India-UK Defence Collaboration
Introduction
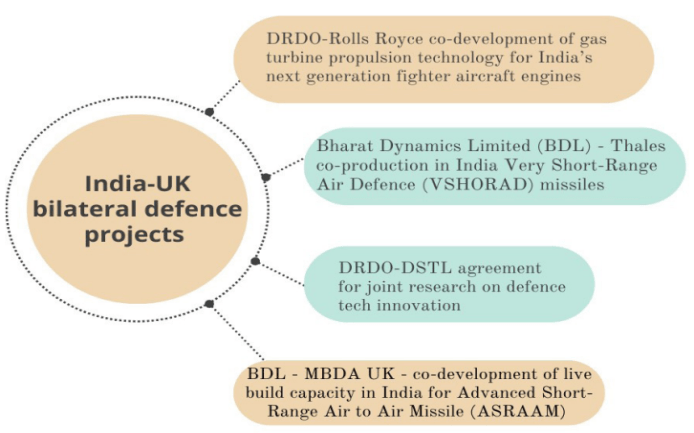
India and the United Kingdom have signed multiple agreements aimed at enhancing bilateral defence collaboration.
Key Agreements and Collaborations in India-UK Defence Partnership
Defence Partnership–India (DP-I):
The UK’s Ministry of Defence has established a dedicated programme office aimed at serving as a centralized hub for bilateral defence collaboration, promoting deeper cooperation and fostering economic growth in both nations.
Laser Beam Riding MANPADs (LBRM):
India and the UK have entered into a contract for the procurement of Laser Beam Riding Man Portable Air Defence Systems (MANPADS). The initial delivery of High Velocity Missiles (STARStreak) and associated launchers is scheduled for this year.
Lightweight Multirole Missiles (LMM):
This initiative seeks to integrate Indian and British industries into the global defence supply chain, enhancing collaborative efforts in missile technology.
Advanced Short-Range Air-to-Air Missile (ASRAAM):
A partnership has been established to create an assembly and testing facility for the ASRAAM missile in Hyderabad, promoting local manufacturing capabilities.
Integrated Full Electric Propulsion (IFEP) System:
A Statement of Intent was signed to design and develop an Integrated Full Electric Propulsion (IFEP) system for India’s forthcoming Landing Platform Dock (LPD) fleet. Both nations are also aiming to create India’s inaugural maritime Land-Based Testing Facility, with objectives to deploy the LPD by 2030.
Key Challenges
India-UK defence cooperation has faced obstacles due to the ‘three-I’ challenge, which includes:
- Foreign Investment regulations
- Intellectual Property Rights concerns
- Indigenous Content Requirements
The agreements signify a crucial advancement in India-UK defence collaboration, particularly in essential domains like air defence and maritime propulsion. They align with India’s Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) initiative, emphasizing the enhancement of indigenous defense capabilities and technological progress.
Q: Which of the following factors has posed a challenge to India-UK defense cooperation?
- Currency Exchange Rates
- The ‘three-I’ challenge: Foreign Investment, Intellectual Property Rights, and Indigenous Content Requirements
- Language Barriers
- Geographical Distance
Answer: B) The ‘three-I’ challenge: Foreign Investment, Intellectual Property Rights, and Indigenous Content Requirements
India’s Pharmaceutical Exports Set for 10x Growth
Introduction
India’s pharmaceutical exports are anticipated to soar to $350 billion by 2047, representing a 10-15 times increase from current levels.
Overview of India’s Pharmaceutical Industry
Recognized internationally as the “Pharmacy of the World,” India’s pharmaceutical industry has played a pivotal role in supplying vaccines, essential medicines, and medical supplies during the COVID-19 pandemic and continues to do so. The sector has demonstrated significant innovative capabilities, solidifying its position as a vital component of the global pharmaceutical value chain.
Current Global Market Status
- India stands as the largest global supplier of generic drugs, contributing 20% to worldwide sales.
- India ranks third in terms of drug and pharmaceutical production by volume.
- Exports span approximately 200 countries and territories.
- The primary export destinations include the USA, Belgium, South Africa, the UK, and Brazil.
