Bharat Forecasting System Launched
Syllabus :GS 1/Geography
- The Ministry of Earth Sciences has launched the Bharat Forecasting System (BFS) to revolutionize weather prediction in India.
- Developed by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune, BFS delivers highly localized weather forecasts with a cutting-edge 6 km grid resolution—the highest in the world.
- It enables more accurate prediction of small-scale weather phenomena across India.
- Powered by Supercomputer Arka (Speed: 11.77 petaflops, Storage: 33 petabytes), BFS now generates forecasts in 4 hours, compared to 10 hours by the earlier system, Pratyush.
- It focuses on the tropical belt (30°S to 30°N), including entire India, and surpasses global models from the U.S., UK, and Europe (with 9–14 km resolution).
- It integrates data from 40 Doppler Weather Radars (to be scaled to 100) and provides nowcasting for the next 2 hours.
- BFS boosts India’s self-reliance in weather prediction and enhances disaster preparedness, agricultural planning, water resource management, and public safety at local levels.
- It supports India’s commitment to the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction and marks a major leap in India’s capability to deliver accurate, timely, and actionable forecasts from national to panchayat-level scale.
With reference to the Bharat Forecasting System (BFS), consider the following statements:
- It is the first global model to offer sub-10 km resolution for weather forecasts.
- It uses a combination of ensemble and deterministic forecasting techniques.
- It has real-time integration with satellite-derived precipitation and land-surface data.
- It is developed under the National Monsoon Mission by IITM, Pune.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 2, 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Correct Answer: C. 2, 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
- The Bharat Forecasting System (BFS) does indeed offer a 6 km × 6 km grid resolution, which is among the highest globally for operational regional weather models.
- However, it is not the first model globally to offer sub-10 km resolution.
- Some non-global or specialized regional models (e.g., Japan’s JMA models, or high-resolution models for small regions in Europe) have already operated at similar or finer resolutions.
- Also, BFS is not a global model — it is designed primarily for the tropical belt (30°S to 30°N), including India, so the claim of being a first global model is inaccurate.
- The BFS employs ensemble forecasting (multiple simulations for probabilistic forecasts) and deterministic forecasting (single high-accuracy prediction).
- This hybrid approach improves both accuracy and confidence intervals in weather prediction.
BFS integrates real-time observational data from multiple sources:
- Satellite data (for cloud cover, precipitation, temperature)
- Land-surface observations (e.g., soil moisture, surface temperature)
- Doppler Weather Radars (currently 40, expanding to 100)
- This enhances both short-term (nowcasting) and medium-range forecasts.
Iran Slams Trump’s Plan to Rename Persian Gulf
Syllabus: GS2/IR/GS1/Places in News
- Former U.S. President Donald Trump’s proposal to rename the Persian Gulf as the ‘Arabian Gulf’ or ‘Gulf of Arabia’ sparked sharp criticism from Iran, which viewed the move as a direct challenge to its national identity and historical heritage.
- The suggestion reportedly surfaced in anticipation of Trump’s visit to Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates.
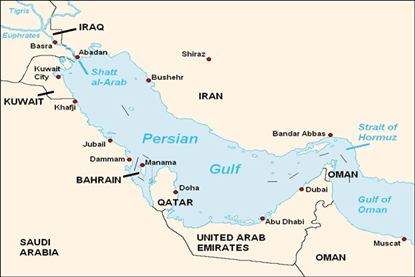
About the Dispute:
- The Persian Gulf is a geopolitically and economically vital water body located in Western Asia.
- It connects to the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea through the strategically crucial Strait of Hormuz.
- The countries bordering it are Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Qatar, and the UAE.
- While Iran insists on the historical term Persian Gulf, Arab Gulf States (except Iran) often refer to it as the ‘Arabian Gulf’ or simply ‘the Gulf’, sparking an ongoing naming dispute that reflects deeper regional rivalries and identity politics.
Historical Background:
- The term Persian Gulf is rooted in antiquity, referring to Persia, the former name of Iran. In 1935, Reza Shah Pahlavi officially changed the country’s international name from Persia to Iran, asserting that Persia was an exonym (a name given by outsiders) and promoting Iran, the country’s endonym (a native name), to reinforce national sovereignty.
- This naming controversy continues to carry geopolitical weight, symbolizing broader tensions between Iran and its Arab neighbors.
