Indian Ocean: Strategic Significance & India’s Role
The Indian Ocean Region (IOR) faces significant geopolitical competition and security challenges, prompting India to advocate for multilateral maritime collaboration, such as a “coordinated flotilla,” as highlighted by External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar.
Overview of the Indian Ocean: The third-largest ocean, spanning approximately 9,600 km from the Bay of Bengal to Antarctica and 7,800 km from South Africa to Western Australia. It boasts a 70,000 km coastline encompassing major economies.
Demographics: Home to 35% of the world’s population and 40% of the global coastline.
Historical Significance: Named after India, reflecting its historical influence on maritime trade. Served as a crucial trade route since the first millennium, connecting India with the Arab world, Southeast Asia, and Africa. The Silk Route and spice trade flourished through the Indian Ocean, linking Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Strategic Importance:
- A vital global trade route, facilitating 70% of the world’s container traffic.
- 80% of India’s external trade and 90% of its energy imports transit through the Indian Ocean.
- Critical oil supply routes from West Asia to India, China, Japan, and Europe pass through the region.
- India’s central position grants strategic control over key maritime chokepoints:
- Strait of Hormuz (Iran-Oman), vital for oil shipments.
- Bab el-Mandeb (Yemen-Djibouti), the gateway to the Red Sea & Suez Canal.
- Strait of Malacca (Indonesia-Malaysia), a key trade passage for East Asia.
Challenges in the Indian Ocean Region:
Maritime Security Threats: Frequent pirate attacks and trafficking, particularly near Somalia and the Gulf of Aden.
Economic & Environmental Issues: Overfishing and deep-sea mining threaten marine ecosystems.
Climate Change & Rising Sea Levels: Small island nations face coastal erosion and the risk of submersion.
Humanitarian Crises & Disasters: Natural disasters such as cyclones, tsunamis, and oil spills necessitate coordinated disaster response.
Geopolitical Rivalries: Growing influence of the U.S., China, UK, and France fuels power struggles in the region.
India’s Policy Shift in the Indian Ocean:
Strengthening Regional Ties: India actively engages with IOR nations through:
- Indian Ocean Conference (IOC).
- Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
- Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS).
- Colombo Security Conclave.
SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region):
Launched in 2015 under PM Modi, aiming to:
- Strengthen India’s leadership in the IOR.
- Ensure free and open sea lanes for secure global trade.
- Promote sustainable maritime development.
Enhancing Blue-Water Capabilities:
Naval Expansion: Modernizing the navy with indigenous aircraft carriers and advanced submarines.
Maritime Surveillance: Deployment of P-8I Poseidon aircraft and satellite-based tracking systems.
Quad Cooperation: Collaboration with the U.S., Japan, and Australia on maritime security, anti-submarine warfare, and intelligence sharing.
Which of the following statements BEST describes the strategic significance of the Indian Ocean Region (IOR)?
- It is the largest ocean, covering the majority of the Earth’s surface.
- It is primarily a fishing ground, with limited impact on global trade and geopolitics.
- It is a crucial global trade route, controlling key maritime chokepoints, and vital for energy supplies, influencing trade and geopolitics.
- It is strategically important only for India due to its geographical proximity.
Correct Answer: c. It is a crucial global trade route, controlling key maritime chokepoints, and vital for energy supplies, influencing trade and geopolitics.
India-U.S. Partnership on Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA) Technologies
The India-U.S. partnership on Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA) technologies, solidified during PM Modi’s recent visit to the US with the launch of the Autonomous Systems Industry Alliance (ASIA), represents a significant advancement in maritime security cooperation. This collaboration is particularly noteworthy as India is the only country with whom the U.S. defense industry is partnering on such sensitive technologies.
Understanding Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA):
UDA encompasses the ability of a nation or organization to monitor, detect, and assess activities occurring beneath the surface of oceans and seas. It is vital for:
- Maritime Security
- Resource Management
- Environmental Protection
- Disaster Response
Significance of the India-U.S. UDA Cooperation:
Geopolitical and Strategic Importance:
- Strengthening Maritime Domain Awareness (MDA) and, critically, UDA is essential for India’s national security.
- Addresses China’s increasing naval presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Enhances submarine detection and tracking capabilities.
- Supports increased cooperation within the Quad (India, U.S., Australia, Japan) to counter shared threats.
Defense Technology Collaboration:
The U.S. is providing cutting-edge underwater surveillance and anti-submarine warfare (ASW) technologies, including:
- Sea Picket: An autonomous sonar surveillance system by Thayer Mahan.
- Wave Glider: An Unmanned Surface Vehicle (USV) by Boeing’s Liquid Robotics, with plans for co-production with Sagar Defence Engineering (60 units).
- Low-Frequency Active Towed Sonar: Discussions between L3 Harris and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) are ongoing.
