Project Secure
Syllabus: Environment
- Project SeaCURE is an ambitious initiative launched on England’s south coast, designed to enhance the ocean’s role in addressing climate change.
- This pioneering pilot project, based in Weymouth, aims to extract carbon dioxide (CO₂) directly from seawater.
- Funded by the UK government, it explores cutting-edge technologies to improve the ocean’s ability to absorb and store CO₂.
The Project’s Goal
- SeaCURE targets the ocean as a powerful carbon sink, where CO₂ concentrations are higher than in the atmosphere.
- By removing carbon from seawater, the project seeks to develop a scalable, cost-effective solution to reduce atmospheric CO₂ levels.
- It is part of the UK’s broader strategy to explore and scale up carbon capture technologies that can mitigate climate change.
How It Works
- The process begins by pumping seawater into a specialized facility, where it undergoes acidification.
- This treatment helps convert dissolved carbon into gas, which is then captured before it escapes back into the atmosphere.
- The captured CO₂ is concentrated using sustainable materials, such as charred coconut husks, for safe and secure storage.
- Afterward, the treated seawater is neutralized and returned to the ocean, ready to absorb more CO₂.
Potential Impact
- SeaCURE has the potential to remove vast amounts of CO₂. If just 1% of the world’s surface seawater were processed, estimates suggest that up to 14 billion tonnes of CO₂ could be removed from the atmosphere each year.
- For this to be viable, however, the entire operation would need to be powered by renewable energy, such as floating solar panels, ensuring that the carbon removal process itself doesn’t contribute to further emissions.
Challenges and Concerns
- While SeaCURE holds promise, it faces several challenges.
- The process of generating the acid and alkaline materials needed for carbon extraction is energy-intensive.
- If the required energy is not sourced sustainably, the environmental benefits could be diminished or even undone.
- Additionally, there are concerns about the potential ecological impact of releasing large volumes of altered seawater back into the ocean, which could affect marine ecosystems.
The Issue of Ocean Acidification
- Project SeaCURE also highlights the growing problem of ocean acidification.
- As the oceans absorb increasing amounts of CO₂, their pH levels drop, making them more acidic.
- This shift in the ocean’s chemistry can negatively affect marine life, especially organisms that rely on carbon for essential processes, such as coral reefs and shellfish.
- Managing this balance is crucial to ensuring that solutions like SeaCURE do not unintentionally harm marine ecosystems.
Looking Ahead
- SeaCURE is one of 15 pilot projects funded by the UK’s carbon capture program, with experts seeing it as a crucial step toward achieving net-zero emissions.
- By refining and scaling up ocean-based carbon capture techniques, the ocean could become a more deliberate tool in the fight against climate change—provided the environmental challenges are carefully managed.
- The future of SeaCURE and similar projects could significantly shape how we address the climate crisis on a global scale.
Which of the following trade-offs must be managed to ensure the success and sustainability of Project SeaCURE?
- Energy consumption vs. net carbon reduction
- Ocean chemistry balance vs. sequestration efficiency
- Technological scalability vs. ecological sensitivity
- Freshwater availability vs. seawater usage
Select the correct code:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1, 2, and 3 only
C. 2, 3, and 4 only
D. All of the above
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statements 1, 2, and 3 are valid trade-offs in SeaCURE:
- The process must be powered sustainably (1).
- Altering ocean chemistry through repeated treatment could affect marine life (2).
- Expanding the project globally must consider ecological risks (3).
- Statement 4 is incorrect because SeaCURE uses seawater, not freshwater, so freshwater availability isn’t a direct concern.
Priyanka Chopra, Ang Lee, Megan Thee Stallion to Be Honoured at 4th Annual Gold House Gold Gala
Syllabus: Awards
- The 4th Annual Gold House Gold Gala returns in grandeur on May 10, 2025, at the Music Centre in Downtown Los Angeles, bringing together over 600 of the world’s most influential leaders in celebration of Asian Pacific excellence. This year’s gala shines a spotlight on individuals who have reshaped global culture through creativity, leadership, and advocacy.
