Judiciary Can’t Function as Super Parliament: Vice President
Syllabus:Polity
Vice President’s Criticism
- Accused the judiciary of acting as a “super Parliament”.
- Criticized Article 142 of the Constitution, calling it a “nuclear missile against democratic forces”, available to the judiciary 24×7.
- The remarks came after the Supreme Court set a 3-month deadline for the President to act on bills pending with state governors and invoked Article 142 to deem 10 bills as approved.
What is Article 142?
- Grants the Supreme Court the power to “pass any order necessary to do complete justice” in any pending case.
- Originally intended as an extraordinary provision to ensure justice in situations where the law is silent or inadequate.
Example:
- Vishaka Guidelines (1997) – issued in the absence of sexual harassment laws, later formed the basis for the PoSH Act (2013).
- Concerns about Article 142
- Vague Definition: The term “complete justice” is subjective and lacks a precise definition.
- Judicial Overreach: Allows the judiciary to potentially interfere in the domains of the legislature or executive.
- Violation of Separation of Powers: Risks converting judicial activism into judicial legislation.
Judicial Activism vs Judicial Overreach
|
India’s Manuscripts in UNESCO Memory of the World Register
Newly Added:
Bhagavad Gita:Dialogue between Krishna and Arjuna, dated to the 2nd or 1st century BCE.
- Contains 700 verses across 18 chapters; serves as a spiritual and philosophical guide.
Natyashastra by Bharatmuni:
- Ancient Sanskrit treatise on drama, music, dance, and aesthetics.
- Regarded as the foundation of Indian performing arts, dated around the 2nd century BCE.
UNESCO Memory of the World Programme
- Launched in 1992.
- Aims to preserve and promote access to documentary heritage of outstanding universal value.
- Other Indian Inscriptions in the Register:
- Rig Veda, Gilgit Manuscripts, Works of Abhinavagupta, Maitreyayvarakarana (Pala period), among others.
Global Entry:
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948) is also newly included in the register.
Consider the following statements regarding the Vishaka Guidelines:
- They were issued by the Supreme Court using Article 142.
- They formed the basis for the PoSH Act, 2013.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: C
Explanation:
- Statement 1: “They were issued by the Supreme Court using Article 142.” – Correct
- The Vishaka Guidelines were laid down by the Supreme Court in 1997 in the case Vishaka & Others v. State of Rajasthan & Others, to address sexual harassment of women at the workplace. At the time, there was no legislation in India specifically dealing with workplace sexual harassment. The Supreme Court invoked Article 142 of the Constitution to formulate binding guidelines, ensuring “complete justice” in the absence of statutory law.
- Statement 2: “They formed the basis for the PoSH Act, 2013.” – Correct.
- The Vishaka Guidelines acted as a legal framework for preventing and redressing sexual harassment at workplaces for over a decade.In 2013, Parliament passed the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, commonly known as the PoSH Act, which was largely based on the Vishaka Guidelines.
Sterkfontein Caves
Syllabus: GS1/ History and Culture
- Location: Situated around 50 km northwest of Johannesburg, South Africa, the Sterkfontein Caves are a key attraction within the Cradle of Humankind.
- Geological Features: Formed primarily from dolomitic limestone, the caves are known for their dramatic stalactites and stalagmites, shaped over millions of years.

Palaeoanthropological Importance:
- Among the world’s richest sources of hominid fossils.
- Landmark discoveries include:
- “Mrs Ples” – a well-preserved skull of Australopithecus africanus.
- “Little Foot” – one of the most complete Australopithecus skeletons ever found.
- These fossils indicate early human ancestors lived in the region up to 5 million years ago.
Heritage Status: Recognized for its outstanding value, the site was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1999.
With reference to the Sterkfontein Caves, consider the following statements:
- The caves are primarily composed of basaltic rock, which facilitated the preservation of early hominid fossils.
- The discovery of the “Little Foot” skeleton has contributed to the hypothesis that hominins existed in southern Africa much earlier than previously thought.