Impact on India’s Defense Capabilities:
Significantly strengthens India’s anti-submarine warfare (ASW) capabilities, complementing existing assets:
- 12 P-8I Poseidon Maritime Patrol Aircraft
- 24 MH-60R Multi-Role Helicopters (being inducted)
- 15 MQ-9B Sea Guardian UAVs (part of a 31-unit contract, deliveries from 2029).
Technology Transfer, “Make-in-India,” and Economic Benefits:
- First-of-its-kind co-production and technology transfer in sensitive underwater systems.
- Strengthens India’s defense manufacturing ecosystem under the “Make in India” & “Atmanirbhar Bharat” initiatives.
Challenges and Considerations:
Technology Transfer and Data Security: Concerns regarding the secure sharing of sensitive UDA data and maintaining sovereign control over surveillance systems.
Financial and Operational Challenges: The high cost associated with procurement, deployment, and maintenance of advanced underwater systems.
Technology Dependence: Reliance on high-end research and funding for advanced sonar and AI systems.
Legal and Diplomatic Complexities: Potential for tensions with neighboring nations in disputed waters due to UDA activities.
Environmental Impact: The use of sonar technologies can negatively impact marine biodiversity and aquatic ecosystems.
Conclusion:
UDA is a critical component of maritime security, economic sustainability, and environmental conservation. India’s focus on UDA, in collaboration with the U.S. and Quad partners, is especially significant given the increasing Chinese presence in the Indian Ocean. This collaboration is set to significantly enhance India’s maritime defense capabilities and strategic positioning in the region.
The primary strategic driver behind the India-U.S. collaboration on Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA) is:
- To counter the growing naval presence of China in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- To improve India’s fishing industry.
- To promote tourism in the Indian Ocean.
- To enhance environmental protection in the IOR.
Correct Answer: a. To counter the growing naval presence of China in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
Changing Employment Sector in India
Transformation of Employment Sectors in India
The composition of the working middle class in India has undergone a significant transformation, particularly since the economic reforms of 1991. A clear shift has occurred from public to private sector employment.
Early Dynamics: Post-independence, the Indian middle class was largely shaped by the public sector. In 1995, public sector employment stood at 19.47 million, dwarfing the organized private sector, which employed 8.06 million.
Recent Trends: By 2012, the number of employees in central, state, quasi-government bodies, and local bodies decreased to 17.61 million, while the number of private organized sector employees increased to 11.97 million.
- Key Sectoral Trends & Examples
- Decline in Public Sector Employment:
Indian Railways: experienced a significant decrease in regular employees between 1990-91 and 2022-23, falling from 1.65 million to 1.19 million.
- Growth in IT Sector Employment: IT Companies: TCS and Infosys illustrate the rise of the IT sector. In 2004-05, TCS and Infosys had 45,714 and 36,750 employees, which surged to 448,464 and 242,371 employees respectively, fifteen years later.
- Restructuring of the Banking Sector:
Banking Shift: In 1991-92, public sector banks accounted for 87% of the total employees in scheduled commercial banks. By the end of 2023-24, the private sector banks employed 8.74 lakh employees, compared to less than 7.5 lakh in public sector banks.
III. Drivers of Change
Economic Liberalization: The economic reforms of 1991 spurred private sector growth, creating more job openings.
Attraction of Private Sector: Higher salaries, better benefits, and opportunities for professional growth and career advancement compared to the public sector have drawn the middle class to private sector jobs.
Shifting Work Culture: The private sector often promotes a more dynamic and performance-driven environment, appealing to an ambitious workforce.
Limited Public Sector Opportunities: The stagnation and high competition for public sector jobs, coupled with the growth in private sector opportunities, have contributed to this trend.
Entrepreneurial Growth: The rise of entrepreneurship and start-ups provides alternate choices and is encouraging a shift toward private businesses and self-employment.
- Challenges and Problems
Labour Transition in Agriculture: India hasn’t achieved a structural transition from agriculture to other sectors.
Agriculture Sector’s workforce: The agriculture sector’s share in the workforce fell from 64% in 1993-94 to 42.5% in 2018-19 but has increased to 46.2% in 2023-24.
Informal Employment: Most of the service-sector jobs are informal and low-paying. A large number of socially and economically disadvantaged groups are engaged in these informal economic activities.
Informal Sector Growth – Reasons:
- A mismatch between the education system and industry requirements leads to inadequately skilled graduates.
- A divide between rural and urban regions hinders access to quality training programs and industry experience.
- The expansion of the informal sector is attributed to emerging gig economy platforms and contract labour.
- Workers find flexibility and choice in informal employment.
Informal Sector – Challenges:
- Wages are low and the workers are exploited.
- Social security benefits are limited for such workers.