Event Snapshot
- Name: 4th Annual Gold House Gold Gala
- Date: May 10, 2025
- Location: Music Centre, Downtown Los Angeles
- Attendance: 600+ distinguished guests
- Theme: First Light — Honoring pioneers who have lit the path for others to follow
Honorees & Awards
Priyanka Chopra Jonas
- Award: Global Vanguard Honor (Inaugural Recipient)
- Recognition: For a remarkable 25-year career spanning Bollywood and Hollywood.
- Impact: A global ambassador for underrepresented voices and Asian Pacific visibility in entertainment.
Ang Lee
- Acclaimed Director: Life of Pi, Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon, Brokeback Mountain
- Recognition: Celebrated for redefining global cinema and championing Asian narratives across genres.
Megan Thee Stallion
- Cultural Powerhouse: Honored for her influence on music, advocacy, and allyship.
- Contribution: Recognized as a bridge-builder for marginalized voices and supporter of Asian Pacific stories.
Jon M. Chu
- Visionary Filmmaker: Crazy Rich Asians, Wicked
- Recognition: For transforming the portrayal of Asian communities in mainstream media and inspiring future storytellers.
Theme – “First Light”
- This year’s theme pays homage to the trailblazers — the “firsts” in their fields or identities — who ignited transformative change. As Gold House CEO Bing Chen stated, the gala “launches the next wave of culture,” honoring those whose achievements have opened doors for future generations.
A Cultural Milestone
- The Gold Gala stands as a cornerstone of cultural recognition, highlighting innovation, heritage, and leadership within the Asian Pacific community.
- It also builds momentum ahead of the highly anticipated 2025 A100 List—a definitive index of the top 100 Asian Pacific change makers—set to be revealed on May 1.
- With its blend of star power and social purpose, the Gold Gala continues to be a powerful platform for celebrating those shaping the future of global culture.
In the context of cultural representation and symbolic capital, the conferring of the Global Vanguard Honor to Priyanka Chopra signifies which of the following?
- Institutionalization of diasporic identity in global pop culture
- Reversal of cultural hegemony through performative activism
- Recognition of intersectionality within global media systems
- Structural democratization of award systems globally
Select the correct code:
- 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2, 3, and 4 only
D. 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Priyanka Chopra’s award represents the mainstreaming of diasporic South Asian identity into global cultural frameworks.
- Statement 3 is correct: Her career reflects intersectionality—navigating multiple identities across gender, geography, and industry.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: Her activism is substantive, not merely performative.
- Statement 4 overstates the effect; while the award symbolizes inclusivity, it does not reflect system-wide structural democratization.
Maharashtra Governor Presents Yashraj Bharti Samman Awards 2025
Syllabus: Awards
- Yashraj Bharti Samman 2025: Honoring Grassroots Excellence in Healthcare, Education, and Governance
- In a landmark ceremony held at the Raj Bhavan, Mumbai, Maharashtra Governor C.P. Radhakrishnan conferred the 3rd edition of the Yashraj Bharti Samman to three outstanding grassroots organizations for their transformative contributions in healthcare, education for sustainable development, and governance.

Award Overview
- Award Name: Yashraj Bharti Samman
- Edition: 3rd
- Purpose: Recognizes individuals or organizations making significant grassroots-level contributions across key sectors that shape inclusive development.
2025 Honorees and Contributions
- Jan Swasthya Sahayog (Chhattisgarh)
- Sector: Healthcare
- Achievement: Delivering specialist-led medical care in remote tribal areas of Chhattisgarh.
Focus: Advocates health equity and ensures access to affordable, expert-driven healthcare in underserved regions.
Pratham Education Foundation
- Sector: Education for Sustainable Development
- Achievement: Revolutionizing basic education in India through innovative learning models.
Notable Program: ASER (Annual Status of Education Report), a pioneering initiative for tracking and improving learning outcomes across rural India.
Services Plus Platform (National Informatics Centre)
- Sector:Governance
Achievement: A robust digital infrastructure enabling transparent and efficient delivery of citizen-centric e-services. - Developed By: National Informatics Centre (NIC), the platform is a model for digital governance and public service reform.
Event Highlights
- Location: Mumbai, Raj Bhavan
- Dignitaries Present:
- Dilip Walse Patil, Former Speaker, Maharashtra Legislative Assembly
- Amitabh Kant, G-20 Sherpa for India
- Organized by: Office of the Governor of Maharashtra
Governor’s Address: Vision for Inclusive Development
Education:
- Concern over declining learning standards despite a high number of schools.
