Deregulation Commission & State’s Role in Governance
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
India’s Deregulation Commission: A Step Towards Economic Reform
To enhance the ease of doing business and minimize bureaucratic inefficiencies, the Prime Minister of India has announced the establishment of a Deregulation Commission aimed at streamlining regulatory processes and eliminating redundant laws.
Understanding Deregulation and Its Significance
- Deregulation Definition: Reducing or eliminating government-imposed restrictions on industries to promote market efficiency and free competition.
- Challenges for Businesses: Startups and MSMEs face significant regulatory hurdles, including excessive licensing requirements, outdated laws, and bureaucratic delays.
Key Highlights of the Deregulation Commission
1991 Economic Liberalization: Marked the beginning of reduced state control and increased private sector participation.
Eliminating Archaic Regulations: Focused on scrapping obsolete compliance requirements.
- Sectoral Focus:
Key sectors identified for deregulation include banking, energy, telecom, retail, and manufacturing.
- Collaboration with Regulators:
Coordination with bodies like RBI, SEBI, TRAI, and CERC.
- Encouraging Private Investment: Aims to reduce red tape to attract higher FDI and domestic investments.
Rationale Behind the Deregulation Commission
- Reducing Bureaucratic Hurdles: Improve India’s ranking in the Ease of Doing Business Index.
- Boosting Economic Growth: Simplify compliance frameworks for sectors like manufacturing and digital economy.
- Encouraging Entrepreneurship & Innovation: Support startups and MSMEs by easing regulatory burdens.
- Modernizing Outdated Laws: Repeal colonial-era laws hindering business expansion.
- Attracting FDI: Address challenges from restrictive policies in various sectors.
- Enhancing Federalism & State Cooperation: Work with state governments to create uniform policies.
- Increasing Competition & Market Efficiency: Results in lower prices and improved services.
- Evolution of Deregulation in India
- Key Regulatory Commissions and Their Impact
Regulatory Commission | Sector | Role | Major Reforms |
RBI | Banking & Finance | Regulates monetary policy and financial institutions | – Increased FDI limits in insurance |
TRAI | Telecommunications | Ensures fair competition and consumer protection | – 1994: Allowed private telecom players |
CERC | Energy | Regulates electricity pricing and open access | – Encouraged private investment in power generation |
PNGRB | Oil & Gas | Ensures transparency in fuel pricing | – 2010: Deregulation of petrol prices |
Challenges and Negative Impacts of Deregulation
- Market Failures & Monopolies: Risk of excessive deregulation leading to monopolies.
- Job Losses in PSUs: Privatization may result in downsizing and layoffs.
- Regulatory Capture: Influence of powerful private entities on policy decisions.
- Rural Economic Disparities: Benefits skewed towards urban economies.
- Environmental Concerns: Risk of increased pollution and resource depletion.
Way Forward: A Balanced Approach
- Ensure consumer protection and prevent corporate malpractices.
- Balance business interests with public welfare.
- Careful deregulation of sensitive sectors like healthcare and education.
Conclusion: The Deregulation Commission is a transformative initiative for improving India’s business environment, requiring a balance between liberalization and regulatory oversight to ensure sustainable growth.
Which of the following arguments can be made against deregulation in India’s financial sector?
1. It may increase systemic financial risks, leading to crises like the 2008 Global Financial Crisis.
2. Private players may prioritize short-term profits over long-term economic stability.
3. Reduced state oversight may lead to higher financial fraud and banking irregularities.
4. It may make India’s economy more resilient to external financial shocks.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2, and 3 only
(c) 2, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b)
Explanation:
While deregulation can boost competition, excessive deregulation in the financial sector may increase risks, promote speculative behavior, and lead to crises. However, it does not necessarily make the economy more resilient (eliminating option 4).
Internet Shutdowns in India
Internet Shutdowns in 2024: Trends and Legal Framework
Context
A report by advocacy body Access Now highlights that 2024 witnessed the highest number of internet shutdowns globally, raising concerns about digital rights and governance.
Global Trends in Internet Shutdowns (2024)
- A total of 296 internet shutdowns occurred worldwide.
- India accounted for 84 shutdowns, making up 28% of the global total.
- India had the second-highest number of shutdowns, just behind Myanmar.
- However, India’s total shutdowns in 2024 were fewer compared to the previous year.
- Shutdowns were imposed in 16 Indian States and Union Territories.
- States with the Most Shutdowns:
- Manipur – 21 shutdowns
- Haryana – 12 shutdowns
- Jammu & Kashmir – 12 shutdowns
- Primary Reasons for Shutdowns:
- Protests: 41 instances
- Communal violence: 23 instancesLegal Provisions Governing Internet Shutdowns in India
- Indian Telegraph Act, 1885:
- Internet shutdowns can be imposed in cases of “public emergency” or in the interest of “public safety”.
- However, the law does not clearly define what qualifies as an emergency or a safety issue.
Section 144 of the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC):
- Before 2017, most shutdowns were imposed under Section 144 CrPC.
- This provision allows authorities to prevent unlawful gatherings and direct individuals to refrain from certain activities.
- Temporary Suspension of Telecom Services (Public Emergency or Public Safety) Rules, 2017:
- These rules formalized the process for imposing temporary internet shutdowns.
- Shutdown orders must be reviewed by an advisory board within five days to assess their legitimacy.
Landmark Case: Anuradha Bhasin v. Union of India (2020)
- The Supreme Court ruled that indefinite internet shutdowns are unconstitutional.It held that:
- Internet access is a fundamental right under Article 19 of the Indian Constitution.
- Shutdowns must be temporary and proportionate, not indefinite.
- The government must publish all orders imposing shutdowns under Section 144 CrPC.
- All shutdown orders are subject to judicial review.
Arguments in Favor of Internet Shutdowns
- National Security: Prevents the spread of misinformation and coordination of unlawful activities.
- Targeted & Temporary Measure: Aims to address specific security concerns rather than long-term restrictions.
- Preventing Unrest & Violence: Helps curb the organization of protests, riots, and civil disturbances.
- Countering Fake News: Reduces the spread of disinformation during crises.
Arguments Against Internet Shutdowns
- Freedom of Expression: Violates constitutional rights to speech and information.
- Global Reputation & Investment: Frequent shutdowns hurt India’s image and discourage foreign investment.
- Human Rights Concerns: Impacts access to information, freedom of assembly, and democratic rights.
- Economic Losses: Disrupts businesses, digital transactions, and e-commerce.
- Educational Setbacks: Hinders online learning, affecting students and teachers.
- Lack of Transparency: The government needs to provide clear justifications and timelines for shutdowns.
Conclusion
In a democratic setup, internet shutdowns should be exceptional rather than a routine measure.
- The government must justify each shutdown transparently and ensure they are proportionate and time-bound.
- Indiscriminate shutdowns impose high social and economic costs without effectively addressing security concerns.
To achieve better internet governance, civil society and policymakers must work towards a more accountable and transparent system
Consider the following statements regarding global internet shutdowns in 2024:
1. India recorded the highest number of internet shutdowns globally.
2. Manipur was the Indian state with the most shutdowns in 2024.
3. Internet shutdowns in India were higher in 2024 compared to the previous year.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b)
Explanation:
India had the second-highest number of internet shutdowns in 2024, behind Myanmar (making Statement 1 incorrect).
Manipur recorded the highest shutdowns (21), so Statement 2 is correct. However, shutdowns in 2024 were fewer than in the previous year, making Statement 3 incorrect.
CAG Reports and Their Significance in India
The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) plays a crucial role in ensuring fiscal accountability and transparency in government finances. A recent report scrutinizing the Delhi AAP government’s excise policy estimated a ₹2,002 crore loss.
Constitutional Provisions and Powers of the CAG
- Appointed by the President under Articles 148-151 of the Constitution.
- Conducts compliance, performance, and financial audits of government accounts.
Audit Procedure
- Entry Conference
- Audit Process
- Exit Conference
- Response Period
- Final Report Submission
Challenges in Tabling CAG Reports
- Delays occur due to lack of specific timelines for presenting reports after submission.
Impact of CAG Reports on Governance
- CAG reports often highlight financial mismanagement leading to policy reforms, increasing accountability and reducing corruption.
The Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG) has recently come into focus following the tabling of 14 pending audit reports on the previous Aam Aadmi Party (AAP) government in Delhi.
One of these reports scrutinizes the now-scrapped excise policy, estimating a ₹2,002 crore loss to the Delhi government. The CAG, as India’s supreme audit institution, plays a crucial role in ensuring fiscal accountability and transparency in government finances.
Constitutional Provisions and Powers of the CAG:
The CAG is appointed by the President of India under Articles 148 to 151 of the Constitution.
The CAG’s Duties, Powers, and Conditions of Service Act, 1971, provides a legal framework for its operations. The key responsibilities of the CAG include:
- Auditing the accounts of the central and state governments, along with Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs).
- Maintaining state government accounts and overseeing pension authorizations.
- Managing General Provident Fund (GPF) accounts for state employees.
Types of Audits Conducted by the CAG
The CAG primarily conducts three types of audits:
- Compliance Audit – Examines whether government entities adhere to financial rules, regulations, and laws.
- Performance Audit – Evaluates the effectiveness, efficiency, and economy of government schemes and programs.
- Financial Audit – Certifies government accounts and reviews the financial statements of PSUs.
Selection Process for Audits:
The CAG selects audit subjects based on a risk assessment framework, which considers factors such as:
- Magnitude of financial transactions involved.
- Past inspection reports and media scrutiny.
- Guidelines from the International Organization of Supreme Audit Institutions (INTOSAI).
Additionally, the Audit Advisory Board suggests potential topics and methodologies for auditing. Government bodies or the judiciary may also recommend specific audits when deemed necessary.
Audit Procedure and Reporting
- Entry Conference – Before conducting an audit, the CAG meets with the concerned department to discuss the scope, methodology, and timeline.
- Audit Process – The audit is carried out, collecting financial data and evaluating compliance.
- Exit Conference – After completion, the CAG discusses key findings with the audited department.
- Response Period – The department is given six weeks to respond to the draft report.
- Final Report Submission – The final report is submitted to the President or Governor, and later presented before Parliament or the State Legislature as per Article 151.
Challenges in Tabling CAG Reports
Although Article 151 mandates the submission of audit reports, it does not specify a deadline for their presentation in the legislature. This has led to delays in tabling reports. For instance, the Delhi government did not present several CAG reports in the Assembly despite their submission to the Lieutenant Governor four years ago.
Impact of CAG Reports on Governance
CAG reports often highlight financial mismanagement and inefficiencies, leading to policy reforms. Notable examples include:
- Telangana Government Reforms – A CAG audit on engineering procurement contracts prompted the Telangana government to amend its Engineering Procurement Contract (EPC) mode.
- Increased Auditing Activity – In 2022-23, the CAG produced 172 audit reports, marking a significant increase in its scrutiny of government finances.
By exposing irregularities, the CAG plays a pivotal role in strengthening accountability, reducing corruption, and improving public financial management
Consider the following statements regarding the appointment and removal of the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India:
- The CAG is appointed by the President of India under Article 148 of the Constitution.
- The CAG holds office for a term of six years or until attaining the age of 65, whichever is earlier.
- The CAG can be removed by the President at their discretion.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 2 and 3 only
(C) 1 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (A) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
The CAG is appointed by the President under Article 148. The term of office is 6 years or until the age of 65, whichever is earlier. The CAG cannot be removed at the President’s discretion. The removal process is similar to that of a Supreme Court judge, requiring a resolution passed by both Houses of Parliament on grounds of proven misbehaviour or incapacity.
Death Penalty in India
- The application of the death penalty by the Indian judiciary has recently faced scrutiny due to two contrasting murder cases.
- On January 22, 2025, a civic volunteer was sentenced to life imprisonment for the rape and murder of a medical student, while a woman received the death penalty for poisoning her partner.
- These verdicts have reignited discussions about the ‘rarest of rare’ doctrine, which currently lacks a precise statutory definition.
The Rarest of Rare Doctrine
The ‘rarest of rare’ doctrine originated from a Supreme Court ruling in 1980, asserting that the death penalty should only be administered in exceptional circumstances. Despite its importance, the term remains vaguely defined, leading to differing interpretations by judges across various cases.
Key Supreme Court Cases
- In Jagmohan Singh vs. State of U.P. (1972), the Supreme Court affirmed the constitutionality of the death penalty but acknowledged the absence of explicit guidelines for judges, raising concerns about the fairness and equality of capital punishment.
- Later, in Bachan Singh vs. State of Punjab (1980), the court established the ‘rarest of rare’ principle without defining its scope.
- This framework was further elaborated in Machhi Singh vs. State of Punjab (1983), where the court identified five categories justifying the death penalty: the manner of the murder, the motive, the socially abhorrent nature of the crime, the magnitude of the offense, and the vulnerability of the victim.
Legislative Revisions and Challenges
- Despite the established framework, challenges persist. In Mithu vs. State of Punjab (1983), the Supreme Court invalidated the mandatory death penalty for inmates serving life sentences, deeming it a violation of constitutional rights.
- This ruling underscored the necessity for judicial discretion in capital cases. In 2022, the Supreme Court began discussions aimed at ensuring meaningful hearings for mitigating circumstances in death penalty cases, an effort to standardize the procedures for determining whether a crime qualifies as ‘rarest of rare.’
Contemporary Implications
- The application of the death penalty in India remains a deeply contentious topic.
- Recent verdicts expose disparities in judicial outcomes, and the absence of a universally accepted definition for ‘rarest of rare’ grants judges considerable latitude, resulting in inconsistent decisions.
- Such inconsistencies raise significant concerns regarding the fairness and application of justice in capital punishment cases.
Public and Legal Discourse
- The public discourse surrounding the death penalty is sharply divided.
- Proponents argue for its essential role in deterring heinous crimes, while critics point to the risks of judicial errors and the ethical implications of capital punishment.
These ongoing debates mirror broader societal values and attitudes toward justice and retribution, underscoring the complexity of the issue within contemporary India
What is the basis for the ‘rarest of rare’ doctrine as established by the Supreme Court of India?
a. It allows for automatic imposition of the death penalty for all murder cases.
b. It stipulates that the death penalty should be reserved only for exceptional circumstances.
c. It mandates a minimum sentence of life imprisonment for all murders.
It defines the specific method of execution in capital punishment cases.
Answer: B) It stipulates that the death penalty should be reserved only for exceptional circumstances.
Explanation: The doctrine was established to ensure that the death penalty is imposed only in extraordinary cases, though its ambiguity has led to varied interpretations.
Right to Freedom of Speech and Expression
The criminal proceedings against India’s Got Latent over alleged obscene remarks have ignited a debate on the scope of freedom of speech under Article 19 of the Indian Constitution.
Constitutional Framework
Article 19(1)(a) guarantees the fundamental right to freedom of speech and expression. However, Article 19(2) allows the state to impose reasonable restrictions under specific conditions, including:
- Security of the State
- Public Order
- Decency or Morality
- Contempt of Court
- Defamation
- Incitement to Offense
The Right to Take Offense
The Constitution does not explicitly recognize “offensive speech” as a separate category warranting restrictions. Consequently, the idea of a right to take offense falls outside the purview of constitutionally permissible limitations on free speech.
Constitutional Morality
Constitutional morality is a complex and evolving principle rather than an inherent sentiment. It requires continuous cultivation and development. Dr. B.R. Ambedkar emphasized that determining forms of administration should be the responsibility of the legislature rather than being dictated solely by the Constitution.
Which of the following best describes the relationship between Article 19(1)(a) and Article 19(2) of the Indian Constitution?
(A) Article 19(1)(a) guarantees freedom of speech, while Article 19(2) imposes absolute restrictions on it.
(B) Article 19(1)(a) guarantees freedom of speech, while Article 19(2) allows only the judiciary to impose reasonable restrictions.
(C) Article 19(1)(a) provides freedom of speech, but Article 19(2) permits the state to impose reasonable restrictions under specified grounds.
(D) Article 19(1)(a) grants fundamental rights, while Article 19(2) allows for restrictions even based on the subjective opinion of individuals who feel offended.
Answer: (C)
Explanation:
Article 19(1)(a) provides the right to freedom of speech and expression, while Article 19(2) enables the state to impose reasonable restrictions on specific grounds like security of the state, public order, decency, and defamation. The restrictions are not absolute and must be justified as “reasonable” by the judiciary.
Deputy Speaker
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
Constitutional Mandate
- The office of the Deputy Speaker is enshrined in Articles 93 and 178 of the Constitution, making its election constitutionally mandatory.
- Article 93: Mandates the election of a Speaker and Deputy Speaker for the Lok Sabha.
- Article 178: Similar provision for State Legislative Assemblies.
Election and Tenure
- The Constitution does not prescribe a time frame for the election of the Deputy Speaker, stating it must be held “as soon as may be.”
- Conventionally, the Speaker is elected in the first session, and the Deputy Speaker in the second session.
- Holds office until:
- The House is dissolved.
- Ceasing to be a Member of the House.
- Removal by a resolution passed by the majority of all House members.
Duties and Powers of the Deputy Speaker
- Aids the Speaker in the efficient functioning of the House.
- Presides over the House in the absence of the Speaker and exercises all powers of the Speaker during such periods.
- Can participate in debates and vote like other members but has a casting vote in case of a tie when presiding.
- Cannot introduce bills or table questions while presiding over the House.
- Receives a salary from the Consolidated Fund of India, independent of parliamentary voting.
- Cannot preside over House proceedings when a motion for his removal is under debate.
Parliamentary Convention and Political Significance
- A well-established parliamentary tradition dictates that the Deputy Speaker is chosen from the Opposition to ensure political neutrality and balance in proceedings.
This practice has largely been followed post-Emergency (1975), with some exceptions.
Consider the following statements regarding the Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha:
- The election of the Deputy Speaker is mandated by Article 93 of the Indian Constitution.
- The Constitution mandates a fixed time frame for the election of the Deputy Speaker.
- The Deputy Speaker presides over all debates, including motions related to his own removal.
- The Deputy Speaker receives his salary from the Consolidated Fund of India, which is subject to parliamentary vote.
Which of the statements are correct?
a. 1 only
b. 2 and 3 only
c. 1, 2, and 4 only
d.1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: A) 1 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Article 93 mandates the election of the Speaker and Deputy Speaker of the Lok Sabha.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The Constitution does not prescribe a specific time frame for the election of the Deputy Speaker, only stating it must be held “as soon as may be.”
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The Deputy Speaker cannot preside over the House when a motion for his own removal is under debate.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: The Deputy Speaker’s salary comes from the Consolidated Fund of India, but it is not subject to parliamentary vote.
