Dokra Art
Syllabus: GS1/ Art & Culture

- In a notable gesture, Prime Minister Narendra Modi presented a Dokra Brass Peacock Boat with a Tribal Rider to the Thai Prime Minister.
About Dokra Art
- Dokra art, an ancient craft dating back over 4,000 years to the Indus Valley Civilization, is known for its rich history and craftsmanship.
- The iconic Dancing Girl sculpture from Mohenjo-daro is one of the most famous examples of this art form.
- The name “Dokra” is believed to have originated from the Dhokra Damar tribes of West Bengal.
- A defining characteristic of Dokra art is its use of the lost wax casting technique.
- This method involves creating a mold that is only used once and then broken, ensuring that each Dokra artifact is unique in its design.
- In recognition of its cultural significance, the Dokra art from Bankura in West Bengal was granted a Geographical Indication (GI) Tag in 2008, further highlighting the importance of preserving this ancient art form.
Consider the following statements about Dokra Art:
- Dokra Art traces its origins to the Indus Valley Civilization.
- The Dhokra Damar tribes of West Bengal are credited with the name and origin of Dokra Art.
- The Geographical Indication (GI) tag for Dokra of Bankura was granted in 2005.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct – Dokra art is believed to have origins dating back to the Indus Valley Civilization. The famous “Dancing Girl” sculpture from Mohenjo-daro is considered an example of early casting techniques that later influenced Dokra art.
- Statement 2: Correct – The name “Dokra” is believed to have originated from the Dhokra Damar tribes in West Bengal, who are the primary practitioners of this art form.
- Statement 3: Incorrect – The GI tag for Dokra of Bankura, West Bengal, was granted in 2008, not 2005.
Gaza Strip
Syllabus: GS1/ Places in News
- Israel has gained control over more than 50% of the Gaza Strip’s territory since resuming its military operations against Hamas.
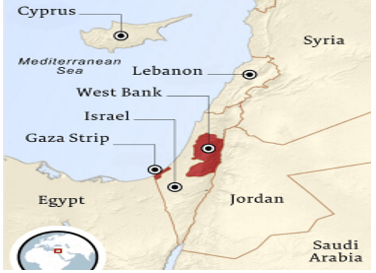
About the Gaza Strip:
- Location: The Gaza Strip is a small region situated along the eastern Mediterranean coast. It borders Israel to the north and east and Egypt to the southwest, covering approximately 365 square kilometers.
- Conflict Zone: The Gaza Strip has been the site of recurring conflicts between Israel and Hamas, with major wars occurring in 2008, 2012, 2014, and most recently in 2023–2024.
- Humanitarian Crisis: Due to the ongoing blockade and repeated conflicts, the Gaza Strip faces severe humanitarian challenges, including high unemployment, limited access to clean water, electricity, and healthcare, and widespread poverty.
With reference to the Gaza Strip, consider the following statements:
- It shares a border with both Israel and Jordan.
- It has an area less than that of the Indian city of Mumbai.
- It lies along the Red Sea coast.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Gaza shares borders with Israel and Egypt, not Jordan.
- Statement 2 is correct: Gaza Strip’s area is approx. 365 sq km, which is less than Mumbai’s area (~603 sq km).
- Statement 3 is incorrect: It lies along the eastern Mediterranean Sea, not the Red Sea.
Palna Scheme Under Mission Shakti
Syllabus: GS2/ Health

Context:
- The Palna Scheme addresses the pressing childcare needs of working mothers by offering quality crèche services, thereby facilitating their participation in the workforce without compromising the well-being of their children.
- The scheme also contributes to the recognition and formalization of unpaid care work, aligning with Sustainable Development Goal 8 – promoting decent work and economic growth.
About the Scheme:
- Launched in 2022, the Palna Scheme is the restructured version of the erstwhile National Crèche Scheme.
- It functions under the ‘Samarthya’ sub-scheme of the umbrella programme ‘Mission Shakti’.
- The scheme is Centrally Sponsored, with a Centre-State funding pattern:
- 60:40 for States and UTs with legislature.
