1.Polity
Changes in Chief Election Commissioner Appointment Process
A recent meeting involved Prime Minister Narendra Modi, Home Minister Amit Shah, and Leader of Opposition Rahul Gandhi to appoint a successor to retiring Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) Rajiv Kumar. The meeting highlighted changes in the appointment process and raised concerns about the new law governing these appointments.
Previous Appointment Process:
- Procedure: The President of India appointed the CEC and Election Commissioners based on the Prime Minister’s advice.
- Legislation: There was no formal legislation governing the appointment process.
- Succession: Typically, the most senior Election Commissioner (based on the date of appointment) succeeded the outgoing CEC.
- Ambiguity: The seniority rule had potential ambiguity when Commissioners were appointed on the same day.
Introduction of the New Law:
- Legislation: The Chief Election Commissioner and Other Election Commissioners (Appointment, Conditions of Service and Term of Office) Act, 2023 governs the new appointment process.
- Search Committee: A search committee led by the Law Minister creates a shortlist of candidates.
- Selection Committee: A selection committee comprising the Prime Minister, the Leader of Opposition, and a Cabinet Minister reviews the shortlist.
Role of the Selection Committee:
- Flexibility: The selection committee can consider candidates beyond the initial shortlist.
- Goals: Aims to enhance transparency and accountability in appointing electoral officials.
Eligibility Criteria and Terms of Service:
- Eligibility: Candidates must have held a position equivalent to a Secretary in the Government of India. They must also possess integrity and experience in managing elections.
- Reappointment: Officials are not eligible for reappointment.
- Term Limit: The maximum term of service is six years for any individual in these roles.
- Reasons for the Change in Appointment Process:
- Supreme Court Intervention: The change was influenced by Supreme Court interventions.
- Constitutional Considerations: The Supreme Court noted that the Constitution did not intend for the Executive to have exclusive authority over these appointments.
- Mandate for Change: The Supreme Court’s ruling mandated a more inclusive selection process, leading to the new law.
On-going Legal Challenges: Challenge to the New Law: The Association for Democratic Reforms has contested the removal of the Chief Justice of India from the selection committee.
Supreme Court Review: The Supreme Court is set to hear these petitions, raising questions about Parliament’s authority to modify judicial rulings through legislation
Who appoints the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and Election Commissioners under the previous appointment process?
A) The Parliament of India
B) The Prime Minister of India
C) The President of India, based on the Prime Minister’s advice
D) The Supreme Court of India
Answer and Explanation: C) The President of India, based on the Prime Minister’s advice
The information clearly states that the President appoints them based on the Prime Minister’s advice, under the previous procedure.
President of India issued Proclamation imposing President’s rule in Manipur
This marks the 11th instance of President’s Rule being imposed in the state, with the last time being in 2001-02, putting the State Assembly under suspended animation.
Constitutional Basis: Article 356 of the Constitution allows for the imposition of President’s Rule in a state. This happens when the President, acting on a report from the State Governor, is convinced that the state government can no longer function according to the Constitution.
Duration and Approval:
- Initial Period: President’s Rule is initially in effect for two months.
- Parliamentary Approval: To extend beyond two months, both houses of Parliament must approve it by a simple majority.
- Extension Limits: If approved, President’s Rule can be extended for a maximum of three years, with parliamentary approval required every six months.
- Revocation: The President can end President’s Rule at any time through a subsequent proclamation.
Consequences of President’s Rule:
- The President assumes control of the State Government’s functions and the Governor’s powers.
- The President can transfer the powers of the State Legislature to Parliament.
- The High Court continues to operate as usual.
S R Bommai Vs Union of India (1994)
Supreme Court held that the proclamation under Article 356 was subject to judicial review.
The President can only dissolve a state legislative assembly after Parliament’sapproval of the proclamation, and until then, the assembly remains suspended.
To extend President’s Rule beyond the initial period, what is required?
a) Approval from the State Assembly
b) Approval from the President
c) Approval from both houses of Parliament
d) A referendum in the state
Correct Answer: c) Approval from both houses of Parliament
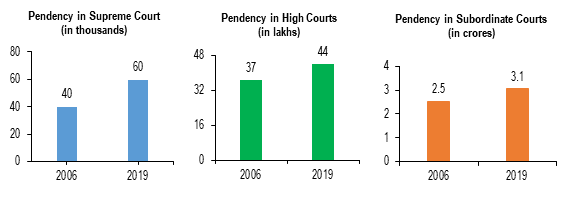
Issue of Pendency of Cases in Indian Judiciary
Issue of Pendency of Cases in Indian Judiciary
This is a concise summary of the problem of case backlogs in the Indian judiciary and the Supreme Court’s efforts to address it.
About : The Supreme Court first endorsed the appointment of ad-hoc judges in its 2021 ruling in Lok Prahari v. Union of India. These judges were authorised to hear only criminal appeals as part of a bench led by a sitting judge.
Backlog: As of January 2025, High Courts were hampered with a disgusting backlog of 62 lakh cases.
Legal Basis:
Article 224A: This constitutional provision allows the Chief Justice of a High Court to appoint retired judges with the President’s permission.
Lok Prahari v. Union of India (2021): The Supreme Court case that established the conditions for appointing ad-hoc judges, including the requirement that the High Court has a significant number of vacancies.
Background and Context: The Supreme Court has previously allowed ad-hoc judges but has identified a lack of use of the provision.
Why the Backlog? Causes: The article lists several contributing factors to the massive backlog of cases:
Insufficient Judges: A low judge-to-population ratio.
Increased Litigation: More cases are being filed due to a growing population and complex socio-economic issues.
Delays in the Justice System: Procedural inefficiencies, adjournments, and delays in evidence.
Lack of Infrastructure: Under-equipped and under-staffed courts.
Bureaucratic Challenges: Administrative inefficiencies and lack of modernization.
Impact of the Backlog: Consequences: The backlog has several negative consequences:
Delay in Justice: Cases take years to resolve.
Increased Number of Under trials: More people are waiting in prison for their trials.
Increased Costs: Financial strain on litigants and the government.
Overburdened Judges: Burnout and further delays.
Erosion of Public Confidence: Reduced trust in the judicial system.
Efforts to Address the Issue: Solutions and Reforms: The article highlights various initiatives to tackle the backlog:
Judicial Reforms: Increasing the number of judges, improving infrastructure, and using technology (e-courts).
Alternate Dispute Resolution (ADR): Promoting arbitration, mediation, and conciliation.
E-Courts and Technology: Digitizing court proceedings for online hearings and streamlined case management.
Fast Track Courts: Establishing special courts for specific types of cases to expedite proceedings.
What is one of the initiatives being taken to address the backlog?
a. Reducing the number of judges
b. Discouraging the use of technology
c. Promoting Alternate Dispute Resolution (ADR)
d.Decreasing the number of fast-track courts
Correct Answer: c) Promoting Alternate Dispute Resolution (ADR)
Article 371 and Coal Mining in Meghalaya
In Meghalaya, discussions have emerged regarding the potential use of Article 371 of the Indian Constitution to restart rat-hole coal mining, coinciding with the state’s preparations for elections. The Voice of the People Party (VPP) is advocating for this change, drawing comparisons to Nagaland, which has similar provisions.
About Article 371
Article 371 grants special powers to certain northeastern states in India, providing them with autonomy over land and resources. It allows local customs and laws to take precedence. For example, Nagaland benefits from Article 371A, which safeguards its land and resources from central legislation. This has significant implications for governance and resource management in the region.
Impact on Coal Mining
Since April 2014, coal mining in Meghalaya has been banned due to environmental concerns. This ban, imposed by the National Green Tribunal (NGT) and upheld by the Supreme Court, has created challenges for the industry. The VPP contends that Article 371 could enable the resumption of mining activities, akin to Nagaland, where local laws prevent NGT intervention. This proposal raises important questions about environmental regulations and local governance.
Sixth Schedule vs. Article 371
Meghalaya operates under the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution, which empowers autonomous councils to oversee local affairs. However, there is on-going debate over the compatibility of Article 371 and the Sixth Schedule. Some political leaders argue that the two provisions cannot coexist effectively, highlighting the complexities of governance in tribal areas and the need to balance local autonomy with national regulations.
Electoral Context: The upcoming elections for the Khasi Hills Autonomous District Council (KHADC) and the Jaintia Hills Autonomous District Council (JHADC) hold significant importance. The VPP’s emphasis on Article 371 may sway voter opinions. Notably, the councils feature low representation of women candidates despite a higher number of female voters, raising concerns about gender representation in local governance.
Recent Developments
Recently, agreements for scientific coal mining at three sites in Meghalaya were signed by the Coal Controller. The Chief Minister stated that these agreements aim to stimulate the economy and generate employment.
However, the ongoing discussions around Article 371 and mining practices continue to dominate the political landscape. The results of the elections may have a profound impact on the future of coal mining and local governance in the state
What trend has been observed in the upcoming elections for the Khasi Hills Autonomous District Council (KHADC) and the Jaintia Hills Autonomous District Council (JHADC)?
a. An increase in male representation at all levels of government.
b. Very low representation of women candidates despite a higher number of female voters.
c. Profit-driven policies dominating party manifestos.
d. Full gender parity achieved in candidate nominations.
Answer: B) Very low representation of women candidates despite a higher number of female voters
2. Defence
India-U.S. Partnership on Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA) Technologies:
The India-U.S. partnership on Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA) technologies, solidified during PM Modi’s recent visit to the US with the launch of the Autonomous Systems Industry Alliance (ASIA), represents a significant advancement in maritime security cooperation. This collaboration is particularly noteworthy as India is the only country with whom the U.S. defence industry is partnering on such sensitive technologies.
Understanding Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA):
UDA encompasses the ability of a nation or organization to monitor, detect, and assess activities occurring beneath the surface of oceans and seas. It is vital for:
- Maritime Security
- Resource Management
- Environmental Protection
- Disaster Response
Significance of the India-U.S. UDA Cooperation:
Geopolitical and Strategic Importance:
- Strengthening Maritime Domain Awareness (MDA) and, critically, UDA is essential for India’s national security.
- Addresses China’s increasing naval presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Enhances submarine detection and tracking capabilities.
- Supports increased cooperation within the Quad (India, U.S., Australia, Japan) to counter shared threats.
Defence Technology Collaboration:
The U.S. is providing cutting-edge underwater surveillance and anti-submarine warfare (ASW) technologies, including:
- Sea Picket: An autonomous sonar surveillance system by Thayer Mahan.
- Wave Glider: An Unmanned Surface Vehicle (USV) by Boeing’s Liquid Robotics, with plans for co-production with Sagar Defence engineering (60 units).
- Low-Frequency Active Towed Sonar: Discussions between L3 Harris and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) are ongoing.
Impact on India’s Defence Capabilities:
Significantly strengthens India’s anti-submarine warfare (ASW) capabilities, complementing existing assets:
- 12 P-8I Poseidon Maritime Patrol Aircraft
- 24 MH-60R Multi-Role Helicopters (being inducted)
- 15 MQ-9B Sea Guardian UAVs (part of a 31-unit contract, deliveries from 2029).
Technology Transfer, “Make-in-India,” and Economic Benefits:
- First-of-its-kind co-production and technology transfer in sensitive underwater systems.
- Strengthens India’s defence manufacturing ecosystem under the “Make in India” & “Atmanirbhar Bharat” initiatives.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Technology Transfer and Data Security: Concerns regarding the secure sharing of sensitive UDA data and maintaining sovereign control over surveillance systems.
- Financial and Operational Challenges: The high cost associated with procurement, deployment, and maintenance of advanced underwater systems.
- Technology Dependence: Reliance on high-end research and funding for advanced sonar and AI systems.
- Legal and Diplomatic Complexities: Potential for tensions with neighbouring nations in disputed waters due to UDA activities.
- Environmental Impact: The use of sonar technologies can negatively impact marine biodiversity and aquatic ecosystems.
Conclusion: UDA is a critical component of maritime security, economic sustainability, and environmental conservation. India’s focus on UDA, in collaboration with the U.S. and Quad partners, is especially significant given the increasing Chinese presence in the Indian Ocean. This collaboration is set to significantly enhance India’s maritime defense capabilities and strategic positioning in the region.
The primary strategic driver behind the India-U.S. collaboration on Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA) is:
a. To counter the growing naval presence of China in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
b. To improve India’s fishing industry.
c. To promote tourism in the Indian Ocean.
d. To enhance environmental protection in the IOR.
Answer: A .To counter the growing naval presence of China in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
BrahMos NG Cruise Missile
India is advancing its BrahMos cruise missile program with the development of the BrahMos NG (Next Generation) missile system, scheduled for production starting 2027-28.
- The first flight tests are expected next year.
- The BrahMos NG aims to enhance the capabilities of its predecessor while being lighter and more compact.
Key Features of BrahMos NG:
- Effective Range: Maintains a range of 290 km.
- Compact Design: Designed to fit smaller delivery systems.
- Weight and Dimensions: Weighs approximately 1.6 tonnes and is 6 meters long (compared to the older version’s 3 tonnes and 9 meters).
- Advanced Features: Features a reduced radar cross-section and a homemade seeker with AESA radar technology.
Compatibility and Deployment:
- The BrahMos NG is designed to be compatible with the Russian-origin Sukhoi-30MKI fighter aircraft and the indigenous Light Combat Aircraft Tejas.
