West Bengal’s Triple Elimination Initiative for Infectious Diseases
Syllabus: Science
- West Bengal has launched a pioneering ‘Triple Elimination’ initiative to eradicate mother-to-child transmission of HIV, syphilis, and Hepatitis B by 2026.
- This ambitious project is a joint effort by the West Bengal government, the William J Clinton Foundation, and the World Health Organization (WHO).
- By addressing these diseases collectively, the initiative marks a major step in improving maternal and child healthcare.
Objective of the Triple Elimination Initiative
- The initiative targets three infectious diseases that share similar transmission routes, aiming to reduce morbidity and mortality among mothers and newborns.
- Instead of tackling them in isolation, this integrated approach enhances the effectiveness of disease control programs for HIV, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and viral hepatitis.
Implementation Strategy
- Initially launched as a pilot project in April 2024 in four districts—Coochbehar, Rampurhat, South 24 Parganas, and Diamond Harbour.
- Based on positive outcomes, the initiative was expanded to all 23 districts by March 2025.
- A State Task Force and a Technical Advisory Group were established to oversee implementation and ensure effectiveness.
Screening and Treatment Protocols
- All pregnant women are screened for HIV, syphilis, and Hepatitis B during their prenatal check-ups.
- Those testing positive receive immediate treatment and counseling to prevent transmission.
- To minimize risks during childbirth, deliveries are mandated in medical institutions.
- Newborns of Hepatitis B-positive mothers receive the Hepatitis B Zero Dose vaccine and an HBIG injection within 24 hours of birth to prevent infection.
Overcoming Challenges
- Improved Healthcare Access: The initiative has decentralized syphilis services from district hospitals to block levels, making testing and treatment more accessible for pregnant women.
Localized Delivery Management: HIV and Hepatitis B-positive pregnancies are now managed at the block level, eliminating the need for long-distance travel and ensuring prompt care.
Addressing Stigma: A hyperlocal approach ensures quicker service delivery while reducing social stigma associated with these infections.
Future Prospects
- The success of West Bengal’s Triple Elimination Initiative is seen as a potential model for national implementation.
- With backing from the National AIDS Control Organisation (NACO) and the National Health Mission (NHM), experts believe similar nationwide programs could significantly reduce newborn infections from these diseases across India.
Consider the following statements regarding the ‘Triple Elimination’ initiative of West Bengal:
- The initiative targets the elimination of mother-to-child transmission of HIV, syphilis, and Tuberculosis.
- It was initially launched in selected districts and later expanded to all districts of the state.
- The initiative mandates institutional deliveries for mothers who test positive for any of the three diseases.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The initiative targets HIV, syphilis, and Hepatitis B, not Tuberculosis.
Statement 2 is correct: It started in four pilot districts and later expanded to all 23 districts of West Bengal.
Statement 3 is correct: Institutional deliveries are mandated to reduce transmission risks.
Morocco Launches Water Highway Project
Syllabus:Geography
Overview
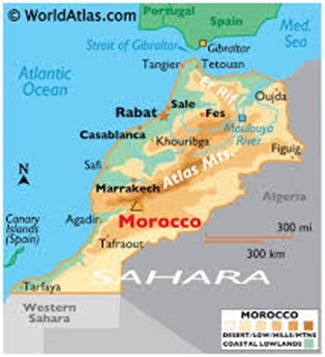
To combat its escalating water crisis, Morocco has launched the “Water Highway” project, aimed at securing drinking water for its most populous cities. The initiative transfers surplus water from the Sebou River to Rabat and Casablanca, addressing severe shortages caused by
climate change and prolonged droughts.
Project Details
The project, costing approximately $728 million, diverts and treats water from the Sebou River before transporting it through a 67-kilometre underground canal.
By March 2025, it had already delivered over 700 million cubic metres of water to urban centres.
Challenges of Water Scarcity
Drought Impact: Morocco has been grappling with a six-year-long drought.
Declining Water Reserves: Annual water supply has dropped from 18 billion cubic metres in the 1980s to just 5 billion cubic metres today.
Uneven Rainfall Distribution: 53% of rainfall occurs in only 7% of the country, creating severe regional imbalances.
Climate Change Implications
Rising Temperatures: Increased evaporation rates further deplete water resources.
Future Water Shortages: Climate models predict reduced rainfall in northern basins, raising concerns about the sustainability of water redirection efforts.
Agricultural Demands
Agriculture employs nearly one-third of Morocco’s workforce, making irrigation a major consumer of water.