- Despite being a key global player in generics, India ranks 11th in terms of pharmaceutical export value.
- The total annual turnover of pharmaceuticals in FY24 was ₹4.17 lakh crore, reflecting an average growth rate of 10.1% over the past five years.
Export Projections
India’s pharmaceutical exports are expected to rise from $27 billion in 2023 to $65 billion by 2030. This growth is anticipated to shift from volume-based to value-driven strategies, focusing on key areas such as Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs), biosimilars, and specialty generics.
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API):
India’s API exports are projected to grow from $5 billion to $80-90 billion by 2047.Global supply chain diversification, particularly in light of the U.S. Biosecure Act, presents an opportunity for India to bolster API production.
Biosimilars:
Current biosimilar exports are valued at $0.8 billion, with expectations to increase fivefold to $4.2 billion by 2030, and to $30-35 billion by 2047.
This growth will be supported by enhanced R&D, regulatory simplifications, and capacity expansions.
Biosimilars are medications that closely resemble biologic drugs created through living systems, showcasing comparable structure and functionality.
Generic Formulations:
Accounting for 70% of India’s pharmaceutical exports, generic formulations are valued at $19 billion.
These exports are projected to grow to $180-190 billion by 2047, with a notable shift towards higher-margin specialty generics.
Policy and Strategic Measures
The Indian government has initiated several programs to promote the pharmaceutical sector and stimulate investment:
- In September 2020, the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme was introduced for the pharmaceutical sector as part of the Self-Reliant India initiative, with a budget of ₹15,000 crore allocated from 2020-2021 to 2028-29.
- Targeted policy measures are vital, including strengthening the API industry, addressing export barriers, and developing country-specific export strategies.
- India supplies 55-60% of UNICEF’s vaccines but should aim to expand its presence in high-value markets through clinical trials and manufacturing investments.
- Key enablers for growth include regulatory harmonization, expansion of PLI, and R&D incentives.
Challenges
India faces several obstacles, including issues related to intellectual property rights and limited R&D capabilities. It is crucial to understand the political, economic, sociocultural, technological, environmental, and legal factors when assessing the opportunities and challenges within the Indian pharmaceutical market.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
As a global leader in generic drug supply, India aims to ascend the value chain by focusing on specialty generics, biosimilars, and innovative products. This strategic shift could position India among the top five nations in export value by 2047. With aspirations to become the “healthcare custodian of the world,” the nation is prioritizing innovation, R&D, and regulatory improvements. Collaboration between academia, industry, and government will be essential in establishing a robust, globally competitive pharmaceutical sector.
Q) Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding India’s position in the global pharmaceutical market?
- India ranks first in terms of pharmaceutical export value.
- India is the largest global supplier of generic drugs, accounting for 20% of global sales.
- India does not export pharmaceuticals to many countries.
- India ranks fourth in drug production by volume.
Answer: B) India is the largest global supplier of generic drugs, accounting for 20% of global sales.
63rd session of the Commission for Social Development (CSoCD)
- India participated in the 63rd session of the Commission for Social Development (CSoCD) held from February 10 to 14, 2025, in New York, USA.
- This delegation was led by Savitri Thakur, Minister of State for the Ministry of Women and Child Development, Government of India.
- The session aimed to foster discussions and collaborations on pressing social development challenges, with a strong emphasis on advancing inclusive social policies and enhancing global social well-being.
- Notably, the event saw the participation of representatives from 49 countries, including ministers from 16 nations such as France, Türkiye, Saudi Arabia, and Sweden. Financial Commitment:
- Total Budget: ₹5,000 crore over five years.
- Specific allocation for fiscal year 2024-25: ₹1,000 crore.
- Minimum project cost under the scheme: ₹3 lakh.
- India actively engaged in key discussions during the session. On February 11, 2025, Savitri Thakur delivered India’s statement at the Ministerial Forum, focusing on the priority theme: “Strengthening Solidarity and Social Cohesion.”
- Thakur underlined that India is guided by the vision of “Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas, Sabka Vishwas” (Development for All), with a central focus on inclusivity.