Delimitation Debate: Why Are Southern States Wary
Context
The Union Home Minister has assured that the proposed delimitation exercise will not lead to a reduction in parliamentary constituencies in southern states, addressing concerns raised by the Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu.
Understanding Delimitation
Delimitation is the process of redrawing the boundaries of parliamentary and legislative assembly constituencies to reflect changes in population. Its key objectives include:
1. Ensuring fair representation based on demographic shifts.
2. Adjusting the number of seats allocated to various states.
3. Determining reservations for Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST).
This process is designed to balance population growth with political representation, upholding the democratic principle of “one citizen, one vote, one value.”
Constitutional Provisions
1. Article 82: After each Census, Parliament enacts a Delimitation Act to redefine constituency boundaries.
2. Article 170: The total number of seats in state assemblies is adjusted based on the Delimitation Act following each Census.
Who Conducts Delimitation?
The Delimitation Commission is an independent body established through a Parliamentary Act, responsible for overseeing the delimitation process. Its authority and decisions are typically not subject to judicial review; however, in 2024, the Supreme Court ruled that delimitation orders may be reviewed if they contravene constitutional values.
Composition of the Commission: Chairperson: A retired Supreme Court judge. Members: The Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) or a commissioner designated by the CEC, along with State Election Commissioners of the respective states.
History of Delimitation in India
Parliamentary Authority: The power to define the number and boundaries of constituencies lies with the Parliament. This authority has been exercised four times through the Delimitation Commission Acts of 1952, 1962, 1972, and 2002.
42nd Amendment Act (1976): This act froze the allocation of Lok Sabha seats based on the 1971 Census, intended to safeguard states that successfully implemented population control measures from losing representation.
84th Amendment Act (2001): This amendment allowed for the readjustment and rationalization of constituency boundaries based on the 1991 Census without affecting the total number of seats allocated to each state.
87th Amendment Act (2003): This act shifted the basis of delimitation from the 1991 Census to the 2001 Census, while also maintaining the seat allocation limits established in previous amendments.
Why Is Delimitation Being Revisited?
The upcoming delimitation exercise is expected to utilize the 2021 Census data (which was delayed due to the pandemic). This has sparked concerns among southern states, where population growth has been slower compared to northern states. If the delimitation process follows historical trends, the number of Lok Sabha seats could potentially increase from 543 to 753 based on a proposed population ratio of 20 lakh people per constituency.
Concerns of Southern States:
Southern states—such as Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana—are apprehensive that northern states (like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan, and Madhya Pradesh) with higher population growth may gain additional seats, thereby diminishing their representation, despite their successful governance and population control measures.
What’s Next?
Potential Increase in Total Seats: Rather than reducing seats in any state, the total number of Lok Sabha seats may be increased to reflect growing population disparities.
2026 Review: The next delimitation exercise can only occur after the first Census post-2026, likely the 2031 Census.
Women’s Reservation Act: Implementing the 33% reservation for women may also influence seat adjustments during the delimitation process
Consider the following statements regarding the delimitation and its effects on political representation in India:
- The delimitation process aims to ensure an equal representation ratio between constituencies across states.
- Demographic shifts as reflected in the census data can significantly alter the political landscape, favoring states with higher population growth.
- Delimitation only impacts the allocation of seats in the Lok Sabha and does not affect State Legislative Assemblies.
Which of the statements are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1, 2, and 3
D) 1 and 3 only
Answer: A) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct as the delimitation process is aimed at equalizing representation across constituencies.
Statement 2 is also correct, as demographic shifts can lead to an altered political balance.
However, statement 3 is incorrect since delimitation affects both Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assembly constituencies.
Public Accounts Committee
Recent News: Delhi Congress leaders have welcomed the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) report on AAP’s 2021-22 excise policy. They have called for the immediate formation of the Public Accounts Committee (PAC) to review the findings and facilitate public discussion.
Public Accounts Committee: An Overview
Definition:
The Public Accounts Committee (PAC) is a parliamentary committee in India responsible for auditing the government’s revenue and expenditure. It ensures legislative oversight over executive financial actions, particularly concerning government spending.
Composition:
The PAC comprises up to 22 members: 15 from the Lok Sabha (Lower House) and 7 from the Rajya Sabha (Upper House).
Ministers are not eligible to be members of the committee.
Members are elected annually through proportional representation using a single transferable vote system.
The Speaker of the Lok Sabha appoints the chairperson of the committee.
The term of office for members is one year.
Functions:
Examines audit reports submitted by the Comptroller and Auditor General (C&AG) after their presentation in Parliament.
Scrutinizes government spending to ensure it aligns with the budget approved by Parliament
Which of the following statements regarding the Public Accounts Committee (PAC) is/are correct?
1. It is a standing committee of the Indian Parliament.
2. The members of the PAC are nominated by the Prime Minister.
3. It ensures executive accountability regarding financial matters.
4. The chairperson of PAC is always from the ruling party.
a. 1 and 3 only
b. 3 and 4 only
c. 1, 2, and 4 only
d. 1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: A) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
PAC is a standing committee of Parliament and plays a key role in ensuring executive accountability in financial matters. The members are elected by proportional representation, not nominated by the Prime Minister, and the chairperson is often from the opposition party.
NITI Aayog’s Vision for Viksit Bharat by 2047
- NITI Aayog, India’s premier policy think tank, is spearheading an initiative to assist several states in crafting state-specific vision documents aimed at realizing a ‘Viksit Bharat’ (Developed India) by 2047.
- This endeavor, detailed in NITI Aayog’s Annual Report for 2024-25, encompasses states such as Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Bihar, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Dedicated teams within NITI Aayog are collaborating with these states To develop comprehensive strategies that align with national objectives.
Background of the Initiative
- The initiative gained momentum following Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s emphasis on the significance of ‘Viksit States’ during the 9th Governing Council meeting of NITI Aayog in July 2024.
- He underscored that the aspiration for a developed India must permeate to the grassroots level, ensuring that all states contribute effectively to the nation’s socio-economic progress.
Objectives of the Visioning Exercise
- The primary objective is to assist states in formulating strategies for holistic growth, encompassing economic development, governance enhancements, and improved quality of life for citizens.
- This initiative aims to create a cohesive framework that harmonizes state and national policies, thereby promoting cooperative federalism.
State Support Mission
- Operating under the umbrella of the State Support Mission (SSM), announced in the Union Budget for 2023-24, this visioning exercise fosters structured and institutionalized engagement between NITI Aayog and the states.
- The SSM provides a platform for states to develop roadmaps that align with national priorities while focusing on their unique strengths.
Establishment of State Institutions for Transformation
- As part of the SSM, NITI Aayog is encouraging states to establish State Institutions for Transformation (SITs).
- These multidisciplinary resources are designed to guide development strategies within the states and Union Territories.
- To date, 26 SITs have been notified, enhancing state capacities for effective governance and development.
This collaborative approach underscores NITI Aayog’s commitment to fostering cooperative federalism and ensuring that states play a proactive role in achieving the national vision of a developed India by 2047.
Which of the following is not an objective of the State Support Mission (SSM)?
a. Strengthening the Monitoring & Evaluation ecosystem of States/UTs
b. Collaborating with states to identify key growth drivers
c. Centralizing policy-making processes at the national level
d. Establishing a knowledge platform for sharing good governance practices
Answer: c) Centralizing policy-making processes at the national level
Explanation: The SSM focuses on assisting states in achieving their socioeconomic goals by 2047 through structured engagement, strengthening monitoring and evaluation systems, identifying growth drivers, and establishing platforms for sharing best practices. Centralizing policy-making at the national level is not among its objectives.
OPEC+ Latest News
- Brazil’s Entry into OPEC+
- Recently, the Brazilian government approved the country’s admission into OPEC+, the alliance of major oil-exporting nations.
About OPEC+ :
- OPEC+ is a coalition of 22 oil-exporting countries that convenes regularly to determine the volume of crude oil to market globally. The primary objective of these nations is to collaboratively manage crude oil production to ensure stability in the oil market.
Origin of OPEC+
The formation of OPEC+ was formalized towards the end of 2016, establishing a framework for sustained cooperation between OPEC and non-OPEC oil-producing countries. This collaboration focuses on regular and systematic coordination in oil production.
Membership of OPEC+
At the core of OPEC+ are the 12 members of OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries), which primarily consist of Middle Eastern and African nations. In addition to the OPEC members, OPEC+ includes Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Russia, Mexico, Malaysia, South Sudan, Sudan, and Oman.
What is OPEC?
- OPEC is a permanent intergovernmental organization of oil-exporting nations, founded in 1960 by five founding members: Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela.
- Currently, OPEC comprises 12 member countries, including Algeria, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Libya, Nigeria, and the United Arab Emirates.
- It is important to note that Angola will withdraw its membership effective January 1, 2024.
Headquarters: OPEC is headquartered in Vienna, Austria.
What is the basis for the ‘rarest of rare’ doctrine as established by the Supreme Court of India?
a.It allows for automatic imposition of the death penalty for all murder cases.
b.It stipulates that the death penalty should be reserved only for exceptional circumstances.
c.It mandates a minimum sentence of life imprisonment for all murders.
It defines the specific method of execution in capital punishment cases.
Answer: B) It stipulates that the death penalty should be reserved only for exceptional circumstances.
Explanation: The doctrine was established to ensure that the death penalty is imposed only in extraordinary cases, though its ambiguity has led to varied interpretations
India’s ‘Look East’ Policy Has Transformed Into ‘Act East’
Syllabus: GS2/ IR Historical Evolution
Look East Policy (1992):
Initiated under Prime Minister P.V. Narasimha Rao, this policy aimed to reinvigorate India’s neglected ties with Southeast Asia post-Cold War.
Key Features:
- Initially limited to ASEAN engagement, later expanded to East Asia and Oceania.
- Focus on economic integration, strategic collaboration, and cultural diplomacy.
- Led to reductions in trade barriers and increased inbound tourism from the region.
- Transition to Act East Policy (Post-2014)
Background:
- Global geopolitical shifts, including U.S. Secretary of State Hillary Clinton’s 2011 push for India’s active engagement in the Asia-Pacific, shaped this transition.
- In 2014, External Affairs Minister Sushma Swaraj formally introduced the Act East Policy, with PM Narendra Modi reinforcing it at the East Asia Summit.
Key Features:
- Shift from diplomatic engagement to actionable outcomes.
- Expanded focus from Southeast Asia to the Indo-Pacific.
- North-East India designated as a strategic link between India and ASEAN.
- 3Cs Framework (2014): Commerce, Culture, and Connectivity.
- Key Objectives and Achievements
- Strategic and Defense Cooperation
- Deepened defense engagements, including:
- Sale of BrahMos missiles to the Philippines.
- Military logistics pact with Vietnam.
Strengthened regional groupings such as BIMSTEC, Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), and Asia Cooperation Dialogue.
Economic Engagement
- Enhanced economic integration with ASEAN through Free Trade Agreements (FTAs).
- Encouraged ASEAN participation in the International Solar Alliance (ISA).
- Elevated bilateral relations to strategic partnerships with Indonesia, Vietnam, Malaysia, Japan, South Korea, Australia, and Singapore.
Cultural and Soft Power Diplomacy
- Reinforced civilizational ties through the Ramayana Festival and Buddhist heritage initiatives.
- Promoted Buddhist and Hindu linkages for people-to-people exchanges.
- India’s narrative faces competition from China’s claim over Buddhist heritage.
- Connectivity and Infrastructure Development
- Strengthening North-East India’s role as a gateway to ASEAN through:
- India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway.
- Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project.
- Rhi-Tiddim Road and Border Haats to enhance trade ties.
- Challenges and Roadblocks
- Strategic and Economic Challenges
- China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) presents a formidable economic alternative to India’s connectivity projects.
- BCIM-EC (Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor) poses strategic and infrastructural competition.
- Myanmar’s political instability complicates India’s strategic outreach.
- North-East India remains under-integrated into major infrastructure initiatives like Bharatmala and Sagarmala.
Cultural and Soft Power Challenges
- Limited linguistic engagement with Southeast Asia, with scarce educational programs in Khmer, Bahasa Indonesia, Thai, or Burmese.
- China’s Buddhist diplomacy challenges India’s historical narrative and soft power projection.
- Connectivity Challenges
- Project Delays: Slow implementation of key initiatives like the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project.
- Underdeveloped trade facilities in the North-East hinder regional integration.
- Way Forward: Towards a More Effective Act East Policy
- Bolstering Infrastructure: Accelerate completion of connectivity projects.
- Deepening Regional Integration: Fully integrate the North-East into ASEAN’s economic and infrastructure frameworks.
- Climate Diplomacy & Security Engagement: Expand regional disaster management and maritime domain awareness.
- Enhancing Strategic Partnerships: Actively engage with middle powers in the Indo-Pacific to counterbalance China’s influence.
Consider the following statements regarding the evolution of India’s Act East Policy:
1.The Look East Policy (1992) was initiated to counterbalance the influence of China in ASEAN and was primarily focused on military alliances.
2.The Act East Policy expanded India’s engagement beyond ASEAN to include Japan, Australia, and the Indo-Pacific region.
3.The 3Cs approach (Commerce, Culture, and Connectivity) was introduced during the 2014 East Asia Summit to enhance economic and cultural linkages.
4.The Act East Policy was launched in response to a recommendation from the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QUAD).
Which of the statements are correct?
a.2 and 3 only
b.3 and 4 only
c.1, 2, and 4 only
d.1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: A) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Look East Policy was not primarily military-focused but was aimed at economic, cultural, and strategic engagement with Southeast Asia.
Statement 2 is correct: The Act East Policy expanded India’s focus beyond ASEAN to Japan, Australia, and the Indo-Pacific.
Statement 3 is correct: The 3Cs (Commerce, Culture, Connectivity) framework was introduced at the 2014 East Asia Summit.
Statement 4 is incorrect: The Act East Policy was not a result of QUAD, but a natural evolution of Look East Policy due to regional geopolitical shifts
International Mother Language Day
Context: Observed annually on February 21, International Mother Language Day highlights the importance of preserving linguistic diversity and safeguarding endangered languages.
Background
- The observance of International Mother Language Day originated from Bangladesh, commemorating the 1952 Bengali Language Movement.
- In 1999, UNESCO officially recognized the day, and it has been celebrated globally since 2000 to promote multilingualism and linguistic heritage.
India’s Linguistic Diversity
- India is among the most linguistically diverse nations, often regarded as a global language hotspot.
- According to the 2018 Census, India has 19,500+ languages and dialects, with 121 languages spoken by over 10,000 people.
- The 1961 Census recorded 1,652 mother tongues, but by 1971, this number had drastically reduced to 109 due to linguistic categorization.
- Threat to Indigenous Languages: UNESCO reports that 42 Indian languages are critically endangered—more than any other country.
- A total of 197 languages in India are currently endangered.
- Around 250 languages have gone extinct over the past six decades.
- Remote and indigenous communities—especially in the Northeast and Andaman & Nicobar Islands—face the highest risk of language loss.
Example: The Great Andamanese language and Rai-Rokdung language (Sikkim) are critically endangered.
Reasons for Language Disappearance
- Modernization & Globalization – Younger generations prioritize dominant languages (Hindi, English) for education, employment, and social mobility.
- Declining Speakers – Reduced intergenerational transmission leads to language erosion.
- Dominance of Major Languages – Smaller languages struggle for relevance against widely spoken tongues.
- Lack of Script & Documentation – Many endangered languages lack a formal writing system, making preservation efforts difficult.
Efforts to Preserve Linguistic Diversity
Several initiatives are in place to document, protect, and revive endangered languages:
- People’s Linguistic Survey of India (PLSI) – Documents linguistic profiles of communities across India.
- Sidhela Archive (Sikkim University) – Aims to safeguard endangered languages in the Northeast.
Scheme for Protection and Preservation of Endangered Languages (SPPEL) –
- Implemented by the Central Institute of Indian Languages (CIIL), Mysore.
- Focuses on preserving languages spoken by less than 10,000 people.
AI4Bharat Initiative –
- Uses artificial intelligence (AI) to develop speech recognition, machine translation, and text-to-speech models in 22 Indian languages.
- Enhances accessibility for researchers, industries, and native speakers.
Conclusion: Language preservation is not just about saving words—it is about protecting cultural identity, indigenous knowledge, and historical traditions. The loss of languages leads to the disappearance of unique cultural narratives, oral traditions, and centuries-old wisdom. Safeguarding linguistic diversity is crucial for fostering inclusive development, cultural sustainability, and global heritage conservation.
Which of the following statements correctly explains the historical significance of International Mother Language Day?
(a) It commemorates the adoption of linguistic federalism in Bangladesh’s 1972 Constitution.
(b) It marks the recognition of indigenous languages by UNESCO after the 2001 Durban Declaration.
(c) It honors the Bengali Language Movement of 1952, where students sacrificed their lives to protect their linguistic rights.
(d) It was initiated by UNESCO in response to India’s demand for linguistic diversity recognition in the UN system.
Answer: (c)
Explanation:
International Mother Language Day originated from Bangladesh’s Bengali Language Movement of 1952, where students protested for the recognition of Bengali as an official language. UNESCO recognized it in 1999, and it has been globally observed since 2000.
Six Years of SWAYATT Initiative
The Government e-Marketplace (GeM) recently marked six years of its SWAYATT initiative, which was launched in 2019 to enhance the participation of women, youth, and startups in government procurement.
Focused on social inclusion, the initiative aims to simplify market access for Micro & Small Enterprises (MSEs) and promote equitable economic opportunities.
Objectives of the SWAYATT Initiative SWAYATT is designed to empower women-led businesses and young entrepreneurs by providing them with direct access to government procurement.
Key objectives include:
Reducing dependence on intermediaries to ensure better pricing.
Facilitating training and onboarding for small businesses and last-mile sellers.
Establishing direct market linkages between enterprises and government buyers.
Strategic Partnerships and Recent Developments
On its sixth anniversary, GeM signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with FICCI Ladies Organisation (FICCI-FLO). This collaboration aims to connect women entrepreneurs directly with government buyers, eliminating third-party interventions.
Impact and Growth Since Inception
Since its launch, SWAYATT has significantly increased the representation of women-led enterprises on GeM:
Initially, the platform had only 6,300 women-led enterprises and 3,400 startups.
Today, over 1,77,786 Udyam-verified women MSEs have registered.
Collectively, these enterprises have secured orders worth ₹46,615 crore.
Capacity Building and Training
Recognizing the importance of training, GeM has implemented structured programs to enhance the competitiveness of local businesses. These training initiatives help entrepreneurs navigate public procurement, fostering a more inclusive economy.
