. Madhav National Park
Syllabus: Environment
Context:
Madhav National Park in Madhya Pradesh has been officially designated as India’s 58th tiger reserve, marking a significant milestone in the country’s wildlife conservation efforts. The announcement was made by Union Environment Minister Bhupender Yadav. This designation makes it the ninth tiger reserve in Madhya Pradesh, reaffirming the state’s commitment to protecting its rich biodiversity. Currently, the reserve is home to five tigers, including two recently born cubs, with plans to introduce two more tigers to strengthen the population.
Significance of Tiger Reserves:
Tiger reserves play a crucial role in wildlife conservation and ecological balance by providing a protected habitat for tigers and other species. These reserves are essential components of India’s broader strategy to preserve biodiversity, prevent poaching, and mitigate human-wildlife conflict. The establishment of new tiger reserves reflects the government’s continued commitment to environmental protection and sustainable ecosystem management.
Madhav National Park: Location and Features
- Location: Shivpuri district, Madhya Pradesh
- Ecosystem: Features a mix of dry deciduous forests, grasslands, and water bodies, making it an ideal habitat for various wildlife species, including tigers.
- Biodiversity: Home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, contributing to the state’s rich natural heritage.
- Tiger Reintroduction Projects in Madhav National Park
- Madhav National Park’s designation as a tiger reserve follows successful tiger reintroduction efforts.
- In 2023, three tigers were introduced as part of a larger initiative to restore tiger populations in Madhya Pradesh.
Similar projects have been successfully implemented in Panna and Nauradehi reserves, contributing to the revival of tiger populations in the region.
Government Support and Conservation Initiatives
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi welcomed the declaration, emphasizing India’s commitment to wildlife conservation and biodiversity protection.
- Madhya Pradesh Chief Minister Mohan Yadav highlighted the state’s leadership in tiger conservation and expressed gratitude for the recognition.
- The government is focusing on habitat restoration, anti-poaching measures, and community involvement to ensure long-term success.
Future Prospects for Madhav Tiger Reserve
- The reserve is expected to grow in importance as more tigers are introduced through planned conservation initiatives.
- Efforts are being made to enhance tiger habitats, ensure prey availability, and engage local communities in conservation efforts.
- The Madhav Tiger Reserve aims to become a model for sustainable wildlife conservation in India.
Challenges in Wildlife Conservation
- Despite positive developments, several challenges persist in tiger conservation:
- Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade: A major threat to tiger populations.
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: Due to urbanization, deforestation, and human encroachment.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: Increased encounters between tigers and local communities.
- Need for Stronger Law Enforcement: Effective monitoring, patrolling, and stricter penalties for wildlife crimes are essential.
- Community Participation: Sustainable conservation requires involvement of local communities in protecting tiger habitats.
With ongoing conservation efforts and government support, Madhav Tiger Reserve is poised to become a thriving sanctuary for tigers and other wildlife, reinforcing India’s status as a global leader in tiger conservation.

Which of the following statements regarding Madhav Tiger Reserve is correct?
- It was originally a hunting ground for the Gwalior royal family.
- It is part of the Bundelkhand Plateau region.
- The park has a significant population of swamp deer (Barasingha).
- It has been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 3, and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- It was originally a hunting ground for the Gwalior royal family – Correct. Madhav National Park, now Madhav Tiger Reserve, was historically used as a hunting ground by the Scindia rulers of Gwalior. The park was later designated as a protected area.
- It is part of the Bundelkhand Plateau region – Correct. Madhav Tiger Reserve is located in the Shivpuri district of Madhya Pradesh, which is geologically part of the Bundelkhand Plateau. The region consists of dry deciduous forests and grasslands, making it suitable for various wildlife species, including tigers.
- The park has a significant population of swamp deer (Barasingha) – Incorrect. Swamp deer (Barasingha) are not found in Madhav Tiger Reserve in significant numbers. Instead, they are primarily found in Kanha National Park in Madhya Pradesh, where conservation efforts have been successful in reviving their population.
