Kanger Valley National Park
Syllabus: Environment
- Kanger Valley National Park (KVNP), situated in the formerly Maoist-affected region of Bastar district in Chhattisgarh, has recently been added to UNESCO’s tentative list of World Heritage Sites under the ‘Natural’ category.
- This recognition highlights the park’s ecological significance and rich biodiversity.
Overview of Kanger Valley National Park
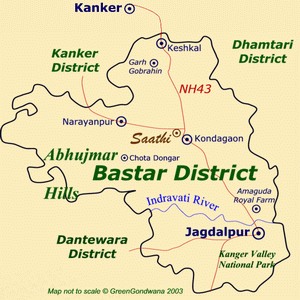
Location & Geography
- KVNP is located in Jagdalpur, Bastar district, Chhattisgarh.
- The park is named after the Kanger River, which flows from Northwest to Southeast through the valley.
- The Kanger River is a tributary of the Kolab River, which eventually merges with the Godavari River.
- The terrain consists of flatlands, gentle slopes, steep inclines, plateaus, deep gorges, valleys, and winding streams.
- The Tirathgarh Waterfall, formed by the Kanger River, cascades from a height of 150 feet, offering a spectacular sight.
- The park houses over 15 limestone caves, including the Kotumsar, Kailash, and Dandak caves, known for their geological formations and underground ecosystems.
Flora
- KVNP exhibits a mixed moist deciduous forest, with dominant species such as Sal, Teak, and Bamboo.
Fauna
- Mammals: The park is home to tigers, leopards, mouse deer, wildcats, sambar, chital, barking deer, langurs, jackals, rhesus macaques, and flying squirrels.
- Avian Species: The aerial biodiversity includes common hill mynas, red jungle fowls, spotted owlets, racket-tailed drongos, and various species of parrots.
The inclusion of Kanger Valley National Park in UNESCO’s tentative list underscores its ecological importance, unique geological formations, and diverse wildlife, making it a crucial conservation site in central India.
Consider the following statements regarding Kanger Valley National Park (KVNP):
- It is located in the Durg district of Chhattisgarh.
- The Kanger River, after flowing through the park, directly merges with the Godavari River.
- KVNP is characterized by the presence of limestone caves, plateaus, deep gorges, and waterfalls.
- It has been included in the tentative list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites under the ‘Cultural’ category.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: (c) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: KVNP is located in Bastar district, not Durg district.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The Kanger River is a tributary of the Kolab River, which eventually joins the Godavari River, but it does not merge directly with the Godavari.
Statement 3 is correct: The park is known for limestone caves, deep gorges, plateaus, waterfalls (Tirathgarh Falls), and diverse topography.
Statement 4 is incorrect: KVNP has been added to UNESCO’s tentative list under the ‘Natural’ category, not the ‘Cultural’ category.
Mount Fuji
Syllabus: Geography
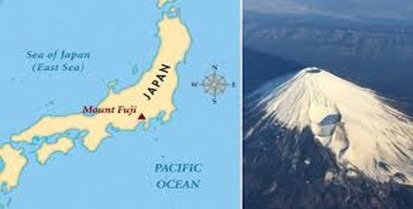
- Japan has announced the introduction of a climbing fee of US$27 for Mount Fuji’s four main trails starting this summer.
- This initiative aims to control overcrowding and enhance safety measures for tourists visiting the iconic peak.
About Mount Fuji
- Tallest Mountain in Japan: Mount Fuji, also known as Fuji-san, stands at 3,776 meters (12,389 feet), making it Japan’s highest peak.
- Location: It is situated on Honshu Island, spanning Yamanashi and Shizuoka prefectures, approximately 100 km southwest of the Tokyo-Yokohama metropolitan area.
- Volcanic Chain: Mount Fuji is part of the Fuji Volcanic Zone, an extensive volcanic chain that stretches from the Mariana Islands and Izu Islands through the Izu Peninsula to northern Honshu.
- Volcanic Status: It is a stratovolcano that has remained dormant since its last eruption in 1707, but it is still classified as active by geologists.
- Cultural Significance: Recognized as one of Japan’s “Three Holy Mountains” alongside Mount Tate and Mount Haku, Fuji holds spiritual and cultural importance.
- UNESCO World Heritage Status: It is a central feature of the Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park, established in 1936, and was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2013.
Formation and Geological History of Mount Fuji
- Traditional Belief: According to legend, Mount Fuji was formed in 286 BCE following a massive earthquake.
