India Pitch for UNSC Reforms
Syllabus: GS2/International Organization
India Calls for UNSC Reform to Ensure Lasting Peace
Security of Peacekeepers
UN peacekeepers today face a multitude of threats, including non-state actors, armed groups, and terrorists. India emphasizes the need for enhanced safety measures and security protocols for peacekeepers. Additionally, India advocates for accountability and justice in cases of crimes committed against peacekeeping forces.
Modernization of Peacekeeping Operations
Recognizing the evolving nature of peacekeeping, India calls for the integration of advanced surveillance, communication, and data analytics in peacekeeping missions. India’s Centre for UN Peacekeeping (CUNPK) offers specialized training programs to equip peacekeepers with modern tools and strategies to meet contemporary challenges effectively.
Funding for Peacekeeping Missions
India underscores the need for well-funded peacekeeping missions. The resources allocated to these missions should be commensurate with their mandates to ensure effective execution and operational success.
Inclusion in Mandate Formation
India advocates for the inclusion of troop-contributing countries in the process of formulating mandates. This approach will enable better adaptation of peacekeeping operations to new realities and ensure that the strategies align with ground-level challenges.
About the United Nations Security Council (UNSC)
The UNSC is one of the principal organs of the United Nations, established in 1945 under the UN Charter to maintain international peace and security. It comprises 15 member states, including five permanent members with veto power—China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States—along with ten non-permanent members elected for two-year terms. The UNSC headquarters is located in New York City.
Need for UNSC Reforms
Current Composition and Representation
The present composition of the UNSC is marked by under-representation and lack of adequate representation of key global regions.
Inability to Address Conflicts
The current structure of the Council has proven ineffective in addressing significant global conflicts, thereby undermining its credibility and primary mandate of upholding international peace and security.
Changing Global Order
Since its inception in 1945, the world order has undergone significant transformations. These new geopolitical realities must be reflected in the permanent membership of the UNSC.
Issue of Veto Power
Only the five permanent members hold veto power, often using it to stall resolutions addressing global crises, such as those in Ukraine and Gaza. The ten non-permanent members, despite being part of the Council, lack veto authority, limiting their influence in decision-making.
Legitimacy Concerns
The concentration of power among the five permanent members creates a perception of inequity, diminishing the legitimacy and effectiveness of the UNSC in addressing contemporary security challenges.
Why India Deserves Permanent Membership in the UNSC
Demographic and Global Representation
India accounts for approximately 18% of the world’s population, making its inclusion in global decision-making bodies like the UNSC a matter of proportional representation.
Economic Strength
India is one of the world’s largest economies, with a significant impact on global stability and development. Its economic contributions align with the UNSC’s objectives of maintaining international peace and security.
Commitment to Peacekeeping
India has consistently been one of the largest contributors to UN peacekeeping missions, demonstrating its strong commitment to global peace and security.
Geopolitical Influence
India’s strategic location in South Asia and the Indo-Pacific region positions it as a crucial player in addressing global security challenges such as terrorism, climate change, and maritime security.
Advocacy for Democratic Values
As the world’s largest democracy, India upholds values of pluralism, tolerance, and inclusivity, which align with the core principles of the UN.
Global Support
India enjoys extensive support from numerous UN member states, including influential nations across different regions, underscoring its potential contribution to strengthening the UNSC’s role in global crisis management.
Challenges in Implementing UNSC Reforms
Veto Power of Permanent Members
- Any proposed reforms require the approval of all five permanent members, who are often reluctant to support changes that might reduce their influence.
Geopolitical and Regional Rivalries
- Regional tensions and geopolitical rivalries further complicate efforts to bring about UNSC reforms.
Complexity of the Reform Process
Reforming the UNSC necessitates an amendment to the UN Charter, which requires a complex and lengthy process involving ratification by a significant number of member states.
Opposition from China
China, as a permanent UNSC member, continues to oppose India’s bid for permanent membership, hindering India’s inclusion in the Council.
