World Heritage Day 2025
Syllabus: GS3/ History and Culture
- Theme 2024: “Heritage under Threat from Disasters and Conflicts: Preparedness and Learning from 60 years of ICOMOS Actions”

Background
- Proposed by the International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS) in 1982
- Officially approved by UNESCO in 1983
- Observed annually to raise awareness about preserving cultural heritage
World Heritage Sites
- Sites of outstanding universal value inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List
- Can be cultural, natural, or mixed
- Protected under the 1972 World Heritage Convention
- India became a signatory in 1977
India on the World Heritage Map
- Home to numerous UNESCO World Heritage Sites and Monuments of National Importance
- Monuments of National Importance (MNI):
- Protected under the AMASR Act, 2010
- Conserved by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI)
- Total MNIs: 3,697
Key Government Initiatives
- Retrieval of Antiquities: 655 artefacts recovered from abroad (1976–2024)
- Adopt a Heritage Scheme: Launched in 2017; revamped in 2023 to involve private/public entities in monument upkeep
- Must-See Portal: Digital platform to promote iconic monuments
- Digitization: National Mission on Monuments and Antiquities (NMMA) is documenting and digitizing heritage assets
- 46th World Heritage Committee Session: Hosted by ASI in 2024, showcasing India’s global cultural leadership
Conclusion: World Heritage Day is a reminder of our collective duty to protect and cherish cultural treasures. Through national commitment and global cooperation, India continues to safeguard its rich heritage for future generations.
Which of the following statements regarding the World Heritage Convention, 1972 is/are correct?
- It is legally binding only on cultural sites and not natural sites.
- It obligates signatory States to report periodically on the conservation status of World Heritage Sites.
- India became a signatory to the Convention even before it was adopted by UNESCO.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 2 and 3 only
Answer: B. 2 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The Convention is applicable to cultural, natural, and mixed sites.
- Statement 2 is correct: Periodic reporting on the conservation status is a mandatory obligation under the convention.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: The convention was adopted in 1972 and India joined in 1977, after its adoption.
Making Primary Health Care Visible, Accessible, and Affordable
Syllabus: GS2/Health
Context
India has been actively reforming its primary healthcare system through progressive policies and programs aimed at overcoming key challenges such as accessibility, affordability, and visibility.
What is Primary Healthcare (PHC)?
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), Primary Health Care is a comprehensive, society-wide approach to health systems that brings essential health and well-being services closer to communities.
- PHC is designed to be accessible, affordable, and inclusive, covering the full spectrum of care—promotive, preventive, curative, rehabilitative, and palliative.
- This approach was first globally recognized in the Alma-Ata Declaration of 1978, which emphasized health care based on scientifically sound and socially acceptable practices as the cornerstone of universal health access.

Key Issues in India’s Primary Healthcare System
Urban vs. Rural Divide:
- Despite proximity to advanced facilities, urban slums face overcrowding and affordability challenges.
- Meanwhile, rural areas—home to over 65% of the population—struggle with a lack of healthcare centers, trained personnel, and poor transport infrastructure.
Human Resource Shortages (2023–24):
- 77% shortfall in surgeons
- 69% shortfall in obstetricians
- 70% shortfall in physicians at Community Health Centres (CHCs)
- 10–25% vacancy in nursing staff across various states
Rising Burden of Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) and Mental Health:
- PHCs now face the added responsibility of addressing lifestyle-related diseases and mental health concerns.
- However, gaps in infrastructure and training often limit their effectiveness.
Key Government Initiatives
National Health Mission (NHM):
India operates an extensive network of healthcare facilities, including:
- 6 lakh Sub-Centres (SCs)
- 26,636 Primary Health Centres (PHCs)
- 6,155 Community Health Centres (CHCs):These act as the first point of contact for most healthcare seekers.
Ayushman Bharat Program (2018):
- Aims to transform the PHC landscape through the creation of Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs), offering expanded services like maternal and child care, mental health, NCD management, and geriatric services.