Scientific Formation:
- The actual formation is more complex and is estimated to have occurred over the last 6 million years on a base that dates back 65 million years.
- First eruptions and initial peaks likely appeared after 700,000 years ago.
Evolution of Mount Fuji:
- Komitake (North slope) and Ashitaka-yama (Southeast) were the earliest formations.
- Stratovolcanic activity led to the rise of Fuji’s main structure after 400,000 years ago.
- Three successive volcanic formations shaped present-day Mount Fuji:
- Komitake (Oldest, forms the base)
- Ko Fuji (“Old Fuji”) – Formed around 100,000 years ago
- Shin Fuji (“New Fuji”) – The most recent formation, completing Fuji’s modern structure.
The implementation of climbing fees reflects Japan’s ongoing efforts to preserve Mount Fuji’s ecosystem and ensure sustainable tourism, balancing its natural, cultural, and geological significance.
Which of the following rivers and water bodies are geographically closest to Mount Fuji?
- Sagami River
- Fuji River
- Lake Biwa
- Suruga Bay
Which one is the Correct Answer?
A) 1 and 3 only
B) 2 and 4 only
C) 1, 2, and 4 only
D) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: C) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Mount Fuji is surrounded by key water bodies and rivers:
- Fuji River (flows near the mountain)
- Sagami River (located close to the eastern side of Mount Fuji)
- Suruga Bay (near the southern coastline of Honshu, close to Mount Fuji)
- Lake Biwa, however, is Japan’s largest freshwater lake but is located in Shiga Prefecture, far from Mount Fuji.
Shishtachar Squad
Syllabus: Social Issues
- The Shishtachar Squad is a dedicated anti-eve-teasing initiative launched by the Delhi Police to enhance women’s safety in public spaces.
- Modeled after Uttar Pradesh’s Anti-Romeo Squads, it employs a comprehensive approach involving prevention, intervention, and victim support.
- Each police district will deploy at least two such squads, with direct supervision by the Assistant Commissioner of Police (ACP) – Crime Against Women (CAW) Cell of the respective district.
Key Features of the Shishtachar Squad:
- Squad Composition: Each squad comprises one inspector, one sub-inspector, five male officers, four female officers, and receives technical assistance from the Anti-Auto Theft Squad.
- Identification of Vulnerable Areas: The Deputy Commissioner of Police (DCP) of each district is responsible for mapping high-risk zones and vulnerable areas where women’s safety is a concern.
- Active Patrolling: The squad conducts regular patrolling in identified sensitive areas and undertakes daily surveillance drives at a minimum of two vulnerable locations.
- Surprise Inspections & Intervention: Officers in plain clothes conduct random checks on public transport and interact with Delhi Transport Corporation (DTC) staff to encourage prompt reporting of harassment incidents.
This initiative seeks to foster a safe and harassment-free environment for women, reinforcing law enforcement’s commitment to women’s security in the national capital.
Consider the following statements regarding the Shishtachar Squad:
- It is a women-led patrolling force established by the Ministry of Home Affairs to address crimes against women nationwide.
- It follows a multi-pronged strategy involving prevention, intervention, and victim assistance.
- The initiative was directly inspired by the ‘Nirbhaya Framework’ for women’s safety in metropolitan cities.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Shishtachar Squad is an initiative of the Delhi Police, not the Ministry of Home Affairs, and is limited to Delhi rather than being a nationwide initiative.
Statement 2 is correct: The squad operates through a multi-layered strategy focusing on prevention, intervention, and victim support to enhance women’s safety in public spaces.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The squad was inspired by Uttar Pradesh’s Anti-Romeo Squads, not the ‘Nirbhaya Framework’.
River Betwa
Syllabus: Geography
- The Betwa River, once a lifeline of the Vindhyas, has nurtured civilizations, sustained kingdoms, and echoed the footsteps of sages and warriors.
- However, today, it struggles for survival—its waters dwindling, its flow fading.
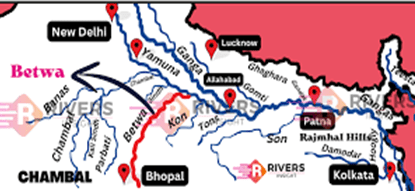
About River Betwa
- Historical Significance: Known in ancient texts as Vetravati, the Betwa River holds deep cultural and spiritual significance, being mentioned in the Vedas and revered in the Mahabharata as a symbol of penance and purity.
Origin & Course:
- It originates from Jhiri village in Raisen district, Madhya Pradesh, within the Vindhya Range, near Narmadapuram (formerly Hoshangabad).