Way Forward
Both permanent and non-permanent membership should reflect the present-day global landscape rather than the post-World War II order. Reforms in the UNSC are imperative to maintain its relevance, legitimacy, and effectiveness in addressing contemporary security challenges. However, achieving consensus among UN member states remains a formidable and ongoing process.
Consider the following arguments against the UNSC’s current veto power structure:
- It enables any one of the P5 members to block international consensus.
- It has been used to shield countries from international scrutiny over human rights violations.
- It allows non-permanent members to influence decisions through alliances with P5 nations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation: The veto power enables P5 members to block resolutions, even if the majority supports them (statement 1 is correct). It has been used to prevent action against allies accused of human rights violations (statement 2 is correct). However, non-permanent members do not have veto power and cannot directly influence decisions (statement 3 is incorrect).
PM-SHRI Scheme
Syllabus: Govt Policies
- A Parliamentary Standing Committee has urged the Education Ministry to release over ₹4,000 crore in pending Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) funds for Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and West Bengal.
- The funds have been withheld due to these st ates not signing the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for the PM SHRI scheme.
- The panel emphasized that SSA predates PM SHRI and plays a crucial role in enforcing the Right to Education (RTE) Act.

Understanding the PM SHRI Scheme
- PM SHRI (PM Schools for Rising India) is a centrally sponsored scheme launched under NEP 2020 to develop 14,500 model schools with a focus on experiential and inquiry-driven learning, 21st-century skill development, eco-friendly infrastructure such as green buildings, water conservation, and waste recycling, and competency-based assessments instead of rote learning.
Key Features of PM SHRI Schools
- Modern infrastructure includes well-equipped labs, libraries, and art rooms. Digital integration ensures smart classrooms and advanced learning tools.
- A holistic learning approach emphasizes play-based and flexible teaching methods. A quality assessment mechanism ensures regular evaluations under the School Quality Assessment Framework (SQAF).
- Schools are selected through a challenge-based process where they must meet performance criteria.
- The scheme has a budget allocation of ₹27,360 crore for five years from 2022-23 to 2026-27, with ₹18,128 crore provided by the central government.
What is Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA)
- SSA is a centrally sponsored scheme designed to ensure universal access to quality education from pre-primary to higher secondary levels.
- It supports state governments in implementing the Right to Education (RTE) Act, which guarantees free and compulsory education for children aged 6-14 years.
Key Focus Areas of SSA
- School infrastructure development includes the construction of classrooms, libraries, and sanitation facilities.
- Teacher training and recruitment aim to enhance teaching quality. The program seeks to improve learning outcomes through curriculum reforms and remedial education.
- Inclusive education initiatives provide support for disadvantaged groups.
- The Parliamentary Panel’s recommendation highlights the critical role of SSA in strengthening India’s education system and ensuring uninterrupted learning opportunities for students.
Consider the following statements regarding the Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA):
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme aimed at ensuring universal access to quality education from pre-primary to higher secondary levels.
- The scheme was launched under the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- SSA is primarily focused on the development of school infrastructure and does not address teacher training or learning outcomes.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation: SSA was launched before NEP 2020 and focuses on multiple aspects of education, including infrastructure, teacher training, and learning outcomes. Statement 2 is incorrect because SSA predates NEP 2020. Statement 3 is incorrect because SSA includes teacher training and learning enhancement measures.
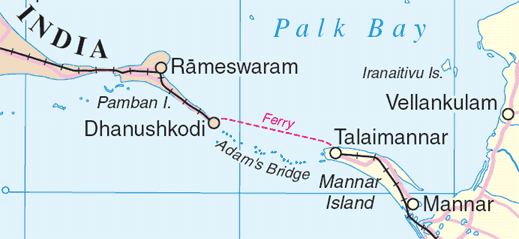
New Pamban Bridge
Syllabus:Geography
KeyHighlights:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi will inaugurate the New Pamban Bridge in Rameshwaram, Tamil Nadu, on April 6, 2025.