- It has been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site – Incorrect. Madhav Tiger Reserve is not a UNESCO World Heritage Site. While India has several UNESCO-listed natural sites (such as Kaziranga, Sundarbans, and Keoladeo National Parks), Madhav Tiger Reserve has not received this designation.
Hantavirus
Syllabus Science and Technology
Context:
- The recent tragic deaths of actor Gene Hackman and his wife Betsy Arakawa have drawn attention to hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS), a rare but severe rodent-borne disease. Arakawa’s death, linked to HPS, has highlighted the risks associated with this virus and the need for greater public awareness.
What is Hantavirus?
- Hantavirus refers to a group of viruses carried by rodents. Transmission to humans occurs through contact with rodent urine, feces, or saliva, primarily from deer mice in the United States. Unlike many infectious diseases, hantavirus does not spread between humans.

Types of Hantavirus Diseases
The impact of hantavirus varies by region, with two major diseases associated with it:
- Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) – Primarily found in the Americas, this severe respiratory disease can be fatal.
- Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS) – More common in Europe and Asia, this disease primarily affects the kidneys.
- Each hantavirus strain is associated with specific rodent hosts, making regional awareness crucial.
Symptoms of Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS)
- Symptoms typically develop between one to eight weeks after exposure.
- Early signs resemble flu-like symptoms, including fatigue, fever, and muscle aches.
- As the disease progresses, severe respiratory distress occurs, leading to shortness of breath and chest tightness.
- Fatality Rate: Approximately 38% of individuals who develop respiratory complications succumb to HPS.
Treatment and Prevention
- No Cure Available: There is currently no antiviral treatment for HPS.
- Early Detection is Crucial: Supportive care, including oxygen therapy and intensive respiratory support, may improve survival chances.
Preventive Measures:
- Avoid exposure to rodent-infested environments.
- Use disinfectants to clean areas with possible rodent activity.
- Refrain from sweeping or vacuuming dry rodent droppings, as this can aerosolize the virus.
- Wear protective masks and gloves when cleaning contaminated areas.
Public Health Awareness and Safety Measures
- Public health officials recommend heightened awareness in regions where rodents are common.
- Using protective gear while cleaning rodent droppings can significantly reduce the risk of exposure.
- Educational initiatives on hantavirus risks and safe hygiene practices can help prevent infections and protect communities.
With no specific cure available, prevention and early detection remain the most effective strategies against hantavirus infections.
Consider the following statements regarding Hantavirus:
- Hantavirus is primarily transmitted through direct human-to-human contact.
- The disease caused by Hantavirus in the Americas is known as Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS).
- The primary rodent carrier of Hantavirus in the United States is the deer mouse.
- Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) has a fatality rate of over 50%.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 4 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 4 only
Answer: (c) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 – Incorrect: Hantavirus does not spread through human-to-human contact. It is transmitted to humans primarily through exposure to rodent urine, feces, or saliva.
Statement 2 – Incorrect: Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) is found in the Americas, while Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS) is more common in Europe and Asia.
Statement 3 – Correct: The deer mouse (Peromyscus maniculatus) is the primary reservoir of Hantavirus in the United States.
Statement 4 – Incorrect: The fatality rate of HPS is approximately 38%, not over 50%.
Exercise Khanjar-XII
Syllabus: Defence
Context:
- The 12th edition of the India-Kyrgyzstan Joint Special Forces Exercise, Khanjar-XII, is scheduled to take place from March 10 to March 23, 2025, in Kyrgyzstan.
- This annual exercise, which began in 2011, alternates between the two countries.
- The Indian contingent consists of troops from the Parachute Regiment (Special Forces), while the Kyrgyzstan contingent includes the Kyrgyz Scorpion Brigade.
- The primary focus of the exercise is to enhance cooperation in counter-terrorism and special operations, particularly in urban and mountainous terrains.
Objectives of Khanjar-XII
The main aim of the exercise is to exchange expertise and best practices in counter-terrorism operations. Key focus areas include:
Sniping techniques
- Complex building interventions
- Mountain warfare training
- These skills are vital for both nations in tackling modern security threats, terrorism, and insurgency.