- Its compact design enables deployment across a wider range of military assets.
International Interest and Export:
- India has already supplied three batteries of the BrahMos system to the Philippines.
- A new export deal with Indonesia, valued at approximately USD 450 million, is in advanced negotiations.
- Indonesia would be the second foreign buyer of the BrahMos system after the Philippines.
Technological Advancements and Future Prospects:
- BrahMos NG’s advanced stealth features and versatility make it suitable for various combat scenarios.
- It is designed for improved performance against electronic countermeasures and can be launched from multiple platforms, including torpedo tubes and vertical launch systems.
- India is advancing its BrahMos cruise missile program with the development of the BrahMos NG (Next Generation) missile system, scheduled for production starting 2027-28.
- The first flight tests are expected next year.
- The BrahMos NG aims to enhance the capabilities of its predecessor while being lighter and more compact.
Key Features of BrahMos NG:
- Effective Range:Maintains a range of 290 km.
- Compact Design:Designed to fit smaller delivery systems.
- Weight and Dimensions:Weighs approximately 1.6 tonnes and is 6 meters long (compared to the older version’s 3 tonnes and 9 meters).
- Advanced Features:Features a reduced radar cross-section and a homemade seeker with AESA radar technology.
- Compatibility and Deployment: The BrahMos NG is designed to be compatible with the Russian-origin Sukhoi-30MKI fighter aircraft and the indigenous Light Combat Aircraft Tejas. Its compact design enables deployment across a wider range of military assets.
- International Interest and Export: India has already supplied three batteries of the BrahMos system to the Philippines. A new export deal with Indonesia, valued at approximately USD 450 million, is in advanced negotiations. Indonesia would be the second foreign buyer of the BrahMos system after the Philippines.
- Technological Advancements and Future Prospects: BrahMos NG’s advanced stealth features and versatility make it suitable for various combat scenarios. It is designed for improved performance against electronic countermeasures and can be launched from multiple platforms, including torpedo tubes and vertical launch systems.
What is a primary advantage of the BrahMos NG compared to its predecessor?
a. Increased effective range.
b. Larger size and weight.
c. Compatibility with fewer aircraft.
d. Lighter weight and more compact design.
Answer: (D) Lighter weight and more compact design.
Explanation: The text explicitly states that the BrahMos NG aims to be lighter and more compact than the older version, allowing it to be used with a wider range of systems
Indian Army and IAF Execute ‘Winged Raider’ in Eastern Theater
- The Indian Army and the Indian Air Force (IAF) have successfully executed the joint military exercise titled ‘Winged Raider’ in the Eastern Theater.
- This strategic drill emphasized special airborne operations aimed at bolstering coordination between the two branches of the armed forces.
- Conducted in a critical operational zone, the exercise forms part of ongoing efforts to enhance rapid deployment capabilities and foster inter-service synergy.
What was the main goal of conducting “Winged Raider” in a key operational zone?
a. To practice humanitarian aid and disaster relief operations
b. To showcase military might and intimidation
c. To enhance coordination and rapid deployment capabilities between the Army and the Air Force
d. To conduct counter-insurgency operations
Answer: C) To enhance coordination and rapid deployment capabilities between the Army and the Air Force
3. Science and Technology
Successful Test of Matsya-6000
Project Overview:
- India’s Deep Ocean Mission aims to enhance the country’s capabilities in ocean exploration.
- The project is led by the National Institute of Ocean Technology.
Matsya-6000 Submersible Overview:
Design and Capacity:
- The submersible has a compact design with a diameter of 2.1 meters.
- It can accommodate three personnel.
Materials and Construction:
- The submersible is constructed from a titanium alloy, allowing it to withstand extreme underwater pressures.
Systems and Features:
- Ballast system for diving.
- Thrusters for multidirectional movement.
- Advanced communication tools, including an acoustic modem and underwater telephone.
- Sophisticated power distribution network.
- Advanced underwater navigation devices.
- Life-support systems for crew safety during missions.
Testing and Development Phases:
Dry Tests:
- Extensive dry tests were conducted to evaluate the submersible’s performance over a 500-meter range.
Wet Tests:
- The submersible was moved to the L&T Shipbuilding facility for wet tests.
- The tests focused on assessing the submersible’s stability, manoeuvrability, and communication capabilities.
- A total of 8 dives were conducted, including both unmanned and manned trials.
Future Prospects:
- Samudrayan Project:
- The project aims to explore ocean depths for resources like precious metals and to study marine biodiversity.
- It is expected to promote ocean literacy and tourism.
Completion Timeline:
- The completion of Matsya-6000 is anticipated by 2026.
- This aligns with India’s broader goals for sustainable ocean resource development.
Significance of Ocean Exploration:
- Sustainable Resource Management:
- India’s role in ocean exploration is crucial for sustainable resource management.
- The government aims to increase the contribution of the blue economy to the national GDP.
- Marine Ecosystems and Resource Development:
- By exploring ocean depths, India seeks to enhance its knowledge of marine ecosystems and develop resources responsibly.
What is the primary objective of India’s Deep Ocean Mission, under which the Matsya-6000 submersible is developed?
A) To establish India as a global leader in deep-sea fishing
B) To enhance the country’s capabilities in ocean exploration and sustainable resource management
C) To develop advanced underwater weaponry for national defense
D) To promote ocean tourism and recreation in the Indian Ocean
Answer and Explanation: B)
- To enhance the country’s capabilities in ocean exploration and sustainable resource management
- The Deep Ocean Mission is a comprehensive initiative to explore the depths of the ocean for various purposes, including resource discovery, understanding marine ecosystems, and promoting the sustainable use of ocean resources.
- The Matsya-6000 submersible is a key component of this mission
ISRO Develops World’s Largest Vertical Propellant Mixer
Key Development:
- On February 13, 2025, ISRO announced the successful development of a 10-tonne Vertical Planetary Mixer, the largest of its kind for solid propellants globally.
- The mixer was designed and manufactured in collaboration with the Central Manufacturing Technology Institute (CMTI) in Bengaluru.
Significance of Solid Propulsion:
- Crucial Role: Solid propulsion plays a key role in India’s space transportation systems.
- Mixing Process: The new mixer will enhance the efficiency and safety of mixing sensitive and hazardous ingredients used in solid rocket motors.
- Impact: Improved mixing will result in higher-quality propellants, which are vital for the success of space missions.
Features:
- Equipped with multiple hydrostatically driven agitators.
- Remotely controlled via a PLC-based system integrated with SCADA stations.
- Advanced technology ensures precise production of solid propellants.
Collaboration and Development Process:
- Partners: The project was a joint effort between the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) and CMTI.
- Teamwork: The development involved close collaboration with academic institutions and industry experts.
- Testing: Successful completion of factory-level acceptance tests confirms its operational capabilities.
- Goal: This initiative highlights India’s commitment to advancing innovation in space technology.
Impact on Indian Space Missions:
Revolutionary Change: The mixer is expected to revolutionize the production of solid rocket motors.
Benefits: It will increase productivity and throughput in the manufacturing process.
Alignment: This development is aligned with India’s broader mission to achieve self-reliance in critical space technologies.
Milestone: The successful development of the mixer marks a significant milestone in enhancing India’s space capabilities.
What is the primary use of solid propulsion systems in India’s space transportation systems?
A) Liquid fuel is used to propel the launch vehicles.
B) Solid propellants provide higher thrust and better control over propulsion.
C) Solid propulsion is not crucial for India’s space transportation systems.
D) The primary use is for satellite communication systems.
Answer and Explanation: B) Solid propellants provide higher thrust and better control over propulsion.
The “Significance of Solid Propulsion” section highlights the importance of solid propulsion in India’s space transportation systems.
Development and Commercialization of Typhoid Vaccine
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) is soliciting expressions of interest (EoI) for the collaborative development and commercialization of a Typhoid and Paratyphoid vaccine.
Interested manufacturers and companies must fulfill specified technical criteria. Shortlisting will be based on their research and development strategies, existing facilities, and overall capabilities.
Typhoid fever is a bacterial illness caused by the bacteria Salmonella Typhi.
The infection is typically transmitted through contaminated food, water, or direct contact with infected individuals. Without proper treatment, Typhoid can be life-threatening.
Antibiotics such as chloramphenicol, ampicillin, and ciprofloxacin are commonly used to treat the infection.
Typhoid fever represents a substantial public health burden in India, with an estimated 4.5 million cases reported each year.
The prevalence is particularly high in urban areas, making it a significant health concern.
Several Typhoid vaccines are currently available in India, including Typbar-TCV,Ty21a, Typhim Vi, and Typherix.
Typhoid conjugate vaccines (TCVs) are approved for children over 6 months of age, while Vi vaccines are suitable for children aged 2 years and older.
TCVs are currently accessible exclusively through the private healthcare sector.
Recent progress in this field includes the development of an enteric fever vaccine technology by the ICMR-National Institute for Research in Bacterial Infections (NIRBI).
This technology utilizes outer membrane vesicles derived from two strains of typhoidal Salmonella.
Consider the following statements regarding the ICMR’s initiative:
- The ICMR is seeking partners for the development and commercialization of a Typhoid and Paratyphoid vaccine.
- Manufacturers will be selected based on their research and development capabilities, facilities, and strategies.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Correct Answer: c) Both 1 and 2
Project Water worth
- Meta has unveiled Project Waterworth, a significant initiative aimed at enhancing global digital connectivity.
- The project’s ambitious scope involves a subsea cable system covering 50,000 kilometers across five continents.
- This initiative, which will connect the U.S., India, Brazil, South Africa, and other regions, will utilize AI-powered technology to improve the efficiency and reliability of internet networks.
- The project features advanced burial techniques to protect cables from ship anchors and environmental hazards in shallower waters.
- The initiative also features new oceanic corridors, providing greater network capacity and resilience.
- Project Waterworth aims to foster international cooperation, digital inclusion, and technological advancements.
What is the goal of the Health Minister’s Cancer Patient Fund (HMCPF)?
a.To reduce the financial burden of treatment.
b. To provide financial assistance up to ₹5 lakh (potentially ₹15 Lakh) for cancer treatment to patients below the poverty line at 27 Regional Cancer Centres (RCCs).
c. To operate Day Care Cancer Centres in district hospitals.
Correct Answer:b. To provide financial assistance up to ₹5 lakh (potentially ₹15 Lakh) for cancer treatment to patients below the poverty line at 27 Regional Cancer Centres (RCCs).
International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER)
The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) project is a groundbreaking initiative in the field of fusion energy. The recent visit of Prime Minister Narendra Modi to the ITER facility in France, alongside French President Emmanuel Macron, highlights the project’s significance and ongoing progress. ITER’s goal is to demonstrate that fusion power can be a clean, sustainable, and nearly limitless energy source.
What is ITER?
ITER is a collaborative international project that began in 1985, aiming to build the world’s largest magnetic fusion device. This ambitious project seeks to replicate the energy production process of the sun by harnessing the energy released from atomic fusion to generate electricity. Thousands of scientists and engineers have contributed to the design and development of ITER, making it a pivotal effort in the search for alternative energy sources.
The Tokamak: A Fusion Device
At the core of ITER is the tokamak, a device designed to confine and stabilize plasma using magnetic fields. In the tokamak, the fusion of atoms releases energy, which is absorbed by the walls and converted into heat. This heat can then be used to produce steam that drives turbines to generate electricity, similar to conventional power plants. The ITER tokamak is expected to begin deuterium-tritium fusion reactions by 2039, marking a critical milestone in the project.
Significance of ITER
The ITER project holds enormous potential for addressing global energy challenges. Fusion energy offers several compelling advantages, such as:
- Abundant Energy Source: Fusion reactions can generate vast amounts of energy from minimal raw materials, like deuterium and tritium.
- Zero Emissions: Fusion energy produces no greenhouse gas emissions, making it an attractive solution for combating climate change.
- Practical Application: ITER’s success is expected to pave the way for practical fusion power plants, providing a clean and sustainable energy source for future generations.
How Will ITER Work?
The primary goal of ITER is to demonstrate the concept of “burning plasmas,” where the energy produced by fusion reactions sustains the plasma’s temperature. The project will also investigate key technologies for future fusion reactors, including tritium breeding concepts. Achieving this goal will bring ITER closer to making fusion energy a reality for commercial use.
Global Collaboration
ITER is a testament to international collaboration, with 33 nations, including seven key member states—China, the European Union, Japan, Korea, Russia, and the United States—working together for decades to develop and operate the ITER experimental device. Their collective aim is to advance fusion technology toward the design of a demonstration reactor.
India’s Role in ITER
India has been an active participant in the ITER project for over two decades, with around 200 Indian scientists and several industry players, including major companies like L&T and TCS, contributing to its success. Prime Minister Modi’s visit to the ITER facility marked a historic moment, as he became the first Head of State to visit the site. This visit underscores India’s commitment to the project and its potential to transform the global energy landscape.
What is the primary goal of the ITER project?
a. To build the world’s largest solar power plant.
b. To demonstrate the feasibility of fusion power as a clean energy source.
c. To research the effects of climate change on the environment.
d. To develop new methods of fossil fuel extraction.
Correct Answer: b) To demonstrate the feasibility of fusion power as a clean energy source.
Towards a Cancer-Free India
Introduction
- Cancer remains a significant public health challenge in India, with projections indicating a rise in cases.
