2 is correct: The disorder prevents sufficient hemoglobin production, leading to severe anemia.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Blood transfusions are lifelong and not limited to early stages. Patients require transfusions every 2-3 weeks.
Statement 4 is correct: Thalassemia is classified as a benchmark disability under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016.
Building Compassion into the Health-Care Structure
Syllabus: GS-II
Introduction
- On February 7, 2025, the World Health Organization (WHO) released a significant report titled ‘Compassion and Primary Health Care,’ emphasizing compassion as a transformative force in global health.
- The report highlights the necessity of integrating compassion into health-care services to enhance patient outcomes and improve provider well-being.
- WHO’s Director-General underscored the importance of compassion in strengthening primary care and advancing quality health services.
The Benefits of Compassionate Health Care
- Compassion in health care extends beyond ethical considerations, offering tangible benefits for both patients and medical professionals.
- For Patients:
- Research from Stanford University’s Centre for Compassion and Altruism Research and Education (CCARE) shows that compassionate care accelerates recovery and reduces hospital stays.
- A Johns Hopkins Hospital study found that simple gestures—such as doctors spending an additional 40 seconds reassuring patients—significantly reduce anxiety and improve healing.
For Medical Professionals:
- Practicing compassion alleviates stress, enhances job satisfaction, and fosters stronger patient-provider relationships.
- Maintaining a balance between emotional involvement and professional detachment prevents burnout, allowing for sustained high-quality care.
- Compassion vs. Empathy and Sympathy
- Compassion is often misinterpreted as empathy, sympathy, or kindness, but these concepts have distinct meanings:
- Sympathy: A temporary feeling of pity for someone’s suffering without deeper emotional involvement.
- Empathy: Feeling and internalizing another person’s pain, which can lead to emotional exhaustion in medical professionals.
- Compassion: A sustainable approach where health-care providers acknowledge suffering and act to alleviate it without becoming overwhelmed.
- By fostering compassion rather than excessive empathy, health professionals can make rational, well-informed decisions while maintaining emotional stability.
The Role of Compassion in Mental Health Care
Mental health disorders, particularly depression and anxiety, have reached alarming levels globally due to factors such as social isolation, economic uncertainty, and trauma. Unlike physical illnesses, mental health conditions are often stigmatized, discouraging individuals from seeking help.
Compassion in Mental Health Treatment:
- Provides a safe space where patients feel understood and valued.
- Encourages open communication, reducing feelings of shame and self-doubt.
- Helps individuals adhere to treatment plans and develop long-term coping mechanisms.
Compassion in Mental Health Recovery
- Compassionate care is particularly vital for individuals who have endured trauma, abuse, or neglect. Survivors of war, violence, and human trafficking require not only medical intervention but also emotional support, patience, and human connection to facilitate recovery.
- Case Study: The Transformation of Pradeep
- Pradeep, a rescued child suffering from severe trauma, was abandoned due to superstitious beliefs.
- At Bal Ashram, a rehabilitation center, caregivers adopted a compassionate approach, allowing him to heal at his own pace rather than forcing him to relive his past.
- Over time, with emotional support and a nurturing environment, he regained his ability to communicate and formed meaningful relationships.
- His recovery highlights the transformative power of compassion in mental health rehabilitation.
Strategies for Implementing Compassionate Health Care
Raising Awareness:
Health-care institutions, policy-makers, and industry leaders must prioritize compassion as a core principle in decision-making.
Training Health-Care Providers:
Medical professionals should undergo experiential learning and specialized training in compassionate care to integrate it effectively into practice.
Ensuring Equitable and Accessible Health Care:
A truly compassionate system must be inclusive, ensuring high-quality treatment for individuals regardless of their socio-economic status, gender, or background.
Conclusion
- Health care is not just about curing diseases; it is about promoting overall well-being. Compassion should be at the heart of medical practice, influencing patient interactions and health-care policies.
- By raising awareness, training professionals, and ensuring accessibility, the global medical community can create a people-centric health-care system rooted in compassion.
- Now is the time to embrace and globalize compassionate care, ensuring that every patient receives dignity, respect, and the quality treatment they deserve.
Consider the following statements regarding the WHO’s report on ‘Compassion and Primary Health Care’:
- The report highlights the role of compassion as a transformative force in global health.
- It primarily focuses on the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in primary health care to enhance patient outcomes.
- The report underscores the importance of emotional involvement over professional detachment for health-care providers.
- It was released by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2025.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1 and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: The WHO report emphasizes the role of compassion as a transformative force in health care.
Statement 2 is incorrect: While technology and AI are being integrated into health care, this report does not primarily focus on AI but on the human aspect of compassionate care.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The report highlights that excessive emotional involvement can lead to burnout, and instead, it promotes a balance between compassion and professional detachment.
Statement 4 is correct: The report was released by WHO in 2025.
WHO Report on Maternal Mortality
Syllabus: Health
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has released a recent study shedding light on the urgent issue of maternal mortality.
- According to the 2020 data, approximately 287,000 women lost their lives due to preventable causes associated with pregnancy and childbirth, translating to nearly 800 deaths per day.
- This report underscores the critical gaps in maternal healthcare and calls for immediate global action.
Primary Causes of Maternal Mortality
- The WHO study identifies haemorrhage and hypertensive disorders as the leading causes of maternal deaths:
- Haemorrhage (27%) – The most common cause, often occurring during or immediately after childbirth.
- Hypertensive disorders (16%) – Conditions such as pre-eclampsia significantly contribute to maternal deaths.
- The prevalence of these causes varies across regions, with sub-Saharan Africa and Western Asia reporting the highest mortality rates.
Regional Disparities in Maternal Mortality
- Maternal mortality rates show stark regional variations, revealing the unequal healthcare challenges across the world:
- Western Asia & Northern Africa: Haemorrhage accounts for 29% of maternal deaths.
- Sub-Saharan Africa: Haemorrhage contributes to 28% of fatalities.
- Australia & New Zealand: A significantly lower rate of 15%.
- Latin America & the Caribbean: Hypertensive disorders are more prevalent in this region.
- These disparities highlight the urgent need for region-specific interventions and improved healthcare systems.
Postpartum Complications and Mortality Risks
- A significant proportion of maternal deaths due to haemorrhage and sepsis occur during the postpartum period, which extends up to 42 days after childbirth.
- In 2020, at least 111 countries reported maternal deaths within this critical window, underscoring the necessity for enhanced postnatal care and continuous monitoring.
Global Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) and SDG Progress
- The global Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) stood at 223 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2020.
- Despite international efforts, this figure signals a stagnation in progress since the adoption of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in 2015.
- The WHO warns that at the current pace, the world is unlikely to meet the SDG target of reducing MMR to below 70 by 2030.
The Need for Strengthened Maternity Care
- The study emphasizes the critical role of high-quality maternity care in reducing maternal deaths. Key priorities include:
- Enhanced antenatal services to identify risks early.
- Rapid emergency interventions to manage complications.
- Stronger postnatal care to monitor and address health risks after childbirth.
WHO’s Global Roadmap for Maternal Health
- Recognizing the urgent need for action, the WHO launched a global roadmap in 2024 to combat postpartum haemorrhage, a leading cause of maternal mortality. Developed in collaboration with over 130 global experts, this roadmap sets priorities for intervention and policy changes.
- The WHO continues to advocate for high-quality, respectful, and accessible maternal healthcare services throughout pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period. Addressing maternal mortality requires global commitment, strategic policies, and enhanced healthcare systems to ensure that no woman dies from preventable pregnancy-related causes.
Consider the following statements regarding the recent WHO report on maternal mortality:
- The report states that approximately 500,000 women died from preventable pregnancy-related causes in 2020.
- Haemorrhage and hypertensive disorders are the leading causes of maternal mortality.
- The Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) target aims to reduce the global maternal mortality ratio (MMR) to below 100 per 100,000 live births by 2030.
- The highest rates of maternal mortality are reported in sub-Saharan Africa and Western Asia.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a.1 and 3 only
b.2 and 4 only
c.1, 2, and 3 only
d.2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The WHO report states that 287,000 women died in 2020 due to preventable maternal causes, not 500,000.
- Statement 2 is correct: Haemorrhage (27%) and hypertensive disorders (16%) are the leading causes of maternal mortality.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The SDG target aims to reduce MMR to below 70 per 100,000 live births, not 100.
- Statement 4 is correct: The highest maternal mortality rates are observed in sub-Saharan Africa and Western Asia.
Genetically Engineered Non-Browning Bananas
Syllabus: S&T
Introduction: A UK-based biotech company, Tropic, has developed a genetically-engineered banana that resists browning.
- This innovation aims to reduce food waste and environmental impact, addressing the significant spoilage rate of bananas, which leads to nearly 50% of global banana crop wastage annually.
- By extending the fruit’s freshness, this advancement contributes to sustainability and efficient resource utilization.
The Science Behind Banana Ripening: Bananas undergo a natural ripening process, transitioning from green to yellow and eventually brown due to the presence of ethylene, a plant hormone. Even after harvest, bananas continue to produce ethylene, which activates genes responsible for the production of polyphenol oxidase (PPO)—an enzyme that reacts with oxygen, causing browning. Physical damage or bruising accelerates this process by increasing ethylene production, leading to faster spoilage.
Development of Non-Browning Bananas:
- Tropic’s genetic modification technique alters the banana’s PPO-producing gene, effectively silencing it.
- This does not stop the ripening process but prevents enzymatic browning, maintaining the fruit’s visual appeal for a longer duration.
- A similar approach has been applied to Arctic apples, which also resist browning.
- This breakthrough in fruit preservation technology could revolutionize post-harvest management, reducing waste and enhancing shelf life.
Environmental Impact of Food Waste:
- Food waste contributes significantly to global carbon emissions.
- In the UK alone, approximately 1.4 million edible bananas are discarded daily, adding to landfill waste and greenhouse gas emissions.
- The introduction of non-browning bananas encourages prolonged consumption, potentially reducing food wastage.