- 90:10 for North-Eastern and Special Category States.
- 100% Central assistance for UTs without legislature.
- It ensures active participation of States/UTs to strengthen implementation, monitoring, and accountability.
Objectives:
- To provide safe, secure, and high-quality crèche services for children aged 6 months to 6 years.
- To support the nutritional needs, health, and early cognitive development of children.
- To facilitate growth monitoring, immunization, and other essential early childhood services.
- The scheme is universal in access, providing services to all mothers, regardless of their employment status.
With reference to the Palna Scheme, consider the following statements:
- It is implemented under the Samarthya sub-scheme of Mission Shakti.
- The scheme is applicable only to mothers who are engaged in formal employment.
- For UTs without legislatures, the entire cost is borne by the Central Government.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Palna is a sub-component of ‘Samarthya’, which is a sub-scheme under ‘Mission Shakti’.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: Crèche services are available to all mothers, irrespective of employment status.
- Statement 3 is correct: For UTs without legislature, the scheme is 100% centrally funded
Judicial Cooperation Between India and Nepal
Syllabus :GS 2/IR/Governance
About the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU):
- The Supreme Court of India and the Supreme Court of Nepal have signed an MoU aimed at enhancing judicial cooperation between the two nations.
- The MoU seeks to promote exchange of information, mutual judicial interactions, and capacity-building programs such as training for judges and court officials.
- It emphasizes the adoption of technology to improve judicial efficiency, streamline court procedures, reduce case backlogs, and enhance citizen-centric services.
- A Joint Working Group (JWG) will be constituted to devise actionable plans and monitor the progress of initiatives under this cooperation framework.
- The MoU also envisions collaboration through judicial exchanges, joint research projects, seminars, and official visits to foster deeper mutual understanding.
Noteworthy Highlights:
- Chief Justice of India (CJI), Sanjiv Khanna, termed the MoU as a “new milestone” in strengthening judicial ties between India and Nepal.
- He highlighted the reciprocal influence of judicial decisions between the two countries—citing Nepal’s adoption of India’s Basic Structure Doctrine and parallels such as the decriminalization of Section 377 of the IPC influencing judicial discourse.
With reference to the recent MoU signed between the Supreme Courts of India and Nepal, consider the following statements:
- The MoU mandates the creation of a permanent judicial tribunal for cross-border legal disputes.
- One of the key aims of the MoU is to promote the use of technology to enhance judicial service delivery and reduce pendency.
- The MoU includes provisions for joint research, training programs, and reciprocal visits of judicial officers.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 2 and 3 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The MoU is focused on cooperation, not adjudication; it does not establish a judicial tribunal for cross-border disputes.
- Statement 2 is correct: Emphasis on the adoption of technology is a key feature—to streamline procedures and reduce backlog.
- Statement 3 is correct: It includes joint research, training, seminars, and judicial exchange programs
New Rules to Get Equivalence Certificates for Foreign Degrees
Syllabus: GS2/ Education
Context:
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) has issued a new regulation aimed at streamlining the recognition and equivalence of academic qualifications obtained from foreign educational institutions.
What is an Equivalence Certificate?
- An Equivalence Certificate is an official document that validates whether an academic qualification—such as a certificate, diploma, or degree—obtained from a foreign university is comparable in level, content, and purpose to a corresponding Indian qualification.
- It is mandatory for individuals seeking to pursue higher education or employment opportunities in India on the basis of foreign qualifications.
Conditions for Granting Equivalence:
For a foreign qualification to be recognized as equivalent, the following conditions must be satisfied:
Institutional Recognition:
- The qualification must be awarded by a foreign institution legally recognized in its home country.
Comparable Academic Standards:
- The academic programme should have entry-level criteria, curriculum structure, and credit systems that are broadly aligned with similar programmes in India.
- May include components such as thesis work, internships, or project-based assessments.
Compliance with Academic Norms:
- The candidate must have pursued the programme in accordance with the academic standards and guidelines of the awarding foreign institution.