- The river follows a northeastern trajectory, coursing through Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh before merging with the Yamuna River east of Hamirpur, spanning 610 km.
- Almost half of its journey traverses the rugged Malwa Plateau, before descending into the Bundelkhand uplands.
- Major Tributaries: The Jamni and Dhasan rivers contribute significantly to its flow.
- Dams & Water Management: The Betwa is dammed at Dukwan and Deogarh, serving irrigation and hydrological regulation purposes.
Cultural & Strategic Importance:
- The Indian Navy honored the river by naming a frigate INS Betwa after it.
- It plays a crucial role in the Ken-Betwa Link Project, an ambitious interlinking initiative to address water scarcity in Bundelkhand.
- Ken-Betwa Link Project (KBLP)
Objective:
- The KBLP aims to transfer surplus water from the Ken River to the Betwa River, mitigating drought conditions in Bundelkhand.
Historical Context:
- It is the first project under the National Perspective Plan (1980) for interlinking rivers.
Project Phases:
Phase I: Involves the construction of the Daudhan Dam Complex, including:
- Low-Level Tunnel
- High-Level Tunnel
- Ken-Betwa Link Canal
- Hydropower facilities
Phase II: Focuses on three major developments:
Lower Orr Dam
Bina Complex Project
Kotha Barrage
The Betwa River stands at a crossroads—either rejuvenated through conservation and interlinking efforts or left to fade into history as a forgotten relic of the past.
Consider the following statements regarding the Betwa River:
- It originates in the Vindhya Range of Uttar Pradesh.
- The river is a major tributary of the Ganga.
- It flows through both Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
- The Indian Navy has named a warship after this river.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Betwa River originates in Jhiri village, Raisen district, Madhya Pradesh, not Uttar Pradesh.
Statement 2 is incorrect: It is a tributary of the Yamuna, not the Ganga.
Statement 3 is correct: It flows through Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh before merging with the Yamuna.
Statement 4 is correct: The INS Betwa, a frigate in the Indian Navy, is named after the river.
PM Internship Scheme
Syllabus: Government Policies
- PM Internship Scheme: Bridging Youth with Industry Experience.
- Union Minister Nirmala Sitharaman recently launched a dedicated mobile application for the Prime Minister Internship Scheme, encouraging more companies to participate in this transformative initiative.
About the PM Internship Scheme
- The PM Internship Scheme is a flagship initiative by the Government of India, designed to equip young individuals with industry exposure and practical experience.
- It focuses on skill development and employment generation, ensuring that youth from economically weaker sections gain valuable insights into real-world professional environments.
Key Features of the Scheme
- Target Beneficiaries: Young individuals aged 21-24 years from low-income households.
- Internship Duration: 12 months in India’s top 500 companies.
- Pilot Phase: Aims to benefit 25 lakh youth.
- Long-Term Goal: Envisions facilitating internships for one crore young individuals over five years.
Sector Coverage: Spans 24 industries, including:
- Oil & Gas
- Energy
- Travel & Hospitality
- Automotive
- Banking & Financial Services
- Eligibility Criteria
Scheme sets the following Eligibility conditions:
Educational Qualifications:
- Passed 10th, 12th, ITI, Polytechnic, or Diploma courses.
- Fresh graduates from non-premier institutions.
Economic & Family Background:
- Belong to a household with an annual income of ₹8 lakh or less (2023-24).
- No family member should hold a government job.
Exclusions:
- Students from IITs, IIMs, National Law Universities (NLUs).
- Individuals holding professional degrees like CA, MBA, MBBS, etc.
Vision & Impact
- This initiative aligns with the government’s broader strategy to bridge the gap between academic learning and professional expertise.
- By focusing on skill enhancement and employment readiness, it paves the way for greater socio-economic mobility among India’s youth.
With reference to the Prime Minister Internship Scheme (PM Internship Scheme), consider the following statements:
- The scheme is open to all young individuals between the ages of 21-30 years.
- It offers internships in only government enterprises to enhance youth participation in public administration.
- The scheme specifically excludes students from IITs, IIMs, and National Law Universities to ensure inclusivity for underrepresented groups.
- The long-term goal of the scheme is to facilitate internships for 5 crore youth over five years.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: (c) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The scheme targets youth aged 21-24 years, not 21-30 years.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Internships are available in both public and private enterprises, covering 24 industries, including energy, automotive, and financial services.