- The event, coinciding with Ram Navami, marks a major milestone in India’s infrastructure development.
- Spanning 2.5 kilometers, the bridge significantly improves connectivity between mainland India and Rameshwaram Island, reducing train travel time from 25-30 minutes to under five minutes.
Engineering Marvel
- The New Pamban Bridge is Asia’s first vertical lift bridge, replacing the century-old structure built in 1914, which was decommissioned in December 2022 due to severe corrosion.
- Constructed by Rail Vikas Nigam Limited (RVNL) at a cost of ₹535 crore, the bridge is designed to accommodate faster trains and increased traffic.
Advanced Features & Challenges
- Electromechanical Lift System: Allows the bridge to be lifted in just five minutes to facilitate maritime movement, operated by a single person.
- Speed Limit: Trains can run at a maximum speed of 75 km/h, except on the vertical lift section, where safety regulations limit speed to 50 km/h.
- Weather Sensitivity: The lifting mechanism is affected by wind speeds exceeding 58 km/h, a frequent occurrence from October to February, potentially impacting operations.
Historical Significance & Connectivity
- The old Pamban Bridge was the sole railway link to Rameswaram until the construction of a road bridge in 1988.
- The new bridge restores a vital rail connection, crucial for local commuters and the influx of pilgrims visiting Rameswaram.
Inauguration & Future Developments
- The inauguration ceremony will include the launch of a new train service between Tambaram and Rameswaram.
- Additionally, the Rameswaram railway station is undergoing redevelopment, with completion expected by September 2025.
Consider the following statements regarding the New Pamban Bridge:
- It is the first vertical lift bridge in Asia.
- The bridge was constructed by the Indian Railways at a cost exceeding ₹700 crore.
- It is designed to accommodate both railway and vehicular traffic.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation:
- The New Pamban Bridge is Asia’s first vertical lift railway bridge (Statement 1 is correct).
- It was constructed by Rail Vikas Nigam Limited (RVNL) at a cost of ₹535 crore, not ₹700 crore (Statement 2 is incorrect).
- The bridge is exclusively for railway traffic and does not accommodate vehicular movement (Statement 3 is incorrect).
Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA)
Syllabus: GS 2/Governance
Context
A Parliamentary Standing Committee has urged the Ministry of Education to resolve the ongoing dispute with West Bengal, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu regarding the non-release of over ₹4,000 crore under the Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA).

Key Issue
- The dispute arises from Tamil Nadu’s refusal to implement the three-language formula under the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and its decision not to sign the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for the PM-SHRI schools
- As a result, SSA funds have been withheld, affecting the state’s education initiatives.
About Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA)
- Implemented by the Department of School Education and Literacy, SSA is a centrally sponsored scheme designed to provide holistic education from pre-primary to Class XII, in alignment with NEP 2020.
- The scheme focuses on ensuring quality, equitable, and inclusive education, catering to students from diverse backgrounds, multilingual needs, and varying academic abilities.
Key Features of SSA
Financial Assistance to States and UTs
- Free uniforms and textbooks for elementary students.
- Reimbursement under the Right to Education (RTE) Act.
- Special training programs and bilingual teaching materials for out-of-school children.
Infrastructure Development
- Construction of school buildings, additional classrooms, and hostels.
- Strengthening of teacher education and ICT-based learning interventions.
Inclusive Education Initiatives
- Establishment and upgradation of schools and hostels in tribal and border areas.
- Support for marginalized communities to ensure universal access to education.
- The resolution of this funding dispute remains crucial for the effective implementation of SSA, ensuring that educational resources reach students without disruption.
Consider the following statements regarding the Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA):
- It is a centrally funded scheme implemented solely by the Ministry of Finance.
- SSA covers education from pre-primary to higher secondary level, aligning with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- The scheme provides financial support to States and UTs for the reimbursement of expenses under the Right to Education (RTE) Act.
