Ali AI Ligang Festival
Syllabus: GS1/ Art & Culture
- The Mising tribe, Assam’s largest tribal community, recently celebrated the Ali Ai Ligang festival, a vibrant event deeply rooted in agriculture, tradition, and cultural heritage.
- Observed on the first Wednesday of the Fagun month (February-March), Ali Ai Ligang has been celebrated for centuries in rural Mising villages.
- Traditionally practicing Jhum cultivation, the Mising people have now transitioned to settled wet paddy farming.
- The festival begins with the hoisting of the Laitom Tomchar (festival flag), followed by offerings to Donyi Polo (Sun and Moon gods) to seek blessings for agricultural prosperity.
- A key highlight of the festival is the Gumrag Dance, performed by both men and women, symbolizing joy, abundance, and prosperity.
The name ‘Ali Ai Ligang’ is derived from which of the following linguistic roots?
- Austroasiatic and Sanskrit influences
- Tai-Ahom and Bodo-Kachari derivations
- Mising-Tani language group
- Dravidian and Indo-Aryan linguistic fusion
Answer: (c) Mising-Tani language group
Explanation: The term ‘Ali Ai Ligang’ originates from the Mising-Tani language group, spoken by the Mising people, who belong to the larger Tani ethnic group of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam. The words ‘Ali’ (roots), ‘Ai’ (fruits), and ‘Ligang’ (sowing) together signify the beginning of seed sowing.
Lepakshi Temple
Syllabus : GS 1/Culture
Historians have urged the government to take necessary steps to secure UNESCO World Heritage status for the Lepakshi Temple in Andhra Pradesh, a significant 16th-century architectural and historical marvel.
About Lepakshi Temple
Located in Lepakshi, Andhra Pradesh, the temple is renowned for its Dravidian-style architecture, intricate stone carvings, and monolithic structures. Dedicated to Lord Veerabhadra, a fierce manifestation of Lord Shiva, the temple stands as a testament to the Vijayanagara architectural grandeur.
UNESCO Recognition and Current Status
In March 2023, UNESCO included the Lepakshi Veerabhadra Temple complex in its provisional list of Heritage Sites. To secure final UNESCO World Heritage status, both the State and Central governments must conduct a detailed study of the temple’s architecture, sculptures, mural paintings, and its world-famous monolithic Nandi (bull) statue, before submitting a comprehensive report for consideration.
The Lepakshi Temple, recently in the news for its UNESCO nomination, is primarily associated with which architectural style?
- Nagara style
- Vesara style
- Dravidian style
- Hemadpanti style
Answer: (c) Dravidian style
Explanation: The Lepakshi Temple follows the Dravidian style of architecture, which is characterized by intricate stone carvings, monolithic sculptures, and richly decorated pillars. This style was predominant in South India, particularly under the Vijayanagara Empire, which constructed the temple in the 16th century.
Honduras
Syllabus: GS1/Places
India has dispatched 26 tons of humanitarian aid to Honduras in response to the devastation caused by Tropical Storm SARA, reinforcing its commitment to global disaster relief efforts.Honduras is a Central American nation, bordered by:
- Guatemala and El Salvador to the west,
- Nicaragua to the south and east,
- Caribbean Sea to the north,
- Pacific Ocean to the south (with a small coastal stretch).
Geographical Highlights
- Second-largest country in Central America (after Nicaragua).
- Official Language:
- Major Rivers: Patuca River, Ulúa River.
- Major Mountain Ranges: Volcanic Highlands, Central American Cordillera.
Honduras’ diverse geography, spanning coastal lowlands, volcanic highlands, and rainforests, makes it prone to tropical storms and hurricanes, necessitating international support during natural disasters.
Consider the following statements regarding Honduras:
- It is the largest country in Central America.
- It has coastlines on both the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean.
- The official language of Honduras is Portuguese.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Nicaragua is the largest country in Central America, not Honduras.
Statement 2 is correct: Honduras has two coastlines, one along the Caribbean Sea (north) and a smaller stretch along the Pacific Ocean (south).
Statement 3 is incorrect: The official language of Honduras is Spanish, not Portuguese.
TraumaticAsphyxia
Syllabus: GS2/ Health
Context
Recently, five out of 18 victims of the stampede at New Delhi Railway Station succumbed to traumatic asphyxia, a life-threatening condition caused by severe chest compression.