Offshore Campus Qualifications:
- Degrees obtained from offshore campuses of foreign universities shall also be considered for equivalence provided that:
- The academic programme adheres to the educational regulations of the host country (where the offshore campus is located), and Complies with the regulations of the country of origin of the parent institution.
With reference to the new UGC regulation on equivalence of foreign degrees, consider the following statements:
- An equivalence certificate is required only for foreign degrees obtained through distance learning.
- Recognition of the foreign awarding institution by its home country is a necessary condition.
- Degrees from offshore campuses are not eligible for equivalence under the new regulation.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 2 and 3 only
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: An equivalence certificate is required for any foreign academic qualification, not just distance learning.
Statement 2 is correct: The awarding institution must be recognized under the laws of its home country.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Degrees from offshore campuses are eligible, provided they meet specific regulatory criteria of both host and home countries.
National Mission on Power Electronics Technology (NaMPET)
Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Context:
- The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has announced the signing of Technology Transfer Agreements (ToT), Memoranda of Agreement (MoA), and Memoranda of Understanding (MoU) between industry partners for the commercialization of technologies developed under the National Mission on Power Electronics Technology (NaMPET).
Significance:
- The initiative highlights the strategic importance of indigenous technology development in the Power Electronics sector, which is vital for India’s push toward sustainable energy, electric mobility, and self-reliance in critical infrastructure.
Key Technologies and Collaborations:
Wireless Charger for Electric Vehicles (EVs):
- Capable of charging a 8 kWh onboard battery within 3 hours.
- Achieves a high charging efficiency of 89.4%.
- Supports the development of an efficient e-mobility ecosystem.
Indigenous Propulsion System for Electric Locomotives:
- MoA signed for the indigenization of a 3-phase propulsion system used in electric locomotives.
- Aligned with the target of 100% electrification of Indian Railways by 2030, ensuring improved performance and reliability.
LVDC (Low Voltage Direct Current) Systems Collaboration:
- An MoU signed between C-DAC and the Kerala Development and Innovation Strategic Council (K-DISC).
- Aims to reduce energy consumption by 20–30%, supporting Kerala’s Carbon Neutrality Roadmap 2050.
About NaMPET (National Mission on Power Electronics Technology):
- A mission-mode initiative launched by MeitY for the research, development, and commercialization of advanced power electronics technologies.
- Implemented by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC), Thiruvananthapuram, with collaboration from academia, research institutions, and industry partners.
Key Focus Areas:
- Microgrids and Smart Grids
- Green and Renewable Energy Integration
- Electric Mobility Infrastructure (e-Mobility)
- Smart Power Quality Centres
- High Voltage Power Electronics
- Startup Support and Technology Outreach
With reference to the National Mission on Power Electronics Technology (NaMPET), consider the following statements:
- It is implemented by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) with support from MeitY.
- One of its objectives is to reduce dependence on imported power electronic systems across critical infrastructure sectors.
- It focuses exclusively on the development of software solutions for green energy.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: NaMPET is implemented by C-DAC with oversight from MeitY.
Statement 2 is correct: The mission aims to indigenize power electronics technologies, reducing foreign dependence.
Statement 3 is incorrect: NaMPET covers hardware-intensive domains such as microgrids, propulsion systems, and e-mobility—not just software.
Biomass Mission
Syllabus: GS 3/Environment
In News:
- The European Space Agency (ESA) is set to launch the Biomass Mission on April 29, 2025, under its Earth Explorer programme.
Need for the Mission:
- Forests act as major carbon sinks, absorbing nearly 16 billion metric tonnes of CO₂ annually and storing about 861 gigatonnes of carbon.
- In 2023, approximately 3.7 million hectares of tropical forests were lost, contributing to 6% of global CO₂ emissions.
- Accurate data on forest biomass and carbon storage is essential to evaluate climate change impacts and improve carbon accounting models.
About the Biomass Mission:
Objective:
- To map and monitor the world’s forests and understand their role in the global carbon cycle, particularly in terms of biomass and carbon sequestration.