- According to Tropic, widespread adoption of this technology could result in CO₂ reductions equivalent to removing 2 million cars from roads annually, marking a major step toward environmental sustainability.
Implications for the Future of Agriculture:
- The success of genetically-engineered bananas could pave the way for similar advancements in other crops.
- Scientists have already applied these techniques to tomatoes, melons, kiwifruits, and mushrooms, enhancing their shelf life and reducing spoilage.
- This innovation signals a new era in agricultural biotechnology, improving crop resilience, sustainability, and global food security.
Conclusion: Tropic’s non-browning banana represents a significant milestone in food science and sustainability. By tackling spoilage issues, this breakthrough contributes to waste reduction, environmental conservation, and efficient agricultural practices. As biotechnology advances, such innovations could play a crucial role in addressing global food security challenges while minimizing environmental impact.
Consider the following statements regarding Tropic’s genetically-engineered banana:
- It prevents ripening entirely to enhance shelf life.
- The modification targets the polyphenol oxidase (PPO) enzyme to reduce browning.
- This technique has previously been applied to other fruits like Arctic apples.
- The primary goal of this innovation is to increase banana production.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation: The genetic modification does not stop ripening but prevents browning by silencing the PPO enzyme. The same technique has been used for Arctic apples. The goal is not to increase production but to reduce food waste and environmental impact.
Viral Meningitis
Viral Meningitis Cases in Kerala: A Public Health Concern: Recent reports indicate that five students from a private school in Kalamassery, Kerala, have exhibited symptoms of viral meningitis. Their samples have been sent to the National Institute of Virology (NIV) for testing. This incident highlights the need for awareness regarding viral meningitis, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
What Is Meningitis?
Meningitis is the inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It can be caused by bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections. Among these, viral meningitis is the most common and is generally less severe than bacterial meningitis.
Severity of Viral Meningitis
Viral meningitis is usually self-limiting and mild, often resolving without long-term complications. However, bacterial meningitis is a medical emergency that requires immediate antibiotic treatment. If untreated, bacterial meningitis can lead to hearing loss, neurological damage, and even death.
Symptoms of Viral Meningitis
Common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Photophobia (sensitivity to light)
In young children, symptoms may be non-specific, such as irritability, poor feeding, and lethargy. Early recognition is essential for prompt medical intervention.
Diagnosis of Viral Meningitis
The gold standard for diagnosing meningitis is a lumbar puncture, which involves collecting cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF analysis helps differentiate viral from bacterial meningitis. If viral meningitis is suspected, RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction) is used to detect specific viruses.
Treatment Approaches
Since viral meningitis is caused by viruses, antibiotics are ineffective. Treatment is primarily supportive, focusing on:
- Pain relief (using analgesics)
- Hydration
- Nutritional support
- Most patients recover fully within one to two weeks.
Recovery and Risks
- Viral meningitis has a high recovery rate with no long-term complications in most cases.
- In contrast, bacterial meningitis can be fatal or cause permanent disabilities if not treated promptly.
Causes of Viral Meningitis
- The most common viruses causing viral meningitis include:
- Enteroviruses (most frequent cause)
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
- Varicella-zoster virus (VZV)
- Mumps virus
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Transmission of Enteroviruses
Enteroviruses spread through:
- Direct contact with an infected person
- Respiratory secretions (coughing, sneezing)
- Fecal-oral contamination
- These viruses are resilient and can survive on surfaces for extended periods. Disinfecting with bleach is an effective way to eliminate them.
Preventive Measures
- Maintaining hygiene (frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with sick individuals)
- Not sharing personal items (such as water bottles and utensils)
- Keeping infected children at home to prevent outbreaks
- Proper sanitation and disinfection
Role of Vaccination in Prevention
Vaccines against bacterial meningitis include those for pneumococcus and meningococcal.
Vaccination against mumps and chickenpox reduces the risk of viral meningitis.
Immunization programs play a crucial role in controlling outbreaks of meningitis.
Consider the following statements regarding viral meningitis:
- It is more severe than bacterial meningitis and requires immediate antibiotic treatment.
- Enteroviruses are the most common cause of viral meningitis.
- Lumbar puncture is the primary diagnostic test for meningitis.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect because viral meningitis is usually mild, whereas bacterial meningitis is more severe and requires urgent antibiotics.
Statement 2 is correct as enteroviruses are the leading cause of viral meningitis.
Statement 3 is correct since lumbar puncture (CSF analysis) is the standard test for diagnosing meningitis.
ASTRA MK-III Renamed Gandiva
Syllabus: GS3/ Defence
- In News: India’s latest and most advanced beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air missile, Astra MK-III, has been officially renamed Gandiva.
Key Features of Gandiva Missile
- Extended Operational Range
- Capable of striking aerial targets at 340 km when launched from an altitude of 20 km.
- Effective up to 190 km when engaging enemy aircraft at 8 km altitude.
- Cutting-Edge Propulsion System
- Powered by a dual-fuel ducted ramjet engine, an advanced propulsion system that utilizes atmospheric oxygen for sustained high-speed flight.
- Operates within a launch speed range of 0.8 to 2.2 Mach and can engage enemy aircraft moving at speeds between 0 and 3.6 Mach.
Advanced Target Neutralization
- Designed to effectively engage and destroy a variety of aerial threats, including fighter jets, bombers, and military transport aircraft.
- The Gandiva missile significantly enhances India’s aerial combat capabilities, offering a superior beyond-visual-range interception system to counter modern aerial threats.
Consider the following statements regarding the Gandiva missile (Astra MK-III):
- It is India’s latest beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air missile.
- It is powered by a solid-fuel rocket engine for sustained high-speed flight.
- It has a maximum operational range of 340 km when launched from an altitude of 8 km.
- It is capable of engaging enemy aircraft moving at speeds between 2.0 and 3.6 Mach.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Correct Answer: (a) 1 and 4 only
Explanation:
Correct – The Gandiva missile is India’s latest beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air missile, enhancing aerial combat capabilities.
Incorrect – It is not powered by a solid-fuel rocket engine but by a dual-fuel ducted ramjet engine, which utilizes atmospheric oxygen for sustained high-speed flight.
Incorrect – The missile has a maximum operational range of 340 km when launched from an altitude of 20 km, not 8 km. At 8 km altitude, it has an effective range of 190 km.
Correct – It is capable of engaging enemy aircraft moving at speeds between 2.0 and 3.6 Mach.
TROPEX-2025
Syllabus: GS3/ Defence
Context
The Theatre-Level Operational Readiness Exercise (TROPEX) 25 is being conducted over a span of three months, from January to March 2025.
About TROPEX 25
- Largest Biennial Maritime Exercise organized by the Indian Navy, with significant participation from the Indian Army, Indian Air Force, and Coast Guard.
- Executed in multiple phases, both in Harbour and at Sea, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of operational preparedness.
Encompasses various dimensions of modern naval warfare, including:
- Cyber and Electronic Warfare Operations
- Live Weapon Firings during the Joint Work-Up Phase
- Amphibious Exercise (AMPHEX) focusing on integrated land-sea operations
- TROPEX 25 serves as a crucial platform for enhancing combat readiness, interoperability, and joint operational synergy among India’s armed forces.
.Consider the following statements regarding TROPEX 25:
- It is an annual maritime exercise conducted by the Indian Navy.
- It involves participation from the Indian Army, Indian Air Force, and the Coast Guard.
- The exercise includes cyber and electronic warfare, live weapon firings, and an amphibious exercise.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
TROPEX is a biennial (not annual) maritime exercise organized by the Indian Navy. It features participation from multiple branches of the armed forces and includes cyber warfare, live weapon firings, and amphibious operations.
Exercise Khanjar-XII
Syllabus: Defence
Context:
- The 12th edition of the India-Kyrgyzstan Joint Special Forces Exercise, Khanjar-XII, is scheduled to take place from March 10 to March 23, 2025, in Kyrgyzstan.
- This annual exercise, which began in 2011, alternates between the two countries.
- The Indian contingent consists of troops from the Parachute Regiment (Special Forces), while the Kyrgyzstan contingent includes the Kyrgyz Scorpion Brigade.
- The primary focus of the exercise is to enhance cooperation in counter-terrorism and special operations, particularly in urban and mountainous terrains.
Objectives of Khanjar-XII
The main aim of the exercise is to exchange expertise and best practices in counter-terrorism operations. Key focus areas include:
Sniping techniques
- Complex building interventions
- Mountain warfare training
- These skills are vital for both nations in tackling modern security threats, terrorism, and insurgency.
Cultural Exchange and Diplomatic Relations
- Beyond military training, Khanjar-XII also serves as a platform for cultural exchange. Participants will engage in cultural activities, including the celebration of Nowruz, a significant Kyrgyz festival.
- This fosters stronger diplomatic ties, mutual respect, and understanding between the two nations.
Strategic Importance
- The exercise underscores the deepening strategic ties between India and Kyrgyzstan.
- It reflects their shared commitment to regional security, counter-terrorism cooperation, and military preparedness.
- By jointly addressing transnational threats, both countries aim to contribute to peace and stability in the region.
Previous Editions of Khanjar Exercise
- Since its inception, the Khanjar series has continuously evolved, enhancing interoperability and operational readiness.
- The 11th edition was held in India in January 2024, building upon past experiences to strengthen counter-terrorism strategies.
India’s Broader Defence Cooperation
- In addition to Khanjar-XII, India is actively expanding its defence partnerships. Recently, India and Japan conducted the 7th Army-to-Army Staff Talks in New Delhi, focusing on:
- Military education
- Technological collaborations
- Operational training
- These initiatives highlight India’s growing defence cooperation with global partners, reinforcing its role in regional security and stability.
With reference to the India-Kyrgyzstan Joint Special Forces Exercise ‘Khanjar-XII,’ consider the following statements:
- The exercise has been conducted annually since 2011 and is held exclusively in Kyrgyzstan.
- The Indian contingent primarily consists of personnel from the Ghatak Platoon of the Indian Army.
- The Kyrgyzstan contingent in Khanjar-XII includes the Kyrgyz Scorpion Brigade.