- Emphasized the need to prioritize quality education over mere infrastructural expansion.
Healthcare:
- Stressed the importance of specialist-led interventions to improve healthcare in tribal and remote regions.
- Promoted a vision of holistic well-being for marginalized communities.
Governance:
- Highlighted the importance of ethical public administration.
- Called for greater public awareness to fight corruption.
- Defined ethical governance as essential for achieving genuine social transformation.
Conclusion
- The Yashraj Bharti Samman 2025 continues to champion grassroots excellence.
- The award recognizes organizations that embody innovation, compassion, and impact.
- It stands as a symbol of sustainable and inclusive development in India.
With reference to the 3rd edition of the Yashraj Bharti Samman held in 2025, consider the following statements:
- Jan Swasthya Sahayog was awarded for pioneering AI-driven healthcare diagnostics in urban slum areas.
- The Pratham Education Foundation’s ASER initiative is primarily aimed at monitoring infrastructure quality in government schools.
- The Services Plus platform, developed by the National Informatics Centre, contributes to governance by enabling citizen access to e-services.
- Governor C.P. Radhakrishnan emphasized ethical governance and citizen awareness as essential to combating systemic corruption.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- A) 1 and 2 only
B) 3 and 4 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: B) 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: Jan Swasthya Sahayog was recognized for providing specialist-led healthcare in remote tribal regions, not for AI-driven diagnostics in urban slums.
- Statement 2 – Incorrect: The ASER initiative by Pratham Education Foundation focuses on tracking and improving learning outcomes, not infrastructure quality.
- Statement 3 – Correct: The Services Plus platform, developed by the National Informatics Centre (NIC), is a citizen-centric digital governance tool that provides transparent and efficient e-services.
- Statement 4 – Correct: Governor Radhakrishnan’s address highlighted the importance of ethical governance and public awareness to fight corruption and ensure inclusive development.
India’s Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) Boosting Welfare Efficiency
Syllabus:Economy
- India’s Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) system has emerged as a transformative tool in public welfare delivery, significantly improving transparency, curbing inefficiencies, and reducing fiscal leakage.
- Introduced to streamline subsidy disbursement, DBT has demonstrated remarkable fiscal prudence and social outreach.
- A recent report by the BlueKraft Digital Foundation assesses the impact of DBT between 2009 and 2024, estimating total savings of ₹3.48 lakh crore and a sixteenfold increase in beneficiaries.
Key Findings from the Report
1.Budgetary Trends Before and After DBT
Pre-DBT Period (2009–2013):
- Subsidies accounted for an average of 16% of total government expenditure.
- Annual subsidy allocation stood at approximately ₹2.1 lakh crore.
- Major leakages and inefficiencies plagued the system.
Post-DBT Implementation (2014–2024):
- Subsidy expenditure reduced to 9% of total government spending by 2023-24.
- Beneficiary numbers increased from 11 crore to 176 crore—an expansion by 16 times.
COVID-19 Exception (2020–21):
- Temporary rise in subsidies due to emergency fiscal interventions.
- Efficiency metrics normalized post-pandemic, affirming DBT’s long-term stability.
2.Sectoral Impact Analysis
Public Distribution System (PDS):
- Contributed ₹1.85 lakh crore in savings—53% of total DBT savings.
- Aadhaar-linked ration cards significantly reduced fraud and duplication.
- MGNREGS (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme):
- Enabled 98% on-time wage transfers.
- Resulted in cumulative savings of ₹42,534 crore.
PM-KISAN (Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi):
- Eliminated 2.1 crore ineligible beneficiaries.
- Total savings amounted to ₹22,106 crore.
Fertilizer Subsidies:
- ₹18,699.8 crore saved due to targeted delivery mechanisms.
- Reduced misuse and inflated fertilizer sales.
3.Correlation and Causality Insights
Strong Positive Correlation (0.71):
- Higher beneficiary coverage is associated with greater DBT-related savings.
Strong Negative Correlation (-0.74):
- A higher proportion of subsidies in total expenditure is linked to lower welfare efficiency.
- Indicates DBT’s role in optimizing public expenditure.