Statement 3 is correct: To promote inclusivity, students from IITs, IIMs, National Law Universities, and professional courses like CA, MBA, MBBS are excluded.
Statement 4 is incorrect: The scheme’s five-year goal is to facilitate internships for 1 crore youth, not 5 crore.
Caracal
Syllabus: Environment
- A rare caracal has been recently sighted in Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve, Rajasthan, generating excitement among wildlife enthusiasts.
About Caracal
- The caracal is a medium-sized, nocturnal wildcat known for its agility and striking black-tipped ears.
- Indian Name: Siya Gosh (Persian: “Black Ear”).
- Scientific Name: Caracal caracal
Distribution & Habitat
- Found in Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia.
- In India, their population is critically low, with an estimated 50 individuals, primarily in Rajasthan and Gujarat.
- They inhabit rocky hills, grasslands, savannas, scrublands, and forests, showcasing high adaptability to various environments.
Physical Features
- Slender body, long legs, and largest among small African cats.
- Size: 8–18 kg in weight, up to 1 meter in length.
- Fur: Short, dense, and varies from tawny-brown to reddish-tan, with whitish underparts.
- Facial markings: Dark lines and white spots around the eyes.
- Distinctive black-tipped ears with tufts, aiding in communication.
Unique Abilities
- Renowned for leaping over 2 meters to catch birds mid-air.
- Can sprint at speeds of up to 80 km/h (50 mph).
- Solitary by nature, but may occasionally form small groups.
- Shy and elusive, making sightings in the wild extremely rare.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern (globally), but faces severe population decline in India.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I (providing the highest level of legal protection in India).
- The recent sighting in Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve highlights the need for focused conservation efforts to protect this elusive species in India.
With reference to the Caracal (Caracal caracal) in India, consider the following statements:
- The caracal is listed as Critically Endangered under the IUCN Red List in India.
- It is known for its ability to leap several meters into the air to catch birds in flight.
- In India, its population is mainly found in Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Madhya Pradesh.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The caracal is listed as “Least Concern” globally on the IUCN Red List, though its population in India is highly threatened.
Statement 2 is correct: Caracals are exceptional jumpers and can leap over 2 meters to catch birds in mid-air.
Statement 3 is incorrect: In India, the caracal is primarily found in Rajasthan and Gujarat, but not significantly in Madhya Pradesh.
Update on elimination of Trachoma and Malaria
Syllabus: Science
- India has been officially declared trauma-free as a public health problem by the World Health Organization (WHO) on October 8, 2024.
- This milestone makes India the third country in the WHO Southeast Asia Region to achieve this status.
- The elimination of Trachoma, a leading cause of preventable blindness, highlights significant advancements in public health, hygiene, and sanitation practices.
Government Initiatives for Trachoma Elimination
- The National Programme for Control of Blindness and Visual Impairment (NPCBVI) played a key role in controlling Trachoma.
India followed the WHO-SAFE Strategy, which includes:
- Surgery for trachomatous trichiasis
- Antibiotics to treat infection
- Facial hygiene promotion
- Environmental cleanliness improvement
- A National Trachomatous Trichiasis (TT-only) survey was conducted in 200 endemic districts between 2021-2024 under WHO guidelines, confirming a decline in prevalence below elimination thresholds.
National Quality Assurance Standards (NQAS)
- The Indian government has implemented the National Quality Assurance Standards (NQAS) to ensure the safety, efficiency, and reliability of public healthcare services.
Initially developed for District Hospitals, it was later extended to:
- Sub-District Hospitals (SDHs)
- Community Health Centers (CHCs)
- Ayushman Arogya Mandir – Urban & Rural Health Centers (AAM-UPHCs, AAM-PHCs, AAM-SHCs)
- Integrated Public Health Laboratories (IPHLs) (launched on June 28, 2024)
- A Virtual Assessment for NQAS certification was introduced to facilitate compliance. As of December 31, 2024, a total of 22,786 health facilities had received NQAS certification.
Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS)
- The Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS) were introduced in 2007 and revised in 2012 and 2022 to define minimum essential services for:
- District & Sub-District Hospitals
- Community Health Centers (CHCs)
- Primary Health Centers (PHCs)
- Sub-Health Centers (SHCs)
These standards ensure better healthcare delivery, patient safety, and public trust in the system.
India’s Exit from the High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) Group for Malaria
- India has exited the High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) group, indicating a major reduction in Malaria prevalence.
- The Government of India adopted a comprehensive, multi-pronged approach under the National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme (NVBDCP).