- The exercise mainly focuses on naval warfare and maritime security cooperation.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 3 only
c) 1, 3, and 4 only
d) 2 and 4 only
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 – Incorrect: While the exercise began in 2011, it is not exclusively held in Kyrgyzstan. It alternates between India and Kyrgyzstan.
Statement 2 – Incorrect: The Indian contingent consists of troops from the Parachute Regiment (Special Forces), not the Ghatak Platoon.
Statement 3 – Correct: The Kyrgyz Scorpion Brigade is the designated unit from Kyrgyzstan participating in the exercise.
Statement 4 – Incorrect: The exercise focuses on counter-terrorism, special operations, and mountain warfare, not naval warfare or maritime security.
Butterflies have been declining the last 20 years
Syllabus: GS 3/Environment
Context:
- A recent study has revealed a 22% decline in butterfly populations across the United States since the year 2000, attributing the loss to insecticide use, climate change, and habitat destruction.
- Monarch butterflies, in particular, have experienced a drastic reduction in numbers.
About Butterflies:
- Scientific Classification: Butterflies belong to the superfamily Papilionoidea within the insect order Lepidoptera, which also includes moths and skippers.
- Global Distribution: They are found worldwide, thriving in diverse ecosystems.
- Thermoregulation: Being cold-blooded, butterflies are unable to regulate their body temperature, making them highly sensitive to environmental conditions.
Life Cycle: Their life cycle consists of four distinct stages:
Egg
Larva (Caterpillar)
Pupa (Chrysalis)
Adult (Imago)
Ecological Importance of Butterflies:
Indicators of Environmental Health:
Butterflies serve as bio-indicators, reflecting changes in climate, pollution levels, and ecological balance.
Crucial to the Food Chain:
They provide sustenance for birds, bats, and insectivorous animals while also serving as hosts for parasitic species.
Vital Pollinators:
Ranking just after bees, wasps, and flies, butterflies significantly contribute to plant
reproduction and biodiversity.
Threats to Butterfly Populations:
- Habitat Loss: Driven by urbanization, deforestation, and land-use changes.
- Climate Change: Alters migration patterns and disrupts breeding cycles.
- Pesticide Use: Insecticides and herbicides negatively impact butterfly populations by poisoning larvae and reducing host plant availability.
Interesting Facts:
- Monarch Butterflies undertake an extraordinary migratory journey, covering distances between 1,200 and 2,800 miles, traveling from the northeastern U.S. and southeastern Canada to central Mexico.
- Marbled Map Butterfly is endemic to the Eastern Ghats and Odisha, making it a unique species of ecological significance.
- Common Birdwing Butterfly, listed under CITES, is frequently found in illegal wildlife trade due to its striking appearance.
Nymphalidae Family represents the most dominant butterfly group, comprising 31.58% of species, likely due to their adaptability to host plants and ecological conditions.
Consider the following statements regarding butterflies:
- Butterflies belong to the order Hemiptera, which also includes moths and dragonflies.
- They are cold-blooded organisms, making them highly sensitive to environmental changes.
- Butterflies undergo incomplete metamorphosis, with only three stages in their life cycle.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Butterflies belong to the order Lepidoptera, not Hemiptera (which includes true bugs like cicadas and aphids). They undergo complete metamorphosis, consisting of four stages (egg, larva, pupa, adult).
Modified Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme
Syllabus: GS 3/Environment /Economy
In News : The Government of India has introduced a revised Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme to strengthen Cooperative Sugar Mills (CSMs) and enhance ethanol production capacity.
About the Modified Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme
- The scheme aims to convert existing sugarcane-based ethanol plants into multi-feedstock facilities, enabling them to utilize alternative sources such as maize and damaged food grains (DFG) for ethanol production.
- It provides interest subvention at 6% per annum or 50% of the bank interest rate, whichever is lower, on loans extended to entrepreneurs.
- The subvention is applicable for five years, including a one-year moratorium period.
- The initiative is aligned with the Government’s Ethanol Blended with Petrol (EBP) Programme, which seeks to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and promote sustainable energy alternatives.
Need for the Scheme
- To promote ethanol production from diverse feedstocks and reduce reliance on sugarcane.
- To enhance financial viability of ethanol distilleries by lowering borrowing costs.
- To support the government’s commitment to clean energy and environmental sustainability.
Did You Know?
- The Government of India has been implementing the Ethanol Blended with Petrol (EBP) Programme nationwide to promote biofuels.
- The EBP Programme aims for 20% ethanol blending with petrol by 2025.
- Various ethanol interest subvention schemes have been introduced from July 2018 to April 2022 to encourage ethanol production and reduce crude oil imports.
- This scheme is a strategic step towards energy security, rural development, and environmental sustainability while supporting the economic interests of sugar mills and grain-based ethanol producers.
Consider the following statements regarding the Modified Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme:
- The scheme allows sugar mills to produce ethanol only from sugarcane-based sources.
- It provides an interest subvention of 6% per annum or 50% of the bank interest rate, whichever is lower.
- The subvention period under this scheme is five years, including a one-year moratorium.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
The scheme allows ethanol production from multiple feedstocks, including maize and damaged food grains, not just sugarcane.
Seagrass Conservation Key to Global Biodiversity
Syllabus: GS3/ Environment, Conservation
Context
A recent review published in Nature Reviews Earth & Environment highlights the alarming decline of seagrass ecosystems globally, with losses occurring at a rate of 1-2% per year due to human activities.
About Seagrasses
- Seagrasses are submerged flowering plants that form dense underwater meadows and have evolved from terrestrial plants to adapt to marine environments.
- Unlike seaweed (algae), seagrasses possess roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and seeds, enabling them to reproduce and sustain ecosystems.
Importance of Seagrass Ecosystems
- Carbon Sequestration & Climate Action
- Often referred to as the “lungs of the sea”, seagrasses sequester carbon up to 35 times faster than tropical rainforests, making them crucial in mitigating climate change.
Biodiversity and Marine Life Protection
- They serve as nurseries for fish species and provide shelter for endangered marine species, supporting ocean biodiversity.
Coastal Protection : Seagrasses act as natural barriers, protecting coastal areas from storms, erosion, and disaster risks.
Economic Significance
- Seagrass meadows provide an estimated economic value of $6.4 trillion annually by sustaining fisheries and boosting coastal tourism.
- Seagrass Distribution in India
India, with a recalculated coastline of 11,098 km (2023-24), has extensive seagrass meadows in:
Gulf of Mannar
Palk Bay
Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Lakshadweep Islands
Gulf of Kutch
Threats to Seagrass Ecosystems
Anthropogenic Activities – Urbanization, pollution, and agricultural runoff.
Weak Law Enforcement – Limited implementation of policies protecting coastal biodiversity.
Biodiversity Loss – Unregulated fishing, boating, and habitat destruction leading to ecosystem degradation.
Global & Indian Restoration Efforts
Global Initiatives
- Seagrass Watch – A citizen science program training volunteers, NGOs, and research organizations to monitor and conserve seagrass habitats worldwide.
- Blue Carbon Initiative – Focuses on carbon sequestration in coastal ecosystems, including mangroves, salt marshes, and seagrasses.
Indian Conservation Initiatives
- National Policy on Marine Fisheries (2017) – Recognizes seagrass meadows as essential coastal ecosystems alongside mangroves and coral reefs.
- Climate Resilience Project – Implemented in Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Odisha, supported by the Global Climate Fund (GCF).
- Seagrass Restoration – Ongoing efforts in Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay to restore degraded seagrass meadows.
Consider the following statements regarding seagrasses:
- Seagrasses are a type of algae that lack roots, stems, and flowers.
- They sequester carbon at a rate much slower than tropical rainforests.
- Seagrass meadows act as natural barriers, protecting coastal areas from erosion and storms.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Explanation:
Incorrect – Seagrasses are not algae; they are flowering plants that evolved from terrestrial plants and adapted to marine environments. Unlike algae, seagrasses have roots, stems, and leaves, and they can produce flowers and seeds.
Incorrect – Seagrasses sequester carbon up to 35 times faster than tropical rainforests, making them one of the most efficient carbon sinks in the world. This ability helps mitigate climate change by reducing atmospheric carbon dioxide.
Correct – Seagrass meadows act as natural barriers, reducing the impact of coastal erosion and storms. Their dense root systems stabilize the seabed, preventing sediment displacement, and their presence helps dissipate wave energy, protecting coastal communities from storm surges.
Madhav National Park
Syllabus: Environment
Context:
- Madhav National Park in Madhya Pradesh has been officially designated as India’s 58th tiger reserve, marking a significant milestone in the country’s wildlife conservation efforts.
- The announcement was made by Union Environment Minister Bhupender Yadav. This designation makes it the ninth tiger reserve in Madhya Pradesh, reaffirming the state’s commitment to protecting its rich biodiversity.
- Currently, the reserve is home to five tigers, including two recently born cubs, with plans to introduce two more tigers to strengthen the population.

Significance of Tiger Reserves:
- Tiger reserves play a crucial role in wildlife conservation and ecological balance by providing a protected habitat for tigers and other species.
- These reserves are essential components of India’s broader strategy to preserve biodiversity, prevent poaching, and mitigate human-wildlife conflict.
- The establishment of new tiger reserves reflects the government’s continued commitment to environmental protection and sustainable ecosystem management.
Madhav National Park: Location and Features
Location: Shivpuri district, Madhya Pradesh
Ecosystem: Features a mix of dry deciduous forests, grasslands, and water bodies, making it an ideal habitat for various wildlife species, including tigers.
Biodiversity: Home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, contributing to the state’s rich natural heritage.
Tiger Reintroduction Projects in Madhav National Park
- Madhav National Park’s designation as a tiger reserve follows successful tiger reintroduction efforts.
- In 2023, three tigers were introduced as part of a larger initiative to restore tiger populations in Madhya Pradesh.
- Similar projects have been successfully implemented in Panna and Nauradehi reserves, contributing to the revival of tiger populations in the region.