- Orbit Type:
It will operate in a Sun-Synchronous Orbit (SSO) at an altitude of 666 km, allowing consistent lighting conditions for data capture.
- Technology Used:
- The mission will deploy a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) operating in the P-band frequency, capable of penetrating dense forest canopies.
- Biomass will be the first satellite to use P-band SAR for such applications.
Applications:
- Measuring above-ground biomass and carbon storage.
- Creating 3D maps of forest height and structure.
- Monitoring ice sheet movements in Antarctica.
- Generating terrain models in heavily vegetated regions.
Earth Explorer Programme:
- The Biomass mission is the seventh mission in the ESA’s Earth Explorer series, which provides crucial scientific data on Earth’s dynamic systems (e.g., atmosphere, biosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere).
Previous missions include:
- GOCE (Gravity field and steady-state Ocean Circulation Explorer) – 2009 to 2013
- EarthCARE (Earth Clouds, Aerosols and Radiation Explorer) – launched in 2024
With reference to the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Biomass Mission, consider the following statements:
- It is the first satellite to use P-band synthetic aperture radar for measuring forest biomass.
- It aims to provide high-resolution data on forest canopy carbon only in the tropical belt.
- The mission will operate from a Sun-Synchronous Orbit.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Biomass is the first satellite to use P-band SAR for this purpose.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: It will map global forests, not just tropical ones.
- Statement 3 is correct: The satellite will be placed in a Sun-Synchronous Orbit (SSO)
Military Space Doctrine
Syllabus :GS 3/Defence
- In News: India is in the process of formulating a Military Space Doctrine and a National Military Space Policy to enhance its preparedness in the evolving space-based security environment.
- About the Military Space Doctrine: The doctrine is being developed as part of India’s broader strategic efforts to address threats in the space domain, especially considering China’s advancements in anti-satellite (ASAT) weapons, electronic jamming, and satellite-disruptive technologies.
- It aims to build a “space culture” within the defense establishment by promoting indigenous research, operational doctrine, strategic vision, and relevant space laws.
- The Defence Space Agency (DSA) is leading the formulation, and the doctrine is expected to be finalized within two to three months.
- It will outline the utilization of space-based assets by the armed forces, with emphasis on integration across services.
About the National Military Space Policy:
- The policy will define the roles and responsibilities of various defense sub-organizations involved in space operations.
- It will provide a framework for inter-agency coordination and strategic use of satellite infrastructure.
Do You Know?
- Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) General Anil Chauhan announced the launch of 52 Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) satellites, in collaboration with ISRO and private industry, with an estimated budget of ₹26,000 crore.
- The DSA is also working on enhancing satellite communication networks and regional navigation systems, such as NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation).
- India’s space sector is at an inflection point, with ambitious goals to increase its share in global space commerce from the current 2% to 10% by 2032 and further to 25% by 2047 (centenary of independence).
MCQ 1. With reference to India’s proposed Military Space Doctrine, consider the following statements:
- It is being developed to counter emerging threats such as anti-satellite weapons and electronic warfare.
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is the nodal agency responsible for its formulation.
- It seeks to promote a “space culture” within the defense establishment, including the development of indigenous space laws.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The doctrine addresses threats like ASAT weapons and jamming.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The Defence Space Agency (DSA), not ISRO, is responsible for the doctrine.
- Statement 3 is correct: The doctrine aims to develop a “space culture” including laws and indigenous research.
MCQ 2 . With reference to India’s proposed Military Space Doctrine, consider the following statements:
- It is being developed to counter emerging threats such as anti-satellite weapons and electronic warfare.
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is the nodal agency responsible for its formulation.
- It seeks to promote a “space culture” within the defense establishment, including the development of indigenous space laws.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The doctrine addresses threats like ASAT weapons and jamming.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The Defence Space Agency (DSA), not ISRO, is responsible for the doctrine.
- Statement 3 is correct: The doctrine aims to develop a “space culture” including laws and indigenous research.
Breakthrough Prize 2025
Syllabus :Miscellaneous
In News: The 2025 Breakthrough Prizes have been announced, recognizing outstanding contributions in the fields of Life Sciences, Mathematics, and Fundamental Physics.