- Introduction of the Welfare Efficiency Index (WEI)
- The report introduces the Welfare Efficiency Index (WEI) as a comprehensive metric to evaluate the performance of DBT in fiscal and social dimensions.
Index Composition:
- DBT Savings (50%) – Total savings from leakage reduction.
- Subsidy Reduction (30%) – Drop in subsidy-to-expenditure ratio from 16% to 9%.
- Beneficiary Growth (20%) – Expansion in program reach.
WEI Trajectory:
- Increased from 0.32 in 2014 to 0.91 in 2023, underscoring a dramatic improvement in the effectiveness of welfare delivery systems.
Conclusion:India’s DBT system has not only yielded substantial fiscal savings but has also enhanced the inclusivity and accountability of public welfare programs.
- With its integration into key sectors and adoption of performance metrics like the Welfare Efficiency Index, DBT serves as a model for digital governance and targeted delivery.
- As the system evolves, it holds the promise of further refining India’s approach to equitable and efficient welfare administration.
With reference to India’s Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) system and its impact between 2009 and 2024, consider the following statements:
- The DBT system has helped reduce subsidy expenditure as a percentage of total government spending from 16% to 9% between 2014 and 2024.
- The cumulative savings of ₹3.48 lakh crore from DBT are largely attributed to reductions in food subsidies through the Public Distribution System (PDS).
- The Welfare Efficiency Index (WEI) increased from 0.32 in 2024 to 0.91 in 2023, indicating significant improvement in welfare program effectiveness.
- PM-KISAN saved ₹42,534 crore by eliminating 2.1 crore ineligible beneficiaries through targeted transfers.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1 and 4 only
D) 1 only
Answer: A) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Correct:The DBT system reduced the subsidy expenditure from 16% to 9% of total government spending between 2014 and 2024, which is a significant achievement in fiscal efficiency.
- Statement 2 – Correct:The cumulative savings of ₹3.48 lakh crore are largely attributed to the reduction in food subsidies, especially through the Public Distribution System (PDS), which contributed ₹1.85 lakh crore in savings, a major part of the total savings.
- Statement 3 – Incorrect:The Welfare Efficiency Index (WEI) increased from 32 in 2014 to 0.91 in 2023, not from 2024 to 2023. This demonstrates a marked improvement in welfare program efficiency over the years.
- Statement 4 – Incorrect: PM-KISAN saved ₹22,106 crore, not ₹42,534 crore. The savings came from eliminating 1 crore ineligible beneficiaries, but the total savings figure is lower than stated in this statement.
Humanoid Robots Compete in Beijing Half-Marathon
Syllabus:S&T
- On April 19, 2025, Beijing made history by hosting the world’s first humanoid robot half-marathon, where robots and human runners participated side by side in a groundbreaking fusion of sports and technology.
- The event, which garnered global media attention, showcased the remarkable advancements in humanoid robotics and artificial intelligence (AI).
- While human participants followed traditional race rules, robots adhered to specially tailored regulations, with engineering support provided throughout the race.
- Despite some mechanical setbacks and frequent pit stops, the event generated significant excitement, curiosity, and discussions about the future role of robots in society.

Key Highlights of the Event
- Date and Venue:Held on April 19, 2025, in Beijing, China.
- The event marked the world’s first humanoid robot half-marathon.
Participants
- The race featured both human runners and humanoid robots of various sizes and designs.
- Robot participants ranged from under 4 feet (120 cm) to 8 meters (5.9 feet) in height.
- 20 engineering teams entered robots into the competition.
Course Layout
- Separate lanes were designated for humans and robots, with a barrier dividing them for safety.
- Unlike human runners, robots required battery change pit stops during the race.
Performance Metrics
- The fastest human completed the race in 1 hour 2 minutes.
- The fastest robot, named “Tiangong Ultra,” finished in 2 hours 40 minutes.
- Robots were awarded in categories such as best gait design, endurance, and innovative form.
Engineering Challenges
- Some robots required human assistance during the race, highlighting the ongoing challenges in balance and coordination.
- A few robots crashed or toppled, exposing the limitations in their current design and functionality.
Public Reaction
- The event received a mixed reception. Some hailed it as a glimpse into the future of AI, while others questioned the credibility of robotic marathons as an accurate measure of AI capabilities.