Government Support and Conservation Initiatives
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi welcomed the declaration, emphasizing India’s commitment to wildlife conservation and biodiversity protection.
- Madhya Pradesh Chief Minister Mohan Yadav highlighted the state’s leadership in tiger conservation and expressed gratitude for the recognition.
- The government is focusing on habitat restoration, anti-poaching measures, and community involvement to ensure long-term success.
Future Prospects for Madhav Tiger Reserve
- The reserve is expected to grow in importance as more tigers are introduced through planned conservation initiatives.
- Efforts are being made to enhance tiger habitats, ensure prey availability, and engage local communities in conservation efforts.
- The Madhav Tiger Reserve aims to become a model for sustainable wildlife conservation in India.
Challenges in Wildlife Conservation
Despite positive developments, several challenges persist in tiger conservation:
- Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade: A major threat to tiger populations.
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: Due to urbanization, deforestation, and human encroachment.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: Increased encounters between tigers and local communities.
- Need for Stronger Law Enforcement: Effective monitoring, patrolling, and stricter penalties for wildlife crimes are essential.
- Community Participation: Sustainable conservation requires involvement of local communities in protecting tiger habitats.
With ongoing conservation efforts and government support, Madhav Tiger Reserve is poised to become a thriving sanctuary for tigers and other wildlife, reinforcing India’s status as a global leader in tiger conservation.
Which of the following statements regarding Madhav Tiger Reserve is correct?
- It was originally a hunting ground for the Gwalior royal family.
- It is part of the Bundelkhand Plateau region.
- The park has a significant population of swamp deer (Barasingha).
- It has been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 3, and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- It was originally a hunting ground for the Gwalior royal family – Correct. Madhav National Park, now Madhav Tiger Reserve, was historically used as a hunting ground by the Scindia rulers of Gwalior. The park was later designated as a protected area.
- It is part of the Bundelkhand Plateau region – Correct. Madhav Tiger Reserve is located in the Shivpuri district of Madhya Pradesh, which is geologically part of the Bundelkhand Plateau. The region consists of dry deciduous forests and grasslands, making it suitable for various wildlife species, including tigers.
- The park has a significant population of swamp deer (Barasingha) – Incorrect. Swamp deer (Barasingha) are not found in Madhav Tiger Reserve in significant numbers. Instead, they are primarily found in Kanha National Park in Madhya Pradesh, where conservation efforts have been successful in reviving their population.
- It has been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site – Incorrect. Madhav Tiger Reserve is not a UNESCO World Heritage Site. While India has several UNESCO-listed natural sites (such as Kaziranga, Sundarbans, and Keoladeo National Parks), Madhav Tiger Reserve has not received this designation.
Amrut Biodiversity Park

Introduction
- The Amrut Biodiversity Park, inaugurated by Lieutenant Governor V.K. Saxena in 2025, is a major environmental initiative in Delhi.
- Spread across 90 hectares along NH-24 in the Yamuna floodplains, the park is part of the Delhi Development Authority’s (DDA) efforts to restore and rejuvenate the region’s ecosystem.
- It aims to enhance urban green spaces while fostering environmental awareness.
Ecosystem Restoration
- Previously used for agriculture and settlements, the park underwent a major transformation to revive the floodplain ecosystem.
Water Management:
- Six new water bodies were created with a combined capacity of 225 million litres.
- These help store stormwater and reduce flood risks during monsoons.
- The park features jute-reinforced slopes and riverine grass communities to stabilize the land and improve groundwater recharge.
Biodiversity and Green Cover
A key aspect of the park is its diverse plantation, aimed at enhancing biodiversity.
Trees Planted: Around 14,500 trees, including Neem, Peepal, and Mango.
Shrubs and Grasses: 18,000 shrubs and over 3.21 lakh riverine grasses have been introduced.
Bird Habitat Creation: The rich biodiversity is expected to attract bird species, contributing to a vibrant ecosystem.
Public Engagement and Recreational Spaces
- To promote community involvement, the park features designated public spaces along NH-24.
- Thematic Walking Tracks: Inspired by India’s freedom struggle, pathways are named after key events like the Dandi March and the First War of Independence.
- Nature Interaction Areas: Visitors can explore and connect with Delhi’s ecological heritage.
Hydrology and Water Conservation
- The park’s hydrology has been carefully restored through sustainable measures.
- Dredging and Water Flow Management: Existing catchments were deepened to enhance water retention and flow regulation during monsoon seasons.
- Sustainable Water Bodies: Efforts are in place to ensure that these remain functional year-round, contributing to floodplain health.
Environmental Concerns and Challenges
While the park has been praised for its green initiative, it has also faced criticism from environmentalists.
- Flood Risk: Some experts argue that the area remains prone to seasonal inundation.
- Financial Feasibility: Concerns have been raised about the long-term sustainability of maintaining the park.
- DDA’s Response: The authorities remain optimistic, emphasizing the park’s ecological benefits and its role in urban reforestation.
Future Plans and Development
- The DDA plans to further enhance the visitor experience with additional facilities:
- Café Establishment: A proposed eco-friendly café will provide refreshments for visitors.
- Recreational Spaces: The park is envisioned as a relaxation hub for joggers, nature enthusiasts, and families.
Conclusion
The Amrut Biodiversity Park represents a significant step in Delhi’s environmental restoration efforts. While challenges persist, its focus on biodiversity, water conservation, and public engagement makes it a valuable addition to the city’s green infrastructure.
Consider the following statements regarding the Amrut Biodiversity Park in Delhi:
- It is located along NH-44 in the Yamuna floodplains.
- The park has six water bodies with a total capacity of 225 million litres for stormwater management.
- It features jute-reinforced slopes and riverine grass communities to stabilize the floodplain ecosystem.
- The park was developed under the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC)’s green initiative.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 3 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 2, and 4 only
d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 – Incorrect: The Amrut Biodiversity Park is along NH-24, not NH-44.
Statement 2 – Correct: The park includes six water bodies with a combined capacity of 225 million litres, designed to manage storm water and reduce flood risks.
Statement 3 – Correct: Jute-reinforced slopes and riverine grasses have been introduced for soil stabilization and groundwater recharge.
Statement 4 – Incorrect: The park was developed by the Delhi Development Authority (DDA), not DMRC.
World Air Quality Report 2024
Syllabus: GS3/ Environmental Pollution
Key Findings of the Report
- India ranks as the fifth most polluted country globally, with an average PM2.5 concentration of 50.6 μg/m³, which is 10 times higher than the WHO’s annual guideline of 5 μg/m³.
- In 2023, India was the third most polluted country.
- Delhi remains the most polluted capital city, recording an average PM2.5 level of 91.8 μg/m³, making it the world’s worst capital in terms of air quality.
- Among the 20 most polluted cities worldwide, 13 are in India, with Byrnihat (Assam-Meghalaya border) being the worst affected.
- 3% of countries (126 out of 138) exceeded WHO’s PM2.5 annual safety limits.
- Only 17% of global cities met WHO’s air pollution standards.
- 5 concentrations declined in Southeast Asian countries, but transboundary haze and El Niño effects remain significant air pollution challenges.
Understanding Air Pollution & Its Impact
What is Air Pollution?
- Air pollution occurs when harmful substances such as particulate matter (PM), toxic gases, and chemical compounds are released into the atmosphere, degrading air quality and harming living beings.
Major Air Pollutants
Particulate Matter (PM10 & PM2.5): Fine particles from industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and construction dust.
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO₂): Emitted from vehicles and industries, contributes to acid rain and respiratory diseases.
Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂): A byproduct of burning fossil fuels, causes lung irritation and acid rain.
Ozone (O₃): A major urban smog component, damages lung function.
Carbon Monoxide (CO): Produced by incomplete combustion, leads to oxygen deprivation in the bloodstream.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) & Lead: Harmful industrial emissions affecting neurological and respiratory health.
Concerns Associated with Air Pollution
Health Implications
- Increased cases of respiratory diseases, lung infections, and cardiovascular disorders.
- Children, elderly, and people with pre-existing conditions are most vulnerable.
Environmental Damage
- Contributes to climate change, biodiversity loss, and soil & water contamination.
- Leads to crop damage and reduced agricultural productivity.
- Economic & Social Costs
- Increased healthcare expenses due to pollution-related diseases.
- Economic losses due to workforce inefficiency and reduced productivity.
Government Initiatives to Combat Air Pollution in India
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) – 2019
- Aims to reduce PM2.5 and PM10 levels by 20-30% by 2024 in targeted cities.
- Focuses on air quality monitoring, stricter emission regulations, and public awareness campaigns.
- Bharat Stage VI (BS-VI) Emission Standards – 2020
- Stricter vehicle fuel norms to cut vehicular pollution.
- Introduction of low-sulfur fuels and advanced emission control technologies.
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY)
- Provides subsidized LPG connections to reduce dependence on biomass and firewood, preventing indoor pollution.
- FAME Scheme (Faster Adoption & Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles)
- Promotes electric and hybrid vehicles to cut vehicular emissions.
- Encourages investment in EV charging infrastructure and subsidies for EV adoption.
- Green Initiatives for Sustainable Habitat (GRIHA)
- Promotes eco-friendly construction and energy-efficient buildings.
- Encourages use of solar power, rainwater harvesting, and green architecture.
- Waste Management & Cleanliness Programs
- Swachh Bharat Abhiyan focuses on urban cleanliness and solid waste management.
- Stricter regulations on plastic waste reduction and clean disposal practices.
- Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM)
- Regulates air pollution control measures in the Delhi-NCR region.
- Ensures better coordination and enforcement of environmental laws.
- Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP)
- Emergency pollution control measures based on air quality levels.
- Includes odd-even vehicle schemes, construction bans, and strict emission regulations in Delhi-NCR.
- Promotion of Public Transport & Green Mobility
- Expansion of metro networks, electric buses, and carpooling initiatives.
- Encouragement of non-motorized transport like cycling & pedestrian-friendly zones.
Way Forward
- Strengthen nationwide air quality monitoring and enforce stricter emissions control.
