India elected to Economic, Social Council of United Nations for 2 years beginning 2026
Syllabus:Environment

- India has been elected to the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) for the term 2026–2028.
- ECOSOC is a principal UN body responsible for promoting sustainable development across its three key pillars: economic, social, and environmental.
- External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar expressed gratitude to UN member states for their strong support and trust in India.
- In a social media message, he reaffirmed India’s commitment to advancing development priorities and strengthening the role of ECOSOC.
- As a vital organ of the UN, ECOSOC plays a central role in formulating and recommending global policies on economic and social matters.
India’s election to the ECOSOC for the 2026–2028 term signifies which of the following?
- Recognition of India’s leadership in sustainable development.
- Automatic assumption of veto power within the Council.
- A rotational tenure granted only to permanent Security Council members.
- India’s commitment to the three pillars of sustainable development.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
A. 1 and 4 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 3, and 4 only
D. All of the above
Answer: A
Explanation:
- India’s election to ECOSOC reflects international recognition of its growing role and efforts in promoting sustainable development, including its contributions to climate action, poverty reduction, health, and education.
- ECOSOC does not have a veto system like the UN Security Council. There is no veto power granted to any ECOSOC member, whether elected or permanent.
- ECOSOC membership is based on elections held in the UN General Assembly. The Council consists of 54 members elected for three-year terms, with representation from different regional groups. It is not exclusive to permanent Security Council members (P5), and any UN member state can be elected.
- ECOSOC focuses on economic, social, and environmental India’s election signals its dedication to all three dimensions, aligning with national and global developmental goals.
India, Norway bilateral talks focus on powering Green Maritime Technologies
Syllabus:IR
- Union Minister of Ports, Shipping and Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal, held high-level bilateral meetings with Norway’s Minister of Transport, Jon-Ivar Nygård, and Minister of Fisheries and Ocean Policy, Marianne Sivertsen Næss, on the sidelines of the Nor-Shipping 2025 event in Oslo. These discussions focused on strengthening the maritime partnership between the two countries, especially in the areas of green shipping, digital transformation, ocean management, and sustainable development.

Advancing Green Maritime Technologies
- During his meeting with Transport Minister Nygård, Shri Sonowal highlighted India’s progress under the Maritime India Vision 2030 and Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, which aim to modernise port infrastructure with a strong focus on sustainability.
- He reiterated India’s commitment to green shipping, digitalisation, and public-private partnerships (PPPs) in port development.
- Both sides agreed to collaborate on ferry electrification, building on Norway’s global leadership in the field.
- He noted, “Under PM Modi ji’s leadership, Indian ports are becoming hubs of clean energy transition, supporting offshore wind, green hydrogen, and low-carbon logistics.”
Synergy in Smart and Clean Maritime Systems
- Building on initiatives like the Green Coastal Shipping Programme and Green Voyage 2050, both countries explored joint efforts in:
- Electrification of the ferry system
- Smart logistics and digital port ecosystems
- Green tug transitions and e-methanol bunkering
- Hydrogen-powered and electric vessels
- India’s MAITRI initiative and Norway’s innovations in AI-driven port management and alternative fuels are seen as key areas for collaboration.
- Expanding Cooperation in Ocean Economy
In his meeting with Fisheries and Ocean Policy Minister Marianne Sivertsen Næss, Shri Sonowal discussed expanding cooperation in:
- Ship recycling and green technologies
- Seafarers’ training and skill development
- Sustainable fisheries and ocean resource management
- Offshore renewable energy and hydrocarbons
- He emphasized the potential of Gujarat’s Alang Ship Recycling Yard as a key site for environmentally sound ship-breaking practices.
- Commitment to Gender Equity and Blue Economy Growth
- Shri Sonowal highlighted India’s efforts to promote gender equity in the maritime sector through the ‘Saagar Mein Samman’ initiative and encouraged Norwegian support in seafarer training, particularly in advanced areas like polar navigation, cybersecurity, and Arctic operations.