- In 2023, estimates suggest over 1.4 million cancer cases were reported. The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and its National Cancer Registry Programme (NCRP) play a crucial role in tracking cancer trends and informing policy decisions.
- The government is committed to strengthening cancer care through various policies, interventions, and financial assistance schemes.
Union Budget 2025-26: A Focus on Cancer Care
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare receives a substantial allocation of Rs. 99,858.56 crore in the Union Budget 2025-26, demonstrating the government’s commitment to healthcare.
Specific initiatives targeting cancer care include:
- Day Care Cancer Centers: Expansion of accessible treatment options through the establishment of Day Care Cancer Centers in district hospitals, aiming for 200 centers in 2025-26.
- Customs Duty Exemptions: Reducing the financial burden of treatment by exempting 36 lifesaving drugs and medicines for cancer and other diseases from Basic Customs Duty (BCD), offering concessional customs duty of 5% for six lifesaving medicines, and providing full BCD exemptions for specified drugs and medicines under Patient Assistance Programmes.
Holistic Cancer Control: Key Government Programs
- The Indian government employs a multi-pronged approach to combat cancer, centered around the following programs:
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS): This program focuses on the prevention, early detection, and management of non-communicable diseases, including oral, breast, and cervical cancers.
Key components include:
- Cancer Screening: Implementing screening programs for oral, breast, and cervical cancers at the community level.
- Early Detection & Awareness: Raising public awareness through health workers and digital platforms.
- Infrastructure Strengthening: Establishing Tertiary Cancer Centers (TCCs) and State Cancer Institutes (SCIs).
- The NPCDCS has led to the establishment of numerous facilities nationwide, improving access to cancer screenings and care.
- 770 District NCD Clinics
- 233 Cardiac Care Units
- 372 District Day Care Centres
- 6,410 Community Health Centre NCD Clinics
Strengthening of Tertiary Care for Cancer Scheme: This scheme enhances specialized cancer care facilities to improve access to treatment across states. It has led to the establishment of 19 State Cancer Institutes (SCIs) and 20 Tertiary Care Cancer Centres (TCCCs).
Additionally, institutions like the National Cancer Institute (NCI) in Jhajjar, Haryana, and the Chittaranjan National Cancer Institute (CNCI) in Kolkata are providing cutting-edge treatment and research opportunities.
Ayushman Bharat Yojana: This initiative provides universal health coverage, particularly for vulnerable populations. It ensures timely treatment for cancer patients and covers chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and surgical oncology. As of 2024, over 90% of registered cancer patients have commenced treatment under this scheme.
The Health Minister’s Cancer Patient Fund (HMCPF): This fund provides financial assistance up to ₹5 lakh (potentially ₹15 Lakh) for cancer treatment to patients below the poverty line at 27 Regional Cancer Centres (RCCs).
National Cancer Grid (NCG): This network ensures standardized, high-quality cancer care across India. With 287 member organizations, the NCG treats over 750,000 new cancer patients annually, representing over 60% of India’s cancer burden. It collaborates with Ayushman Bharat – PMJAY to streamline treatment costs and has contributed to the development of electronic health records.
Advancing Cancer Research and Treatment
India is making strides in cancer research and treatment, exemplified by the following:
- India’s First Indigenous CAR-T Cell Therapy: NexCAR19: This ground-breaking therapy, developed through a collaboration between IIT Bombay, Tata Memorial Centre, and ImmunoACT, offers an affordable and effective treatment for blood cancers.
- Quad Cancer Moon-shot Initiative: A partnership between India, the US, Australia, and Japan to eliminate cervical cancer across the Indo-Pacific region. The initiative focuses on scaling up screening and vaccination programs, advancing research, and strengthening global collaboration.
- Expansion of ACTREC: The Advanced Centre for Treatment, Research, and Education in Cancer (ACTREC) is undergoing a major expansion to revolutionize cancer research, treatment, and patient care.
Awareness Generation
The Indian government is actively working to raise awareness about cancer prevention and treatment through:
- Community Awareness: Strengthening preventive measures through Ayushman Aarogya Mandir by promoting wellness activities and targeted communication.
- Media Campaigns: Utilizing print, electronic, and social media to increase public awareness.
- Government Support: Providing funds to states for awareness programs under the National Health Mission (NHM).
- Healthy Eating Promotion: Encouraging nutritious food choices through the Eat Right India campaign.
- Fitness Initiatives: Promoting physical activity through the Fit India Movement and yoga programs by the Ministry of AYUSH.
Conclusion: India is making significant progress in its fight against cancer through comprehensive policies, expanded healthcare infrastructure, financial assistance schemes, and advancements in research and treatment.
The Union Budget 2025-26 highlights the government’s commitment to strengthening cancer care, improving access to treatment, and reducing financial burdens on patients.
While challenges remain in ensuring equitable access and early detection, continued investment in awareness, lifestyle interventions, and technology-driven solutions will be crucial for building a comprehensive and inclusive cancer care system in India.
What is the goal of the Health Minister’s Cancer Patient Fund (HMCPF)?
a. To reduce the financial burden of treatment.
b. To provide financial assistance up to ₹5 lakh (potentially ₹15 Lakh) for cancer treatment to patients below the poverty line at 27 Regional Cancer Centres (RCCs).
c. To operate Day Care Cancer Centres in district hospitals.
Correct Answer:b. To provide financial assistance up to ₹5 lakh (potentially ₹15 Lakh) for cancer treatment to patients below the poverty line at 27 Regional Cancer Centres (RCCs).
Paris AI Action Summit
Introduction
- Cancer continues to be a significant public health challenge in India, with projections indicating an increase in cases in the coming years.
- In 2023, estimates suggest over 1.4 million cancer cases were reported. The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and its National Cancer Registry Programme (NCRP) play a critical role in monitoring cancer trends and guiding policy decisions.
- The government remains committed to enhancing cancer care through various policies, interventions, and financial assistance schemes.
Union Budget 2025-26: A Focus on Cancer Care
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has been allocated Rs. 99,858.56 crore in the Union Budget 2025-26, emphasizing the government’s dedication to healthcare. Specific initiatives focused on cancer care include:
- Day Care Cancer Centers: Expansion of treatment options with the establishment of Day Care Cancer Centers in district hospitals, aiming for 200 centers by 2025-26.
- Customs Duty Exemptions: Reducing the financial burden on patients by exempting 36 lifesaving cancer medicines from Basic Customs Duty (BCD). Additionally, concessional customs duties of 5% for six lifesaving drugs and full BCD exemptions for certain medicines under Patient Assistance Programmes will be offered.
Holistic Cancer Control: Key Government Programs
The Indian government uses a multi-faceted approach to combat cancer through the following programs:
National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS): This program focuses on the prevention, early detection, and management of non-communicable diseases, including cancers such as oral, breast, and cervical. Key components include:
Cancer Screening: Screening programs for oral, breast, and cervical cancers at the community level.
Early Detection & Awareness: Raising public awareness through health workers and digital platforms.
Infrastructure Strengthening: Establishing Tertiary Cancer Centers (TCCs) and State Cancer Institutes (SCIs).
The NPCDCS has contributed to the creation of numerous facilities nationwide, enhancing access to cancer screenings and care:
- 770 District NCD Clinics
- 233 Cardiac Care Units
- 372 District Day Care Centres
- 6,410 Community Health Centre NCD Clinics
Strengthening of Tertiary Care for Cancer Scheme: This initiative improves specialized cancer care facilities to ensure better access across states. It has led to the establishment of 19 State Cancer Institutes (SCIs) and 20 Tertiary Care Cancer Centres (TCCCs). Additionally, institutions like the National Cancer Institute (NCI) in Jhajjar, Haryana, and the Chittaranjan National Cancer Institute (CNCI) in Kolkata are offering advanced treatment and research opportunities.
Ayushman Bharat Yojana: This scheme provides universal health coverage, especially for vulnerable populations. It ensures timely treatment for cancer patients, covering chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and surgical oncology. As of 2024, more than 90% of registered cancer patients have started treatment under this scheme.
The Health Minister’s Cancer Patient Fund (HMCPF): This fund offers financial assistance of up to ₹5 lakh (potentially ₹15 lakh) for cancer treatment for low-income patients at 27 Regional Cancer Centres (RCCs).
National Cancer Grid (NCG): This network aims to standardize high-quality cancer care across India. With 287 member organizations, the NCG treats over 750,000 new cancer patients annually, covering more than 60% of the country’s cancer burden. The NCG collaborates with Ayushman Bharat – PMJAY to streamline treatment costs and has also played a role in developing electronic health records.
Advancing Cancer Research and Treatment
India is making substantial progress in cancer research and treatment, as seen in the following initiatives:
- India’s First Indigenous CAR-T Cell Therapy: NexCAR19: A breakthrough therapy developed in collaboration between IIT Bombay, Tata Memorial Centre, and ImmunoACT, providing an affordable and effective treatment for blood cancers.
- Quad Cancer Moon-shot Initiative: A partnership between India, the US, Australia, and Japan aimed at eliminating cervical cancer across the Indo-Pacific region. The initiative focuses on scaling up screening and vaccination programs, advancing research, and fostering global collaboration.
- Expansion of ACTREC: The Advanced Centre for Treatment, Research, and Education in Cancer (ACTREC) is undergoing significant expansion to enhance cancer research, treatment, and patient care.
Awareness Generation
The Indian government is actively raising awareness about cancer prevention and treatment through the following efforts:
- Community Awareness: Strengthening preventive measures through Ayushman Aarogya Mandir by promoting wellness activities and targeted communication.
- Media Campaigns: Utilizing print, electronic, and social media to increase public awareness.
- Government Support: Allocating funds to states for awareness programs under the National Health Mission (NHM).
- Healthy Eating Promotion: Encouraging nutritious food choices through the Eat Right India campaign.
- Fitness Initiatives: Promoting physical activity through the Fit India Movement and yoga programs by the Ministry of AYUSH.
Conclusion
India is making significant strides in its fight against cancer through comprehensive policies, expanded healthcare infrastructure, financial assistance schemes, and advancements in research and treatment. The Union Budget 2025-26 reflects the government’s ongoing commitment to enhancing cancer care, improving access to treatment, and reducing the financial burden on patients. While challenges remain in ensuring equitable access and early detection, continued investment in awareness, lifestyle interventions, and technology-driven solutions will be critical for building a robust and comprehensive cancer care system in the country.
What opportunity did the Paris AI Action Summit provide for India and France?
a. To establish a military alliance against China.
b. To dominate the global AI market.
c. To showcase their soft power in the AI domain.
d. To lobby for stricter AI regulations.
Correct Answer: C To showcase their soft power in the AI domain
IIT Madras and ISRO Develop IRIS Chip
The Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IIT Madras) and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) have achieved a significant milestone in semiconductor technology with the development and successful testing of an aerospace-quality SHAKTI-based semiconductor chip named IRIS (Indigenous RISC-V Controller for Space Applications). This accomplishment is a part of India’s broader push for self-reliance in technology, aligned with the ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ mission.
Background of the SHAKTI Project
The SHAKTI project, initiated under the ‘Digital India RISC-V’ initiative, is supported by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology. The initiative aims to promote the indigenous development of microprocessor-based products. RISC-V, an open-source Instruction Set Architecture (ISA), provides the necessary flexibility and security to design customized processors.
Development Process of the IRIS Chip
The IRIS chip was designed by the ISRO Inertial Systems Unit (IISU) in Thiruvananthapuram and executed by IIT Madras. The entire process, including chip design, fabrication, and packaging, was carried out within India. The chip was manufactured at the Semiconductor Laboratory (SCL) in Chandigarh and packaged by Tata Advanced Systems in Karnataka.
Features and Applications of the IRIS Chip
The IRIS chip is designed for a wide range of applications, including Internet of Things (IoT) devices and computing systems that meet strategic requirements. It features fault-tolerant internal memories to enhance reliability and incorporates custom functional modules such as CORDIC and WATCHDOG timers, making it particularly suitable for space mission applications.
Significance of the Achievement
This development marks a crucial step toward achieving self-reliance in semiconductor technology within India. The IRIS chip is the third in the series of SHAKTI chips, following RIMO in 2018 and MOUSHIK in 2020. The successful booting of the chip highlights India’s advancing capabilities in creating a robust semiconductor ecosystem.
Future Prospects
ISRO plans to conduct flight tests on a product based on the IRIS controller in the near future. The successful development of this chip is expected to significantly enhance the performance of future embedded controllers for space missions.
What is the significance of the successful booting of the IRIS chip?
a. It indicates the chip will fail in future tests.
b. It highlights India’s capability in developing a semiconductor ecosystem.
c. It proves that RISC-V is obsolete.
d. It shows that space applications are unnecessary.
Answer: B) It highlights India’s capability in developing a semiconductor ecosystem.
Government schemes
9 Years of Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana
The Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY), launched in 2016 by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, marked its nine-year anniversary on February 18, 2025. This crucial scheme has become a key pillar of support for Indian farmers, helping stabilize their incomes and promote modern agricultural practices.
Core Objectives and Coverage:
- The primary aim of PMFBY is to protect farmers from financial difficulties caused by unpredictable natural disasters.
- The scheme offers comprehensive insurance coverage for losses resulting from events such as droughts, floods, hailstorms, and pest infestations.
