Pahalgam Terror Attack and Suspension of the Indus Waters Treaty
Syllabus:IR
- The Cabinet Committee on Security, chaired by PM Narendra Modi, has approved a 5-point action plan in response to a terrorist attack in Baisaran Valley (Pahalgam), Jammu and Kashmir, which claimed the lives of 26 civilians.
- The Resistance Front (TRF), a proxy group of the Pakistan-based Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT), claimed responsibility.
- TRF emerged in 2020 following the elimination of LeT’s leadership in 2018 and the revocation of Article 370 in 2019.
- It was designated a terrorist organization under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, 1967 in 2023.
India’s 5-Point Action Plan After the Pahalgam Terror Attack
- Suspension of the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT):India has suspended the 1960 treaty, leveraging water diplomacy to pressure Pakistan to end cross-border terrorism.
- Closure of the Attari-Wagah Border:The Integrated Check Post at Attari, Punjab has been shut, halting all movement of people and goods.
- Only those who crossed over legally can return by May 1, 2025.
- Revocation of SAARC Visa Exemption for Pakistan:India has cancelled SAARC Visa Exemption Scheme (SVES) for Pakistani nationals.
- All existing visas under this scheme are now void.
- Expulsion of Pakistani Military Advisors:Pakistan’s Defence, Naval, and Air Advisors in India have been declared persona non grata.
- India will also recall its military advisors from Islamabad.
- Diplomatic Downgrade:India will reduce its diplomatic staff in Islamabad from 55 to 30 by May 1, 2025, effectively freezing bilateral dialogue.
Geopolitical Factors Behind the Attack
- India’s Kashmir Policy: Pakistan perceives the revocation of Article 370 and Kashmir’s integration into India as a threat to its claim over Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK).
International Isolation of Pakistan:
- Diminished support from traditional allies (U.S., Gulf countries, even China).
- Post-2021 U.S. withdrawal from Afghanistan reduced Pakistan’s strategic importance.
- Economic Instability:
- Severe inflation, institutional weaknesses, and rising Baloch insurgency.
- Declining investor confidence and worsening GDP outlook.
Global Messaging:
- The attack coincided with PM Modi’s visit to Saudi Arabia and the U.S. Vice President’s trip to India—suggesting Pakistan’s attempt to reassert regional influence.
The Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) – Background and Significance
- Signed in 1960, mediated by the World Bank after 9 years of negotiation.
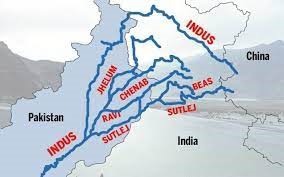
Water Allocation:
- Eastern Rivers (Ravi, Beas, Sutlej) – India
- Western Rivers (Indus, Jhelum, Chenab) – Pakistan
- Set up a Permanent Indus Commission and a multi-level dispute resolution mechanism.
India’s Recent Actions:
- 2023 & 2024: Issued notices to modify the IWT due to disputes over projects like Kishanganga and Ratle.
- Suspension Justified Under: Article 62 of the Vienna Convention, allowing treaty withdrawal due to fundamental changes in circumstances (i.e., cross-border terrorism).
Implications of IWT Suspension
For India:
- Gains freedom in river management and can:
- Conduct reservoir flushing outside the monsoon period.
- Fast-track hydroelectric projects on western rivers.
- Deny project inspections to Pakistan.
- Note: Suspension won’t immediately affect Pakistan’s water supply due to India’s current infrastructure limits.
For Pakistan:
- Major water security risks—80% of agriculture depends on Indus waters.
- Threats to:
- Food and water supply
- Power generation
- Economic stability (Indus system fuels 25% of Pakistan’s GDP)
- May seek World Bank arbitration, and approach allies like China—but economic constraints limit retaliation.
India’s Key Dams on the Indus System
- Kishanganga (Jhelum): Operational since 2018; diverts water from a key Mangla Dam tributary.