Experts advocate for the adoption of water-efficient farming practices to mitigate the crisis.
Future Prospects
While the Water Highway provides short-term relief, experts question its long-term feasibility due to unpredictable northern river surpluses.
There is a growing push for alternative solutions, including desalination plants, to ensure sustainable water supply for urban populations.
Consider the following statements regarding Morocco’s “Water Highway” project:
- The project aims to divert water from the Sebou River primarily for agricultural irrigation.
- It involves a 67-kilometre underground canal to transport treated water.
- The project is entirely funded by the World Bank as part of its climate adaptation initiatives.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- The project primarily provides drinking water to Rabat and Casablanca, not agricultural irrigation (Statement 1 is incorrect).
- It indeed involves a 67-km underground canal for water transport (Statement 2 is correct).
- While the project costs $728 million, there is no mention of exclusive World Bank funding; it is a Moroccan initiative (Statement 3 is incorrect).
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana Milestones
Syllabus: Schemes
The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) remains a cornerstone of India’s financial inclusion strategy as of the financial year 2024-25. Launched on August 15, 2014, the initiative has now reached a major milestone, with 55 crore beneficiaries and a cumulative balance of ₹2.5 lakh crore in these accounts. The scheme continues to drive banking accessibility and financial empowerment, particularly among marginalized sections of society.
Key Features of PMJDY
PMJDY promotes financial inclusion by enabling zero-balance savings accounts, fostering a habit of savings among the unbanked population. It provides access to banking services, credit, insurance, and pension schemes, thus integrating beneficiaries into the formal financial system.
Demographic Insights
- Total Beneficiaries: 14 crore (as of March 2025)
- Rural and Semi-Urban Beneficiaries: 67% of total account holders
- Women Account Holders: 71 crore, constituting 56% of total beneficiaries
Financial Impact
- Average Account Balance: ₹4,726
- Contribution to Banking Liquidity: Increased deposits have enhanced the financial ecosystem.
- Direct Benefit Transfers (DBT): The scheme has facilitated transparent subsidy distribution.
Digital Integration and Payments
- The scheme actively supports digital transactions through RuPay debit cards:
- Total RuPay Cards Issued: 77 crore (as of March 2025)
- Boost to Digital Economy: The availability of digital payment tools has accelerated cashless transactions.
Economic and Social Implications
- Financial Inclusion Index: Rose from 4 in 2017 to 64.2 in 2024, indicating a significant improvement in financial accessibility.
- Access to Financial Products: Expansion of micro-insurance, pension schemes, and small credit facilities.
- Enhanced Investments: Improved financial access has led to increased investments in education, healthcare, and livelihood opportunities.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its achievements, PMJDY faces several hurdles:
- Dormant Accounts: 3 crore accounts remain inactive, requiring strategies for re-engagement.
- Credit Accessibility: The introduction of innovative micro-credit products and formal credit scoring mechanisms is necessary to strengthen financial stability.
- Private Sector Participation: Increased involvement of private banks could further enhance financial outreach.
Women’s Empowerment
- The scheme has played a pivotal role in enhancing women’s financial independence, as reflected in the high proportion of female account holders (56%). This shift signals greater economic empowerment and participation of women in financial decision-making.
- PMJDY continues to be a transformative initiative, bridging financial disparities and promoting economic resilience across India.
Consider the following statements regarding the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY):
- It was launched under the Ministry of Finance to promote financial inclusion.
- PMJDY accounts are required to maintain a minimum balance of ₹500 to remain active.
- The scheme includes access to micro-insurance and pension schemes.
- Only public sector banks are allowed to open PMJDY accounts.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 1, 2, and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- PMJDY was launched under the Ministry of Finance to ensure financial inclusion (Statement 1 is correct).
- PMJDY accounts are zero-balance accounts, meaning there is no requirement for a minimum balance (Statement 2 is incorrect).
- The scheme provides access to micro-insurance and pension schemes such as Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana and Atal Pension Yojana (Statement 3 is correct).
- Both public and private sector banks can open PMJDY accounts (Statement 4 is incorrect).
Japan’s Megaquake Threat
Syllabus: Geography
Japan faces an increasing risk of catastrophic megaquakes, particularly along the Nankai Trough, where seismic activity has heightened concerns. Recent government estimates underscore the potential for massive casualties and severe economic losses, emphasizing the need for enhanced disaster preparedness. This urgency follows a magnitude 7.1 earthquake in 2024, which caused significant injuries and damage.