- This essential financial safety net enables farmers to recover from setbacks and continue their agricultural activities.
Government Commitment and Investment:
The Union Cabinet recently approved the continuation of PMFBY and the Restructured Weather-Based Crop Insurance Scheme (RWBCIS) through 2025-26, reaffirming the government’s strong commitment. A substantial budget of ₹69,515.71 crore has been allocated to support these vital schemes.
Technological Integration:
PMFBY leads the way in adopting advanced technology to enhance efficiency and accuracy. Satellite imagery, drones, and remote sensing technologies are employed for:
- Crop area estimation
- Yield assessment
- Damage evaluation
The implementation of the YES-TECH system during Kharif 2023 further improves the precision of yield estimates, resulting in more timely and fair claim settlements.
Key Advantages for Farmers:
PMFBY offers several significant benefits to farmers:
- Subsidized Premiums: Farmers pay a maximum premium of 2% for Kharif crops and 1.5% for Rabi crops, with the government covering the remaining cost.
- Comprehensive Risk Coverage: The scheme provides protection against a wide range of risks.
- Timely Compensation: Farmers typically receive compensation within two months of harvest, minimizing delays and preventing financial distress.
- Coverage for Prevented Sowing: Farmers can claim indemnity if adverse weather conditions prevent them from planting crops.
Growing Participation and Impact:
- PMFBY has seen steady growth in participation since its launch.
- In the 2023-24 period, non-loanee farmers accounted for 55% of total coverage, reflecting increased trust and confidence in the scheme.
- Several state governments have waived premium contributions for farmers, further easing their financial burden.
Global Recognition:
PMFBY is now the largest crop insurance scheme in the world based on the number of farmer applications. Its success serves as a benchmark for similar initiatives worldwide.
What is the primary goal of the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) scheme?
A) To promote modern agricultural practices in India
B) To shield farmers from financial hardships arising from natural calamities
C) To provide subsidies to farmers for purchasing farm inputs
D) To promote the use of organic farming practices in India
Answer and Explanation: B) To shield farmers from financial hardships arising from natural calamities
PMFBY is aimed at providing financial protection to farmers in case of crop losses due to natural calamities such as droughts, floods, hailstorms, and pest infestations.
This ensures that farmers can recover from financial setbacks and continue their agricultural activities.
NAMASTE Scheme
The NAMASTE (National Action for Manual Scavenging System Transformation) scheme is designed to ensure zero fatalities and make the sanitation sector safer for workers. Union Minister for Social Justice and Empowerment (SJ&E), Dr. Virender Kumar visited Jammu recently. On the occasion, he distributed Ayushman health cards and PPE kits to Safai Mitras under the flagship NAMASTE Scheme
NAMASTE Scheme Objectives:
- Zero Fatalities: The primary aim is to eliminate fatalities among sanitation workers.
- Skilled Workforce: Ensuring all sanitation work is performed by skilled workers.
- Elimination of Contact: Eliminating direct contact with human faecal matter.
- Worker Collectivization: Promoting the formation of Self-Help Groups (SHGs) to empower sanitation workers.
Key Features of NAMASTE:
- Identification of Workers: Identification of Sewer and Septic Tank Workers (SSWs).
- Training: Providing occupational training for workers.
- PPE Kits: Distributing Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) kits.
- Health Insurance: Offering health insurance under the Ayushman Bharat scheme.
- Financial Support: Providing financial support to promote mechanization and enterprise development.
- Combating Manual Scavenging: The NAMASTE scheme helps address the manual scavenging problem by promoting mechanization. The scheme also facilitates training to sanitation workers.
Government Support:
- The government is actively pursuing legislative measures to support sanitation workers.
- These measures include the Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation (Amendment) Bill.
- There are also provisions for compensation to families of sanitation workers who have died while performing their duties.
- The Act also provides protection to sanitation workers under the Scheduled Castes, ensuring their rights and dignity.
The NAMASTE scheme also aims to:
a.Promote the use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) kits.
b. Eliminate the need for mechanization in the sanitation sector.
c. Enhance the skills of sanitation workers and make the sanitation sector safer.
d. Reduce the compensation given to families of sanitation workers who have died on duty.
Answer: (C) Enhance the skills of sanitation workers and make the sanitation sector safer.
Explanation: The text mentions the provision of health insurance, financial support, and PPE kits under the NAMASTE scheme.
The President of India Inaugurates Aadi Mahotsav – 2025
The Aadi Mahotsav 2025, a flagship initiative of the Tribal Co-operative Marketing Development Federation of India Limited (TRIFED), was inaugurated by Hon’ble President of India, Smt. Droupadi Murmu, at the Major Dhyan Chand National Stadium in New Delhi.
The festival, which will run from February 16 to 24, 2025, showcases the diverse culture, arts, crafts, cuisine, and commerce of India’s tribal communities.
Key Highlights of Aadi Mahotsav 2025
- Over 600 tribal artisans from 30 states and union territories will participate
- in the festival.
- 500 performing artists will showcase mesmerizing tribal dance forms, including Chhau Dance, Kalbelia Dance, Gaur Mariya Dance, Siddhi Dhamal Dance, and Angi Ger Dance.
- 25 tribal food stalls will offer indigenous cuisines from different regions, providing a unique culinary experience.
- The festival will feature live painting sessions, interactive sessions with artisans, and state and international pavilions showcasing unique tribal crafts.
Empowering Tribal Artisans and Entrepreneurs
Hon’ble President Smt. Droupadi Murmu emphasized the significance of Aadi Mahotsav in empowering tribal artisans and entrepreneurs. She highlighted the importance of education in the development of tribal society, citing the example of over 1.25 lakh tribal children being provided school education through Eklavya model residential schools.
Transformative Initiatives for Tribal Welfare
Under the leadership of Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi, the government has launched transformative initiatives for the holistic development of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs). These include:
- PM-JANMAN Abhiyan, with a budget of ₹24,000 crore, ensuring doorstep delivery of essential services.
- Dharti Aba Janjati Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan, with a budget of ₹80,000 crore, focusing on connecting tribal villages to roads and mobile networks, providing permanent housing, and ensuring tribal citizens benefit from government welfare schemes.
Support from Union Ministers
- Union Minister for Tribal Affairs, Shri Jual Oram, commended the festival, stating that it is a testament to the rich cultural heritage of tribal communities.
- Minister of State for Tribal Affairs, Shri Durga Das Uikey, highlighted the festival’s economic impact, stating that it strengthens the livelihoods of tribal artisans by providing access to national and international markets.
Global Recognition
- Aadi Mahotsav 2025 has garnered international attention, with delegations from Sri Lanka and Indonesia participating in the festival.
- The event has also seen the signing of MoUs with design institutes, corporate houses, and e-commerce platforms, further expanding opportunities for tribal entrepreneurs.
A Movement for Tribal Empowerment
Aadi Mahotsav is more than just a festival – it is a movement fostering economic self-reliance, cultural preservation, and social empowerment for India’s tribal communities. By bridging tradition with modernity, the event ensures that tribal India’s invaluable contributions are recognized, respected, and celebrated globally.
Which initiative, launched by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi, aims to connect tribal villages to roads and mobile networks?
a) PM-JANMAN Abhiyan
b) Dharti Aba Janjati Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan
c) Aadi Mahotsav
d) Tribal Welfare Scheme
Answer: b) Dharti Aba Janjati Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan
63rd session of the Commission for Social Development (CSoCD)
India participated in the 63rd session of the Commission for Social Development (CSoCD) held from February 10 to 14, 2025, in New York, USA.
- This delegation was led by Savitri Thakur, Minister of State for the Ministry of Women and Child Development, Government of India.
- The session aimed to foster discussions and collaborations on pressing social development challenges, with a strong emphasis on advancing inclusive social policies and enhancing global social well-being.
- Notably, the event saw the participation of representatives from 49 countries, including ministers from 16 nations such as France, Türkiye, Saudi Arabia, and Sweden. Financial Commitment:
- Total Budget: ₹5,000 crore over five years.
- Specific allocation for fiscal year 2024-25: ₹1,000 crore.
- Minimum project cost under the scheme: ₹3 lakh.
- India actively engaged in key discussions during the session. On February 11, 2025, Savitri Thakur delivered India’s statement at the Ministerial Forum, focusing on the priority theme: “Strengthening Solidarity and Social Cohesion.”
- Thakur underlined that India is guided by the vision of “Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas, Sabka Vishwas” (Development for All), with a central focus on inclusivity.
- Through initiatives such as the JAM TRINITY (Jan Dhan, Aadhar, Mobile), the country has achieved significant financial inclusion for marginalized communities, particularly for women, persons with disabilities, and the elderly.
- Furthermore, India has embraced a “Women-led Development” approach, ensuring that women play a vital role in shaping the nation’s development trajectory.
- The minister elaborated on large-scale programs aimed at bridging the gender digital divide, promoting digital and financial literacy, particularly in rural areas.
- These initiatives have empowered millions of women entrepreneurs, facilitating their transition from start-ups to scalable businesses.
What is the main goal of India’s participation in the 63rd session of the CSoCD?
a. To promote women’s empowerment
b. To accelerate global progress and support the Commission’s efforts in crafting a just world for all
c. To discuss human rights issues
d. To promote sustainable development
Answer: B) To accelerate global progress and support the Commission’s efforts in crafting a just world for all
Environment
TrailGuard AI
TrailGuard AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming anti-poaching strategies in wildlife conservation.
- Recent technological advancements have led to reductions in poaching incidents.
- The Similipal Tiger Reserve in Odisha exemplifies AI’s effectiveness in wildlife protection through TrailGuard AI.
Key Facts About Similipal Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Mayurbhanj District, Odisha (northernmost part).
- Area: Covers 2750 sq.km.
- Features: Famous waterfalls (Joranda, Barehipani), part of Mayurbhanj Elephant Reserve.
- Terrain: Hilly and undulating, with grasslands and forests.
History & Protection Status:
- Tiger Reserve (1973) under Project Tiger.
- Wildlife Sanctuary (1979).
- National Park proposal (1980).
- UNESCO Biosphere Reserve (2009).
About TrailGuard AI:
- Consists of 100-150 cameras equipped with an AI model.
- Function: Monitors the reserve and identifies poachers.
- Detection: Detects movement and captures images.
- Analysis: AI analyzes images for threats.
- Response: Enables wildlife officials to respond quickly to potential poaching activities.
Impact on Poaching Incidents:
- Arrests & Seizures: Facilitated the arrest of 96 poachers and seizure of over 86 firearms in the past year.
- Identification: Proved effective in identifying poachers through photo identification.
- Results: Led to successful house raids.
- Potential: Officials believe poaching could decrease by up to 80% with continued use.
Operational Mechanism:
- Power Mode: Cameras operate on a low-power mode, switching to high-power on movement detection.
- On-site Inference: Perform AI inference on-site, classifying objects.
- Image Transmission: Images deemed as threats sent to control room within 30-40 seconds.
- Enforcement: Rapid communication enables timely enforcement actions.
Collaboration with Local Communities:
- Behavioral Change: The presence of AI technology has altered the behaviour of local communities.
- Impact: Many villagers avoid entering the forest.
- Engagement: The forest department is engaging with these communities to facilitate safe access and conduct awareness programmes.
Future Prospects and Applications:
- Expansion: TrailGuard AI’s success at Similipal has prompted interest in deployment in other regions.
- Implementation: The system has been implemented in multiple states (Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh).
- Potential: Potential extends beyond anti-poaching to monitoring wildlife and managing human-wildlife conflicts.
Advantages of TrailGuard Technology:
- Design: Compact and durable.
- Battery Life: Long battery life (six months to a year).
- Cost-Effectiveness: Accessible for conservation efforts.
- Theft Prevention: Unique design minimises risk of theft.
What is the primary function of TrailGuard AI in wildlife conservation?
A) To track the migratory patterns of tigers.
B) To monitor the overall health of the forest ecosystem.
C) To identify and alert wildlife officials to potential poaching activities.
D) To facilitate the collection of scientific data on wildlife behavior.
Answer and Explanation: C) To identify and alert wildlife officials to potential poaching activities.The text highlights that TrailGuard AI’s core function is to monitor the reserve and identify potential threats, specifically poaching incidents, through image analysis and rapid communication.
Key Facts about Parambikulam Tiger Reserve
Headline & Focus: A faunal survey adds 15 new species, highlighting the rich biodiversity of the reserve. The survey highlights the vibrant biodiversity and the importance of the reserve.
Key Points:
- The survey adds 15 new species to the checklist.
- The Forest Department performed the survey.
- The survey was in the Parambikulam Tiger Reserve.
About Parambikulam Tiger Reserve:
- Location: The reserve is located in the districts of Palakkad and Thrissur in Kerala.
- Protection Status: It’s a Tiger Reserve declared under Project Tiger.
- Area: The area covers 391 sq.km.
- Rivers: The Parambikulam, Sholayar, and Thekkady rivers flow through the reserve.
- Importance: The reserve is home to four tribes.
The tribes are Kadar, Malasar, Muduvar, and Mala Malasar.
Flora: The reserve’s is home to diverse flora, including mixed deciduous, evergreen, and semi-green habitats.
It also has other habitats such as montane and marshy grasslands, along with teak plantations, supporting its rich biodiversity.
Fauna: The reserve is a host to diverse fauna.