- The Sterkfontein Caves are part of a transboundary World Heritage Site shared by South Africa and Namibia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 2 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 2 and 3 only
Answer: A. 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect:The Sterkfontein Caves are not composed of basaltic rock but dolomitic limestone. This sedimentary rock, not basalt (which is igneous), has aided in fossil preservation due to its slow-forming mineral deposits and cave structures.
- Statement 2 – Correct: The “Little Foot” skeleton is a nearly complete fossil of Australopithecus, discovered in these caves. Its dating to around 3.5 million years ago has pushed back the timeline for hominin presence in southern Africa, challenging earlier East Africa-centric models of early human evolution.
- Statement 3 – Incorrect: The Sterkfontein Caves are part of the Cradle of Humankind, a UNESCO World Heritage Site located entirely within South Africa. It is not a trans boundary site and does not extend into Namibia.
Davis Strait Proto-Microcontinent
Syllabus:Geography
- A hidden landmass, termed the Davis Strait proto-microcontinent, has been recently discovered beneath the waters of the Davis Strait, located between Baffin Island (Canada) and Greenland.
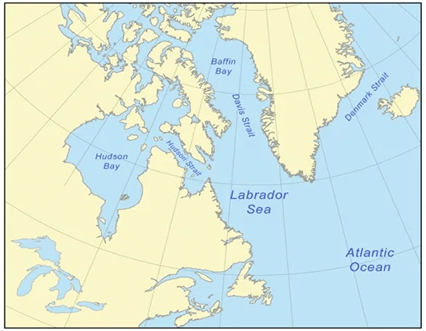
About the Proto-Microcontinent:
- It is a submerged primitive microcontinent, formed as a result of the tectonic evolution of the Davis Strait.
- The microcontinent comprises thickened continental crust measuring 19–24 km in thickness, flanked by narrow bands of thinner crust (15–17 km) that separate it from Greenland and Baffin Island.
- It formed due to plate tectonic reconfiguration millions of years ago, which reshaped the Earth’s crust in the region.
Davis Strait – Key Geographical and Geological Features:
- Located between southeastern Baffin Island and southwestern Greenland, it links Baffin Bay (north) and the Labrador Sea (south).
- It forms part of the Northwest Passage, a strategic Arctic maritime route connecting the Atlantic and Arctic Oceans.
- The strait spans approximately 650 km north-south and is 200 to 400 miles wide, making it one of the broadest straits globally.
- It exhibits complex geological features such as underwater basins and ridges, formed by strike-slip faulting along the Ungava Fault Zone (~45–62 million years ago).
- These tectonic shifts influenced the formation of Baffin Bay, the Labrador Sea, and ultimately, the Davis Strait.
With reference to the Davis Strait proto-microcontinent, recently discovered in the North Atlantic, consider the following statements:
- It is located between the Canadian island of Newfoundland and Greenland.
- It consists of thinned oceanic crust and lies along a tectonic plate boundary.
- It is a submerged primitive continental fragment formed due to ancient strike-slip faulting.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Correct Answer: B. 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Incorrect:The Davis Strait lies between Baffin Island (not Newfoundland) and Greenland. Newfoundland is located further south and not part of this tectonic context.
- Statement 2: Incorrect:The proto-microcontinent is made of thickened continental crust, not oceanic crust. Also, while it lies in a tectonically complex region, it is not directly along a present-day active tectonic plate boundary, but formed due to past tectonic shifts.
- Statement 3: Correct:The Davis Strait proto-microcontinent is a submerged primitive continental fragment. It was formed millions of years ago due to strike-slip faulting (particularly along the Ungava Fault Zone), which reconfigured the crust between Greenland and Baffin Island.
Pir Panjal Railway Tunnel
Syllabus: Geography
Context:
- The Udhampur–Srinagar–Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL) project is a transformative initiative aimed at improving all-weather connectivity between Jammu & Kashmir and the rest of India.
- With the completion of the Katra–Sangaldan section, uninterrupted rail access to the Kashmir Valley has been achieved.