- Promote green energy solutions such as solar and wind power to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Enhance industrial pollution regulations and implement carbon pricing mechanisms.
- Encourage community participation through awareness campaigns and eco-friendly initiatives.
- India’s battle against air pollution demands a multi-sectoral approach involving policy reforms, technological advancements, and active citizen participation to ensure a cleaner and healthier environment.
Regarding the World Air Quality Report 2024, consider the following statements:
- India is ranked as the third most polluted country
- Byrnihat, a town on the Assam-Meghalaya border, is the most polluted city in India.
- Delhi is the second most polluted capital city in the world in terms of PM2.5 concentration.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer:(b)
Explanation: India is the fifth most polluted country (not third). Delhi remains the most polluted capital city, not the second.
Sarus Crane
A rare sighting of the Sarus Crane (Grus antigone) has been reported in the Saikhowa region of Tinsukia, Assam, drawing the attention of birdwatchers and wildlife enthusiasts.
About the Sarus Crane
Tallest Flying Bird: The Sarus Crane holds the distinction of being the tallest flying bird in the world.
Scientific Name: Grus Antigone
Distribution
- Found in Southeast Asia, northern India, and northern Australia.
- In India, their population is densely distributed along the Gangetic plains and eastern Rajasthan, with lower densities further south.
- Unlike many other crane species, the Sarus Crane is non-migratory.
Habitat
- Prefers wetlands, including canals, marshes, and ponds.
- Often found in proximity to human habitation.
Distinctive Features of the Sarus Crane
- Height: 152-156 cm, making it the tallest of all flying birds.
- Wingspan: Can reach up to 5 meters.
- Weight: Ranges from 5 to 12 kg.
- Plumage: Mostly grey with a naked red head, upper neck, and pale red legs.
White Markings: A white patch on the top of the head and a small white spot behind the eye.

Social Behavior:
- Considered the least social of all cranes, usually seen in pairs or small groups of three to four.
- Monogamous species—pairs bond for life.
- Nesting:
- Nests are built in wetlands or flooded paddy fields.
- Lifespan:
- Generally 30 to 40 years, though some crane species have been recorded to live up to 80 years.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Listed in Appendix II
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule IV
- The Sarus Crane population faces threats from habitat destruction, wetland degradation, and human disturbances. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensuring the survival of this iconic species.
Consider the following statements regarding the Sarus Crane (Grus antigone):
- It is the tallest non-flying bird in the world.
- Sarus Cranes are migratory birds that travel across different regions based on seasonal changes.
- In India, they are predominantly found in the Gangetic plains and eastern Rajasthan.
- The Sarus Crane is listed as “Endangered” on the IUCN Red List.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
- The Sarus Crane is the tallest flying bird, not a non-flying bird. (Statement 1 is incorrect)
- Unlike many other crane species, the Sarus Crane is non-migratory and remains in its habitat throughout the year. (Statement 2 is incorrect)
- In India, its population is densely distributed along the Gangetic plains and eastern Rajasthan, with lower densities in the south. (Statement 3 is correct)
- The Sarus Crane is classified as “Vulnerable” on the IUCN Red List, not “Endangered.” (Statement 4 is incorrect.
International Women’s Day
Syllabus: GS1/Society
About International Women’s Day (IWD):
- Celebrated annually on March 8 to honor women’s contributions and advocate for gender equality.
Historical Background:
- Declared as International Women’s Day by Vladimir Lenin in 1922 to recognize women’s role in the 1917 Russian Revolution.
- Officially recognized by the United Nations in 1977.
Themes for 2025:
- United Nations (UN) Theme: “For All Women and Girls: Rights. Equality. Empowerment.”
- Official IWD Theme: “Accelerate Action.”
2025 Significance:
- Marks 30 years since the adoption of the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action, a global framework for advancing women’s rights.
Legal Framework for Women Empowerment in India:
Constitutional Provisions:
Article 14: Ensures equality before the law.
Article 15: Prohibits discrimination based on sex.
Article 51A(e): Encourages citizens to renounce practices that violate women’s dignity.
Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP):
Article 39: Advocates equal livelihood opportunities and equal pay.
Article 42: Ensures maternity relief.
Challenges Faced by Women in India:
- Gender Discrimination: Social and cultural biases limiting opportunities.
- Limited Access to Education: Especially in rural areas, restricting future prospects.
- Economic Inequality: Wage disparity, job limitations, and financial dependence.
- Safety Concerns: High rates of gender-based violence, harassment, and trafficking.
- Health & Reproductive Rights: Limited access to quality healthcare and maternal services.
- Child Marriage: Affects health, education, and independence.
- Political Underrepresentation: Low participation in decision-making roles.
- Social Norms & Expectations: Rigid gender roles restricting freedom.
- Workplace Harassment: Insufficient protective measures.
India’s Commitment to International Women’s Rights:
- India is a signatory to key global treaties and agreements, including:
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948)
- International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR, 1966)
- Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW, 1979)
- Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action (1995)
- United Nations Convention Against Corruption (2003)
- Agenda 2030 for Sustainable Development
Key Achievements in Women Empowerment in India:
- Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam, 2023: Reserves one-third of seats for women in Lok Sabha, State Legislative Assemblies, and Delhi Assembly.
- National Sex Ratio: Improved to 1020 females per 1000 males (NFHS-5).
- Maternity Leave: Extended to 26 weeks.
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana:2 crore accounts opened.
- PM Awas Yojana Gramin: 72% of houses are owned by women.
- Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR): Reduced to 97 per lakh live births (2018-20) from 130 per lakh (2014-16).
- Abolition of Triple Talaq: Strengthening legal rights for Muslim women.
- Women in Armed Forces:
- Permanent commission granted in 12 Arms and Services.
- Agniveer recruitment for women in all three defense services.
- Women in STEM: 43% of STEM graduates in India are women—the highest in the world.
Government Initiatives for Women Empowerment:
- Mission Shakti (2021-2025): Focuses on women’s welfare, safety, and empowerment.
- Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao: Aims to improve female child survival and education.
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana: Encourages savings for girl children.
- Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram: Ensures free maternity healthcare.
- PM Matru Vandana Yojana: Provides financial support for pregnant women.
- Mission Saksham Anganwadi & Poshan 2.0: Focuses on improving women’s health through better nutrition.
- WISE-KIRAN (Women in Science & Engineering): Supported 1,962 women scientists (2018-2023).
- Nari Shakti Puraskar: Recognizes outstanding contributions of women.
- Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2017: Extends paid maternity leave to 26 weeks.
This comprehensive framework ensures a holistic approach to gender equality and women’s empowerment in India.
Consider the following statements regarding International Women’s Day (IWD):
- It was first declared as International Women’s Day by the United Nations in 1922.
- The year 2025 marks 30 years since the adoption of the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action.
- The official United Nations (UN) theme for IWD 2025 is “Accelerate Action.”
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 2 only
Explanation: Vladimir Lenin, not the UN, declared March 8 as International Women’s Day in 1922.The UN theme for IWD 2025 is “For All Women and Girls: Rights. Equality. Empowerment.”, while “Accelerate Action.” is the official IWD theme.
Golden Passport Program of Vanuatu
Syllabus: GS 1/Places
Context:
Former IPL chief Lalit Modi has renounced his Indian passport and obtained citizenship in Vanuatu, an island nation in the South Pacific Ocean that offers a “golden passport” program through its Citizenship by Investment (CBI) scheme.
Vanuatu: Geographical & Strategic Overview
Location: Situated in the South Pacific Ocean, approximately 800 km west of Fiji and 1,770 km east of Australia.
Tectonic Activity: Lies within the Pacific Ring of Fire, a region known for high seismic and volcanic activity, making it prone to earthquakes and tsunamis.
Golden Passport Program: Citizenship by Investment (CBI) Scheme
- Overview & Process
- Vanuatu’s CBI program allows individuals to acquire citizenship through financial contributions.
- Investment Requirement: Citizenship costs between $135,500 to $155,500, with additional provisions for a family of four.
- Processing Time: Citizenship is typically granted within 30 to 60 days after submission of the application.
- Key Benefits of Vanuatu Citizenship
- Passport Strength: Ranked 51st in the Henley Passport Index, ahead of Saudi Arabia, China, India, and Indonesia.
- Tax Haven Status: No personal income tax, capital gains tax, inheritance tax, or wealth tax, making it attractive for high-net-worth individuals.
- Economic Reliance: Offshore financial services form a crucial component of Vanuatu’s revenue generation strategy.
- Scandals & Criticism
Security Concerns: Individuals with criminal backgrounds have been granted citizenship, raising concerns about the potential misuse of the program.
EU & UK Backdoor Entry Risk: The scheme is viewed as a loophole for accessing European markets, triggering scrutiny from global regulators.
Money Laundering Risks: Vanuatu’s lax taxation and financial regulations pose concerns over potential illicit financial activities.
With reference to Vanuatu’s Citizenship by Investment (CBI) program, consider the following statements:
- Vanuatu is an island nation located in the Indian Ocean, known for its rich biodiversity.
- The Citizenship by Investment (CBI) program allows individuals to obtain Vanuatu’s citizenship by purchasing real estate in the country.
- Vanuatu ranks higher than India in the Henley Passport Index and is considered a tax haven due to the absence of personal income tax.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a.1 and 2 only
b.3 only
c.2 and 3 only
d.1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect. Vanuatu is located in the South Pacific Ocean, not the Indian Ocean.
Statement 2 is incorrect. Vanuatu’s CBI program does not require real estate purchases; instead, it grants citizenship in exchange for financial contributions to the government.
Statement 3 is correct. Vanuatu ranks 51st in the Henley Passport Index, higher than India, and has no personal income tax, capital gains tax, or inheritance tax, making it a tax heaven.
Chagos Archipelago
Syllabus : GS 1/ Places In News
About Chagos Archipelago
- The Chagos Archipelago is a group of 58 islands located approximately 500 km south of the Maldives in the Indian Ocean.