- It hosts one of the densest gaur populations and has many mammals, including Bengal tigers, Asian elephants, and the more uncommon lion-tailed macaques.
- The reserve is home to two endemic species of the region. The two endemic species are Tomp, and Garro
- The reserve is home to the endemic species of the region.
What is the primary significance of the recent faunal survey conducted in the Parambikulam Tiger Reserve?
A) To assess the economic viability of extracting timber from the reserve.
B) To identify and document new species, highlighting the reserve’s biodiversity.
C) To evaluate the impact of tourism on the reserve’s ecosystem.
D) To determine the optimal locations for establishing new human settlements.
Answer and Explanation: B) To identify and document new species, highlighting the reserve’s biodiversity.
The headline clearly states the focus of the survey: to add new species to the checklist, thereby highlighting the richness of the reserve’s biodiversity.
Parliamentary Panel Recommends Minimum Price for Paddy Residue to Curb Stubble Burning
A parliamentary panel has suggested establishing a minimum price mechanism for paddy residue, similar to the Minimum Support Price (MSP) for crops, to discourage farmers from burning crop residue in the fields.
Why is Stubble Burning a Concern?
Stubble burning, a practice primarily prevalent in Punjab, Haryana, and western Uttar Pradesh, results in severe air pollution in Delhi-NCR, causing smog and high PM2.5 levels, worsening respiratory diseases. It also harms soil fertility, increases dependence on chemical fertilizers, and contributes to climate change by releasing greenhouse gases.
Why Do Farmers Burn Stubble?
- Time constraints between paddy harvesting and wheat sowing.
- High costs of alternative methods, despite subsidies.
- Lack of a fixed market price for selling paddy straw.
- Limited awareness and inadequate incentives.
Key Recommendations:
- Minimum Price for Paddy Residue: A mechanism should be set up to benchmark and notify minimum prices annually before the Kharif harvest season. The price should cover farmers’ collection costs, including labor and machinery expenses.
- Subsidies: The government should subsidize machinery like happy seeders, rotavators, and mulchers for in-situ paddy straw management.
- Promotion of Short-Duration Paddy Varieties: State governments should discourage long-duration paddy varieties like PUSA 44 and promote short-duration alternatives.
- Developing a National Bioenergy Policy: A unified national policy to integrate agricultural residue into bioenergy production.
- Others: Address ex-situ crop residue management costs, provide financial incentives, improve supply chain infrastructure, and raise awareness among farmers to ensure economic viability and environmental sustainability.
What is the primary purpose of the parliamentary panel’s recommendation to establish a minimum price mechanism for paddy residue?
a. To increase the income of farmers.
b..To encourage farmers to burn crop residue.
c. To discourage farmers from burning crop residue.
d. To support the use of chemical fertilizers.
Answer: (C) To discourage farmers from burning crop residue.
Explanation: The text clearly states that the panel suggests a minimum price to discourage farmers from burning crop residue.
Sagar Island
Climate change, particularly rising sea levels and erosion, is having a significant impact on Sagar Island in West Bengal’s Sundarbans, with a particular focus on the annual Gangasagar Mela and the threats to the Kapil Muni temple. This issue also touches on the political aspects of the event, the struggles faced by the local community, and the dynamics between the Centre and the State regarding financial assistance.
Key Points:
Gangasagar Mela:
- The Gangasagar Mela is an annual religious fair held on Sagar Island during Makar Sankranti.
- It attracts millions of pilgrims who come to take a holy dip at the confluence of the Ganga and the sea.
- The West Bengal government promotes the event and provides the necessary arrangements.
- The state government claims over a crore of pilgrims attend the mela, though these figures are often questioned.
- There are calls for the mela to be granted national status by the central government, similar to the Kumbh Mela.
Erosion and Climate Change:
- Rising sea levels are causing severe erosion on Sagar Island, with the sea encroaching on the Kapil Muni temple, threatening its existence.
- Erosion is affecting local communities by disrupting fishing and leading to more displacement due to frequent cyclones.
- Climate change experts argue that the large-scale infrastructure development for the mela is contributing to increased erosion, violating Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) guidelines.
Kapil Muni Temple:
- The Kapil Muni temple, a sacred site on Sagar Island, is central to the Gangasagar Mela.
- The temple is increasingly threatened by the advancing sea, with priests raising concerns about its future.
Government Initiatives and Accusations:
- A ₹4,100-crore project is proposed between the West Bengal government and the World Bank to strengthen embankments and mitigate erosion in the Sundarbans.
- The West Bengal government accuses the Union government of not cooperating on funding for the Gangasagar Mela, unlike the support given for the Kumbh Mela.
- The Chief Minister has appealed to the Kapil Muni temple trust to allocate funds for constructing concrete embankments to protect the temple.
Local Community Impact:
- Villages like Bamkimnagar are suffering due to the rising sea levels and cyclones, with many people losing their livelihoods as salinity increases and fishing becomes restricted during the mela.
- Communities frequently face displacement to cyclone relief shelters.
- Mangrove deforestation for construction activities worsens the impact of tidal surges, while youth migration is on the rise due to diminishing local employment opportunities.
Political Dimensions:
- The Trinamool Congress government’s promotion of the Gangasagar Mela is seen as a “soft Hindutva push” to counter the influence of the BJP.
- Shankaracharya has expressed concerns about the erosion and tree cutting for infrastructure but has also criticized the State government’s plan to build a Lord Jagannath temple.
Environmental Concerns:
- Large-scale construction on the island’s ecologically fragile beaches has exacerbated erosion.
- Destruction of mangrove forests for infrastructure projects increases the island’s vulnerability to tidal surges and storm damage.
Contradictions and Concerns:
- The claims of high pilgrim numbers have been questioned by RTI activists.
- Shankaracharya has raised concerns about the cost of development in the region, questioning whether it is worth the environmental degradation amidst the ongoing threat of climate change.
What does the West Bengal government accuse the Union government of regarding the Gangasagar Mela?
a.Interfering with the arrangements for the fair.
b. Not providing adequate financial support compared to the Kumbh Mela.
c. Promoting religious tourism in other states at the expense of West Bengal.
d. Imposing restrictions on the number of pilgrims allowed to visit the island.
Correct Answer: b) Not providing adequate financial support compared to the Kumbh Mela
6. Biology / Microbiology / Cytology (Cell Biology)
Ovoid cells
Key Information
- Discovery: Researchers have discovered a new type of neuron, named “ovoid cells” that plays a fundamental role in recognition memory.
- Function: Ovoid cells get activated when we encounter something new and play an important role in recognizing objects.
- Impact: This discovery could aid in understanding and treating brain disorders and memory impairments like Alzheimer’s disease, Autism Spectrum Disorder, and epilepsy.
Additional points about Ovoid Cells:
- Location: These cells are present in the hippocampus.
- Number: The cells are present in small numbers.
- Shape: These cells’ egg-like shapes give them their name.
- Significance: The specialized neurons get activated each time we encounter something new and store the objects in the memory and allow us to recognize them months potentially years later.
- Function: They trigger a process that stores those objects in memory and allows us to recognize them months potentially even years later.
- Distinctiveness: They are distinct from other neurons in their cellular and functional levels and also in the neural circuitry.
- Neurons:
- Neurons are known as a nerve cell and are specialized cells in the nervous system.
- They play a key role in processing and transmitting information within the body.
- They are the basic building blocks of the nervous system.
What is the primary function of the newly discovered “ovoid cells”?
A) To regulate motor functions within the central nervous system
B) To play a fundamental role in recognition memory, particularly for novel objects
C) To transmit sensory information from the peripheral nervous system to the brain
D) To facilitate language processing and speech comprehension
Answer and Explanation: B) To play a fundamental role in recognition memory, particularly for novel objects.
The key finding is that ovoid cells are activated when we encounter something new and are crucial for the process of recognizing objects and storing those memories.
FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE (FMD)
Foot and mouth disease (FMD) is a highly contagious viral disease affecting livestock, leading to significant economic repercussions. In response, the Union Government has implemented several measures, outlined below:
National Animal Disease Control Programme (NADCP): Launched in 2019, this initiative offers 100% central assistance to states and Union Territories for FMD vaccination. As of 2021, NADCP has been incorporated into the Livestock Health and Disease Control Programme (LHDCP).
Centralized Procurement and Supply: The government oversees the procurement and supply of quality FMD vaccines and ear tags for states and Union Territories.
Financial Support for States and UTs: Financial assistance is provided for the purchase of vaccination accessories, enhancement of cold chain infrastructure, and awareness initiatives for stakeholders.
Support for Research Institutions: Financial backing is extended to various research institutions, including the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), National Institute of Foot and Mouth Disease (NIFMD) in Bhubaneswar, Indian Veterinary Research Institutes (IVRI) in Bareilly and Bengaluru, and the National Institute of Veterinary Epidemiology and Disease Informatics (NIVEDI) in Bengaluru, for FMD-related activities.
Data Management: Data on livestock registration using ear tags and vaccination records is uploaded to the Bharat Pashudhan portal.
Vaccination Statistics: As of January 2025, a total of 107.34 crore vaccinations against FMD have been administered under the NADCP. The vaccinations have been conducted in rounds, with the following figures: 16.91 crore for Round I, 24.18 crore for Round II, 24.23 crore for Round III, and 24.84 crore for Round IV. Rounds V and VI are currently underway, with 14.89 crore and 2.29 crore vaccinations completed, respectively.
Review Mechanisms: On August 17, 2024, the Department conducted a review to assess progress towards achieving an FMD-free Bharat. Regional review meetings are organized twice a year, gathering representatives from all states and Union Territories to evaluate ongoing initiatives, address challenges, and share best practices. Additionally, national meetings, such as the monsoon meet and various conclaves, are held to review FMD control measures with state and UT officials.
Reduction in Outbreaks: There has been a notable decline in FMD outbreaks, dropping by over 60% in the five years following the implementation of NADCP. Recent outbreaks are sporadic and generally affect a limited number of animals.
Surveillance and Monitoring: Timely sampling plans are shared with states, while seromonitoring indicates an increasing trend in protective titres. Additionally, serosurveillance values are demonstrating a decreasing trend, highlighting the success of the vaccination program.
Support under LHDCP: The LHDCP offers 100% assistance to all states and Union Territories for controlling and eradicating FMD in accordance with the scheme’s operational guidelines. Although establishing FMD-free zones is viewed as an intermediate measure tailored to regional needs, currently, nine states—Gujarat, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Punjab, Haryana, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Uttarakhand—have been identified for special focus to achieve FMD-free status. Further expansion to include additional states will depend on specific needs and circumstances.
What is the name of the organization providing financial backing to research institutions under the FMD control program?
a. Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR)
b. National Institute of Foot and Mouth Disease (NIFMD)
c. Indian Veterinary Research Institutes (IVRI)
d.National Institute of Veterinary Epidemiology and Disease Informatics (NIVEDI)
Answer: a) Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR)
International Relations
Indian Ocean: Strategic Significance & India’s Role
The Indian Ocean Region (IOR) faces significant geopolitical competition and security challenges, prompting India to advocate for multilateral maritime collaboration, such as a “coordinated flotilla,” as highlighted by External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar.
Overview of the Indian Ocean: The third-largest ocean, spanning approximately 9,600 km from the Bay of Bengal to Antarctica and 7,800 km from South Africa to Western Australia. It boasts a 70,000 km coastline encompassing major economies.
Demographics: Home to 35% of the world’s population and 40% of the global coastline.
Historical Significance: Named after India, reflecting its historical influence on maritime trade. Served as a crucial trade route since the first millennium, connecting India with the Arab world, Southeast Asia, and Africa. The Silk Route and spice trade flourished through the Indian Ocean, linking Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Strategic Importance:
- A vital global trade route, facilitating 70% of the world’s container traffic.
- 80% of India’s external trade and 90% of its energy imports transit through the Indian Ocean.
- Critical oil supply routes from West Asia to India, China, Japan, and Europe pass through the region.
- India’s central position grants strategic control over key maritime chokepoints:
- Strait of Hormuz (Iran-Oman), vital for oil shipments.
- Bab el-Mandeb (Yemen-Djibouti), the gateway to the Red Sea & Suez Canal.
- Strait of Malacca (Indonesia-Malaysia), a key trade passage for East Asia.
Challenges in the Indian Ocean Region:
Maritime Security Threats: Frequent pirate attacks and trafficking, particularly near Somalia and the Gulf of Aden.
Economic & Environmental Issues: Overfishing and deep-sea mining threaten marine ecosystems.
Climate Change & Rising Sea Levels: Small island nations face coastal erosion and the risk of submersion.
Humanitarian Crises & Disasters: Natural disasters such as cyclones, tsunamis, and oil spills necessitate coordinated disaster response.
Geopolitical Rivalries: Growing influence of the U.S., China, UK, and France fuels power struggles in the region.
India’s Policy Shift in the Indian Ocean:
Strengthening Regional Ties: India actively engages with IOR nations through:
- Indian Ocean Conference (IOC).
- Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
- Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS).
- Colombo Security Conclave.
SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region):
Launched in 2015 under PM Modi, aiming to:
- Strengthen India’s leadership in the IOR.
- Ensure free and open sea lanes for secure global trade.
- Promote sustainable maritime development.
Enhancing Blue-Water Capabilities:
Naval Expansion: Modernizing the navy with indigenous aircraft carriers and advanced submarines.