Aesthetic and Humanness
- Many teams focused on the “humanness” of their robots, dressing them in shoes, boxing gloves, and headbands.
- A notable robot featured a feminine appearance, with the ability to wink and smile, enhancing its anthropomorphic appeal.
Policy and Industrial Context
- The event aligns with China’s strategic goals to lead in AI and robotics as part of its broader economic development plans.
- It also raises important ethical and industrial questions about the integration of AI and robots into daily life.
Consider the following statements regarding the world’s first humanoid robot half-marathon held in Beijing in April 2025:
- The humanoid robots participated in separate lanes from human runners, with a safety barrier between them, and required battery pit stops during the race.
- The fastest robot, “Tiangong Ultra,” completed the race in 1 hour 2 minutes, matching the pace of the fastest human runner.
- The event demonstrated China’s leadership ambitions in AI and robotics, aligning with its broader economic growth strategies, including addressing industrial and ethical concerns regarding AI integration in daily life.
- One of the robots in the competition featured a “feminine appearance,” which enhanced its anthropomorphic qualities, leading to significant public interest in robot aesthetics.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
A) 1, 3, and 4 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1 and 4 only
D) 1, 3, and 2 only
Answer: A) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Correct:The humanoid robots participated in separate lanes from human runners, with a safety barrier between them. Additionally, robots needed battery pit stops, unlike the human participants who did not need any such breaks.
- Statement 2 – Incorrect:The fastest robot, “Tiangong Ultra”, took 2 hours 40 minutes to finish the race, not 1 hour 2 minutes, which was the time taken by the fastest human runner. Therefore, the time mentioned in Statement 2 is incorrect.
- Statement 3 – Correct:The event highlighted China’s strategic ambition to be at the forefront of AI and robotics development, which is part of the country’s broader vision for economic growth. It also raised important ethical and industrial questions about how AI and robotics should be integrated into daily life, reflecting China’s policy direction in these fields.
- Statement 4 – Correct:A notable robot in the competition was designed with a “feminine appearance”, which included anthropomorphic features such as the ability to wink and smile. This design element garnered significant public attention, emphasizing the growing interest in robot aesthetics and human-robot interaction.
Alamosaurus
Syllabus:Science
- Alamosaurus is recognized as one of the largest dinosaurs to have ever existed. This herbivorous sauropod lived in North America during the late Cretaceous period, approximately 100.5 to 66 million years ago.
- Known for its massive size, Alamosaurus is the only sauropod species found in North America from the Upper Cretaceous period.
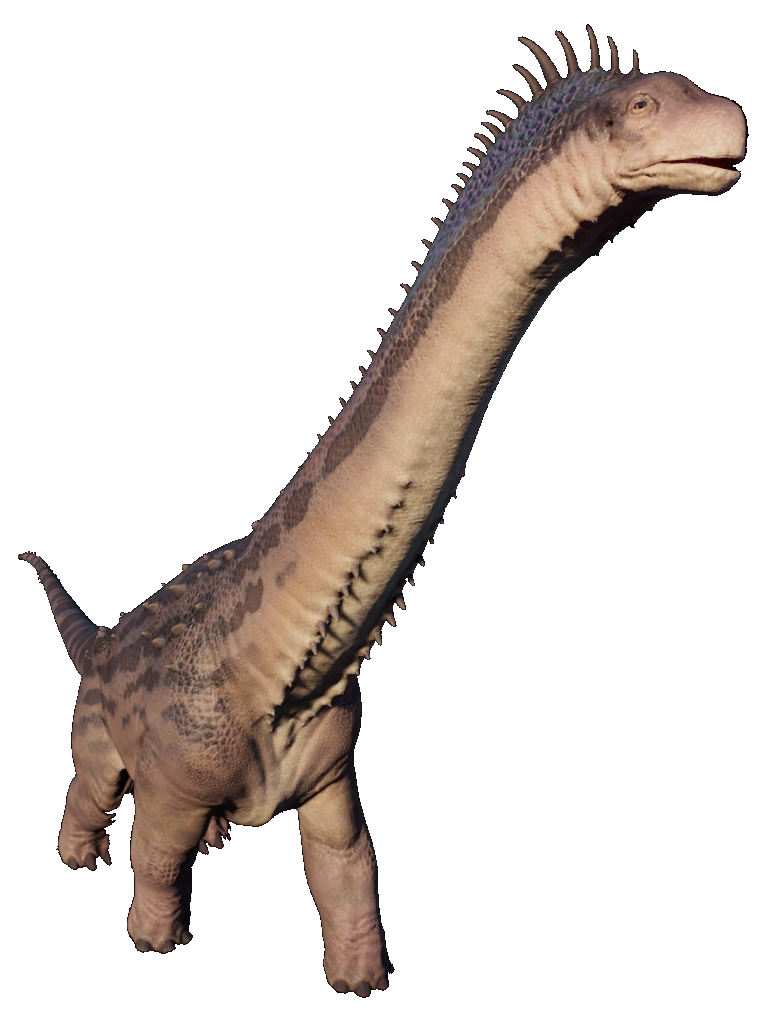

- As part of the sauropod group, Alamosaurus shares the title of being one of the largest land animals to have ever evolved.