- Ratle (Chenab): Under construction; could reduce flow to Pakistan’s Punjab.
- Shahpurkandi (Ravi): Diverts Ravi water to Indian channels.
- Ujh (Ravi): Planned dam to further reduce Pakistan’s water access.
India’s Long-Term Strategic Roadmap
- Strengthen Deterrence
- Enhance border security with high-tech surveillance and smart fencing.
- Maintain a modern, responsive military presence.
- Leverage Global Forums
- Highlight Pakistan’s support for terrorism at the UN Security Council.
- Use Article 51 of the UN Charter to advocate for collective action.
- Push for FATF blacklisting of Pakistan for terror financing.
- Internal Security & Social Cohesion
- Deploy counter-radicalization efforts in border regions.
- Promote unity through public awareness on pluralism and peace.
With reference to the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT), consider the following statements:
- The IWT allocates the three eastern rivers to Pakistan and the three western rivers to India.
- The Treaty allows India unrestricted use of western rivers for hydroelectricity, subject to specific design constraints.
- Article XII of the Treaty provides for its suspension in case of material breach by either party.
- India’s suspension of the IWT in 2025 is the first such instance since the treaty’s inception.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 4 only
D. 2, 3 and 4 only
Answer: B. 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The eastern rivers (Ravi, Beas, Sutlej) are allocated to India, and the western rivers (Indus, Jhelum, Chenab) to Pakistan.
- Statement 2 is correct: India is allowed limited non-consumptive use of western rivers, such as for hydroelectric projects, but subject to design limitations.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: There is no provision in Article XII for suspension due to material breach. However, under Article XII(3), the treaty can be modified through mutual agreement. India’s recent action is being justified under Article 62 of the Vienna Convention, not under IWT itself.
- Statement 4 is correct: This is indeed the first time since 1960 that India has suspended the treaty.
SAARC Visa Exemption Scheme
Syllabus:IR
- Following the terror attack in Pahalgam, Jammu & Kashmir, the Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) has revoked the SAARC Visa Exemption Scheme (SVES) for Pakistani nationals.
- This move is a firm diplomatic measure in response to Pakistan’s continued sponsorship of cross-border terrorism.

What is the SAARC Visa Exemption Scheme (SVES)?
- Launched: 1992, based on a decision from the 4th SAARC Summit (1988, Islamabad).
- Objective: To promote regional integration and people-to-people connectivity among SAARC nations.
- Mechanism: Eligible individuals are issued a Special Travel Document (Visa Sticker) that permits visa-free travel within member states.
Coverage
- Applicable to 24 categories, including:
- Heads of State
- Parliamentarians
- Judges
- Senior officials
- Businesspersons
- Journalists
- Sportspersons, etc.
- Visa Stickers are typically valid for one year, issued by the home country, and subject to immigration clearance.
- India-Specific Provisions under SVES
- Nepal and Bhutan citizens: Visa-exempt under longstanding bilateral agreements.
Pakistani nationals:
- Initially granted multiple-entry business visas for 10 locations.
- In 2015, India revised the rules to extend visa validity up to three years and expanded access to 15 designated cities for special-category Pakistani businessmen.
- Sri Lanka: Eligible for India’s e-Tourist Visa facility.
- India: Its citizens enjoy visa-free entry into Nepal and Bhutan, and are eligible for business visas in other SAARC countries.
India’s Revocation of SVES for Pakistan
- As per CCS notification:
- All SVES visas issued to Pakistani nationals stand cancelled.
- Those currently in India under SVES must exit the country.
- This decision effectively freezes high-level and non-official travel between India and Pakistan under the SAARC framework.
- Note: The Kartarpur Corridor Agreement (2019)—a separate bilateral initiative—allows visa-free pilgrimage for Indian citizens to the Gurdwara Darbar Sahib in Pakistan. This remains unaffected for now.