Key Strategies for Malaria Reduction
- Disease Management
- Early case detection through active, passive, and sentinel surveillance
- Complete and effective treatment for all detected cases
- Strengthening referral services for severe malaria cases
- Rapid response mechanisms for malaria outbreaks
- Integrated Vector Management (IVM)
- Indoor Residual Spraying (IRS) in high-risk regions
- Long-Lasting Insecticidal Nets (LLINs) in endemic zones
- Use of larvivorous fish & bio-larvicides in urban malaria-prone areas
- Environmental engineering & source reduction measures to eliminate breeding sites
- Supportive Interventions
- Behavior Change Communication (BCC) to educate communities
- Inter-Sectoral Convergence for coordinated disease control efforts
- Capacity building of health workers and field staff
These strategic efforts have significantly reduced malaria transmission, paving the way for India’s goal of Malaria elimination by 2030.
With reference to India’s elimination of Trachoma as a public health problem, consider the following statements:
- India followed the SAFE strategy recommended by WHO, which includes measures like surgery, antibiotics, face washing, and environmental improvement.
- The National Trachomatous Trichiasis (TT-only) survey was conducted under the National Programme for Control of Blindness and Visual Impairment (NPCBVI) to assess prevalence.
- India is the first country in the WHO Southeast Asia Region to eliminate Trachoma as a public health problem.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: WHO’s SAFE strategy (Surgery, Antibiotics, Facial cleanliness, Environmental improvement) was implemented in India.
Statement 2 is correct: The TT-only survey was conducted across 200 endemic districts to determine prevalence.
Statement 3 is incorrect: India is the third country in the WHO Southeast Asia Region (not the first) to eliminate Trachoma as a public health problem.
NAVAL EXERCISE - VARUNA 2025

- The 23rd edition of the bilateral naval exercise VARUNA, a symbol of the robust Indo-French maritime partnership, is scheduled to take place from March 19 to 22, 2025.
- Since its inception in 2001, VARUNA has grown into a pivotal naval collaboration, enhancing interoperability and operational synergy between the two nations.
- This year’s edition will witness an impressive array of complex maritime drills, spanning sub-surface, surface, and aerial domains.
- The exercise will be marked by the joint participation of aircraft carriers INS Vikrant and FS Charles de Gaulle, supported by their respective fighter aircraft, destroyers, frigates, and an Indian Scorpene-class submarine—reflecting the formidable naval capabilities of both countries.
Key Features of VARUNA 2025:
Advanced Air Defence Drills & Fighter Exercises
- Simulated air-to-air combat featuring the French Rafale-M and Indian MiG-29K, enhancing tactical proficiency.
Anti-Submarine Warfare Operations
- Focus on underwater domain awareness through rigorous submarine-hunting and detection exercises.
Surface Warfare Operations
- Coordinated fleet manoeuvres and combat engagements to refine operational synchronisation.
Maritime Patrol and Surveillance
- Deployment of maritime patrol aircraft to bolster situational awareness and intelligence gathering.
Replenishment-at-Sea Exercises
- Strengthening of logistical cooperation and sustainment capabilities for extended maritime operations.
- By facilitating mutual learning and best practice exchanges, VARUNA 2025 reinforces the ability of both navies to operate seamlessly, even in highly complex maritime scenarios.
- This exercise reaffirms the shared commitment of India and France to ensuring a free, open, and secure maritime domain, further solidifying their strategic partnership in global maritime security.
With reference to the bilateral naval exercise VARUNA, consider the following statements:
- It is conducted exclusively in the Indian Ocean region.
- The exercise involves the participation of aircraft carriers from both India and France.
- Anti-submarine warfare is a key component of the exercise.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: While VARUNA is frequently conducted in the Indian Ocean region, it has also been held in the Mediterranean Sea in certain editions.
Statement 2 is correct: The 2025 edition features the participation of INS Vikrant and FS Charles de Gaulle, showcasing both nations’ naval capabilities.
Statement 3 is correct: Anti-submarine warfare is a major focus area, enhancing underwater domain awareness.
SwaYaan initiative
Syllabus: Government Policies
- The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), in collaboration with the Drone Federation of India (DFI), has launched the National Innovation Challenge for Drone Application and Research (NIDAR) under the SwaYaan initiative.
- This initiative aims to bolster capacity building in Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) by fostering applied research and entrepreneurship in drone technology.
- The event, held at Electronics Niketan, witnessed participation from key government officials, industry leaders, and students across India through video conferencing.