- Comprehensive Primary Health Care (CPHC):As outlined in the National Health Policy 2017, this initiative promotes universal health coverage by integrating traditional medicine systems (AYUSH) with modern healthcare delivery.
- Focus on Underserved Areas: Programs such as the Aspirational District Program (ADP) and Aspirational Block Program (ABP) target healthcare improvements in the most backward regions.
- PM Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM): With an investment of ₹64,180 crore, this mission strengthens healthcare infrastructure and builds resilience against future health emergencies.
- Women-Led Initiatives: Over 1.9 crore women are involved in Self Help Groups (SHGs), playing a key role in spreading awareness about primary healthcare services and promoting community health participation.
Global Support and Collaborations
- Universal Health Coverage (UHC):A global commitment to ensuring equitable access to quality health services without financial hardship. Scaling up PHC in developing nations could save 60 million lives and extend average life expectancy by 3.7 years by 2030.
- Global Health Programs: Initiatives like the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria and the Gavi Alliance help integrate PHC with disease-specific strategies and immunization efforts.
Way Forward
- Infrastructure DevelopmentExpanding the reach and functionality of HWCs, especially in remote areas, and investing in telemedicine to bridge the urban-rural healthcare divide.
- Increasing Awareness:Strengthening community outreach and health education to improve service visibility and community participation.
- Enhancing Affordability:Continued focus on reducing out-of-pocket expenses through schemes like PM-JAY to ensure financial protection for all.
With reference to India’s efforts in integrating traditional medicine systems in primary healthcare, consider the following statements:
- AYUSH services are being incorporated under the Comprehensive Primary Health Care model.
- The National Health Policy 2017 explicitly mentions the role of traditional systems in achieving Universal Health Coverage (UHC).
- Ayurveda and Yoga are restricted to wellness centres and not used in curative services.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Answer:A
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: AYUSH is a core part of the Comprehensive Primary Health Care model.
- Statement 2 is correct: The National Health Policy 2017 promotes integrating AYUSH into the mainstream for achieving UHC.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: AYUSH is used in both preventive and curative aspects, not restricted to wellness.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology
Syllabus :GS 3/Science and Technology
- The Kerala State Electricity Board (KSEB), in collaboration with IIT Bombay, has launched a pilot project to explore the feasibility and implementation of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology in Kerala.
- While this technology remains in a nascent stage in India, it holds transformative potential for the country’s energy landscape.
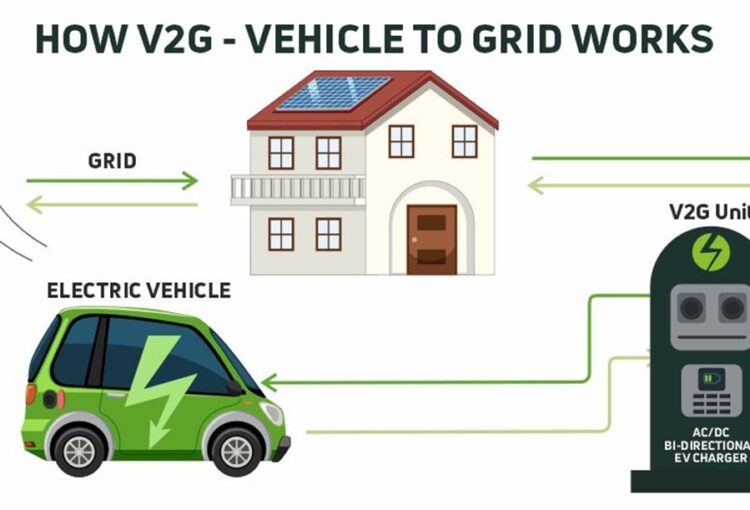
Understanding Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) is an emerging energy solution that facilitates two-way energy flow between electric vehicles (EVs) and the power grid.