About the Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS)
Composition:
- Chairperson: Prime Minister of India
- Members: Ministers of Defence, Home Affairs, External Affairs, and Finance
- Attendees: May include Chiefs of Defence Staff, service chiefs, and senior national security officials.
- Role: Apex decision-making body on matters related to:
- National security
- Defence policy
- Strategic foreign affairs
- Internal law and order
- Historical Significance
- First convened during the 1947–48 Indo-Pak War under PM Jawaharlal Nehru.
- Institutionalized post the 1999 Kargil conflict, becoming a formally structured entity.
Key meetings during:
- 1971 Indo-Pak War
- 1999 Kandahar hijack (IC-814)
- Major cross-border terror incidents and strategic crises.
Following the terror attack in Pahalgam, the Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) revoked the SAARC Visa Exemption Scheme (SVES) for Pakistani nationals. With reference to the SAARC Visa Exemption Scheme, consider the following statements:
- The SAARC Visa Exemption Scheme (SVES) was launched in 1992 to promote regional integration among SAARC nations.
- The SVES allows visa-free travel for a select group of individuals across SAARC countries.
- India has revoked the SVES for Pakistani nationals, freezing all travel under this scheme for them.
- The Kartarpur Corridor Agreement of 2019 is unaffected by the revocation of SVES.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1, 2, and 3 only
B) 1, 2, 3, and 4
C) 2, 3, and 4 only
D) 1 and 4 only
Answer: B) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The SAARC Visa Exemption Scheme (SVES) was launched in 1992 based on the decision from the 4th SAARC Summit (1988) to promote regional integration and people-to-people connectivity among SAARC nations.
- Statement 2 is correct: Under the SVES, 24 categories of individuals (including heads of state, parliamentarians, senior officials, businesspersons, journalists, etc.) are eligible for a Special Travel Document (Visa Sticker) that permits visa-free travel within SAARC countries.
- Statement 3 is correct: Following the terror attack in Pahalgam, the Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) has revoked the SVES for Pakistani nationals. This decision cancels all SVES visas and mandates that those currently in India under the SVES must exit the country.
- Statement 4 is correct: The Kartarpur Corridor Agreement (2019), which allows visa-free pilgrimage for Indian citizens to the Gurdwara Darbar Sahib in Pakistan, remains unaffected by the revocation of the SVES.
Davis Strait
Syllabus: GS1/Places in News
- A team of scientists from the UK and Sweden has uncovered a hidden landmass beneath the icy waters of the Davis Strait.
- This landmass, now named the Davis Strait proto-microcontinent, was discovered during an ocean floor study in the region.
Key Details:
- Composition: The proto-microcontinent consists of unusually thick continental crust.
- Size: It spans between 12 to 15 miles (approximately 19 to 24 kilometers).
- Location: It is submerged beneath the western offshore waters of Greenland.
- Nature: This microcontinent is a primitive fragment of crust, which never fully separated when Greenland and North America drifted apart in ancient geological history.
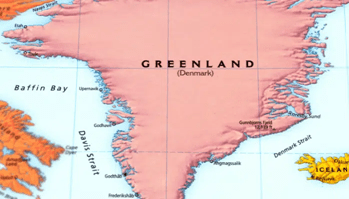
About the Davis Strait:
- Location: The Davis Strait lies between Canada’s Baffin Island and Greenland.
- Connection: It connects the Labrador Sea (part of the Atlantic Ocean) in the south to Baffin Bay in the north.
- Formation: Straits like the Davis Strait are narrow waterways formed by geological phenomena such as tectonic shifts, connecting two large bodies of water.
A recent discovery by a team of scientists from the UK and Sweden uncovered a hidden landmass beneath the icy waters of the Davis Strait. Based on the given details, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- The newly discovered landmass is named the Davis Strait proto-microcontinent, consisting of unusually thick continental crust.
- The Davis Strait lies between Greenland and Canada’s Baffin Island, connecting the Atlantic Ocean with the Arctic Ocean.