- The islands remained uninhabited until the late 18th century, when the French brought laborers from Africa and India to work on newly established coconut plantations.
- In 1814, France ceded the islands to Britain as part of a colonial agreement.
British Control and Mauritius’ Claim
- In 1965, the United Kingdom established the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT), with the Chagos Islands as a central part.
- Chagos was historically administered as part of Mauritius, another British colony, but when Mauritius gained independence in 1968, the Chagos Islands remained under British control.
- Mauritius asserts sovereignty over Chagos, citing its historical ties predating British colonial rule.
Strategic Importance
The largest atoll, Diego Garcia, is home to a major U.S. military base, making the region geopolitically significant.
Consider the following statements regarding the Chagos Archipelago:
- The Chagos Archipelago consists of 58 islands located approximately 500 km south of the Maldives in the Indian Ocean.
- The islands were uninhabited until the late 18th century, when the British brought laborers from Africa and India.
- In 1814, the Chagos Islands were ceded to Britain by France as part of a colonial agreement.
- Diego Garcia, the largest atoll in the Chagos Archipelago, hosts a French naval base.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Chagos Archipelago is a group of 58 islands located 500 km south of the Maldives in the Indian Ocean.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The French, not the British, brought laborers from Africa and India to work on coconut plantations.
- Statement 3 is correct: France ceded the Chagos Islands to Britain in 1814.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: Diego Garcia hosts a S. military base, not a French naval base.
Parvatmala Pariyojana
Syllabus: GS3/ Geography
- Cabinet Approves Ropeway Projects in Uttarakhand Under Parvatmala Pariyojana
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA), chaired by the Prime Minister, has approved two major ropeway projects in Uttarakhand under the National Ropeways Development Programme – Parvatmala Pariyojana.
About Parvatmala Pariyojana
- Announced in the Union Budget 2022 under the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) mode.
- Implemented by National Highway Logistics Management Limited (NHLML) under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH).
- Aims to develop 250+ ropeway projects covering 1,200 km within five years.
Significance of Ropeway Projects:
- Enhances Connectivity – Overcomes transport challenges in remote and hilly areas.
- Boosts Tourism & Economy – Facilitates pilgrimage and adventure tourism, stimulating local economic growth.
- Efficient & Direct Transport – Provides a direct aerial route, bypassing difficult terrains.
- Eco-Friendly – Requires minimal deforestation and land degradation, ensuring sustainable development.
Consider the following statements regarding the Parvatmala Pariyojana:
- It was launched in the Union Budget 2022 under the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) mode.
- It is implemented by the National Highway Logistics Management Limited (NHLML) under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH).
- The project aims to develop 500+ ropeway projects covering 2,500 km within five years.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Parvatmala Pariyojana was announced in the Union Budget 2022 under the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) mode to improve connectivity in hilly and remote areas through ropeway projects.
- Statement 2 is correct: The implementation of this project is being carried out by National Highway Logistics Management Limited (NHLML), which operates under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH).
Statement 3 is incorrect: The project aims to develop 250+ ropeway projects covering approximately 1,200 km within five years, not 500+ projects covering 2,500 km. Therefore, this statement is factually incorrect.
Parvatmala Pariyojana
Syllabus: GS3/ Infrastructure
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA), chaired by the Prime Minister, has approved two significant ropeway projects in Uttarakhand under the National Ropeways Development Programme – Parvatmala Pariyojana.
About Parvatmala Pariyojana
- Launched in the Union Budget 2022 under the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) mode.
- Implemented by the National Highway Logistics Management Limited (NHLML) under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH).
- Aims to develop over 250 ropeway projects, covering 1,200 km within five years.
Significance of Ropeways:
- Enhanced Connectivity: Facilitates transportation in remote and hilly regions, improving accessibility.
- Tourism & Economic Growth: Promotes tourism and generates employment opportunities.
- Efficient Transport: Offers a direct aerial route, reducing travel time and overcoming difficult terrains.
Eco-Friendly Approach: Minimizes deforestation and land degradation, making it a sustainable infrastructure solution.
Consider the following statements regarding the Parvatmala Pariyojana:
- It was announced in the Union Budget 2022 under the Viability Gap Funding (VGF) mode.
- The programme is implemented by the National Highway Logistics Management Limited (NHLML) under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH).
- It aims to develop over 500 ropeway projects covering 2,500 km within five years.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The Parvatmala Pariyojana was announced in the Union Budget 2022, but it follows the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) mode, not the Viability Gap Funding (VGF) mode.
- Statement 2 is correct: The programme is implemented by NHLML, which is a subsidiary of the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) under MoRTH.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The actual target is to develop 250+ ropeway projects covering 1,200 km in five years, not 500 projects covering 2,500 km.
La Nina
Syllabus: Geography
- La Niña is a climatic phenomenon characterized by the cooling of surface ocean waters along the tropical west coast of South America.
- It is the opposite phase of El Niño, which is associated with unusually warm ocean temperatures in the equatorial Pacific.
- Together, these events form the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle, influencing global weather patterns.
- La Niña is identified when sea surface temperatures decrease by more than 0.5°C (0.9°F) for at least five consecutive three-month seasons.
Causes of La Niña
- La Niña occurs due to the accumulation of cooler-than-normal waters in the tropical Pacific, a region between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
- This cooling is driven by unusually strong trade winds and ocean currents, which push warm surface waters westward, allowing cold, deep ocean water to rise to the surface—a process known as upwelling.
- This significant drop in sea-surface temperature alters global atmospheric circulation patterns.
Effects of La Niña
Impact on Air Pressure and Rainfall
- La Niña reduces air pressure over the western Pacific, leading to increased rainfall.
- Southeast Asia experiences stronger summer monsoons, benefiting agriculture in regions like northwest India and Bangladesh.
Risk of Flooding in Australia
- While La Niña enhances rainfall for agriculture in South Asia, severe events can lead to excessive precipitation and flooding in northern Australia.
Global Rainfall Patterns
- Increased rainfall occurs in southeastern Africa and northern Brazil.
- Conversely, La Niña raises air pressure over the central and eastern Pacific, causing drier conditions in those regions.
Drier Conditions in Certain Areas
- The west coast of tropical South America, the Gulf Coast of the United States, and the pampas of South America experience reduced rainfall and prolonged dry spells.
Boost to the Fishing Industry
- The upwelling effect brings cold, nutrient-rich waters to the surface, fostering plankton growth.
- This supports marine ecosystems, benefiting fish populations and the fishing industry, particularly in regions like the eastern Pacific.
Duration and Seasonal Trends:
- La Niña events typically last between one and three years, whereas El Niño events are usually shorter, lasting less than a year. Both phenomena tend to peak during the Northern Hemisphere winter, significantly influencing global weather patterns.
- By shaping rainfall distribution, ocean currents, and atmospheric circulation, La Niña plays a crucial role in global climate variability, impacting agriculture, economies, and ecosystems worldwide.
Consider the following statements regarding La Niña:
- It is associated with the cooling of sea surface temperatures in the eastern and central Pacific Ocean.
- It leads to an increase in air pressure over the western Pacific, resulting in reduced monsoon activity in South Asia.
- It enhances upwelling, which benefits marine ecosystems and fisheries in the eastern Pacific.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: La Niña is characterized by cooler-than-normal sea surface temperatures in the eastern and central Pacific.
Statement 2 is incorrect: La Niña lowers air pressure over the western Pacific, leading to stronger monsoons in South Asia, not weaker ones.
Statement 3 is correct: Upwelling caused by La Niña brings nutrient-rich cold water to the surface, which boosts marine productivity and benefits fisheries.
Karnataka’s Controversial Sharavathi Hydroelectric Project
Project Overview
- Located in Karnataka, the project aims to generate 2,000 MW of electricity.
- It also seeks to supply drinking water to Bengaluru.
- Consists of upper and lower reservoirs with a pumped storage mechanism.
- Modeled after Telangana’s Kaleshwaram project.
- Requires five tunnels and eight pumping stations.
- Estimated cost: ₹8,000 crore.
Environmental Concerns
- Threatens the Sharavathi Valley, a biodiversity hotspot in the Western Ghats.
- Home to endangered species like the Lion-tailed Macaque and Great Indian Hornbill.
- Requires clearing 360 acres of protected forest land within a wildlife sanctuary.
- Karnataka’s forest cover is only 20%, below the national target of 33%.
- Potential violations of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
Technical and Economic Viability
- Consumes more electricity than it generates (Deficit project).
- Expected to generate 12,000 MWh annually, but requires 14,833 MWh for pumping.
- Raises concerns about economic feasibility due to increased energy demand.
- May require additional costly energy projects to compensate for the shortfall.
Legal and Procedural Challenges
- The Karnataka High Court has issued a stay order on the bidding process.
- Allegations of corruption and favoritism in awarding the contract to MEIL.
- Karnataka Power Corporation Limited (KPCL) under scrutiny for irregularities.
- Critics highlight lack of transparency and rushed bidding process.
Political and Public Reactions
- Opposition parties accuse the Congress-led state government of benefiting vested interests.
- Environmental activists and local communities mobilizing protests and legal challenges.
- Reflects the larger conflict between energy expansion and conservation.
Broader National Implications
- Raises concerns over India’s renewable energy goals vs. ecological sustainability.
- Could set a precedent for balancing development and conservation.
- The future of the Western Ghats’ biodiversity remains uncertain.
Consider the following statements regarding the Sharavathi Pumped Storage Hydroelectric Project (PSHP):
- It is designed to generate electricity by utilizing the natural flow of the Sharavathi River without requiring water pumping.
- The project is modeled after Telangana’s Kaleshwaram project.
- The project is located in the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The project requires water pumping uphill during off-peak hours, making it a pumped storage system rather than a conventional hydropower project.
- Statement 2 is correct: The project is modeled after Telangana’s Kaleshwaram project, which also involves water pumping infrastructure.
- Statement 3 is correct: The Western Ghats is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and the project is located within this ecologically sensitive region.
Kursk Region
Russian Offensive in the Kursk Region
- Russian forces have launched a large-scale counteroffensive to reclaim western parts of the Kursk region from Ukrainian troops.