About Traumatic Asphyxia
Traumatic asphyxia is a rare but critical medical emergency that occurs when the upper chest or abdomen is subjected to intense external pressure, leading to restricted respiration and impaired blood circulation.
Causes
This condition is commonly observed in:
- Stampedes (as seen in crowded public spaces).
- Vehicular accidents involving crushing injuries.
- Building collapses and natural disasters.
- Industrial accidents with heavy machinery involvement.
Symptoms
Key clinical manifestations include:
- Cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin due to oxygen deprivation).
- Edema (swelling caused by fluid retention).
- Hemorrhages in the face, neck, upper limbs, and thorax due to increased venous pressure.
Treatment
- Immediate supportive care (oxygen therapy, intravenous fluid resuscitation).
- Management of associated injuries, such as fractures and internal trauma.
- Monitoring for complications, including respiratory distress and cardiac dysfunction.
Timely medical intervention is crucial to improve survival outcomes in traumatic asphyxia cases.
Traumatic asphyxia, recently in the news due to the New Delhi Railway Station stampede, primarily results from:
- Sudden exposure to toxic gases leading to respiratory failure
- Compression of the upper chest or abdomen restricting respiration and circulation
- Neurological dysfunction causing paralysis of respiratory muscles
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) progression in high-altitude regions
Answer: (b) Compression of the upper chest or abdomen restricting respiration and circulation
Explanation: Traumatic asphyxia is caused by severe compressive force on the chest or abdomen, leading to restricted respiratory function and impaired venous return, commonly observed in stampedes, accidents, and building collapses. The other options relate to different medical conditions (toxic gas exposure, neurological disorders, and chronic diseases) that do not directly cause traumatic asphyxia.
V.O.Chidambaranar Port
Syllabus: GS3/ Infrastructure
Context
The V.O. Chidambaranar (VOC) Port Authority is assessing the feasibility of establishing a shipbuilding facility in Thoothukudi, Tamil Nadu.
About VOC Port
- Location: Situated on the southeastern coast of India in the Gulf of Mannar, at latitude 8° 45’N and longitude 78° 13’E.
Strategic Importance:
- Proximity to major East-West international maritime routes enhances its role as a key trade hub.
- Facilitates trade connectivity between India, Southeast Asia, and global markets.
Natural and Operational Advantages:
- Well-sheltered from storms and cyclonic disturbances, ensuring uninterrupted port activities.
- A deep-water, all-weather port, operational 24/7, 365 days a year, capable of handling large vessels efficiently.
This initiative aligns with India’s vision to boost domestic shipbuilding capabilities and strengthen its blue economy.
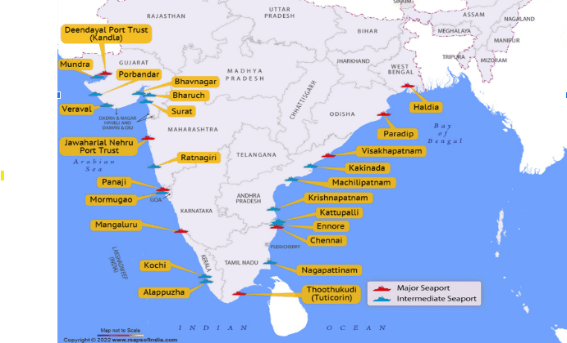
The V.O. Chidambaranar (VOC) Port, where a new shipbuilding facility is being explored, is strategically significant because:
(a) It is the only deep-water port on the eastern coast of India.
(b) It is located along major East-West international maritime trade routes.
(c) It primarily serves as a naval base for India’s maritime security operations.
(d) It is a riverine port that provides access to the Indian hinterland via inland waterways.
Answer: (b) It is located along major East-West international maritime trade routes.
Explanation:
- The VOC Port is a major trade hub due to its proximity to the East-West international sea routes, facilitating global maritime commerce.
- Option (a) is incorrect because other deep-water ports also exist on India’s eastern coast, such as Chennai and Visakhapatnam.
- Option (c) is incorrect as VOC Port primarily handles commercial shipping, not naval operations.
- Option (d) is incorrect because VOC Port is a coastal deep-water port, not a riverine port.
Prime Minister’s Awards for Excellence in Public Administration
Syllabus : GS 2/Governance
Context
The Prime Minister’s Awards for Excellence in Public Administration, 2024, received over 1,500 nominations, reflecting widespread participation from districts and government organizations.