- The proto microcontinent is a new geological formation, resulting from recent tectonic shifts and drifting apart of Greenland and North America.
- The size of the landmass spans approximately 12 to 15 kilometers beneath the waters.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1, 2, and 4 only
C. 1, 3, and 4 only
D. 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer:B. 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The Davis Strait proto-microcontinent consists of unusually thick continental crust, and it is indeed the landmass recently uncovered by scientists.
- Statement 2 is correct: The Davis Strait is located between Canada’s Baffin Island and Greenland, and it connects the Labrador Sea to Baffin Bay. The statement erroneously mentions the Arctic Ocean, but this does not affect the geographical connection between the two bodies of water.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The proto-microcontinent is a primitive fragment of crust that never fully separated during the ancient geological split between Greenland and North America. It is not a new formation created by recent tectonic shifts.
- Statement 4 is correct: The size of the landmass is between 12 to 15 miles (approximately 19 to 24 kilometers), as stated.
Years of SVAMITVA Scheme
Syllabus :GS 2/Governance
- Launched: April 24, 2020 (National Panchayati Raj Day)
- Ministry: Ministry of Panchayati Raj
Objective:
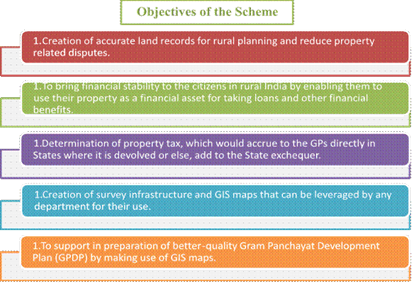
- Provide legal ownership papers for houses and land in villages using drones and mapping technology.
- Facilitate access to loans, dispute resolution, and support better planning.
Implementation:
- Led by the Survey of India
- Tech Partner: National Informatics Centre Services Inc. (NICSI)
- Budget: ₹566.23 crores (FY 2020-21 to FY 2024-25, with extension to FY 2025-26)
Progress:
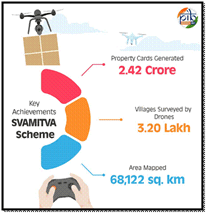
- 42 Crore property cards created.
- 61 Lakh villages covered.
- Drone surveys completed in 3.20 Lakh villages.
- 68,122 sq. km area covered.
Consider the following statements regarding the SVAMITVA (Survey of Villages and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas) scheme:
- Launched on April 24, 2020, by the Ministry of Panchayati Raj.
- Aims to provide legal ownership documents for rural properties using drone and mapping technology.
- Implemented solely by the Ministry of Panchayati Raj, with no involvement from state governments.
- As of July 2024, drone surveys have been completed in approximately 3.12 lakh villages, covering 2.03 crore property cards.
Which of the above statements are correct?
A) 1, 2, and 4 only
B) 1, 3, and 4 only
C) 2 and 4 only
D) 1 and 4 only
Answer: A) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct. The SVAMITVA scheme was launched on April 24, 2020, by the Ministry of Panchayati Raj on National Panchayati Raj Day.
- Statement 2: Correct. The scheme aims to provide legal ownership documents for rural properties using drone and mapping technology, facilitating access to loans and reducing property disputes.
- Statement 3: Incorrect. While the Ministry of Panchayati Raj is the nodal ministry, the implementation involves collaboration with state governments, state revenue departments, and the Survey of India.
- Statement 4: Correct. As of July 2024, drone surveys have been completed in approximately 3.12 lakh villages, and 2.03 crore property cards have been prepared in 1.30 lakh villages.
PoshanTracker Application
Syllabus: GS2/ Governance
- The Poshan Tracker is a mobile-based, ICT-enabled application developed by the Ministry of Women and Child Development (MoWCD) under Mission Poshan 2.0.
- It serves as a comprehensive tool for Anganwadi Workers (AWWs) to monitor and manage maternal and child nutrition services in real time.
