Socotra Island
Syllabus :Geography
Ecological Importance:
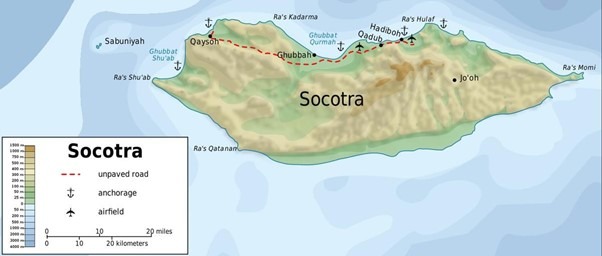
- Socotra Island, located about 340 km southeast of Yemen in the Indian Ocean, is often called the Galápagos of the Indian Ocean due to its unique biodiversity. A UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2008, it hosts over 37% endemic plant species, including the iconic Dragon’s Blood tree and frankincense.
Geography and Environment:
- Spanning 3,796 sq km, the island features coastal plains, a limestone plateau, and the Hagghier Mountains. Its semi-desert climate and strong monsoonal winds have helped preserve its distinct ecosystem.
Political and Strategic Context:
- Socotra is officially part of Yemen but is heavily influenced by UAE-backed forces and the Southern Transitional Council. The UAE maintains a military presence, citing humanitarian and security roles.
Local Economy:
- The island’s economy is based on fishing, pearl diving, livestock herding, and small-scale farming. However, isolation and limited resources pose economic challenges.
Health Emergency:
- Socotra faces a severe health crisis, especially among women and children. Global Acute Malnutrition (GAM) affects 10.9% of children under five, with 1.6% suffering from Severe Acute Malnutrition (SAM).
Humanitarian Response:
- A joint two-year programme by the UAE and WHO aims to reduce maternal and child mortality due to malnutrition. It includes:
- Strengthening healthcare infrastructure
- Training local medical staff
- Enhancing access to essential medications
- Improving emergency preparedness and disease surveillance
Sustainable Goals:
- Community awareness campaigns and upgraded health systems are key components. The initiative supports long-term resilience and improved health security for Socotra and contributes to broader healthcare development across Yemen.
Consider the following statements regarding Socotra Island:
- It lies closer to the Horn of Africa than to the Arabian Peninsula.
- Its designation as a UNESCO World Heritage Site was primarily based on its cultural significance.
- The island’s endemic biodiversity is attributed in part to historical isolation caused by strong monsoonal winds.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer:B
Explanation:
- Statement 2 is incorrect – Socotra’s UNESCO status is based on ecological (not cultural) significance.
- Geographical Location: Socotra Island is situated approximately 340 km southeast of Yemen, and geographically, it is closer to the Horn of Africa, particularly Somalia, than it is to the Arabian Peninsula.
- The island lies in the northwestern Indian Ocean, making its position strategically and ecologically significant.
Bar Council of India Decision to Allow Foreign Lawyers
Syllabus: Polity
- Chief Justice of India (CJI) B.R. Gavai lauded the Bar Council of India (BCI) for amending its 2022 rules to permit foreign lawyers and law firms to practice in India in a limited capacity, particularly in areas of international law and arbitration.
- The revised rules allow foreign legal professionals to practice foreign and international law and to participate in arbitration proceedings held in India.
- However, they are explicitly prohibited from appearing before Indian courts, tribunals, or practicing Indian law.
- This reform is driven by the need to enhance arbitration standards as India positions itself as a global arbitration destination—highlighted by its 5th rank globally in arbitration case volume, according to the ICC Report 2024.
- It also facilitates the globalization of legal services, enabling reciprocal market access for Indian lawyers abroad.

- Furthermore, the inclusion of foreign firms is expected to strengthen India’s growing institutional arbitration ecosystem—such as the MCIA in Mumbai, DIAC in Delhi, and IIAC in New Delhi—through increased credibility and caseloads.
- The reform addresses talent shortages in niche legal areas like climate litigation, technology law, and cross-border commercial arbitration by allowing international collaboration and knowledge transfer.
- Nevertheless, its implementation faces significant challenges. Domestic protectionism raises concerns among Indian legal professionals over potential job displacement in elite advisory sectors.
- Reciprocity and regulatory complexities arise due to restrictive legal entry rules in many foreign jurisdictions, potentially hindering mutual legal access.