Cultural Exchange and Diplomatic Relations
- Beyond military training, Khanjar-XII also serves as a platform for cultural exchange. Participants will engage in cultural activities, including the celebration of Nowruz, a significant Kyrgyz festival.
- This fosters stronger diplomatic ties, mutual respect, and understanding between the two nations.
Strategic Importance
- The exercise underscores the deepening strategic ties between India and Kyrgyzstan.
- It reflects their shared commitment to regional security, counter-terrorism cooperation, and military preparedness.
- By jointly addressing transnational threats, both countries aim to contribute to peace and stability in the region.
Previous Editions of Khanjar Exercise
- Since its inception, the Khanjar series has continuously evolved, enhancing interoperability and operational readiness.
- The 11th edition was held in India in January 2024, building upon past experiences to strengthen counter-terrorism strategies.
India’s Broader Defence Cooperation
In addition to Khanjar-XII, India is actively expanding its defence partnerships. Recently, India and Japan conducted the 7th Army-to-Army Staff Talks in New Delhi, focusing on:
- Military education
- Technological collaborations
- Operational training
These initiatives highlight India’s growing defence cooperation with global partners, reinforcing its role in regional security and stability.
With reference to the India-Kyrgyzstan Joint Special Forces Exercise ‘Khanjar-XII,’ consider the following statements:
- The exercise has been conducted annually since 2011 and is held exclusively in Kyrgyzstan.
- The Indian contingent primarily consists of personnel from the Ghatak Platoon of the Indian Army.
- The Kyrgyzstan contingent in Khanjar-XII includes the Kyrgyz Scorpion Brigade.
- The exercise mainly focuses on naval warfare and maritime security cooperation.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 3 only
c) 1, 3, and 4 only
d) 2 and 4 only
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 – Incorrect: While the exercise began in 2011, it is not exclusively held in Kyrgyzstan. It alternates between India and Kyrgyzstan.
Statement 2 – Incorrect: The Indian contingent consists of troops from the Parachute Regiment (Special Forces), not the Ghatak Platoon.
Statement 3 – Correct: The Kyrgyz Scorpion Brigade is the designated unit from Kyrgyzstan participating in the exercise.
Statement 4 – Incorrect: The exercise focuses on counter-terrorism, special operations, and mountain warfare, not naval warfare or maritime security.
Glass-Ceiling Index
syllabus: Index and Reports
Context:
- International Women’s Day (IWD) is observed annually on March 8 to recognize women’s achievements and advocate for gender equality. As part of the occasion, The Economist publishes its yearly Glass-Ceiling Index, assessing workplace conditions for women in 29 OECD countries.
About the OECD
The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is an international organization comprising 38 member countries committed to democracy and free-market economies.
- Established: December 14, 1960
- Founder Nations: 18 European countries, along with the S. and Canada
- Headquarters: Paris, France
Key Functions:
- Publishes economic reports, data, and forecasts.
- Fights bribery and financial crimes globally.
- Maintains a blacklist of tax havens (countries with unfair tax practices).
- India’s Status: Not a member but collaborates with OECD on economic policies.
Glass-Ceiling Index: Ranking Criteria
The Glass-Ceiling Index ranks 29 OECD nations based on a ten-point system evaluating workplace conditions for women:
- Higher education completion rate among women
- Percentage of women taking the GMAT exam (for business schools)
- Women’s workforce participation
- Gender pay gap
- Women in management roles
- Women on corporate boards
- Women in government positions
- Cost of child care after subsidies
- Paid maternity leave duration
- Paid paternity leave duration
Top 10 Countries for Working Women (2024)
- Sweden (Rank 1, replacing Iceland)
- Iceland (Dropped from No.1 due to fewer women in management roles—declined from 39.6% to 36.8%)
- Finland
- Norway
- Portugal
- New Zealand
- France
- Spain
- Denmark
- Australia
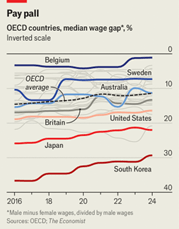
Key Highlights:
- Sweden overtook Iceland as the top-ranking country for gender equality at work.