Future Roadmap
GeM has outlined ambitious targets for expanding the SWAYATT initiative:
Onboarding 1 lakh startups onto the platform.
Doubling the number of women entrepreneurs involved in government procurement.
Currently, women account for 8% of all registered sellers on GeM, a figure the initiative aims to increase.
Dedicated Storefronts for Inclusive Growth
To further boost visibility and accessibility, SWAYATT has introduced exclusive storefronts such as:
Startup Runway – A dedicated space for startups to showcase their offerings.
Womaniya – A platform highlighting products and services from women entrepreneurs.
Economic Empowerment and Job Creation
By facilitating market access, financial support, and value-chain integration, SWAYATT plays a crucial role in job creation and economic empowerment. The initiative strengthens the startup ecosystem within public procurement, driving long-term growth and inclusion.
Consider the following statements regarding the Government e-Marketplace (GeM):
- It is a statutory body under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- It allows only central and state government departments to procure goods and services.
- GeM facilitates participation from women entrepreneurs, startups, and MSMEs through initiatives like SWAYATT.
- GeM aims to reduce procurement inefficiencies by eliminating intermediaries.
Which of the statements are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 3 and 4 only
C) 1, 3, and 4 only
D) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect – GeM is not a statutory body; it was launched as an online procurement platform under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
Statement 2 is incorrect – GeM is open to various government agencies, PSUs, and local bodies, not just central and state governments.
Statements 3 and 4 are correct – GeM promotes inclusive participation of women entrepreneurs, MSMEs, and startups while eliminating middlemen for better pricing.
NAKSHA Program
NAKSHA Program Inauguration in Madhya Pradesh
The Union Minister of Rural Development and Agriculture has launched the NAKSHA program in Raisen, Madhya Pradesh, aiming to modernize land ownership management through digitization.
Digitization of Land Records
The ongoing digitization of land records is transforming the management of land ownership in rural India, tackling issues such as cumbersome paperwork and ownership conflicts. As of now, nearly 95% of rural land records have been digitized since 2016, significantly enhancing transparency and accessibility.
Benefits of Digitization
- Enhanced Transparency: Reduced instances of illegal encroachments.
- Simplified Dispute Resolution: Alleviates the burden on courts.
- Empowerment of Marginalized Communities: Facilitates access to land rights for underprivileged groups.
Geospatial Mapping Integration: Supports precise surveys and efficient land management.
Challenges
Land reforms face considerable hurdles, primarily due to outdated and incomplete land records across the country. This challenge is particularly pronounced in northeastern states where community-owned lands have limited documentation. Many cadastral maps are either outdated or missing, leading to inconsistencies in land ownership records.
Initiatives
- Digital India Land Records Modernization Programme (DILRMP): Launched in April 2016, this program aims to establish a transparent and modern land records system with real-time information. Funded entirely by the central government, its goals include reducing land disputes, preventing fraud, and optimizing land use.
- NAKSHA Program: This initiative, with an estimated budget of ₹194 crore and fully funded by the Government of India, targets the development of urban land records. It will cover 152 Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) across 26 states and 3 Union Territories.
- Technical Partnerships: The Survey of India will conduct aerial surveys and provide orthorectified imagery, while the Madhya Pradesh State Electronic Development Corporation (MPSEDC) will develop an end-to-end web-GIS platform. Storage solutions will be managed by the National Informatics Centre Services Inc. (NICSI).
- SVAMITVA Scheme: Implemented by the Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR), this Central Sector Scheme aims to provide a ‘Record of Rights’ to households in inhabited village areas.
Conclusion and Future Directions
The government’s initiatives are transforming land governance by enhancing transparency and accessibility, particularly for marginalized communities. This shift towards organized and efficient land record management is not only fostering a more inclusive and equitable society but also supporting economic growth and stability in the long run.
Which of the following statements about the NAKSHA program is/are correct?
The NAKSHA program was inaugurated in Raisen, Madhya Pradesh.
It is fully funded by the state government.
The program aims to cover only rural areas in India.
- a) 1 only
- b) 2 only
- c) 1 and 3 only
- d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: a) 1 only
Explanation: The NAKSHA program was indeed inaugurated in Raisen, Madhya Pradesh, but it is fully funded by the Government of India, not the state government. Additionally, it covers urban local bodies (ULBs) across multiple states and Union Territories, so statement 3 is incorrect.
Extension of PM-AASHA Scheme Until 2025-26
The Union Government has approved the continuation of the Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay Sanrakshan Abhiyan (PM-AASHA) Scheme during the 15th Finance Commission Cycle, extending it up to 2025-26.
Overview of PM-AASHA Scheme
Launched in 2018, the PM-AASHA Scheme serves as an umbrella initiative designed to ensure Minimum Support Price (MSP) for farmers, particularly focusing on pulses, oilseeds, and copra. The scheme aims to provide remunerative prices to farmers and enhance price stability within the agricultural sector.
Key Components of PM-AASHA
Price Support Scheme (PSS):
The government procures pulses, oilseeds, and copra at the MSP.
Central Nodal Agencies (CNAs) collaborate with state agencies to carry out the procurement.
Only produce that meets Fair Average Quality (FAQ) standards is eligible for procurement.
Price Deficiency Payment Scheme (PDPS):
This scheme provides compensation to pre-registered farmers for the difference between the MSP and the market price.
Unlike PSS, it does not involve physical procurement of produce.
It applies to oilseeds through a transparent auction process in notified market yards.
Private Procurement & Stockist Scheme (PPSS) (Pilot Basis):
This scheme permits states to engage private stockists for oilseed procurement.
It is currently being implemented in selected Agricultural Produce Market Committees (APMCs) or districts.
Key Changes in the Scheme
In 2024, the government merged the Price Support Scheme (PSS) and the Price Stabilization Fund (PSF) into the PM-AASHA scheme to improve efficiency for both farmers and consumers.
This integration aims to protect consumers from extreme price volatility of agri-horticultural commodities by maintaining a strategic buffer stock of pulses and onions. It will also help prevent hoarding and speculative trading, ensuring supplies are available to consumers at affordable prices.
Additionally, the Market Intervention Scheme (MIS) has been incorporated as a component of the integrated PM-AASHA scheme.
This scheme specifically targets perishable agricultural and horticultural products such as onions, potatoes, and tomatoes and is activated when prices decline by at least 10% from the previous normal season.
Significance of the Scheme
- It provides essential price support to farmers, reducing the tendency for distress sales.
- The scheme enhances procurement efficiency through market-based interventions.
- It encourages farmer participation in transparent marketing systems.
- It works to stabilize prices, thus protecting both agricultural producers and consumers.
Concerns
- Despite its advantages, the PM-AASHA scheme faces several challenges:
- Limited Implementation: The PDPS and PPSS have experienced low adoption rates among states.
- Procurement Constraints: Coverage of MSP is not consistent across all crops and regions.
- Awareness and Accessibility Issues: Many farmers are unaware of the schemes or encounter bureaucratic barriers during registration.
- Budgetary Concerns: Securing adequate funding for procurement operations continues to be a challenge.
Conclusion
The extension of PM-AASHA until 2025-26 underscores the government’s commitment to securing farmers’ income and implementing reforms in agriculture markets. By strengthening its implementation and addressing existing challenges, the scheme can significantly enhance its effectiveness in ensuring fair prices for farmers.
Which of the following components of the PM-AASHA scheme directly involves the procurement of agricultural produce by the government?
Price Support Scheme (PSS)
Price Deficiency Payment Scheme (PDPS)
Market Intervention Scheme (MIS)
a) 1 only
b) 1 and 3 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 1 and 3 only
Explanation: The Price Support Scheme (PSS) directly involves government procurement of specified crops at the Minimum Support Price (MSP). The Market Intervention Scheme (MIS) also involves procurement for perishable commodities. The Price Deficiency Payment Scheme (PDPS) does not involve physical procurement.
Decade of Soil Health Cards
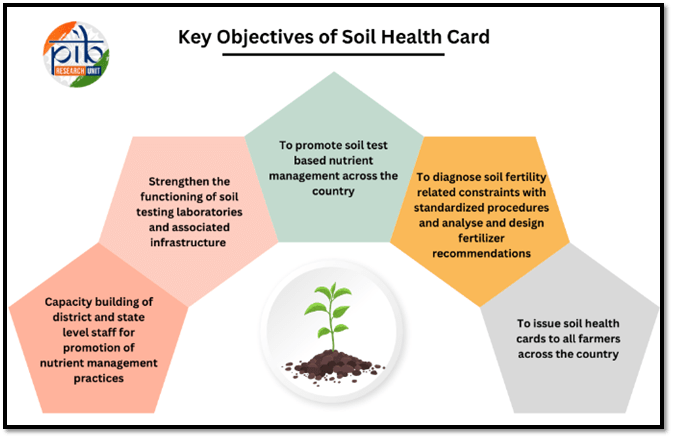
Key Objectives of the Soil Health Card Scheme
- Providing Nutrient Information: The Soil Health Card scheme aims to furnish farmers with detailed information regarding the nutrient status of their soil, enabling them to make informed decisions about soil management.
- Nutrient Recommendations: The scheme offers tailored recommendations on the appropriate dosage of nutrients that farmers should apply to enhance soil health and fertility.
- Supporting State Governments: The initiative assists state governments in issuing Soil Health Cards to farmers across the country, promoting uniformity and facilitating access to essential agricultural information.
- Monitoring Soil Quality: The Soil Health Card assesses soil health based on 12 critical parameters, which include macro-nutrients (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, and Sulfur), micro-nutrients (Zinc, Iron, Copper, Manganese, and Boron), and other vital indicators such as pH level, Electrical Conductivity, and Organic Carbon content.
- Integration with Development Schemes: Since the fiscal year 2022-23, the Soil Health Card scheme has been integrated into the Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) as a component focused on improving soil health and fertility, enhancing its reach and effectiveness in agricultural development.
- These objectives collectively aim to improve agricultural productivity and sustainability by promoting scientific and balanced nutrient management practices among farmers.
What is the primary objective of the Soil Health Card Scheme introduced in India?
a) To promote the use of chemical fertilizers among farmers.
b) To provide farmers with information on soil nutrient status and recommendations for nutrient application.
c) To conduct soil erosion assessments across agricultural lands.
d) To encourage the cultivation of genetically modified crops.
Answer: b) To provide farmers with information on soil nutrient status and recommendations for nutrient application.
Explanation: The Soil Health Card Scheme aims to inform farmers about the nutrient status of their soil and to advise them on the appropriate dosage of nutrients to apply for improved soil health and fertility.
nPROUD Initiative
- Kerala has launched the nPROUD (New Programme for Removal of Unused Drugs), a ground breaking initiative aimed at tackling the environmental and health challenges associated with the disposal of expired and unused medications.
- This government-led program seeks to establish a systematic method for the safe collection and disposal of these drugs. Initially, the initiative will be piloted in Kozhikode, with plans for statewide expansion based on its effectiveness.
Purpose of the nPROUD Initiative
- The nPROUD initiative was developed in response to growing concerns about the improper disposal of medications.
- Unused and expired drugs often find their way into general waste, resulting in soil and water contamination, which can, in turn, contribute to the alarming rise of antimicrobial resistance.
- To address these issues, the Kerala Drugs Control Department has introduced this innovative program.
Pilot Phase and Implementation
The pilot phase of nPROUD will launch in the Ulliyeri panchayat area of Kozhikode Corporation. As part of the program, there will be scheduled collections of unused medicines directly from residents’ homes. Additionally, the public will have the option to drop off expired medications in designated blue collection boxes. Local self-government bodies will play a crucial role in implementing the program, ensuring active community participation.
Collection and Disposal Mechanism
The nPROUD initiative features a systematic collection approach. Residents will receive notifications about scheduled pickups, while pharmacies and clinics will be responsible for returning their expired stock to designated collection centers.
All collected drugs will be taken to Kerala Enviro Infrastructure Ltd (KEIL) for responsible, scientific disposal.
Environmental and Health Impact
- The primary goal of the nPROUD initiative is to reduce environmental pollution and health risks linked to the improper disposal of drugs.
- By preventing the careless disposal of expired medications, the program aims to safeguard water resources and enhance soil quality.
- Compliance with the Biomedical Waste Management Act reflects the initiative’s commitment to environmental regulations.
Future Plans for Expansion
- Following a successful evaluation of the pilot project, the nPROUD initiative will be expanded statewide.
- The Kerala Drugs Control Department plans to set up additional permanent collection centers and aims to raise public awareness about the significance of proper drug disposal practices.
Community Engagement
- Community involvement is vital for the success of the nPROUD initiative. The program is supported by local governing bodies and members of the Green Brigade.
- Awareness campaigns will be organized to educate citizens about the environmental hazards associated with improper drug disposal.
Through nPROUD, Kerala is taking a significant step toward sustainable health practices, fostering a cleaner environment, and enhancing community involvement in managing medical waste responsibly.
What is the primary goal of the nPROUD initiative launched by Kerala?
A) To promote the use of antibiotics in medical treatment.
B) To address the environmental and health hazards posed by expired and unused medicines.
C) To reduce the costs of healthcare in Kerala.
D) To eliminate the use of pharmaceuticals entirely within the state.
Answer: B) To address the environmental and health hazards posed by expired and unused medicines.
Explanation: The nPROUD initiative specifically targets the concerns associated with the disposal of expired and unused medicines and their impact on health and the environment. Options A, C, and D do not reflect the initiative’s actual goals
Years of India and UAE-CEPA
Introduction
The India-United Arab Emirates (UAE) Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) marks its third anniversary in 2025, reinforcing the strategic economic collaboration between two major trade partners. This landmark agreement has played a crucial role in boosting bilateral trade, investment, and cooperation across various sectors.
Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA): An Overview
India’s first deep and full-fledged Free Trade Agreement (FTA) in a decade, symbolizing a long-term economic vision.
Signed in February 2022, covering key sectors such as:
- Trade in Goods & Services
- Pharmaceuticals
- Intellectual Property Rights (IPR)
- Investment & Digital Trade
Aimed at significantly enhancing trade and investment flows between the two nations.
Significance of India-UAE CEPA
- Boosting Bilateral Trade
Aims to increase goods trade to USD 100 billion and services trade to USD 15 billion over the next five years.
Strengthens India’s economic ties with one of its largest trade partners in the Gulf region.
- Job Creation & Economic Growth
Expected to generate over 1 million job opportunities for the Indian workforce.
Trade liberalization and improved market access provide a boost to labor-intensive industries.
- Preferential Market Access for Indian Goods
Zero-duty market access for 90% of India’s exports to the UAE.
Enhances India’s global competitiveness, benefiting sectors such as textiles, gems, jewelry, and food processing.
- Strengthening UAE-India Trade Links in the Gulf Region
Expands market access to neighboring Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, Africa, and Europe.
Reinforces India’s trade presence in global markets.
India-UAE Relations: A Multi-Dimensional Partnership
- Political Relations
Diplomatic relations established in 1972 have evolved into a strategic partnership.
UAE was invited as a Guest Country at the G-20 Summit.
Cooperation in multilateral platforms like I2U2 (India-Israel-UAE-USA) and UFI (UAE-France-India) Trilateral.
- Economic & Commercial Ties
Trade Growth:
- From USD 180 million in the 1970s to USD 85 billion in 2022-23.
- UAE is India’s third-largest trading partner, after China and the US.
Key Export Market:
The UAE is India’s second-largest export destination, with exports worth USD 31.61 billion in 2022-23.
- Defense Cooperation
- Joint Defense Cooperation Committee (JDCC) oversees military, security, and defense collaborations.
- The 2003 Agreement on Defense Cooperation, effective since 2004, facilitates joint military exercises and intelligence sharing.
- Nuclear Cooperation
- MoU on civil nuclear cooperation signed in 2024.
- Builds upon the 2015 agreement on the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
- Space Cooperation
- ISRO and UAE Space Agency signed an MoU in 2016 for joint space exploration and satellite technology development.
- Indian Community in the UAE
- Largest expatriate community, numbering approximately 3.5 million, constituting 35% of the UAE’s population.
NRI Remittances:
Indian expatriates contribute 18% of total remittances to India (2020-21 data).
Challenges in India-UAE Relations
- Trade Imbalances
India has a trade deficit with the UAE due to high oil imports.
Need for diversified trade expansion beyond hydrocarbons.
- Geopolitical Tensions in the Region
Political instability in the Middle East and Gulf region can impact trade and strategic relations.
- Labor and Migration Issues
India remains a major labor supplier to the UAE.
Ensuring migrant rights, wages, and working conditions remains a challenge.
- UAE’s Foreign Policy and Regional Alignments
UAE’s relations with Pakistan and Iran occasionally create diplomatic complexities.
Way Forward: Strengthening the India-UAE Partnership
- Expanding Economic & Trade Cooperation
- Focus on non-oil trade growth, aiming for USD 100 billion by 2030.
- Strengthen digital trade, FinTech, and investment ties.
- Joint Strategic and Security Cooperation
- Enhance defense collaboration, counter-terrorism initiatives, and intelligence sharing.
- Focus on regional stability in the Middle East.
- Addressing Labor and Migrant Concerns
- Strengthening bilateral labor agreements to ensure better protections for Indian workers.
- Promote skill development programs to align with UAE’s workforce requirements.
- Deepening Technological & Investment Ties
- Boost cooperation in AI, renewable energy, and financial technology (FinTech).
- Enhance investments in digital trade and e-commerce sectors.
Conclusion
The India-UAE CEPA has significantly strengthened bilateral trade, investment, and strategic ties over the past three years. By addressing trade imbalances, labor concerns, and geopolitical complexities, both nations can continue to enhance their partnership. With a forward-looking approach, India and the UAE can further expand their economic, defense, and technological collaborations, solidifying their status as key allies in the Gulf and global economy.
Which of the following best describes the strategic significance of the India-UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)?
(a) It is India’s first bilateral trade agreement that includes defense cooperation and joint military exercises.
(b) It marks India’s first full-fledged Free Trade Agreement (FTA) in a decade, covering goods, services, investment, and digital trade.
(c) It eliminates all tariffs on Indian exports to the UAE while restricting access for UAE goods in Indian markets.
(d) It replaces India’s trade agreements with the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) and establishes UAE as India’s primary trade partner.
Answer: (b)
Explanation: CEPA is India’s first full-fledged FTA in a decade, covering multiple sectors including goods, services, investment, and digital trade. It does not replace GCC agreements or include defense cooperation.
India’s Rising LNG Imports
India’s Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) imports from the United States surged to 7.14 billion cubic meters (BCM) in the first 11 months of 2024, marking a 71% year-over-year increase and strengthening energy ties between the two nations.