- Through initiatives such as the JAM TRINITY (Jan Dhan, Aadhar, Mobile), the country has achieved significant financial inclusion for marginalized communities, particularly for women, persons with disabilities, and the elderly.
- Furthermore, India has embraced a “Women-led Development” approach, ensuring that women play a vital role in shaping the nation’s development trajectory.
- The minister elaborated on large-scale programs aimed at bridging the gender digital divide, promoting digital and financial literacy, particularly in rural areas.
- These initiatives have empowered millions of women entrepreneurs, facilitating their transition from start-ups to scalable businesses.
As India works diligently towards realizing the 2030 Agenda for sustainable development, enhancing women’s participation in the workforce remains a key priority.
The country’s robust social protection model features 26 weeks of paid maternity leave, maternity benefits reaching 37.5 million mothers, a network of One-Stop Centres, and an integrated National Women’s Helpline.
Additionally, early childhood care, nutrition, and education initiatives provide essential support to over 100 million children, mothers, and adolescent girls.
India endorsed the resolution on the priority theme and is advancing the concept of saturation in social protection to ensure the delivery of essential services to the most impoverished populations, thereby addressing multidimensional poverty.
The nation’s rights-based approach to universal health coverage, which includes reproductive health, clean cooking fuel, safe drinking water, sanitation, and affordable housing, has significantly transformed the lives of women and marginalized communities.
Furthermore, over 40 million homes have been constructed for the poor, with many women serving as either sole or joint owners.
Almost 100 million women have been linked to self-help groups (SHGs), contributing to economic transformation and grassroots leadership.
In conclusion, India remains fully committed to accelerating global progress and supporting the Commission’s efforts in crafting a just world for all.
Q: What is the main goal of India’s participation in the 63rd session of the CSoCD?
- To promote women’s empowerment
- To accelerate global progress and support the Commission’s efforts in crafting a just world for all
- To discuss human rights issues
- To promote sustainable development
Answer: B) To accelerate global progress and support the Commission’s efforts in crafting a just world for all
Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD)?
The Hyderabad-based company Biovet, part of the Bharat Biotech group, has announced that its vaccine for Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) in dairy cattle and buffaloes, named Biolumpivaxin, has received official licensing from the Central Drug Standards Control Organization (CDSCO)..
Overview of Lumpy Skin Disease
- Lumpy Skin Disease is an infectious viral condition affecting cattle and water buffalo.
- Causative Agent: The disease is caused by the Lumpy Skin Disease Virus (LSDV), which is part of the genus Capripoxvirus within the Poxviridae family (which also includes smallpox and monkeypox viruses).
- Zoonotic Transmission: LSDV is not zoonotic; humans cannot contract the virus from infected animals.
- Geographical Spread: Initially identified in Africa, Lumpy Skin Disease has since spread to various regions, including the Middle East, Asia, and Eastern Europe.
- Host Specificity: This disease is specifically harmful to cows, with a lesser impact on buffalo. The morbidity rate tends to be higher in cattle compared to buffalo.
- Economic Impact: Lumpy Skin Disease significantly affects livestock economics by causing temporary declines in milk production, potential sterility in bulls, damage to hides, and in severe cases, death.
Transmission of Lumpy Skin Disease
- Lumpy Skin Disease is primarily transmitted through blood-feeding insects such as certain flies, mosquitoes, and ticks.
- Infected animals can spread the virus through their oral and nasal secretions, which may contaminate shared feeding and water troughs.
- Consequently, the disease can spread either through direct contact with vectors or through contaminated feed and water sources.
Symptoms of Lumpy Skin Disease
- High fever
- Swollen superficial lymph nodes
- Distinctive multiple nodules or lumps on the skin
- In severely affected animals, especially those lacking prior exposure to the virus or possessing low immunity, the disease may lead to death.
- Treatment and Prevention
- Currently, there is no specific treatment for Lumpy Skin Disease. Therefore, vaccination is the most effective preventive measure against the virus. Infected animals are typically provided with supportive care, which may include antibiotics, pain relievers, and wound care sprays to manage symptomatic issues.