Nankai Trough: A Seismic Hotspot
The Nankai Trough is a 900-kilometer-long undersea fault located off Japan’s Pacific coast, extending from Shizuoka to Kyushu. It lies at the convergence of the Philippine Sea Plate and the Eurasian Plate, where tectonic subduction generates immense geological strain. This process makes the region highly susceptible to large-scale earthquakes and tsunamis.
Probability of a Megaquake
Japanese seismic experts estimate a 70-80% probability of a magnitude 8 to 9 earthquake occurring in the Nankai Trough within the next 30 years. Historical patterns suggest a recurrence interval of 100 to 200 years, with the last major event striking in 1946. This high probability has intensified efforts to bolster earthquake preparedness.
Projected Human and Economic Toll
Casualty Estimates
- A megaquake could result in an estimated 298,000 deaths.
- 215,000 fatalities from tsunami impacts.
- 73,000 deaths from building collapses and fires.
- Around 23 million people—nearly 10% of Japan’s population—could be displaced.
- The time of occurrence (e.g., winter nights) could increase mortality rates due to exposure and infrastructure failures.
Economic Impact
- Financial losses could exceed $2 trillion, accounting for inflation-adjusted damage assessments.
- The projected economic losses represent nearly 50% of Japan’s GDP.
- Large-scale disruptions in transportation, commerce, and manufacturing would severely impact both domestic and global markets.
Lessons from Past Disasters
- Japan’s disaster preparedness strategy has been shaped by previous catastrophes, particularly the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, which:
- Caused over 18,000 deaths.
- Led to the Fukushima nuclear crisis, emphasizing the vulnerability of critical infrastructure.
- Highlighted the need for more robust early-warning systems and disaster response mechanisms.
Preparedness and Mitigation Strategies
The Japanese government has adopted multi-layered disaster preparedness measures, including:
- Public education campaigns to enhance citizen awareness of evacuation protocols.
- Infrastructure upgrades, such as earthquake-resistant buildings and seawalls.
- Advanced seismic warning systems, capable of detecting early tremors and triggering automatic alerts.
- Despite these efforts, experts caution that the magnitude and scale of a Nankai Trough megaquake could surpass past disasters, necessitating continuous improvements in disaster resilience.
Scientific Monitoring and Risk Assessment
- Japan’s seismological research institutions and government agencies actively monitor the Nankai Trough’s seismic activity through:
- Real-time tectonic movement tracking to detect early indicators of seismic shifts.
- Studies suggesting that magnitude 7+ earthquakes in the region could trigger larger tremors.
- Continuous refinement of predictive models to improve earthquake forecasting.
Conclusion
The looming risk of a Nankai Trough megaquake demands sustained vigilance and adaptive preparedness measures. While Japan has made significant progress in disaster resilience, the potential for mass casualties and economic upheaval necessitates ongoing investment in infrastructure, early-warning systems, and public readiness programs
Consider the following statements regarding Japan’s seismic vulnerability:
- The recurrence interval of large earthquakes in the Nankai Trough region is approximately 100-200 years.
- The Nankai Trough megathrust earthquakes have the potential to trigger both tsunamis and volcanic eruptions.
- The 2011 Tōhoku earthquake occurred along the Nankai Trough, leading to the Fukushima nuclear disaster.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: A) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Historical data indicate that megaquakes in the Nankai Trough recur every 100-200 years, with the last major event occurring in 1946.
- Statement 2 is correct: Subduction zone earthquakes can create tsunamis by displacing seawater, and they can also affect nearby volcanic systems due to the redistribution of underground stresses.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The 2011 Tōhoku earthquake (Magnitude 9.1) did not occur in the Nankai Trough but along the Japan Trench, which lies to the northeast of Japan. The Tōhoku quake triggered the Fukushima nuclear crisis, but it is unrelated to the Nankai Trough.
Gangotri National Park Opens For Tourists
Syllabus:Environment
- The gates of Gangotri National Park, situated in Uttarkashi district, Uttarakhand, have officially opened for tourists today.
- Encompassing approximately 2,390 square kilometers, the park serves as a crucial habitat for the snow leopard, along with other notable wildlife such as the black bear, brown bear, musk deer, blue sheep (Bharal), and Himalayan Monal.
- Due to the impact of landslides and glacial movements, restoration efforts are currently underway on the Gangotri-Gomukh trek, with authorities striving to reopen the route at the earliest.