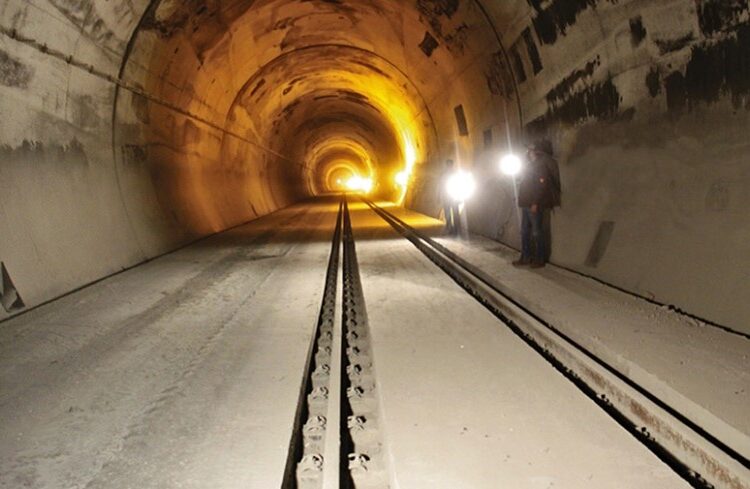

About Pir Panjal Railway Tunnel:
- Alternate Name: Banihal Railway Tunnel
- Length:2 km – India’s longest railway transportation tunnel
- Location: Connects Quazigund (Kashmir Valley) to Banihal (Jammu region), passing under the Pir Panjal Range
- Rail Gauge: India’s only broad-gauge mountain railway tunnel
- Part of: USBRL’s 202-km core segment
Pir Panjal Range – Geographical and Strategic Significance:
- Mountain System: Part of the Lesser Himalayas, extending across Himachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir
Key Peaks:
- Indrasan – 6,221 m
- Deo Tibba – 6,001 m
Hydrological Importance:
- Acts as a watershed separating the Chenab River basin from the Beas and Ravi basins
- Source region for tributaries of the Jhelum and Indus Rivers
Important Passes & Routes:
- Pir Panjal Pass (3,490 m): Traversed by the historic Mughal Road, linking Poonch and Rajouri with Srinagar
- Banihal Pass: Jawahar Tunnel (2.5 km) enables road connectivity between Banihal and Qazigund
Cultural and Strategic Importance:
- Region is home to popular destinations like Gulmarg
- Historically served as a vital trade route connecting Kashmir with the rest of India
With reference to the Pir Panjal Range and the Pir Panjal Railway Tunnel, consider the following statements:
- The Pir Panjal Railway Tunnel connects Quazigund in the Kashmir Valley with Banihal in the Jammu region and is India’s longest rail transportation tunnel.
- The Pir Panjal Range forms a part of the Greater Himalayas and acts as a major watershed between the Jhelum and Sutlej rivers.
- The Mughal Road and Jawahar Tunnel both traverse passes located in the Pir Panjal Range.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B. 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Correct:The Pir Panjal Railway Tunnel, also called the Banihal Tunnel, is India’s longest transportation railway tunnel at 2 km and connects Quazigund (Kashmir) with Banihal (Jammu).
- Statement 2: Incorrect:The Pir Panjal Range is part of the Lesser Himalayas, not the Greater Himalayas.Also, it separates the Chenab River basin from the Beas and Ravi rivers, not the Sutlej.
- Statement 3: Correct:Both the Mughal Road (via Pir Panjal Pass) and the Jawahar Tunnel (under Banihal Pass) are strategic routes traversing the Pir Panjal Range.
INS Sunayna
Syllabus:Defence
- INS Sunayna recently arrived at Nacala Port, Mozambique, as part of its deployment to Africa under the Indian Ocean Ship (IOS) SAGAR
About INS Sunayna
- Second Saryu-class Offshore Patrol Vessel (OPV) of the Indian Navy.
- Indigenously designed and built by Goa Shipyard Limited.
- Commissioned on 15th October 2013 at Kochi; operates under Southern Naval Command.
- Roles: Fleet support, coastal and offshore patrolling, ocean surveillance, SLOC monitoring, and escort duties.

Key Features
- Powered by two diesel engines, enabling speeds over 25 knots.
- Equipped with Automatic Power Management System, modern navigation, communication, and electronic support systems.
- Armament: 76 mm gun with electro-optic fire control, Close-In Weapon Systems (CIWS), CHAFF launchers.
- Can carry an onboard helicopter for extended maritime reach.