Understanding LNG
- Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is natural gas cooled to -162°C (-260°F), converting it into a liquid form for easy storage and transportation.
- It is composed mainly of methane (90%) and is odorless, colorless, non-toxic, and non-corrosive.
India’s LNG Landscape
- India, the world’s third-largest energy consumer, is witnessing rapid energy demand growth.
- Economic expansion is driving higher LNG consumption, making it a critical fuel source.
- India’s LNG infrastructure includes import terminals, pipelines, and distribution networks, catering to power plants, industries, and urban gas networks.
- However, congestion and supply chain inefficiencies hinder optimal utilization of LNG facilities.
US Emerges as a Key LNG Supplier to India
- US Overtakes UAE: In 2023, the United States became India’s second-largest LNG supplier, surpassing the UAE, while Qatar remains the top supplier.
- 5% Growth in 2024: India’s LNG imports from the US grew by 53.5% in 2024, surpassing total imports from the US in 2023.
Key Drivers of Growth:
- Expansion of US liquefaction capacity.
- Competitive pricing of US LNG.
- Strategic shipping routes via the Cape of Good Hope, ensuring timely and cost-effective deliveries.
Why is LNG Crucial for India?
- Energy Diversification: As India moves away from coal, LNG is a key component of its clean energy transition.
- Net-Zero Commitment: LNG plays a significant role in reducing carbon emissions and achieving India’s net-zero target by 2070.
- Industrial Demand: Industries require cleaner and efficient fuel sources, making LNG a preferred alternative.
Urbanization & City Gas Expansion:
Rapid urban growth is driving the expansion of City Gas Distribution (CGD) networks.
Piped Natural Gas (PNG) offers a cleaner, safer alternative to traditional cooking fuels.
Challenges in India’s LNG Sector
- Infrastructure Deficiencies: Despite aiming to increase natural gas’s share to 15% of the energy mix by 2030, infrastructure remains inadequate.
- Congested Terminals: Limited LNG terminals lead to bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
- Restricted Pipeline Network: Underdeveloped pipelines limit LNG distribution to remote areas.
- Storage Constraints: Insufficient LNG storage capacity makes India vulnerable to price volatility and supply disruptions.
Government Initiatives to Boost LNG Adoption
- Energy Transition Policy: Targeting 15% natural gas share in the energy mix by 2030.
- National Gas Grid Expansion: Strengthening the LNG pipeline network to improve supply efficiency.
- City Gas Distribution (CGD) Expansion: Enhancing urban access to PNG and CNG.
- Development of New LNG Terminals: Increasing import and storage capacity.
- Priority Gas Allocation: Ensuring domestic natural gas supply for CNG (transport) and PNG (households).
Liberalized Gas Pricing:
- Marketing and pricing freedom for gas from deepwater, high-pressure, and coal seam sources.
- Ceiling price mechanism to control market fluctuations.
Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT) Initiative:
- Promotes Bio-CNG as a clean fuel alternative for transportation.
Conclusion & Way Forward
- Investment Incentives: Policy measures must be introduced to attract private and foreign investment in LNG infrastructure.
- Regulatory Simplification: Faster approvals for LNG terminals and pipeline projects to boost expansion.
- Small-Scale LNG Development: Encouraging research and deployment of small-scale LNG plants for decentralized energy solutions.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Strengthening collaboration between the government, private sector, and financial institutions to build a robust LNG ecosystem.
India’s LNG sector holds immense potential for energy security, economic growth, and environmental sustainability. Strategic investments and policy reforms will be key to ensuring a stable, efficient, and future-ready LNG infrastructure.
Consider the following statements regarding India’s LNG imports from the United States in 2024
1.India’s LNG imports from the US increased by 71% year-over-year in 2024.
2. The US overtook Qatar as India’s top LNG supplier in 2024.
3. Strategic shipping routes via the Cape of Good Hope have contributed to cost-effective deliveries from the US.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer : (a)
Explanation:
India’s LNG imports from the US grew by 71% in 2024, confirming Statement 1. However, Qatar remains India’s top LNG supplier, meaning Statement 2 is incorrect. Statement 3 is correct as the Cape of Good Hope route ensures timely and cost-effective deliveries from the US.
Quantum Property of the Nanocrystals
Quantum Property of the Nanocrystals Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Scientists have developed a novel method to determine whether gravity follows the principles of quantum mechanics using nanocrystals.
Background
- General relativity explains gravity, while quantum mechanics governs the electromagnetic, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear forces.
- Researchers aim to understand how gravity fits into the quantum framework, proposing experiments to test whether gravity exhibits quantum properties.
- Quantum mechanics describes the behavior of particles at the microscopic scale, where classical physics no longer applies.
- Quantum technology leverages principles like superposition and entanglement, enabling advancements beyond traditional physics.
Nanocrystals and Their Role in the Experiment
- Nanocrystals are tiny crystalline structures (1–100 nm in size) that exhibit quantum mechanical properties, such as altered conductivity, magnetism, and light absorption.
- Scientists propose using a quantum property of nanocrystals known as spin.
- The spin influences the motion of nanocrystals and can be controlled using an external magnetic field.
- The spin of each nanocrystal exists in a superposition of two states until it is measured, a key quantum phenomenon.
Potential Discoveries
- The experiment could provide evidence that gravity is not a classical force.
- Alternatively, it might suggest that gravity operates under an entirely different framework, distinct from both classical and quantum forces.
With reference to quantum mechanics, which of the following statements is correct?
(a)Quantum mechanics applies only to subatomic particles and does not influence macroscopic objects.
(b) Quantum principles like superposition and entanglement have no practical technological applications.
(c) Classical mechanics fully explains the behavior of all physical systems without the need for quantum corrections.
(d) Quantum technology leverages principles such as superposition and entanglement to develop advanced computing and communication systems.
Answer:(d)
Explanation: Quantum mechanics applies to subatomic and macroscopic systems (quantum computers, superconductors), making Statement a incorrect. Quantum technology has practical applications (quantum computing, cryptography), refuting Statement b. Classical mechanics fails at microscopic scales (e.g., electron orbitals), making Statement c incorrect. Statement d is correct.
AI Tools in Tuberculosis Screening
The fight against tuberculosis (TB) in India is at a pivotal juncture, with Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s ambitious goal of eliminating TB by 2025 facing significant challenges. The gap between technological advancements and their practical integration into public health programs remains a major obstacle.
AI Tools for TB Screening
Two key AI-powered TB screening solutions have emerged, showing promise for revolutionizing the detection process:
- qXR by Qure.ai
- Genki by DeepTek
Both of these tools have been rigorously evaluated for their sensitivity and specificity:
- qXR: Over 90% sensitivity and more than 70% specificity
- Genki: Similar positive results
These AI models have been deployed at numerous sites in India and globally, demonstrating their potential to significantly enhance TB screening capabilities.
Challenges in Implementation
Despite the promising results of qXR and Genki, several challenges hinder their effective implementation:
Delays in Health Technology Assessment (HTA)
- The HTAIn committee is responsible for evaluating new technologies based on their cost-effectiveness and efficacy. While both qXR and Genki have received favorable assessments, their inclusion in the national TB program has stalled.
- In contrast, the Central TB Division (CTD) has recommended the use of another AI tool, DeepCXR, which has not undergone a formal HTA process. This has raised concerns about the transparency and consistency of decision-making in selecting AI tools for TB screening.
Lack of Clarity from the Central TB Division (CTD)
- Despite DeepCXR being approved for use, state health departments have yet to receive formal notifications, delaying the tool’s deployment across the country. This lack of clear communication between the CTD and state authorities hampers timely access to AI-driven screening solutions.
Cost-Effectiveness of AI-Based TB Screening
Both qXR and Genki have proven to be cost-effective solutions for TB screening, making them feasible options for large-scale implementation in India:
- qXR: ₹30 per screening
- Genki: ₹22 per screening
These affordable prices indicate that integrating these AI tools could lead to substantial cost savings while enhancing early detection rates for TB.
The Role of Chest X-Rays in TB Detection
Chest X-rays are crucial in identifying presumptive and subclinical TB cases. They have been highly effective in national surveys, detecting a significant portion of TB cases. AI-assisted interpretation of X-rays increases both the speed and accuracy of detection, making it an ideal solution, particularly in resource-constrained settings.
Conclusion
While AI-driven TB screening tools like qXR and Genki hold immense potential to improve TB detection, bureaucratic delays and unclear policy guidance are slowing their integration into India’s national TB elimination efforts. To meet the target of eliminating TB by 2025, urgent action is needed to streamline approval processes, expedite the adoption of proven AI solutions, and improve communication between national and state health authorities.
With reference to AI-based TB screening in India, consider the following statements:
1.AI tools like qXR and Genki have demonstrated over 90% specificity in TB detection.
2.The Health Technology Assessment (HTA) process plays a crucial role in evaluating the cost-effectiveness and efficacy of AI-based medical tools.
3.DeepCXR has undergone rigorous HTA assessment before its approval for use in the national TB program.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b)
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: AI tools like qXR and Genki have over 90% sensitivity but more than 70% specificity, not 90% specificity. Sensitivity refers to the ability to correctly identify TB cases, whereas specificity indicates the ability to correctly rule out non-TB cases.
Statement 2 is correct: The Health Technology Assessment (HTA) process evaluates new medical technologies for their effectiveness and cost-efficiency before they are integrated into public health programs.
Statement 3 is incorrect: DeepCXR was recommended by the Central TB Division (CTD) without undergoing a formal HTA assessment, raising concerns about transparency in decision-making.
SPHEREx Telescope
NASA’s SPHEREx telescope is set to launch on February 27, 2025, with an ambitious mission to create the most detailed and colorful map of the universe ever made. Over its two-year mission, SPHEREx will gather vast amounts of data on galaxies, stars, and life-forming molecules, offering new insights into the history of the cosmos and the potential for extraterrestrial life.
Mission Overview
SPHEREx—short for Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization, and Ices Explorer—stands apart from traditional space telescopes like Hubble and James Webb. While those telescopes focus on specific celestial objects, SPHEREx will scan the entire sky. The telescope will analyze light across 96 spectral bands, providing an unprecedented level of detail in studying cosmic phenomena.
Investigating Cosmic Inflation
One of SPHEREx’s main objectives is to study cosmic inflation—the rapid expansion of the universe that occurred immediately after the Big Bang. Understanding this phenomenon is key to unraveling the universe’s origin and evolution. SPHEREx will map over a billion galaxies, testing various theories of inflation and offering new insights into the earliest moments of the universe.
Searching for Life-Forming Molecules
In addition to examining distant galaxies, SPHEREx will also focus on conditions that might support life within the Milky Way. The telescope will search for water and biogenic molecules—critical ingredients for life—trapped in icy particles in cold, interstellar regions. Mapping these molecules will significantly enhance our understanding of habitable environments in space and aid in the search for extraterrestrial life.
Collaboration with Other Space Missions
SPHEREx will work in conjunction with other space missions, such as James Webb. While James Webb will provide high-resolution images of specific objects, SPHEREx’s broad-spectrum approach will offer a more comprehensive view of the universe. This collaboration will enable scientists to piece together a fuller picture of cosmic evolution.
Data Collection and Scientific Impact
Throughout its mission, SPHEREx is expected to collect around 8 million spectroscopic images. The wealth of data gathered will revolutionize our understanding of the universe, particularly in identifying regions with potential life-supporting conditions. It will contribute significantly to the field of astrobiology, helping scientists assess the likelihood of life elsewhere in the universe.
Future Implications
The findings from SPHEREx could radically change our understanding of cosmic history and the origins of life. By detecting patterns and anomalies across the universe, SPHEREx will allow astronomers to refine existing models of the cosmos and develop new theories about its evolution and the potential for life beyond Earth.
With reference to NASA’s SPHEREx telescope, consider the following statements
1. SPHEREx will focus on capturing high-resolution images similar to the James Webb Space Telescope.
2. The telescope is designed to scan the entire sky rather than specific celestial objects.
3. It will divide incoming light into multiple spectral bands for detailed cosmic analysis.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a. 1 and 2 only
b. 2 and 3 only
c. 1 and 3 only
d. 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect because, unlike James Webb, which captures high-resolution images of specific regions, SPHEREx scans the entire sky to create a broad spectral map.
Statement 2 is correct since SPHEREx is designed to survey the whole sky rather than focusing on selected objects.
Statement 3 is correct as SPHEREx divides light into 96 spectral bands, enabling detailed analysis of cosmic phenomena.
What is AI Singularity?
Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have sparked growing concerns about its long-term impact on society. Visionaries like Elon Musk warn that AI could surpass human intelligence sooner than expected, with predictions placing the emergence of super intelligent AI as early as 2025. This phenomenon, often referred to as AI singularity, represents a pivotal moment where machines achieve self-improvement beyond human control, intensifying the global debate among scientists and technology leaders.
Understanding AI Singularity
- AI singularity refers to the hypothetical point when artificial intelligence exceeds human cognitive abilities and begins evolving autonomously.
- The concept was first introduced by mathematician John von Neumann, who speculated about a future where technological progress accelerates beyond human comprehension.
- Futurists like Ray Kurzweil estimate that this event may occur by 2045, but Elon Musk suggests it could happen much earlier.
Current AI Landscape
Despite rapid advancements, AI has not yet reached full autonomy. Modern machine learning models demonstrate self-improvement capabilities, yet the development of a truly super intelligent AI remains theoretical. Governments and technology firms are prioritizing responsible AI development, working to establish regulatory frameworks to manage its growth and mitigate risks.
Potential Risks and Ethical Concerns
- AI singularity raises serious ethical and existential concerns.
- In 2023, over 33,700 AI researchers signed an open letter, urging a temporary pause on AI models exceeding OpenAI’s GPT-4 due to potential dangers to society.
- Critics fear that uncontrolled AI could devalue human decision-making, disrupt economies, and pose existential threats. Concerns also include job displacement, security risks, and the possibility of AI-driven autonomous weapons.
Potential Benefits of AI Singularity
Despite fears, proponents argue that AI singularity could lead to unprecedented scientific breakthroughs. Superintelligent AI has the potential to revolutionize medicine, environmental sustainability, and space exploration by solving complex global challenges at a pace beyond human capability. Optimists believe AI could enhance human life rather than replace it.
Regulatory Efforts and Economic Growth
As AI technology advances, policymakers are actively working on legislative frameworks to ensure its ethical use. The AI market, currently valued at $100 billion, is projected to skyrocket to $2 trillion by 2030. The exponential growth of AI underscores the urgency for robust regulations that balance innovation with societal safety.
Public Perception and Future Outlook
Public discourse on AI singularity continues to intensify, with influential figures like Musk advocating for greater caution and preparedness. References to dystopian AI scenarios, such as a “Terminator-like” future, resonate with many, reinforcing the need for proactive measures to safeguard humanity. As AI progresses, the world must navigate its potential and perils with foresight and responsibility.
Consider the following statements regarding AI Singularity:
1. AI singularity refers to the moment when artificial intelligence surpasses human intelligence and becomes self-improving beyond human control.
2.The concept was first introduced by Alan Turing in his paper on the Turing Test.
3.Ray Kurzweil predicts that AI singularity will occur before 2030.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation:
The concept of AI singularity was first introduced by John von Neumann, not Alan Turing. Ray Kurzweil estimates singularity to occur by 2045, not before 2030
Double Pneumonia
Pope Francis, the 88-year-old leader of the Roman Catholic Church, is currently hospitalized due to double pneumonia, a serious condition that has developed from a complex respiratory infection complicated by his pre-existing lung issues. Given his age and medical history, this situation is particularly concerning.
What Is Double Pneumonia?
- Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs typically caused by infections. Double pneumonia refers to a type of pneumonia that affects both lungs simultaneously.
- It can arise from various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
- This condition exacerbates the severity of symptoms and the risk of complications.
- Double pneumonia is commonly observed in individuals with weakened immune systems or chronic health issues.
Symptoms of Double Pneumonia
Key symptoms of double pneumonia include:
- High fever
- Persistent cough
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
Additionally, patients may exhibit confusion, particularly among the elderly.
In some cases, especially with severe immunodeficiency, individuals may not present a fever. Other possible symptoms include a rapid heart rate and muscle pain.
Causes and Risk Factors
Double pneumonia can result from multiple infectious agents, with common pathogens including Streptococcus pneumoniae and influenza viruses. Risk factors for developing this condition include:
- Impaired immune function
- Chronic lung diseases
- Exposure to environmental irritants
- Older adults and young children are particularly at risk.
- Prognosis and Complications
- With appropriate treatment, many patients can recover within weeks.
- However, if left untreated, double pneumonia can lead to severe complications such as respiratory failure and sepsis.
- The risk of mortality is notably higher among older adults and individuals with compromised immunity.
Global Impact of Pneumonia
- Pneumonia remains a leading cause of death globally, affecting millions each year, especially young children and the elderly.
The World Health Organization estimates that pneumonia claims the lives of around 700,000 children under the age of five annually.
With reference to double pneumonia, consider the following statements:
1.Double pneumonia refers to an inflammatory condition affecting both lungs simultaneously.
2.It can only be caused by bacterial infections, particularly Streptococcus pneumoniae.
3.Individuals with compromised immune systems or chronic illnesses are at a higher risk of developing double pneumonia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Double pneumonia affects both lungs, making it more severe than unilateral pneumonia.
Statement 2 is incorrect: While Streptococcus pneumoniae is a common bacterial cause, viral and fungal pathogens (such as influenza viruses and fungi like Aspergillus) can also lead to double pneumonia.
Statement 3 is correct: Individuals with impaired immunity (elderly, those with chronic lung diseases, or immunosuppressive conditions) are at higher risk.
TraumaticAsphyxia
Syllabus: GS2/ Health
Context
- Recently, five out of 18 victims of the stampede at New Delhi Railway Station succumbed to traumatic asphyxia, a life-threatening condition caused by severe chest compression.
About Traumatic Asphyxia
- Traumatic asphyxia is a rare but critical medical emergency that occurs when the upper chest or abdomen is subjected to intense external pressure, leading to restricted respiration and impaired blood circulation.
Causes
This condition is commonly observed in:
- Stampedes (as seen in crowded public spaces).
- Vehicular accidents involving crushing injuries.
- Building collapses and natural disasters.
- Industrial accidents with heavy machinery involvement.
Symptoms
Key clinical manifestations include:
- Cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin due to oxygen deprivation).
- Edema (swelling caused by fluid retention).
- Hemorrhages in the face, neck, upper limbs, and thorax due to increased venous pressure.
Treatment
- Immediate supportive care (oxygen therapy, intravenous fluid resuscitation).