- Tamil Nadu’s refusal to sign the MoU for PM SHRI schools has led to the withholding of SSA funds.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3, and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (b) 2, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: SSA is a centrally sponsored scheme, not fully funded by the Centre. It is implemented by the Department of School Education and Literacy, under the Ministry of Education, not the Ministry of Finance.
Statements 2, 3, and 4 are correct: SSA ensures education from pre-primary to higher secondary level, provides financial support for RTE reimbursement, and has faced funding issues due to Tamil Nadu’s refusal to sign the PM SHRI MoU.
Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY)
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
- The opposition has raised concerns over inadequate implementation of maternity benefits mandated under the National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013, attributing it to insufficient budgetary allocation.

About Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY)
- PMMVY is a maternity benefit program aligned with the provisions of the NFSA, 2013. Since 2022, it has been implemented under Mission Shakti, an umbrella scheme aimed at women’s empowerment.
Eligibility
- The scheme primarily targets socially, economically disadvantaged, and marginalized women.
Benefits
- Financial Assistance: Provides ₹5,000 to pregnant and lactating women to support maternal health and nutrition.
- Supplementary Support: Additional benefits under Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY) raise the total maternity assistance to approximately ₹6,000.
- Nutritional Support: Pregnant and lactating mothers receive free meals through Anganwadi centers during pregnancy and up to six months postpartum to meet essential dietary requirements.
Mission Shakti and Second Child Benefits
- Under Mission Shakti, a maternity benefit of ₹6,000 is provided for the second child, but only if the child is a girl, to encourage positive social attitudes towards female children.
Consider the following statements regarding Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY):
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme implemented under the provisions of the National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013.
- The scheme provides financial assistance for the first two live births, irrespective of gender.
- PMMVY was subsumed under Mission Shakti in 2022 to streamline maternity benefits and women’s empowerment initiatives.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: PMMVY is implemented under NFSA, 2013, making maternity benefits a legal entitlement.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: The scheme provides benefits only for the first live birth, except under Mission Shakti, where ₹6,000 is given for the second child only if it is a girl.
- Statement 3 is correct: PMMVY was integrated into Mission Shakti in 2022 to enhance efficiency in women-centric welfare schemes.
Betting and Gambling are State Subjects
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
Context
- Union Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw has reiterated that betting and gambling fall under the jurisdiction of State governments.
- Between 2022 and 2025, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has issued 1,410 blocking directives for websites associated with online betting, gambling, and gaming.
Regulatory Framework
Finance Act, 2023
- Imposes a 30% income tax on net winnings from online gaming, effective from the assessment year 2024-25.
- Ensures tax compliance for online gaming earnings.
Goods and Services Tax (GST) Regulations
- 28% GST applied to online gaming transactions from October 1, 2023.
- Online gaming platforms must register under the Simplified Registration Scheme of the IGST Act.
- The GST Intelligence Headquarters has the authority to direct the blocking of unregistered platforms violating the IGST Act.
State Jurisdiction Over Betting and Gambling
- Betting and gambling fall under the State List of the Constitution.
- States are responsible for the prevention, investigation, and prosecution of offenses related to betting and gambling.
- The Central Government provides advisories and financial assistance to states for capacity building in enforcement.
Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023
- Introduces legal penalties for unauthorized betting and gambling, with imprisonment ranging from 1 to 7 years along with monetary fines.
Other Initiatives
- Ministry of Education has issued advisories for parents and teachers to address the risks of online gaming addiction.
- Ministry of Information and Broadcasting has implemented guidelines for advertisements related to online gaming, mandating disclaimers on financial risks and addiction potential.
Regarding the taxation of online gaming in India, consider the following statements:
- The Finance Act, 2023 introduced a 30% income tax on net winnings from online gaming, effective from the assessment year 2023-24.