What is IOS SAGAR?
- Indian Ocean Ship SAGAR is a unique Indian Navy initiative to engage navies and maritime agencies across the Southwest Indian Ocean Region.
- Supports training for sea-riders from Friendly Foreign Nations (FFNs).
- Aligned with India’s SAGAR doctrine – Security and Growth for All in the Region.
- Reinforces India’s image as a preferred security partner and first responder in the Indian Ocean Region.
Tagline: “One Ocean, One Mission”.
With reference to INS Sunayna and the IOS SAGAR initiative, consider the following statements:
- INS Sunayna is an indigenously built stealth frigate of the Indian Navy under the Eastern Naval Command.
- IOS SAGAR is aimed at enhancing maritime cooperation with countries of the Southwest Indian Ocean Region.
- The IOS SAGAR initiative is part of India’s Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) doctrine.
- INS Sunayna can carry a helicopter and is equipped with Close-In Weapon Systems (CIWS).
Which of the above statements are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2, 3 and 4 only
C. 1, 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: B. 2, 3 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: INS Sunayna is an offshore patrol vessel (OPV), not a stealth frigate, and it is based under the Southern Naval Command, not Eastern.
- Statement 2 – Correct: IOS SAGAR focuses on maritime collaboration with Southwest Indian Ocean Region countries.
- Statement 3 – Correct: The initiative is aligned with India’s SAGAR doctrine (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
- Statement 4 – Correct: INS Sunayna is equipped with CIWS and can carry a helicopter.
HEALD Initiative
Syllabus:Health
- The Union Home Minister recently launched the HEALD Initiative (Healthy Liver Education and Alcohol-associated Liver Disease Prevention), a pioneering nationwide program aimed at addressing the growing burden of liver diseases across India.
About HEALD
- Launched by: Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences (ILBS), New Delhi.
- Objective: To prevent and manage alcohol-associated liver diseases through an integrated, multi-sectoral approach.

Components:
- Public awareness campaigns on liver health and alcohol risks.
- Early screening and detection of liver disorders.
- Psychological support and medical treatment for alcohol use disorder.
- Comprehensive liver disease management and rehabilitation.
- Community outreach and policy reform to reduce stigma around alcohol dependence.
Key Principle:
“Behind every failed liver lies a missed opportunity” – HEALD aims to eliminate these missed opportunities through timely intervention and awareness.
- Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences (ILBS)
- Established: 2009
- Location: Vasant Kunj, New Delhi
- Governing Body: Government of the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi
- Legal Status: Autonomous institute under the Societies Registration Act, 1860
Specialization:
- Mono-super speciality hospital focusing exclusively on liver and biliary diseases.
- Provides advanced diagnosis, treatment, research, and training in liver care.
With reference to the HEALD Initiative recently launched in India, consider the following statements:
- It is a nationwide liver disease prevention program launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- It focuses on public education, early screening, and treatment of alcohol-associated liver diseases.
- The initiative integrates mental health support and policy reform to reduce the stigma around alcohol dependence.
- The Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences (ILBS), which launched the program, is governed directly by the Ministry of AYUSH.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 2, and 4 only
D. 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: B. 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: HEALD was not launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare but by the Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences (ILBS).
- Statement 2 – Correct: HEALD focuses on public awareness, early screening, and treatment of alcohol-associated liver diseases.
- Statement 3 – Correct: The program aims to reduce stigma by integrating mental health support, community outreach, and policy reforms.
- Statement 4 – Incorrect: ILBS is an autonomous institute established by the Government of the National Capital Territory of Delhi, not under the Ministry of AYUSH.
India’s first Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (PFBR)
Syllabus:Science and Technology
- India’s first Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor, located in Kalpakkam, Tamil Nadu, is expected to be commissioned in the coming year.
- It marks a significant milestone in the second stage of India’s three-stage nuclear power programme.
About PFBR:
- The Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (PFBR) is a 500 MWe sodium-cooled fast breeder reactor.
- It is being developed by Bharatiya Nabhikiya Vidyut Nigam Limited (BHAVINI), a public sector undertaking under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE).