Maritime Surveillance: Deployment of P-8I Poseidon aircraft and satellite-based tracking systems.
Quad Cooperation: Collaboration with the U.S., Japan, and Australia on maritime security, anti-submarine warfare, and intelligence sharing.
Which of the following statements BEST describes the strategic significance of the Indian Ocean Region (IOR)?
a. It is the largest ocean, covering the majority of the Earth’s surface.
b. It is primarily a fishing ground, with limited impact on global trade and geopolitics.
c. It is a crucial global trade route, controlling key maritime chokepoints, and vital for energy supplies, influencing trade and geopolitics.
d. It is strategically important only for India due to its geographical proximity.
Correct Answer: c. It is a crucial global trade route, controlling key maritime chokepoints, and vital for energy supplies, influencing trade and geopolitics.
Exercise Komodo:
The Indian Navy is actively participating in Exercise Komodo 2025, a non-combat military exercise aimed at fostering maritime cooperation among friendly nations. The exercise is being hosted by the Indonesian Navy in Bali, Indonesia, and has been underway since 2014.
Exercise Komodo: A Platform for Maritime Cooperation
- Exercise Komodo is a multilateral naval exercise that brings together naval forces from various countries to promote maritime cooperation, enhance interoperability, and strengthen partnerships in the Indo-Pacific region.
- This aligns with India’s SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) vision, which emphasizes the importance of maritime security and stability in the region.
Participation by INS Shardul and P8I Long Range Maritime Surveillance Aircraft
The Indian Navy is participating in Exercise Komodo 2025 with INS Shardul and P8I Long Range Maritime Surveillance aircraft. This demonstrates India’s commitment to strengthening maritime partnerships and enhancing regional security through collaborative efforts.
Objectives of Exercise Komodo
The primary objectives of Exercise Komodo include:
- Fostering maritime cooperation among friendly nations
- Enhancing interoperability with ASEAN Navies and QUAD partners
- Promoting regional security and stability through collaborative efforts
By participating in Exercise Komodo, the Indian Navy is contributing to the security and stability of the Indo-Pacific region, while also strengthening its relationships with friendly nations.
Which of the following is the primary objective of Exercise Komodo?
a. Fostering economic cooperation among nations
b. Enhancing regional security and stability through collaborative efforts
c. Promoting tourism and cultural exchange among nations
d. Enhancing space exploration and research efforts
Answer: b) Enhancing regional security and stability through collaborative efforts
Early Warnings for All (EW4All) Initiative
The United Nations launched the Early Warnings for All (EW4All) initiative in 2022 with the goal of implementing effective early warning systems (EWS) by the end of 2027.
The initiative aims to protect vulnerable populations from hazardous weather and climate events.
Funding Landscape for Early Warning Systems:
- Increased Funding: Funding for early warning systems reached unprecedented levels in 2023.
- Uneven Distribution: Investment is not evenly distributed. Five countries (China, Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Indonesia) account for 54% of national EWS investments.
- Funding Gaps: Small Island Developing States (SIDS) and Least Developed Countries (LDCs) face funding gaps.
- Global Observatory: The Global Observatory for Early Warning System Investments, launched in December 2024, tracks and optimizes these investments.
Financial Imbalance in EWS Investments:
- Loan Dependency: Only 25% of reported EWS financing comes from grants, with the remaining 75% sourced from loans and credits.
- This financial imbalance poses challenges for sustainability.
Project Overview and Global Reach:
- Project Coverage: As of February 2025, the observatory documented 329 projects across 127 countries in Africa, Asia, the Americas, and Oceania.
- Project Status: 276 projects are ongoing, with 53 in the pipeline.
- Major Financiers: The World Bank and the Green Climate Fund are among the major financing institutions involved.
- Prioritization: The initiative seeks to prioritize resources for the most vulnerable communities.
Collaboration and Technological Integration:
- International Collaboration: The observatory will deepen collaboration with international finance institutions.
- AI Integration: It will leverage artificial intelligence to improve analytical capabilities.
- Evidence-Based Decision-Making: This integration aims to categorize EWS funding more precisely and support evidence-based decision-making.
Global Status of Multi-Hazard Early Warning Systems:
- MHEWS Coverage: A 2024 report on Multi-Hazard Early Warning Systems (MHEWS) found that half of the countries in most regions have established MHEWS.
- Regional Variance: The Asia and Pacific region leads with 67% coverage, while the Americas and Caribbean lag behind at 40%.
Urgency of Addressing Funding Gaps:
- Critical Deadline: As the 2027 target approaches, addressing funding gaps is crucial for the success of EW4All.
- Equitable Access: Equitable access to financial resources is vital to ensure EWS reach those in need.
Mitigation of Impacts: This is vital to mitigate the impacts of climate change and save lives
Which of the following statements best describes the primary challenge facing the Early Warnings for All (EW4All) initiative as the 2027 deadline approaches?
a. The lack of technological advancements in early warning systems.
b. The uneven distribution of funding, with a significant reliance on loans and credits, particularly impacting vulnerable nations.
c. The absence of international collaboration among financial institutions.
d. The lack of projects implemented across different regions.
Answer: (B) The uneven distribution of funding, with a significant reliance on loans and credits, particularly impacting vulnerable nations.
Explanation:
The text highlights the following key issues:
- Uneven Funding: The text emphasizes the uneven distribution of EWS funding, with a few countries receiving the majority.
- Loan Dependency: The high percentage of funding coming from loans/credits is presented as a challenge.
- Impact on Vulnerable Nations: The funding gaps faced by SIDS and LDCs are explicitly mentioned, stressing the impact on those most at risk.
- 2027 Deadline: The “Urgency of Addressing Funding Gaps” section clearly states that addressing these funding issues is crucial for the initiative’s success as the 2027 target date approaches.
Concerns Related To China’s Dam Project
A Massive Hydropower Dam: China plans to build a 60 GW hydropower dam on the Brahmaputra River (Yarlung Tsangpo) in Tibet. This project is the central focus of the news.
Scale and Context:
- Capacity: 60 GW, three times the capacity of the Three Gorges Dam.
- Location: Great Bend of the Brahmaputra in Medog County, Tibetan Autonomous Region.
- China’s Goal: Reduce reliance on fossil fuels and achieve carbon neutrality by 2060.
- Previous Projects: China has experience with large dam projects, including the Three Gorges Dam and Zangmu Dam.
The River: Yarlung Tsangpo/Brahmaputra:
- Origin: Flows through Arunachal Pradesh (India, as Siang), Assam (India, as Brahmaputra), and Bangladesh.
- Basin: Extends to Bhutan (96% of its area).
Implications of the Mega-Dam Project:
Environmental and Ecological Concerns:
- Altered Water Flow and Sediment Reduction: Dams trap sediment, reducing soil fertility for downstream agriculture in India and Bangladesh.
- Increased Risk of Flash Floods: Sudden water releases could cause devastating floods. The article emphasizes past incidents.
- Biodiversity Loss and Habitat Destruction: Threat to aquatic species, including the Gangetic dolphin.
- Glacial Melt and Climate Change Effects: The Tibetan Plateau is a critical region for the Earth’s cryosphere and global climate, and this project can influence climate patterns.
- Seismic Risks: The dam’s location in a seismically active region raises concerns about earthquakes, landslides, and environmental degradation.
Geopolitical Ramifications:
- India’s Vulnerability: India fears China could use its control over the river for strategic purposes, controlling water flow.
- Legal and Diplomatic Challenges:
- China is not a signatory to the UN Convention on the Law of the Non-navigational Uses of International Watercourses.
- The India-China Expert Level Mechanism (ELM) exists for data sharing but lacks a comprehensive treaty.
- Conflict with Southeast Asian Nations: Similar concerns exist regarding the Mekong River (shared with several countries in the region).
Economic and Social Impact: Forced relocation of communities and disruption to irrigation and fishing, threatening food security.
India’s Response and Possible Strategies:
- Developing its Own Water Infrastructure: Building dams and hydropower projects in Arunachal Pradesh (e.g., Siang Upper Multipurpose Project).
- Strengthening Diplomacy: Engaging with Bangladesh and other regional stakeholders for a united front on water management.
- Enhancing Satellite Monitoring and Early Warning Systems: Improving surveillance and flood prediction.
What is a significant risk associated with the dam’s location in a seismically active region?
a Earthquakes and landslides
b. Floods and droughts
c. Tsunamis and storms
d. Volcanic eruptions and wildfires
Correct Answer: a) Earthquakes and landslides
Global Corruption Index
The Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) ranks 180 countries based on the perceived level of public sector corruption, using a scale of 0 to 100, where 0 represents highly corrupt and 100 signifies very clean governance. Below are the key highlights and trends:
Overall Results:
- Denmark holds the top spot as the least corrupt country globally.
- South Sudan ranks as the most corrupt, with a score of only 8 points.
- The CPI measures public sector corruption across 180 countries and territories, with a scale from 0 (highly corrupt) to 100 (very clean).
India’s Ranking:
- India ranks 96th, falling three positions from 93rd last year.
- India’s CPI score has decreased from 39 in 2023 to 38 in 2024.
Rankings of Neighboring Countries:
- Pakistan: 135th position.
- Sri Lanka: 121st position.
- Bangladesh: 149th position.
- China: 76th position.
Global Trends:
- Major global powers like the United States and France saw declines in their CPI scores.
- The U.S. score dropped from 69 to 65, now ranking 28th, down from 24th.
- France’s score fell by 4 points to 67, dropping to 25th position.
- Russia’s corruption score continued to decline, reflecting the growing authoritarianism after the Ukraine invasion.
Corruption’s Broader Impacts:
- The report highlights the negative effects of corruption on climate change efforts.
- Corruption often results in the mismanagement of climate funds and impedes effective policy-making.
- High levels of corruption are seen as a barrier to environmental progress, worsening the consequences of global warming.
The Global Corruption Landscape:
- Since 2012, 148 countries have either stagnated or worsened in their corruption levels.
- Corruption is presented as a major obstacle to democracy, stability, and the protection of human rights globally.
Call to Action:
- The report calls on the international community to make combating corruption a priority.
- It stresses the need for actionable steps to address corruption in order to promote sustainable development and strengthen democratic resilience.
India-France Relations:
The visit of the Prime Minister of India to France in February 2025 marked a significant milestone in bilateral relations, leading to major agreements in nuclear energy, defense, artificial intelligence (AI), and Indo-Pacific cooperation. This visit highlighted the growing strategic partnership between the two countries.
Key Outcomes from the Recent Summit
Nuclear Energy Cooperation:
- Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) and Advanced Modular Reactors (AMRs): India and France signed a letter of intent to jointly design, develop, and produce SMRs and AMRs, combining India’s industrial capabilities with France’s technological expertise.
- Jaitapur Nuclear Project: Both nations reviewed the progress of the long-awaited Jaitapur project, emphasizing its significance for India’s shift to clean energy.
Defense Collaboration:
- Submarines and Missiles: The countries continue to collaborate on the Scorpene submarine project, focusing on indigenizing and integrating air-independent propulsion (AIP) systems developed by the DRDO.
- Helicopter and Jet Engine Production: Discussions were held about jointly manufacturing engines for helicopters and fighter jets.
- Pinaka Multi-Barrel Rocket Launcher: France expressed interest in acquiring India’s Pinaka MBRL system, further strengthening defense ties.
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- India-France AI Roadmap: The two nations committed to creating a safe, secure, and reliable AI framework that aligns with their shared values.
- AI Action Summit: India proposed to host the next AI summit, with 2026 designated as the India-France Year of Innovation.
Indo-Pacific Cooperation:
- Triangular Development Initiatives: Joint projects in third-party countries will focus on addressing climate change and advancing sustainable development goals (SDGs) in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Eurodrone MALE Programme: India’s inclusion as an observer in the European drone program marks a significant development in defense collaboration.
Economic and Cultural Ties:
- Startup Collaboration: Ten Indian startups have joined France’s Station F incubator program.
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI) in France: India’s real-time payment system will be expanded into France.
- Cultural Exchange: The Young Professional Scheme was operationalized to improve legal mobility for students and professionals.
Advantages of Strengthening Bilateral Ties
- Strategic Depth: The enhanced collaboration in defense, nuclear energy, and AI strengthens the strategic partnership.
- Economic Growth: Joint projects in third countries and startup initiatives offer new economic opportunities.
- Technological Advancements: Collaborative efforts in AI and nuclear technologies position both countries as leaders in innovation.
- Global Influence: Cooperation in the Indo-Pacific enhances their roles as crucial stakeholders in ensuring regional stability and development.
Limitations and Challenges
- Implementation Delays: Past delays in projects like Jaitapur raise concerns about timely execution.
- Technological Barriers: Developing advanced technologies such as SMRs and AI requires significant expertise and investment.
- Geopolitical Risks: Diverging views on global issues, particularly China’s role in the Indo-Pacific, could challenge cooperation.
Bureaucratic Hurdles: Complex regulatory frameworks in both countries could impede progress on joint projects.
Which of the following is a potential challenge to the India-France strategic partnership?
a. Lack of skilled workforce
b. Differing perspectives on global issues, such as China’s role in the Indo-Pacific
c. Overlapping economic interests
d. Limited technological expertise
Correct Answer: (b) Differing perspectives on global issues, such as China’s role in the Indo-Pacific
India-UK Defence Collaboration
Introduction: India and the United Kingdom have signed multiple agreements aimed at enhancing bilateral defence collaboration.