- Moreover, foreign firms’ access to greater capital and a global clientele might create unequal competition, putting Indian law firms at a disadvantage.
- Effective oversight is essential to ensure foreign lawyers operate strictly within non-litigious boundaries.
- Despite these concerns, the reform holds considerable significance. It supports India’s ambition to become a global arbitration hub, especially in sectors like infrastructure and international trade.
- The policy also promotes bilateral legal engagement, as demonstrated at the Indo-UK Arbitration Conference, and acts as a catalyst for legal modernization by exposing Indian practitioners to global standards and technologies.
- Importantly, the amendment upholds the Advocates Act, 1961, by preserving the prohibition on foreign lawyers practicing Indian law, thereby safeguarding national legal sovereignty. Additionally, under reciprocity provisions, Indian advocates may now register to practice foreign law abroad without surrendering their right to practice in India.
- In conclusion, the Bar Council’s measured liberalization of foreign legal practice reflects a progressive shift in India’s legal framework. With adequate regulatory vigilance, clarity of rules, and international cooperation, this initiative could significantly elevate India’s global standing in legal consultancy and arbitration.
With reference to the Bar Council of India’s (BCI) regulatory reforms allowing foreign legal professionals in India, consider the following statements:
- The amended BCI rules permit foreign law firms to appear before Indian courts and tribunals in matters pertaining to international commercial disputes.
- Under the revised framework, foreign legal practitioners may advise on international law and participate in arbitration proceedings seated in India, without the requirement of reciprocity from their home jurisdictions.
- The reform aims to enhance India’s position as a global arbitration hub while explicitly preserving the sanctity of the Advocates Act, 1961.
- Indian advocates may now register to practice foreign law abroad, provided they renounce their right to practice in Indian courts under the principle of exclusive domestic jurisdiction.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 3 only
D. 2, 3 and 4 only
Answer: C. 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: The revised BCI rules do not permit foreign firms to appear before Indian courts or tribunals. Their scope is limited strictly to non-litigious matters such as advising on foreign/international law and arbitration.
- Statement 2 – Incorrect: Participation by foreign lawyers is conditional on reciprocity—i.e., Indian lawyers must be allowed similar privileges in the foreign lawyer’s home jurisdiction.
- Statement 3 – Correct: The reforms aim to strengthen India’s global arbitration role while preserving the Advocates Act, 1961, which prohibits foreign lawyers from practicing Indian law.
- Statement 4 – Incorrect: Indian lawyers can register abroad under reciprocity provisions without renouncing their Indian rights. There is no requirement to give up their right to practice in India.
EnviStats India 2025
Syllabus: Environment
Energy Trends:
- Thermal power generation increased from 7.92 lakh GWh (2013–14) to 13.26 lakh GWh (2023–24).
- Renewable energy generation rose significantly from 65,520 GWh to 2.25 lakh GWh over the same period.
Fisheries Sector:
- Inland fish production more than doubled from 61.36 lakh tonnes to 139.07 lakh tonnes.
- Marine fish production also increased, reaching 44.95 lakh tonnes.
- Temperature and Climate:
- Annual mean temperature rose from 25.05°C in 2001 to 25.74°C in 2024.
- Both maximum and minimum temperatures showed a consistent rising trend.
Rainfall Patterns:
- Despite significant inter-annual variability, no clear long-term trend in rainfall was observed—highlighting ongoing monsoonal unpredictability.
- Biodiversity Statistics:
- India supports 1,04,561 faunal species, including:
- 22,404 soil species
- 9,436 freshwater species
- 5,023 mangrove species
Budget Allocation:
- The Environment Sustainability Sector received the highest funding at ₹2,433 crore (2021–22), while Agroforestry received the least.
- New Indicators Added:
- Ramsar sites, sanitation, transport, and electricity access are now included, expanding the report’s thematic breadth.
- Methodology:
- The report adheres to the Framework for the Development of Environment Statistics (FDES 2013), ensuring consistency with global statistical standards.
Strengths of the Report
- Evidence-Based Policy Support: The structured data enables informed planning in climate action and biodiversity conservation.
- Expanded Indicator Set: Inclusion of cross-sectoral indicators reflects a more integrated sustainability approach.
- Energy Transition Insights: Long-term tracking of renewables aids climate policy and international commitments (e.g., Paris Agreement).