- Iceland remains a global leader in gender parity and was the first country to elect a female president (Vigdís Finnbogadóttir, 1980).
- The United States ranked lower, indicating persistent workplace gender inequality.
Economic and Political Participation of Women
- Workforce Trends
- Women’s labour force participation rose to 6% (up from 65.8% the previous year).
- Despite progress, men’s participation remains higher at 81%.
- Women’s representation on corporate boards increased to 33%, indicating a positive shift in leadership roles.
Political Representation
- The OECD average for women’s parliamentary representation is 34%.
- Notable Gains:
- Japan: Increased to 16% (though still low).
- Britain: Reached 41%.
Declines:
- United States: Dropped to 7%.
- Changes in Rankings and Persistent Challenges
- South Korea rose from the bottom to 28th place, marking its first improvement in 11 years.
- Turkey now ranks last, struggling with deeply ingrained societal norms limiting women’s leadership opportunities.
Challenges in Japan, Turkey, and South Korea:
- Persistent gender wage gap.
- Limited female leadership roles in politics and business.
- Cultural expectations hindering workplace equality.
Despite progress, significant barriers remain, particularly in Asia and developing economies, underscoring the need for continued policy reforms and cultural shifts to achieve workplace equality.
With reference to the Glass-Ceiling Index published by The Economist, consider the following statements:
- The index assesses workplace conditions for women in all OECD and non-OECD countries.
- It ranks nations based on factors such as gender pay gap, workforce participation, and representation in leadership roles.
- The United States ranked among the top 10 countries in the 2024 index.
- Sweden replaced Iceland as the top-ranking country in the 2024 edition of the index.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 3 only
b) 2 and 4 only
c) 1, 2, and 3 only
d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: The Glass-Ceiling Index evaluates only 29 OECD countries, not all nations worldwide.
- Statement 2 – Correct: The ranking is based on ten key parameters, including gender pay gap, workforce participation, leadership representation, and childcare costs.
- Statement 3 – Incorrect: The United States ranked lower in 2024, highlighting persistent gender inequality in the workplace.
- Statement 4 – Correct: Sweden replaced Iceland as the top country for working women, primarily due to Iceland’s decline in women’s management roles.
Amrut Biodiversity Park

Introduction
- The Amrut Biodiversity Park, inaugurated by Lieutenant Governor V.K. Saxena in 2025, is a major environmental initiative in Delhi. Spread across 90 hectares along NH-24 in the Yamuna floodplains, the park is part of the Delhi Development Authority’s (DDA) efforts to restore and rejuvenate the region’s ecosystem. It aims to enhance urban green spaces while fostering environmental awareness.
Ecosystem Restoration
- Previously used for agriculture and settlements, the park underwent a major transformation to revive the floodplain ecosystem.
Water Management:
- Six new water bodies were created with a combined capacity of 225 million litres.
- These help store stormwater and reduce flood risks during monsoons.
- The park features jute-reinforced slopes and riverine grass communities to stabilize the land and improve groundwater recharge.
Biodiversity and Green Cover
A key aspect of the park is its diverse plantation, aimed at enhancing biodiversity.
- Trees Planted: Around 14,500 trees, including Neem, Peepal, and Mango.
- Shrubs and Grasses: 18,000 shrubs and over 21 lakh riverine grasses have been introduced.
- Bird Habitat Creation: The rich biodiversity is expected to attract bird species, contributing to a vibrant ecosystem.
Public Engagement and Recreational Spaces
To promote community involvement, the park features designated public spaces along NH-24.
- Thematic Walking Tracks: Inspired by India’s freedom struggle, pathways are named after key events like the Dandi March and the First War of Independence.
- Nature Interaction Areas: Visitors can explore and connect with Delhi’s ecological heritage.
Hydrology and Water Conservation
The park’s hydrology has been carefully restored through sustainable measures.
- Dredging and Water Flow Management: Existing catchments were deepened to enhance water retention and flow regulation during monsoon seasons.
- Sustainable Water Bodies: Efforts are in place to ensure that these remain functional year-round, contributing to floodplain health.