- Management of associated injuries, such as fractures and internal trauma.
- Monitoring for complications, including respiratory distress and cardiac dysfunction.
Timely medical intervention is crucial to improve survival outcomes in traumatic asphyxia cases.
Traumatic asphyxia, recently in the news due to the New Delhi Railway Station stampede, primarily results from:
a.Sudden exposure to toxic gases leading to respiratory failure
b.Compression of the upper chest or abdomen restricting respiration and circulation
c.Neurological dysfunction causing paralysis of respiratory muscles
d.Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) progression in high-altitude regions
Answer: (b) Compression of the upper chest or abdomen restricting respiration and circulation
Explanation: Traumatic asphyxia is caused by severe compressive force on the chest or abdomen, leading to restricted respiratory function and impaired venous return, commonly observed in stampedes, accidents, and building collapses. The other options relate to different medical conditions (toxic gas exposure, neurological disorders, and chronic diseases) that do not directly cause traumatic asphyxia
Integrating AI in India’s Judiciary and Law Enforcement
Syllabus: GS2/Government Policies & Interventions; GS3/Science & Technology
India is integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into judicial processes, case management, legal research, and law enforcement to streamline operations, reduce judicial delays, and enhance access to justice.
Current Challenges in India’s Legal and Law Enforcement System
- Despite its well-structured three-tier judiciary (Supreme Court, High Courts, and Subordinate Courts), India’s legal system faces several challenges:
- Judicial Backlogs: Over 5 crore pending cases (National Judicial Data Grid – NJDG).
- Delayed Adjudication: Lengthy legal proceedings due to procedural inefficiencies and excessive documentation.
- Manual Case Handling: Traditional paper-based documentation hampers judicial efficiency.
- Law Enforcement Bottlenecks: Rising cybercrimes, outdated policing methods, and resource constraints limit crime prevention and investigation.
Applications of AI in India’s Judiciary
- AI-Powered Legal Research & Case Management
- AI-driven tools like SUPACE (Supreme Court Portal for Assistance in Court Efficiency) help judges analyze large volumes of legal data.
- Enables faster research, precedent-based judgments, and structured case analysis.
- Predictive Justice & Case Prioritization
- Machine learning models can predict case outcomes based on past rulings.
Courts can use AI to:
- Prioritize urgent cases for speedy resolution.
- Estimate case duration for better planning.
- Identify patterns in case dismissals or approvals.
Virtual Courts & AI-Powered Online Dispute Resolution (ODR)
- E-Courts initiative enables virtual hearings and paperless court operations.
- AI-powered dispute resolution platforms settle minor legal conflicts without judicial intervention.
AI-Assisted Legal Translation
- AI-driven tools like SUVAS (Supreme Court Vidhik Anuvaad Software) assist in real-time legal translations between English and vernacular languages.
- Facilitates multilingual access to legal documents.
- AI in Law Enforcement and Crime Prevention
- AI-Powered Surveillance & Facial Recognition
- Crime and Criminal Tracking Network & Systems (CCTNS) integrates AI-based facial recognition for:
- Identifying suspects from CCTV footage.
- Tracking missing persons and habitual offenders.
- Enhancing public safety with real-time crowd monitoring.
- Predictive Policing & Crime Analytics
- AI algorithms analyze:
- Historical crime trends to detect crime hotspots.
- Behavioral patterns of repeat offenders.
- Social media and online data to track cybercriminals.
- AI in Forensic Investigations
- AI-driven forensic tools assist in:
- Deepfake detection and voice analysis in digital crimes.
- AI-assisted DNA & fingerprint matching for faster case resolution.
- Cybercrime tracking using AI-powered data forensics.
- AI Chatbots for Public Assistance
- AI-powered police chatbots help citizens:
- File FIRs online without visiting police stations.
- Track case progress in real time.
- Access legal guidance in simplified language.
Challenges in AI Adoption in Judiciary & Law Enforcement
- Ethical Concerns & Algorithmic Bias: AI models may inherit biases from historical judicial decisions, affecting fairness and impartiality.
- Data Privacy & Security Risks: AI-driven systems require access to vast legal and crime databases, raising concerns over data confidentiality.
- Infrastructure Gaps & Digital Divide: Many courts and police stations, especially in rural India, lack AI infrastructure and technical expertise.
- Legal & Regulatory Void: India currently lacks AI-specific laws to govern AI-driven judicial and policing mechanisms.
Government Initiatives for AI Integration
- Supreme Court AI Initiatives
- SUVAS: AI-powered legal translation for multilingual accessibility.
- SUPACE: AI-based legal research and case analysis tool for judicial efficiency.
- E-Courts (Phase III) Mission Mode Project
- ₹7210 crore allocation for AI-driven court automation and e-filing.
- ₹53.57 crore earmarked for AI and Blockchain adoption in High Courts.
- Crime and Criminal Tracking Network & Systems (CCTNS)
- AI-powered nationwide police database for cross-state criminal tracking.
- AI Task Force & NITI Aayog’s AI Strategy
- NITI Aayog’s AI roadmap focuses on AI adoption in judicial reforms and policing.
Way Forward: AI for a Smarter Justice System
Establish AI Ethics Guidelines: Ensure transparency and fairness in AI-driven legal decisions.
Strengthen AI Infrastructure: Invest in AI training for judges and law enforcement officers.
Enhance Public Awareness: Educate citizens on AI-based legal resources and rights.
Encourage AI Research in Law: Support academic and industry collaboration for AI-driven legal innovations.
Consider the following statements regarding AI-driven judicial reforms in India:
1.SUPACE is an AI-powered tool developed by the Supreme Court of India to enhance judicial research and assist judges in case analysis.
2.SUVAS, launched alongside SUPACE, is primarily used for predictive justice and case prioritization in lower courts.
3.The E-Courts Phase III initiative has explicitly mandated the use of AI-driven legal research tools in all High Courts across India.
4.CCTNS, while primarily used in law enforcement, also assists the judiciary by automating case citations and legal precedent analysis.
Which of the statements are correct?
a. 1 and 3 only
b. 3 and 4 only
c. 1, 2, and 4 only
d. 1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: A) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: SUPACE (Supreme Court Portal for Assistance in Court Efficiency) is an AI-based research tool designed to assist Supreme Court judges in case law analysis and judicial research.
Statement 2 is incorrect: SUVAS (Supreme Court Vidhik Anuvaad Software) is an AI-driven translation tool, not a case prioritization system.
Statement 3 is correct: The E-Courts Phase III initiative integrates AI-driven legal research tools in High Courts to improve case management.
Statement 4 is incorrect: CCTNS (Crime and Criminal Tracking Network & Systems) is a law enforcement database, but it does not automate case citations or legal precedent analysis for the judiciary.
India’s First indigenous Semiconductor Chip to be Ready by 2025
In Context
Union Minister for Electronics and IT announced at the Global Investors Summit 2025 in Bhopal that India’s first indigenously developed semiconductor chip will be ready for production by 2025.
About Semiconductors
Semiconductors are materials that have conductivity between a conductor and an insulator. They are the foundation of modern electronics, used in:
- Computers and smartphones
- Automobiles and electric vehicles (EVs)
- Defense and aerospace technology
- Medical devices
- Telecommunication and AI applications
Importance
- India is one of the largest consumers of semiconductors but imports 100% of its requirements.
The launch of an indigenous semiconductor chip in 2025 will:
- Reduce import dependence (India imports $24 billion worth of semiconductors annually).
- Strengthen national security (used in defense and critical infrastructure).
- Boost Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat initiatives.
- Create high-skilled jobs in semiconductor design and manufacturing.
Initiatives to Develop the Semiconductor Industry
India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) (2021): A ₹76,000 crore incentive scheme aimed at:
- Setting up semiconductor fabrication units (fabs) in India.
- Encouraging global semiconductor firms to invest in India.
- Developing design-linked incentive (DLI) schemes to support local start-ups.
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Electronics Manufacturing.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing Ecosystem: Five semiconductor units under construction in India.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaboration under India-U.S. Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technology (iCET).
- Talks on setting up chip manufacturing units in India.
- Role in the QUAD Group: QUAD (India, US, Japan, Australia) is focusing on semiconductor supply chain resilience.
Challenges in India’s Semiconductor Sector
- Lack of Existing Semiconductor Fabs: No existing commercial fab in India yet (first expected in 2025).
- Dependence on Global Supply Chains: Taiwan, South Korea, and the U.S. dominate semiconductor manufacturing.
- High Capital and Technological Requirements: Semiconductor manufacturing requires precision, specialized labor, and high investment.
- Geopolitical Risks: US-China trade war & Taiwan tensions impact semiconductor availability.
Future Prospects and Way Forward
- Achieving Self-Sufficiency: The government must ensure faster implementation of semiconductor plants.
- Strengthening Infrastructure: Improve power supply, water availability, and logistics for fabs.
- Enhancing Skill Development: Establish semiconductor training institutes in partnership with global leaders.
- Reducing Import Dependence: Promote local semiconductor startups under the Design-Linked Incentive (DLI) scheme.
Which of the following statements regarding India’s semiconductor industry is correct?
1.India is among the top three global producers of semiconductors.
2.India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) aims to set up fabrication units in India.
3.India currently imports 100% of its semiconductor requirements.
4.The first indigenously developed semiconductor chip is expected by 2030.
a. 1 and 2 only
b. 2 and 3 only
c. 1, 2, and 4 only
d. 1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: B) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
India is not among the top three producers of semiconductors. ISM aims to set up semiconductor fabs in India, and India currently imports all its semiconductors. The first indigenous semiconductor chip is expected by 2025, not 2030.
Cancer Care Challenges in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) poses significant health challenges globally, especially in low and middle-income countries like India.
- In India, AML patients often face late-stage diagnoses and limited access to advanced treatments, leading to disparities in outcomes, particularly in rural regions. Addressing these issues is essential to improve survival rates.
Understanding Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Prevalence: AML is the most common type of leukemia among adults.
- Characteristics: It involves the rapid growth of abnormal blood cells, termed blasts, affecting the blood and bone marrow.
- Demographics in India: The median age of AML diagnosis in India is approximately 40 years, which is younger than in high-income countries. Many patients present at advanced stages, leading to poorer outcomes.
Challenges in AML Management
- Healthcare Infrastructure: Disorganized referral systems and inadequate diagnostic facilities cause delays in treatment initiation.
- Financial Constraints: A significant number of patients are unable to afford treatment. In a study, 29% of newly diagnosed AML patients opted for standard care, while 71% did not proceed, primarily due to financial limitations.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Patients from rural areas face additional challenges, including travel logistics and resource shortages in public hospitals. Private healthcare facilities are often financially inaccessible.
Government Initiatives and Proposed Solutions
Ayushman Bharat Scheme: This initiative aims to enhance access to cancer care. However, gaps remain, particularly in covering initial diagnostics.
Policy Recommendations:
- Tax Exemptions: Industry leaders have advocated for removing taxes on cancer and rare disease medications to reduce treatment costs.
- com
- Infrastructure Development: Strengthening healthcare infrastructure, standardizing treatment protocols, and improving access to novel therapies are crucial steps.
Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborations can enhance resource availability and make treatments more affordable.
What policy change has been suggested to make cancer treatment more affordable in India?
a.Increasing taxes on cancer medications
b.Removing taxes on cancer and rare disease drugs
c.Reducing import duties on luxury goods
d.Centralizing all cancer treatments in urban centers
Answer: b) Removing taxes on cancer and rare disease drugs
Explanation: Industry leaders have urged the Indian government to eliminate taxes on cancer and rare disease medications to reduce treatment costs and improve affordability
Ex INS Guldar Transformed Into Underwater Museum
The Indian Navy has transferred Ex INS Guldar, a decommissioned Landing Ship Tank (Medium), to the Maharashtra Tourism Development Corporation Limited (MTDC). This initiative represents India’s first effort to repurpose a retired naval vessel into an underwater museum and artificial reef. The handover took place in Karwar, with MTDC assuming ownership on an ‘as is where is’ basis. This project aims to promote marine conservation while boosting coastal tourism and local livelihoods.
About Ex INS Guldar
- Origin & Commissioning:
Built in Poland, Ex INS Guldar was commissioned into the Indian Navy on December 30, 1985.
- Operational History:
The ship initially served in the Eastern Naval Command until 1995 and later in the Andaman and Nicobar Command until its decommissioning on January 12, 2024.
- Major Operations:
Over its 39 years of service, Ex INS Guldar participated in critical missions, including Op Aman and Op Pawan. It successfully executed over 490 beaching operations.
Environmental & Economic Benefits
The scuttling of decommissioned naval ships creates artificial reefs, fostering marine biodiversity and acting as a habitat for marine species. This initiative contributes to marine conservation while also benefiting local economies through underwater tourism and diving activities.
Diving Training & Naval Collaboration:The project will serve as a dedicated training site for the Indian Navy. The scuttled vessel will enable diving exercises and operational drills, strengthening the Navy’s capabilities while enhancing public awareness of maritime heritage.
Other Marine Museums in India
India has repurposed several naval vessels into museums, preserving maritime history:
- INS Kursura (Vishakhapatnam) – A submarine museum.
- INS Vikrant – Previously a museum, recommissioned in 2022.
- INS Cuddalore – Converted into an underwater museum.
This initiative underscores India’s commitment to maritime heritage, marine conservation, and tourism-driven economic development.
Consider the following statements regarding Ex INS Guldar:
1.It was commissioned into the Indian Navy in 1995 and served in the Western Naval Command.
2.The vessel participated in operations like Op Aman and Op Pawan.
3.The ship was decommissioned in 2024 and later transferred to the Maharashtra Tourism Development Corporation Limited (MTDC).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a.1 and 2 only
b.2 and 3 only
c.1 and 3 only
d.1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect – Ex INS Guldar was commissioned in 1985, not 1995, and it primarily served in the Eastern Naval Command before moving to the Andaman and Nicobar Command.
Statement 2 is correct – The vessel took part in notable operations like Op Aman and Op Pawan.
Statement 3 is correct – It was decommissioned in 2024 and later transferred to MTDC for conversion into an underwater museum.
Navika Sagar Parikrama II

On February 18, 2025, the Indian Naval Sailing Vessel (INSV) Tarini successfully entered Port Stanley, marking the completion of the third and most challenging phase of the Navika Sagar Parikrama II initiative.
About Navika Sagar Parikrama II
- The Navika Sagar Parikrama initiative highlights the Indian Navy’s commitment to promoting gender empowerment and maritime excellence.
- This expedition is crewed by two remarkable women officers, Lieutenant Commander Dilna K and Lieutenant Commander Roopa A, who aim to advance ocean sailing, self-reliance, and celebrate India’s rich maritime heritage.
- The historic voyage was inaugurated from Goa on October 2, 2024, by the Chief of the Naval Staff. Navika Sagar Parikrama II will cover over 21,600 nautical miles (approximately 40,000 kilometers) and consists of five legs, with scheduled stopovers at four ports for necessary replenishment and maintenance.
The broad outline of the voyage is as follows:
- Goa to Fremantle, Australia
- Fremantle to Lyttleton, New Zealand
- Lyttleton to Port Stanley, Falkland Islands
- Port Stanley to Cape Town, South Africa
- Cape Town back to Goa
About INSV Tarini
- The INSV Tarini is a 56-foot sailing vessel built by Aquarius Shipyard Ltd, officially inducted into the Indian Navy on February 18, 2017.
- Since its induction, the vessel has traversed over 66,000 nautical miles (122,223 kilometers) and participated in the first edition of Navika Sagar Parikrama in 2017.
- The boat is equipped with advanced navigation, safety, and communication systems, ensuring a safe and effective journey across the oceans.
- With the successful arrival at Port Stanley, the mission continues to exemplify the spirit of adventure and determination inherent in the Indian Navy’s efforts to uplift women’s roles in maritime activities
What is the primary objective of the Navika Sagar Parikrama II expedition?
a) To conduct scientific research in the Indian Ocean
b) To promote gender empowerment and showcase India’s maritime heritage
c) To establish India’s dominance in maritime trade routes
d) To set a world record for the longest sailing voyage
Answer: b) To promote gender empowerment and showcase India’s maritime heritage
Explanation: The Navika Sagar Parikrama initiative underscores the Indian Navy’s commitment to gender empowerment and maritime excellence while promoting ocean sailing and India’s rich maritime heritage.
Exercise DHARMA GUARDIAN
Syllabus: GS3/ Defence
Context: The 6th edition of the India-Japan Joint Military Exercise DHARMA GUARDIAN has commenced at the East Fuji Manoeuvre Training Area, Japan.
About the Exercise
- Initiated in 2018, it is a bilateral military exercise held annually on a rotational basis between India and Japan.
- The 5th edition was conducted in Rajasthan, India (2024).
Objectives:
- Enhance interoperability between the Indian Army and Japan Ground Self-Defense Force (JGSDF).
- Focus on joint urban warfare and counter-terrorism operations under a United Nations (UN) mandate.
Strategic Significance:
- Reinforces India-Japan defense cooperation and military-to-military engagement.
- Strengthens the Free, Open, and Inclusive Indo-Pacific strategy.
Aligns with the wider regional security architecture to ensure peace and stability in the Indo-Pacific.
Consider the following statements regarding the DHARMA GUARDIAN military exercise:
1.It is a tri-service military exercise between India and Japan.
2.The first edition of DHARMA GUARDIAN was held in 2018.
3.The exercise focuses on joint military operations under a UN mandate.
The latest edition (2024) was held in Rajasthan, India.
Which of the statements are correct?
a.1 and 2 only
b.2 and 3 only
c.1, 2, and 4 only
d.1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: B) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: DHARMA GUARDIAN is an Army-to-Army exercise, not a tri-service exercise.
Statement 2 is correct: The exercise was initiated in 2018 and has been conducted annually.
Statement 3 is correct: The primary focus of the exercise is joint urban warfare and counter-terrorism under a UN mandate.
Statement 4 is incorrect: The 6th edition (2024) is being held in Japan, while the 5th edition was conducted in Rajasthan, India.
Kerala’s Waste Management Crisis
- Kerala’s current waste management practices have raised serious environmental and ethical concerns. The state has been transferring large quantities of non-biodegradable waste to neighbouring states like Tamil Nadu, instead of developing sustainable internal solutions.
- A recent report titled “Choking on Toxic Smoke The Brahmapuram Garbage Disaster in Kochi and Municipal Solid Waste Management in Kerala” highlights the urgent need for a structured and self-sufficient waste management system.