- Standing at least 11 meters (36 feet) tall, stretching over 30.5 meters (100 feet) in length, and weighing between 38 to 80 metric tons, it rivaled the size of other giant sauropods like Argentinosaurus, which lived in South America around 97 to 92 million years ago.
- Alamosaurus had a long neck and tail, along with pillar-like limbs, all typical of sauropods. Its back was adorned with armoured spikes, providing protection from potential predators.
- The species went extinct during the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event, marking it as one of the last non-avian dinosaurs to roam the Earth before the mass extinction that wiped out most of the dinosaur species.
Consider the following statements regarding Alamosaurus, one of the largest dinosaurs known to have existed:
- Alamosaurus was the only sauropod found in North America during the Upper Cretaceous period.
- It is estimated to have reached a length of 30.5 meters (100 feet) and weighed between 80-120 metric tons.
- The Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event marked the extinction of Alamosaurus, making it one of the last non-avian dinosaurs.
- Alamosaurus is most closely related to Argentinosaurus, a sauropod that lived in South America during the late Jurassic period.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
A) 1 and 3 only
B) 1 and 4 only
C) 2 and 4 only
D) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: A) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Correct:Alamosaurus is indeed the only known sauropod from the Upper Cretaceous period in North America, making it unique among other sauropods that existed in other parts of the world during that time.
- Statement 2 – Incorrect:While Alamosaurus reached an impressive 5 meters (100 feet) in length, its weight is estimated to be between 38 and 80 metric tons, not between 80-120 metric tons as mentioned in Statement 2.
- Statement 3 – Correct:Alamosaurus went extinct during the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event, one of the most significant extinction events in Earth’s history, and it was one of the last non-avian dinosaurs to walk the Earth.
- Statement 4 – Incorrect:Alamosaurus is more closely related to sauropods like Argentinosaurus, which lived in South America, but Argentinosaurus lived during the Cretaceous period, not the late Jurassic period as stated in Statement 4.
Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC)
Syllabus:Geography
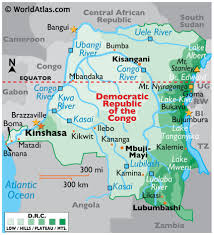
About the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC)
- Capital: Kinshasa
- Size: The second-largest country in Africa (after Algeria) and the largest in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Borders: DRC shares borders with Angola, Burundi, Central African Republic (CAR), Congo, Rwanda, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, and Zambia
- Coastline: Small boundary along the Atlantic Ocean
Geography:
- Major River: Congo River (second-longest river in Africa)
- Vegetation: Predominantly tropical forests
- Unique ecosystems: The Congo Basin is home to the world’s largest tropical peatlands
- Mineral Resources: DRC is rich in cobalt, copper, gold, lithium, iron ore, and coal
Recent Events:
- The April 2025 flooding in Kinshasa, the capital of DRC, was exacerbated by urban mismanagement and infrastructure failure, alongside local rainfall and runoff from the Congo Central Province.
- The urban tributaries, including the Ndjili River and the Lukaya tributary, became overwhelmed, leading to severe flooding in the city. Kinshasa is also listed among the 38 flood hotspots in the Congo Basin due to its exposure to twin flood sources and the growing challenges posed by urbanisation.