Key Agreements and Collaborations in India-UK Defence Partnership
Defence Partnership–India (DP-I):
The UK’s Ministry of Defence has established a dedicated programme office aimed at serving as a centralized hub for bilateral defence collaboration, promoting deeper cooperation and fostering economic growth in both nations.
Laser Beam Riding MANPADs (LBRM):
India and the UK have entered into a contract for the procurement of Laser Beam Riding Man Portable Air Defence Systems (MANPADS). The initial delivery of High Velocity Missiles (STAR Streak) and associated launchers is scheduled for this year.
Lightweight Multirole Missiles (LMM):
This initiative seeks to integrate Indian and British industries into the global defence supply chain, enhancing collaborative efforts in missile technology.
Advanced Short-Range Air-to-Air Missile (ASRAAM):
A partnership has been established to create an assembly and testing facility for the ASRAAM missile in Hyderabad, promoting local manufacturing capabilities.
Integrated Full Electric Propulsion (IFEP) System:
A Statement of Intent was signed to design and develop an Integrated Full Electric Propulsion (IFEP) system for India’s forthcoming Landing Platform Dock (LPD) fleet. Both nations are also aiming to create India’s inaugural maritime Land-Based Testing Facility, with objectives to deploy the LPD by 2030.
Key Challenges
India-UK defence cooperation has faced obstacles due to the ‘three-I’ challenge, which includes:
- Foreign Investment regulations
- Intellectual Property Rights concerns
- Indigenous Content Requirements
The agreements signify a crucial advancement in India-UK defence collaboration, particularly in essential domains like air defence and maritime propulsion. They align with India’s Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) initiative, emphasizing the enhancement of indigenous defence capabilities and technological progress.
Which of the following factors has posed a challenge to India-UK defense cooperation?
A .Currency Exchange Rates
B. The ‘three-I’ challenge: Foreign Investment, Intellectual Property Rights, and Indigenous Content Requirements
C. Language Barriers
D .Geographical Distance
Answer: B) The ‘three-I’ challenge: Foreign Investment, Intellectual Property Rights, and Indigenous Content Requirements
Geography
Gulf of Eilat (Gulf of Aqaba)
Context: Recent research highlights a halt in coral reef growth in the Gulf of Eilat (also known as the Gulf of Aqaba).
Key Facts about the Gulf of Eilat/Aqaba:
Location: Northern Red Sea, nestled between the Sinai and Arabian Peninsulas.
Bordering Nations: Egypt, Israel, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia.
Depth Comparison: Notably deep (1,850 meters) compared to the shallower Gulf of Suez (100 meters).
Ecological Significance: Contains important coral reef ecosystems, considered some of the worlds northernmost.
Consider the following statements regarding the Gulf of Eilat/Aqaba:
- It is located in the southern part of the Red Sea.
- It is bordered by Egypt, Israel, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia.
- It is shallower than the Gulf of Suez.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
a. 1 only
b. 2 only
c. 2 and 3 only
d. 1 and 3 only
Correct Answer: b It is bordered by Egypt, Israel, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia
Lake Sapanca
Lake Sapanca in Türkiye is facing severe environmental degradation due to urbanization, industrial expansion, and agricultural runoff, leading to increased pollution and habitat destruction.
About Lake Sapanca:
Location:
Situated in northwestern Türkiye, between the Gulf of İzmit and Adapazarı Meadow.
Lies in a tectonic depression, running parallel to Iznik Lake.
Bordering Nations:
Türkiye’s Sakarya Province is home to the lake.
The catchment area is 251 km², surrounded by mountains in the south and small hills in the north.
River Inflows: The Lake has multiple inflows from small streams originating from surrounding mountains. It serves as a primary freshwater source for domestic and industrial purposes.
Key Issues:
High nutrient loads (Nitrogen & Phosphorus) due to agricultural runoff & wastewater discharge, leading to eutrophication.
Urban expansion & deforestation reducing water retention capacity.
Seasonal pollution peaks observed in summer due to low water flow.
During which season are seasonal pollution peaks typically observed in Lake Sapanca, and why?
(a) Winter, due to increased snow melt
(b) Spring, due to heavy rainfall
(c) Summer, due to low water flow
(d) Autumn, due to leaf decomposition
Correct Answer: Summer, due to low water flow
Society
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act
Indian Abortion Laws: A Historical Overview
Prior to 1971, abortions were largely criminalized under the Indian Penal Code (IPC), with exceptions only for procedures performed to save a woman’s life. The IPC did not differentiate between desired and unwanted pregnancies, making safe abortion access extremely difficult.
The Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act of 1971:
- The MTP Act was enacted to decriminalize abortion in specific circumstances, recognizing it as a “health” measure.
- Initially, the Act allowed termination up to 20 weeks of pregnancy. A single doctor’s opinion was required for terminations within 12 weeks, and the opinion of two doctors was needed for terminations between 12 and 20 weeks.
The 2021 Amendment to the MTP Act:
Extended Gestational Limit: Rule 3B allowed abortion up to 24 weeks for specific categories of women, including those who experienced a change in marital status during pregnancy, survivors of rape or incest, and other vulnerable women.
Inclusive Language: The amendment broadened the legal scope by replacing “married woman or her husband” with “any woman or her partner,” encompassing pregnancies outside of marriage.
Post-24 Weeks: For pregnancies beyond 24 weeks, a medical board of expert doctors, established by the state government, assesses cases involving substantial fetal abnormalities to determine if termination is permissible.
Current Case: The Bombay High Court recently allowed a 25-week pregnancy termination in a private hospital, illustrating how the legal framework is applied in specific situations
Which of the following accurately describes the legal status of abortion in India prior to the Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act of 1971?
- Abortion was legal and widely accessible, with no gestational limits.
- Abortion was largely criminalized under the Indian Penal Code (IPC), with exceptions only to save a woman’s life.
- Abortion was legal up to 12 weeks of gestation, with a single doctor’s approval required.
- Abortion was regulated by the MTP Act from the beginning, albeit with more stringent rules than present.
Correct Answer: b) Abortion was largely criminalized under the Indian Penal Code (IPC), with exceptions only to save a woman’s life
Marital Rape in India
Indian Abortion Laws: A Historical Overview
Prior to 1971, abortions were largely criminalized under the Indian Penal Code (IPC), with exceptions only for procedures per
Legal Ambiguity and Ongoing Debate: The core reason the topic is in the news is the ongoing legal debate and lack of clarity regarding marital rape in India.
Chhattisgarh High Court Ruling: The Gorakhnath Sharma case highlights the existing legal framework that protects husbands from rape charges for sex with wives over 15. This underscores the current legal immunity.
Supreme Court Petitions: The news mentions that the Supreme Court is actively hearing petitions to criminalize marital rape. This directly reflects the push for legal reform and the desire to challenge the existing status quo.
Contrasting Legal Stances: The news emphasizes the conflict between different legal perspectives:
Existing Law: The Indian Penal Code (IPC) and the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) currently offer immunity to husbands in cases of marital rape (with the exception of those involving wives under 18).
Judicial Rulings: While the law grants immunity, various court rulings (e.g., Independent Thought and KS Puttaswamy) have affirmed the importance of consent, sexual autonomy, and the rights of women. These rulings create a tension with the existing law.
Government’s Stance: The Ministry of Home Affairs’ statement shows reluctance to criminalize marital rape fully, highlighting a differing view from women’s rights advocates and potentially some within the judiciary.
Impact and Relevance of the Law:
- A fundamental Human Rights Issue: The criminalization of marital rape directly impacts women’s rights to personal autonomy, equality, and freedom from violence.
- Comparison to Global Standards: The article highlights that marital rape is criminalized in a majority of countries around the world, and the news of the SC hearing petitions to criminalize marital rape is an indicator of the desire to align with these international standards.
- Recent Judicial Pronouncements: the text highlights that the text highlights that in 2023, the Bombay HC ruled that consensual sex with a minor wife is rape, rejecting the defense of consent in such cases. In 2024, the Madhya Pradesh HC ruled that unnatural sex with a wife is not rape and that a wife’s consent is irrelevant in such matters. These rulings create a tension with the existing law.
- Potential Solutions and Reforms: The article outlines possible actions, such as raising the marriage age, legislative amendments, alternative legal frameworks and reviewing global best practices. These underscore the recognition that changes are needed and highlight the importance of the debate.
In essence, the news is centered on the ongoing legal and social debate in India about whether or not to criminalize marital rape. The differing legal stances, judicial pronouncements, and the desire for reform are all major factors as to why this issue has gained prominence in the news cycleformed to save a woman’s life. The IPC did not differentiate between desired and unwanted pregnancies, making safe abortion access extremely difficult.
The Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act of 1971:
- The MTP Act was enacted to decriminalize abortion in specific circumstances, recognizing it as a “health” measure.
- Initially, the Act allowed termination up to 20 weeks of pregnancy. A single doctor’s opinion was required for terminations within 12 weeks, and the opinion of two doctors was needed for terminations between 12 and 20 weeks.
The 2021 Amendment to the MTP Act:
Extended Gestational Limit: Rule 3B allowed abortion up to 24 weeks for specific categories of women, including those who experienced a change in marital status during pregnancy, survivors of rape or incest, and other vulnerable women.
Inclusive Language: The amendment broadened the legal scope by replacing “married woman or her husband” with “any woman or her partner,” encompassing pregnancies outside of marriage.
Post-24 Weeks: For pregnancies beyond 24 weeks, a medical board of expert doctors, established by the state government, assesses cases involving substantial fetal abnormalities to determine if termination is permissible.
Current Case: The Bombay High Court recently allowed a 25-week pregnancy termination in a private hospital, illustrating how the legal framework is applied in specific situations
What potential solutions are outlined in the article to address the issue of marital rape?
a. Raising the marriage age, legislative amendments, alternative legal frameworks, and reviewing global best practices
b. Only raising the marriage age
c. Only legislative amendments
d. Only alternative legal frameworks
Correct Answer: a) Raising the marriage age, legislative amendments, alternative legal frameworks, and reviewing global best practices
Economy
Sovereign Green Bonds
India, like many emerging markets, is employing sovereign green bonds (SGrBs) to fund its transition to a low-carbon economy. Despite this, investor demand for these bonds has remained weak.
India’s Green Bond Efforts
Since 2022-23, India has issued SGrBs eight times, raising approximately Rs 53,000 crore. However, these issues have struggled to gain traction due to a lack of investor interest, making it challenging for the government to secure a greenium.
Greenium and Bond Yields
Globally, greeniums have reached 7-8 basis points, while in India, it is often at just 2–3 basis points. Greeniums reflect the difference in yield between green bonds and conventional bonds. A higher greenium indicates a lower yield and, therefore, a cost advantage for the issuer.
Green Bonds:
Green bonds are debt instruments issued by governments, corporations, and multilateral banks to raise funds for projects that reduce emissions or enhance climate resilience. These bonds are typically offered at lower yields than conventional bonds, assuring investors that the proceeds will be used exclusively for green investments.
Sovereign Green Bonds (SGrBs)
Sovereign green bonds (SGrBs) are issued by sovereign entities, such as the Government of India. India formulated a framework for issuing these bonds in 2022, defining “green projects” as those that promote:
* Energy efficiency in resource utilization
* Reduced carbon emissions
* Climate resilience
* Improved natural ecosystem
What is the primary purpose of India’s sovereign green bonds (SGrBs)?
a) To raise funds for infrastructure development
b) To promote foreign direct investment
c) To fund the transition to a low-carbon economy
d) To stimulate economic growth
Answer: c) To fund the transition to a low-carbon economy
New Income Tax Bill 2025 Highlights Key Highlights of the New Income Tax Bill 2025
Introduction:
The New Income Tax Bill 2025 was introduced by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in the Lok Sabha on February 13, 2025.
Purpose:This bill aims to replace the 60-year-old Income Tax Act of 1961.
Expected Implementation:
The bill is expected to come into effect in April 2026.
Standing Committee Referral:
After being presented, the Finance Minister requested that the Speaker send the bill to the Parliament’s Standing Committee on Finance for further discussion.
Simplification Efforts:
The bill is designed to be “crisper and simplified.”
It seeks to reduce the number of sections by 25-30% and simplify the language.
Terms like ‘previous year’ will be replaced by ‘tax year,’ and the concept of ‘assessment year’ will be eliminated.
The bill will be streamlined to 566 pages (from over 800 pages in the existing Act).
Modernization of Tax System:
The bill is designed to modernize India’s tax system with key goals outlined by the Finance Ministry:
Enhance readability by removing complex language.
Improve navigability by eliminating redundant provisions.
Make referencing easier by reorganizing sections in a logical order.
Tax Slabs under the New Regime:
0 – ₹4 lakh: 0%
₹4-8 lakh: 5%
₹8-12 lakh: 10%
₹12-16 lakh: 15%
₹16-20 lakh: 20%
₹20-24 lakh: 25%
Above ₹24 lakh: 30%
Relief for Middle Class:
The exemption limit has been raised, and the tax slabs have been adjusted. For salaried employees, the nil tax limit is ₹12.75 lakh per annum, after considering a standard deduction of ₹75,000.
Access to Data:
Tax authorities will have access to:
Email servers
Online investment accounts
Trading and bank accounts
Social media accounts
Digital application servers during searches
Bill Statistics:
Chapters: Reduced from 47 to 23.