About the Awards
- Established: 2006, recognizing exceptional governance and administrative excellence in Central and State Government organizations.
Restructuring:
- 2014: Focused on qualitative governance achievements.
- 2020: Aligned with aspirational district programs and last-mile governance.
- 2021: Revamped to prioritize good governance, innovation, and grassroots impact.
Award Categories for 2024:
- Holistic Development of Districts – Recognizing districts implementing comprehensive governance models.
- Aspirational Blocks Programme – Acknowledging transformative interventions in underdeveloped blocks.
- Innovation – Rewarding novel administrative approaches to governance challenges.
The awards highlight India’s commitment to governance excellence, grassroots development, and scalable innovations.
The Prime Minister’s Awards for Excellence in Public Administration were introduced with the primary objective of:
(a)Encouraging inter-state competition in governance efficiency.
(b)Recognizing innovative public administration models across India.
(c) Strengthening bureaucratic hierarchy for effective policy implementation.
(d) Providing financial incentives for state governments implementing central schemes.
Answer: (b) Recognizing innovative public administration models across India.
Explanation:
The awards acknowledge outstanding work in public administration at the district, state, and central levels.
Option (a) is incorrect because the awards focus on best practices, not competition among states.
Option (c) is incorrect as the awards aim to improve governance, not bureaucratic structures.
Option (d) is incorrect since the awards do not provide financial incentives but serve as recognition of governance excellence.
Technology Adoption Fund
Recently, the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe) introduced a new initiative called the Technology Adoption Fund (TAF).
About the Technology Adoption Fund:
- The Technology Adoption Fund, with a corpus of Rs 500 crore, is designed to foster the growth of India’s space startups.
- Its primary goal is to accelerate the development of homegrown space technologies and reduce India’s dependency on foreign solutions.
Key Features of the Technology Adoption Fund:
Funding Support:
- The fund will provide financial support of up to 60% of the project cost for startups and MSMEs, and 40% for larger industries, with a maximum funding limit of Rs 25 Crores per project.
- It is open to all eligible Non-Government Entities (NGEs) and companies that can demonstrate the commercial viability of their innovations.
Additional Support:
- Along with financial aid, the fund will offer technical guidance and mentoring to help companies navigate challenges during product development.
Commercialization and Market Integration:
- TAF will assist in transitioning early-stage space technologies developed by Indian companies into commercially viable products, aiming to bridge the gap between innovation and commercialization.
Economic Impact:
- The fund will foster the creation of intellectual property, contributing to job creation and economic growth.
- The initiative aims to enhance India’s position in the global space industry by promoting domestic R&D and strengthening collaboration between the private sector and government agencies.
Through this fund, IN-SPACe aims to advance space technology development, enabling India to emerge as a key global player in the space industry.
What is the primary objective of the Technology Adoption Fund (TAF) launched by IN-SPACe?
- To provide scholarships for space science students
- To fund international space missions
- To accelerate the development of indigenous space technology and reduce reliance on imports
- To promote space tourism in India
Answer: c)To accelerate the development of indigenous space technology and reduce reliance on imports
Explanation: The TAF aims to foster the growth of India’s space startups by supporting the development of homegrown space technologies, thereby decreasing dependence on foreign solutions.
Kuno National Park (KNP)
- Kuno National Park, located in Madhya Pradesh, has recently gained attention due to the release of five cheetahs into its wild.
- This park, spanning approximately 750 square kilometers, is situated near the Vindhyan Hills and derives its name from the Kuno River, a tributary of the Chambal River.
- Originally established as a wildlife sanctuary, it was designated a national park in 2018.
- The park’s vegetation is primarily a mix of grasslands and mixed forests, dominated by species such as Kardhai (Anogeissus pendula), Salai (Boswellia serrata), and Khair (Acacia catechu).
- In total, Kuno hosts 123 species of trees, 71 species of shrubs, 32 species of climbers and exotic plants, and 34 species of bamboo and grasses.
- Kuno National Park is home to a diverse array of fauna, including predators like the Indian leopard, sloth bear, Indian wolf, striped hyena, golden jackal, Bengal fox, and dhole.
- Additionally, the park supports over 120 species of birds, contributing to its rich biodiversity
Which significant wildlife reintroduction project is associated with Kuno National Park?