- Difficult to get formal financial services
- Poor quality of life
- Way Forward
Education Reform: Align education with industry demands to prepare students for real-world challenges.
Government Initiatives: Focus on areas like solar energy installation, waste management, and precision agriculture to create new avenues.
Public-Private Partnerships: Foster collaboration in the green sector to ensure training programs are relevant and impactful.
Rural Skilling: Use technology to increase the reach of online learning programs.
Employee Retention: Offer upskilling programs, promote inclusive work environments, and provide mental health support.
What is suggested as a way forward to improve the employment situation in India?
- Further investment in public sector jobs only.
- Bridging the gap between education and industry demands.
- Expanding agricultural employment exclusively.
- Encouraging a decrease in online education access.
Correct Answer: b Bridging the gap between education and industry demands.
Gulf of Eilat (Gulf of Aqaba)
- Context: Recent research highlights a halt in coral reef growth in the Gulf of Eilat (also known as the Gulf of Aqaba).
- Key Facts about the Gulf of Eilat/Aqaba:
- Location: Northern Red Sea, nestled between the Sinai and Arabian Peninsulas.
- Bordering Nations: Egypt, Israel, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia.
- Depth Comparison: Notably deep (1,850 meters) compared to the shallower Gulf of Suez (100 meters).
- Ecological Significance: Contains important coral reef ecosystems, considered some of the world’s northernmost.
Consider the following statements regarding the Gulf of Eilat/Aqaba:
- It is located in the southern part of the Red Sea.
- It is bordered by Egypt, Israel, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia.
- It is shallower than the Gulf of Suez.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1 and 3 only
Correct Answer: b It is bordered by Egypt, Israel, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia.
Development and Commercialisation of Typhoid Vaccine
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) is soliciting expressions of interest (EoI) for the collaborative development and commercialization of a Typhoid and Paratyphoid vaccine.
- Interested manufacturers and companies must fulfill specified technical criteria. Shortlisting will be based on their research and development strategies, existing facilities, and overall capabilities.
- Typhoid fever is a bacterial illness caused by the bacteria Salmonella Typhi.
- The infection is typically transmitted through contaminated food, water, or direct contact with infected individuals. Without proper treatment, Typhoid can be life-threatening.
- Antibiotics such as chloramphenicol, ampicillin, and ciprofloxacin are commonly used to treat the infection.
- Typhoid fever represents a substantial public health burden in India, with an estimated 4.5 million cases reported each year.
- The prevalence is particularly high in urban areas, making it a significant health concern.
- Several Typhoid vaccines are currently available in India, including Typbar-TCV,Ty21a, Typhim Vi, and Typherix.
- Typhoid conjugate vaccines (TCVs) are approved for children over 6 months of age, while Vi vaccines are suitable for children aged 2 years and older.
- TCVs are currently accessible exclusively through the private healthcare sector.
- Recent progress in this field includes the development of an enteric fever vaccine technology by the ICMR-National Institute for Research in Bacterial Infections (NIRBI).
- This technology utilizes outer membrane vesicles derived from two strains of typhoidal Salmonella.
Consider the following statements regarding the ICMR’s initiative:
- The ICMR is seeking partners for the development and commercialization of a Typhoid and Paratyphoid vaccine.
- Manufacturers will be selected based on their research and development capabilities, facilities, and strategies.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- a) 1 only
- b) 2 only
- c) Both 1 and 2
- d) Neither 1 nor 2
Correct Answer: c) Both 1 and 2
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act
Indian Abortion Laws: A Historical Overview
Prior to 1971, abortions were largely criminalized under the Indian Penal Code (IPC), with exceptions only for procedures performed to save a woman’s life. The IPC did not differentiate between desired and unwanted pregnancies, making safe abortion access extremely difficult.
The Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act of 1971:
- The MTP Act was enacted to decriminalize abortion in specific circumstances, recognizing it as a “health” measure.
- Initially, the Act allowed termination up to 20 weeks of pregnancy. A single doctor’s opinion was required for terminations within 12 weeks, and the opinion of two doctors was needed for terminations between 12 and 20 weeks.
The 2021 Amendment to the MTP Act:
Extended Gestational Limit: Rule 3B allowed abortion up to 24 weeks for specific categories of women, including those who experienced a change in marital status during pregnancy, survivors of rape or incest, and other vulnerable women.
Inclusive Language: The amendment broadened the legal scope by replacing “married woman or her husband” with “any woman or her partner,” encompassing pregnancies outside of marriage.
Post-24 Weeks: For pregnancies beyond 24 weeks, a medical board of expert doctors, established by the state government, assesses cases involving substantial fetal abnormalities to determine if termination is permissible.
Current Case: The Bombay High Court recently allowed a 25-week pregnancy termination in a private hospital, illustrating how the legal framework is applied in specific situations.