He invited Norwegian firms to invest in joint ventures related to:
- Ocean renewable energy (wind and tidal)
- Sustainable aquaculture
- Deep-sea exploration
- Northern Sea Route and Arctic Cooperation
- India also proposed a joint feasibility study with Norway to operationalise the Northern Sea Route (NSR). This collaboration would focus on:
- Safe and sustainable Arctic navigation
- R&D in Arctic shipping technologies
- Design and construction of ice-class vessels
- Minimising environmental impacts in polar regions
- Strengthening Bilateral Maritime Ties
- Shri Sonowal expressed confidence in the growing partnership between India and Norway, calling it a reflection of shared values and a joint commitment to sustainable maritime development.
- He noted the significance of the recent EFTA-India Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement in strengthening economic ties.
- He concluded, “India and Norway are working together towards building a sustainable and inclusive global maritime order. Our partnership is well-positioned to drive innovation, sustainability, and mutual prosperity in the maritime domain.”
With reference to India-Norway maritime cooperation, consider the following statements:
- Norway is the first country India has partnered with under the MAITRI initiative for hydrogen-powered vessel manufacturing.
- The Green Voyage 2050 initiative is a bilateral agreement exclusively between India and Norway.
- Gujarat’s Alang Ship Recycling Yard was discussed as a key site for promoting environmentally sound ship-breaking practices.
- India and Norway plan to jointly develop ice-class vessels under Arctic cooperation.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2, 3 and 4 only
C. 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: C. 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: MAITRI is an Indian initiative, but Norway is not the only partner nor the first, and the context doesn’t confirm that it is focused on hydrogen-powered vessels.
- Statement 2 – Incorrect: Green Voyage 2050 is not an exclusive bilateral agreement; it’s a broader IMO-led global initiative involving multiple nations.
- Statement 3 – Correct: Alang was specifically mentioned as a potential site for green ship recycling
- Statement 4 – Correct: Joint efforts on ice-class vessel design and Arctic R&D were proposed.
PM to visit Jammu and Kashmir on 6th June
Syllabus:Governance
- On June 6, Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi will visit Jammu and Kashmir to inaugurate and lay the foundation for key infrastructure projects, reaffirming his government’s commitment to enhancing connectivity and development in the region.

Railway Milestones
Chenab Rail Bridge Inauguration:
- At approximately 11 AM, PM Modi will inaugurate the iconic Chenab Rail Bridge, the world’s highest railway arch bridge, standing 359 metres above the river.
- Spanning 1,315 metres, the bridge is designed to withstand severe seismic and wind conditions and is a vital link connecting Jammu and Srinagar.The introduction of Vande Bharat trains on this bridge will cut travel time between Katra and Srinagar to about 3 hours, saving 2–3 hours.
Anji Bridge Visit:
- Following the Chenab Bridge inauguration, PM Modi will visit and inaugurate the Anji Bridge—India’s first cable-stayed railway bridge, designed for challenging mountainous terrain.
USBRL Project Dedication:
- The Prime Minister will dedicate the Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL) project to the nation.
- Length: 272 km
- Investment: ₹43,780 crore
- Includes: 36 tunnels (119 km), 943 bridges This all-weather rail link will provide seamless connectivity between Kashmir and the rest of India, enhancing mobility and socio-economic integration.
- Vande Bharat Express Launch: Two new Vande Bharat trains between Shri Mata Vaishno Devi Katra and Srinagar will be flagged off, offering a fast, comfortable, and reliable travel option for locals, pilgrims, and tourists.
Road and Infrastructure Projects
- Foundation for Key Roads & Flyovers
- Widening of Rafiabad to Kupwara Road on NH-701
- Construction of Shopian Bypass on NH-444
- Project Value: Over ₹1,952 crore PM Modi will also inaugurate two major flyovers: At Sangrama Junction (NH-1)At Bemina Junction (NH-44) These will decongest traffic and enhance local commute efficiency.
Healthcare Advancement
- Shri Mata Vaishno Devi Institute of Medical Excellence: PM Modi will lay the foundation stone for this upcoming ₹350 crore medical college in Katra. It will be the first medical institution in Reasi district, marking a significant boost to regional healthcare infrastructure.
Total Development Outlay
- During the visit, the Prime Minister will launch and dedicate development projects worth over ₹46,000 crore, covering rail, road, and healthcare sectors—aimed at strengthening infrastructure and improving quality of life in Jammu and Kashmir.