- Meanwhile, instability in eastern DRC, caused by the M23 armed group, continues to lead to mass displacement of people, further complicating the situation in the region.
Consider the following statements about the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC):
- The DRC is the largest country in Sub-Saharan Africa and borders a total of 10 countries.
- Kinshasa, the capital of DRC, faces frequent flooding primarily due to rainfall and the urban mismanagement of its tributaries like the Ndjili River.
- The Congo River is the longest river in Africa, and its basin contains the world’s largest tropical peatlands.
- The current instability in the eastern DRC, caused by the M23 armed group, has resulted in large-scale displacement but has had minimal impact on the capital, Kinshasa.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1, 2, and 3 only
C) 2, 3, and 4 only
D) 1, 3, and 4 only
Answer: B) 1, 2, and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Correct:The DRC is indeed the largest country in Sub-Saharan Africa and shares borders with nine countries, not ten. The DRC borders Angola, Burundi, CAR, Congo, Rwanda, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, and Zambia, but it does not border South Sudan as often incorrectly assumed. This is a small nuance, but it’s critical to the accuracy of this statement.
- Statement 2 – CorrectKinshasa’s flooding has indeed been exacerbated by urban mismanagement and the failure of infrastructure. The flooding is triggered not only by rainfall but also by runoff from nearby provinces. The Ndjili River and the Lukaya tributary in particular have contributed significantly to the situation, which is worsened by the growing challenges of urbanisation.
- Statement 3 – Correct:The Congo River is the second-longest river in Africa, not the longest. The Nile River holds that title. However, the Congo Basin is home to the world’s largest tropical peatlands, a significant ecological feature that plays a vital role in global carbon storage and climate regulation.
- Statement 4 – Incorrect:The instability in eastern DRC, caused by the M23 armed group, has had a severe impact on the broader country, including Kinshasa. While Kinshasa itself may not be the direct site of the conflict, the mass displacement of people, especially from the east, has implications for the country as a whole, including humanitarian, economic, and security concerns.
Gonorrhoea
Syllabus:Science
About Gonorrhoea:
Cause:
- Caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
- Commonly known as ‘the clap’.
Transmission:
- Primarily spread through vaginal, oral, or anal sexual activity.
- Can also be passed from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth, most commonly affecting the baby’s eyes.
- Common Affected Areas:
- Can infect the urethra, rectum, female reproductive tract, mouth, throat, and eyes.
Risk Factors:
- Affects individuals of any age, gender, or anatomy, but particularly common among teens and young adults (15 to 24 years).
Symptoms:
- Many individuals may not exhibit symptoms.
- Symptoms, if present, generally appear 1 to 14 days after exposure.
- Men are more likely to show symptoms, while up to 50% of women may be asymptomatic.
Common symptoms include:
- Sore throat
- Conjunctivitis (eye infection)
- Unusual vaginal or penile discharge
- Pelvic and genital pain
Complications of Untreated Gonorrhoea:
- If left untreated, can cause serious health issues like:
- Infections affecting the skin, joints, heart (endocarditis), and brain (meningitis).
- Infertility in both men and women.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) in women.
- Epididymitis and prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate in men).
- Some complications can cause permanent damage.
Prevention:
- Safe sex practices (e.g., using condoms) can effectively prevent gonorrhoea.
Treatment:
- Most cases can be cured with antibiotics.
- However, some antibiotic-resistant strains have emerged, making new treatments, such as gepotidacin, essential for combating these resistant strains.
Which of the following statements regarding Neisseria gonorrhoeae (the causative agent of gonorrhoea) is/are correct?
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae is capable of causing systemic infections affecting organs such as the heart and brain if left untreated.
- The presence of asymptomatic cases in women leads to an underreporting of gonorrhoea cases, contributing to the spread of antibiotic resistance.
- Gonorrhoea can only be contracted through vaginal sexual contact, as it does not transmit through oral or anal sex.
- The development of antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae is primarily driven by horizontal gene transfer, a common mechanism in bacteria.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 4 only
C) 1, 2, and 4 only
D) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Neisseria gonorrhoeae is capable of causing systemic infections affecting organs such as the heart and brain if left untreated.Correct. If gonorrhoea is not treated, the bacteria can spread beyond the initial site of infection, leading to serious complications such as endocarditis (heart), meningitis (brain), and arthritis. Therefore, this statement is correct.