- A uniform GST rate of 18% applies to all forms of online gaming transactions, effective from October 1, 2023.
- Online gaming platforms must register under the Simplified Registration Scheme of the IGST Act.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
Answer: (c) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- The 30% income tax on net winnings applies from the assessment year 2024-25, not 2023-24.
- A 28% GST, not 18%, is imposed on online gaming from October 1, 2023.
- Online gaming platforms must register under the Simplified Registration Scheme of the IGST Act to ensure tax compliance.
MRI Technology
Syllabus: GS3/ S&T
In News
- India has successfully developed its first indigenously manufactured MRI machine, which will undergo trial runs at AIIMS Delhi.
About MRI Technology
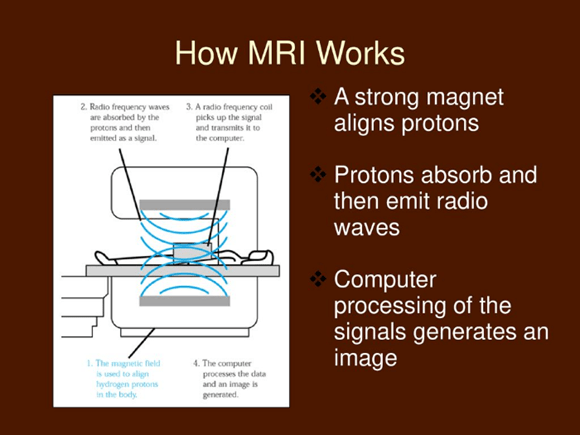
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive medical imaging technique that provides highly detailed images of internal organs, tissues, and structures, particularly the brain, spinal cord, muscles, and joints.
Key Features of MRI Technology
- Radiation-Free Imaging: Unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it safer for repeated diagnostic use.
- High-Resolution Scanning: Utilizes powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to generate precise anatomical images.
- Wide Medical Applications: Essential for detecting neurological disorders, musculoskeletal conditions, and cardiovascular diseases.
Consider the following statements about the applications of MRI technology:
- Functional MRI (fMRI) measures changes in blood oxygenation in the brain.
- MRI is ineffective in imaging soft tissues and is primarily used for bone scans.
- MRI contrast agents enhance the visibility of certain tissues by altering their magnetic properties.
- MRI is widely used for early detection of neurodegenerative disorders.
Which of the above statements are correct?
- A) 1 and 3 only
B) 2 and 4 only
C) 1, 3, and 4 only
D) All of the above
Answer: C) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Functional MRI (fMRI) detects changes in blood oxygenation levels, making it useful for studying brain activity.
Statement 2 is incorrect: MRI is highly effective for imaging soft tissues (brain, muscles, spinal cord) but less effective for bones due to low hydrogen content.
Statement 3 is correct: MRI contrast agents, like Gadolinium-based compounds, improve visibility by affecting magnetic properties.
Statement 4 is correct: MRI is widely used for diagnosing Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and multiple sclerosis at early stages.
Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary
Syllabus:Environment
Location & Significance
- Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary is situated in the Chikkamagaluru and Shivamogga districts of Karnataka and derives its name from the Bhadra River, which flows through the region.

Designation & Conservation Status
- Declared a Wildlife Sanctuary in 1951.
- Upgraded to a Project Tiger Reserve in 1998.
- First tiger reserve in India to complete a village relocation program by 2002.
- Geographical Features
- Core area:16 sq. km.
- Buffer zone:84 sq. km.
- Terrain: Includes hills and valleys, notably Mullayanagiri (the highest peak in Karnataka), Baba Budangiri, and Muthodi ranges.
- Flora of Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary
The sanctuary hosts diverse forest types:
- Southern Moist Mixed Deciduous Forests – Characterized by Teak, Terminalia, and Lagerstroemia
- Dry Deciduous Forests – Includes Pterocarpus (Honne), Grewia (Tadasalu), and Bamboo
- Shola Forests – Supports species such as Cinnamon, Mimusops, and Strobilanthes (Neelakurinji), known for its rare blooming cycle.