Environmental Concerns and Challenges
While the park has been praised for its green initiative, it has also faced criticism from environmentalists.
- Flood Risk: Some experts argue that the area remains prone to seasonal inundation.
- Financial Feasibility: Concerns have been raised about the long-term sustainability of maintaining the park.
- DDA’s Response: The authorities remain optimistic, emphasizing the park’s ecological benefits and its role in urban reforestation.
Future Plans and Development
The DDA plans to further enhance the visitor experience with additional facilities:
- Café Establishment: A proposed eco-friendly café will provide refreshments for visitors.
- Recreational Spaces: The park is envisioned as a relaxation hub for joggers, nature enthusiasts, and families.
Conclusion
The Amrut Biodiversity Park represents a significant step in Delhi’s environmental restoration efforts. While challenges persist, its focus on biodiversity, water conservation, and public engagement makes it a valuable addition to the city’s green infrastructure.
Consider the following statements regarding the Amrut Biodiversity Park in Delhi:
- It is located along NH-44 in the Yamuna floodplains.
- The park has six water bodies with a total capacity of 225 million litres for stormwater management.
- It features jute-reinforced slopes and riverine grass communities to stabilize the floodplain ecosystem.
- The park was developed under the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC)’s green initiative.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 3 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 2, and 4 only
d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 – Incorrect: The Amrut Biodiversity Park is along NH-24, not NH-44.
Statement 2 – Correct: The park includes six water bodies with a combined capacity of 225 million litres, designed to manage storm water and reduce flood risks.
Statement 3 – Correct: Jute-reinforced slopes and riverine grasses have been introduced for soil stabilization and groundwater recharge.
Statement 4 – Incorrect: The park was developed by the Delhi Development Authority (DDA), not DMRC.
Global Terrorism Index (GTI) 2025
Syllabus: Indexes and Reports
- The Global Terrorism Index (GTI) 2025, published by the Institute for Economics and Peace (IEP), analyzes terrorism trends across 163 countries, covering 7% of the world’s population.
- The report assesses terrorism by examining attacks, fatalities, injuries, hostage incidents, and their overall impact on society.
Global Terrorism Trends
- Terrorism saw a resurgence in 2024, reversing a decade-long decline:
- The number of countries affected by terrorism increased from 58 to 66.
- The Islamic State (IS) remains the deadliest terrorist organization
- Lone-wolf attacks surged in the West, contributing to 93% of recent fatalities.
- Pakistan and Afghanistan experienced rising militant activity, making South Asia a terrorism hotspot.

Key Trends in 2024
- Terrorism in the Sahel: The Global Epicenter
- The Sahel region recorded over 50% of all global terrorism deaths.
- Burkina Faso saw the highest number of terrorism-related deaths worldwide, accounting for 20% of the global total.
- Niger recorded a 94% rise in terrorism-related fatalities, reaching 930 deaths in 2024.
- Togo experienced its worst-ever level of terrorism, highlighting how attacks are expanding beyond the Sahel.
- Competition for gold and uranium resources is exacerbating regional violence.
- The Rise of Islamic State and Affiliate Groups
- IS remained the deadliest terrorist group, responsible for 1,805 deaths across 22 countries—primarily in Syria and the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC).
- Tehrik-e-Taliban Pakistan (TTP) saw a 90% surge in attacks, with fatalities rising from 558 to over 1,000.
- Islamic State Khorasan Province (ISK) expanded its operations from one country to five since 2020, launching major attacks in Iran and Russia.
- ISK propaganda is now produced in nine languages, demonstrating its global reach.
- Terrorism in the Middle East
- Terrorist attacks in the Middle East dropped by 7%, but the Israel-Palestine conflict remains a major threat.
- Syria, Israel, and Iran are among the 10 most affected countries.
- Turkey’s influence in Syria is increasing, while Russia, China, and Iran have scaled back their involvement.
- The Kurdish-led Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF), formerly backed by the S., face growing challenges from Turkey’s military expansion.
Western Nations and the Surge of Lone-Wolf Attacks
- Lone-wolf attackers carried out 93% of fatal terrorist incidents, with no direct links to organized groups.