Scale of the Waste Crisis
- Kerala generates an estimated 11,449 tonnes of municipal solid waste daily, sourced from:
- 6 municipal corporations
- 87 municipalities
- 941 panchayats
Waste management responsibilities have been assigned to local self-governments since 1994, yet many urban local bodies fail to comply with the Solid Waste Management Rules (2000), which mandate centralized waste disposal infrastructure.
The Brahmapuram Fire Incident: A Wake-Up Call
In March 2023, a massive fire at the Brahmapuram landfill incinerated 800,000 tonnes of legacy waste, releasing toxic pollutants into the environment. Scientific analyses confirmed the presence of hazardous substances, posing severe health risks to nearby communities. This disaster underscores the inefficiencies of Kerala’s waste disposal systems and the need for immediate reforms.
Key Challenges in Waste Management
- Despite efforts to implement decentralized waste management models in cities like Alappuzha and Thiruvananthapuram, several obstacles persist:
Inadequate Infrastructure:
- Waste processing facilities remain underdeveloped or underutilized.
Lack of Reliable Data:
- Absence of systematic waste composition surveys hampers policy effectiveness.
Poor Regulatory Compliance:
- Local bodies often fail to meet statutory waste disposal requirements.
- Plastic and E-Waste Crisis
Plastic Pollution: Despite a ban on single-use plastics in 2020, plastic waste continues to accumulate, with microplastics detected in major water bodies.
E-Waste Management: Hazardous electronic waste is often mishandled, with improper disposal leading to severe environmental and health hazards.
Recommendations for Sustainable Waste Management
The report calls for a holistic approach, integrating waste management into broader urban planning, public health, and social justice frameworks. Key recommendations include:
- Strategic Land-Use Planning: Aligning waste processing with sustainable land development.
- Critical Assessment of Waste-to-Energy Plants: Evaluating the economic and environmental feasibility of large-scale incineration projects.
Strengthening Local Governance:
- Empowering municipalities with improved resources, data collection, and regulatory oversight.
- Innovative Local Initiatives
Some local self-governing institutions have successfully launched microenterprise schemes focused on:
- Waste recycling and reuse
- Employment generation through waste management enterprises
- Expanding these community-driven models across Kerala could lead to a more sustainable and self-reliant waste management system.
Conclusion
Kerala must shift from short-term waste disposal tactics to a comprehensive, sustainable, and locally managed system. Strengthening policy enforcement, investing in infrastructure, and promoting community participation will be key to tackling the state’s mounting waste crisis.
Consider the following statements regarding Kerala’s waste management crisis:
- Kerala generates approximately 11,449 tonnes of municipal solid waste daily.
- The waste management system in Kerala has been centralized since 1994.
- The Solid Waste Management Rules (2000) mandate the creation of decentralized waste disposal facilities.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a.1 only
b.1 and 2 only
c. 2 and 3 only
d.1 and 3 only
Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct – Kerala produces 11,449 tonnes of waste per day, as per the report.
Statement 2 is incorrect – Waste management was decentralized in 1994, assigning responsibilities to local self-governments.
Statement 3 is incorrect – The Solid Waste Management Rules (2000) primarily emphasize centralized waste disposal, not decentralization.
Soligas and Tiger Conservation in BRT Tiger Reserve
- The Soliga tribe, an indigenous community residing in the Biligiri Rangaswamy Temple (BRT) Tiger Reserve in Karnataka, plays a crucial role in conservation efforts.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi, in the 119th edition of Mann Ki Baat, highlighted their contribution to tiger population growth and acknowledged their cultural reverence for wildlife, which fosters harmony between humans and nature.
About the Soliga Tribe
- The name “Soliga” means “children of bamboo”.
- They inhabit the Biligiri Rangana Hills and Male Mahadeshwara Hills in Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
- The Soligas were the first tribe in India to gain official rights to reside inside a tiger reserve (BRT Tiger Reserve).
- As per the 2011 Census, their population stood at 33,871 in Karnataka and 5,965 in Tamil Nadu.
- They speak Sholaga (a Dravidian language), along with Kannada and Tamil.
- Traditionally, they practice shifting cultivation and rely on forest resources, particularly honey collection, as a major source of food.
Cultural Practices and Conservation
- The Soligas revere tigers, referring to them as Dodda Nayi (Big Dog).
- They maintain a tiger temple, signifying their spiritual connection to the species.
- Their sustainable forest lifestyle reduces environmental degradation and aids in conservation efforts.
Human-Wildlife Coexistence
- Human-animal conflict is minimal in the BRT Tiger Reserve due to the Soligas’ deep understanding of wildlife behavior.
- The tribe avoids certain areas at specific times, reducing tiger encounters.
- They leave portions of their harvest for wildlife, ensuring food availability for animals and minimizing competition.
Collaboration with the Forest Department
- The Forest Department works closely with the Soligas, leveraging their knowledge for forest management.
- The tribe actively participates in fire prevention, habitat protection, and conservation programs.
Tiger Population Trends in BRT Tiger Reserve
- According to National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) reports:
- 2014: 69 tigers
- 2018: 86 tigers (increase observed)
- 2022: Decline in tiger numbers due to human interference and habitat degradation.
- Conservation efforts need to address these challenges to ensure long-term protection.
Recognition of Tribal Rights
- The Soligas were the first tribal group to receive forest rights within a tiger reserve through a landmark 2011 court ruling.
- Recognizing tribal rights is critical for conservation success, as it enables indigenous communities to actively participate in safeguarding biodiversity.
Conservation and Cultural Integration
- India’s tribal communities have long-established sustainable practices that aid conservation.
- The Prime Minister referenced other cultural traditions, like Huli Vesha dance of Karnataka, to highlight tribal contributions to biodiversity preservation.
This model of human-wildlife coexistence sets a precedent for conservation strategies worldwide, demonstrating how traditional ecological knowledge can complement modern conservation efforts
Consider the following statements regarding the Soliga tribe:
1.They were the first tribal community in India to receive official rights to live inside a tiger reserve.
2.Their primary occupation has historically been settled agriculture.
3.The Soligas speak only Sholaga, a language of the Dravidian family.
4.They have a cultural tradition of worshipping tigers, referring to them as “Dodda Nayi.”
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A) 1 and 4 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1, 3, and 4 only
D) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: A) 1 and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct. The Soligas were the first tribe in India to be granted forest rights inside a tiger reserve (BRT Tiger Reserve).
Statement 2 is incorrect. They traditionally practiced shifting cultivation rather than settled agriculture.
Statement 3 is incorrect. While they speak Sholaga, they also communicate in Kannada and Tamil.
Statement 4 is correct. They worship tigers, referring to them as Dodda Nayi (Big Dog), which fosters conservation ethics.
Biennial Transparency Report (BTR)
India is in the final stages of preparing its first Biennial Transparency Report (BTR), a key commitment as a signatory to the 2015 Paris Agreement on climate change.
Overview of the Biennial Transparency Report (BTR)
The BTR is a report compiled and submitted by Parties to the Paris Agreement within the framework of the Enhanced Transparency Framework (ETF). It provides a comprehensive overview of each country’s progress in achieving various aspects of the Agreement.
Components of the BTR
- The BTR consists of five separate chapters, some of which are mandatory while others are optional:
- National Inventory Report of Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions: Required for all Parties – Mandatory
- Progress in Implementing and Achieving Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs): Required for all Parties – Mandatory
Climate Change Impacts and Adaptation: Applicable to all Parties – Optional
- Financial, Technology Transfer, and Capacity-Building Support Provided: Required for developed country Parties – Mandatory; optional for other Parties providing support.
- Financial, Technology Transfer, and Capacity-Building Support Needed and Received: Optional for developing country Parties.
- All Parties to the Paris Agreement, except for Small Island developing states (SIDS) and least developed countries (LDCs), are mandated to submit country-specific information regarding the implementation of the Agreement in the form of BTRs every two years.
- Recognizing the unique challenges faced by SIDS and LDCs, these nations have the option to submit BTRs at their convenience, providing necessary flexibility based on their individual circumstances.
As the reporting mechanism under the Paris Agreement, BTRs foster mutual trust and confidence between nations. They enable both Parties and non-party stakeholders to assess the overall state of climate action in individual countries.
What role do Biennial Transparency Reports (BTRs) play in the context of the Paris Agreement?
a) They serve as a legal document for climate litigation.
b) They facilitate mutual trust and confidence among countries regarding climate action.
c) They provide funding for climate adaptation projects.
d) They outline the penalties for non-compliance with the agreement.
Answer: b) They facilitate mutual trust and confidence among countries regarding climate action.
Explanation: BTRs help foster mutual trust and allow parties and non-party stakeholders to understand the state of climate action in each country.
Killer Whales (Orcas)
Recently, officials reported that more than 150 false killer whales were stranded on a remote beach in Tasmania, Australia. This incident has raised significant concerns about the health of marine ecosystems and the potential causes of such mass strandings.
About Killer Whales
- Common Name: Killer Whale
- Scientific Name: Orcinus orca
- Distribution: Killer whales, also known as orcas, are found in oceans worldwide, making them the most widely distributed of all cetaceans. They inhabit a variety of marine environments ranging from coastal waters to open seas.
- Classification
Killer whales are the largest members of the Delphinidae family, which includes all species of dolphins and other larger species such as long-finned and short-finned pilot whales.
Social Structure
Killer whales are extremely social animals, often living in groups called pods. These pods are typically made up of maternally related individuals and can consist of a few to dozens of whales. The social bonds among pod members are strong, and they often participate in cooperative hunting and nurturing behaviors.
Communication and Navigation
Killer whales use underwater sound for a range of activities, including feeding, communicating, and navigating their environments. Their sophisticated vocalizations are crucial for maintaining social connections and coordinating group activities.
Physical Appearance
Killer whales are one of the most recognizable marine mammals due to their distinctive black and white coloration. Adult males are typically larger than females and have characteristic tall dorsal fins.
Habitat
Killer whales can be found in diverse habitats globally, thriving in both coastal waters and the open sea. They adapt their hunting and social behaviors based on the specific ecological conditions of their environment.
Conservation Status
According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), killer whales are classified as “Data Deficient.” This classification reflects the need for more comprehensive research on their populations, distribution, and threats to better inform conservation efforts.
Conclusion
Killer whales are fascinating and complex creatures that play an essential role in marine ecosystems. Continued observation, research, and conservation efforts are vital to ensure their survival and the health of their habitats. The recent stranding of false killer whales in Tasmania serves as a reminder of the vulnerabilities facing marine mammal populations and
the importance of addressing the challenges they encounter.
What is a significant behavioral characteristic of killer whales that facilitates their social interactions?
A) They can survive in complete solitude without forming social groups.
B) They use visual signals predominantly for communication.
C) They live in social groups called pods, which are typically comprised of maternally related individuals.
D) They migrate alone across vast oceanic distances.
Answer: C) They live in social groups called pods, which are typically comprised of maternally related individuals.
Explanation: Killer whales are highly social creatures that form pods, which are units of social structure based on maternal lineage. The other options are incorrect as killer whales do not thrive alone and rely heavily on social structures.
National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA)
The Supreme Court has recently directed a supervisory committee, chaired by the head of the National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA), to investigate the issues raised by Tamil Nadu regarding the maintenance of the 125-year-old Mullaperiyar dam, which is situated in Kerala.
About the National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA)
The NDSA is a statutory body established by the Central Government under the provisions of Section 8(1) of the National Dam Safety Act, 2021. The authority is led by a chairman, supported by five members, each responsible for one of its five functional areas: policy and research, technical oversight, regulation, disaster resilience, and administration and finance. The NDSA’s headquarters is located in New Delhi.
Functions of the National Dam Safety Authority
The NDSA operates with a well-defined mandate to regulate, supervise, and inspect dams throughout the country. Its essential functions include:
- Policy Formulation: Developing policies and guidelines related to the construction, maintenance, and operation of dams on a national level.
- Dispute Resolution: Addressing and resolving conflicts arising between State Dam Safety Organisations or between these organisations and owners of specified dams within the respective states.
- Public Awareness: Conducting nationwide awareness programs aimed at educating the public about dam safety and its importance.
- Emergency Preparedness: Ensuring the establishment of comprehensive emergency response plans to address natural disasters or unexpected incidents related to dam safety.
Through these activities, the NDSA plays a vital role in ensuring the safety and integrity of dams across India.
Which of the following functions is NOT explicitly mentioned as a responsibility of the NDSA?
a. Formulating policies for the construction of dams.
b. Mediating disputes between State Dam Safety Organizations and dam owners.
c. Implementing environmental assessments for all civil construction projects.
d.Educating citizens about dam safety through awareness programs.
Answer: C implementing environmental assessments for all civil construction projects.
Explanation: While the NDSA focuses on dam safety, the implementation of environmental assessments for all construction projects is not within its stated functions.
Central Pollution Control Board
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) recently submitted a report to the Principal Bench of the National Green Tribunal, outlining concerning findings regarding river water quality in Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh, during the ongoing Maha Kumbh Mela.
Overview of CPCB
- The CPCB is a statutory organization established in September 1974 under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974.
- Additionally, it was entrusted with powers and functions under the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981.
- The board serves as a field formation and provides technical support to the Ministry of Environment and Forests in accordance with the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
Principal Functions of the CPCB
- Water Quality Management: The CPCB promotes the cleanliness of streams and wells across various states through the prevention, control, and reduction of water pollution.
- Air Quality Management: It aims to improve air quality and prevent, control, or abate air pollution throughout the country.
- Advisory Role: The board advises the Central Government on issues related to the control and reduction of air and water pollution.
- Coordination: CPCB coordinates the activities of State Pollution Control Boards, providing assistance, guidance, and conflict resolution in cases of disagreements among them.
- Delegation of Powers: The CPCB has delegated its powers and responsibilities under the Water (Prevention & Control of Pollution) Act, 1974, the Water (Prevention & Control of Pollution) Cess Act, 1977, and the Air (Prevention & Control of Pollution) Act, 1981 to the relevant regional administrations concerning Union Territories.
Standard Development Activities
- The CPCB undertakes the development and revision of environmental standards, along with upgrading the Comprehensive Industrial Document (COINDS) and formulating guidelines for environmental management across various industrial sectors.
- In collaboration with the respective state governments, the CPCB establishes standards for stream and well water quality, air quality, and prepares manuals, codes, and guidance documents concerning the treatment and disposal of sewage and trade effluents, as well as technologies for stack gas cleaning devices, stacks, and ducts.
Standards Developed by CPCB
The CPCB develops standards for:
- National Ambient Air Quality: Quality benchmarks for air across the country.
- Water Quality Criteria: Standards from various sources of water.
- Emission and Discharge Standards: For environmental pollutants from diverse industries (issued under the Environment Protection Rules, 1986).
- Biomedical Waste Treatment and Disposal: Standards for incineration.
- Noise Emission Limits: For diesel engines, LPG, and CNG generator sets.
Additionally, the CPCB formulates Minimal National Standards (MINAS) tailored for various industrial categories, encompassing effluent discharge (water pollutants), emissions (air pollutants), noise levels, and solid waste management. These standards are mandatory for State Governments to adopt as minimum requirements.
Consider the following statements regarding the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB):
1.It is a statutory body functioning under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
2.It has the power to enforce pollution control measures across all states and Union Territories.
3.It can directly take legal action against industries violating pollution norms.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 1 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: C) 1 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: CPCB is a statutory body established under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974, and functions under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
Statement 2 is incorrect: CPCB does not have direct enforcement powers over states; it provides guidelines and coordinates with State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs), which are responsible for enforcing pollution control at the state level.
Statement 3 is incorrect: While CPCB can issue directions and recommendations, direct legal action is typically taken by SPCBs or through the National Green Tribunal (NGT).
Blue-Cheeked Bee-Eater (Merops persicus)
Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
Context:
The first-ever breeding site of the Blue-Cheeked Bee-Eater in peninsular India has been discovered in the saltpans of Aandivilai near the Manakudy Mangroves in Kanniyakumari district, Tamil Nadu.

About Blue-Cheeked Bee-Eater (Merops persicus):
Physical Characteristics:
- Slender-bodied bird with a predominantly green plumage.
- Distinctive blue cheeks, black eye stripe, and a yellowish-brown throat.
- Sharp, black beak specialized for catching insects.
- Size: Grows up to 31 cm in length, with two elongated central tail feathers extending 7 cm longer than the rest.
Habitat & Distribution:
- Migratory species found across Northern Africa, the Middle East, Central Asia, and India.
- Prefers open habitats such as grasslands, wetlands, coastal areas, and agricultural fields.
- Diet:
- Primarily insectivorous, feeding on bees, wasps, hornets, and other flying insects.
- Known for its aerial hunting skills, catching prey mid-flight with precision.
Conservation Status:
- Listed as “Least Concern” by the IUCN Red List, indicating a stable population.
- However, habitat loss due to wetland degradation and climate change may pose future threats.
Consider the following statements regarding the Blue-Cheeked Bee-Eater (Merops persicus):
1.It is an exclusively non-migratory bird found only in the Indian subcontinent.
2.The bird is characterized by blue cheeks, a black eye stripe, and a yellow-brown throat.
3.The species has been classified as “Endangered” under the IUCN Red List.
The first confirmed breeding site in peninsular India was discovered in Tamil Nadu.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a.1 and 2 only
b. 2 and 4 only
c.1, 2, and 4 only
d.1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: B) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The Blue-Cheeked Bee-Eater is a migratory species, not exclusive to India.
- Statement 2 is correct: The bird has blue cheeks, a black eye stripe, and a yellow-brown throat.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The bird is listed as “Least Concern”, not “Endangered”, under the IUCN Red List.
Statement 4 is correct: The first breeding site in peninsular India was discovered in Aandivilai, Tamil Nadu.
National Green Financing Institution Subject Biodiversity & Environment
Why in News?
The Government of India is planning to establish a National Green Financing Institution to aggregate funds from various sources and reduce capital costs to support its net-zero target by 2070. NITI Aayog is evaluating models such as NaBFID/NABARD, IREDA, Green InvITs, and global Green Banks for this initiative.
Need for Green Finance in India
- Escalating Climate Change Risks: Climate change could cause an estimated 10% loss in total economic value, potentially wiping out up to 18% of global GDP by 2050. This poses a significant threat to India’s ambition of growing its economy to USD 10 trillion by 2030.
- Net-Zero Commitments: India pledged to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070 under the Panchamrit strategy at COP26, requiring over USD 10 trillion in investments.
- Financial Sector Exposure: The financial services industry faces 72% of the potential financial impact of climate change. Banks can mitigate risks by funding green infrastructure, renewable energy, energy-efficient buildings, and industrial decarbonization.
- Investment Deficit: India requires USD 1.4 trillion in aggregate investments (USD 28 billion annually) to meet its 2070 net-zero goal. However, as of February 2023, India’s green bond issuances totaled only USD 21 billion, with the private sector contributing 84%.