Which of the following accurately describes the legal status of abortion in India prior to the Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act of 1971?
- Abortion was legal and widely accessible, with no gestational limits.
- Abortion was largely criminalized under the Indian Penal Code (IPC), with exceptions only to save a woman’s life.
- Abortion was legal up to 12 weeks of gestation, with a single doctor’s approval required.
- Abortion was regulated by the MTP Act from the beginning, albeit with more stringent rules than present.
Correct Answer: b) Abortion was largely criminalized under the Indian Penal Code (IPC), with exceptions only to save a woman’s life.
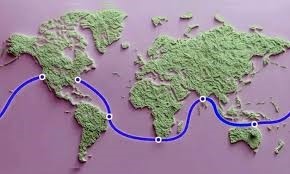
Project Water worth
- Meta has unveiled Project Waterworth, a significant initiative aimed at enhancing global digital connectivity.
- The project’s ambitious scope involves a subsea cable system covering 50,000 kilometers across five continents.
- This initiative, which will connect the U.S., India, Brazil, South Africa, and other regions, will utilize AI-powered technology to improve the efficiency and reliability of internet networks.
- The project features advanced burial techniques to protect cables from ship anchors and environmental hazards in shallower waters.
- The initiative also features new oceanic corridors, providing greater network capacity and resilience.
- Project Waterworth aims to foster international cooperation, digital inclusion, and technological advancements.
Which global technology giant has recently unveiled Project Waterworth, a significant initiative aimed at enhancing global digital connectivity?
- a) Google
- b) Amazon
- c) Meta
- d) Microsoft
Answer: c)Meta
Exercise Komodo:
The Indian Navy is actively participating in Exercise Komodo 2025, a non-combat military exercise aimed at fostering maritime cooperation among friendly nations. The exercise is being hosted by the Indonesian Navy in Bali, Indonesia, and has been underway since 2014.
Exercise Komodo: A Platform for Maritime Cooperation
- Exercise Komodo is a multilateral naval exercise that brings together naval forces from various countries to promote maritime cooperation, enhance interoperability, and strengthen partnerships in the Indo-Pacific region.
- This aligns with India’s SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) vision, which emphasizes the importance of maritime security and stability in the region.
Participation by INS Shardul and P8I Long Range Maritime Surveillance Aircraft
The Indian Navy is participating in Exercise Komodo 2025 with INS Shardul and P8I Long Range Maritime Surveillance aircraft. This demonstrates India’s commitment to strengthening maritime partnerships and enhancing regional security through collaborative efforts.
Objectives of Exercise Komodo
The primary objectives of Exercise Komodo include:
- Fostering maritime cooperation among friendly nations
- Enhancing interoperability with ASEAN Navies and QUAD partners
- Promoting regional security and stability through collaborative efforts
By participating in Exercise Komodo, the Indian Navy is contributing to the security and stability of the Indo-Pacific region, while also strengthening its relationships with friendly nations.
Which of the following is the primary objective of Exercise Komodo?
- Fostering economic cooperation among nations
- Enhancing regional security and stability through collaborative efforts
- Promoting tourism and cultural exchange among nations
- Enhancing space exploration and research efforts
Answer: b) Enhancing regional security and stability through collaborative efforts
Sovereign Green Bonds
India, like many emerging markets, is employing sovereign green bonds (SGrBs) to fund its transition to a low-carbon economy. Despite this, investor demand for these bonds has remained weak.
India’s Green Bond Efforts
Since 2022-23, India has issued SGrBs eight times, raising approximately Rs 53,000 crore. However, these issues have struggled to gain traction due to a lack of investor interest, making it challenging for the government to secure a greenium.
Greenium and Bond Yields
Globally, greeniums have reached 7-8 basis points, while in India, it is often at just 2–3 basis points. Greeniums reflect the difference in yield between green bonds and conventional bonds. A higher greenium indicates a lower yield and, therefore, a cost advantage for the issuer.
Green Bonds:
Green bonds are debt instruments issued by governments, corporations, and multilateral banks to raise funds for projects that reduce emissions or enhance climate resilience. These bonds are typically offered at lower yields than conventional bonds, assuring investors that the proceeds will be used exclusively for green investments.
Sovereign Green Bonds (SGrBs)
Sovereign green bonds (SGrBs) are issued by sovereign entities, such as the Government of India. India formulated a framework for issuing these bonds in 2022, defining “green projects” as those that promote:
* Energy efficiency in resource utilization
* Reduced carbon emissions
* Climate resilience
* Improved natural ecosystems
What is the primary purpose of India’s sovereign green bonds (SGrBs)?
a) To raise funds for infrastructure development
b) To promote foreign direct investment
c) To fund the transition to a low-carbon economy
d) To stimulate economic growth
Answer: c) To fund the transition to a low-carbon economy