About the Breakthrough Prize:
- Established in 2013 by prominent tech leaders including Mark Zuckerberg & Priscilla Chan, Sergey Brin, Anne Wojcicki (23&Me), and Yuri & Julia Milner.
- Often referred to as the “Oscars of Science”, it is one of the most prestigious global science awards. Awards are presented annually in three main categories: Life Sciences, Fundamental Physics, and Mathematics.
- Each prize carries a monetary reward of $3 million, significantly higher than that of the Nobel Prize.
2025 Winners:
- The Fundamental Physics Prize was awarded to 13,508 scientists from four CERN collaborations for their contributions to the discovery of the Higgs boson and advancements in particle physics.
- The Life Sciences Prizes recognized path-breaking research in weight-loss drugs, Multiple Sclerosis (MS) treatment, and gene-editing technologies.
- The Mathematics Prize was awarded to Dennis Gaitsgory for his work on the Langlands conjecture, a deep theory linking number theory and geometry.
Consider the following statements regarding the Breakthrough Prize:
- It was established to promote public awareness and appreciation of scientific achievements in core research fields.
- It is awarded annually in four major categories, including Artificial Intelligence and Space Technology.
- It is known for awarding a larger monetary prize than the Nobel Prize.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: One of the aims of the Breakthrough Prize is to increase public interest in science and honor groundbreaking work.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The prize is awarded in three categories – Life Sciences, Mathematics, and Fundamental Physics (not AI or Space Technology).
- Statement 3 is correct: Each prize carries a reward of $3 million, which is indeed larger than the Nobel Prize.
10 Years Of PM MUDRA Yojana
Schemes
Objective:
- To provide collateral-free institutional credit to micro and small enterprises, especially in rural and semi-urban areas, promoting entrepreneurship and self-employment.
Loan Categories under MUDRA
- Shishu: Up to ₹50,000 – For startups and early-stage businesses
- Kishor: ₹50,001 – ₹5 lakh – For growing small businesses
- Tarun: ₹5 lakh – ₹20 lakh – For business expansion and established unitsKey Statistics (As of April 2025)
- Total Loans Sanctioned: 52+ crore
- Total Disbursed Amount: ₹32.61 lakh crore
- Women Beneficiaries: 68%
- SC/ST/OBC Beneficiaries: 50%
- Trend: Rise in Kishor and Tarun categories → Increasing entrepreneurial ambition
Recognition & Impact
Recognized by: International Monetary Fund (IMF)
Key Impacts:
- Enhanced credit access to MSMEs
- Empowered first-generation entrepreneurs
- Shift towards job creators over job seekers
- Promoted inclusive growth and gender equity
Implementing Agencies
- Apex Body: MUDRA (Micro Units Development and Refinance Agency)
- Loan Disbursal Partners:
- Public Sector Banks (PSBs)
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- Cooperative Banks
- Microfinance Institutions (MFIs)
- Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
Consider the following statements regarding the MUDRA Yojana:
- It provides credit guarantees to medium-scale industries.
- It focuses exclusively on urban entrepreneurial ecosystems.
- It supports first-generation entrepreneurs through institutional finance.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 3 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 2 and 3 only
Correct Answer: B) 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect:The MUDRA Yojana is aimed at micro and small enterprises, not medium-scale industries. It provides collateral-free credit to small entrepreneurs but does not provide credit guarantees. Credit guarantees are typically handled by separate schemes like CGTMSE (Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises).
- Statement 2 is incorrect:The scheme does not focus exclusively on urban areas. In fact, one of its primary objectives is to empower entrepreneurs in rural and semi-urban regions, where access to formal credit is limited. It plays a crucial role in promoting inclusive growth in underdeveloped areas.
- Statement 3 is correct:MUDRA supports first-generation entrepreneurs—those without any prior business background—by offering institutional finance through banks and financial institutions. This helps them start or expand micro/small businesses without collateral, fostering self-employment and entrepreneurship.