- The reactor uses mixed oxide (MOX) fuel, which consists of plutonium and uranium. Unlike conventional reactors that use water as a coolant, the PFBR employs liquid sodium, enabling higher operational temperatures and improved thermal efficiency.
- Construction began in 2004, and although the project was originally slated for completion in 2010, it has experienced multiple delays.
Key Features:
- The PFBR operates as a fast neutron reactor, using fast neutrons instead of thermal neutrons, which allows it to breed more fissile material than it consumes.
- This design contributes to energy sustainability by creating new fuel through the reprocessing of used nuclear material, particularly plutonium.
- The reactor includes advanced safety systems such as a robust containment structure and passive cooling mechanisms that enhance safety by preventing overheating.
India’s Three-Stage Nuclear Programme:
- Stage One involves the use of natural uranium in Pressurised Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) and Light Water Reactors (LWRs) to produce electricity and plutonium.
- Stage Two utilises the plutonium generated in Stage One to fuel Fast Breeder Reactors like the PFBR. This stage is critical for the sustainable expansion of India’s nuclear energy capacity.
- Stage Three aims to harness India’s abundant thorium reserves. It involves Advanced Heavy Water Reactors (AHWRs) that use a combination of thorium and uranium-233 to establish a closed nuclear fuel cycle. This stage is intended to ensure long-term energy security through thorium-based energy production.
With reference to India’s Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (PFBR), consider the following statements:
- PFBR uses natural uranium as primary fuel to breed plutonium-239.
- It employs liquid sodium as a coolant to facilitate operation at higher temperatures.
- It marks the beginning of Stage III of India’s nuclear power programme.
- It is designed to produce more fissile material than it consumes.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 1, 3 and 4 only
D. 2, 3 and 4 only
Answer: B. 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1: Incorrect: PFBR does not use natural uranium as primary fuel. Instead, it uses Mixed Oxide (MOX) fuel, a blend of plutonium-239 and uranium-238. The plutonium is derived from the reprocessing of spent fuel from Stage I PHWRs. The reactor breeds more plutonium-239 by converting U-238 into Pu-239 using fast neutrons.
- Statement 2: Correct: One of the defining features of PFBR is the use of liquid sodium as coolant instead of water. Sodium’s excellent heat transfer properties and its high boiling point allow the reactor to operate at higher temperatures with better thermal efficiency.
- Statement 3: Incorrect: PFBR represents the second stage of India’s nuclear power programme. Stage III involves the use of thorium and uranium-233 in Advanced Heavy Water Reactors (AHWRs). PFBR helps in producing fissile material (Pu-239) for use in the eventual thorium-based Stage III.
- Statement 4: Correct:A fast breeder reactor is specifically designed to produce more fissile material (like Pu-239) than it consumes. This is what makes the PFBR integral to India’s plan for a self-sustaining fuel cycle.
Enzymes and Coenzymes
Syllabus:Biology

- A recent edition of the journal Nature spotlighted a significant development in agricultural biotechnology by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Beijing.
- The article, titled “Gene-edited plants make the jump from farm to factory”, discusses the creation of biofortified rice varieties that have been genetically engineered to enhance coenzyme production.
About Enzymes and Coenzymes:
- Enzymes are specialized proteins that catalyse biochemical reactions, thereby facilitating essential cellular processes.
- Many enzymes depend on auxiliary molecules known as cofactors to function effectively.
- When these cofactors are organic, they are referred to as coenzymes.
- Coenzymes bind to enzymes and play a crucial role in driving various metabolic reactions necessary for life.
Coenzyme Q (Ubiquinone):
- Coenzyme Q (CoQ), also known as ubiquinone, is a lipid-soluble antioxidant made up of multiple isoprene units.
- It exists in different forms, from CoQ1 to CoQ10, and is vital for mitochondrial energy production.
CoQ is a key player in the electron transport chain, the process through which cells generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency in biological systems.