- Reintroduction of the Bengal tiger
- Reintroduction of the Asiatic lion
- Reintroduction of the Indian rhinoceros
- Reintroduction of the African cheetah
Answer: d) Reintroduction of the African cheetah
Explanation: Kuno National Park has been selected as the site for the reintroduction of African cheetahs into India, aiming to restore the species that became extinct in the country in the mid-20th century
AI Tools for Real-Time Antibiotic Resistance Tracking
A collaborative initiative involving IIIT-Delhi, CHRI-PATH, Tata 1mg, and the Indian Council of Medical Research has led to the development of AMRSense, an AI-powered tool designed to analyze routine hospital data to provide timely insights into antibiotic resistance patterns.
The findings were published in The Lancet Regional Health – Southeast Asia, highlighting a six-year study across 21 tertiary care centers in India.
About AMRSense Tool
Data Utilization: AMRSense leverages existing hospital data, such as blood and urine cultures, to predict trends in antibiotic resistance.
Predictive Analytics: The tool identifies relationships between pairs of antibiotics and monitors resistance changes over time, enabling healthcare providers to anticipate resistance patterns and make informed treatment decisions.
Cost-Effectiveness: By utilizing routine hospital data, AMRSense offers a more affordable approach compared to traditional genomic methods.
AMROrbit Scorecard
In addition to AMRSense, researchers have developed the AMROrbit Scorecard, a visual tool that represents resistance trends for hospitals. By comparing local data with global averages, the scorecard helps identify areas requiring intervention, aiming to position hospitals within an optimal quadrant of low resistance and low change rates.
Clinical and Public Health Implications
- The integration of AI tools like AMRSense enhances decision-making in both clinical and public health contexts.
- Clinicians can make informed choices based on real-time data, while hospitals can strengthen antimicrobial stewardship initiatives through actionable insights.
Limitations and Future Directions
- The effectiveness of AMRSense depends on the availability of consistent surveillance data. In regions lacking digital access to such data, the model’s applicability may be limited.
- Future efforts aim to incorporate environmental factors and antibiotic sales data to provide a comprehensive understanding of antimicrobial resistance.
Global Context of Antimicrobial Resistance
- Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is an escalating global concern.
- The World Health Organization emphasizes the need for robust surveillance systems. By leveraging AI, countries like India can play a pivotal role in addressing this crisis.
- Integrating hospital data with broader public health metrics is essential for comprehending and combating AMR.
Which of the following statements about the AMRSense tool is incorrect?
- AMRSense utilizes routine hospital data to predict antibiotic resistance trends.
- The tool employs traditional genomic methods to analyze resistance patterns.
- It identifies relationships between pairs of antibiotics and monitors resistance changes over time.
- AMRSense’s effectiveness depends on the availability of consistent surveillance data.
Answer: B
Explanation: Statement B is incorrect because AMRSense does not rely on traditional genomic methods; instead, it utilizes routine hospital data, such as blood and urine cultures, to analyze and predict antibiotic resistance patterns.This approach is more cost-effective compared to genomic methods. The other statements accurately describe the functionalities and dependencies of the AMRSense tool.
Skill Gap Mapping:
India is actively collaborating with international organizations to address workforce skill gaps. The Ministry of Labour and Employment recently engaged with the International Labour Organisation (ILO), the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), and Germany to discuss a feasibility study for skill gap mapping. These discussions occurred during the first G20 Employment Working Group meeting in South Africa.
Skill Gap Mapping Feasibility Study
- Target Sectors: The study will focus on Information Technology, green jobs, and care-related roles.
- Financial Commitment: India has pledged €810,000 to fund the study.
- Timeline: A draft report is anticipated by June 2026.
This initiative aims to enhance the international mobility of qualified Indian professionals by aligning their skills with global standards.
Collaboration with the Netherlands
Discussions with the Netherlands centered on the Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) and the concept of ‘Living Wages.’ The objective is to improve living standards through sustainable wage systems. Collaboration with the ILO and the Netherlands is considered vital for advancing these initiatives.
Bilateral Engagement with Germany
India and Germany deliberated on the Joint Declaration of Intent (JDI) established in October 2024. This agreement focuses on enhancing cooperation in global supply chains, human-centric artificial intelligence, and the gig economy. India is committed to fostering innovative projects and creating an inclusive future of work.
Technological Innovations in Labour Welfare
- eShram Portal: A national database for unorganized workers, facilitating access to social security benefits.
- National Career Service (NCS) Portal: Connects job seekers with employers, mobilizing over 440 million vacancies and registering 4 million employers.