Tables: Increased from 18 to 57.
Provisions Removed: 1,200 provisions and 900 explanations have been eliminated.
Word Count: Reduced from 5.12 lakh to 2.6 lakh words.
Tax Certainty:
The bill seeks to minimize litigation and provide clear interpretations, aiming for greater tax certainty.
Support for Key Sectors:
The bill includes provisions supporting:
Startups
Digital businesses
Renewable energy investments (Clauses 11-154)
Dispute Resolution:
The Dispute Resolution Panel will now be required to pass speaking orders with clear reasons when deciding on objections raised by taxpayers.
Detailed Framework for Non-Profits:
A more detailed framework is established for non-profit organizations (Clauses 332-355).
Cryptocurrency Provisions:
New provisions for virtual digital assets are introduced, along with updated tax rates (Clauses 67-91).
Updated Return Timeline:
The timeframe for filing updated returns is extended from two to four years.
Reduced Sections:
The bill aims to reduce the total number of sections by 25-30%.
Largely Unchanged Concepts:
Concepts such as indirect transfers, GAAR, capital gains, SEP, taxation of royalty/FTS, tax rates, and residential status will remain largely unchanged.
Modernization of the Structure:
The bill will restructure 298 sections (effectively transforming 819 sections) into 536 clauses.
Backlogs:
A time limit will be set for disposing of appeals at the first appellate authority level.
Simpler Language:
The bill prioritizes simplification of language to make the legislation more accessible.
Tax Year Terminology:
The terms ‘assessment year’ and ‘previous year’ will be replaced with ‘tax year.’
Taxpayer-Centered Reforms:
The Finance Minister highlighted the bill as part of the Center’s taxpayer-centered reforms.
Suggestions:
The income tax portal continues to invite suggestions from the public regarding the new tax bill under the section labeled ‘new’.
The New Income Tax Bill extends the timeframe for filing updated returns from:
a. 1 year to 3 years
b. 2 years to 4 years
c. 3 years to 5 years
d. There is no change in the timeframe.
Answer: b) 2 years to 4 yearst investment
Devolution Index Report
The recently released Devolution Index Report marks a pivotal step forward for rural local self-governance in India. This comprehensive document evaluates the state of decentralization across various states and Union Territories, aiming to empower Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) and bring the vision of “Local Self Government” outlined in the 73rd Constitutional Amendment to life.
About the Devolution Index
The Devolution Index is the outcome of extensive research and analysis, measuring India’s progress in decentralization across six key dimensions: Framework, Functions, Finances, Functionaries, Capacity Building, and Accountability. These dimensions are vital for assessing the effectiveness of Panchayati Raj Institutions in fulfilling their roles.
Key Dimensions of the Index
Framework: Evaluates the legal and institutional structures that support Panchayati Raj.
Functions: Examines the breadth of responsibilities assigned to Panchayats.
Finances: Assesses the financial autonomy and resource allocation for local bodies.
Functionaries: Reviews the availability and effectiveness of human resources for executing Panchayat duties.
Capacity Building: Focuses on the training and development of Panchayat members.
Accountability: Evaluates mechanisms ensuring transparency and responsibility in local governance.
Empowerment of Panchayats
The Index specifically measures the autonomy of Panchayats in decision-making, reflecting the essence of Article 243G of the Indian Constitution, which empowers state legislatures to devolve powers to Panchayats over 29 subjects listed in the Eleventh Schedule.
Utility for Multiple Stakeholders
The Devolution Index serves a wide array of stakeholders:
Citizens: Gain greater transparency regarding Panchayat operations and resource distribution.
Elected Representatives: Receive data-driven insights that can support their advocacy for reforms.
Government Officials: Get a strategic roadmap for implementing decentralization policies effectively.
Policymakers: Can assess the state of local governance and identify areas in need of urgent reforms.
Alignment with the Viksit Bharat Vision
This initiative aligns with the Viksit Bharat vision, where empowered and developed Panchayats are the foundation of rural transformation. The Devolution Index promotes inclusive growth and sustainable development at the grassroots level.
Future Implications
The Devolution Index is set to strengthen India’s cooperative federalism. It encourages states to recognize areas for improvement and adopt best practices to enhance the functioning of Panchayati Raj Institutions. Ultimately, this initiative is critical for improving local governance and ensuring more responsive governance in rural India.
How can citizens benefit from the Devolution Index?
A) By receiving monetary compensation
B) By increased transparency regarding Panchayat operations and resource distribution
C) By direct involvement in legislative processes
D) By obtaining employment in government offices
Answer: B) By increased transparency regarding Panchayat operations and resource distribution
Tobin Tax
The U.S. President Donald Trump’s administration is contemplating implementing a Tobin Tax on capital flows, a decision that could potentially disrupt global financial markets.
About the Tobin Tax: Definition: The Tobin Tax is a levy on foreign exchange transactions designed to discourage short-term speculative trading. Typically, it involves a small tax rate (0.1%-0.5%) applied to currency conversions to reduce volatility in financial markets.
Origin and Theory: Proposed in 1972 by Nobel laureate James Tobin, the tax was conceived as a response to currency market instability following the collapse of the Bretton Woods system. Tobin’s objective was to “throw sand in the wheels” of currency speculation, thereby stabilizing exchange rates.
Key Features:
- Application to currency transactions to discourage short-term speculation.
- A low tax rate intended to prevent market disruption.
- Potential revenue generation for public welfare or development projects.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
Market Stability | Reduces speculative trading and market volatility. | May reduce market liquidity. |
Revenue Generation | Can generate substantial revenue for governments. | Difficult to implement uniformly across nations. |
Currency Protection | Helps protect weaker currencies from speculative attacks. | May increase transaction costs for businesses and investors. |
Fairer Global Economy | Limits the financial power of hedge funds and large investors. | Could incentivize financial transactions to move to tax-free zones or offshore havens. |
India’s Perspective: India does not currently have a direct Tobin Tax on currency transactions. However, the Securities Transaction Tax (STT), introduced in 2004, serves as a similar tax on stock market transactions. Additionally, Foreign Portfolio Investments (FPIs) are subject to taxation, which indirectly influences capital flows.
What is the typical tax rate associated with a Tobin Tax on currency conversions?
(a) 5%-10%
(b) 1%-2%
(c) 0.1%-0.5%
(d) 10%-20%
Correct Answer: 0.1%-0.5%
India’s Pharmaceutical Exports Set for 10x Growth
Introduction
India’s pharmaceutical exports are anticipated to soar to $350 billion by 2047, representing a 10-15 times increase from current levels.
Overview of India’s Pharmaceutical Industry
Recognized internationally as the “Pharmacy of the World,” India’s pharmaceutical industry has played a pivotal role in supplying vaccines, essential medicines, and medical supplies during the COVID-19 pandemic and continues to do so. The sector has demonstrated significant innovative capabilities, solidifying its position as a vital component of the global pharmaceutical value chain.
Current Global Market Status
- India stands as the largest global supplier of generic drugs, contributing 20% to worldwide sales.
- India ranks third in terms of drug and pharmaceutical production by volume.
- Exports span approximately 200 countries and territories.
- The primary export destinations include the USA, Belgium, South Africa, the UK, and Brazil.
- Despite being a key global player in generics, India ranks 11th in terms of pharmaceutical export value.
- The total annual turnover of pharmaceuticals in FY24 was ₹4.17 lakh crore, reflecting an average growth rate of 10.1% over the past five years.
Export Projections
India’s pharmaceutical exports are expected to rise from $27 billion in 2023 to $65 billion by 2030. This growth is anticipated to shift from volume-based to value-driven strategies, focusing on key areas such as Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs), biosimilars, and specialty generics.
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API):
India’s API exports are projected to grow from $5 billion to $80-90 billion by 2047.Global supply chain diversification, particularly in light of the U.S. Biosecure Act, presents an opportunity for India to bolster API production.
Biosimilars:
- Current biosimilar exports are valued at $0.8 billion, with expectations to increase fivefold to $4.2 billion by 2030, and to $30-35 billion by 2047.
- This growth will be supported by enhanced R&D, regulatory simplifications, and capacity expansions.
- Biosimilars are medications that closely resemble biologic drugs created through living systems, showcasing comparable structure and functionality.
Generic Formulations:
- Accounting for 70% of India’s pharmaceutical exports, generic formulations are valued at $19 billion.
- These exports are projected to grow to $180-190 billion by 2047, with a notable shift towards higher-margin specialty generics.
Policy and Strategic Measures
The Indian government has initiated several programs to promote the pharmaceutical sector and stimulate investment:
- In September 2020, the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme was introduced for the pharmaceutical sector as part of the Self-Reliant India initiative, with a budget of ₹15,000 crore allocated from 2020-2021 to 2028-29.
- Targeted policy measures are vital, including strengthening the API industry, addressing export barriers, and developing country-specific export strategies.
- India supplies 55-60% of UNICEF’s vaccines but should aim to expand its presence in high-value markets through clinical trials and manufacturing investments.
- Key enablers for growth include regulatory harmonization, expansion of PLI, and R&D incentives.
Challenges
India faces several obstacles, including issues related to intellectual property rights and limited R&D capabilities. It is crucial to understand the political, economic, sociocultural, technological, environmental, and legal factors when assessing the opportunities and challenges within the Indian pharmaceutical market.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
As a global leader in generic drug supply, India aims to ascend the value chain by focusing on specialty generics, biosimilars, and innovative products. This strategic shift could position India among the top five nations in export value by 2047. With aspirations to become the “healthcare custodian of the world,” the nation is prioritizing innovation, R&D, and regulatory improvements. Collaboration between academia, industry, and government will be essential in establishing a robust, globally competitive pharmaceutical sector
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding India’s position in the global pharmaceutical market?
a. India ranks first in terms of pharmaceutical export value.
b. India is the largest global supplier of generic drugs, accounting for 20% of global sales.
c. India does not export pharmaceuticals to many countries.
d. India ranks fourth in drug production by volume.
Answer: B) India is the largest global supplier of generic drugs, accounting for 20% of global sales.
Indian Art & Culture
Dorka Metal Craft
Gift: Prime Minister of India gifted a Dokra artwork to French President Emmanuel Macron at the AI Summit in Paris.
Definition: Non-ferrous metal casting technique using the lost-wax casting method.
Characteristics:
Primitive simplicity
Unique folk motifs
Handcrafted designs (no joints)
Materials: Mainly brass and copper-based alloys.
Designs: Figures of:
Elephants
Horses
Religious deities
Lamps
Jewellery
Tribal motifs
Regions Found:
Jharkhand
Chhattisgarh
Odisha
West Bengal
Telangana
Madhya Pradesh
Rajasthan
Tamil Nadu
GI Tag: Adilabad Dokra (Telangana) received a Geographical Indicator (GI) tag in 2018.
Casting Methods:
Solid Casting (South India): Single wax piece for the mould.
Hollow Casting (Central & Eastern India): Clay core with wax overlay.
Uniqueness: Each piece is unique because the mould is destroyed during the process.
Origins: Indus Valley Civilization (e.g., Mohenjo-daro’s “Dancing Girl”).
Practitioners: Dhokra Damar tribes (originated from Odisha and West Bengal).
Which state’s Dokra craft received a Geographical Indication (GI) tag in 2018?
a. Odisha
b. West Bengal
c. Telangana
d. Chhattisgarh
Correct Answer: c)Telangana
Kashi Tamil Sangamam
- Kashi Tamil Sangamam 3.0 (KTS 3.0) is scheduled to take place from 15th to 24th February 2025.
- The event is organized by the Ministry of Education, Government of India, in collaboration with other ministries and the Government of Uttar Pradesh.
- IIT Madras and BHU are the implementing agencies for the program.
Objective of KTS 3.0:
- To rediscover and reaffirm the age-old links between Tamil Nadu and Kashi.
- To celebrate the deep-rooted bonds between the two regions.
- To provide an opportunity for scholars, students, philosophers, traders, artisans, artists, and people from other walks of life to come together, share their knowledge, and learn from each other’s experiences.
Key Features of KTS 3.0:
- 1000 delegates from Tamil Nadu will participate in the event, categorized into five groups: Students, Teachers, and Writers; Farmers and Artisans; Professionals and Small Entrepreneurs; Women; and Start-up, Innovation, Edu-Tech, Research.
- An additional 200 students of Tamil origin studying in various CUs will also be a part of the event.
- The event will feature an exhibition on Sage Agastya and his contributions, seminars, workshops, book release, and more.
- Participation of youth in all categories has been encouraged this year.
Previous Celebrations of KTS:
- KTS was celebrated for one month in 2022.
- KTS 2.0 was celebrated for a fortnight in 2023.
- In both editions, there were overwhelming responses from people of Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh.
Registration and Implementation:The registration portal for KTS 3.0 was launched on 15th January 2025 and was open till 1st February 2025.
- IIT Madras will be the sender institution, and BHU will be the receiving institution, as in the earlier editions.
What is the main objective of KTS 3.0?
a. To promote tourism between Tamil Nadu and Kashi
b. To rediscover and reaffirm the age-old links between Tamil Nadu and Kashi
c. To organize cultural events and festivals
d. To conduct business and trade between the two regions
Answer: B) To rediscover and reaffirm the age-old links between Tamil Nadu and Kashi