- Terrorism in Europe doubled, with attacks rising to 67 in 2024.
- Western nations saw a 63% increase in terrorism-related incidents, with a worrying rise in teenage radicalization:
- 42% of all terrorism arrests in the UK involved under-18s.
- Germany suffered Europe’s deadliest terrorist attack of 2024.
- Online radicalization has become a major driver, with extremists using social media, gaming platforms, and encrypted messaging apps to recruit followers.
The Impact of the Gaza Conflict
The Gaza war triggered a surge in hate crimes and regional instability:
- Terrorism deaths in Iran increased sharply.
- Antisemitic and Islamophobic hate crimes surged worldwide, especially in the United States (200% increase in antisemitic incidents).
- Islamophobia incidents in the West rose by 300% in just two months.
Conclusion: A Growing Global Threat
The GTI 2025 report highlights a worsening global terrorism landscape, with more countries affected than in previous years.
- The Sahel remains the most volatile region, while the Middle East continues to grapple with instability.
- The rise of lone-wolf attackers in the West, fueled by online radicalization, presents a growing security concern.
- Geopolitical conflicts, including the Gaza war and resource-driven violence, continue to drive extremism.
While some regions have seen a decline in terrorist activity, the overall trend points to a more fragmented yet persistent global threat.
Consider the following statements regarding the Global Terrorism Index (GTI) 2025:
- It is published by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC).
- The index assesses terrorism by evaluating attacks, fatalities, injuries, hostage incidents, and their overall impact.
- The report covers 163 countries, accounting for 99.7% of the world’s population.
- The number of countries affected by terrorism has declined compared to the previous year.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 4 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 2, and 3 only
d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: The GTI is published by the Institute for Economics and Peace (IEP), not UNODC.
- Statement 2 – Correct: The index evaluates attacks, fatalities, injuries, hostage incidents, and their impact on society.
- Statement 3 – Correct: It covers 163 countries, representing 7% of the world’s population.
- Statement 4 – Incorrect: The number of countries affected by terrorism increased from 58 to 66, indicating a worsening trend.
Vitiligo and Gut Bacteria
Bacteria syllabus Science and Technology
Recent studies have highlighted a potential breakthrough in the treatment of vitiligo, a chronic autoimmune disorder that leads to skin depigmentation. This condition, which affects a significant portion of the global population, has both cosmetic and psychological impacts. Emerging research suggests that gut-friendly bacteria may play a key role in slowing its progression, opening new possibilities for treatment.

Understanding Vitiligo
- Vitiligo occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing skin pigment.
- This results in white patches on the skin, which can appear anywhere on the body but are most noticeable on the face, hands, and arms.
- While often perceived as a cosmetic issue, vitiligo can lead to social stigma and emotional distress, especially in individuals with darker skin tones.
- The condition affects 5% to 2% of the global population, with higher prevalence reported in regions like Gujarat and Rajasthan in India.
New Research Findings
- Recent studies from Northwestern University have discovered a natural compound derived from gut-friendly bacteria that could slow vitiligo progression.
- Pre-clinical trials in mice showed that this microbial compound reduced pigment loss by 74%.
- The compound works by reducing harmful killer T cells while increasing protective regulatory T cells, helping to restore immune balance.
- These findings suggest that modifying the gut microbiome could become a novel therapeutic approach for vitiligo.
Importance of Early Intervention
- Vitiligo often appears during adolescence or between the ages of 40 and 50.
- The condition is more pronounced in individuals with darker skin, leading to greater emotional and social distress.
- Early intervention can help stabilize pigment loss, improving treatment outcomes and quality of life for patients.
Future Treatment Possibilities
- Researchers are now exploring ways to translate these findings into human treatments:
- Current options include weekly injections, but more accessible alternatives like topical ointments or food additives are also being considered.
- Further studies are needed to determine the optimal dosage, duration, and long-term effectiveness of these treatments.
Broader Implications
- This research could have applications beyond vitiligo, potentially benefiting other autoimmune diseases with similar immune system dysfunction.