These platforms exemplify India’s commitment to leveraging technology for labor welfare.
Importance of International Collaboration
India’s proactive engagement with international partners underscores its dedication to enhancing workforce skills and standards. Such collaborations aim to align India’s workforce capabilities with global requirements, thereby boosting employability and economic growth.
Which of the following sectors is NOT a focus of India’s skill gap mapping feasibility study?
- Information Technology
- Green jobs
- Care-related roles
- Manufacturing
Answer: D) Manufacturing
Explanation: The skill gap mapping feasibility study targets Information Technology, green jobs, and care-related roles. Manufacturing is not among the sectors specified for this particular study.
Haryana Witness Protection Scheme 2025
The Haryana Witness Protection Scheme 2025, introduced by the Nayab Singh Saini-led BJP government, aims to enhance the safety and security of witnesses as the state implements new criminal laws.
The scheme categorizes witnesses based on threat perception into three distinct categories:
- Category A: Witnesses facing life-threatening situations.
- Category B: Witnesses facing threats to their safety, reputation, or property, including that of their family.
- Category C: Witnesses experiencing moderate threats such as harassment or intimidation.
- The scheme applies to witnesses of offenses punishable by death, life imprisonment, or imprisonment of seven years or more, covering crimes under the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita and the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012.
- Protective measures include preventing encounters between witnesses and accused during investigations or trials, monitoring communications, and providing close protection services.
- Witnesses may request identity changes or relocation, with the competent authority assessing such requests based on threat analysis.
- Protection measures are provided for specific durations, not exceeding three months at a time.
- Each district will establish a witness protection cell, led by the deputy commissioner of police or superintendent of police, responsible for implementing witness protection orders.
Which of the following statements about the Haryana Witness Protection Scheme 2025 is incorrect?
- The scheme categorizes witnesses into three threat perception categories: A, B, and C.
- It applies to offenses punishable by death, life imprisonment, or imprisonment of seven years or more.
- Witness protection measures are provided indefinitely until the threat is neutralized.
- Each district will establish a witness protection cell led by the deputy commissioner of police or superintendent of police.
Answer: C
Explanation: Statement C is incorrect because, under the Haryana Witness Protection Scheme 2025, protection measures are provided for specific durations, not exceeding three months at a time, and are proportional to the level of threat. This ensures periodic assessment and appropriate allocation of resources. The other statements accurately reflect the scheme’s provisions.
Cancer Care Challenges in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) poses significant health challenges globally, especially in low and middle-income countries like India.
- In India, AML patients often face late-stage diagnoses and limited access to advanced treatments, leading to disparities in outcomes, particularly in rural regions. Addressing these issues is essential to improve survival rates.
Understanding Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Prevalence: AML is the most common type of leukemia among adults.
- Characteristics: It involves the rapid growth of abnormal blood cells, termed blasts, affecting the blood and bone marrow.
- Demographics in India: The median age of AML diagnosis in India is approximately 40 years, which is younger than in high-income countries. Many patients present at advanced stages, leading to poorer outcomes.
Challenges in AML Management
- Healthcare Infrastructure: Disorganized referral systems and inadequate diagnostic facilities cause delays in treatment initiation.
- Financial Constraints: A significant number of patients are unable to afford treatment. In a study, 29% of newly diagnosed AML patients opted for standard care, while 71% did not proceed, primarily due to financial limitations.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Patients from rural areas face additional challenges, including travel logistics and resource shortages in public hospitals. Private healthcare facilities are often financially inaccessible.
Government Initiatives and Proposed Solutions
- Ayushman Bharat Scheme: This initiative aims to enhance access to cancer care. However, gaps remain, particularly in covering initial diagnostics.
Policy Recommendations:
- Tax Exemptions: Industry leaders have advocated for removing taxes on cancer and rare disease medications to reduce treatment costs.
- com
- Infrastructure Development: Strengthening healthcare infrastructure, standardizing treatment protocols, and improving access to novel therapies are crucial steps.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborations can enhance resource availability and make treatments more affordable.
What policy change has been suggested to make cancer treatment more affordable in India?
- Increasing taxes on cancer medications
- Removing taxes on cancer and rare disease drugs
- Reducing import duties on luxury goods
- Centralizing all cancer treatments in urban centers
Answer: b) Removing taxes on cancer and rare disease drugs
Explanation: Industry leaders have urged the Indian government to eliminate taxes on cancer and rare disease medications to reduce treatment costs and improve affordability.