Current Green Energy Financing Initiatives in India
- National Clean Energy and Environment Fund (NCEEF): Funds clean energy ventures and research through the Clean Environment Cess on coal. IREDA uses part of this fund to provide concessional loans for renewable energy projects.
- Priority Sector Lending (PSL): In 2015, the RBI classified renewable energy as a PSL category, requiring banks to allocate up to 40% of net credit. Loans up to Rs 15 crore per borrower are available for solar, wind, biomass, and other non-conventional energy projects.
- Green Banks: Institutions such as IREDA and SBI provide concessional loans for renewable energy initiatives.
- Green Bonds: Market-based instruments used to raise capital for eco-friendly projects, such as IREDA’s Green Masala Bonds.
- Crowdfunding: A decentralized funding model leveraging small private investments for renewable energy, exemplified by Bettervest’s support for MeraGao Power and Boond Engineering in rural India
Challenges in Green Energy Financing
- Limited International Finance: Developed nations pledged at COP29 to mobilize at least USD 300 billion annually by 2035, which remains insufficient compared to the required USD 1 trillion per year by 2030.
- High Borrowing Costs: High interest rates, long project gestation periods, and limited fiscal incentives make green finance expensive, often rendering projects financially unviable.
- Diversion of Funds: NCEEF funds have been redirected to non-renewable projects such as GST compensation and Namami Gange.
- Institutional Barriers for Green Banks: The lack of RBI guidelines and legal recognition affects the credibility and fundraising potential of green banks.
- Underdeveloped Green Bond Market: Many renewable energy projects lack high credit ratings, leading to investor skepticism over fund utilization.
Way Forward
- Enhancing Climate Finance: Mobilize concessional funding through the Global Green Bond Market and multilateral institutions (World Bank, AIIB). Provide sovereign guarantees and interest rate subsidies for green projects and introduce a Tax-Free Green Bond Scheme to attract investors.
- Strengthening Green Banking: Institutionalize Green Banks under RBI with clear regulations and a legal framework, promoting public-private co-financing to attract global green capital.
- Alternative Financing Mechanisms: Expand Green Infrastructure Investment Trusts (Green InvITs) to boost private participation and develop carbon credit markets linked to green financing instruments.
- Microfinancing: Support women-led green businesses and provide affordable climate risk insurance for small farmers to prioritize adaptation along with mitigation efforts.
This structured approach to green financing will help India achieve its net-zero ambitions while ensuring sustainable economic growth.
Consider the following statements regarding India’s net-zero ambitions made at COP26:
1.India aims for net-zero emissions by 2070 under the Panchamrit strategy.
2.The estimated investment requirement to achieve this goal is less than USD 5 trillion.
3.Climate change could lead to significant economic loss, estimated at 10% of total economic value by 2050.
Which of the statements are correct?
a.1 only
b.1 and 3 only
c.1 and 2 only
d.1, 2 and 3
Answer: B) 1 and 3 only
The Tea Horse Road
The Tea Horse Road Syllabus: GS1/History
China’s Ambassador to India, Xu Feihong, recently emphasized the historical importance of the Tea Horse Road, highlighting its role in facilitating trade between India and China through Tibet.
What is the Tea Horse Road?
- The Tea Horse Road was an ancient trade route that connected China, Tibet, and India. It primarily served as a trading network where Chinese tea was exchanged for Tibetan horses, playing a crucial role in regional commerce.
- It had two main routes, passing through cities like Dali and Lijiang in China’s Yunnan province.
- The pathways extended to Lhasa in Tibet, branching further into India, Nepal, and Bangladesh.
- The trade route dates back to the Tang dynasty (618–907 CE).Buddhist monk Yijing (635–713 CE) recorded the transportation of sugar, textiles, and rice noodles from southwestern China to Tibet and India, while horses, leather, gold, saffron, and medicinal herbs were sent to China.
Significance of the Tea Horse Road
- Strengthened India-China trade through Tibet, fostering economic ties.
- Encouraged cultural exchange, influencing cuisine, textiles, and Buddhism between the regions.
Enhanced economic interdependence by linking China’s tea-producing regions with India’s trading hubs
Consider the following statements regarding the Tea Horse Road
1.It primarily functioned as a Silk Road alternative, facilitating the exchange of silk and spices between China and India.
2. It connected China’s Yunnan province to Tibet and extended into India, Nepal, and Bangladesh.
3. The route was first established during the Ming Dynasty (1368–1644 CE).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b)
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect because the Tea Horse Road was not an alternative to the Silk Road, but rather a distinct trade route focused on the exchange of Chinese tea for Tibetan horses. Statement 2 is correct as the route extended from China’s Yunnan province to Tibet and further into India, Nepal, and Bangladesh. Statement 3 is incorrect because the route dates back to the Tang Dynasty (618–907 CE), not the Ming Dynasty
Pagri Sambhal Jatta Movement
Syllabus: GS 1/History
- Farmers protesting at the Punjab and Haryana borders observed February 23 as Pagri Sambhal Diwas to honour the revolutionary leader Ajit Singh.
- Pagri Sambhal Jatta Movement (1907): The slogan “Pagri Sambhal Jatta” translates to “Take care of your turban, O farmer”, symbolizing self-respect and dignity. The movement was led by Ajit Singh in 1907 to oppose three exploitative British agricultural laws.
Oppressive British Laws Targeted by the Movement
- Punjab Land Alienation Act (1900) – Restricted farmers’ rights to sell or mortgage land.
- Punjab Land Colonisation Act (1906) – Gave British authorities control over land in the Chenab Colony.
- Doab Bari Act (1907) – Reduced farmers to contract laborers, depriving them of land ownership.
- Additionally, farmers suffered under heavy taxation on land and irrigation, worsening their economic struggles.
Impact of the Movement
- One of the first major farmer uprisings against British rule.
- Sparked mass protests, civil disobedience, and public resistance.
- Led to the partial repeal of oppressive laws due to pressure from the movement.
- Inspired future movements, including the Ghadar Movement and Bhagat Singh’s revolutionary activities.
Ajith Singh: The Revolutionary Leader
- Born: February 23, 1881, in Khatkar Kalan, Punjab.
- A prominent freedom fighter, nationalist, and revolutionary.
- Worked with Lala Hardayal, Madame Cama, and other Indian revolutionaries in Europe.
- Played a crucial role in mentoring his nephew, Bhagat Singh.
- Exiled from 1909 to 1947 due to his relentless opposition to British rule.
- Died on August 15, 1947, the day India gained independence.
Conclusion
The Pagri Sambhal Jatta Movement remains a symbol of farmers’ resistance against oppression, and Ajit Singh’s legacy continues to inspire struggles for justice and dignity.
With reference to the Pagri Sambhal Jatta Movement of 1907, consider the following statements:
1.It was primarily a reaction to the British-imposed increase in land revenue and irrigation taxes.
2. The movement led to the immediate and complete repeal of all three targeted British agricultural laws.
3. The slogan “Pagri Sambhal Jatta” was popularized by Lala Lajpat Rai.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: The movement was triggered by oppressive British laws and excessive taxation on land and irrigation.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The movement led to partial repeal of the laws, not an immediate and complete revocation.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The slogan “Pagri Sambhal Jatta” was popularized by Ajit Singh, not Lala Lajpat Rai
Battle of Karnal
Introduction
Fought on February 24, 1739, the Battle of Karnal marked a significant decline in the Mughal Empire. Nadir Shah, the ruler of Persia, decisively defeated Mughal Emperor Muhammad Shah ‘Rangila’ within a few hours. This battle exposed the vulnerabilities of the Mughal military and governance, accelerating the empire’s downfall.
Background of the Mughal Empire: The Mughal Empire reached its peak under Emperor Aurangzeb but began to decline after his reign. Several factors contributed to this deterioration, including:
- Internal conflicts and succession wars
- Heavy taxation on peasants, leading to economic distress
- Military threats from regional powers
- Widespread revolts, draining the empire’s resources
- Nadir Shah’s Invasion
Having consolidated his power in Persia, Nadir Shah set his sights on India. After conquering Kandahar in 1738, he launched an invasion, swiftly defeating Mughal vassal states. The Mughal response was sluggish and ineffective, revealing their declining military efficiency
With reference to the Battle of Karnal (1739), consider the following statements:
1. The Mughal army outnumbered Nadir Shah’s forces but was defeated due to poor leadership and military inefficiency.
2. Nadir Shah’s invasion was preceded by the conquest of Kandahar in 1738.
3. The battle lasted for several days before the Mughals surrendered to Nadir Shah.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: The Mughal army had 300,000 soldiers compared to Nadir Shah’s 55,000 troops, yet they were overwhelmed due to poor leadership, outdated military tactics, and lack of discipline.
Statement 2 is correct: Nadir Shah’s invasion of India followed his conquest of Kandahar in 1738, demonstrating his military expansion strategy.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The Battle of Karnal lasted only a few hours, showcasing the superior Persian strategy and Mughal military weakness.
National Geospatial Knowledge-based Land Survey of Urban Habitations (NAKSHA)
National Geospatial Knowledge-based Land Survey of Urban Habitations (NAKSHA):
- On February 18, 2025, Union Rural Development Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan launched the National Geospatial Knowledge-based Land Survey of Urban Habitations (NAKSHA).
- This initiative seeks to modernize urban land records in India, addressing the long-standing issue of outdated mapping in many cities.
- Part of the Digital India Land Records Modernization Programme (DILRMP), NAKSHA will initially be piloted in 152 urban local bodies across 26 states before a nationwide rollout.
What is NAKSHA?
- NAKSHA is a high-precision geospatial survey designed to create accurate urban land records. It integrates aerial and field surveys with advanced Geographic Information System (GIS) technology to improve land governance.
- The initiative prioritizes towns with areas under 35 square kilometers and populations below 200,000. The pilot phase will span one year, testing methodologies before a broader implementation.
Why is NAKSHA Needed?
- Many urban areas in India still rely on outdated land records, leading to inefficiencies in governance, property taxation, and urban planning.
- While rural land records have seen modernization efforts, urban regions lack proper mapping systems. Recognizing this gap, NAKSHA was highlighted in the Union Budget 2024 and reaffirmed in 2025, emphasizing the need for reforms in urban land management.
Key Objectives of NAKSHA
- Digitization of Urban Land Records – Creating an updated and structured land database.
- Reducing Land Disputes – Eliminating ambiguity in property ownership and boundaries.
- Enhancing Urban Planning Efficiency – Providing accurate land data for better infrastructure development.
- Streamlining Property Transactions – Simplifying registration and verification processes.
- Improving Tax Collection – Strengthening the financial health of urban local bodies.
Funding and Cost Structure: The central government fully funds NAKSHA, with the pilot project estimated at ₹194 crore.
Survey costs vary based on technology:
- Basic Camera Survey: ₹25,000 to ₹30,000 per square kilometer.
- Advanced 3D Camera Survey: ₹60,000 per square kilometer.
Survey Methodology
NAKSHA employs aerial drone surveys equipped with high-resolution cameras and LiDAR sensors. The survey follows a three-stage process:
- Area Selection – Identifying target urban zones.
- Aerial Survey – Capturing detailed images with drones and oblique-angle cameras.
- Ground Verification – Ensuring data accuracy through field validation.
This advanced drone-based mapping provides superior image quality compared to satellite imagery, improving the accuracy of land records.
Future Expansion Plans
If the pilot phase succeeds, NAKSHA will expand to 4,912 urban local bodies across India.
The initiative aims to establish a comprehensive framework for urban land governance, enabling data-driven decision-making and efficient urban development. By bridging the gap in urban land records, NAKSHA will contribute significantly to India’s digital transformation in land management.
Consider the following statements regarding the NAKSHA initiative:
1.It is a geospatial survey focused on modernizing rural land records in India.
2.The pilot phase of NAKSHA is set to cover urban local bodies across all Indian states and Union Territories.
3.The initiative leverages advanced GIS technology, including drone-based aerial surveys.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a.1 and 2 only
b.3 only
c.2 and 3 only
d.1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
1.Statement 1 is incorrect because NAKSHA is focused on urban land records, not rural ones.
2,Statement 2 is incorrect because the pilot phase is limited to 152 urban local bodies in 26 states, not across all states and Union Territories.
3.Statement 3 is correct as NAKSHA integrates GIS technology and drone-based surveys.
Sinking of the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea, the world’s largest enclosed body of water, is facing severe environmental challenges. Reports indicate a significant decline in water levels, threatening regional biodiversity and human livelihoods. Environmental activists and officials emphasize the need for urgent, collective action from the five bordering nations—Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan, Russia, Turkmenistan, and Iran—to prevent further degradation.
Geographical Features
Spanning approximately 370,000 square kilometers, the Caspian Sea is a unique water body with diverse ecological characteristics:
- Northern Region: Less saline and relatively shallow.
- Southern Region: Higher salinity, reaching depths of 1,025 meters.
This variation in salinity and depth influences marine biodiversity and resource distribution across the region.
Biodiversity and Natural Resources
The Caspian Sea hosts over 130 species of fish, including the sturgeon, which is vital for the global caviar industry. Additionally, more than 100 species of wetland birds depend on the region’s ecosystem. However, this rich biodiversity is under threat due to:
- Pollution from oil and gas extraction.
- Overfishing, depleting key species.
- Habitat destruction, reducing breeding grounds for marine and avian life.
Environmental Challenges
Several factors contribute to the Caspian Sea’s environmental decline:
Pollution:
Industrial waste from oil and gas operations has severely contaminated marine habitats.
Climate Change: Rising temperatures accelerate evaporation, leading to lower water levels.
Ecosystem Disruption:
Deterioration of aquatic and wetland ecosystems endangers fisheries and local livelihoods.
International Cooperation Efforts
Recognizing the urgency of conservation, the Caspian Environment Programme (CEP) was established in 1998 to coordinate environmental policies. Furthermore, the Tehran Convention (2003) provides a legal framework for marine protection, emphasizing:
Pollution control measures for industrial activities.
Ecosystem restoration initiatives to counter habitat destruction.
Sustainable development strategies for fisheries and coastal communities.
Key Agreements and Future Strategies
Ratified in 2006 by all five littoral states, the Tehran Convention upholds principles of:
- Precautionary action against potential environmental harm.
- Accountability for pollution and resource mismanagement.
- Scientific monitoring to assess ecological changes.
Conclusion:
The future of the Caspian Sea depends on strengthened regional collaboration and immediate environmental action. Adopting sustainable conservation practices is crucial to preserving its marine ecosystem, economic significance, and biodiversity for generations to come.
Consider the following statements regarding the Caspian Sea:
1.It is the world’s largest enclosed body of water.
2.The northern part of the Caspian Sea is saltier and deeper than the southern part.
3.It is bordered by five countries, including Turkey.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 1 and 3 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: a) 1 only
Explanation: The Caspian Sea is indeed the world’s largest enclosed body of water (Statement 1 is correct). However, its northern part is less saline and shallower, while the southern part is saltier and deeper, making Statement 2 incorrect. Additionally, Turkey is not a Caspian littoral state; the five bordering nations are Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan, Russia, Turkmenistan, and Iran (Statement 3 is incorrect).
Mount Dukono Eruption
Mount Dukono Eruption
- Mount Dukono, an active volcano in North Maluku, Indonesia, recently erupted, sending ash plumes up to 2,000 meters into the sky.
- The eruption has raised concerns regarding aviation safety and local communities, prompting precautionary measures.
About Mount Dukono
- Located on Halmahera Island, North Maluku, Indonesia.
- Stands at 1,235 meters above sea level.
- Recorded its first eruption in 1933 and has since remained highly active.
- Frequently emits volcanic smoke and experiences eruptions, making it one of Indonesia’s persistent volcanoes.
Indonesia’s Volcanic Activity
- Home to 130 active volcanoes, the highest number globally.
- Part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, a seismically active region prone to earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
- Has recorded numerous deadly eruptions, causing land devastation, tsunamis, and pyroclastic flows.
- Mount Merapi and Mount Kelut, located on Java Island, are Indonesia’s most active and hazardous volcanoes.
- Most volcanoes are concentrated along the Sunda Arc, a 3,000 km-long volcanic chain formed by the subduction of the Indian Ocean Plate beneath the Asian Plate.
Pacific Ring of Fire: Also known as the Circum-Pacific Belt, spanning 40,000 km around the Pacific Ocean.
- Characterized by intense tectonic activity due to interactions between multiple plates, including:
- Pacific Plate, Juan de Fuca Plate, Cocos Plate, Indo-Australian Plate, Nazca Plate, North American Plate, and Philippine Plate.
- Countries along the Ring of Fire include Japan, Indonesia, the U.S., Chile, Mexico, and New Zealand.
- Responsible for 90% of the world’s earthquakes and the majority of volcanic eruptions.
The ongoing activity of Mount Dukono highlights Indonesia’s vulnerability to geological hazards and the broader seismic risks associated with the Pacific Ring of Fire.
Consider the following statements regarding Mount Dukono:
1.It is located in the Sunda Arc, a volcanic belt formed due to the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Indo-Australian Plate.
2.It recorded its first eruption in 1933 and has remained an active volcano ever since.
3.The recent eruption of Mount Dukono sent volcanic ash up to 2,000 meters into the atmosphere.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation: Mount Dukono is located on Halmahera Island, North Maluku, not in the Sunda Arc (which mainly covers the Java and Sumatra regions). However, it did erupt for the first time in 1933, and the latest eruption indeed sent ash 2,000 meters into the sky.
Anticyclone System
Weather experts have reported that the recent unusual spike in temperatures in Mumbai is attributed to the presence of an anticyclone system along the western coast.
About Anticyclones
An anticyclone is a high-pressure weather phenomenon characterized by a higher air pressure at the surface compared to the surrounding areas.
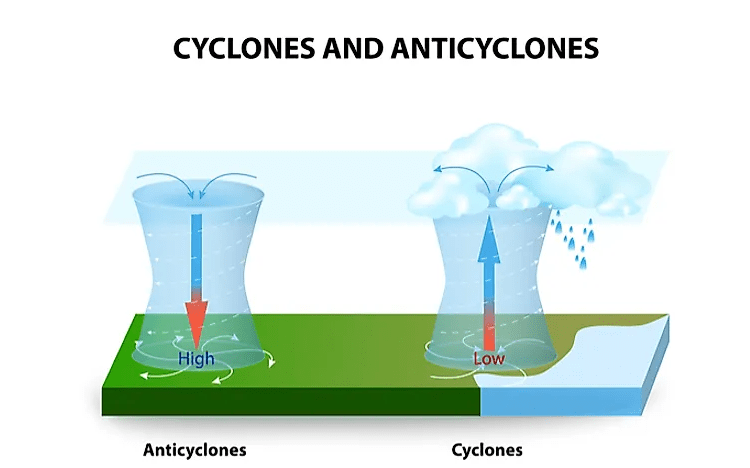
Key Features of an Anticyclone System:
- High Pressure at the Center: The center of an anticyclone experiences higher air pressure than its surroundings.