- The development and approval of Biolumpivaxin represent a significant advancement in the prevention of Lumpy Skin Disease, providing a much-needed tool to protect livestock health and the agricultural economy.
Q: Which of the following best describes the impact of Lumpy Skin Disease on cattle and buffalo?
- It affects only buffalo without any symptoms.
- It primarily affects cows with a higher morbidity rate.
- It has no economic impact.
- It primarily affects goats only.
Answer: B) It primarily affects cows with a higher morbidity rate.
Bangladesh Launches ‘Operation Devil Hunt’
- Bangladesh has initiated a significant security operation named “Operation Devil Hunt,” aimed at apprehending loyalists of former Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina.
- This action follows violent protests during which gangs allegedly associated with Hasina’s regime attacked demonstrators.
- The interim government, headed by Muhammad Yunus, has pledged to restore stability and uphold democratic principles.
- The unrest was ignited by rumors of Hasina potentially making a public address from exile in India, resulting in violent demonstrations that included the destruction of properties associated with her family.
- Meanwhile, tensions have escalated between India and Bangladesh due to India’s condemnation of the demolition of the Bangabandhu Memorial Museum.
Q: What has caused tensions between India and Bangladesh recently?
- A) Trade disputes
- B) India’s condemnation of the demolition of the Bangabandhu Memorial Museum
- C) Water resource management issues
- D) Border security clashes
Answer: B) India’s condemnation of the demolition of the Bangabandhu Memorial Museum
Indian Army and IAF Execute ‘Winged Raider’ in Eastern Theater
- The Indian Army and the Indian Air Force (IAF) have successfully executed the joint military exercise titled ‘Winged Raider’ in the Eastern Theater.
- This strategic drill emphasized special airborne operations aimed at bolstering coordination between the two branches of the armed forces.
- Conducted in a critical operational zone, the exercise forms part of ongoing efforts to enhance rapid deployment capabilities and foster inter-service synergy.
Q: What was the main goal of conducting “Winged Raider” in a key operational zone?
- To practice humanitarian aid and disaster relief operations
- To showcase military might and intimidation
- To enhance coordination and rapid deployment capabilities between the Army and the Air Force
- To conduct counter-insurgency operations
Answer: C) To enhance coordination and rapid deployment capabilities between the Army and the Air Force

2 Comments
AmandaHookyledb
March 6, 2025“Eres como un libro intrigante que quiero leer. Vamos a empezar https://rb.gy/44z0k7?Teve ?”
Antonioqmj
March 8, 2025Здравствуйте дамы и владыки!
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1q6enLZyDpCDYfhXC6F55qWsHicNjYd_B/view?usp=sharing
Конический мотор-редуктор – этто редукторная часть, заключающаяся с рваной передачи индустриального назначения, использующая коническую этап, служащую для перенаправления кинетического направления общее направление на угол в 90 градусов, а также стационарный чи мобильный энергетический привод сверху входе.В принципе, уголочек между ходким а также тихоходным валами что ль пребывать различным в течение подчиненности через плана и квалификации редукторного механизма. Исходя изо экономических и еще технологических суждений, целесообразнее стравливать редукторы всего приводными валами унтер ровным углом.Как правило, нынешние конические редукторы при фабрике крутящего обстоятельства совмещают яко коническую передачу, так и еще одно или чуть-чуть цилиндрических ступеней. Через этой текстуре, коническо-цилиндрическая гидротрансмиссия имеет большой широта передаточных взглядов, у нарицательной доставляемой мощности 0,18кВт до 160кВт.Преимущество конических редукторов:Сомкнутость у перпендикулярной текстуре передачи крутящего мигом;Устойчивость для кратковременным, неустойчивым перегрузкам и режимам вещицы не без; густыми пусковыми моментами.Недостатки конических передач:Экстремальность и дороговизна производства конической передачи;Непозволительность значительных осевых (а) также радиальных нагрузок на уик-энд вал.
Наша юрконтора занимается реализацией со стороны высших властей 10 лет лучших редукторов различных паспортов и производителей.
Нам хорэ уютно видеть у нас сверху сайте
Увидимся!