- This development marks a significant escalation in the ongoing conflict, with strategic and historical implications.
About the Kursk Region
Geographical Significance:
- Kursk is a city and the administrative center of Kursk Oblast, located along Russia’s southwestern border.
- It lies approximately 450 km south of Moscow, along the upper Seym River.
- The region is part of the Black Earth Belt, known for its exceptionally fertile soil.
- Kursk has a moderately continental climate, characterized by significant seasonal variations.
Historical Importance:
- Kursk is one of Russia’s oldest cities, first recorded in 1032.
- In 1240, the city was destroyed by the Tatars and remained in ruins until 1586, when it was rebuilt as a military outpost.
Battle of Kursk (July–August 1943):
- The city was a key battleground during World War II, witnessing the largest tank battle in history.
- The German defeat in Kursk marked a turning point in the Eastern Front.
Economic and Industrial Landscape:
- Kursk has a diverse industrial base, with key sectors including:
- Machine building
- Food processing
- Electronic equipment production
- Synthetic fiber manufacturing
- These industries contribute significantly to the region’s economic growth.
Recent Developments & Ongoing Conflict
- In the summer of 2024, Ukrainian forces launched a surprise lightning offensive, capturing parts of Russia’s Kursk region.
- However, Ukraine’s hold on Kursk has weakened, as Russia intensifies its counteroffensive to reclaim lost territory.
- The Russian advance threatens Kyiv’s sole territorial bargaining chip, making this battle crucial for both sides at a critical juncture in the war.
Consider the following statements regarding the Kursk region:
- Kursk is located in the Black Earth Belt, known for its highly fertile soil.
- The Battle of Kursk in World War II was the largest naval battle in history.
- The city of Kursk was first mentioned in historical records in the 13th century.
- Kursk has a continental climate with distinct seasonal variations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3, and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Kursk is part of Russia’s Black Earth Belt, known for its highly fertile soil, making it agriculturally significant.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The Battle of Kursk (1943) was the largest tank battle in history, not a naval battle.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: Kursk was first mentioned in 1032, which is in the 11th century, not the 13th century.
- Statement 4 is correct: Kursk has a moderately continental climate with distinct seasonal variations.
Chagos Archipelago
syllabus: Geography
- The Chagos Archipelago, situated in the Indian Ocean, has been at the center of a long-standing territorial dispute between Mauritius and the United Kingdom.
- Although Mauritius gained independence in 1968, the UK retained control over Chagos.
- In recent years, the UK has formally acknowledged Mauritius’ claims to the archipelago, but tensions persist, particularly regarding Diego Garcia, a strategically significant military base.
Historical Background
- The Chagos Archipelago consists of over 60 islands, with Diego Garcia being the largest and most strategically vital. Initially uninhabited, Chagos saw its first permanent settlements in the 18th century.
- The French claimed the islands in the 1700s, but following the Napoleonic Wars, the British took control.
- Over time, the islands became plantation hubs, heavily reliant on slave and indentured labor.
Creation of the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT):
- In 1965, the UK established the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT), incorporating Chagos as part of a broader Cold War strategy to maintain military influence in the Indian Ocean.
- The UK paid Mauritius £3 million for the separation of Chagos from its territory.
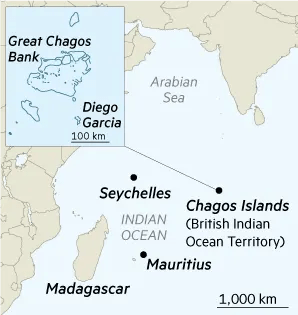
Strategic Importance of Diego Garcia
- By the 1970s, the United States constructed a military base on Diego Garcia, leading to the forced displacement of the Chagossian population to Mauritius and Seychelles.
- The base became fully operational in 1986 and has since played a pivotal role in US military operations across the region.
International Legal Rulings
Mauritius has long contested UK sovereignty over Chagos:
- 2017: The UN General Assembly sought an advisory opinion from the International Court of Justice (ICJ) regarding Chagos’ legal status.
- 2019: The ICJ ruled that the UK’s administration over Chagos was unlawful and that it should return the islands to Mauritius.
- The UN General Assembly subsequently urged the UK to withdraw from Chagos.
Recent Developments
- In 2024, the UK and Mauritius signed a landmark agreement, formally recognizing Mauritius’ sovereignty over Chagos while allowing the UK to maintain control over Diego Garcia for 99 years.
- However, this deal has drawn criticism, particularly from the Chagossians, who were excluded from negotiations and remain uncertain about their right to resettlement.
Geopolitical Implications and Future Challenges
- The agreement has heightened concerns over China’s expanding influence in the Indian Ocean, as Mauritius strengthens its strategic ties with Beijing.
- Analysts warn that the deal may disrupt the regional balance of power, with potential implications for security and military strategy.
- Meanwhile, the Chagossians’ future remains uncertain, with ongoing discussions regarding resettlement and compensation.
- The Chagos dispute continues to be a significant geopolitical issue, influencing regional diplomacy, legal debates, and military strategy in the Indian Ocean region.
Which of the following international organizations has been involved in the Chagos sovereignty dispute?
- International Court of Justice (ICJ)
- United Nations General Assembly (UNGA)
- European Union (EU)
- African Union (AU)
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 2, and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: c) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation: The International Court of Justice (ICJ) and the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) played key roles in ruling against UK sovereignty over Chagos. The African Union (AU) has also supported Mauritius’ claim. However, the European Union (EU) has not been directly involved in the dispute.
Glass-Ceiling Index
syllabus: Index and Reports
Context:
- International Women’s Day (IWD) is observed annually on March 8 to recognize women’s achievements and advocate for gender equality. As part of the occasion, The Economist publishes its yearly Glass-Ceiling Index, assessing workplace conditions for women in 29 OECD countries.
About the OECD
- The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is an international organization comprising 38 member countries committed to democracy and free-market economies.
- Established: December 14, 1960
- Founder Nations: 18 European countries, along with the S. and Canada
- Headquarters: Paris, France
Key Functions:
- Publishes economic reports, data, and forecasts.
- Fights bribery and financial crimes globally.
- Maintains a blacklist of tax havens (countries with unfair tax practices).
- India’s Status: Not a member but collaborates with OECD on economic policies.
- Glass-Ceiling Index: Ranking Criteria
The Glass-Ceiling Index ranks 29 OECD nations based on a ten-point system evaluating workplace conditions for women:
- Higher education completion rate among women
- Percentage of women taking the GMAT exam (for business schools)
- Women’s workforce participation
- Gender pay gap
- Women in management roles
- Women on corporate boards
- Women in government positions
- Cost of child care after subsidies
- Paid maternity leave duration
- Paid paternity leave duration
Top 10 Countries for Working Women (2024)
- Sweden (Rank 1, replacing Iceland)
- Iceland (Dropped from No.1 due to fewer women in management roles—declined from 39.6% to 36.8%)
- Finland
- Norway
- Portugal
- New Zealand
- France
- Spain
- Denmark
- Australia
Key Highlights:
- Sweden overtook Iceland as the top-ranking country for gender equality at work.
- Iceland remains a global leader in gender parity and was the first country to elect a female president (Vigdís Finnbogadóttir, 1980).
- The United States ranked lower, indicating persistent workplace gender inequality.
- Economic and Political Participation of Women
Workforce Trends
- Women’s labour force participation rose to 6% (up from 65.8% the previous year).
- Despite progress, men’s participation remains higher at 81%.
- Women’s representation on corporate boards increased to 33%, indicating a positive shift in leadership roles.
Political Representation
- The OECD average for women’s parliamentary representation is 34%.
- Notable Gains:
- Japan: Increased to 16% (though still low).
- Britain: Reached 41%.
- Declines:
- United States: Dropped to 7%.
- Changes in Rankings and Persistent Challenges
- South Korea rose from the bottom to 28th place, marking its first improvement in 11 years.
- Turkey now ranks last, struggling with deeply ingrained societal norms limiting women’s leadership opportunities.
Challenges in Japan, Turkey, and South Korea:
- Persistent gender wage gap.
- Limited female leadership roles in politics and business.
- Cultural expectations hindering workplace equality.
- Despite progress, significant barriers remain, particularly in Asia and developing economies, underscoring the need for continued policy reforms and cultural shifts to achieve workplace equality.
With reference to the Glass-Ceiling Index published by The Economist, consider the following statements:
- The index assesses workplace conditions for women in all OECD and non-OECD countries.
- It ranks nations based on factors such as gender pay gap, workforce participation, and representation in leadership roles.
- The United States ranked among the top 10 countries in the 2024 index.
- Sweden replaced Iceland as the top-ranking country in the 2024 edition of the index.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 3 only
b) 2 and 4 only
c) 1, 2, and 3 only
d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 – Incorrect: The Glass-Ceiling Index evaluates only 29 OECD countries, not all nations worldwide.
Statement 2 – Correct: The ranking is based on ten key parameters, including gender pay gap, workforce participation, leadership representation, and childcare costs.
Statement 3 – Incorrect: The United States ranked lower in 2024, highlighting persistent gender inequality in the workplace.
Statement 4 – Correct: Sweden replaced Iceland as the top country for working women, primarily due to Iceland’s decline in women’s management roles.
Global Terrorism Index (GTI) 2025
Syllabus: Indexes and Reports
- The Global Terrorism Index (GTI) 2025, published by the Institute for Economics and Peace (IEP), analyzes terrorism trends across 163 countries, covering 7% of the world’s population.
- The report assesses terrorism by examining attacks, fatalities, injuries, hostage incidents, and their overall impact on society.
Global Terrorism Trends
- Terrorism saw a resurgence in 2024, reversing a decade-long decline:
- The number of countries affected by terrorism increased from 58 to 66.
- The Islamic State (IS) remains the deadliest terrorist organization
- Lone-wolf attacks surged in the West, contributing to 93% of recent fatalities.
- Pakistan and Afghanistan experienced rising militant activity, making South Asia a terrorism hotspot.