Awards and Recognition
- In 2024, the Poshan Tracker received the National Award for e-Governance (Gold), recognizing its excellence in digital governance and innovation in public administration.
Key Features and Functionality
- Real-Time Monitoring: Enables Anganwadi Workers (AWWs) to track daily activities such as Growth Measurement, Take Home Ration (THR) distribution, and Hot Cooked Meals (HCM).
- Comprehensive Beneficiary Management: Manages data for pregnant women, lactating mothers, children (0-6 years), and adolescent girls, ensuring timely interventions.
- Data Integration: Integrates with platforms like the RCH and UWIN portals, facilitating seamless coordination across health and welfare services.
- Multilingual Support: Available in 22 regional languages, making it accessible to a diverse user base.
- Beneficiary Communication: Features SMS alerts to beneficiaries upon delivery of THR, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Impact and Reach
- Coverage: As of 2024, the application has been adopted by over 14 lakh Anganwadi Workers.
- Beneficiary Onboarding: More than 7 crore beneficiaries have been onboarded, with over 1.24 crore THR distributions and 68.79 lakh HCMs tracked.
- Growth Monitoring: Utilizes WHO growth charts to assess children’s growth, aiding in the early identification of malnutrition issues.
Integration with Other Initiatives:
- Poshan Maah and Poshan Pakhwada: Annual campaigns to raise awareness about nutrition, during which activities are recorded on the Poshan Tracker’s Jan Andolan Dashboard.
- PM Gati Shakti Portal: Geo-mapping and onboarding of Anganwadi Centres to enable focused interventions.
Conclusion
- The Poshan Tracker exemplifies India’s commitment to leveraging technology for enhancing public health services, ensuring that nutritional interventions reach the most vulnerable populations effectively and efficiently.
Consider the following statements regarding the Poshan Tracker initiative under Mission Poshan 2.0:
- The Poshan Tracker application is utilized exclusively by Anganwadi Workers (AWWs) to monitor the growth of children aged 0–6 years.
- The application integrates with the RCH and UWIN portals to facilitate comprehensive monitoring of nutritional services.
- The Ministry of Women and Child Development won the National Award for e-Governance 2024 (Gold) for the Poshan Tracker initiative.
- As of September 2024, the Poshan Tracker has covered over 8.9 crore children, with 8.57 crore measured in a single month through routine monthly growth measurements.
Which of the above statements are correct?
A) 1, 2, and 3 only
B) 2, 3, and 4 only
C) 1, 3, and 4 only
D) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: D) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct. The Poshan Tracker is primarily used by Anganwadi Workers to monitor the growth of children aged 0–6 years, ensuring timely interventions for nutritional issues.
- Statement 2: Correct. The application integrates with platforms like the RCH and UWIN portals, facilitating seamless coordination across health and welfare services.
- Statement 3: Correct. The Ministry of Women and Child Development won the National Award for e-Governance 2024 (Gold) for the Poshan Tracker initiative, recognizing its excellence in digital governance and innovation in public administration.
- Statement 4: Correct. As of September 2024, the Poshan Tracker has covered over 8.9 crore children, with 8.57 crore measured in a single month through routine monthly growth measurements, showcasing its extensive reach and impact.
Tobacco Farming
Syllabus: GS3/Agriculture
- The Social Welfare Minister of Andhra Pradesh has assured support to tobacco farmers who are facing challenges due to low bids and delayed procurement processes.
Tobacco Farming in India:
- Tobacco cultivation in India was introduced by the Portuguese in 1605. India is the second-largest producer of tobacco globally, after China. Additionally, India ranks as the second-largest exporter of unmanufactured tobacco (in terms of quantity), following Brazil.
- Tobacco is primarily grown in states like Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, and Bihar. Among these, Gujarat leads, accounting for 45% of the tobacco cultivation area and 30% of the total production. It also has the highest productivity in the country, followed by Andhra Pradesh.