Launch and Key Highlights
- The challenge was officially inaugurated by Shri S. Krishnan, Secretary, MeitY, who unveiled the NIDAR concept video, launched the website and registration portal, and released the official rulebook and poster.
- Addressing the attendees, Shri Krishnan underscored the transformative role of drones in sectors such as agriculture, disaster management, logistics, healthcare, and infrastructure, emphasizing the need to scale the NIDAR initiative to contribute to India’s goal of becoming a global drone hub by 2030.
- T. G. Sitharam, Chairman, AICTE, highlighted the necessity of integrating the NIDAR challenge into engineering curricula across the country.
- Stressing the importance of collaboration between academia, startups, and industry, he called for innovative engagement in drone technology research and development.
Objectives and Focus Areas of NIDAR
- The NIDAR challenge aims to inspire India’s student and research community to develop collaborative autonomous drones to address real-world challenges in two key domains.
- Disaster Management – Scout and Deliver Drones.
- Autonomous drones for scouting disaster-affected areas.
Assisting survivors through communication and parcel delivery. - Precision Agriculture – Scan and Spray Drones.
- Drones for crop health monitoring.
Precision-based pesticide and nutrient delivery. - Support, Incentives, and Participation
- The challenge offers a prize pool of INR 40 Lakhs, along with startup incubation opportunities, cloud computing credits, software support, and internship placements with India’s leading drone companies.
- Over 100 student teams from higher education institutions are expected to participate, showcasing innovative solutions to challenges in agriculture and disaster response.
- The competition will be conducted in multiple phases, including technology presentation, business case development, and final operational demonstration.
- This comprehensive evaluation will assess the technical skills, problem-solving abilities, teamwork, and entrepreneurial acumen of participants, preparing them for leadership roles in emerging technology domains.
Role of Drone Federation of India (DFI)
- As India’s premier industry body representing over 550 drone companies and 5500 drone pilots, the Drone Federation of India (DFI) will play a crucial role in mentoring student teams by providing industry exposure and guiding them through the innovation process.
Significance of NIDAR in India’s Drone Ecosystem
- The launch of NIDAR represents a strategic milestone in advancing India’s drone research, development, and commercialization.
- It reinforces the Government of India’s efforts to promote entrepreneurship in academia while bridging the gap between technological innovation and real-world applications.
About SwaYaan Initiative
- The SwaYaan initiative, approved by MeitY in July 2022, focuses on capacity building in Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) through formal and non-formal educational programs.
- Its goal is to train 42,560 individuals and develop a skilled workforce in drone technology.
Implementation Model and Key Areas
- The initiative follows a hub-and-spoke model, involving 30 premier institutions, including IISc Bangalore, IITs, IIITs, NITs, CDAC, and NIELIT.
- It is structured around five key research themes, Drone Electronics, GNC Algorithms and Simulation, Aeromechanics, Drone Applications, and Allied UAS Technologies.
- To date, over 14,000 individuals have been trained under SwaYaan.
Notable Achievements
- Launch of M.Tech in UAS Engineering at IIT Kanpur.
- Introduction of minor degree programs in drone technology.
- Successful execution of multiple bootcamps and workshops.
- The program actively engages industry partners through innovation challenges and industry meets, reinforcing the critical link between academic training and industry requirements in drone technology.
Conclusion
The NIDAR challenge, under the SwaYaan initiative, is set to be a game-changer for India’s drone industry, fostering cutting-edge research, skill development, and entrepreneurship. By encouraging technological innovation in drone applications, the initiative is poised to strengthen India’s position as a global leader in unmanned aerial systems.
Which of the following statements regarding the NIDAR challenge is/are correct?
- It is launched by the Ministry of Civil Aviation in collaboration with the Drone Federation of India (DFI).
- The challenge provides incentives such as startup incubation, cloud computing credits, and software support.
- The competition includes multiple evaluation phases such as Technology Presentation, Business Case Development, and Final Operational Demonstration.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 2 and 3 only
(C) 1 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (B) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect because NIDAR is launched by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), not the Ministry of Civil Aviation.
Statements 2 and 3 are correct as the challenge offers startup incubation, cloud computing credits, and software support, along with a rigorous multi-phase evaluation process.

2 Comments
P NARASIMHA CHARYA
March 19, 2025Hi sir…plz send various papers GS paper clips also in daily current affairs in telegram channel…i regularly follow your current affairs…very useful to all…tq sir…
karthik
March 29, 2025Thank you for your feedback and suggestion. We will implement it as soon as possible