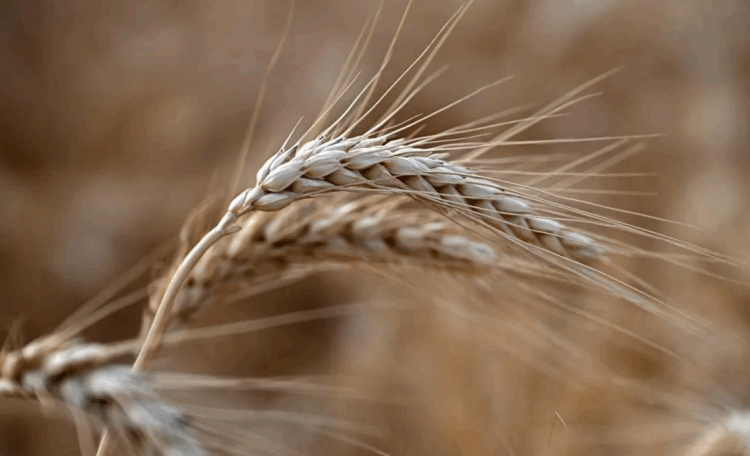
CoQ9 in Plants:
- CoQ9, which contains nine isoprene units, is mainly found in cereal crops such as rice, wheat, oats, barley, corn, rye, and millet.
- It is also present in various plants, including bamboo, cinnamon, avocado, barley, and pepper.
- Given its natural occurrence in staple crops, CoQ9 has been identified as a promising candidate for biofortification to enhance the nutritional content of food.
- Importance of CoQ10 for Human Health
CoQ10 plays a vital role in mitochondrial energy generation and is especially abundant in organs with high energy demands, such as the heart. - Although CoQ9 is present in many plant-based foods, the human body often requires additional CoQ10 supplementation.
- This need arises due to factors such as aging, genetic variations, and certain neurological or metabolic disorders.
With reference to Coenzyme Q (Ubiquinone) and its relevance in agricultural and human health contexts, consider the following statements:
- Coenzyme Q9 is a water-soluble antioxidant predominantly produced in legumes and oilseeds, while CoQ10 is lipid-soluble and primarily found in animal tissues.
- Gene-edited rice varieties enriched with CoQ10 may directly alleviate mitochondrial disorders in humans through regular dietary intake.
- Coenzymes, unlike cofactors, are always inorganic molecules essential for enzymatic reactions.
- Biofortification of staple crops with coenzymes aims to enhance cellular metabolism and reduce age-related degenerative conditions.
How many of the above statements are correct?
A. Only one
B. Only two
C. Only three
D. All four
Answer: B. Only two
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: CoQ9 is lipid-soluble, not water-soluble, and it is predominantly found in cereal crops like rice, wheat, barley, etc., not primarily in legumes and oilseeds. CoQ10 is also lipid-soluble and found in animal tissues and used by humans. Thus, this statement is factually incorrect on both counts.
- Statement 2 – Incorrect: Although gene-edited rice enriched with coenzymes represents a nutritional advancement, dietary CoQ10 from plants does not directly alleviate mitochondrial disorders. CoQ10 bioavailability from plant sources is limited, and therapeutic use typically requires concentrated supplements. Therefore, this statement overstates the effect.
- Statement 3 – Incorrect: This is a factual inversion. Coenzymes are always organic molecules (e.g., vitamins, NAD+, FAD) that act as cofactors. Inorganic cofactors include metal ions like Mg²⁺, Zn²⁺. So, this statement is entirely incorrect.
- Statement 4 – Correct:This is accurate. Biofortification with molecules like CoQ9/CoQ10 aims to enhance cellular metabolism and may help in preventing degenerative conditions linked to aging, as CoQ10 plays a vital role in energy production and acts as an antioxidant.
Indian Air Force Participates In Multinational Exercise Desert Flag-10 In Uae
Syllabus: Defence

- A contingent of the Indian Air Force (IAF) has arrived at Al Dhafra Air Base in the United Arab Emirates to take part in Exercise Desert Flag-10, a major multinational air combat exercise.
- The IAF is participating with MiG-29 and Jaguar fighter aircraft.
- Exercise Desert Flag is being hosted by the UAE Air Force and features the participation of air forces from Australia, Bahrain, France, Germany, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the Republic of Korea, Turkey, the UAE, the United Kingdom, and the United States, alongside India. The exercise is scheduled to be held from 21 April to 08 May 2025.