With reference to the geopolitical discourse surrounding the Persian Gulf naming controversy, consider the following statements:
- The term “Persian Gulf” has been historically recognized in international treaties and cartographic references predating modern nation-states in West Asia.
- The Strait of Hormuz, connecting the Persian Gulf to the Arabian Sea, lies entirely within the territorial waters of Iran.
- The move by some Arab states to promote the term “Arabian Gulf” is aligned with pan-Arab political assertions post-World War II.
- The United Nations has officially adopted “Arabian Gulf” as the standardized name for international usage.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2, 3 and 4 only
C. 1, 2 and 3 only
D. 1 and 4 only
Correct Answer: A. 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Correct: The name Persian Gulf has been consistently used in historical maps, naval treaties, and geographical references dating back over two millennia, especially in Greek, Roman, and Islamic sources.
- It remains the official designation used by the United Nations.
- Statement 2 – Incorrect: The Strait of Hormuz is not entirely within Iranian waters. It is a narrow waterway bordered by both Iran to the north and Oman (specifically the Musandam exclave) to the south, making it an international strait subject to maritime law.
- Statement 3 – Correct: The push to rename the Persian Gulf as the Arabian Gulf gained momentum particularly in the mid-20th century, in line with the rise of Pan-Arab nationalism and the political identity consolidation of Arab states in the Gulf region.
- Statement 4 – Incorrect: The United Nations and most international organizations continue to use “Persian Gulf” as the official name. Any alternative naming is considered politically charged and is not recognized by global institutions.
Moringa
Syllabus: GS2/ Health
- The PKM1 variety of Moringa oleifera has gained global attention for its adaptability and benefits, particularly in African nations such as Senegal, Rwanda, and Madagascar.
About Moringa (Moringa oleifera)
- Origin and Distribution:
- Indigenous to India, especially the Himalayan foothills.
- Now extensively cultivated across South Asia, Africa, and the tropical zones of Central and South America.
Agronomic Characteristics:
- Grows best in deep sandy loam soils with a pH range of 6.5 to 8.0.
- Suited to semi-arid and tropical climates, with an ideal temperature range of 25–30°C.
- Noted for its drought resistance and rapid growth, enabling multiple harvests annually.
Medicinal and Health Applications:
- Revered in Ayurveda for treating over 300 ailments.
- Possesses anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anti-diabetic properties.
- Its seeds exhibit coagulating properties, making them effective in water purification.
With reference to the PKM1 variety of Moringa oleifera, consider the following statements:
- It is a genetically modified variety developed for enhanced drought resistance.
- PKM1 is known for faster growth and higher pod yield compared to traditional Moringa varieties.
- The cultivation of PKM1 has been promoted in parts of Sub-Saharan Africa for food security purposes.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B
Explanation:
- PKM1 is not genetically modified; it is a selectively bred variety known for high productivity and adaptability.
- It is widely promoted in African nations as part of nutritional security initiatives.
NAMASTE Yojana
Syllabus :GS 2/Welfare Schemes
- A special event was recently held in Madhya Pradesh to spotlight the National Action Plan for Mechanized Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) scheme.
About NAMASTE Yojana:
- Launched in July 2023 through collaboration between the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, the NAMASTE scheme is designed to promote the safety and dignity of sanitation workers across urban India.
- The scheme emphasizes the prevention of hazardous cleaning practices by promoting the use of trained and certified sanitation workers who follow safe cleaning protocols. It seeks to enhance occupational safety through capacity building and by improving access to personal protective equipment (PPE), safety devices, and mechanized cleaning machines.
Which of the following ministries are jointly responsible for the implementation of the NAMASTE scheme?
- Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
- Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs
- Ministry of Labour and Employment
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
Select the correct answer using the code below:
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1, 2 and 3 only
D) All of the above
Answer:A
Explanation: NAMASTE is a convergence between the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
One Big Beautiful Bill Act
Syllabus: GS2/ International issues
- The United States House of Representatives has passed the One Big Beautiful Bill Act (OBBBA) of 2025, designed to reform the country’s economic and immigration policies.
Key Provisions of OBBBA:
- Permanent Tax Cuts: The act permanently enshrines the tax cuts introduced under the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), including increased standard deductions and reduced tax brackets.