Climatic Conditions for Tobacco Cultivation:
- Tobacco in India thrives when the mean temperature is between 20°C and 27°C. It is not typically cultivated in regions where the annual rainfall exceeds 1200 mm.
- Tobacco plants, especially cigar and binder varieties, prefer sandy to loamy red soils. The crop requires significant amounts of nitrogen, potassium, calcium, and magnesium for optimal growth.
The Tobacco Board:
- The Tobacco Board was established in 1976 under the Tobacco Board Act, 1975. Its primary responsibilities include ensuring the smooth functioning of the tobacco farming system, securing fair and remunerative prices for tobacco farmers, and promoting tobacco exports from India.
Consider the following statements regarding tobacco cultivation and the Tobacco Board in India:
- Tobacco cultivation in India was introduced by the Portuguese in 1605.
- India is the second-largest producer of tobacco globally, after China.
- The Tobacco Board was established in 1976 under the Tobacco Board Act, 1975.
- Gujarat accounts for 45% of the total tobacco production in India.
Which of the above statements are correct?
A) 1, 2, and 3 only
B) 2, 3, and 4 only
C) 1, 2, and 4 only
D) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: B) 2, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Incorrect. Tobacco cultivation in India was introduced by the Portuguese in 1605.
- Statement 2: Correct. India is the second-largest producer of tobacco globally, after China.
- Statement 3: Correct. The Tobacco Board was established in 1976 under the Tobacco Board Act, 1975.
- Statement 4: Correct. Gujarat accounts for 45% of the total tobacco production in India.
Nano-sulphur
Syllabus: GS3/Agriculture
- Scientists from The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI) have developed nano sulphur, which has been shown to increase mustard yield by 30-40%.
About DMH-11 (Genetically Modified Mustard): DMH-11 is a genetically-modified variety of mustard that has been shown to increase the average per hectare yield by 10-40% in various multi-site trials. Traditional mustard varieties typically yield around 1-1.8 tonnes per hectare.
Significance of Nano Sulphur:
- Nano sulphur is an environmentally friendly product that utilizes biological agents such as plant-promoting bacteria, which secrete enzymes and metabolites to enhance plant growth.
- It can replace up to 50% of traditional sulphur fertilizers, leading to potential additional earnings of up to ₹12,000 per acre for farmers.
Cost-Effectiveness:
- A 500-milliliter bottle of nano sulphur costs around ₹450, making it significantly cheaper than conventional sulphur fertilizers, which range from ₹900 to ₹1,800 per bag, depending on the grade.
- Role of Sulphur in Agriculture:
Sulphur is a crucial component in the formation of amino acids like cysteine and methionine, which are essential for protein synthesis. This makes it especially important for legumes, oilseeds (such as mustard), and cereals. Sulphur also enhances the oil content in oilseeds like canola and sunflower, improves grain quality in cereals like wheat, and enhances the flavor of alliums such as onions and garlic.
Consider the following statements regarding nano sulphur and its role in agriculture:
- Nano sulphur, developed by TERI scientists, has been shown to increase the yield of mustard by 30-40%.
- DMH-11, a genetically modified mustard variety, yields an average of 1-1.8 tonnes per hectare.
- Nano sulphur can replace up to 50% of traditional sulphur fertilizers and can result in an additional income of up to ₹12,000 per acre for farmers.
- Sulphur plays a vital role in boosting oil content in oilseeds like sunflower and canola, but not in mustard.
Which of the above statements are correct?
A) 1, 2, and 3 only
B) 1, 3, and 4 only
C) 2 and 4 only
D) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: A) 1, 2, and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct. Nano sulphur, developed by TERI scientists, has been proven to increase mustard yields by 30-40%. This product is a breakthrough in improving agricultural productivity.
- Statement 2: Correct. DMH-11, the genetically modified mustard, has shown an increase in yield by 10-40% in various trials, with the average yield being 1-1.8 tonnes per hectare for traditional varieties.