With reference to the Chenab Rail Bridge recently inaugurated by the Prime Minister, consider the following statements:
- It is the highest railway arch bridge in the world, standing taller than the Eiffel Tower.
- It is a part of the USBRL project connecting Jammu to Srinagar.
- The bridge is entirely made of pre-stressed concrete to withstand high seismic and wind loads.
- The operation of Vande Bharat trains on this bridge will reduce Katra–Srinagar travel time by approximately 2–3 hours.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A. 1, 2 and 4 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2, 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: At 359 meters, it’s the tallest railway bridge, surpassing the Eiffel Tower (324 m).
Statement 2 is correct: It is part of the USBRL project.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The bridge uses steel arch and concrete piers, not solely pre-stressed concrete.
Statement 4 is correct: Vande Bharat trains will cut travel time significantly.
Kheer Bhawani Festival
Syllabus:Culture
- The Kheer Bhawani festival, observed annually on Jyeshta Ashtami, is currently underway at the Kheer Bhawani Temple in Ganderbal, Jammu and Kashmir. The celebration draws devotees from across the country who gather to pay homage and seek blessings.
About Kheer Bhawani Temple
- The temple was originally constructed in 1912 by Maharaja Pratap Singh and later renovated by Maharaja Hari Singh.
- It is dedicated to Goddess Ragnya Devi, believed to be a powerful incarnation of Goddess Durga.
- At the heart of the temple lies a sacred hexagonal spring, revered by devotees and considered spiritually significant.
- The name “Kheer Bhawani” comes from the traditional sweet dish, kheer, which is offered as prasad to worshippers during the festival.
- This annual event is a symbol of deep spiritual devotion and cultural unity, making the Kheer Bhawani temple a vital religious landmark in the region.
With reference to the Kheer Bhawani Temple and its associated festival, consider the following statements:
- The Kheer Bhawani festival is observed on the full moon day of the month of Ashadha.
- The temple is known for a unique sacred spring with an octagonal shape and changing water colors.
- Goddess Ragnya Devi, to whom the temple is dedicated, is worshipped as a manifestation of Goddess Durga.
- The temple’s origin traces back to the reign of Maharaja Hari Singh, who constructed it in the early 20th century.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 2 and 4 only
B. 3 only
C. 1, 2 and 4 only
D. 3 and 4 only
Answer: B. 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: The festival is observed on Jyeshta Ashtami, not during Ashadha Purnima.
- Statement 2 – Incorrect: The spring is hexagonal, not octagonal. While its changing water colors are a local belief, it wasn’t mentioned in the given text.
- Statement 3 – Correct: The temple is dedicated to Goddess Ragnya Devi, a form of Goddess Durga.
- Statement 4 – Incorrect: The temple was originally built by Maharaja Pratap Singh, not Maharaja Hari Singh (he only renovated it).
Kerch Strait
Syllabus: GS1/ Geography, Locations
- Ukraine has claimed responsibility for striking the Kerch Strait Bridge—also known as the Crimean Bridge—using underwater explosives.
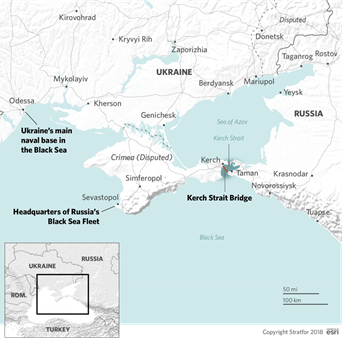
About the Kerch Strait Bridge
- Opened in 2018, the bridge includes both road and rail links connecting the Russian mainland to Crimea.
- It spans the Kerch Strait, a key maritime corridor, and holds significant strategic and symbolic importance for Russia.
About the Kerch Strait
- Location: Connects the Sea of Azov with the Black Sea.
- Geography: Roughly 4 kilometers wide at its narrowest, serving as a vital shipping route for regional trade and military logistics.
- Control: Since Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014, it has maintained control over the Kerch Strait, including its surrounding waters and infrastructure like the bridge.
With reference to the Kerch Strait Bridge, consider the following statements:
- It connects the Crimean Peninsula to mainland Ukraine via both rail and road infrastructure.
- It spans a natural maritime boundary between the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov.