- This innovation allows EVs to function as decentralized mobile energy storage units, thereby enhancing the sustainability, flexibility, and resilience of grid infrastructure.
- G2V (Grid-to-Vehicle): EVs are charged from the electricity grid.
- V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid): EVs discharge stored electricity back into the grid.
- By enabling energy transfer in both directions, V2G technology contributes to load balancing, demand-side management, and renewable energy integration.
Key Benefits of V2G Technology
- Peak Load Management:Helps prevent grid overload during peak demand hours by supplying energy from EV batteries.
- Renewable Energy Storage:Enables the storage of surplus solar or wind energy generated during off-peak hours and its redistribution during demand peaks.
- Enhanced Grid Stability:EVs can act as spinning reserves, adjusting their power supply to stabilize voltage and frequency fluctuations, especially from intermittent renewable sources.
- Policy Levers:Adoption can be incentivized through smart charging systems, Time-of-Use (ToU) tariffs, and financial rewards for EV owners participating in V2G services.
Challenges to V2G Integration
- Regulatory Hurdles:Implementation is constrained by fragmented, evolving, and often region-specific regulatory frameworks, which lack standardization.
- Technical Constraints:Unpredictable EV usage patterns, non-uniform charging behaviors, and the current lack of bi-directional charging infrastructure limit practical deployment.
- Cybersecurity Risks:With real-time data exchange and grid connectivity, V2G systems are vulnerable to data breaches, hacking, and system disruption, necessitating robust cybersecurity protocols.
Global Adoption and Applications
- Europe, the U.S., and the U.K. have already adopted V2G solutions at scale.
- EV owners receive monetary compensation for feeding energy back into the grid during peak periods.
- In California, V2G technology supports emergency grid stabilization, offering power during outages and crises.
Conclusion and Way Forward
- V2G technology presents a paradigm shift in energy and transport convergence. It holds immense potential to:
- Provide ancillary grid services such as frequency regulation and spinning reserves
- Act as a buffer for renewable energy, facilitating the transition toward a decarbonized energy economy
- Enhance grid resilience and reliability, especially as EV adoption surges and distributed energy resources proliferate
Future Outlook:
- India must prioritize pilot projects, infrastructure development, and regulatory harmonization.
- A data-driven approach to optimize EV charging behavior will be critical in ensuring grid reliability and long-term sustainability.
With reference to Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology, consider the following statements:
- It allows bidirectional flow of electricity between the power grid and electric vehicles.
- It is limited to charging EVs from the grid during off-peak hours.
- V2G supports grid resilience and renewable energy integration.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer:B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: V2G allows two-way energy flow between EVs and the grid.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: That describes only Grid-to-Vehicle (G2V), not the full V2G capability.
- Statement 3 is correct: V2G helps balance loads, stabilize voltage, and support renewables.
India’s Trade Deficit with China Widened
Syllabus: GS2/IR
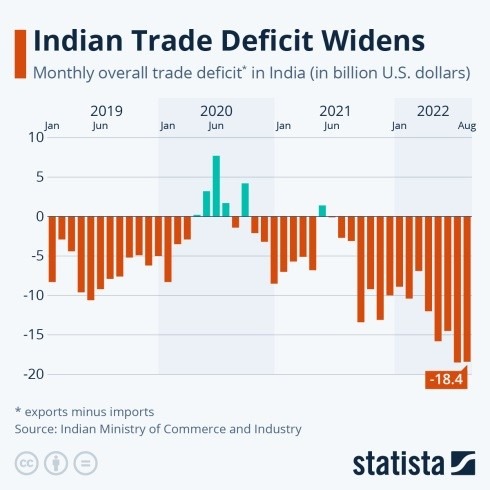
- India’s trade deficit with China reached an all-time high of $99.2 billion in the fiscal year 2024–25, raising economic, strategic, and policy concerns.