- Biodiversity Focus: Highlights India’s ecological richness, especially in soil and aquatic ecosystems.
Key Gaps and Challenges
- Lack of Regional Rainfall Analysis: Absence of state or district-level trends hampers local climate preparedness.
- No Causal Linkage: The report presents data without analyzing drivers or outcomes of environmental degradation.
- Delayed Data Cycles: Retrospective datasets reduce effectiveness for real-time policy responses, especially in air quality and urban planning.
- Limited Climate Vulnerability Mapping: Rising temperature trends are not complemented with region-specific risk and adaptation metrics.
Recommendations
- Integrate Real-Time Monitoring: Leverage ISRO’s satellite data and IoT technologies for timely environmental intelligence.
- Regional Disaggregation: Publish data at state/district level to support decentralised governance.
- Link with SDGs: Align indicators directly with national targets under SDG Goals 6, 7, 13, 14, and 15.
- Improve Accessibility: Create public-facing dashboards and visual platforms to democratise environmental information.
Conclusion
- EnviStats India 2025 marks a significant step in systematising environmental data in line with global standards. However, to transform statistics into actionable insights, India must invest in real-time, regionalised, and policy-linked data systems. A dynamic and inclusive environmental statistics infrastructure will be crucial for India’s sustainable and climate-resilient development.
With reference to “EnviStats India 2025” released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI), consider the following statements:
- India’s renewable energy generation has witnessed a more than threefold increase in the last decade, overtaking thermal power generation in absolute terms as per 2023–24 data.
- The report adheres to an international framework for environmental statistics, enabling structured cross-country comparability.
- The inland fish production in India is more than three times the marine fish production, as per the latest available data.
- The report incorporates real-time climate vulnerability mapping and evaluates the adaptive capacity of districts facing rising temperatures.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A. 2 and 3 only
B. 1, 2 and 4 only
C. 1 and 4 only
D. 2 and 3 only
Answer: A. 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect:While renewable energy has increased significantly (from ~65,520 GWh to ~2.25 lakh GWh), thermal energy still remains higher at 13.26 lakh GWh (2023–24). Thus, renewable energy has not overtaken thermal power in absolute terms.
- Statement 2 – Correct:The report follows the FDES 2013 (Framework for Development of Environment Statistics), which is a UN-backed international classification model.
- Statement 3 – Correct:Inland fish production (139.07 lakh tonnes) is indeed more than three times marine fish production (44.95 lakh tonnes), as per 2023–24 data.
- Statement 4 – Incorrect:The report does not include real-time climate vulnerability mapping or district-level adaptive capacity assessment; this was mentioned as a shortcoming in the analysis.
Pratima Barwa – The Unsung Torchbearer of Tribal Hockey
Syllabus:Society
- In the remote tribal region of Simdega, Jharkhand—where sports infrastructure was nearly non-existent—Pratima Barwa emerged as a quiet revolution. Her aspiration to represent India in hockey was shattered by a knee injury, but she chose not to surrender to fate. Instead, she channelled her loss into purpose. Armed only with a worn-out bicycle and unwavering determination, she cycled across distant villages, identifying young talent buried in obscurity. Without formal training tools, her coaching thrived on empathy, resilience, and a fierce belief in her students’ potential.
- Pratima faced cultural resistance and poverty head-on, persuading reluctant parents to let their daughters step onto the field. In doing so, she challenged both gender and social barriers, nurturing sport not just as a game but as a vehicle for identity and dignity. Today, Salima Tete, the captain of India’s women’s hockey team, is a living embodiment of Pratima’s grassroots legacy. Her makeshift academy may have lacked modern facilities, but it became a sanctuary where tribal girls found strength, voice, and aspiration.
In the context of grassroots development and ethics in public life, consider the following statements about the role exemplified by individuals like Pratima Barwa:
- Her model of sports coaching primarily demonstrates the principle of utilitarianism, wherein the greatest good for the greatest number is prioritized over individual losses.
- The intervention aligns with the capability approach of development, by enhancing real freedoms and opportunities for marginalized individuals.
- Her initiative best reflects Kantian ethics, where duty is performed irrespective of personal gain or consequence.
- The transformation facilitated by her work indicates the importance of institutional support, without which such social change is nearly impossible.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 4 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 2 and 4 only
D. 2, 3 and 4 only
Correct Answer: B. 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: While the outcome benefited many, her motivation was not rooted in utilitarian logic, but rather in moral duty and compassion.