Fauna of Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary
- Mammals: Includes Tigers, Leopards, Dholes (Wild Dogs), Gaurs, Sambar Deer, Barking Deer, and Elephants.
- Birds: Over 250 species, including Grey Junglefowl, Malabar Parakeet, Hill Myna, Malabar Trogon, and Hornbills.
- Reptiles: Features King Cobra, Russell’s Viper, Indian Monitor Lizard, and Marsh Crocodiles.
- Butterflies: Hosts rare species like Yamfly, Baronet, Crimson Rose, Southern Birdwing, and Great Orange Tip.
Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary remains a crucial site for biodiversity conservation, playing a vital role in Karnataka’s ecological balance.
Consider the following statements regarding the geographical features of Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Mullayanagiri, the highest peak in Karnataka, is located within the sanctuary.
- The sanctuary has both core and buffer zones, with a total area exceeding 1,000 square kilometers.
- The Bhadra River, which originates in the Eastern Ghats, flows through the sanctuary.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Mullayanagiri (1,930 meters), the highest peak in Karnataka, is part of the Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary region.
Statement 2 is correct: The sanctuary consists of a 500.16 sq. km core zone and a 571.84 sq. km buffer zone, making a total area of 1,072 sq. km.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The Bhadra River originates in the Western Ghats, not the Eastern Ghats, and it flows through the sanctuary before joining the Tungabhadra River.
Lyme Disease Treatment Breakthrough
Syllabus:Science
- Scientists have identified a critical enzyme, BbLDH (Borrelia burgdorferi lactate dehydrogenase), as a key factor in the survival and infectivity of Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacterium responsible for Lyme disease.
- This discovery presents a promising avenue for developing targeted treatments against Lyme disease and other tick-borne infections.
About Lyme Disease
- Lyme disease, or Lyme borreliosis, is a bacterial infection caused by Borrelia burgdorferi.
- It is transmitted to humans via bites from infected blacklegged ticks (Ixodes scapularis in North America and Ixodes ricinus in Europe).
- The disease is prevalent in the northeastern and midwestern United States, as well as parts of Europe and Asia.
- Symptoms include a bull’s-eye rash (erythema migrans), fever, fatigue, and headaches. If untreated, it can lead to severe complications, affecting the joints, heart, and nervous system.
Role of BbLDH in Borrelia burgdorferi
- BbLDH (lactate dehydrogenase) is an essential enzyme that facilitates the bacterium’s metabolic processes.
- Unlike most organisms, B. burgdorferi does not require thiamin (vitamin B1) for metabolism. Instead, BbLDH is critical for converting pyruvate to lactate, which helps maintain the NADH/NAD+ balance—a process vital for bacterial growth and infectivity.
Research Findings & Implications
- Scientists employed genetic, biochemical, and structural analyses, including X-ray crystallography, to determine BbLDH’s function.
- Loss-of-function studies demonstrated that disrupting BbLDH impairs the bacterium’s ability to survive and infect hosts, confirming its indispensable role in B. burgdorferi’s life cycle.
Therapeutic Potential of BbLDH Inhibitors
- High-throughput screening has identified several promising BbLDH inhibitors that could form the basis of genus-specific treatments.
- Unlike broad-spectrum antibiotics, these inhibitors specifically target Borrelia burgdorferi, reducing the risk of disrupting beneficial microbiota.
- The lead researcher, Chunhao Li, emphasized that BbLDH’s unique biochemical properties make it an optimal drug target for Lyme disease therapeutics.
Broader Applications & Future Research
- The study not only enhances our understanding of Lyme disease but also provides insights into LDH-dependent metabolic pathways in other tick-borne pathogens.
- This could pave the way for innovative treatments for a range of vector-borne diseases, strengthening global public health efforts against tick-borne infections.