Overview of Trade Dynamics
- Bilateral trade between India and China totaled $127.7 billion in 2024–25, making China India’s second-largest trading partner after the United States.
- Imports from China: Rose to $113.5 billion, driven by demand for electronics, solar components, and batteries.
- Exports to China: Fell sharply to $14.3 billion, deepening the trade imbalance.
Causes of India’s Rising Trade Deficit with China
- High Dependence on Chinese Imports:
- Key sectors such as electronics, pharmaceuticals (APIs), chemicals, and textiles rely heavily on intermediate goods and raw materials from China.
- Dominance in Capital and Consumer Goods:
- China is a primary source for electrical machinery, telecom equipment, and mobile phones, owing to its cost competitiveness and manufacturing scale.
- Narrow and Low-Value Export Basket:
- India’s exports are largely primary commodities like iron ore, cotton, and copper, with minimal value addition and limited diversification.
Market Access Barriers:
- Indian products face regulatory restrictions, non-tariff barriers, and weak consumer demand in the Chinese domestic market.
Global Supply Chain Positioning:
- Chinese firms have deep integration in global value chains, supplying diverse and competitively priced goods worldwide.
India’s Evolving Industrial Base:
- Despite initiatives like ‘Make in India’, domestic manufacturing—especially in high-tech and industrial machinery—is still not at par with China’s capabilities.
Concerns Arising from the Trade Imbalance
- Rising Imports Forecast: Chinese imports are projected to increase by 20% as exporters seek alternative markets amid rising tariffs in the U.S.
- MSME Vulnerability: Influx of low-cost Chinese goods adversely impacts India’s MSME sector, leading to job losses, reduced competitiveness, and industrial stagnation.
- Strategic and Cyber security Risks: Heavy imports of telecom and surveillance equipment raise alarms about data security and national cybersecurity.
- Macro-Economic Pressure: The trade deficit exacerbates the Current Account Deficit (CAD), putting downward pressure on the rupee and straining foreign exchange reserves.
- Geopolitical Paradox: Dependence on China for critical imports appears strategically contradictory, given ongoing border tensions and strained diplomatic ties.
- Innovation Gap: Reliance on Chinese technology underscores India’s lag in high-tech R&D and manufacturing, challenging long-term economic sovereignty.
Government Initiatives to Address the Deficit
- Trade Remedies: The Directorate General of Trade Remedies (DGTR) monitors and counters unfair trade practices.
- ‘Vocal for Local’ Campaign: Aims to generate consumer awareness and promote domestically manufactured goods.
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme: Covers 14 strategic sectors, providing financial support to boost domestic manufacturing and export capacity.
Export Promotion Schemes:
- TIES (Trade Infrastructure for Export Scheme) and MAI (Market Access Initiatives) enhance export readiness.
- APEDA supports agro-exporters through financial aid.
- MPEDA promotes marine exports via infrastructure upgrades, lab testing, and technical assistance.
- Districts as Export Hubs:Focuses on identifying district-level export potential, resolving bottlenecks, and empowering local manufacturers.
Conclusion and Way Forward
- India’s growing trade dependence on China has supported cost-effective production and consumer affordability but has also created significant economic vulnerabilities.
To ensure strategic autonomy and economic resilience, India must:
- Diversify its import sources to reduce over-reliance.
- Strengthen domestic manufacturing through the Make in India mission and PLI schemes.
- Enhance technological capabilities to boost high-value exports.
- Import substitution must not mean protectionism but a balanced trade framework rooted in competitiveness, innovation, and strategic foresight.
Which of the following sectors contributes significantly to India’s trade deficit with China due to import dependence on intermediate or capital goods?
- Pharmaceuticals
- Solar energy
- Textiles
- Telecommunications
Select the correct answer using the code below:
A. 1, 2 and 3 only
B. 1, 2 and 4 only
C. 2, 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer😀
Explanation:
- APIs (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients) in pharma
- Solar components like PV cells
- Textile machinery and raw inputs (like dyes, synthetics)
- Telecom hardware (routers, 5G, mobile handsets).All these are imported heavily from China, contributing to the deficit.