- Statement 2 is correct: The capability approach (Amartya Sen, Martha Nussbaum) focuses on enhancing individuals’ freedoms and opportunities, which her work clearly enabled for tribal girls.
- Statement 3 is correct: Her actions stemmed from a sense of moral obligation, without regard for personal benefit — closely aligned with Kantian deontological ethics.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: Her achievements came despite the absence of institutional support, which is precisely what makes the story powerful and exemplary.
Ayush Nivesh Saarthi Portal
Syllabus:Governance
Context:
- India has launched the ‘Ayush Nivesh Saarthi’ portal to channel investments into the Ayush sector, positioning the country as a global hub for traditional medicine and wellness-based entrepreneurship.
- The Ayush Nivesh Saarthi Portal is a specialized digital platform created to facilitate investments in India’s Ayush sector—covering Ayurveda, Yoga, Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy.
- It is spearheaded by the Ministry of Ayush and developed in collaboration with Invest India.
Core Objectives:
- The portal aims to streamline and accelerate investments in Ayush-focused enterprises, attract Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and private capital in traditional medicine, and consolidate relevant policy frameworks, market access, and incentives into a unified digital interface.
- Salient Features: It incorporates an investor-first design with a user-friendly interface and guided support.
- An integrated policy dashboard centralizes access to state and central Ayush policies, incentive schemes, and investment-ready projects. The portal offers a dynamic approval mechanism for real-time processing of investor queries and clearances.
- It is globally accessible and aligned with FDI norms, supporting 100% FDI under the automatic route in the Ayush sector, thus promoting ease of entry and operation.
Strategic Significance:
- The portal provides a boost to the traditional medicine economy, which saw a 17% CAGR between 2014 and 2020. It strengthens India’s position in the $13 billion global wellness tourism market through Medical Value Travel (MVT), empowers startups and MSMEs by enabling innovation in natural health products, serves as an instrument of health diplomacy by presenting India as a sustainable wellness leader, and fosters a shift toward a preventive health culture.
Conclusion:
- The Ayush Nivesh Saarthi portal is not merely a digital tool but a strategic policy measure to globalize India’s traditional medicine ecosystem, encourage ethical investment, and establish a resilient, wellness-driven healthcare economy.
Consider the following statements with reference to India’s ‘Ayush Nivesh Saarthi’ portal:
- It enables centralized investor clearance for both domestic and foreign entities under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- The portal supports 100% Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in Ayush-based ventures through the automatic route.
- It integrates Medical Value Travel (MVT) incentives into its investor dashboard to promote India’s wellness tourism sector.
- It mandates that all Ayush-based MSMEs listed must be certified under the WHO-GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) framework.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 2, 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: B. 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The nodal ministry for the portal is the Ministry of Ayush, not the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Statement 2 is correct: The portal supports 100% FDI under the automatic route in the Ayush sector.
- Statement 3 is correct: Promoting Medical Value Travel (MVT) is a stated strategic goal of the portal.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: While quality standards like WHO-GMP are encouraged, the portal does not mandate that all MSMEs be WHO-GMP certified at the time of listing.
Chenab Railway Bridge
Syllabus:Geography
- The Prime Minister of India is set to inaugurate the Chenab Railway Bridge, marking the full completion of the Udhampur–Srinagar–Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL)—a transformative step in connecting the Kashmir Valley to the rest of the country.
- The Chenab Railway Bridge is a monumental steel-arch bridge built over the Chenab River in Jammu & Kashmir.
- Officially recognized as the world’s tallest railway bridge, it stands at an astonishing 359 meters—35 meters taller than the Eiffel Tower.
- It spans between Bakkal and Kauri villages in Reasi district and forms a vital segment of the USBRL project, connecting Katra to Sangaldan and facilitating direct rail access to Srinagar.

- Executed by Konkan Railway Corporation and constructed by a joint venture of Afcons Infrastructure, Ultra Construction (South Korea), and VSL India, the bridge measures 1,315 meters in total length, including 530 meters of approaches and a 785-meter main arch span.
- Engineered to withstand winds up to 266 km/h, it is designed for seismic Zone V earthquakes with magnitudes up to 8, operable in temperatures as low as –20°C, and blast-resistant to withstand explosions equivalent to 40 tonnes of TNT.