- Statement 3: Correct. Nano sulphur can replace up to 50% of conventional sulphur fertilizers, leading to increased earnings of up to ₹12,000 per acre for farmers, as it is more cost-effective than traditional sulphur fertilizers.
- Statement 4: Incorrect. Sulphur enhances the oil content not just in sunflower and canola, but also in mustard. It plays an essential role in oilseed crops, including mustard, by boosting oil content.
Galaxy NGC 1052-DF2
Syllabus :GS 3/Space
- Astronomers at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have studied the unusual absence of dark matter in the galaxy NGC 1052-DF2, a finding that challenges conventional theories of galaxy formation.
Dark Matter:
- Dark matter constitutes about 27% of the universe but does not interact with light, making it invisible.
- It can only be detected through its gravitational effects. Along with dark energy, it accounts for approximately 95% of the universe’s total mass-energy content.
- The remaining less than 5% consists of visible matter, such as planets, stars, and galaxies.
- NGC 1052-DF2:NGC 1052-DF2 is an ultra-diffuse galaxy that is comparable in size to the Milky Way, but it contains far fewer stars and only 1/400th the expected amount of dark matter.
- This galaxy is notable for its extreme deficiency of dark matter, making it a rare anomaly even among other ultra-diffuse galaxies.
- It has a total mass of around 340 million solar masses, most of which comes from stars, indicating an unusually low amount of dark matter compared to galaxies like the Milky Way.
Latest Developments:
- In a recent study, researcher K. Aditya modeled the galaxy using stellar density data.
- The model showed that mass models with a “cuspy” dark matter halo—where dark matter is dense at the center—did not match the observed data.
- This suggests that NGC 1052-DF2 may either lack dark matter altogether or possess it in a very diffuse form.
- This discovery raises new questions regarding galaxy formation and the elusive nature of dark matter.
Consider the following statements regarding dark matter and the galaxy NGC 1052-DF2:
- Dark matter makes up approximately 27% of the universe and interacts with light, making it detectable through conventional methods.
- NGC 1052-DF2 is an ultra-diffuse galaxy that contains around 1/400th the expected amount of dark matter compared to typical galaxies like the Milky Way.
- Research conducted by K. Aditya suggests that the mass models with a “cuspy” dark matter halo align with the observations of NGC 1052-DF2.
- NGC 1052-DF2’s mass is predominantly from stars, with very little contribution from dark matter, challenging conventional galaxy formation theories.
Which of the above statements are correct?
A) 1, 2, and 4 only
B) 2, 3, and 4 only
C) 1, 2, and 3 only
D) 2 and 4 only
Answer: A) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Incorrect. While dark matter does make up about 27% of the universe, it does not interact with light, which is why it is invisible. It can only be detected through its gravitational effects, not through conventional observation methods like light.
- Statement 2: Correct. NGC 1052-DF2 is an ultra-diffuse galaxy that has only 1/400th the expected amount of dark matter compared to typical galaxies like the Milky Way. This makes it an outlier in terms of dark matter content.
- Statement 3: Incorrect. Research by K. Aditya indicates that mass models with a “cuspy” dark matter halo (which is denser at the center) do not match the observed data for NGC 1052-DF2. This suggests that the galaxy may lack dark matter or have it in a very diffuse form, not conforming to the expected models.
- Statement 4: Correct. The galaxy’s total mass is primarily derived from stars, with very little contribution from dark matter. This observation challenges standard theories of galaxy formation, as it does not conform to the usual models of how galaxies should develop and behave in terms of dark matter.
Schemes for Sportspersons in India
Syllabus: Miscellaneous
- The Government of India (GOI) has demonstrated a strong commitment to enhancing the sports ecosystem by establishing a robust framework of support for athletes at every stage of their careers.
- This comprehensive approach is designed to uplift the sports culture in India and provide essential resources to athletes.
Current Developments
- India has made remarkable progress in the sports sector, largely due to substantial government backing through various initiatives and schemes.