With reference to Lyme disease, consider the following statements:
- It is caused by a virus and transmitted through mosquito bites.
- The disease is endemic only to North America and has no reported cases in Europe or Asia.
- If left untreated, Lyme disease can affect multiple organ systems, including the nervous system and heart.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Lyme disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, not a virus. It is transmitted through infected blacklegged tick bites, not mosquitoes.
Statement 2 is incorrect: While Lyme disease is prevalent in North America, it is also reported in Europe and parts of Asia.
Statement 3 is correct: If left untreated, the disease can lead to complications affecting the nervous system, joints, and cardiovascular system.
What is Dx-EDGE Initiative?
Syllabus:GS3 Economy
Overview
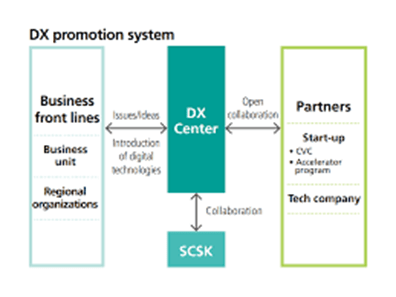
- India has launched the ‘Digital Excellence for Growth and Enterprise’ (Dx-EDGE) initiative to empower micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) with digital tools and skills. This initiative is a collaborative effort between the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), NITI Aayog, and the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE). It aims to enhance the competitiveness and resilience of MSMEs through.
Objectives of Dx-EDGE
- The initiative is designed to future-proof MSMEs by providing access to advanced technologies, digital skills, and innovation. It aligns with India’s vision of Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by ensuring widespread digital adoption across the sector.
Key Challenges Faced by MSMEs
- Despite their critical role in India’s economy, MSMEs face several challenges, including:
- Limited technology adoption affecting efficiency and productivity.
- Lack of a skilled workforce to leverage digital tools.
- Difficulties in obtaining quality certifications, impacting market access.
- Addressing these challenges is essential for improving operational efficiency and global competitiveness.
Public-Private-Academia Partnership (PPAP)
- Dx-EDGE adopts a Public-Private-Academia Partnership (PPAP) model, integrating expertise from private enterprises, government agencies, and academic institutions. This multi-stakeholder approach is crucial for driving MSMEs’ digital transformation.
Establishment of Digital Excellence Centres
- A key component of Dx-EDGE is the creation of Digital Excellence Centres, which will:
- Assist MSMEs in formulating digital transformation strategies.
- Provide training and resources to ensure effective technology adoption.
- Serve as innovation hubs to bridge knowledge gaps in digitalisation.
Role of Education and Skill Development
- The initiative emphasises workforce upskilling to align with global manufacturing standards. This focus on education and skill development ensures that MSMEs can effectively integrate Industry 4.0 technologies.
Future Impact
- Dx-EDGE is expected to:
- Enhance MSME competitiveness in domestic and global markets.
- Drive economic growth by boosting productivity and efficiency.
- Strengthen India’s digital ecosystem, accelerating the transition to a digitally advanced economy.
- By fostering digital excellence, this initiative positions India’s MSMEs as key drivers of economic resilience and technological innovation.
Consider the following statements regarding the ‘Digital Excellence for Growth and Enterprise’ (Dx-EDGE) initiative:
- It is a joint initiative of the Ministry of MSME, NITI Aayog, and the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII).
- The initiative focuses solely on providing financial assistance to MSMEs for digital adoption.
- Digital Excellence Centres established under Dx-EDGE will play a role in formulating digital transformation strategies for MSMEs.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
Answer: (c) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect because the Dx-EDGE initiative is a collaboration between NITI Aayog, CII, and AICTE, not the Ministry of MSME.
Statement 2 is incorrect as Dx-EDGE focuses on digital capacity building, innovation, and skill development, rather than just financial assistance.
Statement 3 is correct as Digital Excellence Centres will guide MSMEs in identifying tailored digital transformation paths.