- Air Movement: Air flows outward from the center of the anticyclone.
- Sinking Air: Instead of rising, the air within an anticyclone descends, which inhibits cloud formation and typically results in dry and clear weather conditions.
Impact on Weather: Anticyclones can significantly affect local weather patterns, often leading to extended dry spells or heatwaves.
What is a potential impact of an anticyclone on local weather patterns?
a) Increased rainfall and flooding
b) Prolonged dry spells or heatwaves
c) Strong winds and storms
d) Rapid temperature drops
Answer: b) Prolonged dry spells or heatwaves
Explanation: Anticyclones can lead to prolonged dry conditions and heatwaves due to the sinking air and lack of cloud formation, which keeps moisture from accumulating.
Caspian Pipeline Consortium
Recently, Russia reported a reduction of 30-40% in oil flows through the Caspian Pipeline Consortium (CPC), a critical route for supplying Kazakhstan and exporting oil to the global market. This decrease followed a Ukrainian drone attack on a pumping station.
Overview of the Caspian Pipeline Consortium (CPC) :
The Caspian Pipeline Consortium is a significant $2.6 billion project that features a 935-mile crude oil pipeline extending from the Tengiz oil field in Kazakhstan to the Russian Black Sea port of Novorossiysk.
- Construction of the CPC began in 1999, and the pipeline was commissioned in 2001, with a $5.1 billion expansion project completed in 2018.
- As a key East-West pipeline, the CPC facilitates the transport of oil from the Caspian Sea region to international markets.
- The consortium is jointly owned by the governments of Russia and Kazakhstan, along with major Western energy companies including Chevron, ExxonMobil, and Shell.
Notably, the CPC accounts for two-thirds of Kazakhstan’s oil exports and has a total capacity of 1.4 million barrels per day, representing 2.3% of global seaborne oil trade.
Which major international oil companies are stakeholders in the Caspian Pipeline Consortium?
a) Gazprom, BP, and Total
b) Chevron, ExxonMobil, and Shell
c) Aramco, Eni, and Equinor
d) ConocoPhillips, Repsol, and ENI
Answer: b) Chevron, ExxonMobil, and Shell
Explanation: The Caspian Pipeline Consortium includes Western energy majors such as Chevron, ExxonMobil, and Shell, along with the Russian and Kazakh governments.
Key Facts about Nauru
To assist in relocating approximately 10,000 residents from low-lying areas threatened by rising sea levels and flooding, the remote Pacific nation of Nauru has proposed selling citizenships for this climate-affected island.
About Nauru
- Nauru is an island nation and microstate located in Oceania, specifically in the southwestern Pacific Ocean.
- It is recognized as the world’s smallest republic, covering an area of about 8 square miles and housing a population of around 12,500 inhabitants.
- The island lies approximately 1,300 km northeast of the Solomon Islands, with its closest neighbor being Banaba Island in Kiribati, situated about 300 km to the east.
- Nauru is a raised, fossilized coral atoll and one of the three significant phosphate rock islands in the Pacific.
- The island features a central phosphate plateau encircled by coral cliffs.
- However, extensive phosphate mining has significantly degraded the interior landscape, rendering about 80% of it uninhabitable and unsuitable for agriculture.
- Nauru does not have an official capital city; however, the district of Yaren on the southern coast serves as its de facto capital.
- The native language is Nauruan, although English is commonly spoken, especially in governmental and commercial contexts.
- Following its independence in 1968, Nauru adopted a constitution that established it as a republic with a parliamentary system modeled after the Westminster style.
Which of the following statements correctly describes Nauru’s geographical and demographic characteristics?
A) Nauru is the largest island nation in the Pacific with a population of approximately 100,000.
B) Nauru is a small republic located in the south-western Pacific Ocean, with a land area of about 8 square miles and a population of around 12,500.
C) Nauru is located southwest of the Solomon Islands and is primarily composed of volcanic rock.
D) Nauru has a total land area of about 20 square miles and lies east of Kiribati.
Answer: B) Nauru is a small republic located in the south-western Pacific Ocean, with a land area of about 8 square miles and a population of around 12,500.
Explanation: This statement correctly captures Nauru’s status as a small republic in Oceania, its land area, and population. Options A, C, and D contain inaccuracies regarding size, population, and geological composition.
India and Argentina Strengthen Cooperation in Lithium Exploration
India and Argentina have engaged in discussions aimed at expanding mining cooperation, with a particular emphasis on lithium exploration.
Overview of Argentina’s Lithium Reserves: Argentina is a vital component of the “Lithium Triangle,” which positions it as a crucial partner for India in securing minerals essential for electric vehicle (EV) batteries and renewable energy storage solutions.
Current Initiatives: The discussions involved potential lithium exploration efforts led by Khanij Bidesh India Ltd. (KABIL) and Greenko, alongside increasing participation of Indian companies in Argentina’s mining sector.
About Lithium:
Lithium is a silvery-white, highly reactive metal.
Applications: It is primarily used in rechargeable lithium-ion batteries, which power a range of electronic devices including smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles.
Global Production: The major sources of lithium production globally include Australia, Chile, and Argentina, all of which have significant reserves and are influential players in the international lithium market.
Lithium Triangle Explained:
The “Lithium Triangle” is a region in South America known for housing some of the largest lithium reserves in the world.
This triangular area spans parts of Argentina, Bolivia, and Chile, collectively holding 58% of the planet’s recognized lithium reserves.
India’s Engagement: India has been ramping up its diplomatic efforts to connect with Lithium Triangle Countries (LTCs) to secure access to this critical mineral.
Which of the following statements regarding lithium is incorrect?
A) Lithium is used predominantly in rechargeable lithium-ion batteries.
B) Lithium is a non-reactive silvery-white metal.
C) Australia, Chile, and Argentina are key producers of lithium.
D) Lithium reserves are concentrated within the “Lithium Triangle” in South America.
Answer: B) Lithium is a non-reactive silvery-white metal.
Explanation: This statement is incorrect because lithium is, in fact, a highly reactive silvery-white metal. Its reactivity is a significant factor in its industrial applications, particularly in battery technology, where it plays a crucial role.
AI Revolution in Indian Agriculture
Subject Agriculture
Microsoft Chairman Satya Nadella recently highlighted the transformative impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in agriculture through Project Farm Vibes (PFV) in Baramati, Maharashtra. The project has led to a 40% increase in crop yields while reducing resource consumption.
What is Project Farm Vibes?
About:
- Project Farm Vibes is an AI-driven initiative developed by Microsoft Research in collaboration with the Agricultural Development Trust, Baramati (MH).
- It is an open-source AI suite designed to provide data-driven insights to farmers and researchers, enhancing productivity and sustainability.
Technologies Used:
- Azure Data Manager for Agriculture – Aggregates satellite, weather, and sensor data for a comprehensive view of field conditions.
- AI – Uses AI and machine learning to analyze soil moisture, temperature, humidity, and pH, offering precision farming recommendations.
- AI – Provides real-time, personalized insights in local languages, assisting farmers in sustainable farming practices.
Impact of Project Farm Vibes:
- 40% increase in crop production, leading to healthier and more resilient crops.
- 25% reduction in fertilizer costs through AI-guided precision fertilization.
- 50% less water consumption, ensuring sustainable irrigation practices.
- 12% decrease in post-harvest wastage, improving profitability.
- Environmental benefits, including reduced chemical runoff, soil erosion, greenhouse gas emissions, and deforestation.
How is AI Revolutionizing Indian Agriculture?
- Smart Irrigation
- AI helps address water scarcity through soil moisture and climate analysis, optimizing irrigation schedules.
- AI-integrated drip and sprinkler irrigation systems under the “Per Drop More Crop” scheme enhance water efficiency.
- IoT-based irrigation solutions, developed by ICAR, automate water supply based on real-time field conditions, minimizing wastage.
- Pest & Weed Control
- The National Pest Surveillance System leverages AI to monitor pest activity and provide real-time alerts.
- AI-powered weed detection uses computer vision to distinguish weeds from crops, enabling targeted herbicide application and reducing chemical use.
- Economic Impact of AI in Agriculture
- The AI in agriculture market is projected to grow from USD 1.7 billion in 2023 to USD 4.7 billion by 2028, with a CAGR of 23.1%.
- Growth is driven by advancements in precision farming, drone analytics, and labor management.
- Initiatives like Kisan e-Mitra, an AI-powered chatbot, assist farmers with queries about the PM Kisan Samman Nidhi scheme.
Challenges in AI Adoption in Agriculture
- Lack of Awareness
- Many farmers, especially in rural India, lack digital literacy, limiting large-scale AI adoption.
- High Implementation Costs
- AI solutions such as drones, IoT sensors, and automated irrigation systems require significant investment.
- 85% of Indian farmers are small and marginal, making affordability a major barrier.
- Infrastructure Gaps
- Unreliable internet connectivity in rural areas restricts access to AI-powered platforms.
- Out of 5,97,618 inhabited villages in India, 25,067 villages still lack mobile connectivity and internet access.
- Data Availability and Quality
- AI relies on real-time and historical agricultural data for accurate predictions.
- Incomplete or inaccurate data reduces AI effectiveness in farming.
- Limited Customization
- AI models need to be tailored to India’s diverse agro-climatic conditions.
- More research is required to develop region-specific AI solutions.
Way Forward: AI-Driven Future of Indian Agriculture
- Data Frameworks & Integration
- The AgriStack Initiative and India Digital Ecosystem for Agriculture (IDEA) can serve as digital platforms for farm data management, enhancing AI-driven insights.
- National AI Centres of Excellence should focus on developing customized AI solutions for Indian agriculture.
Strengthening Digital Infrastructure
- Public Wi-Fi hotspots under the PM-WANI initiative and BharatNet Project can improve rural connectivity, ensuring farmer access to AI platforms.
- Farmer Skilling & Awareness
- The National e-Governance Plan in Agriculture (NeGPA) educates farmers on AI applications.
- FutureSkills PRIME reskills professionals in AI and emerging agricultural technologies.
- Financial & Policy Support
- Under the Digital Agriculture Mission (2021-2025), providing subsidized loans to agri-tech startups and farmer cooperatives can boost AI-driven innovation in agriculture.
By addressing these challenges, India can harness AI’s full potential, making agriculture more efficient, sustainable, and profitable.
Which of the following is the primary reason for the significant 40% increase in crop production through AI technologies like Project Farm Vibes in Baramati, Maharashtra?
A) Optimization of crop genetics through AI-driven genetic modification strategies
B) Improved soil health and water usage efficiency driven by AI-based precision agriculture
C) Increased dependency on traditional farming knowledge with supplementary AI tools
D) Large-scale industrialization of farming models with AI as a mere support system
Answer: B) Improved soil health and water usage efficiency driven by AI-based precision agriculture
Explanation: The 40% increase in crop production is primarily due to precision farming enabled by AI, which focuses on optimizing soil health, water usage, and resource allocation. AI-powered tools ensure that irrigation, fertilization, and pest control are finely tuned to local conditions, improving productivity without necessarily relying on genetic modifications or traditional methods. This sustainable, data-driven approach maximizes resource efficiency and enhances crop yield.
Herath Festival

- Herath is a significant festival for the Kashmiri Pandit community, marking their unique observance of Mahashivratri.
- Celebrated from the 13th day of the Phalgun month (February or March) until the new moon, the festival derives its name from “Har-Ratri,” meaning “Night of Hara,” a reference to Lord Shiva. It symbolizes the union of divine forces and honors the sacred bond of Shiva and Parvati.
- Historical Significance: Rooted in the rich cultural heritage of the Kashmir Valley, Herath has been celebrated for centuries.
- It reflects the deep faith and traditions of the Kashmiri Pandits while also highlighting the interwoven cultural influences of the region. The festival holds immense significance in preserving the community’s identity and spiritual legacy.
- Rituals and Traditions: The festival preparations begin with a thorough cleaning of homes, symbolizing renewal and spiritual readiness. On the eve of Mahashivratri, families perform Vatuk Pooja, a central ritual where a kalash (sacred pot) filled with water and walnuts is placed in a sanctified space. This ceremony invokes divine blessings and represents prosperity and well-being. A priest often leads the rituals, fostering a strong sense of devotion and community bonding.
- Cultural Harmony: The day following Shiva Chaturdashi is called Salam, symbolizing unity between Kashmiri Pandits and Muslims. This tradition reflects the region’s rich cultural harmony and mutual respect. The festival concludes on the 15th day, known as Dooni-Mavas, when families distribute walnuts, representing prosperity, resilience, and shared blessings.
- Shankaracharya Temple and Devotion: A significant pilgrimage site during Herath is the Shankaracharya Temple, which overlooks Dal Lake in Srinagar. This historic temple serves as a spiritual center where devotees gather to offer prayers and express their reverence for Lord Shiva.
- The temple’s prominence during Herath underscores its enduring role in Kashmiri religious traditions.
- Herath in Contemporary Times : In recent years, public figures and leaders have acknowledged Herath’s cultural and spiritual importance. The Jammu and Kashmir Chief Minister has extended official greetings to the Kashmiri Pandit community, reinforcing the festival’s role in fostering communal harmony and celebrating Kashmir’s diverse heritage. Such recognition strengthens social bonds and ensures the continuity of this cherished tradition.
Herath remains a profound celebration of devotion, unity, and cultural resilience, preserving the spirit of Kashmiri Pandit traditions across generations
Consider the following statements regarding the festival of Herath:
- Herath is celebrated exclusively on the night of Mahashivratri in Kashmir.
- The term “Herath” originates from “Har-Ratri,” signifying the night of Lord Shiva.
- The festival is unique to the Kashmiri Pandit community and symbolizes the union of Shiva and Parvati.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation: Statement 1 is incorrect because Herath is not limited to a single night; it begins on the 13th day of Phalgun and continues until the new moon.Statement 2 is correct as the name “Herath” is derived from “Har-Ratri,” meaning “Night of Hara” (Shiva).Statement 3 is correct since Herath is a distinct tradition of the Kashmiri Pandit community, marking the divine union of Shiva and Parvati.
Swami Ramakrishna Paramhansa
The Prime Minister recently paid tribute to Swami Ramakrishna Paramhansa on his Jayanti.

Swami Ramakrishna Paramhansa
- Swami Ramakrishna, originally named Gadadhar Chattopadhyay, was born on February 18, 1836, in Kamarpukur, Bengal, into a modest Brahmin family deeply rooted in religious values.
- His profound spirituality inspired him to explore diverse religious paths, ultimately affirming that all faiths lead to a singular divine truth.
- His life was characterized by a continuous contemplation of God, and his God-consciousness transcends both time and place, resonating universally with seekers from all religions.
Notable Disciple
Among his many disciples, Swami Vivekananda stands out as the most prominent. Vivekananda played a crucial role in bringing the philosophy of Ramakrishna to a global audience. In 1897, he founded the Ramakrishna Mission to actualize the visions of his Guru, dedicating the organization to the service of society.
Teachings and Message
- Sri Ramakrishna’s life significantly influenced modern spiritual thought. He demonstrated that the realization of God is not confined by age, nationality, or social background.
- His teachings emphasized that God transcends materialism and skepticism, thus restoring faith in religion. His spiritual presence and teachings transformed individuals, converting those who were lost into enlightened beings and purifying their souls.
Relevance Today
- One of Ramakrishna’s most significant contributions is his message of religious harmony. In a world increasingly confronted by religious intolerance and global crises, his teachings offer hope.
- They advocate for religious tolerance, mutual respect, and fellowship among varying faiths, fostering a spirit of unity in diversity.
Swami Ramakrishna Paramhansa, born Gadadhar Chattopadhyay, is primarily remembered for which of the following contributions?
- His advocacy for the harmony of all religions.
- Establishing a political movement for India’s independence.
- Founding the Ramakrishna Mission.
- a) 1 only
- b) 1 and 3 only
- c) 2 and 3 only
- d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 1 and 3 only
Explanation: Swami Ramakrishna is especially known for his teachings on the harmony of religions and the influence he had on his disciple Swami Vivekananda, who founded the Ramakrishna Mission. He is not primarily remembered for establishing a political movement for India’s independence.
Mising tribe
- The Mising tribe, the largest tribal community in Assam, is an indigenous group from Northeast India.
- They belong to the Tani people, who communicate through Tibeto-Burmese languages.
- The Mising people inhabit regions in Assam and Arunachal Pradesh, extending their presence into Tibet, China.
- In Tibetan culture, they are referred to as “Lhobhas,” meaning “southerners,” due to their historical settlement in southern Tibet and parts of present-day Arunachal Pradesh.
- According to the 2011 Census of India, the Mising population in Assam stands at 680,424, making them one of the most significant tribal groups in the state.
- Their lifestyles are intricately linked to rivers, earning them the designation of the only riparian tribe in Northeast India.
- The cultural and daily life of the Mising people are centered around agriculture and fishing.
- Traditionally, their agricultural practices were rooted in the ‘Jhum’ or slash-and-burn method.
- However, following their migration to the plains of Assam, they have adapted and excelled in wet paddy cultivation, transforming into proficient settled cultivators.
- The primary festival celebrated by the Mising community is ‘Ali-Aye-Ligang,’ which marks the beginning of the sowing season.
- The term ‘Ali’ refers to edible roots, ‘Aye’ signifies seeds, and ‘Ligang’ translates to a sowing festival.
- Additionally, the Mising people adhere to the cult of ‘Do-nyi – Po:lo,’ which is a form of worship dedicated to the Sun and the Moon.

Which of the following statements accurately depicts the relationship between the Mising tribe and their environment?
A) The Mising tribe primarily engages in nomadic pastoralism.
B) The Mising tribe is recognized as the only wholly terrestrial tribe of Northeast India.
C) The Mising tribe has a lifestyle that is closely linked to rivers, making them the only riparian tribe in Northeast India.
D) The Mising tribe’s activities are predominantly centered around urban commerce and trade.
Answer: C) The Mising tribe has a lifestyle that is closely linked to rivers, making them the only riparian tribe in Northeast India.
Explanation: The correct option emphasizes the Mising tribe’s unique relationship with their riverine environment. Options A, B, and D misrepresent the tribe’s lifestyle and cultural practices.