- Collaboration among scientists will be essential to refine the microbial compound and assess its compatibility with existing vitiligo treatments.By leveraging the power of the gut microbiome, researchers may unlock new, non-invasive therapies that could revolutionize the treatment of vitiligo and other immune-related conditions.
Consider the following statements regarding vitiligo:
- Vitiligo is an autoimmune disorder that leads to the destruction of keratinocytes, resulting in depigmented patches on the skin.
- The condition has a higher prevalence in regions like Gujarat and Rajasthan in India.
- The emotional and social impact of vitiligo is more pronounced in individuals with darker skin tones.
- The disease primarily manifests in childhood and is rarely observed after the age of 30.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 4 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 2, and 4 only
d) 2, 3, and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Incorrect: Vitiligo results from the destruction of melanocytes, not keratinocytes.
- Statement 2 – Correct: Studies indicate that vitiligo has a higher prevalence in regions like Gujarat and Rajasthan in India.
- Statement 3 – Correct: Since vitiligo causes visible depigmentation, individuals with darker skin tones often experience greater emotional and social distress.
- Statement 4 – Incorrect: Vitiligo commonly appears during adolescence or between ages 40-50, but it is not strictly confined to childhood.
Surat Food Security Saturation Campaign

Syllabus: Government schemes
Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the Surat Food Security Saturation Campaign Programme in Limbayat, Surat, reinforcing the government’s commitment to ensuring food security for the underprivileged. The initiative, aimed at benefiting over 2.3 lakh people, underscores Surat’s collective spirit in supporting the marginalized.
Objectives of the Campaign: The campaign is designed to expand the reach of the National Food Security Act (NFSA), ensuring that no eligible individual is left out. Over 2.5 lakh new beneficiaries have been identified, including elderly individuals and differently-abled persons. The initiative moves beyond political appeasement and focuses on fair and inclusive food distribution. Beneficiaries will receive free rations and nutritious food, helping combat hunger and malnutrition.
Government Initiatives for Food Security: The government has implemented several schemes to enhance food security across India: Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana (PMGKY) – Launched during COVID-19 to provide free food grains to the poor. PM Poshan Scheme – Ensures nutritious meals for school children, improving their health and learning outcomes. Saksham Anganwadi Program – Focuses on maternal and child nutrition, enhancing early childhood development. PM Matru Vandana Yojana – Provides financial aid to pregnant women, promoting maternal and infant health.
Emphasis on Nutrition and Hygiene: Eliminating malnutrition and anaemia is a government priority. Surat has set an example in hygiene and cleanliness, complementing the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan. The Har Ghar Jal campaign ensures clean drinking water, improving public health and sanitation.
Financial Inclusion and Support for the Poor: To empower the underprivileged, the government has introduced key financial initiatives: One Nation, One Ration Card (ONORC) – Allows beneficiaries to access rations from anywhere in India, ensuring food security for migrants. Mudra Yojana – Provides collateral-free loans to small businesses and entrepreneurs. PM SVANidhi Yojana – Offers financial support to street vendors, enabling economic self-reliance.
Strengthening the Middle Class: The government recognizes the middle class as a pillar of economic growth. Recent tax relief measures allow middle-class families to retain more income. New tax slabs support financial stability and encourage investment and savings.
Surat’s Economic Growth and Infrastructure Development: Surat is a major hub for textiles, chemicals, and MSMEs. To boost economic activity, the government has invested in MSME-friendly loan schemes, enabling business expansion. Infrastructure projects such as the Surat Metro and the new airport terminal improve connectivity and quality of life.
Women Empowerment Initiatives: Women’s empowerment remains a key focus of the government. Women are encouraged to share their success stories, inspiring greater participation in economic and social development. Special events and programs celebrate women’s contributions across various sectors.
The Surat Food Security Saturation Campaign is a significant milestone in ensuring that every citizen has access to essential nutrition and financial support, fostering growth, inclusivity, and empowerment.
Consider the following statements regarding the Surat Food Security Saturation Campaign:
- The campaign aims to strengthen the implementation of the National Food Security Act (NFSA) by including newly identified beneficiaries.