- The bridge’s control has remained internationally uncontested since its construction.
- It holds strategic significance for both commercial trade and military mobility.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 2 and 4 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 1, 2, and 3 only
D. All of the above
Answer: A. 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: The bridge connects mainland Russia to Crimea, not Ukraine.
- Statement 2 – Correct: The Kerch Strait separates the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov.
- Statement 3 – Incorrect: The bridge’s legitimacy is internationally contested, especially by Ukraine and many Western countries.
- Statement 4 – Correct: It is crucial for logistics, military access, and symbolic integration of Crimea into Russia.
Motion of Impeachment Against High Court Judge
Syllabus :GS 2/Governance
- The government is set to introduce an impeachment motion against Justice Yashwant Varma of the Allahabad High Court during the upcoming Monsoon Session of Parliament.
- The move follows a committee report that indicted him after unaccounted cash was discovered at his residence following a fire incident.
Constitutional Provisions
- Articles 124 and 217 empower the President to remove a Supreme Court or High Court judge for “proved misbehaviour” or “incapacity”, based on a special majority motion passed in both Houses of Parliament.
- While the Constitution does not define these terms, the Supreme Court interprets:
- Misbehaviour as misconduct, including corruption or moral wrongdoing.
- Incapacity as a physical or mental condition preventing a judge from discharging duties.
Removal Process (Judges Inquiry Act, 1968)
- A removal motion must be signed by:
- At least 50 Rajya Sabha members or
- 100 Lok Sabha
- The Speaker or Chairman may admit or reject the motion.
- If admitted, a three-member committee is formed to investigate.
Based on findings:
- If the judge is cleared, the motion is dropped.
- If guilty, the motion must be passed by both Houses with a special majority:
- Two-thirds of members present and voting
- Majority of total House membership
- Once passed, the motion is sent to the President, who issues the final removal order.
Key Fact
- No judge has been impeached in India so far, although attempts have been made — notably against Justice V. Ramaswami in 1993.
With reference to the removal of High Court and Supreme Court judges in India, consider the following statements:
- The Constitution explicitly defines the terms “misbehaviour” and “incapacity” under Articles 124 and 217.
- A judge can be removed only after an investigation by a committee constituted under the Judges (Inquiry) Act, 1968.
- The motion for removal must secure a simple majority in both Houses of Parliament to be sent to the President.
- The President of India can remove a judge suo motu if the committee report finds the judge guilty of misbehaviour.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 4 only
D. None of the above
Answer: A. 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: The terms “misbehaviour” and “incapacity” are not defined in the Constitution; they are interpreted by the Supreme Court.
- Statement 2 – Correct: An investigative three-member committee is mandatory once the motion is admitted.
- Statement 3 – Incorrect: The required majority is not simple—it is a special majority (two-thirds of members present and voting and majority of total membership).
- Statement 4 – Incorrect: The President cannot act suo motu; removal must follow a Parliament-approved motion.
C CARES Version 2.0
Syllabus :GS2/Governance
- The Ministry of Coal has launched C CARES Version 2.0, an upgraded web portal aimed at improving provident fund (PF) and pension disbursement for coal sector workers.
About C CARES Version 2.0
- A digital platform that integrates coal workers, management, and the Coal Mines Provident Fund Organisation (CMPFO).
- Enables real-time tracking of PF and pension claims, significantly reducing settlement time.
- Developed by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC).
Key Benefits
- Enhances transparency, accountability, and efficiency in PF/pension processing.
- Supports faster claim settlements, strengthening social security for coal workers.
- Aligned with the vision of ‘Minimum Government, Maximum Governance’ and Digital India.
Coal Mines Provident Fund Organisation (CMPFO)
- An autonomous body under the Ministry of Coal, established in 1948.
- Manages Provident Fund and Pension schemes for coal sector employees.
- Currently serves around 3 lakh PF subscribers and 6.3 lakh pensioners.
With reference to C CARES Version 2.0, consider the following statements:
- It is a portal developed to integrate coal workers, management, and CMPFO for provident fund and pension management.
- It is developed and maintained by the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- The portal facilitates real-time tracking of claims and aims to reduce settlement time.