- Statement 2: The presence of asymptomatic cases in women leads to an underreporting of gonorrhoea cases, contributing to the spread of antibiotic resistance.Correct. Gonorrhoea is often asymptomatic in women, meaning many cases go undiagnosed and untreated. This results in unintentional transmission and provides opportunities for the bacteria to develop resistance to antibiotics. This is a key factor in the rising antibiotic resistance observed in gonorrhoea strains.
- Statement 3: Gonorrhoea can only be contracted through vaginal sexual contact, as it does not transmit through oral or anal sex.Incorrect. Gonorrhoea can be contracted through vaginal, oral, or anal sexual activity. Therefore, this statement is false.
- Statement 4: The development of antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae is primarily driven by horizontal gene transfer, a common mechanism in bacteria.Correct. Antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae is largely driven by horizontal gene transfer, where the bacteria exchange genetic material, including resistance genes, with other bacterial species. This mechanism significantly contributes to the spread of resistance.
Strait of Gibraltar
Syllabus:Geography
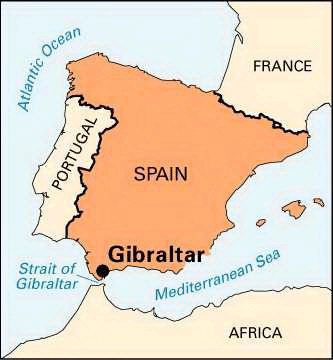
- The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow body of water that separates Europe from Africa, linking the Mediterranean Sea to the Atlantic Ocean.
Geographical Location and Borders:
- The Strait is bordered by Spain and the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar to the north, and Morocco and the Spanish enclave of Ceuta to the south.
- It is approximately 58 km in length and has a width of about 13 km at its narrowest point, situated between Morocco’s Point Cires and Spain’s Point Marroquí.
- The western end, located between Spain’s Cape Trafalgar and Morocco’s Cape Spartel, has a width of around 43 km.
- The eastern end, between the Rock of Gibraltar in the north and Mount Hacho (or Jebel Moussa) in the south, has a width of approximately 23 km. These two prominent land features are known as the Pillars of Heracles.
Depth and Formation:
- The depth of the Strait varies between 300 and 900 meters.
- The Strait was formed due to the northward movement of the African Plate towards the European Plate, a process that caused the gap between the high plateau of Spain and the Atlas Mountains of Northern Africa.
Water Flow:
- The Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean have different salinity levels. The highly saline Mediterranean waters flow outward and beneath the less saline Atlantic waters, which flow inward and above the Mediterranean current.
Strategic Importance:
- The Strait of Gibraltar is the only natural passage connecting the Atlantic Ocean with the Mediterranean Sea, making it one of the busiest waterways in the world.
- An important port on the Strait is the Moroccan port of Tanger-Med, located near Tangier.
- The Strait of Gibraltar serves as a vital geographical and economic link between two continents and plays a significant role in global shipping and trade routes.
Consider the following statements regarding the Strait of Gibraltar:
- The Strait of Gibraltar connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea.
- The width of the Strait of Gibraltar at its narrowest point is approximately 13 km.
- The depth of the Strait of Gibraltar ranges from 300 to 900 meters.
- The movement of the African Plate toward the European Plate led to the formation of the Strait.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2, 3, and 4 only
C) 3 and 4 only
D) 2, 3, and 4 only
Correct Answer: D) 2, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: The Strait of Gibraltar connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Atlantic Ocean, not the Red Sea. Hence, this statement is incorrect.
- Statement 2: The width of the Strait at its narrowest point is approximately 13 km, which is correct. This occurs between Morocco’s Point Cires and Spain’s Point Marroquí.
- Statement 3: The depth of the Strait varies between 300 and 900 meters, which is also correct.
- Statement 4: The formation of the Strait is indeed due to the northward movement of the African Plate towards the European Plate, which caused the gap between Spain’s high plateau and the Atlas Mountains of Northern Africa. This statement is accurate.