- Excise Tax on Remittances: Introduces a 3.5% excise tax on remittances sent by non-citizens, intended to discourage undocumented immigration and raise federal revenue.
- Raising the Debt Ceiling: Authorizes an increase in the U.S. debt ceiling, which limits the maximum amount of national debt the Treasury can accumulate.
- Fiscal Prudence Measures: Implements spending cuts by targeting inefficiencies, waste, fraud, and abuse in federal programs.
Implications:
- For the U.S. Economy: Provides tax relief to middle-income households, encouraging consumer spending and economic growth. However, concerns persist about long-term fiscal sustainability, particularly due to simultaneous tax reductions and increased defense expenditures.
- For Remittance-Dependent Countries: The new excise tax on remittances may adversely affect countries such as Mexico, India, and the Philippines, where remittances are vital for household income and foreign exchange reserves.
Consider the following statements about the One Big Beautiful Bill Act (OBBBA) 2025 recently passed by the U.S. House of Representatives:
- It permanently extends tax cuts introduced under the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, including reductions in corporate tax rates.
- It imposes a 3.5% excise tax on remittances sent by non-citizens residing in the U.S.
- The bill authorizes an increase in the U.S. debt ceiling, which limits the Treasury’s borrowing authority.
- It includes provisions to increase government spending on welfare programs to support immigrant communities.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A) 1, 2, and 3 only
B) 2 and 4 only
C) 1, 3, and 4 only
D) All of the above
Explanation:
- It permanently extends tax cuts introduced under the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, including reductions in corporate tax rates.
- While the OBBBA does permanently extend some tax cuts introduced under the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), especially those affecting individuals such as increased standard deductions and lower tax brackets, it does not specifically include new provisions to extend corporate tax cuts, which had already been made permanent under the original TCJA.
- So, the statement is partially true, but the mention of corporate tax rate reductions being extended under OBBBA is inaccurate.
- But in context of UPSC-type questions, when a statement includes both correct and incorrect elements, it is considered incorrect. Therefore, this makes the statement wrong.
- However, considering ambiguity in how the statement is phrased (as many understand the corporate tax cuts were already made permanent in 2017), some interpretations may still accept it as correct if the focus is broadly on extending TCJA tax cuts — which the bill does. So this becomes a borderline case.
Tianwen-2 Mission
Syllabus :GS 3/Space
About the Tianwen-2 Mission
- China is preparing to launch its first asteroid sampling mission, Tianwen-2, targeting the near-Earth asteroid 469219 Kamo‘oalewa. This mission aims to both collect material from the asteroid and advance China’s deep-space exploration capabilities.
- Primary Objective: Investigate and retrieve samples from Kamo‘oalewa using either a “touch-and-go” technique or an “anchor and attach” method.
- Scientific Goals: Enhance understanding of asteroid composition, structure, and origins, contributing to planetary defense and solar system research.
- Global Significance: If successful, China will become only the third country—after the United States and Japan—to collect and return samples from an asteroid.
About Kamo‘oalewa
- Discovered in 2016 by the Pan-STARRS 1 telescope in Hawaii.
- It is classified as a quasi-satellite asteroid—a small body that orbits the Sun but remains close to Earth due to its unique, elliptical path.
- Estimated to have been in its current orbit for around 100 years, and is expected to maintain it for approximately 300 more years.
With reference to the Tianwen-2 mission, consider the following statements:
- The mission will use gravity-assist maneuvers from Earth’s Moon to reach the target asteroid.
- Tianwen-2 intends to collect subsurface material using a drill-based anchor system.
- Upon completion, China would become the first country to perform both sample collection and in-situ chemical analysis on an asteroid.
- The mission targets a quasi-satellite asteroid which shares Earth’s orbital region but does not orbit the Earth.
Which of the above statements are correct?
A) 1, 2 and 3 only
B) 2 and 4 only
C) 1 and 4 only
D) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer:C)1and4only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is plausible; missions to near-Earth objects often use gravity assists (while not explicitly stated, it aligns with mission norms).
- Statement 2 is incorrect; the anchor and attach method has been proposed, but not a confirmed drill-based subsurface system.
- Statement 3 is incorrect; in-situ analysis has been done by missions like Hayabusa2, and China is not the first to attempt both sample collection and on-site analysis.