- The Khelo India Programme, launched in 2016-17, is central to this effort. The program aims to nurture a sporting culture at the grassroots level, identifying and supporting athletes at various stages of their development.
- For the financial year 2025–26, the GOI has allocated a record budget of ₹3,794 crore, focusing on critical areas such as athlete training, infrastructure development, and talent enhancement.
Key Schemes for Athletes
RESET Programme (2024):Launched to empower retired athletes by providing them with education and job opportunities, ensuring a smooth transition from sports to other career avenues.Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay National Welfare Fund for Sportspersons
This fund offers comprehensive support to sportspersons, including:
- A one-time ex-gratia of up to ₹5 lakh.
- A monthly pension of ₹5,000.
- Medical assistance of up to ₹10 lakh.
- Support for injuries sustained during training or competition, up to ₹10 lakh.
- Support for Families of Deceased Sportspersons: Financial aid is available for the families of deceased athletes and other support personnel, including coaches, referees, and physiotherapists. The maximum aid for families is ₹5 lakh, and for support personnel, ₹2 lakh.
- Human Resources Development in Sports:This initiative focuses on promoting research, providing global exposure, and enhancing skills in sports science and coaching, ultimately helping India compete at the global level.
- Scheme for Sports and Games for the Disabled:Aimed at fostering inclusive sports at the grassroots level for people with disabilities, ensuring equal opportunities for all athletes.
- Panchayat Yuva Krida aur Khel Abhiyan (PYKKA):This program strengthens sports infrastructure and organizes events at the village and block levels, encouraging participation at the grassroots.
- Assistance to National Sports Federations (ANSF):Financial aid is provided to National Sports Federations for coaching, training, and participation in international competitions.
- National Sports Development Fund (NSDF):The NSDF works to fill the gaps in athlete support and infrastructure through public-private partnerships, facilitating long-term sustainable growth in the sports sector.
- Pension for Meritorious Sportspersons:Aimed at providing lifelong financial security to athletes who have made significant contributions to Indian sports.
- National Sports Awards:These prestigious awards recognize the achievements of athletes and motivate others to strive for excellence in sports.
By continually supporting athletes through such initiatives, the government aims to establish a thriving sports culture and empower athletes to reach their full potential. These schemes not only provide financial support but also ensure that India remains competitive on the global sports stage.
Consider the following statements regarding India’s sports development initiatives:
- The Khelo India Programme, launched in 2016-17, aims to build a sporting culture at the grassroots level and support athletes across all levels.
- The RESET Programme, introduced in 2024, empowers retired athletes through education and job opportunities.
- The Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay National Welfare Fund for Sportspersons offers one-time ex-gratia aid of up to ₹5 lakh, a monthly pension of ₹5,000, medical assistance up to ₹10 lakh, and support up to ₹10 lakh for injuries sustained during training or competitions.
- The National Sports Development Fund (NSDF) bridges gaps in athlete support and infrastructure with public-private funding.
Which of the above statements are correct?
A) 1, 2, 3, and 4
B) 1 and 4 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1 and 3 only
Answer: A) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct. The Khelo India Programme, launched in 2016-17, aims to build a sporting culture at the grassroots level and support athletes across all levels. It focuses on talent identification, infrastructure development, and community engagement in sports.
- Statement 2: Correct. The RESET Programme, introduced in 2024, empowers retired athletes through education and job opportunities. This initiative helps former athletes transition into post-sport careers and contributes to their financial independence.
- Statement 3: Correct. The Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay National Welfare Fund for Sportspersons offers one-time ex-gratia aid of up to ₹5 lakh, a monthly pension of ₹5,000, medical assistance up to ₹10 lakh, and support up to ₹10 lakh for injuries sustained during training or competitions. This fund provides financial security and support to sportspersons in need.
- Statement 4: Correct. The National Sports Development Fund (NSDF) bridges gaps in athlete support and infrastructure with public-private funding. It aims to promote excellence in sports by providing financial assistance for various sports development activities.