Key Trends in 2024
- Terrorism in the Sahel: The Global Epicenter
- The Sahel region recorded over 50% of all global terrorism deaths.
- Burkina Faso saw the highest number of terrorism-related deaths worldwide, accounting for 20% of the global total.
- Niger recorded a 94% rise in terrorism-related fatalities, reaching 930 deaths in 2024.
- Togo experienced its worst-ever level of terrorism, highlighting how attacks are expanding beyond the Sahel.
- Competition for gold and uranium resources is exacerbating regional violence.
- The Rise of Islamic State and Affiliate Groups
- IS remained the deadliest terrorist group, responsible for 1,805 deaths across 22 countries—primarily in Syria and the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC).
- Tehrik-e-Taliban Pakistan (TTP) saw a 90% surge in attacks, with fatalities rising from 558 to over 1,000.
- Islamic State Khorasan Province (ISK) expanded its operations from one country to five since 2020, launching major attacks in Iran and Russia.
- ISK propaganda is now produced in nine languages, demonstrating its global reach.
- Terrorism in the Middle East
- Terrorist attacks in the Middle East dropped by 7%, but the Israel-Palestine conflict remains a major threat.
- Syria, Israel, and Iran are among the 10 most affected countries.
- Turkey’s influence in Syria is increasing, while Russia, China, and Iran have scaled back their involvement.
- The Kurdish-led Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF), formerly backed by the S., face growing challenges from Turkey’s military expansion.
Western Nations and the Surge of Lone-Wolf Attacks
- Lone-wolf attackers carried out 93% of fatal terrorist incidents, with no direct links to organized groups.
- Terrorism in Europe doubled, with attacks rising to 67 in 2024.
Western nations saw a 63% increase in terrorism-related incidents, with a worrying rise in teenage radicalization:
- 42% of all terrorism arrests in the UK involved under-18s.
- Germany suffered Europe’s deadliest terrorist attack of 2024.
- Online radicalization has become a major driver, with extremists using social media, gaming platforms, and encrypted messaging apps to recruit followers.
The Impact of the Gaza Conflict
- The Gaza war triggered a surge in hate crimes and regional instability:
- Terrorism deaths in Iran increased sharply.
- Antisemitic and Islamophobic hate crimes surged worldwide, especially in the United States (200% increase in antisemitic incidents).
- Islamophobia incidents in the West rose by 300% in just two months.
Conclusion: A Growing Global Threat
- The GTI 2025 report highlights a worsening global terrorism landscape, with more countries affected than in previous years.
- The Sahel remains the most volatile region, while the Middle East continues to grapple with instability.
- The rise of lone-wolf attackers in the West, fueled by online radicalization, presents a growing security concern.
- Geopolitical conflicts, including the Gaza war and resource-driven violence, continue to drive extremism.
- While some regions have seen a decline in terrorist activity, the overall trend points to a more fragmented yet persistent global threat.
Consider the following statements regarding the Global Terrorism Index (GTI) 2025:
- It is published by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC).
- The index assesses terrorism by evaluating attacks, fatalities, injuries, hostage incidents, and their overall impact.
- The report covers 163 countries, accounting for 7% of the world’s population.
- The number of countries affected by terrorism has declined compared to the previous year.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 4 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 2, and 3 only
d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 – Incorrect: The GTI is published by the Institute for Economics and Peace (IEP), not UNODC.
Statement 2 – Correct: The index evaluates attacks, fatalities, injuries, hostage incidents, and their impact on society.
Statement 3 – Correct: It covers 163 countries, representing 99.7% of the world’s population.
Statement 4 – Incorrect: The number of countries affected by terrorism increased from 58 to 66, indicating a worsening trend.
Wheat and Sugar Crop Outlook for 2025
- The agricultural sector in 2025 presents a complex scenario for key rabi crops, Particularly wheat and sugar.
- While wheat production appears stable, uncertainties persist regarding final yields.
- In contrast, sugar output faces significant challenges, potentially impacting food inflation.
Wheat Production Status
- Wheat remains a crucial rabi crop in India. As of early 2025, government wheat stocks stand at approximately 140 lakh tonnes, a significant rise from last year’s 75 lakh tonnes.
- The opening stocks for the upcoming procurement season are expected to be higher, providing a buffer against supply shortages.
- The government is limiting open market sales to stabilize prices and prevent speculative hoarding.
Procurement and Price Trends
- Current wheat prices in Delhi: ₹2,950 – ₹3,000 per quintal, higher than the previous year.
- Government intervention: Stocking limits have been imposed on traders and retailers to curb hoarding.
- Harvest timeline: The new crop is expected between March and April 2025, with potential price adjustments based on production levels.
Weather Conditions and Yield Outlook
- Weather remains a critical factor in determining wheat yields. Reports suggest favorable conditions in central India, with an anticipated 15-20% increase in yields compared to last year.
- The crucial grain-filling stage depends on stable temperatures, ideally remaining below 35°C.
- Favorable weather could help boost production and ease inflationary concerns.
Sugar Production Challenges:
- Unlike wheat, sugar production is witnessing a downturn. Initial estimates projected a gross production of 333 lakh tonnes, but recent assessments have revised the figure downward.
- As of February 2025, net sugar production stands at 220 lakh tonnes, a decline from the previous year’s levels.
Factors Contributing to Declining Sugar Output
- Suboptimal rainfall in key sugar-producing states such as Maharashtra and Karnataka has affected sugarcane availability.
- Pest infestations and crop diseases have further reduced yields.
- The production decline could lead to a demand-supply imbalance, especially during the festive season.
Sugar Price Trends and Government Response
- Ex-factory sugar prices:
- Uttar Pradesh: ₹40.10 – ₹41.10 per kg
- Maharashtra: ₹38 – ₹38.70 per kg
- Rising prices pose inflationary risks, prompting potential government interventions such as stock limits or import facilitation to stabilize supply.
- As the season progresses, weather patterns, market trends, and policy interventions will play a crucial role in shaping the final production and pricing landscape for both wheat and sugar.
Consider the following statements regarding wheat production in India for 2025:
- The government’s wheat stock in early 2025 is significantly lower than in the previous year.
- The new wheat crop is expected to arrive between March and April 2025.
- The government has imposed stocking limits on traders and retailers to curb hoarding and stabilize prices.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect – The government’s wheat stock in early 2025 is 140 lakh tonnes, which is higher than the previous year’s 75 lakh tonnes.
Statement 2 is correct – The wheat harvest is expected between March and April 2025.
Statement 3 is correct – The government has imposed stocking limits on traders and retailers to prevent hoarding and stabilize prices.inflation.
What is Geet Gawai?
Syllabus: Art and Culture
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s recent visit to Mauritius highlighted the deep-rooted cultural connections between India and the island nation.
- A warm reception featuring the traditional Bhojpuri performance, Geet Gawai, underscored the enduring legacy of the Indian diaspora in Mauritius.
- More than just a musical tradition, Geet Gawai is a cherished cultural expression that reflects the identity and heritage of Indo-Mauritians.
What is Geet Gawai?
- Geet Gawai is a traditional Bhojpuri musical art form, primarily performed by women during significant life events, especially weddings.
- The performance typically begins with hymns invoking deities, followed by uplifting songs that celebrate joy and unity.
- Recognizing its cultural significance, UNESCO inscribed Geet Gawai in its list of Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity in December 2016.
Historical Origins
- The roots of Geet Gawai in Mauritius date back to the migration of Indian indentured laborers. Between 1834 and the early 1900s, nearly 500,000 Indians, predominantly from Bhojpuri-speaking regions, were brought to Mauritius.
- Despite hardships, they preserved their traditions, passing them down through generations. Geet Gawai remains a testament to their resilience and cultural pride.
Rituals and Community Bonding
- Traditionally, Geet Gawai is an integral part of pre-wedding ceremonies, where women gather to prepare items like turmeric and rice while singing devotional and celebratory songs.
- This practice strengthens familial bonds and fosters a sense of community among the Bhojpuri-speaking population.
- Its oral transmission over generations ensures the continuity of this vibrant tradition.
Bhojpuri Language in Mauritius
- Bhojpuri holds a significant place in Mauritius’ linguistic and cultural landscape.
- As per the 2011 Census, around 5.3% of the Mauritian population speaks Bhojpuri. Beyond daily communication, the language plays a vital role in political campaigns, literature, and cultural expressions.
- Recognizing its importance, the Mauritian government has introduced Bhojpuri in primary education to promote its preservation.
Mauritius – A “Mini India”
- Often called “Mini India”, Mauritius embodies strong Indian cultural influences.
- The Indo-Mauritian community actively participates in Indian festivals, wears traditional attire, and practices customs rooted in their ancestral heritage. This cultural vibrancy showcases India’s enduring impact on the island’s identity.
Government Efforts to Preserve Bhojpuri Culture
- The Government of Mauritius has implemented several initiatives to safeguard Bhojpuri heritage:
- The Bhojpuri-Speaking Union Act was enacted to encourage the use and development of the language.
- The Bhojpuri Mahotsav, a festival dedicated to celebrating Bhojpuri culture, was introduced, though its progress was affected by the pandemic.
Conclusion
- The Geet Gawai tradition and the continued presence of Bhojpuri in Mauritius serve as powerful reminders of India’s historical and cultural imprint on the island.
- Through sustained efforts in language preservation and cultural initiatives, Mauritius continues to honor and celebrate its deep-rooted ties with India.
Consider the following statements regarding Geet Gawai:
- It is a Bhojpuri musical tradition performed exclusively by men.
- It was inscribed in UNESCO’s list of Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity in 2016.
- The tradition has its roots in the migration of Tamil laborers to Mauritius.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Geet Gawai is primarily performed by women, making Statement 1 incorrect.
- It was indeed inscribed in UNESCO’s Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity list in 2016, making Statement 2 correct.
The tradition was brought to Mauritius by Bhojpuri-speaking Indian indentured laborers, not Tamil laborers, making Statement 3 incorrect.