- Statement 4 is correct — Kamo‘oalewa is a quasi-satellite of Earth, meaning it orbits the Sun but remains in Earth’s orbital vicinity.
Pumped Storage Hydropower Syllabus
Syllabus: GS3/ Energy and Infrastructure
Context:
- The Central Electricity Authority (CEA) has identified major private players like Greenko, Adani Green, and JSW Energy to spearhead India’s goal of achieving 24 GW of Pumped Storage Hydropower (PSH) capacity by 2032.
What is Pumped Storage Hydropower (PSH)?
- PSH is a hydroelectric energy storage system used for grid load balancing.
It works by pumping water from a lower reservoir to an upper reservoir using surplus renewable energy (e.g., solar) during low demand. - During peak demand, water is released back down to generate electricity, effectively acting as a renewable energy “battery”.
Current Status in India (as of 2024):
- Installed capacity: < 5 GW
- Target by 2032:24 GW (across 39 projects)
- Under construction: ~10 GW (3 GW expected in FY25)
Key states:
- Andhra Pradesh: 16 GW
- Maharashtra:13GW
(Together, 57% of future PSH capacity)
Importance of PSH in India:
- Grid Stability: Crucial for integrating intermittent sources like solar and wind by offering dispatchable, reliable power.
- Economic Viability: Offers higher Internal Rate of Return (IRR) than standalone solar or wind.
- Energy Security: Reduces dependence on imported energy storage components.
With reference to Pumped Storage Hydropower (PSH) in India, consider the following statements:
- PSH projects help in maintaining grid stability by providing dispatchable power to balance variable renewable energy sources.
- The Internal Rate of Return (IRR) for PSH projects is generally lower than for standalone solar or wind power plants.
- Unlike battery energy storage systems (BESS), PSH projects are free from critical mineral supply chain dependencies.
- PSH plants provide instantaneous power output, making them more suitable for frequency regulation than BESS.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 1, 2, and 4 only
D. 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: A. 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: PSH offers flexible, dispatchable power for grid stability.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: PSH has slightly higher IRR than standalone solar/wind.
- Statement 3 is correct: PSH depends on local water/land, not imported minerals.
- Statement 4 is incorrect: BESS provides instantaneous power, not PSH.
Matryoshka
Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
- At its 2025 I/O developer conference, Google unveiled AI Matryoshka, a comprehensive AI integration strategy.
About AI Matryoshka:
- AI Matryoshka is Google’s visionary framework that integrates AI models and capabilities throughout its entire digital ecosystem.
- Inspired by the concept of Russian nesting dolls (Matryoshkas), each AI component is embedded within another, creating a layered system where each level reinforces and enhances the next.
- This model ensures that AI is deeply embedded into all of Google’s products and services—whether in the cloud, on-device, or at the edge.
Significance:
- Layered Integration: Each AI layer is tightly coupled with others, ensuring coherent, intelligent behavior across devices and platforms.
- Hardware-Software Synergy: Enables optimal coordination between physical devices and software-based intelligence.
- Scalability and Specialization: Different layers offer varying levels of specialization, from lightweight on-device models to powerful cloud-based systems.
- Adaptive Intelligence: The system dynamically shifts between cloud and on-device processing based on task complexity and device capability.
- Overall, AI Matryoshka represents a shift toward a unified, context-aware AI ecosystem, enabling Google to deliver smarter, more responsive user experiences.
With reference to Google’s AI Matryoshka framework introduced in 2025, consider the following statements:
- It is primarily designed for training monolithic AI models on central cloud infrastructure.
- It promotes dynamic load shifting between edge devices and cloud-based systems depending on the computational requirements.
- It allows multi-level specialization, enabling reusability of AI functions across various layers of the Google ecosystem.
- It ensures that all AI processing is exclusively conducted on-device for enhanced privacy.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A. 1 and 4 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 2 and 4 only
D. 2, 3 and 4 only
Answer:B 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect because Matryoshka is not limited to monolithic cloud-based AI; it involves modular, layered AI across platforms.
- Statement 2 is correct: It allows dynamic load shifting based on the complexity and capability of devices.
- Statement 3 is correct: It promotes reusability and specialization at various levels (edge, cloud, etc.).
- Statement 4 is incorrect: AI Matryoshka is not exclusive to on-device processing; it includes cloud integration as well.