India’s Global Pharmaceutical Footprint
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- With the vision of establishing India as the world’s leading provider of affordable and high-quality medicines, the Department of Pharmaceuticals has catalyzed a remarkable transformation in India’s global pharmaceutical footprint.

Current Status of the Pharmaceutical Sector
- Market Size (FY 2023–24): Valued at USD 50 billion, comprising:
- Domestic consumption: USD 23.5 billion
- Exports: USD 26.5 billion
Global Standing:
- India is the largest provider of generic medicines, accounting for 20% of global supply by volume.
- Ranked third globally in terms of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) production, holding an 8% share of the global API industry.
- Contribution to Economy: The pharmaceutical sector contributes approximately 72% of India’s GDP.
Key Segments: Generic drugs, over-the-counter (OTC) medicines, bulk drugs, vaccines, biosimilars, biologics, and contract research & manufacturing.
India: The ‘Pharmacy of the World’
India has earned this title owing to its low-cost, high-quality medicines.
A global leader in vaccine production, India is:
- UNICEF’s largest supplier, meeting 55–60% of its vaccine demand.
- Fulfilling 99% of WHO’s DPT, 52% of BCG, and 45% of measles vaccine
- Foreign Investment:
The sector attracted US$ 22.52 billion in FDI (2000–2024), highlighting investor confidence and global reliance.
Medical Devices Sector: An Emerging Engine of Healthcare
- An integral part of India’s healthcare system, covering:
- Electro-medical equipment, implants, diagnostics, disposables, and surgical instruments.
- FDI Inflows (April–December 2024):₹11,888 crore across pharmaceuticals and medical devices.
Government Interventions and Policy Support
Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes:
- For Pharmaceuticals: To boost high-value products and innovation.
- For Medical Devices: To reduce import dependency and scale manufacturing.
- For Bulk Drugs (APIs/KSMs/DIs): To strengthen self-reliance in critical raw materials.
- Bulk Drug Parks Scheme (2020–26):Aims to develop common infrastructure to lower production costs and promote domestic API manufacturing.
- Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP):Ensures the availability of affordable quality generic medicines through a network of dedicated retail outlets.
Conclusion and Outlook
- India’s pharmaceutical and medical devices sectors exemplify the country’s strengths in science, innovation, affordable healthcare, and manufacturing prowess. With supportive policies, growing FDI, and global recognition, the sector is poised to reach USD 130 billion by 2030.
- Ensuring robust regulatory frameworks, boosting R&D capabilities, and strengthening supply chains will be critical to sustaining this momentum and reinforcing India’s position as a global healthcare leader.
Consider the following statements regarding India’s pharmaceutical exports:
- India supplies more than 50% of global demand for vaccines through UNICEF.
- The majority of India’s pharma exports are patented drugs.
- India fulfills over 90% of WHO’s demand for DPT vaccines.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Answer:B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: India supplies 55–60% of vaccines procured by UNICEF.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: India primarily exports generic, not patented, medicines.
- Statement 3 is correct: India supplies 99% of WHO’s DPT vaccine demand.
Intermediate-Mass Black Hole (IMBH)
Syllabus:GS3/Space
In the News
- Indian astronomers have successfully detected and measured an Intermediate-Mass Black Hole (IMBH) in the dwarf spiral galaxy NGC 4395 using the 6-metre Devasthal Optical Telescope (DOT).
About NGC 4395
- A dwarf spiral galaxy located ~14 million light-years from Earth.
- It is one of the closest and faintest known Seyfert galaxies, characterized by a low surface brightness.
- Seyfert Galaxies possess active galactic nuclei (AGNs) powered by supermassive black holes, emitting radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum.
- The central black hole in NGC 4395 is around 10,000 solar masses.