- Its estimated lifespan is 120 years, with trains running at speeds up to 100 km/h. Strategically, the bridge enhances logistical and security access to a border-sensitive region, symbolizes engineering excellence overcoming fractured Himalayan geology, ensures uninterrupted railway connectivity to the Kashmir Valley fostering national integration, and promotes tourism, employment, and regional development in Jammu & Kashmir.
- Globally, it stands as a landmark in civil engineering, showcasing India’s infrastructure prowess.
- The Chenab Railway Bridge represents national resolve, strategic vision, and technological brilliance, opening a new chapter in Kashmir’s integration and development and redefining the boundaries of possibility in Indian infrastructure.
Consider the following statements about the Chenab Railway Bridge:
- It is the tallest railway bridge in the world, exceeding the height of the Eiffel Tower.
- The bridge is designed to withstand earthquakes up to magnitude 9 on the Richter scale.
- It forms a crucial part of the Udhampur–Srinagar–Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL) project.
- The construction of the bridge involved collaboration between Indian and South Korean firms.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 and 3 only
B) 1, 3 and 4 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: B) 1, 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Chenab Railway Bridge is the tallest railway bridge in the world at 359 meters, taller than the Eiffel Tower.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The bridge is designed to withstand earthquakes up to magnitude 8, not 9.
- Statement 3 is correct: It is a critical part of the USBRL project.
- Statement 4 is correct: The construction involved a joint venture between Indian and South Korean companies.
Waste Picker Enumeration App
Syllabus:GovernanaceTop of Form
- The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment launched a Nationwide Waste Picker Enumeration App under the NAMASTE scheme to formalize, empower, and provide social security to waste pickers.
About the Waste Picker Enumeration App:
- It is a digital platform designed to enumerate, identify, and support waste pickers through social security and livelihood-based interventions under the NAMASTE Scheme.
- The initiative is led by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) in collaboration with the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), and implemented via the National Safai Karamcharis Finance & Development Corporation (NSKFDC).
- The app aims to recognize waste pickers as essential workers in India’s solid waste management system and to provide them with identity, protection, and formal integration into urban waste management systems.

Key Features:
- Large-scale profiling targeting enumeration of 2.5 lakh waste pickers, issuing occupational identity cards for formal recognition.
- Health and safety coverage including health insurance under Ayushman Bharat and distribution of personal protective equipment and seasonal safety kits.
- Skill and livelihood support through training and capital subsidies for waste collection vehicles to promote sustainable livelihoods.
- Strengthening waste management systems by supporting the formation of waste picker collectives to manage 750 dry waste collection centres across urban areas.
- Knowledge-based empowerment through resources like the Mainstreaming Waste Picker Collectives Guide and the Charting Change socio-economic insights report.
About NAMASTE Scheme:
- The National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) is a Central Sector Scheme launched in July 2023 to formalize and rehabilitate sanitation workers engaged in hazardous cleaning and solid waste management. The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment acts as the nodal ministry, with the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) as a convergence partner. The National Safai Karamcharis Finance & Development Corporation is the implementing agency. The scheme aims to ensure dignity, safety, and livelihood for sewer workers, septic tank cleaners, and waste pickers, and to eliminate manual scavenging by promoting mechanized, skilled sanitation services.
Consider the following statements regarding the Nationwide Waste Picker Enumeration App under the NAMASTE scheme:
- The app is implemented by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs as the nodal ministry.
- It aims to provide occupational identity cards to waste pickers for their formal recognition.
- Health insurance coverage under Ayushman Bharat is a part of the benefits extended to waste pickers through the app.
- The scheme exclusively targets manual scavengers and excludes waste pickers.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 2 and 3 only
B) 1, 2 and 4 only
C) 2, 3 and 4 only
D) 1 and 4 only
Answer: A) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The nodal ministry for the app is the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, not the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- Statement 2 is correct: The app aims to issue occupational identity cards to waste pickers for formal recognition.
- Statement 3 is correct: Waste pickers get health insurance benefits under Ayushman Bharat through the app.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: The scheme targets both manual scavengers and waste pickers; it does not exclude waste pickers.
International Institute of Administrative Sciences (IIAS)
Syllabus:Goveranace
India secured the Presidency of the International Institute of Administrative Sciences (IIAS) for the 2025–2028 term by winning 61.7% of the votes in an election held in Brussels.