- Additionally, this year marks the inauguration of two new trekking routes within Gangotri National Park.
- Trekkers will be permitted access to these trails between May and October, enhancing adventure tourism opportunities in the region.
Consider the following statements regarding Gangotri National Park:
- It is located in the Chamoli district of Uttarakhand.
- The park is home to species like the Himalayan Monal, musk deer, and Bharal.
- Gangotri Glacier, the source of the Yamuna River, is situated within the park’s boundaries.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- Gangotri National Park is located in the Uttarkashi district, not Chamoli (Statement 1 is incorrect).
- The park houses species such as the Himalayan Monal, Bharal (blue sheep), musk deer, and snow leopard (Statement 2 is correct).
- The Gangotri Glacier, within the park, is the source of the Ganga River, not the Yamuna River (Statement 3 is incorrect).
BIMSTEC summit and India’s unilateral role in Bay of Bengal
Syllabus: Economy
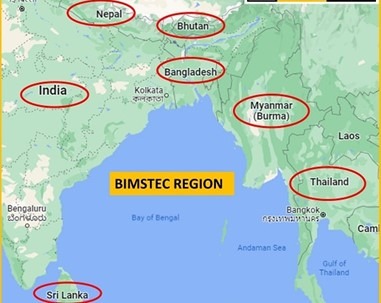
- As Prime Minister Narendra Modi prepares for the upcoming BIMSTEC Summit, India’s diplomatic efforts remain focused on the aftermath of the devastating earthquake in Myanmar, a key BIMSTEC member.
- The tragedy has also affected Thailand, highlighting the region’s interconnectedness. While India contributes to relief and rehabilitation efforts, a broader challenge looms—revitalizing BIMSTEC as a functional regional bloc.
BIMSTEC’s Evolution and Challenges
- Established in 1997, BIMSTEC took 25 years to secure a formal charter, ratified in 2023. The upcoming summit in Bangkok will unveil a vision document and new initiatives, including a maritime connectivity project.
- However, BIMSTEC continues to suffer from the perception of being a mere SAARC alternative—a sentiment reinforced when Pakistan blocked SAARC’s connectivity agreements in 2014, forcing India to look eastward.
The Bay of Bengal, once a natural hub of trade, culture, and political influence, saw its historical bonds fragmented due to:
- Colonial Disruptions: The British Raj unified the region under a colonial framework, but its decline, coupled with Japan’s rise, redrew strategic lines.
- World War II and Cold War Conflicts: Japan’s expansion in Asia, followed by post-war decolonization and Cold War rivalries, marginalized the Bay of Bengal in global geopolitics.
- Economic Isolation: Post-colonial policies in India and Myanmar distanced the region from emerging commercial flows.
- Fragmented Regional Politics: Ongoing tensions, such as Bangladesh-Myanmar disputes and India-Bangladesh frictions post-Hasina’s ouster, continue to hinder regional cooperation.
- Despite these obstacles, BIMSTEC has one advantage over SAARC—no member wields a veto over its progress. However, the forum still lacks ASEAN’s institutional strength and mutual trust.
The Case for India’s Unilateral Actions
While multilateral and bilateral approaches remain vital, India must also pursue independent initiatives to energize Bay of Bengal regionalism. Thailand’s visa-free entry for Indians demonstrates unilateralism’s power—a single policy dramatically boosted India-Thailand engagement, achieving what years of BIMSTEC negotiations on connectivity could not.
India’s Strategic Priorities
To strengthen regional integration, India must act on multiple fronts:
- Strengthening Regional Trade & Connectivity
- Persist with BIMSTEC institutional development and economic integration efforts.
- Maintain regional trade relations amid global economic disruptions.
- Minimize fallout from Bangladesh’s shifting political landscape.
- Advancing Bilateral Partnerships
- Enhance trade & connectivity agreements with individual BIMSTEC members.
- Modi’s upcoming bilateral talks in Thailand and Sri Lanka must focus on economic cooperation.
- Unilateral Economic & Strategic Initiatives
- Reassess tariff structures to develop independent trade policies with BIMSTEC nations.
- Strengthen the Andaman & Nicobar Islands as a regional maritime and economic hub.
- Modernize seafaring regulations & port infrastructure along India’s eastern coast.
- By leveraging its $4 trillion economy, India can drive Bay of Bengal regionalism forward, using positive unilateralism as a force multiplier for economic and strategic integration.
Consider the following statements regarding BIMSTEC:
- Unlike SAARC, BIMSTEC has no member state with a veto power over collective decisions.