- Intermediate-Mass Black Holes (IMBHs)
- Mass Range: Between stellar-mass and supermassive black holes (approx. 100–100,000 solar masses).
- Considered the “missing link” in black hole evolution.
- Serve as seeds for the growth of supermassive black holes, helping explain early universe galaxy formation.
Why Are IMBHs Hard to Detect?
- IMBHs emit faint radiation and are often located in small or dim galaxies.
- Traditional detection methods (like X-ray or radio observation) are less effective.
- Require advanced instruments and high-precision spectroscopy like that of DOT.
Key Highlights of the Discovery
- Offers strong evidence for the size-luminosity relationship in low-luminosity AGNs.
- Provides one of the most accurate mass estimates of an IMBH to date.
- The black hole is accreting matter at 6% of its Eddington (theoretical maximum) rate.
- Marks a significant step forward in understanding black hole growth and galaxy evolution.
About Devasthal Optical Telescope (DOT)
- Commissioned: 2016
- Location: Nainital, Uttarakhand
- Operator: ARIES (Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences)
- Significance: India’s largest optical telescope, equipped for visible and near-infrared imaging and spectroscopy.
- A national facility aiding advanced astronomical research.
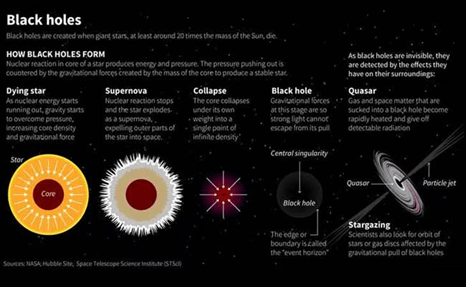
Understanding Black Holes
- A black hole is a space region with gravitational force so intense that not even light can escape.
- Predicted by Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity (1915).
- The term “black hole” was coined by John Archibald Wheeler in the 1960s.
- Typically formed when massive stars collapse post-supernova.
Types of Black Holes
- Stellar-Mass Black Holes
- Mass: Few to tens of solar masses
- Formation: Collapse of massive stars post-supernova
- Intermediate-Mass Black Holes (IMBHs)
- Mass: 100 to ~100,000 solar masses
- Significance: Bridge between stellar and supermassive types
- Supermassive Black Holes
- Mass: Hundreds of thousands to billions of solar masses
- Location: Cores of most galaxies (e.g., Milky Way)
Consider the following statements about the Devasthal Optical Telescope (DOT):
- It is India’s largest radio telescope located in Ladakh.
- It is operated by ARIES and specializes in optical and near-infrared observations.
- It was instrumental in detecting an intermediate-mass black hole in the galaxy NGC 4395.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect (DOT is an optical, not a radio telescope, and it’s in Nainital, not Ladakh).
- Statements 2 and 3 are correct
Guru Tegh Bahadur
Syllabus: GS1/History
- The Prime Minister paid tribute to Sri Guru Tegh Bahadur on the occasion of his Parkash Purab, honouring his legacy of sacrifice and spiritual leadership.
- Sri Guru Tegh Bahadur: A Life of Courage and Compassion

Early Life
- Born on 1 April 1621 in Amritsar, Guru Tegh Bahadur was the ninth Sikh Guru and the youngest son of Guru Hargobind Sahib.
- Originally named Tyag Mal, he earned the title “Tegh Bahadur” (Brave Wielder of the Sword) for his valour in battle.
- He married Mata Gujri and was the father of Guru Gobind Singh, the tenth Sikh Guru.
Spiritual Journey and Teachings
- Guru Tegh Bahadur led a life dedicated to meditation, spiritual wisdom, and selfless service.
- He travelled extensively across the Indian subcontinent, spreading the teachings of Sikhism, promoting social reform, and establishing preaching centres.
- Martyrdom and Sacrifice
- In 1675, Guru Tegh Bahadur was martyred in Delhi under the orders of Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb.