NITI Aayog’s Vision for Viksit Bharat by 2047
- NITI Aayog, India’s premier policy think tank, is spearheading an initiative to assist several states in crafting state-specific vision documents aimed at realizing a ‘Viksit Bharat’ (Developed India) by 2047.
- This endeavor, detailed in NITI Aayog’s Annual Report for 2024-25, encompasses states such as Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Bihar, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Dedicated teams within NITI Aayog are collaborating with these states to develop comprehensive strategies that align with national objectives.
Background of the Initiative
- The initiative gained momentum following Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s emphasis on the significance of ‘Viksit States’ during the 9th Governing Council meeting of NITI Aayog in July 2024.
- He underscored that the aspiration for a developed India must permeate to the grassroots level, ensuring that all states contribute effectively to the nation’s socio-economic progress.
Objectives of the Visioning Exercise
- The primary objective is to assist states in formulating strategies for holistic growth, encompassing economic development, governance enhancements, and improved quality of life for citizens.
- This initiative aims to create a cohesive framework that harmonizes state and national policies, thereby promoting cooperative federalism.
State Support Mission
- Operating under the umbrella of the State Support Mission (SSM), announced in the Union Budget for 2023-24, this visioning exercise fosters structured and institutionalized engagement between NITI Aayog and the states.
- The SSM provides a platform for states to develop roadmaps that align with national priorities while focusing on their unique strengths.
Establishment of State Institutions for Transformation
- As part of the SSM, NITI Aayog is encouraging states to establish State Institutions for Transformation (SITs).
- These multidisciplinary resources are designed to guide development strategies within the states and Union Territories.
- To date, 26 SITs have been notified, enhancing state capacities for effective governance and development.
This collaborative approach underscores NITI Aayog’s commitment to fostering cooperative federalism and ensuring that states play a proactive role in achieving the national vision of a developed India by 2047.
Which of the following is not an objective of the State Support Mission (SSM)?
- Strengthening the Monitoring & Evaluation ecosystem of States/UTs
- Collaborating with states to identify key growth drivers
- Centralizing policy-making processes at the national level
- Establishing a knowledge platform for sharing good governance practices
Answer: c) Centralizing policy-making processes at the national level
Explanation: The SSM focuses on assisting states in achieving their socioeconomic goals by 2047 through structured engagement, strengthening monitoring and evaluation systems, identifying growth drivers, and establishing platforms for sharing best practices. Centralizing policy-making at the national level is not among its objectives.
Andaman Sea
- An earthquake measuring 5.2 on the Richter scale recently struck the
- Andaman Sea, approximately 296 kilometers northwest of Banda Aceh, Indonesia.
- The seismic event occurred at a depth of 57 kilometers beneath the seabed. Given its magnitude and depth, the earthquake posed a low risk of triggering a tsunami.
Geological Context of the Andaman Sea:
- The Andaman Sea is a seismically active region due to its complex tectonic setting.
- It is part of the larger Sunda Plate, bordered by the Indian Plate to the northwest and the Australian Plate to the southeast.
- The ongoing convergence of these plates has led to the formation of the Andaman Basin, characterized by undersea ridges, trenches, and faults.
- A prominent feature is the Andaman Trench, resulting from the subduction of the Indian Plate beneath the Eurasian Plate.
- This tectonic activity renders the region prone to frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Ecological Significance:
- Beyond its geological importance, the Andaman Sea boasts rich biodiversity.
- It supports extensive coral reef systems, seagrass meadows, and mangrove forests, which serve as critical habitats for numerous marine species.
Additionally, the sea is a vital stopover for migratory birds along the East Asian-Australasian Flyway, underscoring its ecological significance.
Which of the following statements accurately describes the tectonic setting of the Andaman Sea?
- It is located at the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate.
- It is part of the Eurasian Plate, interacting with the African Plate to the west.
- It is situated on the Sunda Plate, bordered by the Indian Plate to the northwest and the Australian Plate to the southeast.
- It lies entirely within the Indian Plate, with no significant tectonic interactions.
Answer: c) It is situated on the Sunda Plate, bordered by the Indian Plate to the northwest and the Australian Plate to the southeast.
Explanation:
The Andaman Sea’s tectonic complexity arises from its position on the Sunda Plate, interacting with the converging Indian and Australian Plates. This dynamic interplay leads to significant geological features and seismic activity in theregion..