- It focuses primarily on providing subsidized food grains to beneficiaries in Surat.
- The initiative has identified over 2.5 lakh new beneficiaries, including the elderly and differently-abled individuals.
- The campaign extends beyond food security, incorporating elements of nutrition, hygiene, and financial inclusion.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 3 only
b) 1, 3, and 4 only
c) 2 and 4 only
d) 1, 2, and 3 only
Answer: (b) 1, 3, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Correct: The campaign aims to expand the coverage of NFSA, ensuring that no eligible person is left out.
- Statement 2 – Incorrect: Beneficiaries receive free rations and nutritious food, not just subsidized grains.
- Statement 3 – Correct: Over 2.5 lakh new beneficiaries have been identified under the campaign.
- Statement 4 – Correct: The initiative integrates nutrition, hygiene (Swachh Bharat Abhiyan), and financial inclusion.
Modified Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme
syllabus: Government schemes
The Government of India has introduced a modified Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme to enhance the operational viability of Cooperative Sugar Mills (CSMs). This initiative enables these mills to upgrade their existing sugarcane-based ethanol plants into multi-feedstock facilities, allowing the use of grains such as maize and damaged food grains (DFG) alongside sugarcane. The objective is to ensure year-round production, improve efficiency, and strengthen the ethanol industry.
Ethanol Production in India: Ethanol production in India primarily depends on sugarcane, but its crushing period lasts only 4-5 months annually, limiting production capacity. To address this, the government is promoting the diversification of feedstocks to ensure consistent ethanol output. The Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme targets a 20% ethanol blend with petrol by 2025, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and enhancing energy security.
Modified Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme: The scheme offers financial assistance in the form of an interest subvention of 6% per annum or 50% of the bank interest rate, whichever is lower. This support is applicable for loans provided by banks or financial institutions over five years, including a one-year moratorium. By easing financial constraints, the initiative encourages CSMs to expand their ethanol production beyond sugarcane-based operations.
Benefits of Multi-Feedstock Conversion: The shift to multi-feedstock plants provides several advantages:
Year-Round Production: Using grains and agricultural residues ensures continuous ethanol output, even outside the sugarcane season.
- Improved Efficiency: Diversified raw materials enhance the mills’ operational flexibility and financial sustainability.
- Economic Growth: Supporting local grain production reduces dependence on sugarcane, strengthening the agricultural economy.
Impact on Ethanol Production Targets: India has set ambitious ethanol production targets under the EBP Programme. As of February 2025, the blending rate reached 19.6%, indicating significant progress toward the 20% goal. Enhanced production capabilities from CSMs are expected to play a key role in meeting this target.
Future Prospects for Cooperative Sugar Mills: The modified scheme provides a transformative opportunity for CSMs. By embracing a multi-feedstock approach, these mills can ensure long-term sustainability while contributing to India’s renewable energy goals. Additionally, leveraging locally available grains promotes self-sufficiency and strengthens the rural economy. This strategic shift marks a crucial step in making ethanol production more resilient and efficient in the coming years.
Consider the following statements regarding the Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme:
- It provides an interest subvention of 6% per annum or 50% of the bank interest rate, whichever is lower.
- The scheme allows Cooperative Sugar Mills (CSMs) to upgrade their sugarcane-based ethanol plants into multi-feedstock facilities.
- The financial support under this scheme is provided for a period of ten years, including a two-year moratorium.
- It aims to facilitate year-round ethanol production by diversifying the feedstock to include maize and damaged food grains (DFG).
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1, 2, and 4 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1, 3, and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (a) 1, 2, and 4 only
Explanation:
- Statement 1 – Correct: The scheme provides an interest subvention of 6% per annum or 50% of the bank interest rate, whichever is lower.
- Statement 2 – Correct: It allows CSMs to upgrade their sugarcane-based ethanol plants into multi-feedstock facilities.
- Statement 3 – Incorrect: The financial assistance is provided for five years, including a one-year moratorium, not ten years with a two-year moratorium.
- Statement 4 – Correct: The scheme encourages the use of maize and damaged food grains (DFG) for ethanol production.