- The primary objective of the exercise is to conduct complex and varied aerial combat missions, promoting the exchange of operational knowledge and best practices among some of the world’s leading air forces. Such multilateral engagements foster interoperability, enhance mutual understanding, and strengthen defence cooperation among the participating nations.
- The Indian Air Force’s involvement in the exercise reflects India’s broader strategic commitment to enhancing defence ties and building regional and global military partnerships.
Consider the following statements regarding Exercise Desert Flag-10:
- It is a biennial naval exercise hosted by the United Arab Emirates, with participation limited to GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) countries.
- The Indian Air Force is participating with Su-30MKI and Rafale aircraft in the 2025 edition of the exercise.
- The exercise aims to enhance interoperability and operational synergy among participating air forces through complex air combat scenarios.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1 and 2 only
Answer: B. 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: Exercise Desert Flag is not a naval exercise; it is an air combat exercise. Moreover, it is not restricted to GCC countries. It includes air forces from diverse nations, such as Australia, Germany, the Republic of Korea, and the United States, indicating a global participation beyond the Gulf region.
- Statement 2 – Incorrect: The Indian Air Force is participating in Exercise Desert Flag-10 with MiG-29 and Jaguar aircraft, not Su-30MKI or Rafale jets, which India uses in other exercises like Garuda or Red Flag.
- Statement 3 – Correct: The objective of the exercise is to conduct complex and diverse fighter engagements, encouraging the exchange of operational knowledge and best practices to enhance interoperability among various air forces.
India’s first satellite, Aryabhata, completes 50 years
Syllabus:S&T
- India’s first satellite, Aryabhata, marks its 50th anniversary today. Launched on April 19, 1975, Aryabhata was named in honour of the ancient Indian mathematician and astronomer of the same name.
- Developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), the satellite was launched from Kapustin Yar in the then Soviet Union (USSR), highlighting Indo-Soviet collaboration in space technology during that era.
Key Features and Objectives:
- Design: Aryabhata was built as a 26-sided polyhedron, approximately 4 metres in diameter, and weighed 360 kilograms.
- Solar Power: Of its 26 faces, 24 were fitted with solar panels, excluding the top and bottom, to harness solar energy.
- Mission Objectives: The satellite was intended to conduct experiments in Solar Physics, Aeronomy, and X-ray Astronomy.

Operational Challenges and Legacy:
- Though it suffered a power failure after five days in orbit, causing scientific experiments to cease, Aryabhata continued to transmit data for a short period thereafter. Despite the premature technical setback, the mission was considered a significant milestone.
- The project provided Indian scientists with vital experience in satellite design and space operations, forming the technological and institutional groundwork for ISRO’s future missions.
Historical Significance:
- Aryabhata’s successful launch positioned India as the 11th nation to place a satellite into Earth’s orbit. It marked the beginning of India’s journey into space exploration, establishing a legacy that would later include advanced missions such as Chandrayaan, Mangalyaan, and Gaganyaan.
Consider the following statements regarding Aryabhata, India’s first satellite:
- Aryabhata was completely designed and developed indigenously without any foreign collaboration.
- It was launched with the assistance of the USSR from the Baikonur Cosmodrome.
- The satellite was covered entirely with solar panels for energy generation.
- Despite an early power failure, Aryabhata continued to transmit some data post-failure.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
B. 3 and 4 only
C. 4 only
D. 2, 3 and 4 only
Answer: C. 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: Although Aryabhata was designed and developed by ISRO, it was not completely The launch was made possible through Indo-Soviet cooperation, marking significant foreign collaboration in its deployment.
- Statement 2 – Incorrect: Aryabhata was launched by the USSR, but from Kapustin Yar, not Baikonur Cosmodrome. This distinction is important since Baikonur was used for other major Soviet missions, whereas Kapustin Yar was used for experimental and international launches.
- Statement 3 – Incorrect: Aryabhata was a 26-sided polyhedron, but only 24 of the faces were covered with solar panels. The top and bottom faces were not covered. So the satellite was not entirely solar-panel-covered.
- Statement 4 – Correct: After experiencing a power failure within five days, Aryabhata did continue to transmit limited data for a short while, and more importantly, provided valuable technological experience to Indian scientists.