- BIMSTEC was established as an alternative to SAARC after Pakistan blocked regional connectivity agreements in 2014.
- The BIMSTEC Charter, ratified in 2023, provides a legal framework for the organization’s functioning.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Unlike SAARC, where Pakistan has effectively stalled regional integration, BIMSTEC does not suffer from a veto problem, allowing smoother decision-making.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: BIMSTEC was founded in 1997, long before SAARC’s failure in 2014.
- However, India’s renewed focus on BIMSTEC came after Pakistan blocked SAARC’s connectivity agreements.
- Statement 3 is correct: The BIMSTEC Charter was ratified in 2023, providing a legal and institutional framework for the forum.
What is Alzheimer's Disease?
Syllabus:Science
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
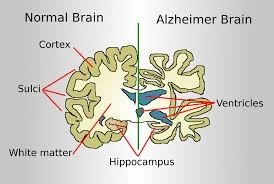
- Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily impacts memory, cognitive function, and reasoning abilities.
- It is the leading cause of dementia, accounting for approximately 60-80% of cases globally.
- The disease disrupts communication between neurons, eventually leading to cognitive decline and loss of functional independence.
What is Early-Onset Alzheimer’s (EOAD)?
While most Alzheimer’s cases emerge after the age of 65, around 5-10% of cases develop earlier, often in individuals in their 40s or 50s. This is classified as Early-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease (EOAD). Unlike late-onset Alzheimer’s, EOAD progresses more rapidly, affecting individuals in their prime working years and leading to severe socio-economic consequences.
- Genetic Influence: EOAD is strongly linked to mutations in three specific genes—APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2, which increase susceptibility to the disease.
- Amyloid Beta and Plaque Formation
- One of the key pathological features of Alzheimer’s disease is the accumulation of amyloid beta proteins, which aggregate to form amyloid plaques in the brain.
- These plaques disrupt neural communication, trigger inflammation, and contribute to neuronal death.
- Therapies targeting amyloid beta aim to reduce plaque accumulation, thereby slowing the disease’s progression.
Gantenerumab: A Promising Breakthrough
- Gantenerumab is an experimental monoclonal antibody drug designed to combat amyloid plaque buildup. Initially discontinued, it has shown renewed promise in recent clinical trials, particularly in patients with genetic mutations linked to EOAD.
Key Findings from the Latest Clinical Trials
- Conducted as a randomized, placebo-controlled study.
- Used brain imaging and blood biomarkers to track disease progression.
- Demonstrated a significant reduction in amyloid plaque accumulation, suggesting potential to slow cognitive decline.
Mechanism of Action: How Gantenerumab Works
- Monoclonal Antibody Targeting:
- Gantenerumab is engineered to specifically bind to amyloid beta proteins, marking them for clearance.
- Immune System Activation:
- Once bound, the drug stimulates microglial cells—the brain’s primary immune defenders—to break down and remove toxic plaques.
- Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier:
- A major challenge in treating neurodegenerative diseases is the blood-brain barrier, which prevents many drugs from reaching the brain.
- Gantenerumab has demonstrated the ability to effectively penetrate this barrier, making it more efficient than several previous Alzheimer’s treatments.
Implications for Alzheimer’s Treatment
- The promising results of Gantenerumab trials signal a potential paradigm shift in Alzheimer’s treatment, particularly for EOAD patients. If further studies confirm its effectiveness, it could become a crucial therapeutic option in slowing disease progression and improving patient outcomes.
With reference to Early-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease (EOAD), consider the following statements:
- EOAD accounts for the majority of Alzheimer’s cases worldwide.
- Genetic mutations in APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 have been associated with EOAD.
- EOAD progresses more slowly than late-onset Alzheimer’s.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: EOAD constitutes only 5-10% of all Alzheimer’s cases, whereas late-onset Alzheimer’s is far more prevalent.
Statement 2 is correct: Mutations in APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 are strongly linked to EOAD and are considered major genetic risk factors.
Statement 3 is incorrect: EOAD progresses more rapidly than late-onset Alzheimer’s, making it more devastating for individuals in their prime working years.
What is Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)?
What is Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)? Syllabus: Science
- Ranchi is set to become the first district in Jharkhand to launch a large-scale campaign aimed at the screening and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), now known as Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD).
Understanding NAFLD (MASLD)
- NAFLD refers to a spectrum of liver conditions caused by fat accumulation in the liver, which is not linked to excessive alcohol consumption. In contrast, when liver fat buildup is due to heavy alcohol use, it is classified as alcohol-associated liver disease.