- He sacrificed his life to defend the religious freedom of Kashmiri Pandits and others, refusing to convert to Islam.
- His supreme sacrifice earned him the title “Hind di Chadar” – the Shield of India.
Legacy and Contribution
- A profound philosopher and poet, his hymns included in the Guru Granth Sahib emphasize fearlessness, devotion, compassion, and righteousness.
- His martyrdom became a powerful symbol of resistance to religious persecution and inspired the creation of the Khalsa by his son Guru Gobind Singh.
- Guru Tegh Bahadur’s legacy continues to inspire generations in the fight for justice and the upholding of human rights.
Consider the following statements about Guru Tegh Bahadur:
- He was the son of Guru Arjan Dev and the father of Guru Gobind Singh.
- He was martyred during the reign of Aurangzeb for opposing religious conversions.
- His teachings are not included in the Guru Granth Sahib.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer:B
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is incorrect: Guru Tegh Bahadur was the son of Guru Hargobind, not Guru Arjan Dev.
- Statement 2 is correct: He was executed by Aurangzeb for refusing to convert and defending the religious freedom of Hindus.
- Statement 3 is incorrect: His hymns are indeed included in the Guru Granth Sahib.
Bhagavad Gita and Natyashastra Added to UNESCO’s Memory of the World Register
Syllabus: GS1/ Art & Culture
- The Bhagavad Gita and Bharat Muni’s Natyashastra manuscripts have been inscribed in UNESCO’s Memory of the World Register.

About UNESCO’s Memory of the World (MoW) Register
- Established: 1992 by UNESCO.
- Purpose: Safeguard rare manuscripts, archival records, and documentary heritage of universal significance from neglect, decay, and loss.
Criteria for Inclusion:
- Outstanding universal value
- Historical, cultural, or social significance
- Authenticity, integrity, and rarity
- As of 2025: The register includes 570 collections from 72 countries and 4 international organizations.
About the Newly Inscribed Indian Manuscripts
- Bhagavad Gita
- Meaning: “The Song of the Lord”
- Attributed to: Sage Vyasa
- Context: Part of the Mahabharata; a dialogue between Krishna and Arjuna on the battlefield of Kurukshetra.
Core Themes:
- Dharma (righteous duty)
- Karma (action)
- Bhakti (devotion)
- Jnana (knowledge)
Significance:
- Foundation of Indian philosophical thought.
- Influenced global thinkers such as Mahatma Gandhi, Albert Einstein, and Aldous Huxley.
- Natyashastra
- Author: Sage Bharat Muni
- Period: ~200 BCE to 200 CE
- Nature: Treatise on performing arts—drama, dance, music
Major Concepts:
- Rasa Theory: Describes 9 emotions (Shringara, Karuna, Veera, etc.) essential to artistic expression.
Technical details on:
- Stagecraft
- Acting & Gestures (Mudras)
- Costumes & Makeup
- Musical instruments
Impact:
- Blueprint for classical Indian dance forms like Bharatanatyam, Kathak, etc.
- Foundation for Indian theatre and performance traditions.
India’s Presence in the MoW Register
- With these inclusions, India now has 14 entries in the UNESCO Memory of the World Register.
- Recent Indian additions to the 2024 MOWCAP (Asia-Pacific Regional Register) include:
- Ramcharitmanas
- Panchatantra
- Sahrdayāloka-Locana
Which of the following statements about UNESCO’s Memory of the World Register is/are correct?
- It aims to protect documentary heritage of exceptional value from destruction and neglect.
- It includes only manuscripts from member states of UNESCO.
- The Bhagavad Gita and Natyashastra were added to the register in 2025.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B. 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: The register preserves heritage with universal significance.
- Statement 2 is incorrect: It is open to UNESCO and non-UNESCO members, as well as international organizations.
- Statement 3 is correct: Both manuscripts were inscribed in 2025