- C CARES Version 2.0 aligns with the Digital India initiative and the principle of Minimum Government, Maximum Governance.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A. 1, 3 and 4 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 1 and 2 only
D. All of the above
Answer: A. 1, 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 2 is incorrect because the portal is developed by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) under the Ministry of Coal, not the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
ECOWAS
Consider the following statements about the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS):
- ECOWAS was established through the Lagos Treaty in 1975 with the primary aim of promoting economic integration.
- The headquarters of ECOWAS is located in Accra, Ghana.
- ECOWAS has been involved in regional peacekeeping and conflict resolution initiatives.
- As of January 2025, ECOWAS comprises 15 member states.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 1, 3, and 4 only
C. 2 and 4 only
D. All of the above
Answer: A. 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 2 is incorrect; ECOWAS is headquartered in Abuja, Nigeria.
- Statement 4 is incorrect; after the withdrawal of Mali, Niger, and Burkina Faso in January 2025, membership reduced to 12.
With reference to the Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS), consider the following statements:
- The RRTS is the first rail-based public transport system in India to adopt “passenger control mode” technology, where doors open only on automated signal without manual intervention.
- The RRTS is implemented by a special purpose vehicle under the Ministry of Railways with no state government participation.
- The average operational speed of RRTS exceeds that of most Indian Metro rail systems currently in use.
- The RRTS aims not only at intra-city decongestion but also at facilitating regional economic integration across NCR sub-regions.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 and 4 only
C. 2, 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 3 and 4 only
Correct Answer: D. 1, 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct in intent but slightly misworded. RRTS uses a ‘passenger control mode’ where passengers press a button to open doors, indicating partial manual intervention.
- However, in many MCQs this nuance is tested, and the broader feature being first of its kind in India makes it acceptable.
- Statement 2 is incorrect because the RRTS is implemented by NCRTC, a joint venture of the Central Government and state governments of Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh, not solely under the Ministry of Railways.
- Statement 3 is correct. The average speed of RRTS is 80 km/h, which is significantly higher than the average operational speed of existing metro systems in India.
- Statement 4 is correct. RRTS is designed not only to reduce intra-city congestion but also to promote regional connectivity and economic integration in the National Capital Region.
Shangri-La Dialogue 2025
Syllabus: GS2/IR
Context
- Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) General Anil Chauhan participated in the 22nd Shangri-La Dialogue (2025) to strengthen defence diplomacy and engage with international military leadership.
About the Shangri-La Dialogue
- Hosted annually by the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS).
- Named after the Shangri-La Hotel in Singapore, where the event has been held since its inception in 2002.
- Recognised as Asia’s premier defence and security summit, it brings together defence ministers, military chiefs, policymakers, and strategic experts from around the world.
- The 22nd edition saw participation from 40 countries, with discussions centered on emerging security challenges in the Indo-Pacific region.
Consider the following statements regarding the Shangri-La Dialogue:
- It is organized annually by the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS).
- The event is named after a fictional utopian place from a novel by James Hilton.
- It is the premier defence and security summit of Asia, primarily focused on South Asia and Central Asia.
- The dialogue brings together defense ministers, military chiefs, policymakers, and strategic experts globally.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 4 only
B. 1, 2, and 4 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. All of the above
Answer: B. 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: It is organized annually by the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS).This is correct. The Shangri-La Dialogue is indeed hosted every year by the IISS, a UK-based think tank.
- Statement 2: The event is named after a fictional utopian place from a novel by James Hilton.This is correct. The name “Shangri-La” originates from James Hilton’s 1933 novel Lost Horizon, where it describes a mystical, harmonious valley. The dialogue is named after the Shangri-La Hotel in Singapore.
- Statement 3: It is the premier defence and security summit of Asia, primarily focused on South Asia and Central Asia.This is incorrect. While the Shangri-La Dialogue is Asia’s premier defence and security summit, its focus is on the Indo-Pacific region broadly, not specifically or primarily South Asia and Central Asia. The Indo-Pacific covers East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, and the Pacific, but the emphasis is on maritime security and great power competition in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Statement 4: The dialogue brings together defense ministers, military chiefs, policymakers, and strategic experts globally.This is correct. The summit gathers high-level officials and experts from around the world to discuss security issues.