- While early-stage NAFLD is often asymptomatic and may not cause immediate harm, it can progress to severe liver complications, including cirrhosis (scarring of the liver), liver failure, and liver cancer if left untreated.
Health Risks Associated with NAFLD
Having an excessive amount of liver fat increases the risk of developing serious metabolic disorders, such as:
- Type 2 diabetes
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Kidney disease
- Cardiovascular complications (especially in diabetic individuals)
Types of NAFLD
NAFLD is categorized into two major forms:
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver (NAFL) – A milder form where fat accumulates in the liver without inflammation or damage.
- Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) – A more severe form that involves inflammation, liver cell damage, and fibrosis, significantly increasing the risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Who is at Risk?
NAFLD can affect individuals of all ages, including children, but it is more prevalent among those with:
- Obesity
- Type 2 diabetes
- Metabolic disorders linked to insulin resistance
Current Treatment Approaches
- There is no specific drug therapy available for NAFLD. Instead, management strategies focus on lifestyle modifications:
- Weight loss: Reducing weight helps decrease fat accumulation, inflammation, and fibrosis in the liver.
- Control of associated conditions: Managing high blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol is essential to prevent disease progression.
- As Ranchi takes a pioneering step in public health intervention against NAFLD, this initiative may serve as a model for other districts in India to address the growing burden of metabolic liver diseases.
Consider the following statements regarding Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), now referred to as Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD):
- It is caused by excessive alcohol consumption and leads to liver fat accumulation.
- It is associated with metabolic disorders like Type 2 diabetes and obesity.
- NAFLD can progress to Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), which increases the risk of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
- It is primarily a genetic disorder with no lifestyle-related risk factors.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect because NAFLD is not caused by alcohol consumption; it results from metabolic dysfunction. Alcohol-induced fatty liver is a separate condition.
- Statement 2 is correct as NAFLD is strongly linked to obesity, insulin resistance, and Type 2 diabetes.
- Statement 3 is correct because NAFLD can progress to NASH, leading to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer).
- Statement 4 is incorrect since while genetics may play a role, lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and obesity are the primary contributors.
Abel Prize 2025
Syllabus:Awards
- The esteemed Abel Prize for mathematics has been awarded to Japanese mathematician Masaki Kashiwara for his groundbreaking contributions to algebraic analysis, representation theory, and sheaf theory.
About the Abel Prize
- The Abel Prize honors exceptional scientific achievements in mathematics.
- Named after Norwegian mathematician Niels Henrik Abel (1802–1829), who made significant contributions to various mathematical fields in his brief lifetime.
- Established in 2002 by the Norwegian Parliament to commemorate Abel’s 200th birth anniversary.
- Administered by the Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters on behalf of the Norwegian government.
- The awardee is selected by an expert committee, which is appointed by the Academy under the guidance of the International Mathematical Union (IMU) and the European Mathematical Society (EMS).
- First presented in 2003, the Abel Prize is often regarded as the “Nobel Prize of Mathematics”, given that the Nobel Prizes do not include a category for mathematics.
- The prize consists of a monetary award of 7.5 million Norwegian kroner (approximately $720,000) and a specially designed glass plaque by Norwegian artist Henrik Haugan.
Abel Prize 2025
- The 2025 Abel Prize has been conferred upon Masaki Kashiwara for his pioneering contributions to algebraic analysis and representation theory, particularly:
- The development of the theory of D-modules, which revolutionized the study of differential equations and their algebraic properties.
- The discovery of crystal bases, an innovation that allows complex algebraic calculations to be represented as simpler graphical structures consisting of vertices and edges.
- His work has not only resolved longstanding mathematical problems but also created new interdisciplinary connections, enabling further advancements in pure and applied mathematics.
Consider the following statements regarding the Abel Prize:
- It is awarded annually by the International Mathematical Union (IMU).
- The prize was established to recognize outstanding achievements in applied mathematics.
- It was first awarded in the year 2002 to commemorate the bicentenary of Niels Henrik Abel’s birth.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) None
Answer: (d) None
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The Abel Prize is awarded by the Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters, not the International Mathematical Union (IMU). However, IMU and the European Mathematical Society (EMS) advise on the selection process.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The Abel Prize recognizes achievements in pure mathematics, not specifically applied mathematics.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: Although the prize was established in 2002, the first Abel Prize was awarded in 2003, not 2002.