This marks India’s first-ever presidency and the first ballot-based election in IIAS’s 100-year history. The IIAS is a global, non-governmental scientific organization established in 1930, dedicated to advancing public administration research and reform through international collaboration.
Headquartered in Brussels, Belgium, it promotes comparative public administration studies, facilitates intercultural dialogue, supports governance reform models, and engages actively in global administrative discourse.The institute organizes three international conferences annually, publishes the International Review of Administrative Sciences in English, French, and Mandarin, serves as a forum for policymakers and scholars from over 90 countries, and collaborates with the United Nations Public Administration Network (UNPAN) and UN Committee of Experts on Public Administration (CEPA).
Consider the following statements about the International Institute of Administrative Sciences (IIAS):
- It is a United Nations specialized agency focused on global administrative reforms.
- The IIAS was established in the early 20th century to advance comparative public administration research.
- It publishes the International Review of Administrative Sciences in multiple languages including English, French, and Mandarin.
- India has previously held the presidency of IIAS before 2025.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1, 2 and 3 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 2, 3 and 4 only
D) 1 and 4 only
Answer: B) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: IIAS is a global non-governmental scientific organization, not a United Nations specialized agency. Although it collaborates with UN bodies like UNPAN and UN CEPA, it is independent and not a UN specialized agency.
- Statement 2 is correct: IIAS was founded in 1930, in the early 20th century, with the aim of advancing comparative public administration research and reform.
- Statement 3 is correct: IIAS publishes the International Review of Administrative Sciences in English, French, and Mandarin.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: India has never held the presidency of IIAS before 2025; this is the first time India will hold it (for 2025–2028).
SEBI’s Operational Framework for ESG Debt Securities
Syllabus:Economy
- SEBI has introduced a comprehensive operational framework for issuing Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) debt securities, covering social bonds, sustainability bonds, and sustainability-linked bonds.
What are ESG Debt Securities?
- These are financial instruments raised exclusively to fund projects that deliver environmental, social, or governance benefits. They include:
- Social Bonds: Focused on social impact initiatives.
- Sustainability Bonds: Target both environmental and social objectives.
- Sustainability-Linked Bonds: Linked to specific ESG performance targets.
Key Features:
- Proceeds must be used solely for eligible sustainable or social projects.
- Bonds must be clearly labelled according to the primary objective of the funded project.
- Issuances must comply with recognized international ESG standards.
- Third-party verification or certification is mandatory.
- Applicable to both public offerings and private placements.
SEBI’s Operational Framework Details:
- Classification: Issuers must categorize bonds as green, social, or sustainability based on the main purpose of the underlying projects, ensuring transparency on impact focus.
Disclosure:
- Initial offer documents should specify project eligibility criteria, selection processes, and a tentative split between financing and refinancing of projects.
- Annual continuous disclosures must include impact metrics and detailed fund utilization reports.
- Independent Review: Issuers are required to engage independent third-party reviewers or certifiers to confirm alignment with ESG principles, enhancing investor confidence.
- Monitoring: Ongoing impact assessments must be conducted to verify that the funded activities genuinely contribute to reducing environmental or social harm.
- Implementation: The framework will apply to all ESG debt issuances starting from June 5, 2025, and aligns with global ESG standards to attract responsible investment.
Consider the following statements about SEBI’s operational framework for Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) debt securities:
- Issuers must classify bonds strictly as green, social, or sustainability bonds based on the primary objective of the underlying projects to ensure clear impact demarcation.
- The framework mandates that all ESG debt securities must be listed on recognized stock exchanges within six months of issuance.
- Continuous annual disclosures are required, detailing impact metrics and utilization of funds raised through ESG debt securities.
- Independent third-party verification or certification of ESG alignment is compulsory under the framework.
- The framework applies to issuances made from January 1, 2025, onwards.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A) 1, 3, and 4 only
B) 1, 2, and 5 only
C) 2, 3, and 4 only
D) 1, 3, 4, and 5 only
Answer: A) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct as issuers must classify bonds by their primary objective (green, social, or sustainability).
- Statement 2 is incorrect; the framework does not mandate compulsory listing within six months.
- Statement 3 is correct; annual disclosures of impact metrics and fund utilization are required.
- Statement 4 is correct; independent third-party verification is mandatory to ensure ESG compliance.
- Statement 5 is incorrect; the framework applies from June 5, 2025, not January 1.
